cross member ISUZU TFS SERIES 1997 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1997, Model line: TFS SERIES, Model: ISUZU TFS SERIES 1997Pages: 1600, PDF Size: 40.98 MB
Page 349 of 1600

BRAKES 5-21
Operation
The operation of the P-valve by the master cylinder
pressure is unchanged up to the brake points
A and B.
If master cylinder fluid pressure penetrates into the second
break point
B, the fluid pressure pressing against the seal
2, (which isolated route 4 and route 5), passing the route
4 of the master cylinder side, overcomes the operating
force of the spring
3 + fluid pressure affecting the seal 2 of
the wheel cylinder, and presses the piston
1 to the right
side, resulting in the opening of the routes
4 and 5, and
canceling of the P-valve operation.
Then, because the master cylinder fluid pressure and the
wheel cylinder fluid pressure, up to the point
C, operate on
the identical surface of the seal
2, both have identical
ascending ratio.
However, because of the operation of spring
3 in the wheel
cylinder side, wheel cylinder fluid pressure operate to
preserve the balance against the master cylinder fluid
pressure on the lower level with the difference in pressure
resulting from this spring.
Valve Maintenance
In the case of fluid leak or other abnormalities, faulty valve
should be replaced.
The valve is set up at the right hand side of the 5th
crossmember near the rear axle.
Note:
The blend proportioning valve is not repairable and must
be replaced as a complete assembly.
BLEEDING OF THE BRAKE HYDRAULIC
CIRCUIT
If air enters the bake lines, it will cause poor brake action.
Therefore, bleeding should be performed if the brakes have
been used with the level of brake fluid in the reservoir
excessively low or if brake pipes have been disconnected in
the course of brake servicing.
Bleeding operation calls for co-operative action of 2 persons.
Set the parking brake firmly while bleeding.
Perform bleeding operation with ENGINE RUNNING, to
prevent damage to push rod seal.
Make sure exhaust is suitably ventilated.
Bleed the hydraulic system with the fluid reservoir filled to
the specified level.
Bleed the system starting with the rear wheel cylinder
farthest from the master cylinder.
A : Load sensing proportioning valve (If so equipped).
Page 393 of 1600

BRAKES 5-65
REAR CABLE ASSEMBLY
Removal Steps
1. Lock nut
2. Adjusting nut
3. Bolt
4. Retainer
5. Clip and bolt ; crossmember
6. Clip and bolt ; side member
7. Clip and bolt ; side member
8. Clip and bolt ; spring eye
9. Clip and bolt ; leaf spring
10. Hand brake rear cable
Installation Steps
10. Hand brake rear cable
9. Clip and bolt ; leaf spring
8. Clip and bolt ; spring eye
7. Clip and bolt ; side member
6. Clip and bolt ; side member
5. Clip and bolt ; crossmember
4. Retainer
3. Bolt
2. Adjusting nut
1. Lock nut
Page 394 of 1600
5-66 BRAKES
Important Operations - Removal
Preparation
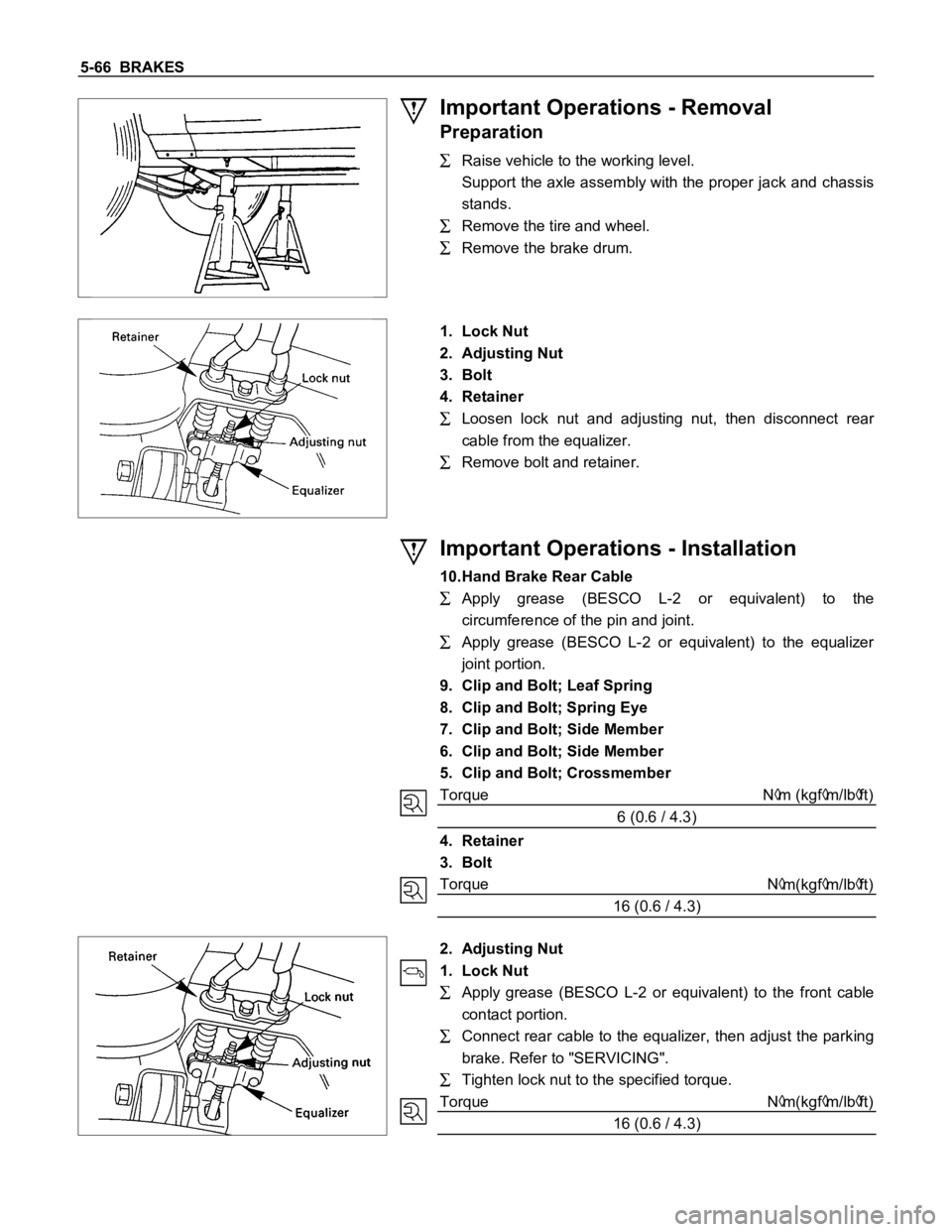
Raise vehicle to the working level.
Support the axle assembly with the proper jack and chassis
stands.
Remove the tire and wheel.
Remove the brake drum.
1. Lock Nut
2. Adjusting Nut
3. Bolt
4. Retainer
Loosen lock nut and adjusting nut, then disconnect rear
cable from the equalizer.
Remove bolt and retainer.
Important Operations - Installation
10.Hand Brake Rear Cable
Apply grease (BESCO L-2 or equivalent) to the
circumference of the pin and joint.
Apply grease (BESCO L-2 or equivalent) to the equalizer
joint portion.
9. Clip and Bolt; Leaf Spring
8. Clip and Bolt; Spring Eye
7. Clip and Bolt; Side Member
6. Clip and Bolt; Side Member
5. Clip and Bolt; Crossmember
Torque N
m (kgfm/lbft)
6 (0.6 / 4.3)
4. Retainer
3. Bolt
Torque N
m(kgfm/lbft)
16 (0.6 / 4.3)
2. Adjusting Nut
1. Lock Nut
Apply grease (BESCO L-2 or equivalent) to the front cable
contact portion.
Connect rear cable to the equalizer, then adjust the parking
brake. Refer to "SERVICING".
Tighten lock nut to the specified torque.
Torque N
m(kgfm/lbft)
16 (0.6 / 4.3)