JAGUAR XJ 1994 2.G AJ16 Engine Manual
Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1994, Model line: XJ, Model: JAGUAR XJ 1994 2.GPages: 73, PDF Size: 2.06 MB
Page 11 of 73
AJ16 Engine Service Manual
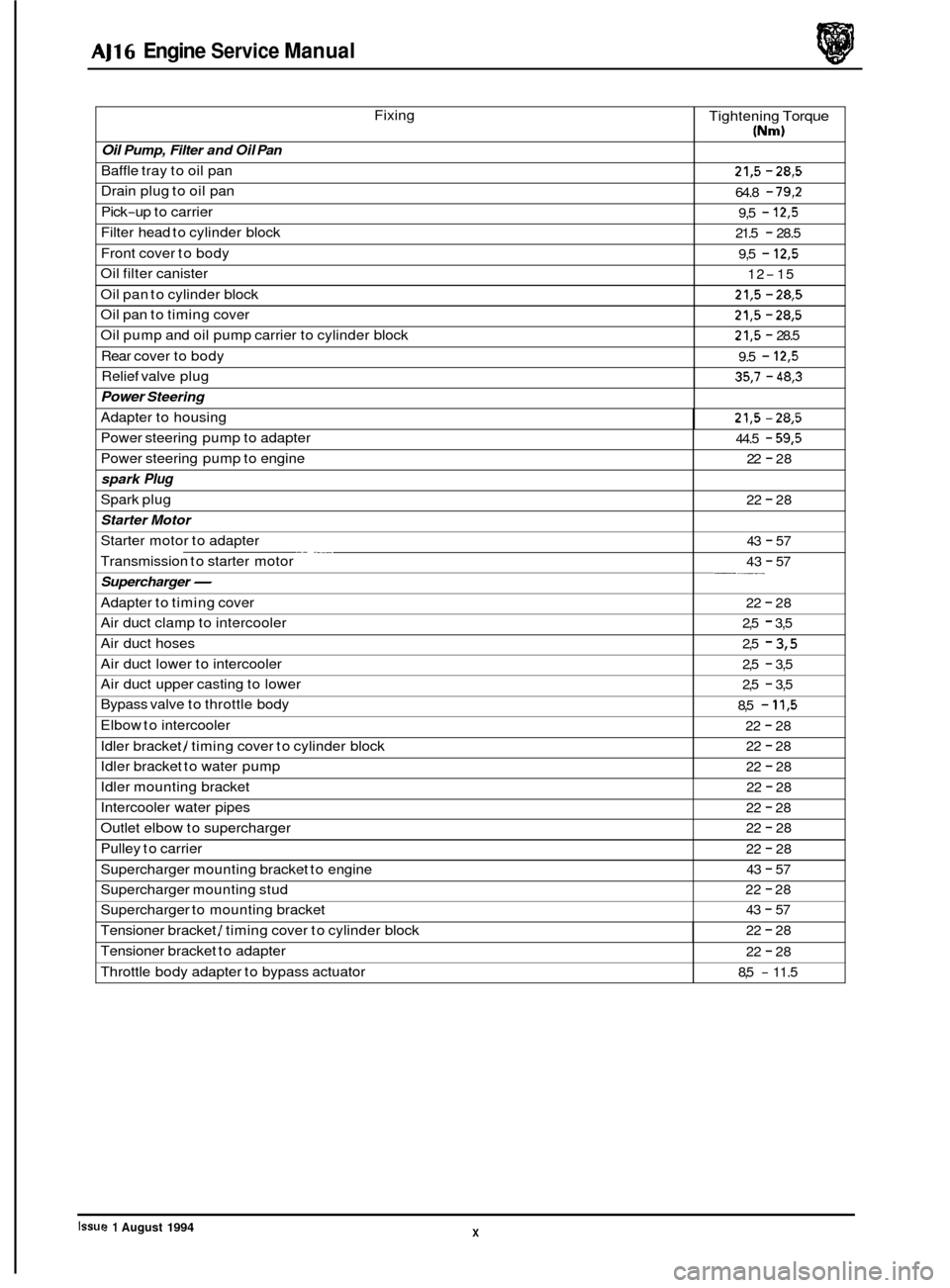
0 Fixing
Oil Pump, Filter and Oil Pan
Baffle tray to oil pan
Drain plug to oil pan
Pick
-up to carrier
Filter head to cylinder block
Front cover to body
Oil filter canister
Oil pan to cylinder block
Oil pan to timing cover
Oil pump and oil pump carrier to cylinder block
Rear cover to body
Relief valve plug Tightening
Torque
(Nm)
21,5 - 28,5
64.8 - 79,2
9,5 - 12,5
21.5 - 28.5
9,5
- 12,5
12-15
21,5 - 28,5
21,5 - 28,5
21,5 - 28.5
9.5
- 12,5
35,7 - 48,3
Power Steering
Adapter to housing 21,5 - 28,5
Power steering pump to adapter
Power steering pump to engine
spark Plug
Starter Motor
Starter motor to adapter
Transmission to starter motor
Supercharger-
Spark plug
--
44.5 - 59,5
22 - 28
22
- 28
43
- 57
43
- 57 -___
Adapter to timing cover
Air duct clamp to intercooler
Air duct hoses
Air duct lower to intercooler 22 - 28
2,5
- 3,5
2,5
- 3,5
2,5 - 3,5
Air duct upper casting to lower
Bypass valve to throttle body
Elbow to intercooler
Idler bracket
/ timing cover to cylinder block
Idler bracket to water pump
X Issue 1 August 1994
2,5 - 3,5
8,5
- 11,5
22 - 28
22
- 28
22
- 28
Idler mounting bracket
Intercooler water pipes
Outlet elbow to supercharger
Pulley to carrier
Supercharger mounting bracket to engine
Supercharger mounting stud 22 - 28
22
- 28
22
- 28
22
- 28
43
- 57
22
- 28
Supercharger to mounting bracket 43 - 57
Tensioner bracket / timing cover to cylinder block 22 - 28
Tensioner bracket to adapter
Throttle body adapter to bypass actuator 22 - 28
8,5
- 11.5
Page 12 of 73

AJ16 Engine Service Manual
~- Fixing Tightening
Torque
r- (Nm)
____ liming Cover L 1 Auxiliary shaft blanking plate to timing cover 9,5 - 12,5
Generator adjuster to timing cover 8,5 - 11,5 ~ __ ____ ~ t Intermediate shaft blanking
plate to timing cover 1 21,5-28,5
I Sensor to timing cover
l Timing cover to cylinder block b+-- 21,5 - 28,5
21,5 - 28,5 _. ______
xi Issue 1 August 1994
Page 13 of 73
AJ16 Engine Service Manual
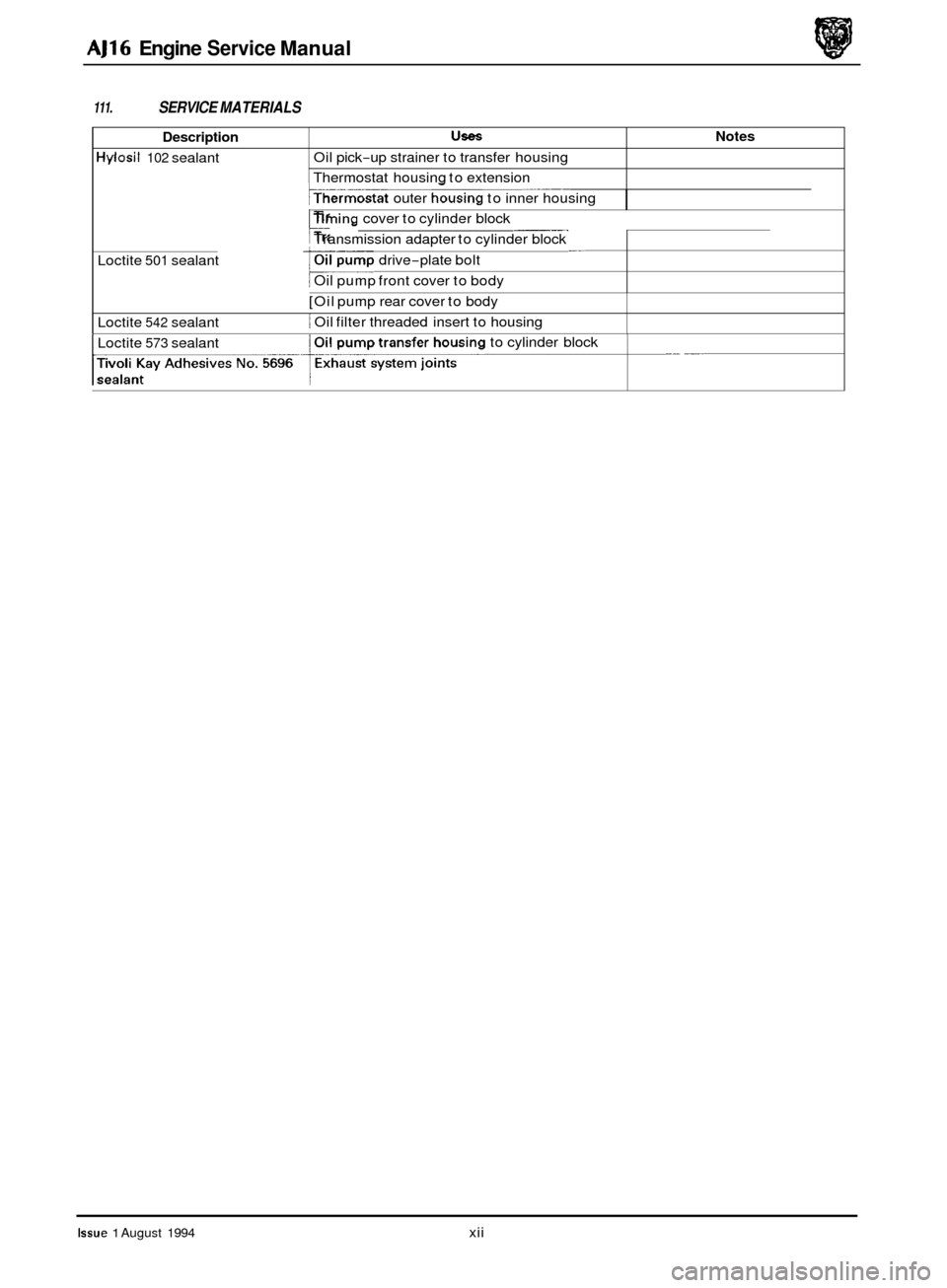
Description
Hylosil 102 sealant
111. SERVICE MATERIALS
UseS Notes
Oil pick-up strainer to transfer housing
Thermostat housing to extension
I jThermostat outer housing to inner housing
Loctite
501 sealant
~. Xming cover to cylinder block
t Transmission adapter to cylinder block
drive
-plate bolt
Oil pump front cover to body
[Oil pump rear cover to body
1 Oil filter threaded insert to housing
Loctite 542 sealant
__ __ Loctite 573 sealant to
cylinder block
Issue 1 August 1994 xii
Page 14 of 73
AJ16 Engine Service Manual
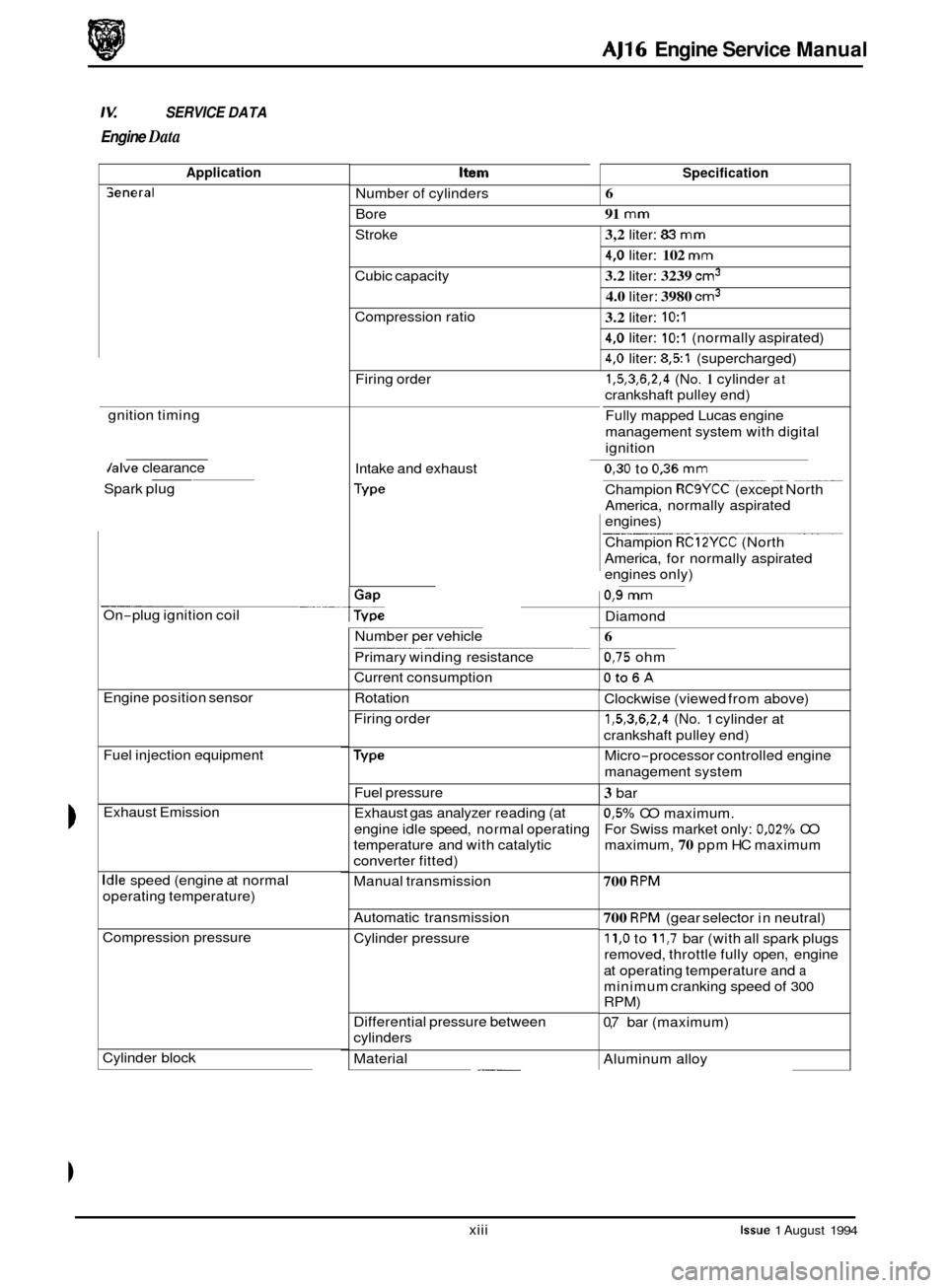
SERVICE DATA
Engine Data
Application Item
Number of cylinders
Bore
Specification
Seneral 6
91
mm
Stroke 3,2 liter: 83 mm
4,O liter: 102 mm
3.2 liter: 3239 cm3
4.0 liter: 3980 cm3
Cubic capacity
Compression ratio
3.2 liter: 1O:l
4,O liter: 1O:l (normally aspirated)
4,O liter: 8,51 (supercharged)
1,5,3,6,2,4 (No. 1 cylinder at
crankshaft pulley end)
Fully mapped Lucas engine
management system with digital
ignition
Firing
order
gnition timing
0
0
0
Jalve clearance
Intake and exhaust 0,30 to 0,36 mm
Champion RCSYCC (except North
America, normally aspirated
engines)
Champion
RC12YCC (North
America, for normally aspirated
engines only)
__ ~ ~
--__ ~~
Spark
plug
0,9 mm
On-plug ignition coil
Diamond
Number per vehicle
Primary winding resistance
Current consumption ~ ~~
6
0,75 ohm
Oto6A
Clockwise
(viewed from above)
1,5,3,6,2,4 (No. 1 cylinder at
crankshaft pulley end)
-
Engine position sensor
Fuel injection equipment
Exhaust Emission Rotation
Firing order
Micro
-processor controlled engine
management system
Fuel pressure
Exhaust gas analyzer reading (at
engine idle speed, normal operating
temperature and with catalytic
converter fitted)
3 bar
0,5% CO maximum.
For Swiss market only:
0,02% CO
maximum,
70 ppm HC maximum
Idle speed (engine at normal
operating temperature) Manual transmission 700 RPM
Automatic
transmission 700 RPM (gear selector in neutral)
11,O to 11,7 bar (with all spark plugs
removed, throttle fully open, engine
at operating temperature and
a
minimum cranking speed of 300
RPM)
0,7 bar (maximum)
Compression pressure
Cylinder pressure
Differential pressure between
cylinders
Aluminum alloy
Cylinder block
. ___ Material
xiii
Issue 1 August 1994
Page 15 of 73

AJ16 Engine Service Manual
kern
For piston grade F
Application
alinder block bore diameter after
boning
Specification
90,990 to 90,998
mm
zylinder head For
piston grade
G
For piston grade H
t0.020 in.
:rankshaft
90,999 to 91,007 mm
91,008 to 91,016 mm
91,513 to 91,526 mm
:onnecting rod To
within 15
gm cm (imbalance to
be corrected by drilling up to four
holes in each balance weight
9,5
mm diameter x 29 mm deep
' maximum)
'iston
'iston diameter Length
between centers
Bore for connecting rod bearing
Connecting rod bearing diametrical
clearance
Connecting rod bearing side
clearance
Bore for small end bushing
Type
Skirt clearance
Grade
F
Grade G
Grade
H
+0.020 in.
Number
of compression rings
'iston ring
____ Blue: 52,990 to 53,000 mm
3,2 liter: 175785 to 175,285 mm
4,O liter: 166,320 to 166,420 mm
56,731 mm
0,023 to 0,059 mm
0,132 to 0,233 mm
26,975 to 27,000 mm
AE413P/PD (BS 1490-198SLM 13TF)
phosphorus treated
0,Ol to 0,026 mm
90,972 to 90,980 mm
90,980 to 90,989 mm
90,990 to 90,998 mm
91,480 to 91,506 mm
2
Material
I Aluminum
alloy
Material
I3,2 liter: cast iron
Number of main bearings
Main bearing type
Journal diameter
Thrust washer thickness
Permissible end float
Balancing
Diametrical clearance
Crankpin diameter
4,O liter: forged steel
7
Vandervell
VP2C
Pink 76,210 to 76,220 mm
White: 76.220 to 76,230 mm
Green: 76,230 to 76,240 mm
2.57 to 2,62 mm
0,lO to 0,28 mm
Number of oil control rings
Gap when fitted in bore 1
Top compression ring:
0,40 to 0,65
mm
Second compression ring: 0,40 to
0,65 mm
Oil control ring: 0.30 to 0,55 mm
Issue 1 August 1994 xiv
Page 16 of 73

AJ16 Engine Service Manual
Item
Type
Length
Outside diameter
Inside diameter
Material ~
Application
Specification
Chamfer locking
3,2
liter: 68,37 to 68,50 mm
4,O liter: 77,12 to 77,25 mm
23,807 to 23,812 mm
14,30 to 14.81 mm
Cast iron
'iston pin
2amshaft
dalve
Number of journals
Nominal
lift
Permissible end float
4djustment of valve clearance 7
9,95 mm
0.13 mm
rlalve Guide
Valve
stem diameter
Valve clearance
Jalve seat Intake
and exhaust: 6,947 to 6,960
mm
Intake and exhaust: 0,30 to 0,36 mm
Jalve seat insert outside diameter Outside
diameter
rappet
lalve spring Standard
- no
groove: 10,993 to
11,005 mm
1st oversize - 1 groove: 11,043 to
11,055
mm (production only)
2nd oversize
- 2 grooves: 1 1,143 to
11,155 mm
:amshaft sprocket
:rankshaft sprocket Diametrical
clearance
Free length
Number
of teeth
ntermediate sprocket
0,02 to 0,05 mm
43,5 mm
30
xv Issue 1 August 1994
Page 17 of 73
AJ16 Engine Service Manual
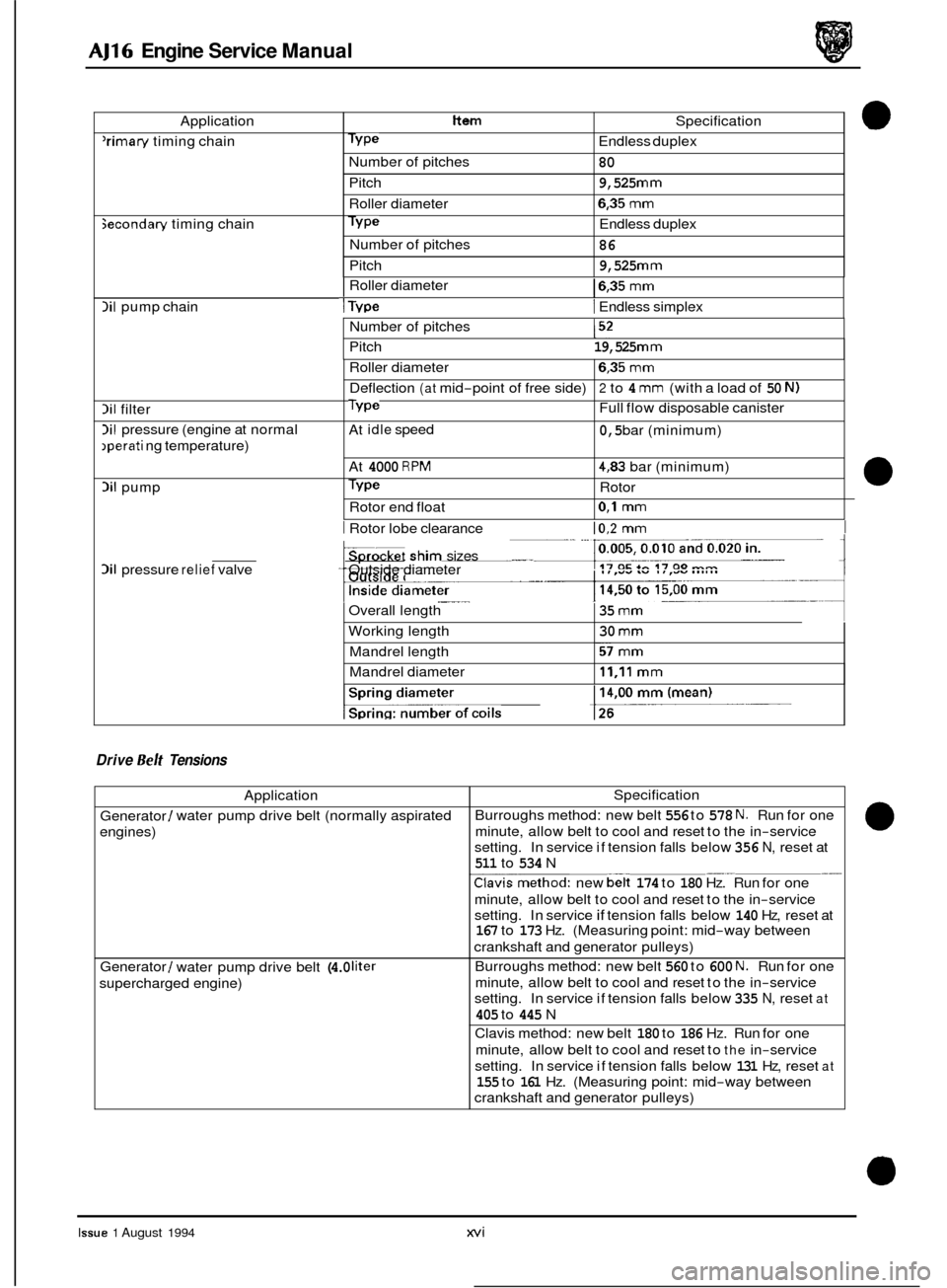
0 Application Item
'rimary timing chain Type
Pitch
Roller diameter
secondan/ timing chain Type
Number of pitches
Pitch
Number of
pitches Specification
Endless duplex
80
9,525
mm
6,35 mm
Endless duplex
86
9,525
mm
lil pump chain
lil filter
lil pressure (engine at normal
,perati ng temperature)
Si1 pump
I Roller diameter 16,35 mm
I Type I Endless simplex
Roller diameter
6,35 mm
Deflection (at mid-point of free side) 2 to 4 mm (with a load of 50 N)
Type Full flow disposable canister
At
idle speed 0,5 bar (minimum)
At
4000 RPM 4,83 bar (minimum)
Type Rotor
Rotor end float
0,l mm
Number of pitches I52
Pitch 19,525 mm
___ Overall length
Working length Mandrel length
Mandrel diameter 35 mm
30 mm
57 mm
11,ll mm
Si1 pressure relief valve
Application
Generator
/ water pump drive belt (normally aspirated
engines)
Generator
/ water pump drive belt (4.0 liter
supercharged engine)
I Rotor lobe clearance 10,2 mm I
Specification
Burroughs method: new belt
556 to 578 N. Run for one
minute, allow belt to cool and reset to the in
-service
setting. In service if tension falls below
356 N, reset at
511 to 534 N
.Clavismethod: new belt 174 to 180 Hz. Run for one
minute, allow belt to cool and reset to the in
-service
setting. In service
if tension falls below 140 Hz, reset at 167 to 173 Hz. (Measuring point: mid-way between
crankshaft and generator pulleys)
Burroughs method: new belt
560 to 600 N. Run for one
minute, allow belt to cool and reset to the in
-service
setting. In service if tension falls below
335 N, reset at
405 to 445 N
Clavis method: new belt
180 to 186 Hz. Run for one
minute, allow belt to cool and reset to
the in-service
setting. In service if tension falls below
131 Hz, reset at
155 to 161 Hz. (Measuring point: mid-way between
crankshaft and generator pulleys)
__ ___
.- ...
pket she sizes ___ Outside diameter
1
1
Drive Belt Tensions
0
Issue 1 August 1994 xvi
Page 18 of 73

AJ16 Engine Service Manual
Application
4ir conditioning compressor drive belt
Supercharger drive belt Specification
Burroughs method: new belt 556 to 578 N (no
retensioning required). In service
if tension falls below
245
N, reset at 378 to 400 N
Clavis method: new belt 167 to 173 Hz (no retensioning
required). In service if tension falls below 85 Hz, reset
at 127 to 133
Hz. (Measuring point: mid-way between
crankshaft and compressor pulleys)
Burroughs method: new belt
993 to 1033 N. Drive the
vehicle for
10 minutes, allow the belt to cool to ambient
(approximately one hour) and reset to the in
-service
setting. In service
at 16000 kilometer (10000 mile)
intervals, reset at 835 to 875
N with the belt cold.
Renew belt at 48000 kilometer (30000
mile) intervals
Clavis method: new belt 119 to 121
Hz. Drive the
vehicle for
10 minutes, allow the belt to cool to ambient
(approximately one hour) and reset to the in
-service
setting.
In service at 16000 kilometer (10000 mile)
intervals, reset
at 11 1 to 113 Hz with the belt cold.
Renew belt at 48000 kilometer (30000 mile) intervals.
(Measuring point mid
-way between crankshaft and
supercharger pulleys)
xvii Issue 1 August 1994
Page 19 of 73

xviii
Page 20 of 73

AJ16 Engine Service Manual
0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION - The engine is available as a 3,2 and 4,O liter unit. A 4,O liter supercharged version is also available. Fuel is supplied
to each cylinder via an injector fed from a regulated fuel rail. To comply with statutory regulations in some countries
and to reduce emissions during the warm
-up period, secondary air is delivered to the exhaust manifold by an electri- cally operated air injection pump. This improves oxidation until the catalytic converters are fully effective. All engine
functions are controlled by an integrated engine management system, which incorporates the on-board diagnostic
system (OBDII).
1.1 Construction
The skirted design crankcase is manufactured in cast aluminum alloy with shrink fit dry cast iron cylinder sleeves.
Thecrankshaft ismanufactured from cast
ironforthe3,2 literengine,forged steel forthe 4,O liter engineand is nitro-car-
burize treated to give a very high quality finish on the bearing surfaces and increase the life of the journals.
The crankshaft is supported by seven iron bearing caps having bearings, which are lead bronze on split steel backed
shells with a lead indium overlay.
Crankshaft end
-float is controlled by half thrust washers fitted on each side of the center main bearing journal. The
connecting rods are manufactured from carbon manganese steel, forged in an 'H' section. The small end bushes are
lead bronze with steel backing, machined to size after being pressed into the connecting rods. The connecting rod bear- ings are of a lead bronze alloy on split steel backed shells and with lead indium overlay.
The pistons are of monometal construction (aluminum) and have a spring assisted micro
-land oil control ring situated
below a barrel-faced internally tapered chrome plated compression ring and an externally stepped taper-faced second-
ary ring.
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy with pent
-roof shaped combustion chambers with cross-flow valve
porting. Running directly in the cylinder head are
twocast iron camshafts retained by machined aluminumcaps. Each
camshaft uses chilled cams to drive two valves per cylinder via chilled cast iron bucket tappets with shim adjustment.
Control of each of the four valves per cylinder is maintained by single valve springs.
The camshafts are operated by a two stage 'duplex' chain drive from the crankshaft. Each stage is controlled by a hy
- draulic tensioner operating through a pivoted rubber-faced curved tensioner blade. The first stage incorporates a three
point drive via the crankshaft, intermediate shaft and auxiliary shaft. The intermediate shaft is live and provides a 0.75 x crank speed drive through the timing cover. This drive access is blanked off. The 'live' auxiliary shaft is driven at
crankshaft speed and is situated on the right hand side of the engine (looking from rear). In addition to driving the
engine position sensor via a set of 2 : 1 reduction spiral gears, it provides an external drive for the power assisted steer- ing pump at the rear. The second stage is a three point drive via the intermediate shaft and two camshafts. The 2:l reduction ratio from crank speed is achieved by the combined ratio of the intermediate and camshaft sprockets sizes.
The oil pump is a rotor
-type mounted on the underside of the front of the crankcase and driven by a 'simplex' chain
from the crankshaft nose. The pump incorporates a built-in pressure relief valve. Below the line of the crankcase, but
abovetheoil pan
oillevel aretwowindagetrays; these prevent oil beingsucked upand thrown into thecrankcasethere- by alleviating windage and power losses through oil surge.
At the rear of the crankshaft is
a new design of lip-type PTFE oil seal which provides a high degree of oil retention. It also allows the use of higher engine speeds and easier serviceability.
1.2 Cylinder Head Design
The four valves per cylinder are smaller in diameter than on a conventional two valve per cylinder engine and have a greater combined effective area. They are also lighter and apply less stress to the operating gear. The design in- creases the power at high engine speeds and allows an efficient combustion of the fuel. It also allows the spark plug
to besituated in its ideal central position which creates efficient combustion and consequently enhancesfuel economy.
1.3 Crankcase Breather
Blow-by gases are recycled via the air intake system to maintain a crankcase depression and so prevent their escape
to the atmosphere. A baffled vent from the camshaft cover is used for both full and part load breathing. For full load
breathing,
a connection is made direct to the clean side ofthe air filter upstream ofthe throttle disc. Part load breathing is provided by a spur off the full load pipe to downstream ofthe throttle disc via the water heated restrictor. In this way,
a crankcase depression is maintained at all throttle settings.
1.4 Lubrication System
Oil is drawn from the oil pan via a gauze filter. Pressurized oil, having been regulated by a relief valve, is then fed via
internal galleries on the left hand side of the cylinder block. Pressurized and filtered oil is fed into the main oil gallery,
the seven main bearings are fed and thence via crankshaft drillings to the connecting rod bearings. The intermediate
shaft, auxiliary shaft and camshaft bearings are pressure lubricated by means of internal drillings directly fed from the
front of the main oil gallery. For some markets an oil cooler is fitted to vehicles with
4,O liter supercharged engines.
The pistons run on hardened steel piston pins offset from the center line of the piston towards the thrust face.
Issue 1 August 1994 1