sensor JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1704 of 3039

Climate Control - Control Components - Component Location
Description and Operation
NOTE: RHD (right-hand drive) vehicle shown, LHD (left-hand drive) vehicle similar.
Component Location Published: 29-May-2014
Item Description 1 Pollution sensor Comments:
where fitted 2 Sunload sensor 3 Ambient air temperature sensor 4 Windshield (Defrost) distribution stepper motor 5 Evaporator temperature sensor
Page 1705 of 3039

7 LH (left-hand) temperature blend stepper motor 8 Control switches 9 Humidity and temperature sensor 10 Air inlet servo motor 11 Blower 12 ATC (automatic temperature control) module 13 Blower control module 14 Face/Feet distribution stepper motor 15 Refrigerant pressure sensor 16 A/C (air conditioning) compressor solenoid valve
Page 1709 of 3039

6 TSD (touch screen display) 7 Integrated control panel 8 Evaporator temperature sensor 9 Humidity and temperature sensor 10 Sunload sensor 11 Refrigerant pressure sensor 12 Pollution sensor Comments:
where fitted 13 Air inlet servo motor 14 A/C (air conditioning) compressor solenoid valve 15 RH (right-hand) outer face level register 16 RH inner face level register 17 LH (left-hand) inner face level register 18 LH outer face level register 19 RH temperature blend stepper motor 20 Face/Feet distribution stepper motor 21 ATC (automatic temperature control) module 22 LH temperature blend stepper motor 23 Windshield (Defrost) stepper motor 24 Blower control module 25 RJB (rear junction box) 26 Blower
Air Inlet Control System Operation
The source of inlet air is automatically controlled unless overridden by pressing the air recirculation switch on the integrated
control panel. During automatic control, the ATC module determines the required position of the recirculation door from its 'comfort' algorithm and, if fitted, the pollution sensor.
The ATC module provides analogue signals to the air inlet servo motor along a hardwired connection. A potentiometer in the motor supplies the ATC module with a position feedback signal for closed loop control.
Air Temperature Control
Cooled air from the evaporator enters the heater assembly, where temperature blend doors direct a proportion of the air
through the heater core to produce the required output air temperature.
The two temperature blend doors operate independently to enable individual temperature settings for the left and right sides
of the passenger compartment. The temperature blend doors are operated by stepper motors, which are controlled by the ATC module using LIN bus messages.
The ATC module calculates the temperature blend stepper motor positions required to achieve the selected temperature and compares it against the current position. If there is any difference, the ATC module signals the stepper motors to adopt the new position.
Air temperature is controlled automatically unless maximum heating (HI) or maximum cooling (LO) is selected. When maximum
heating or cooling is selected, a 'comfort' algorithm in the ATC module adopts an appropriate strategy for air distribution, blower speed, and air source.
Temperature control in one side of the passenger compartment can be compromised by the other side of the passenger
compartment being set to a high level of heating or cooling. True maximum heating or cooling (displayed as 'HI' or 'LO' on the
TSD) can only be selected for the driver's side of the passenger compartment. If 'HI' or 'LO' is selected for the driver's side, the
temperature for the front passenger's side is automatically set to match the driver's side.
If A/C is selected off in the automatic mode, no cooling of the inlet air will take place. The minimum output air temperature from the system will be ambient air temperature plus any heat pick up in the air inlet path.
If the Temp. sync. soft button on the TSD is pressed, the ATC module synchronizes the temperature of the passenger side of the passenger compartment with the driver's side.
Blower Control
When the system is in the automatic mode, the ATC module determines the blower speed required from a comfort algorithm. When the system is in the manual mode, the ATC module operates the blower at the speed selected using either the rotary
Page 1710 of 3039
control switch on the integrated control panel or the + and - soft buttons on the touch screen display (TSD). The ATC module also adjusts blower speed to compensate for the ram effect on inlet air produced by forward movement of the vehicle. As
vehicle speed and ram effect increases, blower motor speed is reduced, and vice versa.
Air Distribution Control
Two air distribution doors are used to direct air into the passenger compartment. The doors are operated by stepper motors,
which are controlled by the ATC module using LIN bus messages.
When the A/C system is in automatic mode, the ATC module automatically controls air distribution into the passenger compartment in line with its 'comfort' algorithm. Automatic control is overridden if any of the TSD air distribution soft buttons
are selected. Air distribution in the passenger compartment will remain as selected until the 'Auto' switch is pressed or a
different manual selection is made.
A/C Compressor Control
When A/C is selected the ATC module maintains the evaporator at an operating temperature that varies with the passenger compartment cooling requirements. If the requirement for cooled air decreases, the ATC module raises the evaporator operating temperature by reducing the flow of refrigerant provided by the A/C compressor. The ATC module closely controls the rate of temperature increase to avoid introducing moisture into the passenger compartment.
If the requirement for cooled air increases, the ATC module lowers the evaporator operating temperature by increasing the flow of refrigerant provided by the A/C compressor.
When A/C is off, the compressor current signal supplied by the ATC module holds the A/C compressor solenoid valve in the minimum flow position, effectively switching off the A/C function.
The ATC module incorporates limits for the operating pressure of the refrigerant system. If the system approaches the high pressure limit, the compressor current signal is progressively reduced until the system pressure decreases. If the system falls
below the low pressure limit, the compressor current signal is held at its lowest setting so that the A/C compressor is maintained at its minimum stroke. This avoids depletion of the lubricant from the A/C compressor.
A/C Compressor Torque
The ATC module transmits refrigerant pressure and A/C compressor current values to the ECM (engine control module) over the medium speed then high speed CAN bus, using the CJB as a gateway. The ECM uses these values to calculate the torque being used to drive the A/C compressor. The ECM compares the calculated value with its allowable value and if necessary forces the ATC module to inhibit the A/C compressor by transmitting the 'ACClutchInhibit' CAN message. This forces the ATC module to reduce the drive current to the A/C compressor solenoid valve, which reduces refrigerant flow. This in turn reduces the torque required to drive the A/C compressor.
By reducing the maximum A/C compressor torque, the ECM is able to reduce the load on the engine when it needs to maintain vehicle performance or cooling system integrity.
Cooling Fan Control
The ATC module determines the amount of condenser cooling required from the refrigerant pressure sensor, since there is a direct relationship between the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant. The cooling requirement is broadcast to the ECM on the medium speed CAN bus. The ECM then controls the temperature of the condenser using the cooling fan.
Programmed Defrost
The programmed defrost DEF switch is located on the integrated control panel. When the switch is pressed, the ATC module instigates the programmed defrost function. When selected, the ATC module configures the system as follows:
Automatic mode off.
A/C on. Selected temperature unchanged.
Air inlet set to fresh air.
Air distribution set to windshield.
Blower speed set to level 6.
Windshield heater (where fitted) and rear window heater on.
The programmed defrost function can be cancelled by one of the following:
Selecting any air distribution switch on the TSD.
Pressing the AUTO switch on the integrated control panel.
A second press of the DEF button.
Switching the ignition OFF.
The blower speed can be adjusted without terminating the programmed defrost function.
Rear Window Heater
Rear window heater operation is only enabled when the engine is running. The ATC module controls operation of the rear window heater using a relay in the RJB. When rear window heater operation is required, the ATC module broadcasts a message to the RJB on the medium speed CAN bus. On receipt of the message, the RJB energizes the relay by providing a ground path for the relay coil. This allows a battery feed to flow across the relay to power the rear window heater element.
Page 1711 of 3039
rear window heater switch is pressed or the engine stops.
Automatic operation during a journey is initiated when low ambient air temperatures are experienced and the vehicle has been
travelling for a set period of time above a threshold speed. In this instance, no feedback is given to the driver to inform him
the rear window heater is operational (the switch LED is not illuminated). The duration of heater operation is variable depending on the ambient air temperature, vehicle speed and the amount of time the vehicle has been travelling.
Windshield Heater (Where Fitted)
Windshield heater operation is only enabled when the engine is running. The ATC module controls operation of the windshield heater using two relays in the EJB (engine junction box). When windshield heater operation is required, the ATC module broadcasts a message to the CJB on the medium speed CAN bus. On receipt of the message, the CJB energizes the relays by providing a ground path for both relay coils. This allows a battery feed to flow across the relays to power the windshield left
and right heater elements.
There are two modes of windshield heater operation; manual and automatic.
Manual operation is activated by pressing the windshield heater switch on the integrated control panel. When the switch is
pressed, the status LED in the switch illuminates and the windshield heater elements are energized. Manual operation is discontinued when the windshield heater switch is pressed a second time, 5 minutes have elapsed (the heating phase), or the
engine stops. If manual operation is discontinued by the engine stopping, the previous heating phase is resumed if the engine
is re-started within 30 seconds.
There are two variants of automatic operation; automatic operation at the start of a journey and automatic operation during a
journey.
Automatic operation at the start of a journey is initiated if the ambient air temperature is below 5 °C (41 °F). In this instance,
the switch LED is illuminated and the heater elements are energized for 6.5 minutes. Automatic operation is discontinued if the windshield heater switch is pressed or the engine stops.
Automatic operation during a journey is initiated when low ambient air temperatures are experienced and the vehicle has been
travelling for a set period of time above a threshold speed. In this instance, no feedback is given to the driver to inform him
the windshield heater is operational (the switch LED is not illuminated) and the duration of operation is variable depending upon the ambient air temperature, vehicle speed and the amount of time the vehicle has been travelling.
Exterior Mirror Heaters
Operation of the exterior mirror heaters is fully automatic and not controllable by the driver. Exterior mirror heater operation is
determined by ambient air temperature and windshield wiper status. When ambient air temperature reaches a pre-determined
level, the ATC module broadcasts an exterior mirror heating request to the door modules over the medium speed CAN bus. On receipt of this message, the door modules provide feed and ground connections to both exterior mirror heater elements.
The amount of time the exterior mirror heaters are operational increases if the windshield wipers are switched on. This ensures
the mirrors remain mist free in damp and wet conditions, where there is an increased risk of misting.
Seat Heaters (Where Fitted)
There are four seat heater settings available; off, 1, 2 and 3, which can be selected on the home and climate control screens
of the TSD. The heat setting is relayed to the vehicle occupants through a graduated display on the TSD.
Operation of the heated seats is controlled by the ATC module. When the ATC module receives a heating request from the TSD, it broadcasts a message to the CJB over the medium speed CAN bus. The CJB then provides a hardwired 12 V supply to the three heater elements in the related front seat. The heater elements, two in the seat cushion and one in the seat squab,
are wired in series. The ATC module monitors seat temperature using a temperature sensor located in each seat cushion. The CJB provides the temperature sensors with a 5 V supply. The level of the returned voltage back to the CJB is proportional to the seat temperature. The value of the return signal is broadcast to the ATC module, over the medium speed CAN bus, which allows it to control the seat temperature to the required level. The ATC module will suspend or disable operation of the seat heaters if any of the following occur:
Battery voltage exceeds 16.5 ± 0.3 V for more than 5 seconds. Seat heating is re-enabled when battery voltage
decreases to 16.2 ± 0.3 V.
If a short or open circuit is detected.
If the seat heat temperature rises significantly above the target temperature setting.
The graduated display on the TSD remains illuminated until the seat heaters are turned off or the engine stops. If the engine
is restarted within 30 seconds the seat heater resumes the previous heating level.
Page 1712 of 3039
bus. Temperature control for the heater element is provided by the steering wheel heater control module which receives a
temperature feedback signal from a NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermistor located within the steering wheel.
ATC Module Component Description
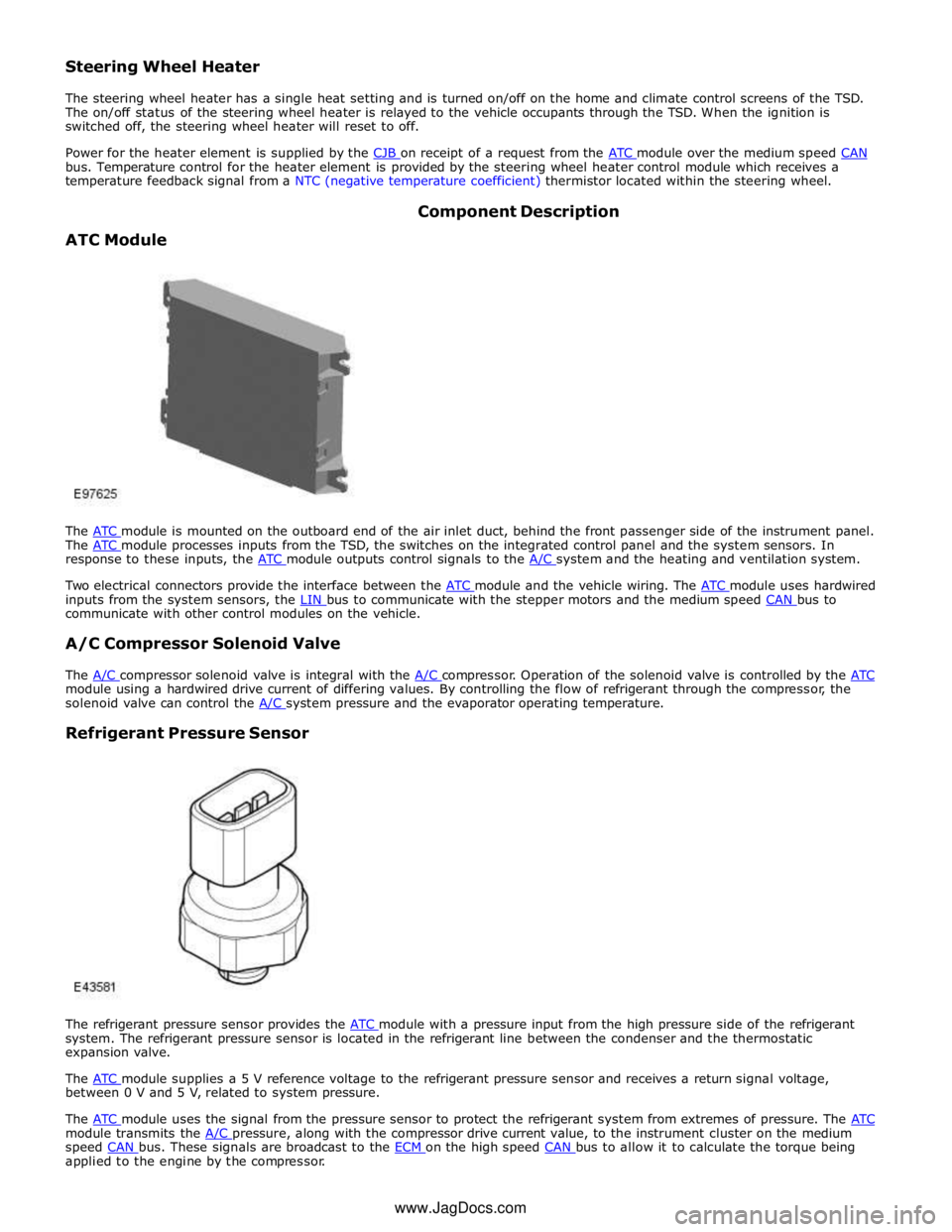
The ATC module is mounted on the outboard end of the air inlet duct, behind the front passenger side of the instrument panel. The ATC module processes inputs from the TSD, the switches on the integrated control panel and the system sensors. In response to these inputs, the ATC module outputs control signals to the A/C system and the heating and ventilation system.
Two electrical connectors provide the interface between the ATC module and the vehicle wiring. The ATC module uses hardwired inputs from the system sensors, the LIN bus to communicate with the stepper motors and the medium speed CAN bus to communicate with other control modules on the vehicle.
A/C Compressor Solenoid Valve
The A/C compressor solenoid valve is integral with the A/C compressor. Operation of the solenoid valve is controlled by the ATC module using a hardwired drive current of differing values. By controlling the flow of refrigerant through the compressor, the
solenoid valve can control the A/C system pressure and the evaporator operating temperature.
Refrigerant Pressure Sensor
The refrigerant pressure sensor provides the ATC module with a pressure input from the high pressure side of the refrigerant system. The refrigerant pressure sensor is located in the refrigerant line between the condenser and the thermostatic
expansion valve.
The ATC module supplies a 5 V reference voltage to the refrigerant pressure sensor and receives a return signal voltage, between 0 V and 5 V, related to system pressure.
The ATC module uses the signal from the pressure sensor to protect the refrigerant system from extremes of pressure. The ATC module transmits the A/C pressure, along with the compressor drive current value, to the instrument cluster on the medium speed CAN bus. These signals are broadcast to the ECM on the high speed CAN bus to allow it to calculate the torque being applied to the engine by the compressor. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1713 of 3039

pressure:
Decreases to 2.1 ± 0.2 bar (31.5 ± 3 lbf/in²); the ATC module loads the A/C compressor again when the pressure increases to 2.3 ± 0.2 bar (33.4 ± 3 lbf/in²).
Increases to 31 ± 1 bar (450 ± 14.5 lbf/in²); the ATC module loads the A/C compressor again when the pressure decreases to 26 ± 1 bar (377 ± 14.5 lbf/in²).
Evaporator Temperature Sensor
The evaporator temperature sensor is a NTC thermistor that provides the ATC module with a temperature signal from the downstream side of the evaporator. The evaporator temperature sensor is mounted directly onto the evaporator matrix fins.
The ATC module uses the input from the evaporator temperature sensor to control the load of the A/C compressor and thus the operating temperature of the evaporator.
Page 1714 of 3039

A capacitive sensor element to measure humidity.
A motor driven fan to draw air through the sensor and over the sensing elements.
The humidity sensor element is built out of a film capacitor on different substrates. The dielectric is a polymer which absorbs
or releases water proportional to the relative humidity of the air being drawn through the sensor, and thus changes the
capacitance of the capacitor. For protection, the sensor element is contained in a nylon mesh cover.
Humidity within the passenger compartment is controlled by raising and lowering the evaporator temperature. An increase in
evaporator temperature increases the moisture content of the air entering the passenger compartment. Lowering the
evaporator temperature reduces the moisture content of the air entering the passenger compartment. Humidity and Temperature Sensor
Page 1715 of 3039

1 LH door mirror 2 Ambient air temperature sensor The ambient air temperature sensor is a NTC thermistor that provides the ATC module with an input of external air temperature. The sensor is hard wired to the ECM and its signal is transmitted to the instrument cluster on the high speed CAN bus. The instrument cluster acts as a gateway and transmits the ambient air temperature signal to the ATC module on the medium speed CAN bus. The sensor is installed in the LH door mirror, and is accessed by removing the mirror glass, cap and actuator.
Sunload Sensor
The sunload sensor consists of two photoelectric cells that provide the ATC module with inputs of light intensity; one as sensed coming from the left of the vehicle and one as sensed coming from the right. The inputs are a measure of the solar
heating effect on vehicle occupants, and are used by the ATC module to adjust blower speed, temperature and distribution to improve comfort.
The sensor is installed in the speaker grill on the upper surface of the instrument panel. Power for the sensor is provided by a
5 V feed from the instrument cluster.
The sensor also contains the active anti-theft alarm indicator.
Refer to: Anti-Theft - Active (419-01 Anti-Theft - Active, Description and Operation). Ambient Air Temperature Sensor
Page 1716 of 3039

as nitrous oxides, sulphur oxides and carbon monoxide. The sensor is attached to the center of the upper front crossmember.
The pollution sensor is powered by an ignition controlled voltage feed from the CJB and provides the ATC module with separate signals of hydrocarbon and oxidized gas levels. With a pollution sensor fitted, the ATC module can control the air inlet source to reduce the amount of contaminants entering the passenger compartment. This function is fully automatic, but can be
overridden by manual selection of the air source using the recirculation switch on the integrated control panel.
If there is a fault with the sensor, the ATC module disables automatic operation of the recirculation door.