wheel JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1885 of 3039

is operated to crank the engine. The GWM is connected to the ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) control module via the high speed
CAN bus. With the vehicle stationary and the engine off after an ECO engine stop, when the driver releases the brake pedal
the ABS control module senses the reduction in brake pressure. This change of brake pressure state is sent as a high speed
CAN message which is received by the GWM and the ECM. The GWM reacts within 105ms to instruct the DBM via the LIN bus
to operate the two contactors in the DBJB to supply the sensitive loads from the secondary battery and supply the TSS motor
direct from the primary battery.
When the engine is running and the generator is supplying power to the vehicle systems, the GWM again instructs the DBM to
operate the two contactors in the DBJB to supply all vehicle systems from the primary battery and the generator and to isolate
the secondary battery.
Secondary Battery Charging
The DBM also controls the charging of the secondary battery. The GWM contains electrical load management software and
monitors both batteries for their state of charge. The primary battery is monitored by the BMS control module which is
connected to the DBM via the LIN bus. The DBM communicates the primary battery condition to the GWM via a LIN bus
connection. The GWM sends a signal to the DBM via the LIN bus to instruct it to apply charging from the generator to the
secondary battery when required. The contactor 2 is closed by the DBJB to complete the secondary battery circuit, and the
generator output is applied to the secondary battery to charge it.
The generator output is controlled by the GWM which monitors and controls the electrical load management system. The
generator is connected to the GWM by a LIN bus allowing the GWM to control the output of the generator to maintain electrical
system load requirements and battery charging.
Electrical Load Management
The electrical load management is controlled by the GWM and the BMS control module.
The GWM will monitor the vehicle system power loads before and during an ECO engine stop.
Before an ECO engine stop, the GWM will transmit a signal to system control modules on the CAN bus to request a power save
on all electrical loads and set a minimum electrical value override. The GWM monitors the vehicle electrical loads and will
inhibit a ECO engine stop until the load current is at a value low enough to be supported by the secondary battery.
If the electrical loads cannot be reduced sufficiently, the GWM will inhibit the ECO engine stop.
When the engine is stopped after an ECO engine stop, the GWM will continue to monitor the primary battery state of charge.
If the primary or secondary battery voltage falls below 11.0V, a level which will result in degraded starting performance or
possible primary battery damage, the GWM will initiate an engine start.
System Inhibits
The ECO stop/start system is inhibited if the dual battery system is not be capable of preventing electrical loads on the
vehicle being subject to unacceptably low voltage levels during ECO stop/start operations due to a fault.
ECO stop/start inhibit monitoring of the primary battery is performed by the BMS control module. If the primary battery voltage
is too low to support an ECO stop/start, then the BMS control module will send a message to the GWM on the LIN bus to
suspend ECO stop/start.
The GWM monitors the secondary battery and the dual battery system components. Any fault found will cause the GWM to
inhibit ECO stop/start and the GWM will record a DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
Fault Diagnosis
The GWM performs passive and active diagnostics on the dual battery system to determine the status of the system
components.
Passive diagnostics can detect faults in the DBJB and can check for stuck open or closed contactors and failure of DBM
contactor command signals.
Active diagnostics is a routine to test the capability of the contactors to respond to open or close command signals sent from
the GWM to the DBM. This routine also checks the FET's (Field Effect Transistors) activate as required. (Refer to Dual Battery
Junction Box below for description of FET operation)
The GWM will also check the dual battery system components for faults in a controlled environment when the generator is
providing a charging output. This will ensure that the detection of a fault will not result in sensitive electrical loads being
subjected to low voltage which may occur during an ECO stop/start with a fault present.
The GWM will illuminate the charge warning indicator in the instrument cluster if fault is detected in the dual battery system
which will result in a degraded power supply.
If a fault is detected the GWM transmits a CAN message to inhibit ECO stop/start operation. In some cases it will record a
DTC, display a warning message in instrument cluster and also illuminate charge warning indicator.
PRIMARY BATTERY - ALL VEHICLES Component Description
The primary battery is located in a plastic tray under the luggage compartment floor in the right side of the luggage
compartment, adjacent to the spare wheel. The battery is vented via a tube which is connected with a T piece to the vent from
Page 1887 of 3039

DUAL BATTERY MODULE (DBM)
The DBM (dual battery module) is located at the rear of the right wheel arch in the luggage compartment, adjacent to the
GWM (gateway module) and the RJB (rear junction box). The DBM is attached to a bracket, which is attached to a second
bracket secured to the vehicle body.
The DBM is connected by two hardwired connections to the DBJB (dual battery junction box). The DBM uses these two
connections to apply battery voltage to the contactor coils in the DBJB. A LIN bus connection from the GWM passes contactor operation signals to the DBM which operates the contactors as applicable.
The GWM will also instruct the DBM to apply charging to the secondary battery via a LIN bus message. The GWM instructs the
DBM of the charging current required for the secondary battery and the DBM applies the requested stabilized current to the
secondary battery via a dedicated connection direct to the secondary battery.
The DBM diagnoses the coils of the contactors and will report a fault via the LIN bus to the GWM.
The DBM receives a fused power supply from the RJB. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1942 of 3039

lb-ft lb-in Audio antenna unit to "D" pillar retaining bolts 9 - 80 Digital Radio antenna pod retaining nuts 5 - 48 Amplifier retaining nuts 7 - 62 Information and entertainment display retaining bolts 2 - 17 Information and entertainment display mounting bracket to Information and entertainment display retaining bolts 3 - 26 Information and entertainment module retaining bolts 3 - 26 Instrument panel speaker retaining screws 2 - 18 Steering wheel audio control switch retaining screws 3 - 26 Subwoofer amplifier retaining nuts 7 - 62 Subwoofer speaker retaining bolts 6 - 53
Page 1944 of 3039

12 Portable audio interface console (Optional) 13 Portable audio module (Optional) 14 Steering wheel remote audio controls
Page 1947 of 3039
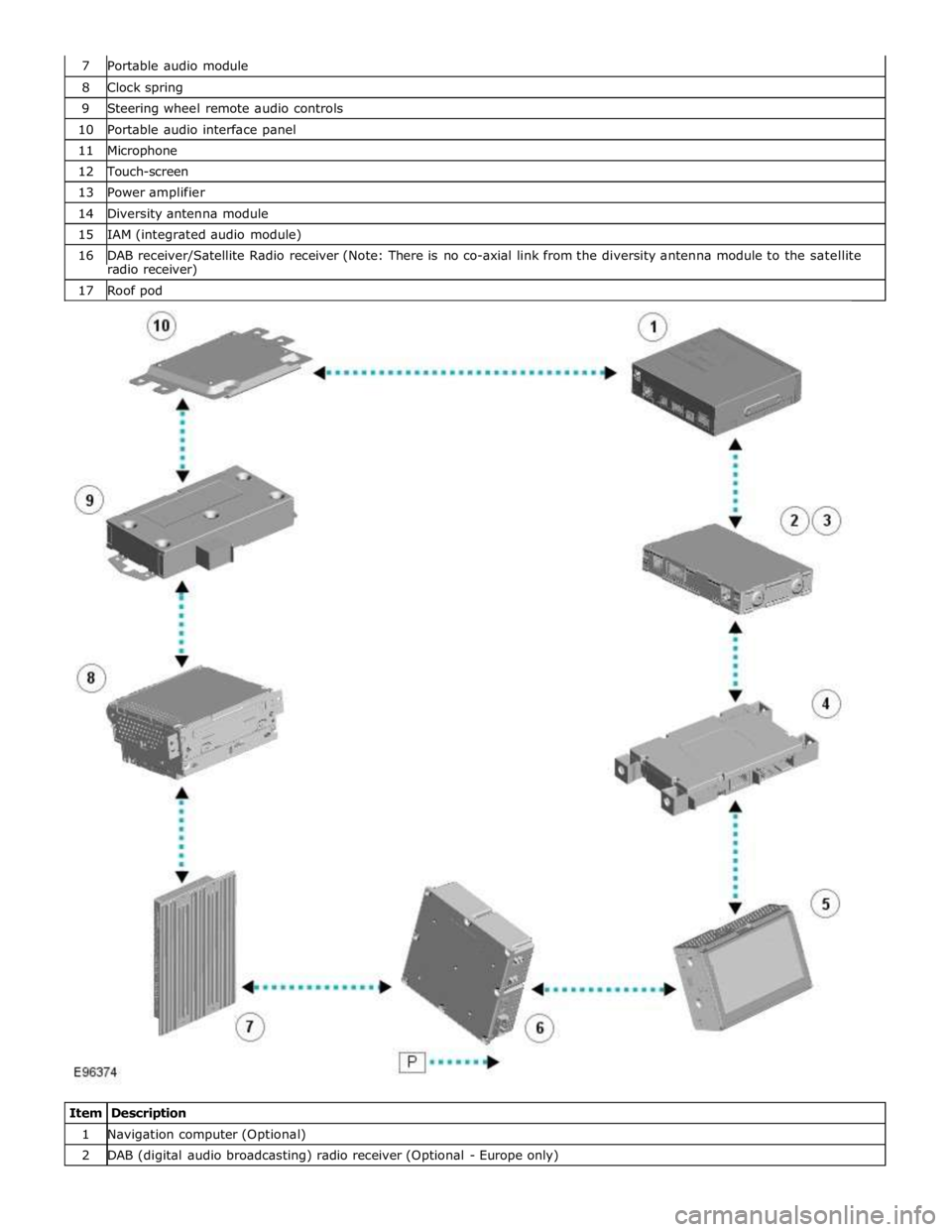
8 Clock spring 9 Steering wheel remote audio controls 10 Portable audio interface panel 11 Microphone 12 Touch-screen 13 Power amplifier 14 Diversity antenna module 15 IAM (integrated audio module) 16 DAB receiver/Satellite Radio receiver (Note: There is no co-axial link from the diversity antenna module to the satellite radio receiver) 17 Roof pod
Item Description 1 Navigation computer (Optional) 2 DAB (digital audio broadcasting) radio receiver (Optional - Europe only)
Page 1949 of 3039

systems.
A typical example of information transfer is vehicle speed information from the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module used to
control the automatic volume control function. The vehicle speed information from the ABS module is sent on the high speed
CAN network and collected by the instrument panel gateway. The signal is passed to the medium speed CAN network and onto the ICM gateway. The ICM calculates the volume adjustment required. The corrected audio volume level signal is sent on the
MOST network to the IAM or Power amplifier (dependant on vehicle equipment level) for output to the speaker system.
AUDIO SYSTEM USER CONTROLS
Touch-Screen
Item Description 1 Touch-screen 2 Home menu button 3 Touch-screen on/off button The Touch-screen forms the basis of the audio system. It communicates with the rest of the audio/infotainment system on the
MOST ring and allows control of the audio system and other infotainment systems from a single point.
The Touch-screen communicates with the IAM on the MOST ring and provides the primary user interface and display of the
audio system controls. No configuration procedure is required if the touch-screen is replaced.
Calibration of the Touch-screen using the Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment enables updates to be downloaded as new
technology becomes available or any fault concerns require software updates.
The touch-screen provides user control of the following systems:
System Functions Audio Radio display AM/FM or DAB, auxiliary and portable audio, digital TV or CD (compact disc) Climate
control Air conditioning, distribution, seats, heated steering wheel, automatic air recirculation Telephone Digit dialer, phone book, last ten calls (made, received, missed) Navigation Destination, stored locations, navigation setup, route options Vehicle
Security, parking, valet mode, trip computer, clock, brightness, contrast, system settings, vehicle settings, display settings
Page 1951 of 3039
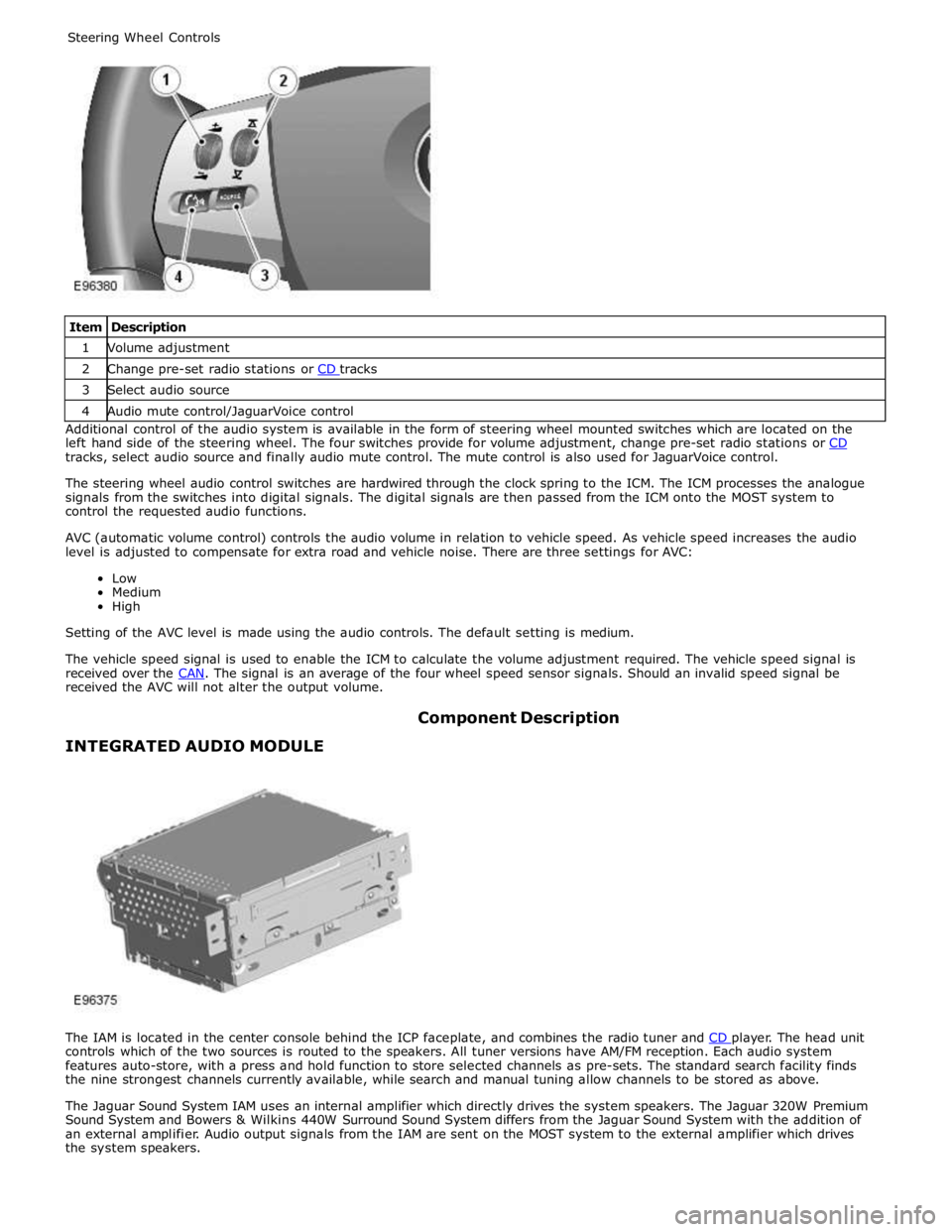
1 Volume adjustment 2 Change pre-set radio stations or CD tracks 3 Select audio source 4 Audio mute control/JaguarVoice control Additional control of the audio system is available in the form of steering wheel mounted switches which are located on the
left hand side of the steering wheel. The four switches provide for volume adjustment, change pre-set radio stations or CD tracks, select audio source and finally audio mute control. The mute control is also used for JaguarVoice control.
The steering wheel audio control switches are hardwired through the clock spring to the ICM. The ICM processes the analogue
signals from the switches into digital signals. The digital signals are then passed from the ICM onto the MOST system to
control the requested audio functions.
AVC (automatic volume control) controls the audio volume in relation to vehicle speed. As vehicle speed increases the audio
level is adjusted to compensate for extra road and vehicle noise. There are three settings for AVC:
Low
Medium
High
Setting of the AVC level is made using the audio controls. The default setting is medium.
The vehicle speed signal is used to enable the ICM to calculate the volume adjustment required. The vehicle speed signal is
received over the CAN. The signal is an average of the four wheel speed sensor signals. Should an invalid speed signal be received the AVC will not alter the output volume.
INTEGRATED AUDIO MODULE Component Description
The IAM is located in the center console behind the ICP faceplate, and combines the radio tuner and CD player. The head unit controls which of the two sources is routed to the speakers. All tuner versions have AM/FM reception. Each audio system
features auto-store, with a press and hold function to store selected channels as pre-sets. The standard search facility finds
the nine strongest channels currently available, while search and manual tuning allow channels to be stored as above.
The Jaguar Sound System IAM uses an internal amplifier which directly drives the system speakers. The Jaguar 320W Premium
Sound System and Bowers & Wilkins 440W Surround Sound System differs from the Jaguar Sound System with the addition of
an external amplifier. Audio output signals from the IAM are sent on the MOST system to the external amplifier which drives
the system speakers.
Page 1960 of 3039

Publi s hed: 11-May-2011
Information and Entertainment System - Speakers - Overview
Des cript ion and Operat ion
Overview
The vehi cl e has t hree l evels of audio s ys t em availabl e:
Jaguar Sound Sys temJaguar Premi um Sound Syst emBowers & W i lkins Surround Sound Sys temThe Jaguar Sound Sys tem has 8 s peakers, compri s ing an i dent ical mid-bas s and t weeter combinati on in each door. Al l
s peaker domes in this sys tem are of st andard t ext il e cons t ructi on. The s peakers are driven direct ly by the IAM (i nt egrat ed
audi o module) i nternal ampli fi er.
The Jaguar 320W Premium Sound Sys tem has 9 s peakers including mid-bas s and t weet ers in t he doors , addi ng a
s ub-woofer in the spare wheel wel l. The s peakers are driven by an Al pi ne AUD 8 ampli fier l ocat ed in t he LH (left-hand)
s ide of t he luggage compartment .
The Bowers & W i lkins 440W Surround Sound Syst em us es an Al pi ne AUD 12 amplifier, a Dolby Pro-Logi c 2 7.1 Surround
Sound Sys t em and has 14 s peakers. This layout adds a mid-range s peaker to each front door whi le ret ai ning a mid-bas s
and t weet er in each rear door. It als o adds an i ns t rument panel center s peaker, 2 s urround-effect speakers i n t he rear
parcel shelf, and has the luggage compart ment-mounted sub-woofer as the Jaguar 320W Premi um Sound Sys t em. The
s peakers are driven by an AUD 12 power ampl ifier located i n t he luggage compartment .
The main s peakers on the Jaguar 320W Premium Sound Sys t em and t he Bowers & W i lkins 440W Surround Sound Syst em
are identi fied by the bright yellow Kevl ar cons truct ed domes which are vis ibl e through the s peaker grill es. The t weeter
s peaker domes are an al uminum cons truct ion. The s ub-woofer s peakers are a text ile dome cons t ructi on.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1964 of 3039

System Operation
The Jaguar Sound Sys tem has 8 s peakers, compri s ing an i dent ical mid-bas s and t weeter combinati on in each door. Al l
s peaker domes in this sys tem are of st andard t ext il e cons t ructi on. The s peakers are driven direct ly by the IAM (i nt egrat ed
audi o module) i nternal ampli fi er.
The Jaguar 320W Premium Sound Sys tem has 9 s peakers including mid-bas s and t weet ers in t he doors , addi ng a
s ub-woofer in the spare wheel wel l. The s peakers are driven by an Al pi ne AUD 8 ampli fier l ocat ed in t he LH s i de of the
luggage compartment .
The Bowers & W i lkins 440W Surround Sound Syst em us es an Al pi ne AUD 12 amplifier, a Dolby Pro-Logi c 2 7.1 Surround
Sound Sys t em and has 14 s peakers. This layout adds a mid-range s peaker to each front door whi le ret ai ning a mid-bas s
and t weet er in each rear door. It als o adds an i ns t rument panel center s peaker, 2 s urround-effect speakers i n t he rear
parcel shelf, and has the luggage compart ment-mounted sub-woofer as the Jaguar 320W Premi um Sound Sys t em. The
s peakers are driven by an AUD 12 power ampl ifier located i n t he luggage compartment .
The main s peakers on the Jaguar 320W Premium Sound Sys t em and t he Bowers & W i lkins 440W Surround Sound Syst em
are identi fied by the bright yellow Kevl ar cons truct ed domes which are vis ibl e through the s peaker grill es. The t weeter
s peaker domes are an al uminum cons truct ion. The s ub-woofer s peakers are a text ile dome cons t ructi on.
Page 1965 of 3039

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Publi s hed: 11-May-2011
Information and Entertainment System - Cellular Phone - Component
Location
Des cript ion and Operat ionItemDescription
IAM (i nt egrat ed audi o module)
Touch-s creen
Ins trument cl us t er
Microphone
St eering wheel cont rol s
Navigat ion Comput er
Power ampli fi er
Speakers
Tel ephone cont rol module
ICM (i nformat ion control modul e)
www.JagDocs.com