Rear Drive JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 148 of 3039
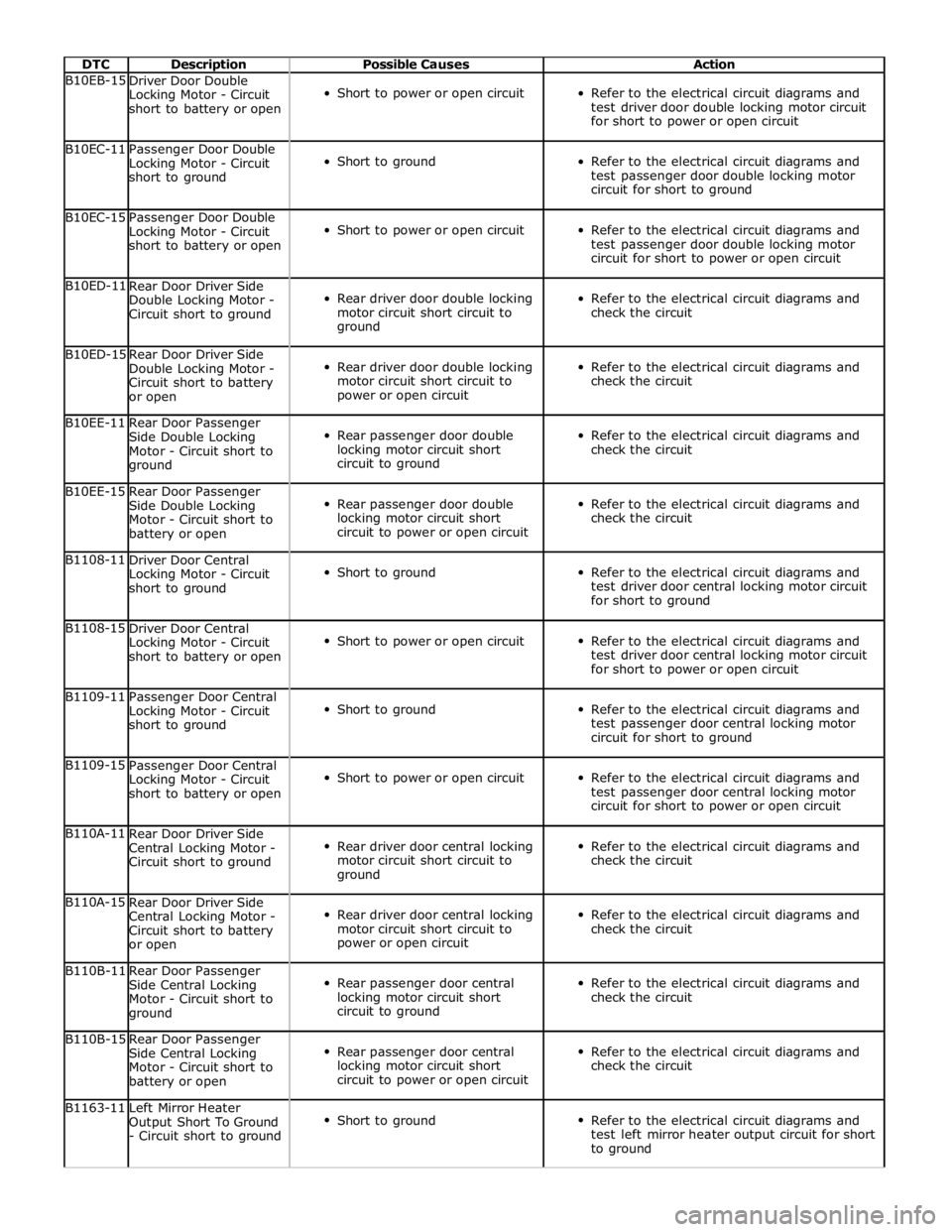
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10EB-15
Driver Door Double
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test driver door double locking motor circuit
for short to power or open circuit B10EC-11
Passenger Door Double
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door double locking motor
circuit for short to ground B10EC-15
Passenger Door Double
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door double locking motor
circuit for short to power or open circuit B10ED-11
Rear Door Driver Side
Double Locking Motor -
Circuit short to ground
Rear driver door double locking
motor circuit short circuit to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B10ED-15
Rear Door Driver Side
Double Locking Motor -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Rear driver door double locking
motor circuit short circuit to
power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B10EE-11
Rear Door Passenger
Side Double Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Rear passenger door double
locking motor circuit short
circuit to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B10EE-15
Rear Door Passenger
Side Double Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Rear passenger door double
locking motor circuit short
circuit to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B1108-11
Driver Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test driver door central locking motor circuit
for short to ground B1108-15
Driver Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test driver door central locking motor circuit
for short to power or open circuit B1109-11
Passenger Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door central locking motor
circuit for short to ground B1109-15
Passenger Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door central locking motor
circuit for short to power or open circuit B110A-11
Rear Door Driver Side
Central Locking Motor -
Circuit short to ground
Rear driver door central locking
motor circuit short circuit to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B110A-15
Rear Door Driver Side
Central Locking Motor -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Rear driver door central locking
motor circuit short circuit to
power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B110B-11
Rear Door Passenger
Side Central Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Rear passenger door central
locking motor circuit short
circuit to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B110B-15
Rear Door Passenger
Side Central Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Rear passenger door central
locking motor circuit short
circuit to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B1163-11
Left Mirror Heater
Output Short To Ground
- Circuit short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test left mirror heater output circuit for short
to ground
Page 150 of 3039
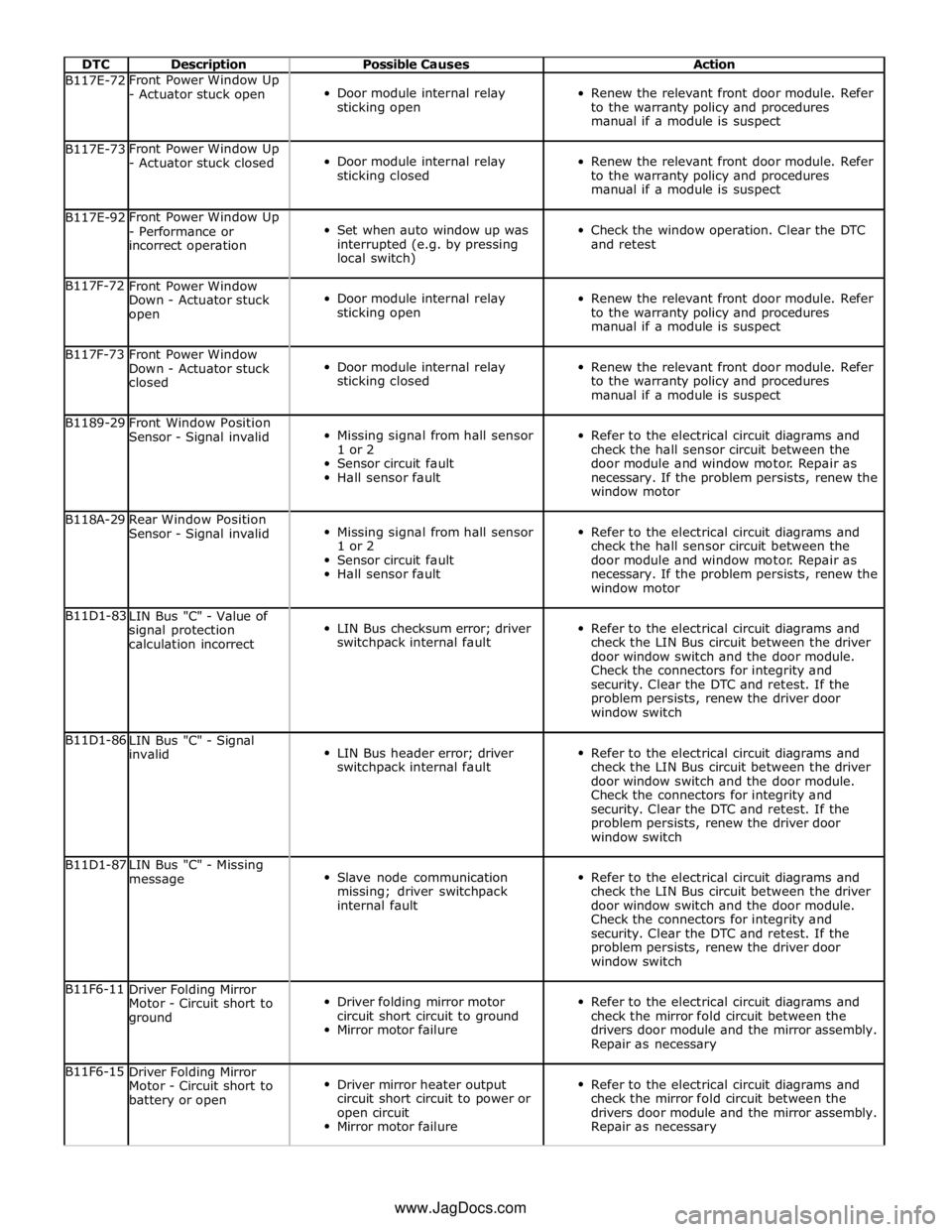
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B117E-72 Front Power Window Up
- Actuator stuck open
Door module internal relay
sticking open
Renew the relevant front door module. Refer
to the warranty policy and procedures
manual if a module is suspect B117E-73 Front Power Window Up
- Actuator stuck closed
Door module internal relay
sticking closed
Renew the relevant front door module. Refer
to the warranty policy and procedures
manual if a module is suspect B117E-92 Front Power Window Up
- Performance or
incorrect operation
Set when auto window up was
interrupted (e.g. by pressing
local switch)
Check the window operation. Clear the DTC
and retest B117F-72
Front Power Window
Down - Actuator stuck
open
Door module internal relay
sticking open
Renew the relevant front door module. Refer
to the warranty policy and procedures
manual if a module is suspect B117F-73
Front Power Window
Down - Actuator stuck
closed
Door module internal relay
sticking closed
Renew the relevant front door module. Refer
to the warranty policy and procedures
manual if a module is suspect B1189-29
Front Window Position
Sensor - Signal invalid
Missing signal from hall sensor
1 or 2
Sensor circuit fault
Hall sensor fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the hall sensor circuit between the
door module and window motor. Repair as
necessary. If the problem persists, renew the
window motor B118A-29
Rear Window Position
Sensor - Signal invalid
Missing signal from hall sensor
1 or 2
Sensor circuit fault
Hall sensor fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the hall sensor circuit between the
door module and window motor. Repair as
necessary. If the problem persists, renew the
window motor B11D1-83
LIN Bus "C" - Value of
signal protection
calculation incorrect
LIN Bus checksum error; driver
switchpack internal fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the LIN Bus circuit between the driver
door window switch and the door module.
Check the connectors for integrity and
security. Clear the DTC and retest. If the
problem persists, renew the driver door
window switch B11D1-86
LIN Bus "C" - Signal
invalid
LIN Bus header error; driver
switchpack internal fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the LIN Bus circuit between the driver
door window switch and the door module.
Check the connectors for integrity and
security. Clear the DTC and retest. If the
problem persists, renew the driver door
window switch B11D1-87
LIN Bus "C" - Missing
message
Slave node communication
missing; driver switchpack
internal fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the LIN Bus circuit between the driver
door window switch and the door module.
Check the connectors for integrity and
security. Clear the DTC and retest. If the
problem persists, renew the driver door
window switch B11F6-11
Driver Folding Mirror
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Driver folding mirror motor
circuit short circuit to ground
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror fold circuit between the
drivers door module and the mirror assembly.
Repair as necessary B11F6-15
Driver Folding Mirror
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Driver mirror heater output
circuit short circuit to power or
open circuit
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror fold circuit between the
drivers door module and the mirror assembly.
Repair as necessary www.JagDocs.com
Page 151 of 3039
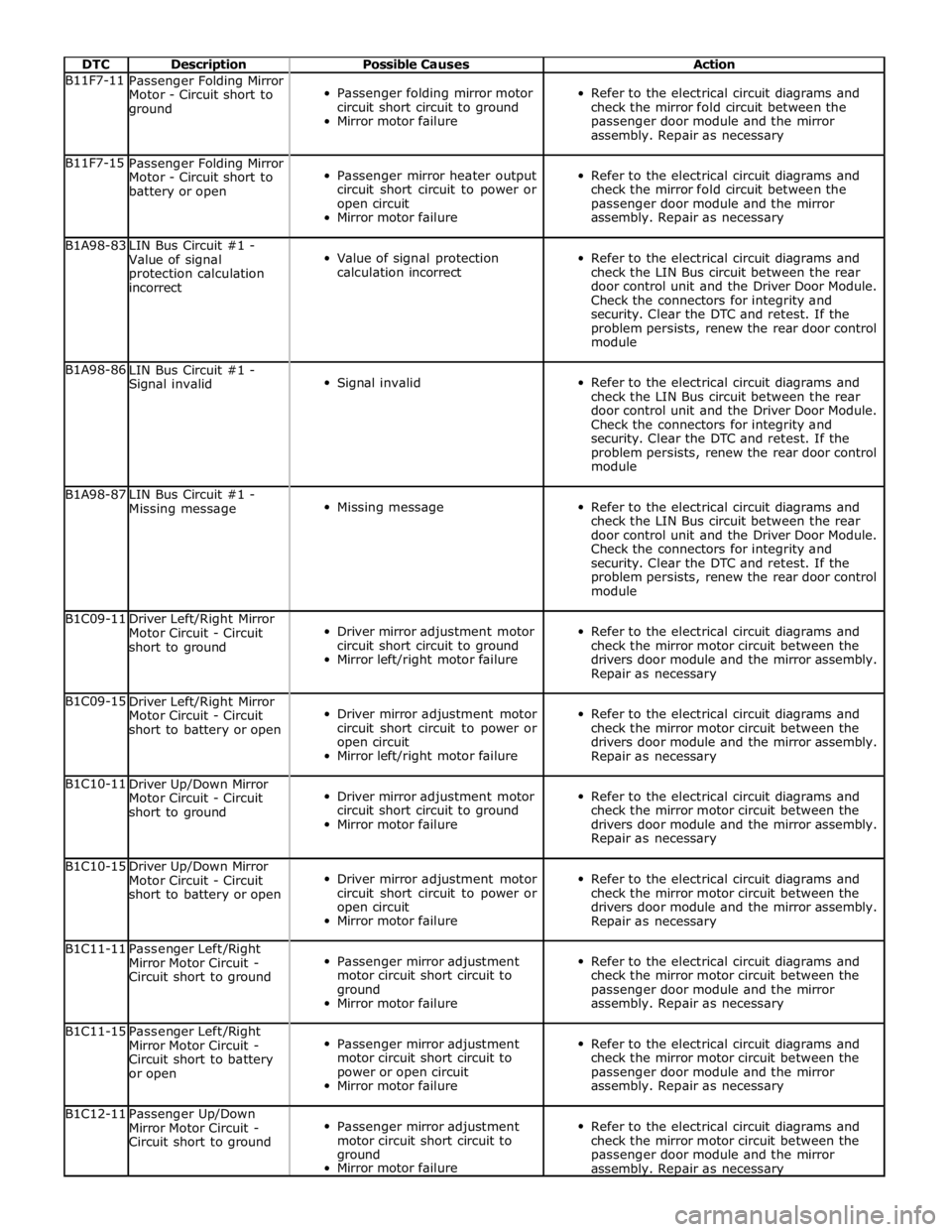
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B11F7-11
Passenger Folding Mirror
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Passenger folding mirror motor
circuit short circuit to ground
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror fold circuit between the
passenger door module and the mirror
assembly. Repair as necessary B11F7-15
Passenger Folding Mirror
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Passenger mirror heater output
circuit short circuit to power or
open circuit
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror fold circuit between the
passenger door module and the mirror
assembly. Repair as necessary B1A98-83
LIN Bus Circuit #1 -
Value of signal
protection calculation
incorrect
Value of signal protection
calculation incorrect
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the LIN Bus circuit between the rear
door control unit and the Driver Door Module.
Check the connectors for integrity and
security. Clear the DTC and retest. If the
problem persists, renew the rear door control
module B1A98-86
LIN Bus Circuit #1 -
Signal invalid
Signal invalid
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the LIN Bus circuit between the rear
door control unit and the Driver Door Module.
Check the connectors for integrity and
security. Clear the DTC and retest. If the
problem persists, renew the rear door control
module B1A98-87
LIN Bus Circuit #1 -
Missing message
Missing message
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the LIN Bus circuit between the rear
door control unit and the Driver Door Module.
Check the connectors for integrity and
security. Clear the DTC and retest. If the
problem persists, renew the rear door control
module B1C09-11
Driver Left/Right Mirror
Motor Circuit - Circuit
short to ground
Driver mirror adjustment motor
circuit short circuit to ground
Mirror left/right motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
drivers door module and the mirror assembly.
Repair as necessary B1C09-15
Driver Left/Right Mirror
Motor Circuit - Circuit
short to battery or open
Driver mirror adjustment motor
circuit short circuit to power or
open circuit
Mirror left/right motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
drivers door module and the mirror assembly.
Repair as necessary B1C10-11
Driver Up/Down Mirror
Motor Circuit - Circuit
short to ground
Driver mirror adjustment motor
circuit short circuit to ground
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
drivers door module and the mirror assembly.
Repair as necessary B1C10-15
Driver Up/Down Mirror
Motor Circuit - Circuit
short to battery or open
Driver mirror adjustment motor
circuit short circuit to power or
open circuit
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
drivers door module and the mirror assembly.
Repair as necessary B1C11-11
Passenger Left/Right
Mirror Motor Circuit -
Circuit short to ground
Passenger mirror adjustment
motor circuit short circuit to
ground
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
passenger door module and the mirror
assembly. Repair as necessary B1C11-15
Passenger Left/Right
Mirror Motor Circuit -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Passenger mirror adjustment
motor circuit short circuit to
power or open circuit
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
passenger door module and the mirror
assembly. Repair as necessary B1C12-11
Passenger Up/Down
Mirror Motor Circuit -
Circuit short to ground
Passenger mirror adjustment
motor circuit short circuit to
ground
Mirror motor failure
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the mirror motor circuit between the
passenger door module and the mirror assembly. Repair as necessary
Page 197 of 3039
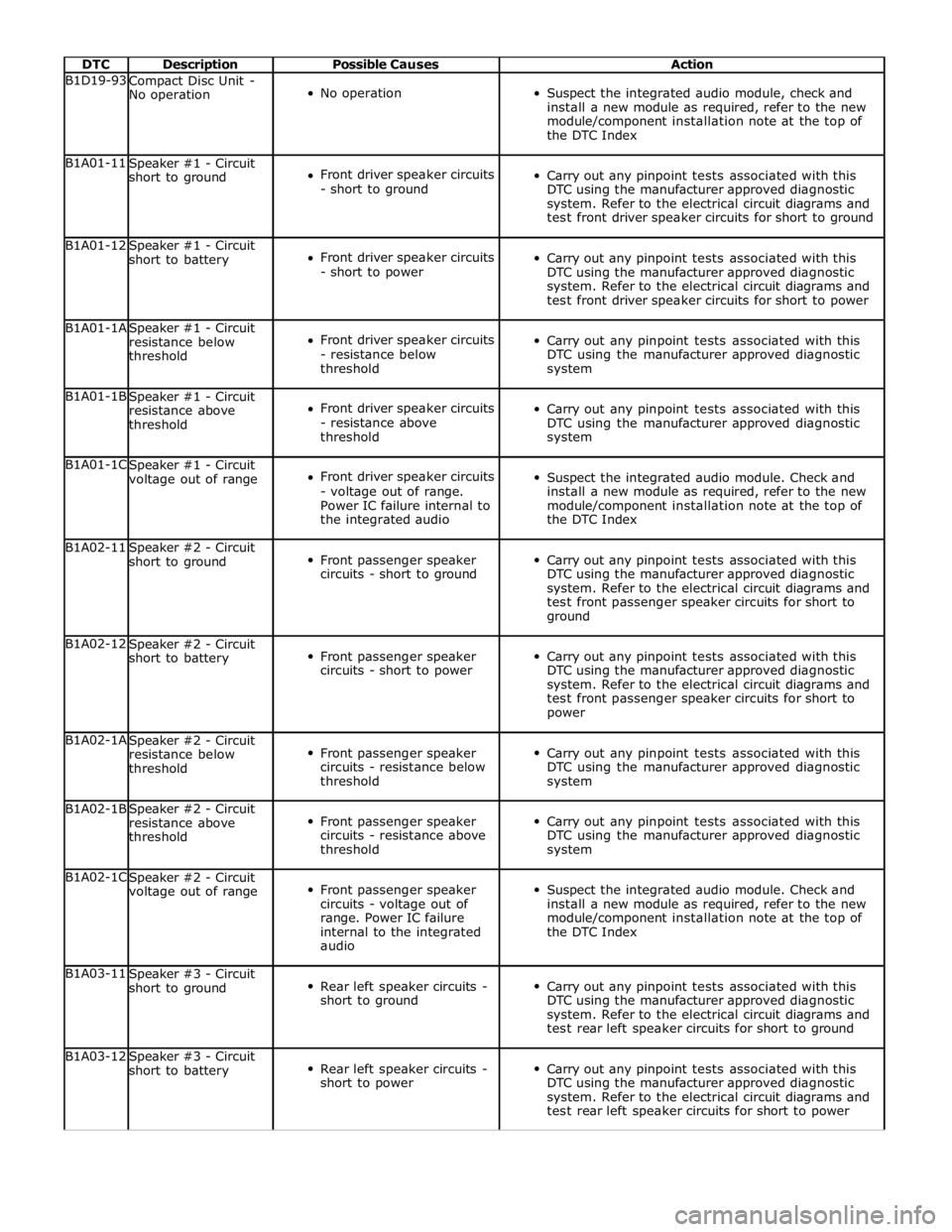
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1D19-93
Compact Disc Unit -
No operation
No operation
Suspect the integrated audio module, check and
install a new module as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index B1A01-11
Speaker #1 - Circuit
short to ground
Front driver speaker circuits
- short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test front driver speaker circuits for short to ground B1A01-12
Speaker #1 - Circuit
short to battery
Front driver speaker circuits
- short to power
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test front driver speaker circuits for short to power B1A01-1A
Speaker #1 - Circuit
resistance below
threshold
Front driver speaker circuits
- resistance below
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system B1A01-1B
Speaker #1 - Circuit
resistance above
threshold
Front driver speaker circuits
- resistance above
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system B1A01-1C
Speaker #1 - Circuit
voltage out of range
Front driver speaker circuits
- voltage out of range.
Power IC failure internal to
the integrated audio
Suspect the integrated audio module. Check and
install a new module as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index B1A02-11
Speaker #2 - Circuit
short to ground
Front passenger speaker
circuits - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test front passenger speaker circuits for short to
ground B1A02-12
Speaker #2 - Circuit
short to battery
Front passenger speaker
circuits - short to power
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test front passenger speaker circuits for short to
power B1A02-1A
Speaker #2 - Circuit
resistance below
threshold
Front passenger speaker
circuits - resistance below
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system B1A02-1B
Speaker #2 - Circuit
resistance above
threshold
Front passenger speaker
circuits - resistance above
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system B1A02-1C
Speaker #2 - Circuit
voltage out of range
Front passenger speaker
circuits - voltage out of
range. Power IC failure
internal to the integrated
audio
Suspect the integrated audio module. Check and
install a new module as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index B1A03-11
Speaker #3 - Circuit
short to ground
Rear left speaker circuits -
short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear left speaker circuits for short to ground B1A03-12
Speaker #3 - Circuit
short to battery
Rear left speaker circuits -
short to power
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear left speaker circuits for short to power
Page 216 of 3039

Published: 17-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Rear
Differential Control Module (RDCM)
Description and Operation
Rear Differential Control Module (RDCM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
If the rear differential control module, rear differential actuator or the rear differential are replaced, the on demand self
test (ODST) must be carried out to calibrate the components
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as needed
The table below lists all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the rear differential control module, for
additional diagnosis and testing information refer to the relevant diagnosis and testing section.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Drive Axle and Differential (205-02 Rear Drive Axle/Differential, Diagnosis and
Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action P0562-00
System Voltage Low -
No sub type
information
Rear differential control
module voltage supply
below 9 volts
Check the battery charge condition, refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check the wiring to
the rear differential control module, repair as
necessary P0563-00
System Voltage High -
No sub type
information
System voltage high
(supply voltage supply
greater than 16 volts)
Check engine control module for stored DTCs,
suspect charging system fault. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check, power and
ground circuit for fault P0604-00
Internal Control Module
Random Access Memory
(RAM) Error - No sub
type information
Rear differential control
module internal error
Clear the DTC and retest. If the problem persists,
renew the control module. Refer to the warranty
policy and procedures manual, or determine if any
prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component P0605-00
Internal Control Module
Read Only Memory
(ROM) Error - No sub
type information
Rear differential control
module internal error
Clear the DTC and retest. If the problem persists,
renew the control module. Refer to the warranty
policy and procedures manual, or determine if any www.JagDocs.com
Page 218 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Rear
Junction Box (RJB)
Description and Operation
Rear Junction Box (RJB)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Rear Junction Box (RJB). For additional
diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action P0460-11
Fuel Level Sensor A
Circuit - Circuit short to
ground
Fuel level sensor A
analogue input circuit -
short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel level sensor A analogue input circuit for short to
ground P0460-15
Fuel Level Sensor A
Circuit - Circuit short to
battery or open
Fuel level sensor A
analogue input circuit -
short to power, open
circuit
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel level sensor A analogue input circuit for short to
power, open circuit P0571-12
Brake Switch A Circuit -
Circuit short to battery
Footbrake switch digital
input signal circuits -
short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
footbrake switch digital input signal circuits for
short to power P1230-12
Fuel Pump Low Speed
Malfunction (VLCM) -
Circuit short to battery
High Side output not
driven - Diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel pump delivery module for short to power
Page 220 of 3039
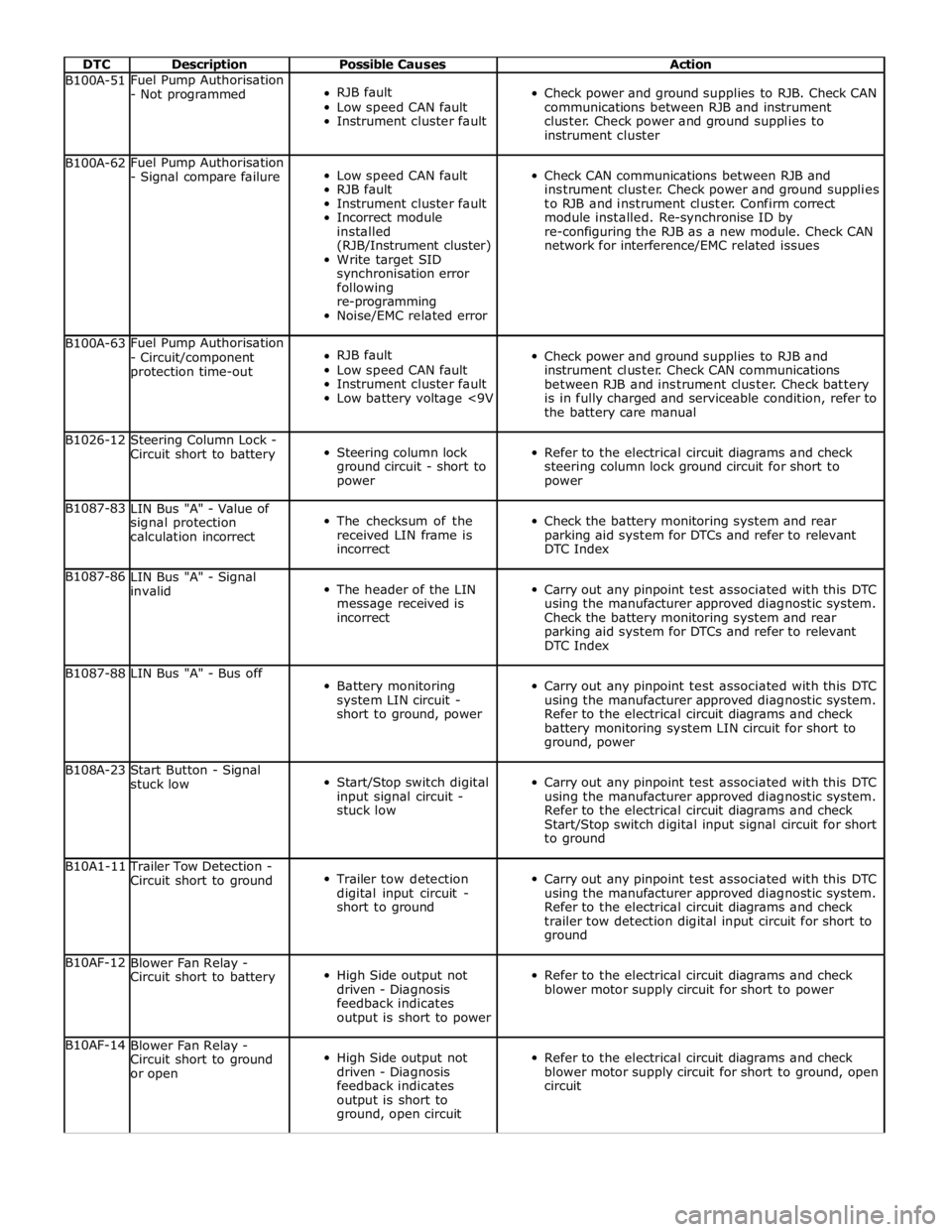
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B100A-51 Fuel Pump Authorisation
- Not programmed
RJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault
Check power and ground supplies to RJB. Check CAN
communications between RJB and instrument
cluster. Check power and ground supplies to
instrument cluster B100A-62 Fuel Pump Authorisation
- Signal compare failure
Low speed CAN fault
RJB fault
Instrument cluster fault
Incorrect module
installed
(RJB/Instrument cluster)
Write target SID
synchronisation error
following
re-programming
Noise/EMC related error
Check CAN communications between RJB and
instrument cluster. Check power and ground supplies
to RJB and instrument cluster. Confirm correct
module installed. Re-synchronise ID by
re-configuring the RJB as a new module. Check CAN
network for interference/EMC related issues B100A-63 Fuel Pump Authorisation
- Circuit/component
protection time-out
RJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault
Low battery voltage <9V
Check power and ground supplies to RJB and
instrument cluster. Check CAN communications
between RJB and instrument cluster. Check battery
is in fully charged and serviceable condition, refer to
the battery care manual B1026-12
Steering Column Lock -
Circuit short to battery
Steering column lock
ground circuit - short to
power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
steering column lock ground circuit for short to
power B1087-83
LIN Bus "A" - Value of
signal protection
calculation incorrect
The checksum of the
received LIN frame is
incorrect
Check the battery monitoring system and rear
parking aid system for DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index B1087-86
LIN Bus "A" - Signal
invalid
The header of the LIN
message received is
incorrect
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Check the battery monitoring system and rear
parking aid system for DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index B1087-88 LIN Bus "A" - Bus off
Battery monitoring
system LIN circuit -
short to ground, power
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
battery monitoring system LIN circuit for short to
ground, power B108A-23
Start Button - Signal
stuck low
Start/Stop switch digital
input signal circuit -
stuck low
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
Start/Stop switch digital input signal circuit for short
to ground B10A1-11 Trailer Tow Detection -
Circuit short to ground
Trailer tow detection
digital input circuit -
short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
trailer tow detection digital input circuit for short to
ground B10AF-12
Blower Fan Relay -
Circuit short to battery
High Side output not
driven - Diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
blower motor supply circuit for short to power B10AF-14
Blower Fan Relay -
Circuit short to ground
or open
High Side output not
driven - Diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is short to
ground, open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
blower motor supply circuit for short to ground, open
circuit
Page 225 of 3039
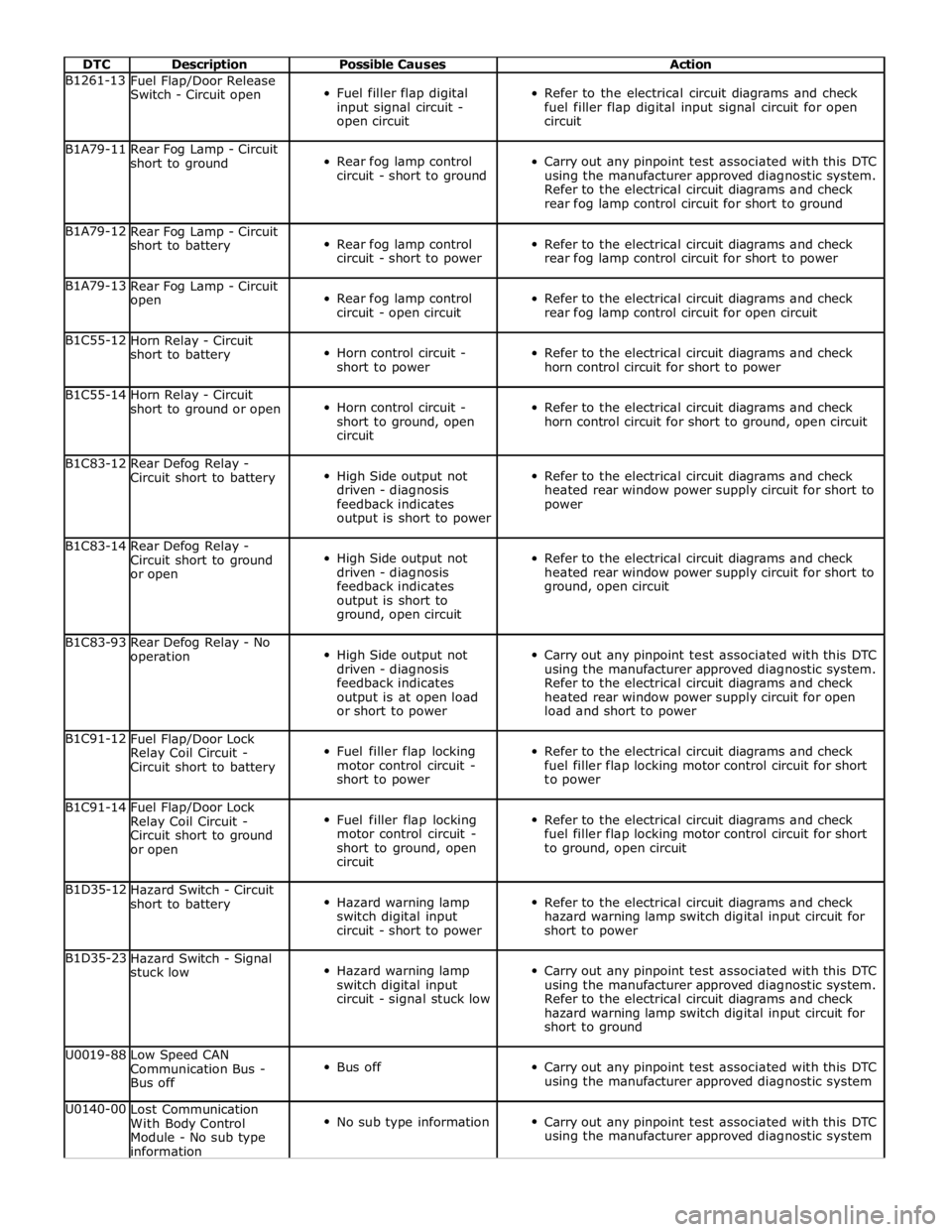
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1261-13
Fuel Flap/Door Release
Switch - Circuit open
Fuel filler flap digital
input signal circuit -
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel filler flap digital input signal circuit for open
circuit B1A79-11
Rear Fog Lamp - Circuit
short to ground
Rear fog lamp control
circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
rear fog lamp control circuit for short to ground B1A79-12
Rear Fog Lamp - Circuit
short to battery
Rear fog lamp control
circuit - short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
rear fog lamp control circuit for short to power B1A79-13
Rear Fog Lamp - Circuit
open
Rear fog lamp control
circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
rear fog lamp control circuit for open circuit B1C55-12
Horn Relay - Circuit
short to battery
Horn control circuit -
short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
horn control circuit for short to power B1C55-14
Horn Relay - Circuit
short to ground or open
Horn control circuit -
short to ground, open
circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
horn control circuit for short to ground, open circuit B1C83-12
Rear Defog Relay -
Circuit short to battery
High Side output not
driven - diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
heated rear window power supply circuit for short to
power B1C83-14
Rear Defog Relay -
Circuit short to ground
or open
High Side output not
driven - diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is short to
ground, open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
heated rear window power supply circuit for short to
ground, open circuit B1C83-93
Rear Defog Relay - No
operation
High Side output not
driven - diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is at open load
or short to power
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
heated rear window power supply circuit for open
load and short to power B1C91-12
Fuel Flap/Door Lock
Relay Coil Circuit -
Circuit short to battery
Fuel filler flap locking
motor control circuit -
short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel filler flap locking motor control circuit for short
to power B1C91-14
Fuel Flap/Door Lock
Relay Coil Circuit -
Circuit short to ground
or open
Fuel filler flap locking
motor control circuit -
short to ground, open
circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel filler flap locking motor control circuit for short
to ground, open circuit B1D35-12
Hazard Switch - Circuit
short to battery
Hazard warning lamp
switch digital input
circuit - short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
hazard warning lamp switch digital input circuit for
short to power B1D35-23
Hazard Switch - Signal
stuck low
Hazard warning lamp
switch digital input
circuit - signal stuck low
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
hazard warning lamp switch digital input circuit for
short to ground U0019-88
Low Speed CAN
Communication Bus -
Bus off
Bus off
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system U0140-00
Lost Communication
With Body Control
Module - No sub type
information
No sub type information
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system
Page 300 of 3039

Noise Conditions
Gear noise is typically a howling or whining due to gear damage or incorrect bearing preload. It can occur at various
speeds and driving conditions, or it can be continuous
Chuckle is a particular rattling noise that sounds like a stick against the spokes of a spinning bicycle wheel. It occurs
while decelerating from approximately 64 km/h (40 miles/h) and can usually be heard all the way to a stop. The
frequency varies with vehicle speed
Knock is very similar to chuckle, though it may be louder and occurs on acceleration or deceleration. The tear down will
disclose what has to be corrected
Check and rule out tires, exhaust and trim items before disassembling the transmission to diagnose and correct gear noise.
The noises described under Road Test usually have specific causes that can be diagnosed by observation as the unit is
disassembled. The initial clues are the type of noise heard on the road test and the driving conditions.
Vibration Conditions
wear. NOTE: New Constant Velocity (CV) joints should not be installed unless disassembly and inspection revealed unusual
Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be caused by the following:
Cut or damaged CV joint boots resulting in inadequate or contaminated lubricant in the outboard or inboard CV joint
bearing housings
Loose CV joint boot clamps
Another component contacting the rear drive half shaft
Worn, damaged or incorrectly installed wheel bearing, suspension or brake component
Vibration at highway speeds may be caused by the following:
Out-of-balance front or rear wheels
Out-of-round tires
Driveline imbalance
Driveline run-out (alignment)
NOTE: Rear drive half shafts are not balanced and are not likely to contribute to rotational vibration disturbance.
Shudder or vibration during acceleration (including from rest) may be caused by the following:
Driveline alignment
Excessively worn or damaged outboard or inboard CV joint bearing housing
Excessively high CV joint operating angles caused by incorrect ride height. Check ride height, verify correct spring rate
and check items under Inoperative Conditions
Excessively worn driveshaft components
Leakage Conditions
1. Inspect the CV joint boots for evidence of cracks, tears or splits.
2. Inspect the underbody for any indication of grease splatter in the vicinity of the rear drive half shaft, outboard and
inboard CV joint boot locations, which is an indication of CV joint boot or CV joint boot clamp damage.
3. Inspect the inboard CV joint bearing housing seal for leakage.
Inoperative Conditions
If a CV joint or rear drive half shaft pull-out occurs, check the following:
suspension components for correct location, damage or wear
bushings for wear
subframe for damage
bent or worn components
- Stabilizer bar link
- Left-hand rear suspension lower arm and bushing
- Right-hand rear suspension lower arm and bushing
- Rear wheel hub and rear drive half shaft
Road Test
A gear-driven unit will produce a certain amount of noise. Some noise is acceptable and may be audible at certain speeds or
under various driving conditions as on a newly paved blacktop road. The slight noise is in no way detrimental and must be
considered normal.
The road test and customer interview (if available) provide information needed to identify the condition and give direction to
the correct starting point for diagnosis.
1. Make notes throughout the diagnosis routine. Make sure to write down even the smallest piece of information, because
Page 301 of 3039

it may turn out to be the most important.
2. Do not touch anything until a road test and a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle have been carried out. Leave the
tire pressures and vehicle load just where they were when the condition was first observed. Adjusting tire pressures,
vehicle load or making other adjustments may reduce the conditions intensity to a point where it cannot be identified
clearly. It may also inject something new into the system, preventing correct diagnosis.
3. Make a visual inspection as part of the preliminary diagnosis routine, writing down anything that does not look right.
Note tire pressures, but do not adjust them yet. Note leaking fluids, loose nuts and bolts, or bright spots where
components may be rubbing against each other. Check the luggage compartment for unusual loads.
4. Road test the vehicle and define the condition by reproducing it several times during the road test.
5. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks as soon as the condition is reproduced. This will identify the correct diagnostic
procedure. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks more than once to verify they are providing a valid result. Remember,
the Road Test Quick Checks may not tell where the concern is, but they will tell where it is not.
Road Test Quick Checks
1. 24-80 km/h (15-50 miles/h): With light acceleration, a moaning noise is heard and possibly a vibration is felt in the
front floor pan. It is usually worse at a particular engine speed and at a particular throttle setting during acceleration at
that speed. It may also produce a moaning sound, depending on what component is causing it. Refer to Tip-In Moan in
the Symptom Chart.
2. Acceleration/deceleration: With slow acceleration and deceleration, a shake is sometimes noticed in the steering
wheel/column, seats, front floor pan, front door trim panel or front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency vibration
(around 9-15 cycles per second). It may or may not be increased by applying brakes lightly. Refer to Idle Boom/Shake
/Vibration in the Symptom Chart.
3. High speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor pan or seats with no visible shake, but with an accompanying sound or
rumble, buzz, hum, drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch pedal depressed or shift control selector lever in
neutral and engine idling. If vibration is still evident, it may be related to wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs
or front wheel bearings. Refer to High Speed Shake in the Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm sensitive: A vibration is felt whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm. It will disappear in neutral
coasts. The vibration can be duplicated by operating the engine at the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary. It
can be caused by any component, from the accessory drive belt to the torque converter which turns at engine speed
when the vehicle is stopped. Refer to High Speed Shake in the Symptom Chart.
5. Noise/vibration while turning: Clicking, popping, or grinding noises may be due to a worn, damaged, or incorrectly
installed front wheel bearing, rear drive half shaft or CV joint.
6. Noise/vibration that is road speed relative: This noise/vibration can be diagnosed independent of engine speed or gear
selected (engine speed varies but torque and road speed remain constant). The cause may be a rear drive
axle/differential whine.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road tests. The road selected
should be reasonably smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a particular condition needs to be identified). A smooth
asphalt road that allows driving over a range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads are unsuitable because of the additional
road noise produced. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road noise variable is eliminated from the test
results.
NOTE: Some concerns may be apparent only on smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on a particular road and only on a particular road, the source of the concern
may be the road surface. If possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note anything which is unusual. Do not
repair or adjust any condition until the road test is carried out, unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition could pose a
hazard to the technician.
After verifying the condition has been corrected, make sure all components removed have been installed.
Lift Test
After a road test, it is sometimes useful to do a similar test on a lift.
When carrying out the high-speed shake diagnosis or engine accessory vibration diagnosis on a lift, observe the following
precautions:
WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (35 miles/h) indicated on the
speedometer since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Speed exceeding 55 km/h (35 miles/h)
or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported could result in tire disintegration, differential failure, constant velocity joint