front drive shaft ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 442 of 3573
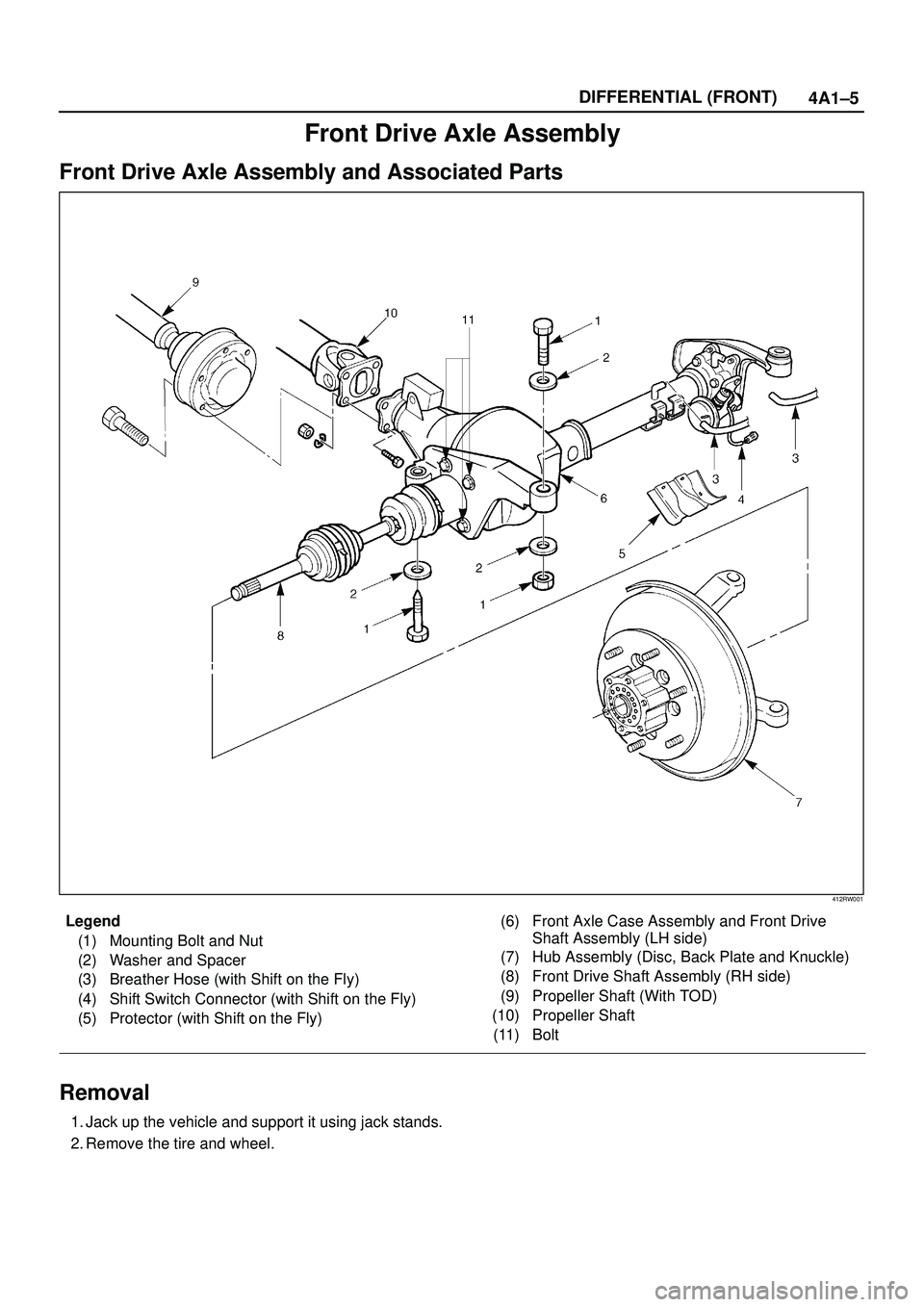
4A1±5 DIFFERENTIAL (FRONT)
Front Drive Axle Assembly
Front Drive Axle Assembly and Associated Parts
412RW001
Legend
(1) Mounting Bolt and Nut
(2) Washer and Spacer
(3) Breather Hose (with Shift on the Fly)
(4) Shift Switch Connector (with Shift on the Fly)
(5) Protector (with Shift on the Fly)(6) Front Axle Case Assembly and Front Drive
Shaft Assembly (LH side)
(7) Hub Assembly (Disc, Back Plate and Knuckle)
(8) Front Drive Shaft Assembly (RH side)
(9) Propeller Shaft (With TOD)
(10) Propeller Shaft
(11) Bolt
Removal
1. Jack up the vehicle and support it using jack stands.
2. Remove the tire and wheel.
Page 443 of 3573
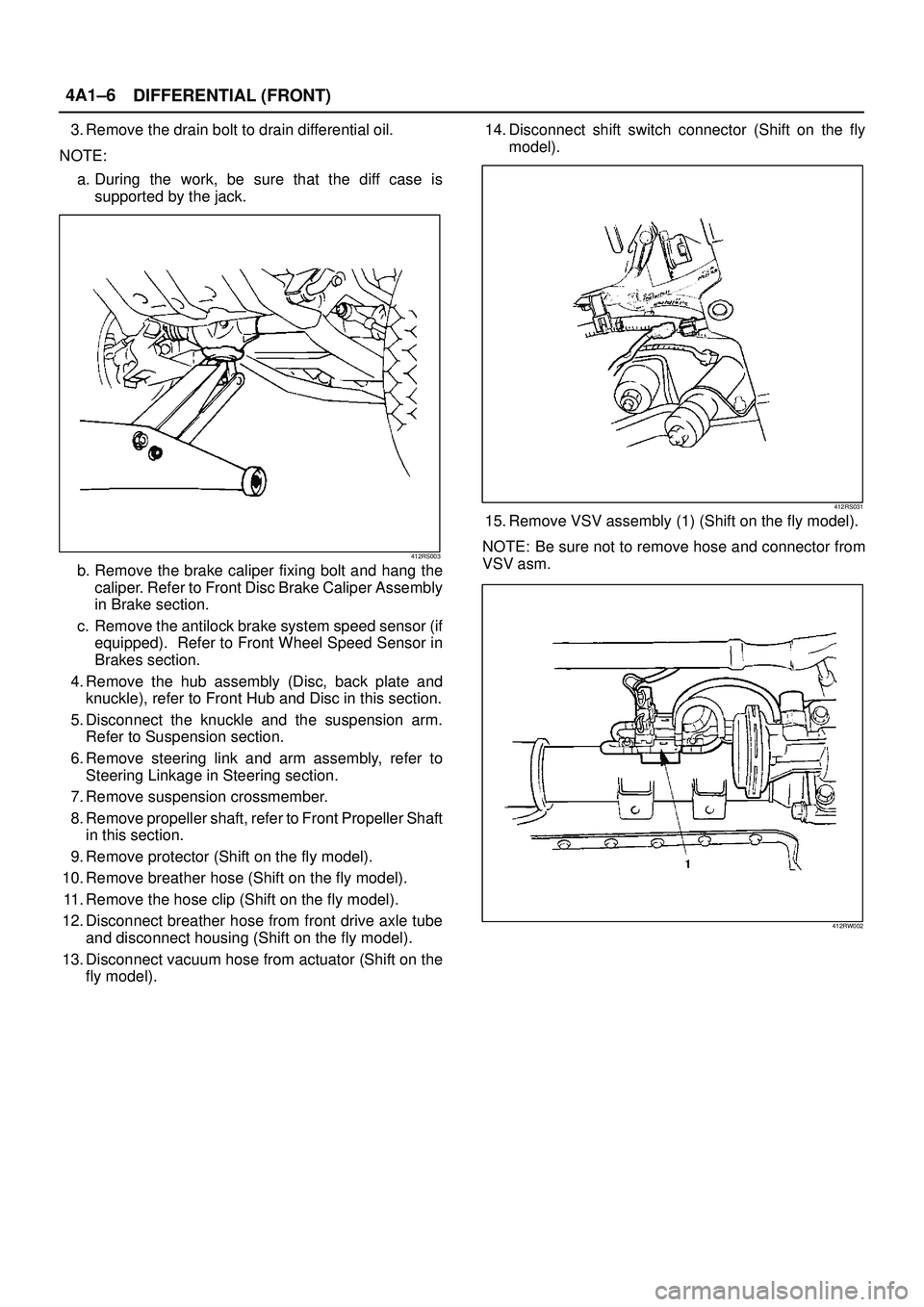
DIFFERENTIAL (FRONT) 4A1±6
3. Remove the drain bolt to drain differential oil.
NOTE:
a. During the work, be sure that the diff case is
supported by the jack.
412RS003
b. Remove the brake caliper fixing bolt and hang the
caliper. Refer to Front Disc Brake Caliper Assembly
in Brake section.
c. Remove the antilock brake system speed sensor (if
equipped). Refer to Front Wheel Speed Sensor in
Brakes section.
4. Remove the hub assembly (Disc, back plate and
knuckle), refer to Front Hub and Disc in this section.
5. Disconnect the knuckle and the suspension arm.
Refer to Suspension section.
6. Remove steering link and arm assembly, refer to
Steering Linkage in Steering section.
7. Remove suspension crossmember.
8. Remove propeller shaft, refer to Front Propeller Shaft
in this section.
9. Remove protector (Shift on the fly model).
10. Remove breather hose (Shift on the fly model).
11. Remove the hose clip (Shift on the fly model).
12. Disconnect breather hose from front drive axle tube
and disconnect housing (Shift on the fly model).
13. Disconnect vacuum hose from actuator (Shift on the
fly model).14. Disconnect shift switch connector (Shift on the fly
model).
412RS031
15. Remove VSV assembly (1) (Shift on the fly model).
NOTE: Be sure not to remove hose and connector from
VSV asm.
412RW002
Page 444 of 3573
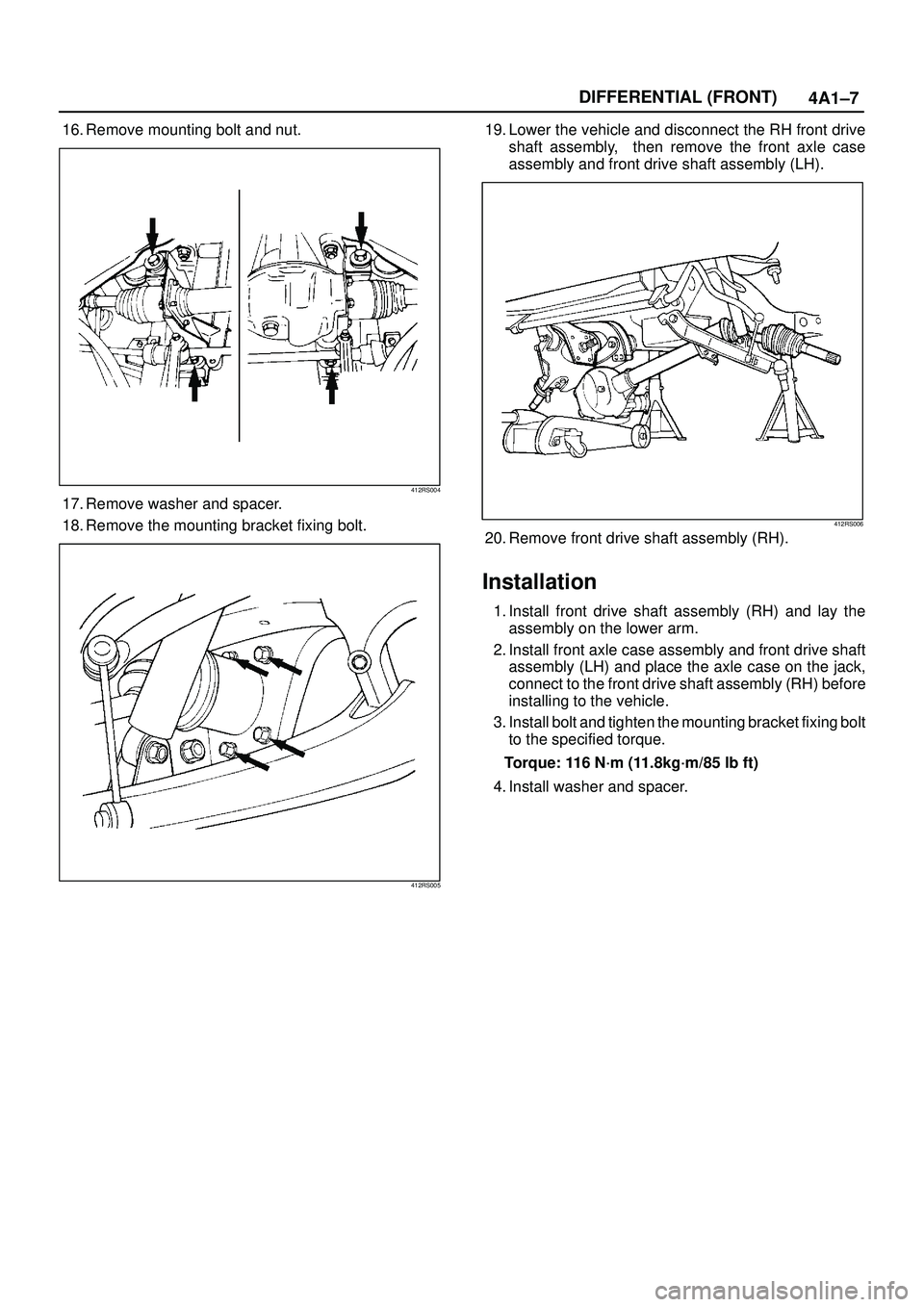
4A1±7 DIFFERENTIAL (FRONT)
16. Remove mounting bolt and nut.
412RS004
17. Remove washer and spacer.
18. Remove the mounting bracket fixing bolt.
412RS005
19. Lower the vehicle and disconnect the RH front drive
shaft assembly, then remove the front axle case
assembly and front drive shaft assembly (LH).
412RS006
20. Remove front drive shaft assembly (RH).
Installation
1. Install front drive shaft assembly (RH) and lay the
assembly on the lower arm.
2. Install front axle case assembly and front drive shaft
assembly (LH) and place the axle case on the jack,
connect to the front drive shaft assembly (RH) before
installing to the vehicle.
3. Install bolt and tighten the mounting bracket fixing bolt
to the specified torque.
Torque: 116 N´m (11.8kg´m/85 lb ft)
4. Install washer and spacer.
Page 470 of 3573

DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 220mm)
4A2A±3
Diagnosis
Many noises that seem to come from the rear axle
actually originate from other sources such as tires, road
surface, wheel bearings, engine, transmission, muffler, or
body drumming. Investigate to find the source of the
noise before disassembling the rear axle. Rear axles, like
any other mechanical device, are not absolutely quiet but
should be considered quiet unless some abnormal noise
is present.
To make a systematic check for axle noise, observe the
following:
1. Select a level asphalt road to reduce tire noise and
body drumming.
2. Check rear axle lubricant level to assure correct level,
and then drive the vehicle far enough to thoroughly
warm up the rear axle lubricant.
3. Note the speed at which noise occurs. Stop the
vehicle and put the transmission in neutral. Run the
engine speed slowly up and down to determine if the
noise is caused by exhaust, muffler noise, or other
engine conditions.
4. Tire noise changes with different road surfaces; axle
noises do not. Temporarily inflate all tires to 344 kPa
(3.5kg/cm
2, 50 psi) (for test purposes only). This will
change noise caused by tires but will not affect noise
caused by the rear axle.
Rear axle noise usually stops when coasting at
speeds under 48 km/h (30 mph); however, tire noise
continues with a lower tone. Rear axle noise usually
changes when comparing pull and coast, but tire
noise stays about the same.
Distinguish between tire noise and rear axle noise by
noting if the noise changes with various speeds or
sudden acceleration and deceleration. Exhaust and
axle noise vary under these conditions, while tire
noise remains constant and is more pronounced at
speeds of 32 to 48 km/h (20 to 30 mph). Further check
for tire noise by driving the vehicle over smooth
pavements or dirt roads (not gravel) with the tires at
normal pressure. If the noise is caused by tires, it will
change noticeably with changes in road surface.
5. Loose or rough front wheel bearings will cause noise
which may be confused with rear axle noise; however,
front wheel bearing noise does not change when
comparing drive and coast. Light application of the
brake while holding vehicle speed steady will often
cause wheel bearing noise to diminish. Front wheel
bearings may be checked for noise by jacking up the
wheels and spinning them or by shaking the wheels to
determine if bearings are loose.
6. Rear suspension rubber bushings and spring
insulators dampen out rear axle noise when correctly
installed. Check to see that there is no link or rod
loosened or metal±to±metal contact.
7. Make sure that there is no metal±to±metal contact
between the floor and the frame.
After the noise has been determined to be in the axle, the
type of axle noise should be determined, in order to make
any necessary repairs.
Gear Noise
Gear noise (whine) is audible from 32 to 89 km/h (20 to 55
mph) under four driving conditions.
1. Driving under acceleration or heavy pull.
2. Driving under load or under constant speed.
3. When using enough throttle to keep the vehicle from
driving the engine while the vehicle slows down
gradually (engine still pulls slightly).
4. When coasting with the vehicle in gear and the throttle
closed. The gear noise is usually more noticeable
between 48 and 64 km/h (30 and 40 mph) and 80 and
89 km/h (50 and 55 mph).
Bearing Noise
Bad bearings generally produce a rough growl or grating
sound, rather than the whine typical of gear noise.
Bearing noise frequently ªwow±wowsº at bearing rpm,
indicating a bad pinion or rear axle side bearing. This
noise can be confused with rear wheel bearing noise.
Rear Wheel Bearing Noise
Rear wheel bearing noise continues to be heard while
coasting at low speed with transmission in neutral. Noise
may diminish by gentle braking. Jack up the rear wheels,
spin them by hand and listen for noise at the hubs.
Replace any faulty wheel bearings.
Knock At Low Speeds
Low speed knock can be caused by worn universal joints
or a side gear hub counter bore in the cage that is worn
oversize. Inspect and replace universal joints or cage and
side gears as required.
Backlash Clunk
Excessive clunk on acceleration and deceleration can be
caused by a worn rear axle pinion shaft, a worn cage,
excessive clearance between the axle and the side gear
splines, excessive clearance between the side gear hub
and the counterbore in the cage, worn pinion and side
gear teeth, worn thrust washers, or excessive drive pinion
and ring gear backlash. Remove worn parts and replace
as required. Select close±fitting parts when possible.
Adjust pinion and ring gear backlash.
Page 506 of 3573

DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 244mm)
4A2B±3
Diagnosis
Many noises that seem to come from the rear axle
actually originate from other sources such as tires, road
surface, wheel bearings, engine, transmission, muffler, or
body drumming. Investigate to find the source of the
noise before disassembling the rear axle. Rear axles, like
any other mechanical device, are not absolutely quiet but
should be considered quiet unless some abnormal noise
is present.
To make a systematic check for axle noise, observe the
following:
1. Select a level asphalt road to reduce tire noise and
body drumming.
2. Check rear axle lubricant level to assure correct level,
and then drive the vehicle far enough to thoroughly
warm up the rear axle lubricant.
3. Note the speed at which noise occurs. Stop the
vehicle and put the transmission in neutral. Run the
engine speed slowly up and down to determine if the
noise is caused by exhaust, muffler noise, or other
engine conditions.
4. Tire noise changes with different road surfaces; axle
noises do not. Temporarily inflate all tires to 344 kPa
(3.5kg/cm
2, 50 psi) (for test purposes only). This will
change noise caused by tires but will not affect noise
caused by the rear axle.
Rear axle noise usually stops when coasting at
speeds under 48 km/h (30 mph); however, tire noise
continues with a lower tone. Rear axle noise usually
changes when comparing pull and coast, but tire
noise stays about the same.
Distinguish between tire noise and rear axle noise by
noting if the noise changes with various speeds or
sudden acceleration and deceleration. Exhaust and
axle noise vary under these conditions, while tire
noise remains constant and is more pronounced at
speeds of 32 to 48 km/h (20 to 30 mph). Further check
for tire noise by driving the vehicle over smooth
pavements or dirt roads (not gravel) with the tires at
normal pressure. If the noise is caused by tires, it will
change noticeably with changes in road surface.
5. Loose or rough front wheel bearings will cause noise
which may be confused with rear axle noise; however,
front wheel bearing noise does not change when
comparing drive and coast. Light application of the
brake while holding vehicle speed steady will often
cause wheel bearing noise to diminish. Front wheel
bearings may be checked for noise by jacking up the
wheels and spinning them or by shaking the wheels to
determine if bearings are loose.
6. Rear suspension rubber bushings and spring
insulators dampen out rear axle noise when correctly
installed. Check to see that there is no link or rod
loosened or metal±to±metal contact.
7. Make sure that there is no metal±to±metal contact
between the floor and the frame.
After the noise has been determined to be in the axle, the
type of axle noise should be determined, in order to make
any necessary repairs.
Gear Noise
Gear noise (whine) is audible from 32 to 89 km/h (20 to 55
mph) under four driving conditions.
1. Driving under acceleration or heavy pull.
2. Driving under load or under constant speed.
3. When using enough throttle to keep the vehicle from
driving the engine while the vehicle slows down
gradually (engine still pulls slightly).
4. When coasting with the vehicle in gear and the throttle
closed. The gear noise is usually more noticeable
between 48 and 64 km/h (30 and 40 mph) and 80 and
89 km/h (50 and 55 mph).
Bearing Noise
Bad bearings generally produce a rough growl or grating
sound, rather than the whine typical of gear noise.
Bearing noise frequently ªwow±wowsº at bearing rpm,
indicating a bad pinion or rear axle side bearing. This
noise can be confused with rear wheel bearing noise.
Rear Wheel Bearing Noise
Rear wheel bearing noise continues to be heard while
coasting at low speed with transmission in neutral. Noise
may diminish by gentle braking. Jack up the rear wheels,
spin them by hand and listen for noise at the hubs.
Replace any faulty wheel bearings.
Knock At Low Speeds
Low speed knock can be caused by worn universal joints
or a side gear hub counter bore in the cage that is worn
oversize. Inspect and replace universal joints or cage and
side gears as required.
Backlash Clunk
Excessive clunk on acceleration and deceleration can be
caused by a worn rear axle pinion shaft, a worn cage,
excessive clearance between the axle and the side gear
splines, excessive clearance between the side gear hub
and the counterbore in the cage, worn pinion and side
gear teeth, worn thrust washers, or excessive drive pinion
and ring gear backlash. Remove worn parts and replace
as required. Select close±fitting parts when possible.
Adjust pinion and ring gear backlash.
Page 540 of 3573
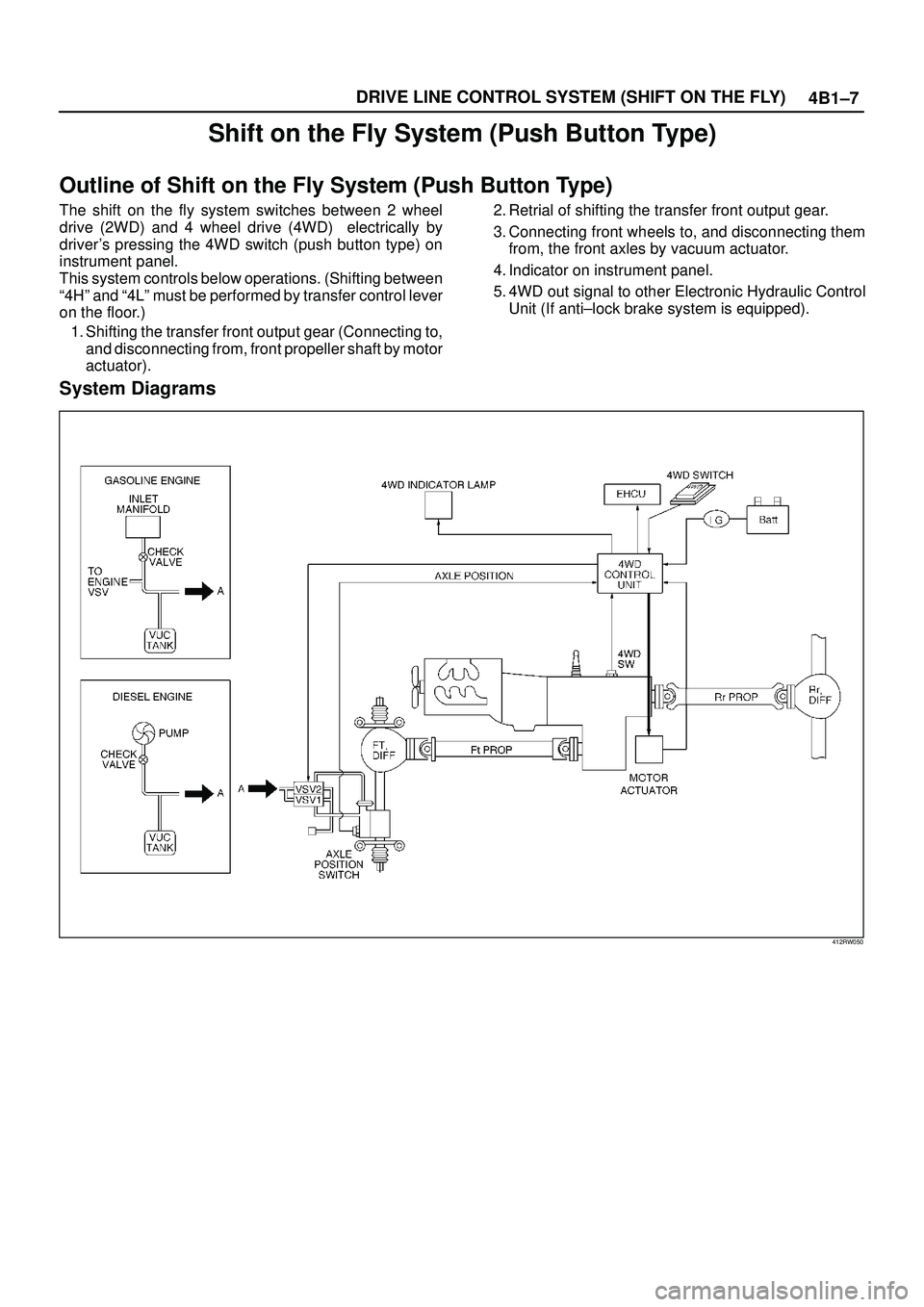
4B1±7 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Shift on the Fly System (Push Button Type)
Outline of Shift on the Fly System (Push Button Type)
The shift on the fly system switches between 2 wheel
drive (2WD) and 4 wheel drive (4WD) electrically by
driver's pressing the 4WD switch (push button type) on
instrument panel.
This system controls below operations. (Shifting between
ª4Hº and ª4Lº must be performed by transfer control lever
on the floor.)
1. Shifting the transfer front output gear (Connecting to,
and disconnecting from, front propeller shaft by motor
actuator).2. Retrial of shifting the transfer front output gear.
3. Connecting front wheels to, and disconnecting them
from, the front axles by vacuum actuator.
4. Indicator on instrument panel.
5. 4WD out signal to other Electronic Hydraulic Control
Unit (If anti±lock brake system is equipped).
System Diagrams
412RW050
Page 541 of 3573
4B1±8
DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
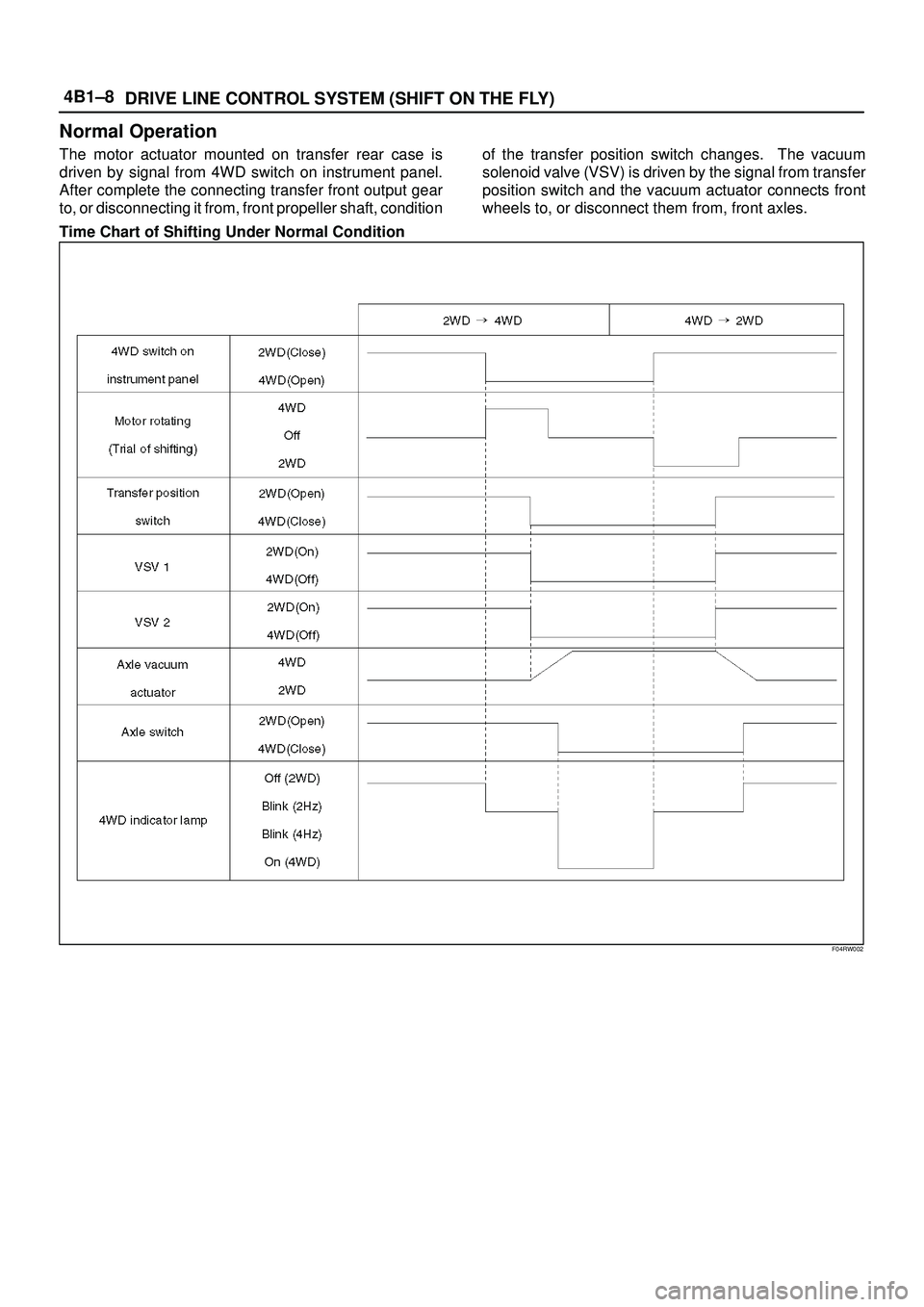
Normal Operation
The motor actuator mounted on transfer rear case is
driven by signal from 4WD switch on instrument panel.
After complete the connecting transfer front output gear
to, or disconnecting it from, front propeller shaft, conditionof the transfer position switch changes. The vacuum
solenoid valve (VSV) is driven by the signal from transfer
position switch and the vacuum actuator connects front
wheels to, or disconnect them from, front axles.
Time Chart of Shifting Under Normal Condition
F04RW002
Page 576 of 3573

4B2±5 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
Front and Rear Speed Sensors
The sensors are built in the transfer case, detect the
rotation of rotors directly coupled to the propeller shafts.
Thirty rectangular pulses are output per one rotation of
the propeller shaft.
261RW045
Electromagnetic Coil
Receives the duty signals from the TOD control unit and
controls the pressing force of the clutch pressure cam.
261RW044
Multi Plate Disk Clutch Pack
Transmits the torque determined by the clutch pressing
force to the front propeller shaft via the front drive chain.
262RW029
Mechanical Lock Sleeve
Couples the front and rear propeller shaft mechanically
when the transfer shaft is in the 4L position.
262RW028
Page 649 of 3573
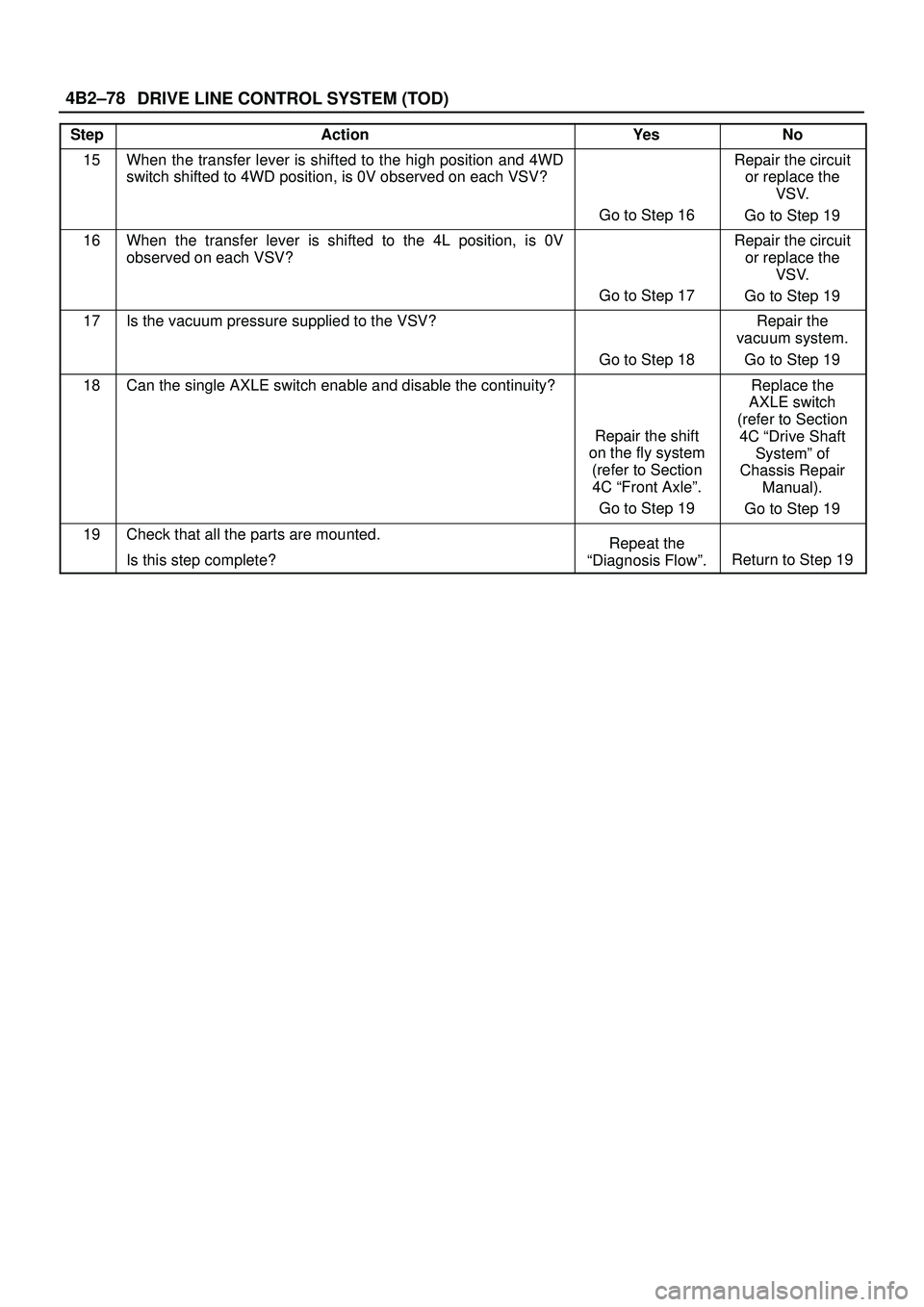
DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD) 4B2±78
StepNo Ye s Action
15When the transfer lever is shifted to the high position and 4WD
switch shifted to 4WD position, is 0V observed on each VSV?
Go to Step 16
Repair the circuit
or replace the
VSV.
Go to Step 19
16When the transfer lever is shifted to the 4L position, is 0V
observed on each VSV?
Go to Step 17
Repair the circuit
or replace the
VSV.
Go to Step 19
17Is the vacuum pressure supplied to the VSV?
Go to Step 18
Repair the
vacuum system.
Go to Step 19
18Can the single AXLE switch enable and disable the continuity?
Repair the shift
on the fly system
(refer to Section
4C ªFront Axleº.
Go to Step 19
Replace the
AXLE switch
(refer to Section
4C ªDrive Shaft
Systemº of
Chassis Repair
Manual).
Go to Step 19
19Check that all the parts are mounted.
Is this step complete?Repeat the
ªDiagnosis Flowº.
Return to Step 19
Page 652 of 3573
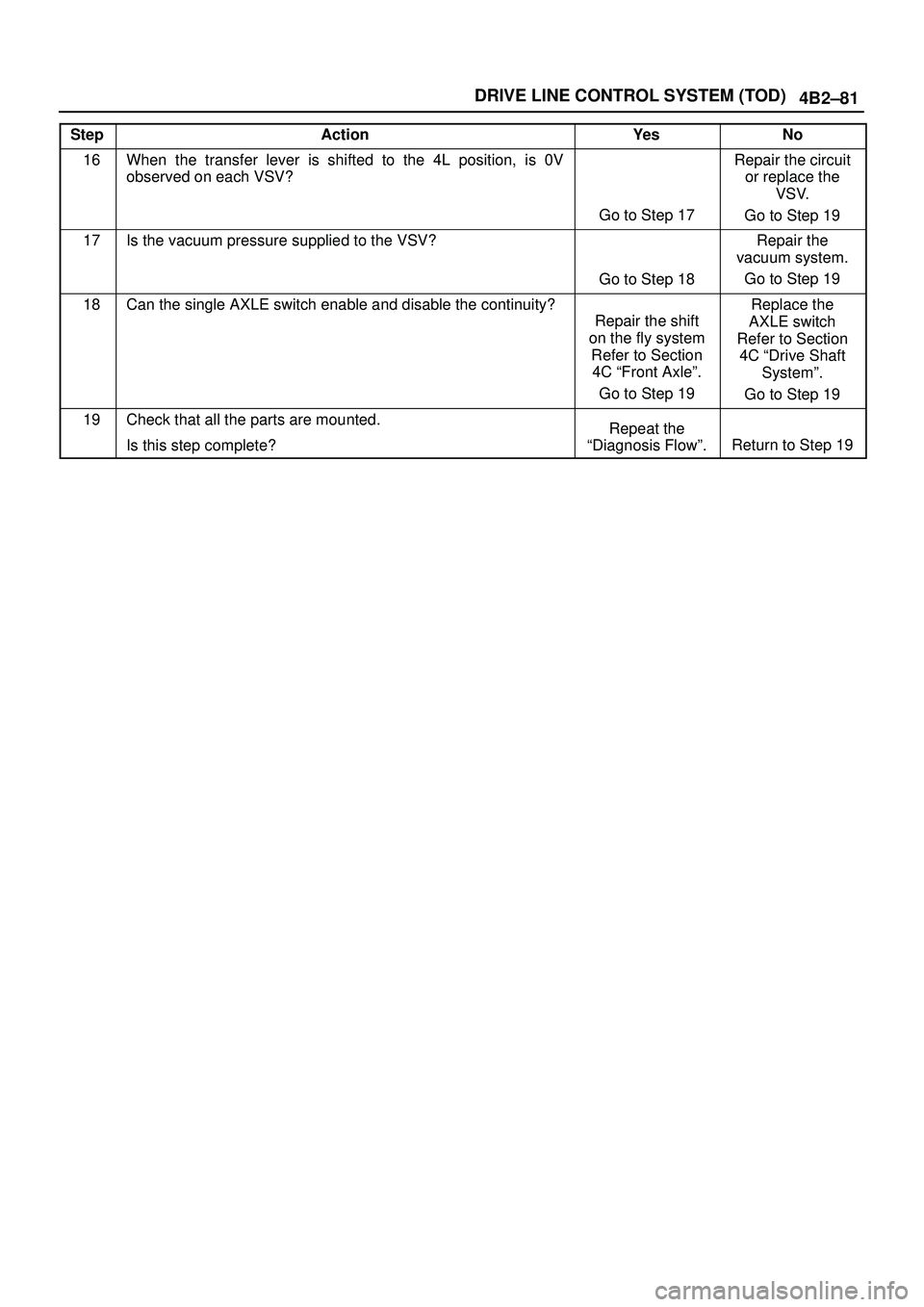
4B2±81 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
StepNo Ye s Action
16When the transfer lever is shifted to the 4L position, is 0V
observed on each VSV?
Go to Step 17
Repair the circuit
or replace the
VSV.
Go to Step 19
17Is the vacuum pressure supplied to the VSV?
Go to Step 18
Repair the
vacuum system.
Go to Step 19
18Can the single AXLE switch enable and disable the continuity?
Repair the shift
on the fly system
Refer to Section
4C ªFront Axleº.
Go to Step 19
Replace the
AXLE switch
Refer to Section
4C ªDrive Shaft
Systemº.
Go to Step 19
19Check that all the parts are mounted.
Is this step complete?Repeat the
ªDiagnosis Flowº.
Return to Step 19