cooling system JAGUAR X308 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1998, Model line: X308, Model: JAGUAR X308 1998 2.GPages: 2490, PDF Size: 69.81 MB
Page 11 of 2490

Valve
Co
ver
LH (12.29.43)
Valve
Cover RH (12.29.44)
Valve
Cover Gasket LH (12.29.40)
Valve
Cover Gasket RH (12.29.41)
Valve
Springs LH
Valve
Springs RH
Variable
Camshaft Timing Oil Con
trol Unit LH (12.65.71)
Variable
Camshaft Timing Oil Control Unit RH (12.65.70)
Variable
Camshaft Timing Oil Control Unit Housing LH (12.65.52)
Variable
Camshaft Timing Oil Control Unit Housing RH (12.65.51)
303‐03A : Engine Cooling
Descriptio
n and Operation
Engine Cooling
Diagnosis and Testing
Engine Cooling
Related Faults / Codes
DTC P0116 ECT circuit range / performance problem
DTC P0125 Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel control
DTC P0117 ECT circuit low input
DTC P0118 ECT circuit high input
DTC P1474 Intercooler coolant pum
p relay malfunction
Pinpoint test A: P0116, P0125
Pinpoint test B: P0117
Pinpoint test C: P0118
Pinpoint test D: P1474
General Procedures
Cooling System Draining, Filling and Bleeding ‐ 3.2L NA V8 ‐ AJ26/4.0L NA V8 –
AJ27
Cooling System Draining, Filling and Bleeding ‐ 4.0L SC V8 ‐ AJ26
Cooling Sy
stem Draining and Vacuum Filling
Removal and Installation
Removal
Engine ‐ Re m
oval
(12.41.01)
Installation
Engine ‐ Installation (12.41.01)
Page 44 of 2490
Electrically Programmable
R
ead-Only memory
EPROM
Ele
c
tronic Secondary Air
Injection
EAIRA p
ump-driven system for providing seco
ndary air using an electric air pump
Engine C
ontrol Module
ECM
End of dashEODR
e
ferring to a vehicle fascia, eg EOD air vent
Engine
C
oolant Level
ECL
Engine
C
oolant
Temperature
ECT
ECT Sen s
or
ECTSTherm
i
stor which provides engine coolant temperature signal to the ECM to
trigger enrichment circuits which increase injector 'on' time for cold start and
warm-up
Engine s
peed
RP
M
Environ m
ental Protection
Agency
EPA
Evaporative EmissionEVAPSy stem designed to prevent fu
el vapor from escaping into the atmosphere.
Typically includes a charcoal filled canister to absorb fuel vapor
Evaporative Emission
Control ValveEVAPP
Exhaust G
as Recirculation
EGRSys
t
em which reduces NOx emissions by adding exhaust gases to the
incoming fuel/air charge
Exhaus t G
as Recirculation
Solenoid Vacuum Valve
EGRS
Exhaus t G
as Recirculation
Temperature Sensor
EGRT Sen s
or
Exhaus
t G
as Recirculation
Valve
EGRV
F
F a
n Control
FCEngine
cooling fan control
F
e
deral Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard (US)
FMV S
S
Fi
gur
e
Fi
g.Illustrati
on reference
Flash
E
lectrically Erasable
Programmable Read-Only
Memory
FEE PR
OM
Flash
E
rasable
Programmable Read-Only
Memory
FEP R
OM
Flywhee
l
Sensor
CKFSSens
or moun
ted so as to be
triggered by each flywheel ring gear tooth to give
an engine speed signal
Fue l
Injectors
FISol
e
noid operated devices that spray a metered quantity of fuel into the inlet
ports
F u
el Pressure Regulator
Control
FP RCControls fuel pressure regu l
ator; used primarily to
give extra fuel at cold
start-up
Fue l
Pump
FP
Fue
l
Pump Monitor
FP
MMonitors operation of fuel pump
Fue l
Pump Relay
FP
R
Fu
el rich/lean
Q
u
alitative evaluation
of air/fuel ratio based on a ratio known as
stoichiometry, or 14.7:1 (Lambda)
F u
ll Scale Deflection
FSDTh
e
maximum indication point on
an analogue meter or gauge
G
Gene
rator
GENRot
a
ting machine which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
G
r
amme centimeter
gcm
Gramm
e
(force)
gf
Gramm
e
(mass)
g
GroundGNDEle
c
trical conductor used
as a common return for an electrical circuit or
circuits, and with a relative zero potential
H
Hard f a
ult
A
fau
lt currently present in the system
HeadlampHL
Heat
ed Oxygen
Sensor
HO2SElectrically
h
eated oxygen sensor which induces fueling corrections
Hertz (frequency)HzFrequ
e
ncy, one cycle per second
High
Moun
ted Stoplamp
HMSL
Page 341 of 2490
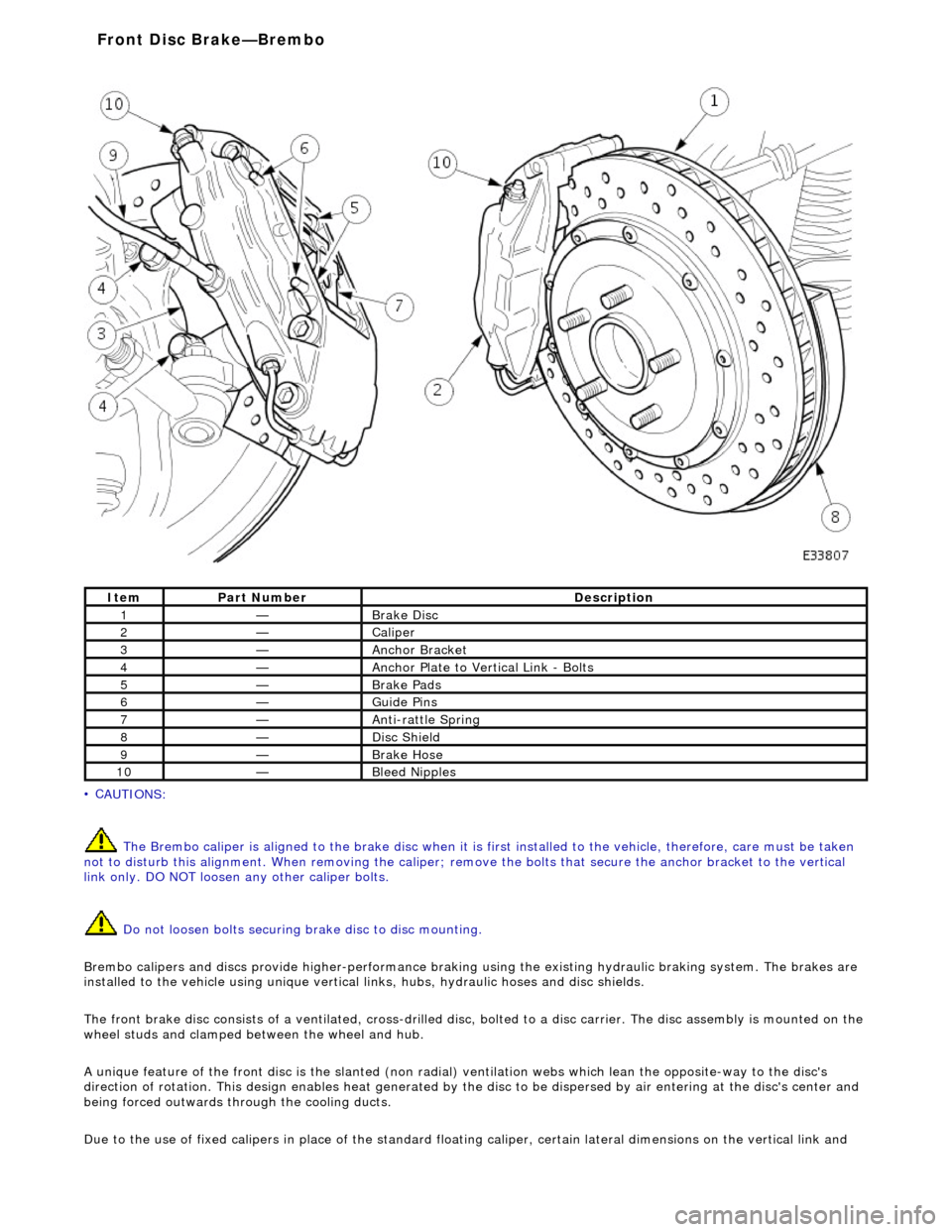
• C
AUTIONS:
The Brembo caliper is aligned to the brak e disc when it is first installed to the vehicle, therefore, care must be taken
not to disturb this alignment. When removi ng the caliper; remove the bolts that secure the anchor bracket to the vertical
link only. DO NOT loosen any other caliper bolts.
Do not loosen bolts securing brake disc to disc mounting.
Brembo calipers and discs provide higher -performance braking using the existing hydraulic braking system. The brakes are
installed to the vehicle using unique vertical links, hubs, hydraulic hoses and disc shields.
The front brake disc consists of a ventilated, cross-drilled disc, bolted to a disc carrier. The disc assemb ly is mounted on the
wheel studs and clamped be tween the wheel and hub.
A unique feature of the front disc is th e slanted (non radial) ventilation webs which lean the opposite-way to the disc's
direction of rotation. This design enables he at generated by the disc to be dispersed by air entering at the disc's center and
being forced outwards through the cooling ducts.
Due to the use of fixed calipers in place of the standard floating caliper, certain lateral dimensions on the vertical link and
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—B
rake Disc
2—Caliper
3—Anch
or Bracket
4—Anchor Pl
ate to Vertical Link - Bolts
5—Brake Pad
s
6—Guide P
ins
7—Anti-r
attle Spring
8—Di
sc Shield
9—Brake Hos
e
10—Bleed Nipp
les
Front Disc Brake—
Brembo
Page 366 of 2490
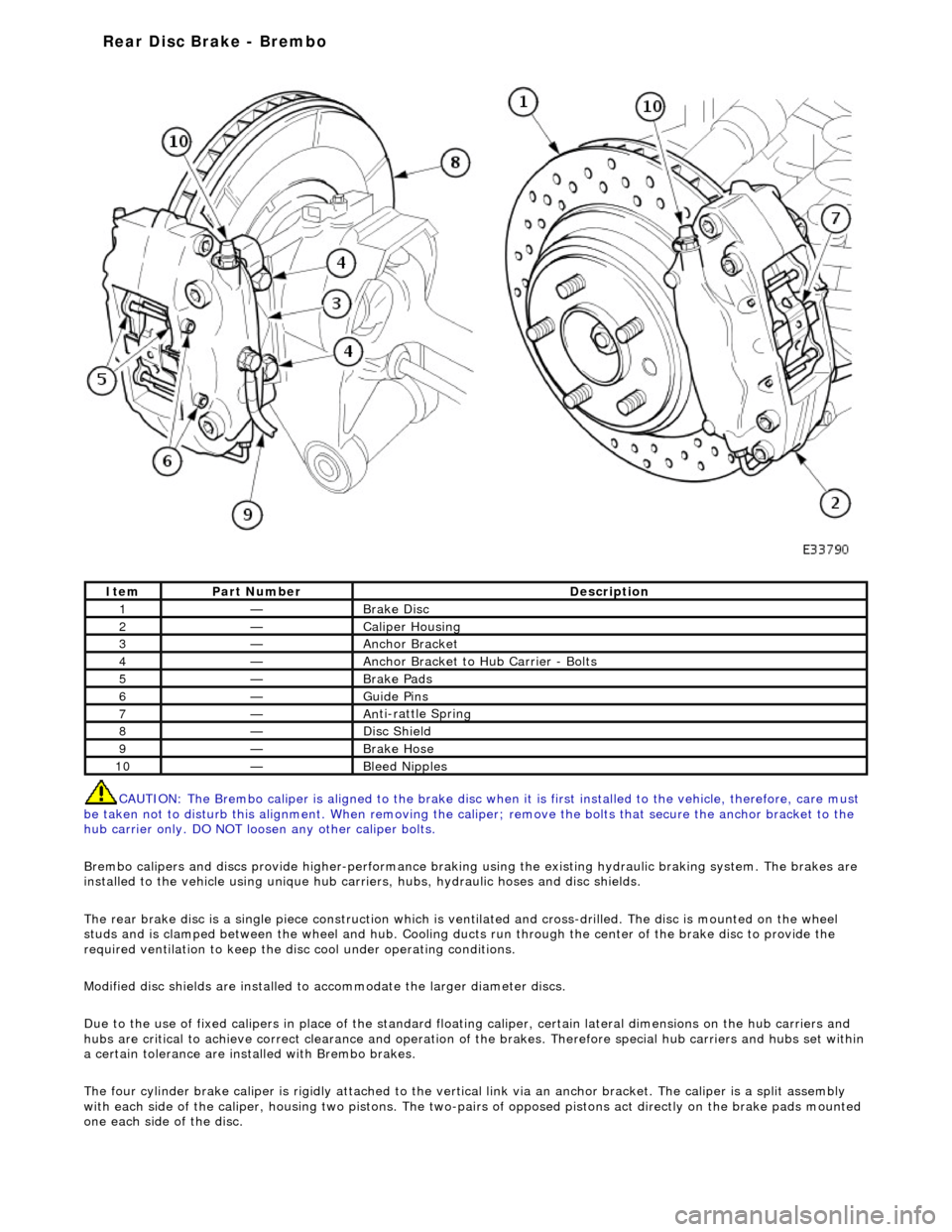
CAUTI O
N: The Brembo caliper is aligned to
the brake disc when it is first installed to the vehicle, therefore, care must
be taken not to disturb this alignment. When removing the ca liper; remove the bolts that secure the anchor bracket to the
hub carrier only. DO NOT loos en any other caliper bolts.
Brembo calipers and discs provide higher -performance braking using the existing hydraulic braking system. The brakes are
installed to the vehicle using unique hub carr iers, hubs, hydraulic hoses and disc shields.
The rear brake disc is a single piece co nstruction which is ventilated and cross-drilled. The disc is mounted on the wheel
studs and is clamped between the wheel and hub. Cooling ducts run through the ce nter of the brake disc to provide the
required ventilation to keep the disc cool under operating conditions.
Modified disc shields are installed to accommodate the larger diameter discs.
Due to the use of fixed calipers in place of the standard floating caliper, certain lateral dimensions on the hub carriers and
hubs are critical to achieve correct cleara nce and operation of the brakes. Therefore special hub carriers and hubs set within
a certain tolerance are inst alled with Brembo brakes.
The four cylinder brake caliper is rigidly attached to the vert ical link via an anchor bracket. The caliper is a split assembly
with each side of the caliper, housing two pistons. The two-pairs of opposed pistons act direct ly on the brake pads mounted
one each side of the disc.
It e
m
Par
t
Number
De
scr
iption
1—Brake D
i
sc
2—Caliper Housin
g
3—Anchor Bracke
t
4—Anchor Bracket to H
u
b Carrier - Bolts
5—Brake Pads
6—Guide Pi
ns
7—An
ti
-rattle Sprin
g
8—Di
sc
Shield
9—Brake Hos
e
10—Bleed Nipp
les
Rear Disc Brake - Brembo
Page 464 of 2490
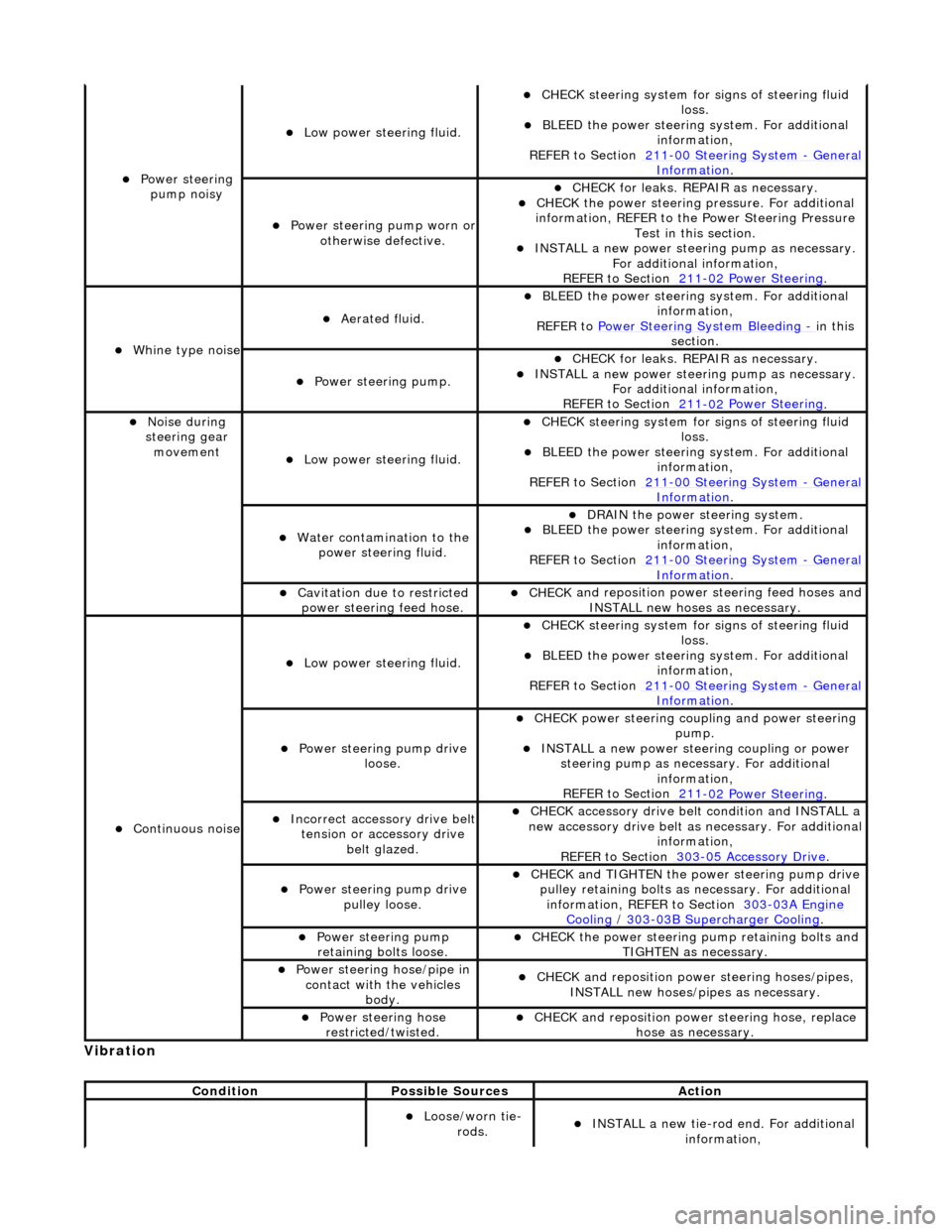
Vibrati
on
Power steeri
ng
pump noisy
Low power steer i
ng fluid.
CHECK
steering system for s
igns of steering fluid
loss.
BLEE D the
power steering system. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 211
-0 0
Steering System
-
Ge n
eral
Informati
o
n
.
Power steeri
ng pump wor
n or
otherwise defective.
CHECK for leaks. R
EPAIR as necessary.
CHECK
the power steering pressure. For additional
information, REFER to th e Power Steering Pressure
Test in this section.
INST ALL a ne
w power steering pump as necessary.
For additional information,
REFER to Section 211
-0 2
Power Steering
.
Wh
in
e type noise
Aerated flui
d.
BLEE
D the
power steering system. For additional
information,
REFER to Power Steering System Bleeding
- in t h
is
section.
Power steering pump.
CHECK for leaks. R
EPAIR as necessary.
INSTALL a ne
w power steering pump as necessary.
For additional information,
REFER to Section 211
-0 2
Power Steering
.
No
i
se during
steering gear movement
Low power steer i
ng fluid.
CHECK
steering system for s
igns of steering fluid
loss.
BLEE D the
power steering system. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 211
-0 0
Steering System
-
Ge n
eral
Informati
o
n
.
Water co
n
tamination to the
power steering fluid.
DR AIN
the power steering system.
BLEE
D the
power steering system. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 211
-00
Steering System
-
Gen
eral
Informati
o
n
.
Cavi
tation due to restricted
po
wer steering feed hose.
CHECK
and reposition power
steering feed hoses and
INSTALL new hoses as necessary.
Continu o
us noise
Low power steer i
ng fluid.
CHECK
steering system for s
igns of steering fluid
loss.
BLEE D the
power steering system. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 211
-0 0
Steering System
-
Ge n
eral
Informati
o
n
.
Power steeri
ng pump dri
ve
loose.
CHECK
power steering coupli
ng and power steering
pump.
IN ST
ALL a new power steering coupling or power
steering pump as nece ssary. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 211
-0 2
Power Steering
.
Incorre
ct
accessory drive belt
tension or accessory drive belt glazed.
CHECK acc
essory drive belt condition and INSTALL a
new accessory drive belt as necessary. For additional
information,
REFER to Section 303
-0 5 Ac
cessory Drive
.
Power steeri
ng pump dri
ve
pulley loose.
CHECK
and TIGHTEN the power steering pump drive
pulley retaining bolts as necessary. For additional
information, REFER to Section 303
-03A En
gine
Coo
ling / 30 3-03
B Supercharger Cooling
.
Power steeri
ng pump
r
etaining bolts loose.
CHECK
the power steering pump retaining bolts and
TIGHTEN as necessary.
Power steering hose/pipe in c
ontact with the vehicles
body.
CHECK
and reposition powe
r steering hoses/pipes,
INSTALL new hoses/pipes as necessary.
Power steeri ng hose
r
estricted/twisted.
CHECK
and reposition powe
r steering hose, replace
hose as necessary.
Conditi
on
Possibl
e Sources
Actio
n
Loose/worn tie-
ro
ds.
INST
ALL a new tie-r
od end. For additional
information,
Page 522 of 2490

diverter val
ve (if fitted) and oil filter.
Main
bearings
which are grooved in the upper positions and plain in
the lower positions. They are manufactured from
aluminium / tin material.
A c
rankshaft with under
cuts and rolled fillets for extra strength.
Fracture
-split connecting rods in sintered-forged steel.
Brackets
bolted to the front of
the cylinder
block are used to mo unt all accessories.
A sin
gle, seven ribbed vee belt
drives the accessories.
An au
tomatic belt tensioner for the front accessory drive,
incorporating a wear indicator.
An advanced en
gine management system inco
rporating electronic throttle control.
The un
it meets the requirements of the CARB OBDII USA legislation.
Ancillary Systems
The an
ci
llary systems, driven by the engine, each have a
detailed Description and Operation along with Diagnostic
Procedures, and Removal and Installation instructions ; refer to the following sections of this manual:
Power Steeri
ng Pump - Section 211-02
Ai
r Conditioning Compressor - Sectio
n 412-03
Engine
C
ooling Pump - Section 303-03
Generator
- Sectio
n 414-02
The drive belt, idler pulley and automatic tensioner are described in Section 303-05.
The engine starting system is described in Section 303-06.
En
gine Management and Emission Control System
Engine Control Modu
le (ECM)
Engine
management and exhaust emissions are controlled by the ECM, which has the
following main functions:
Fu
el injection
Idle
s
peed
Ignition Ev
aporative loss system
Engine
cooling fans Clim
ate control compressor clutch demand
The microprocessor within the ECM receiv es signals from various sensors and other modules and uses a pre-determined
program to compute engine management functions.
Adaptive functions are incorporated in the ECM to cater for co ntinuous adjustments to its computations to suit prevailing
conditions. Because the system also controls emissions to suit all modes, neither CO levels nor idle speed require service
attention or adjustment, except if an error should occur.
On Board Diagnostics are controlled by the ECM with the continuous monitoring of incoming signals and the subsequent
verification against what the module expects to 'see'. Should a si gnal be incorrect or missing, the ECM will substitute a fixed
value to provide the 'limp home mode' and alert the driver of the problem. Fixed values may be adopted for:
Transmission oil
temperature
Mechanica
l
guar
d position
Throttle blade angle Camshaft position
Inta
k
e air temperature
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC), including OBD II codes, are stored in the ECM memo ry and can be read by an appropriate
retrieval tool.
Should either the ECM or TCM fa il, ensure that the control housing cooling fan is operating correctly. Failure of the cooling
fan MUST be rectified before renewing a control module and details of a fa n failure should accompany a returned control
module.
Page 528 of 2490

Speed an
d load
Coo
l
ant temperature
Ti
me el
apsed from start up
Cl
osed l
oop fuelling
Determination of the vapour concentration is made by stepped opening of the EVAP valve and subsequent monitoring of the
fuelling correction. This function is performed prior to purging, so that at the onse t of purging the EVAP valve can be set to
the optimum position. Should the ECM be unable to determine the concentration before purging, a default value is
employed, which is then modified whilst purging is in progress.
When the purging process is operational th e ECM modifies the basic fuelling calculation to maintain the correct air / fuel
ratio.
Purging is inhibited during fuel cut-off and stability / traction control intervention.
Coolant Temperature Sen
sor
Th
e
sensor outputs a voltage to the ECM which decreases as temperature increases.
Cooling Fans
In response to engi
ne coolant temperat
u
re and climate control system demand, the ECM will energize the cooling fans.
Climate Control Compressor
The E
C
M will allow the compressor clutch to be engaged if th
e engine temperature and load demand are normal. Should the
driver require maximum engine powe r or the coolant temperature be high, the request will be denied.
Cranking Signal
The ECM reacts to a signal fr
om th
e Body Processor Module (BPM) when the starter motor relay is energi
zed. This signal is
used to trigger starting, fu el and ignition strategies.
Engine Speed and Cranksh
aft Position
Engine
speed and cran
k position are moni
tored by a sensor which is mounted on the cylinder block (flywheel housing)
behind the crankshaft drive plat e. It indicates rotational speed to the ECM in the form of 12 pulses per crank revolution.
Engine speed is used for synchronization of fuel an d ignition systems, as well as other functions.
Camshaft Position
The ca
mshaft position sensor is mounted at
the rear of Bank 2 cylinder head on the inlet side and provides one signal every
720 degrees of crankshaft rotation. The signal, in conjunction with the signal from the crankshaft position sensor, indicates
to the ECM that the piston of cylinder 1A is approaching TDC on the compression stroke.
Variable Valve
Timing (Where Fitted)
By energi
si
ng a solenoid to allow the pass
age of pressurized oil on each of the inle t camshaft drives, the ECM can vary by a
single stepped amount, the relati ve timing of the inlet valves.
Ign
ition
Ignit
i
on spark is produced by
individual on-plug coil units.
There are two ignition amplifiers; module #1 drives coils 1A, 2B, 3B and 4A, whilst module #2 drives coils 1B, 2A, 3A and
4B. The ECM controls the amplifiers.
Page 650 of 2490
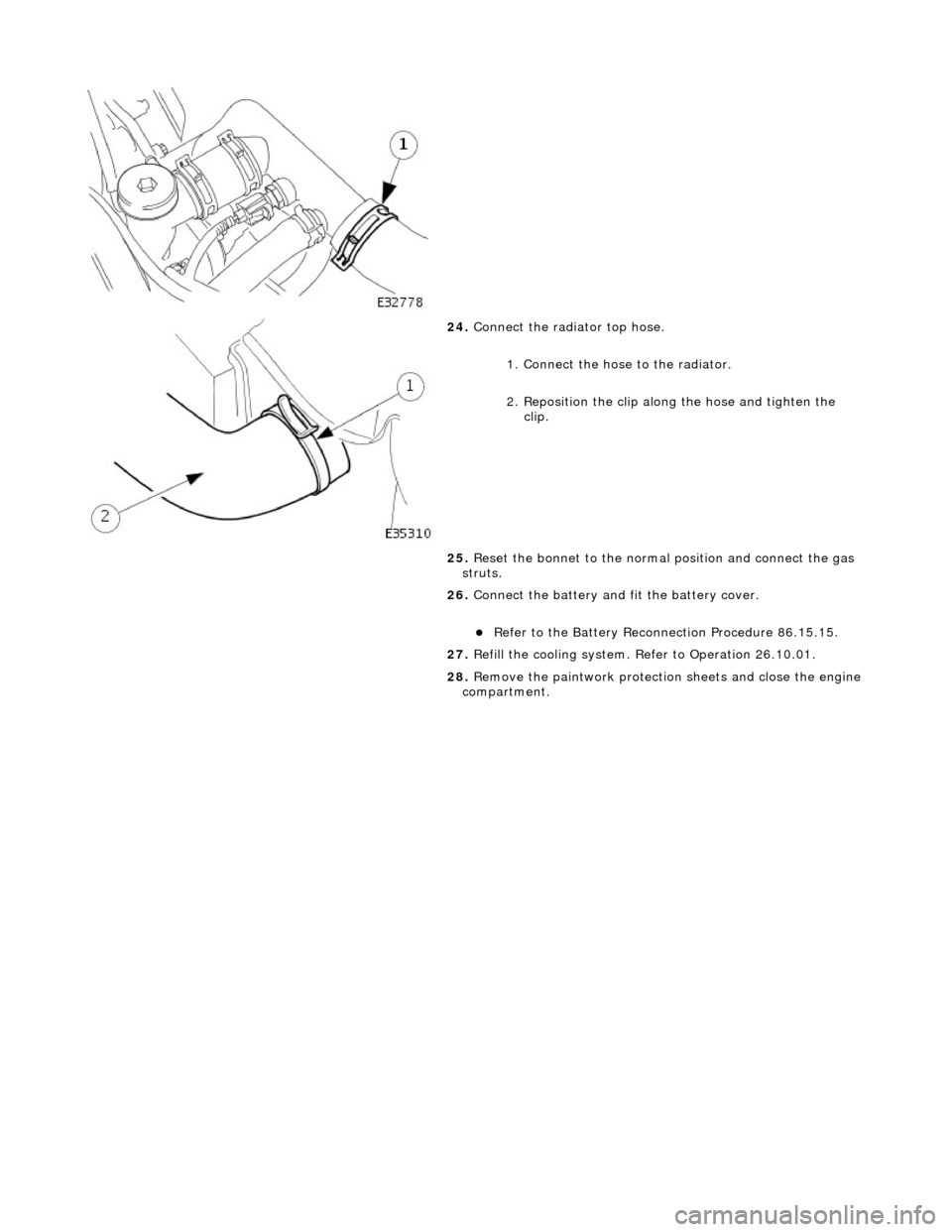
24.
Connect
the radiator top hose.
1. Connect the hose to the radiator.
2. Reposition the clip along the hose and tighten the clip.
25. Reset the bonnet to the normal position and connect the gas
struts.
26. Connect the battery and fit the battery cover.
Refe
r to the Battery Reconnection Procedure 86.15.15.
27. Refill the cooling system. Refer to Operation 26.10.01.
28. Remove the paintwork protection sheets and close the engine
compartment.
Page 659 of 2490
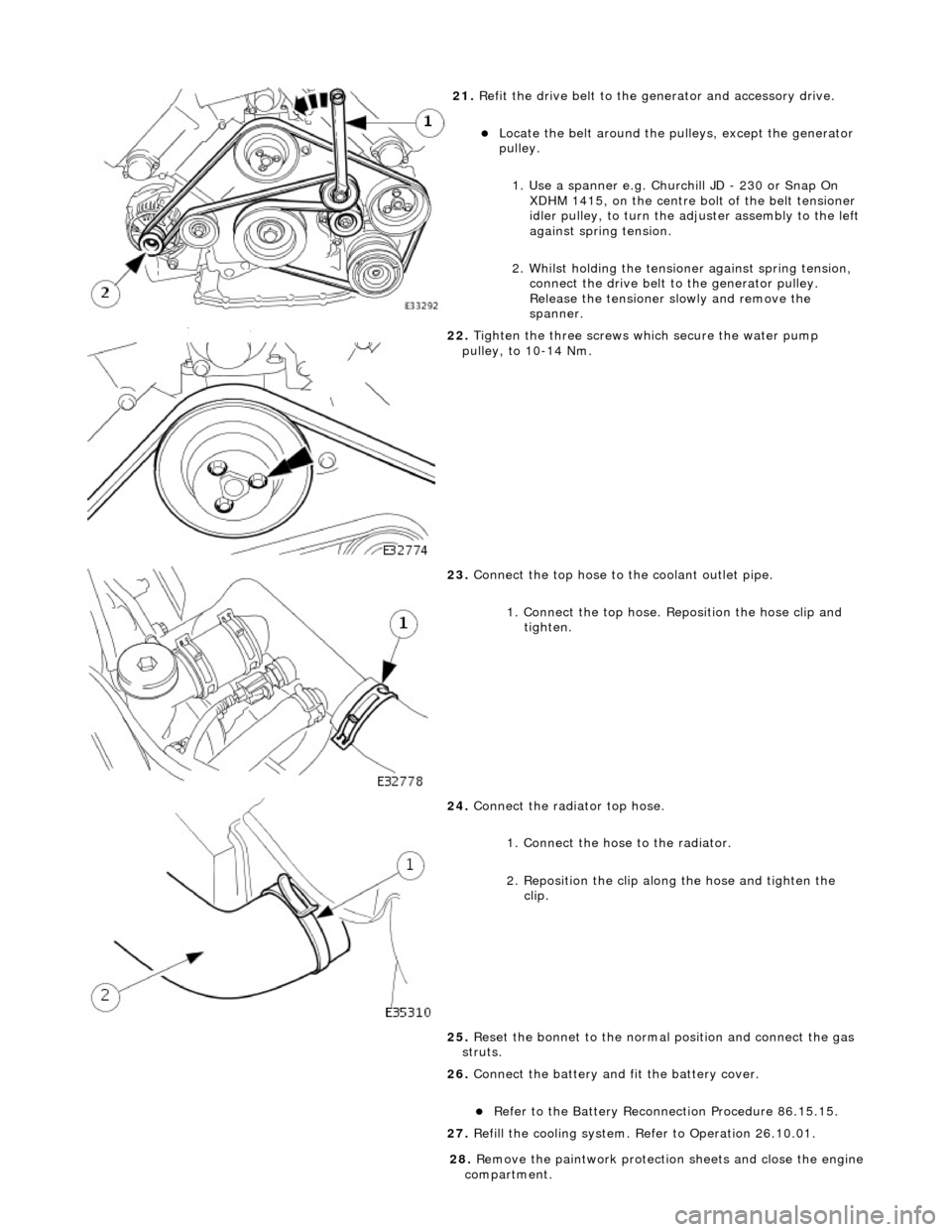
21
.
Refit the drive belt to the generator and accessory drive.
Locat
e the belt around the pulleys, except the generator
pulley.
1. Use a spanner e.g. Churchill JD - 230 or Snap On XDHM 1415, on the centre bo lt of the belt tensioner
idler pulley, to turn the adju ster assembly to the left
against spring tension.
2. Whilst holding the tensioner against spring tension, connect the drive belt to the generator pulley.
Release the tensioner sl owly and remove the
spanner.
22
.
Tighten the three screws wh ich secure the water pump
pulley, to 10-14 Nm.
23
.
Connect the top hose to the coolant outlet pipe.
1. Connect the top hose. Reposition the hose clip and tighten.
24
.
Connect the radiator top hose.
1. Connect the hose to the radiator.
2. Reposition the clip along the hose and tighten the clip.
25. Reset the bonnet to the normal position and connect the gas
struts.
26. Connect the battery and fit the battery cover.
Re
fer to the Battery Reconnection Procedure 86.15.15.
27. Refill the cooling system. Refer to Operation 26.10.01.
28
.
Remove the paintwork protection sheets and close the engine
compartment.
Page 733 of 2490
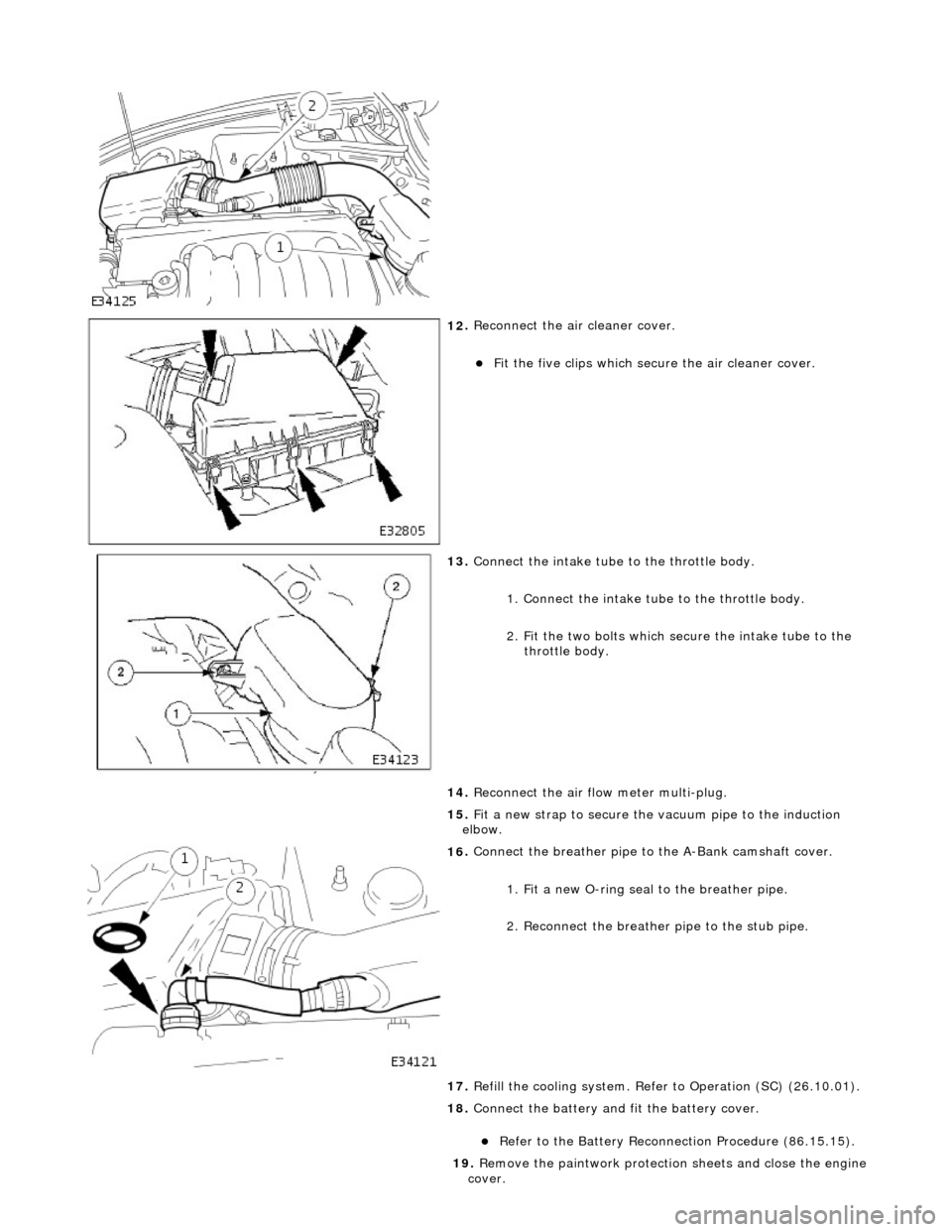
12
.
Reconnect the air cleaner cover.
F
it the five clips which secu
re the air cleaner cover.
13
.
Connect the intake tube to the throttle body.
1. Connect the intake tube to the throttle body.
2. Fit the two bolts which secure the intake tube to the throttle body.
14. Reconnect the air flow meter multi-plug.
15. Fit a new strap to secure the vacuum pipe to the induction
elbow.
16
.
Connect the breather pipe to the A-Bank camshaft cover.
1. Fit a new O-ring seal to the breather pipe.
2. Reconnect the breather pipe to the stub pipe.
17. Refill the cooling system. Refer to Operation (SC) (26.10.01).
18. Connect the battery and fit the battery cover.
Re
fer to the Battery Reconnection Procedure (86.15.15).
19. Remove the paintwork protection sheets and close the engine
cover.