maintenance JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 2 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
LIVING WITH YOUR JAGUAR XJ6
IntroductionPage 0•4
Notes for UK readersPage 0•4
Safety first!Page 0•5
Roadside repairs
IntroductionPage 0•6
If your car won’t startPage 0•6
Jump startingPage 0•7
Wheel changingPage 0•8
Identifying leaksPage 0•9
TowingPage 0•9
Weekly checks
IntroductionPage 0•10
Underbonnet check points Page 0•10
Engine oil levelPage 0•11
Coolant levelPage 0•11
Brake fluid levelPage 0•12
Screen washer fluid level Page 0•12
Power steering fluid level Page 0•13
Wiper bladesPage 0•13
Tyre condition and pressure Page 0•14
BatteryPage 0•15
Bulbs and fusesPage 0•15
Lubricants, fluids and tyre pressuresPage 0•16
MAINTENANCE
Routine maintenance and servicingPage 1•1
Servicing specificationsPage 1•2
Maintenance schedulePage 1•3
Maintenance procedures Page 1•6
Contents
Page 4 of 227

These models are equipped with dual overhead cam in-line six-
cylinder engines. The engines feature a computer-controlled ignition
system and electronic fuel injection. Transmissions are a four-speed
automatic equipped with a lock-up torque converter. The transmission
is mounted to the back of the engine, and power is transmitted to the
fully independent rear axle through a two-piece propshaft. The
differential is bolted solidly to a frame crossmember and drives the
wheels through driveshafts equipped with inner and outer U-joints.
The front suspension is fitted with upper and lower control arms, coil
springs and shock absorbers. The rear suspension is an independent
type suspension which also have coil spring/shock absorber
assemblies and a lower control arm. The rear driveshaft acts as the
upper control arm.
Power-assisted Anti-lock Brake Systems (ABS) with four-wheel disc
brakes are standard equipment on all Jaguar XJ6 models covered in
this manual. Power rack-and-pinion steering is also standard
equipment.
Your Jaguar manual
The aim of this manual is to help you get the best value from your
vehicle. It can do so in several ways. It can help you decide what work
must be done (even should you choose to get it done by a garage). It
will also provide information on routine maintenance and servicing, and
give a logical course of action and diagnosis when random faults
occur. However, it is hoped that you will use the manual by tackling the
work yourself. On simpler jobs it may even be quicker than booking the
car into a garage and going there twice, to leave and collect it. Perhaps
most important, a lot of money can be saved by avoiding the costs a
garage must charge to cover its labour and overheads.
The manual has drawings and descriptions to show the function of
the various components so that their layout can be understood. Tasks
are described and photographed in a clear step-by-step sequence.
Notes for UK readers
Because this manual was originally written in the US, its layout
differs from our UK-originated manuals. The preliminary and reference
sections have been re-written specifically for the UK market, and the
maintenance schedule has been amended to suit UK vehicles.
However, it will be noticed that some references to componentsremain in the US style; the UK equivalent of US components and
various other US words is given in the Section headed “Use of
English”. It should be remembered that the project vehicle used in the
main Chapters of this manual was a left-hand drive US model;
therefore, the position of the steering wheel, steering column and
pedals, etc. will be on the opposite side of the vehicle on UK models.
References to “right” and “left” will need to be considered carefully to
decide which applies to UK models (eg the headlight dipped beams
should be adjusted to dip to the left of the headlight vertical line
described in Chapter 12, instead of to the right on US models). In other
instances, no reference is made to the location of a particular item, but
that item may be located on the opposite side of the vehicle on UK
models. Reference to the underbonnet photos at the start of Chapter 1
will give the reader the location of the engine compartment
components on UK models.
All specifications in the main Chapters of the manual appear in
Imperial form; the equivalent metric values can be calculated using the
“Conversion factors”page.
The only other major difference between UK and US models is in the
level of emission control equipment fitted to the vehicle. To meet the
strict emission standards present in the US, all vehicles for that market
are fitted with various emission control systems (see Chapter 6), most
of which are not fitted to the corresponding UK model, especially so on
early models. Therefore, a lot of the information contained in Chapter 6
is not applicable to UK models.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Jean Preis, Rich Wilson and Ray Marcuse of
Silver Star Jaguar (Thousand Oaks, CA), Rick Calaci of Conejo Imports
(Newbury Park, CA) and Jim Strohmeier and Jonathan Lund of British
Motor Cars (Thousand Oaks, CA), for providing valuable technical
information. Technical writers who contributed to this project include
Jeff Kibler, Robert Maddox and Jay Storer.
We take great pride in the accuracy of information given in this
manual, but vehicle manufacturers make alterations and design
changes during the production run of a particular vehicle of which
they do not inform us. No liability can be accepted by the authors
or publishers for loss, damage or injury caused by any errors in, or
omissions from, the information given.
0•4Introduction
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Haynes mechanic, author and photographer with 1989 Jaguar XJ6
Page 17 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
1
Chapter 1
Routine maintenance and servicing
Air cleaner element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Automatic transmission fluid and filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Battery check and general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Braking system - general check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Crankcase ventilation system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Differential oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Differential oil renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Engine oil and filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Front wheel alignment check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Front wheel bearing check and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
General lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Handbrake shoes check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Headlight beam check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Hose and fluid leak check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Ignition system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Intensive maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Power hydraulic system fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Propshaft check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Spark plug check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Steering and suspension check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1•1
Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 19 of 227

The maintenance intervals in this manual are provided with the
assumption that you, not the dealer, will be carrying out the work.
These are the minimum maintenance intervals recommended by us for
vehicles driven daily. If you wish to keep your vehicle in peak condition
at all times, you may wish to perform some of these procedures moreoften. We encourage frequent maintenance, because it enhances the
efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle.
When the vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a factory-
authorised dealer service department, in order to preserve the factory
warranty.
Maintenance schedule 1•3
1
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Weekly, or every 250 miles (400 km)
m mCarry out all the operations given in “Weekly
checks”at the start of this manual.
m
mRenew the fuel filter (Section 18)
m mCheck the ignition system components (Section 19)
m mCheck the crankcase ventilation system
(Section 20)
m mCheck the condition and tension of the drivebelt(s)
(Section 21)
m mCheck the front wheel bearing adjustment and
repack with grease (Section 22)
m mCheck the propshaft fasteners are tightened to the
specified torque (Section 23)
m mCheck the front wheel alignment (Section 24)
m mCheck the headlight beam alignment (Section 25)
Every 7500 miles (12 000 km)
or 6 months, whichever comes first
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m mRenew the engine oil and filter (Section 3)
m mCheck the spark plugs (Section 4)
m mCheck the power hydraulics fluid level (Section 5)
m mCheck the battery (Section 6)
m mCheck all pipes and hoses for signs of damage or
leakage (Section 7)
m mCheck the automatic transmission fluid level
(Section 8)
m mCheck the differential oil level (Section 9)
m mCheck the condition of the exhaust system
(Section 10)
m mCheck the brake pads and discs for wear and
adjust the handbrake (Section 11)
m mCheck the steering and suspension components
for wear or damage and check the wheel nuts are
tightened to the correct torque (Section 12)
m mCheck the condition of the seat belts (Section 13)
m mLubricate all locks and hinges, and exposed cables
(Section 14)
m mCarry out a road test (Section 15)
Every 2 years, regardless of mileage
m
mRenew the coolant (Section 30)
Every 60 000 miles (96 000 km)
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m
mCheck the handbrake shoes for wear (Section 29)
Every 30 000 miles (48 000 km)
or 2 years, whichever comes first
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m mRenew the automatic transmission fluid and filter
(Section 26)
m mRenew the differential oil (Section 27)
m mRenew the brake fluid (Section 28)
Every 15 000 miles (24 000 km)
or 12 months, whichever comes first
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 16)
m mRenew the air cleaner element (Section 17)
Page 20 of 227
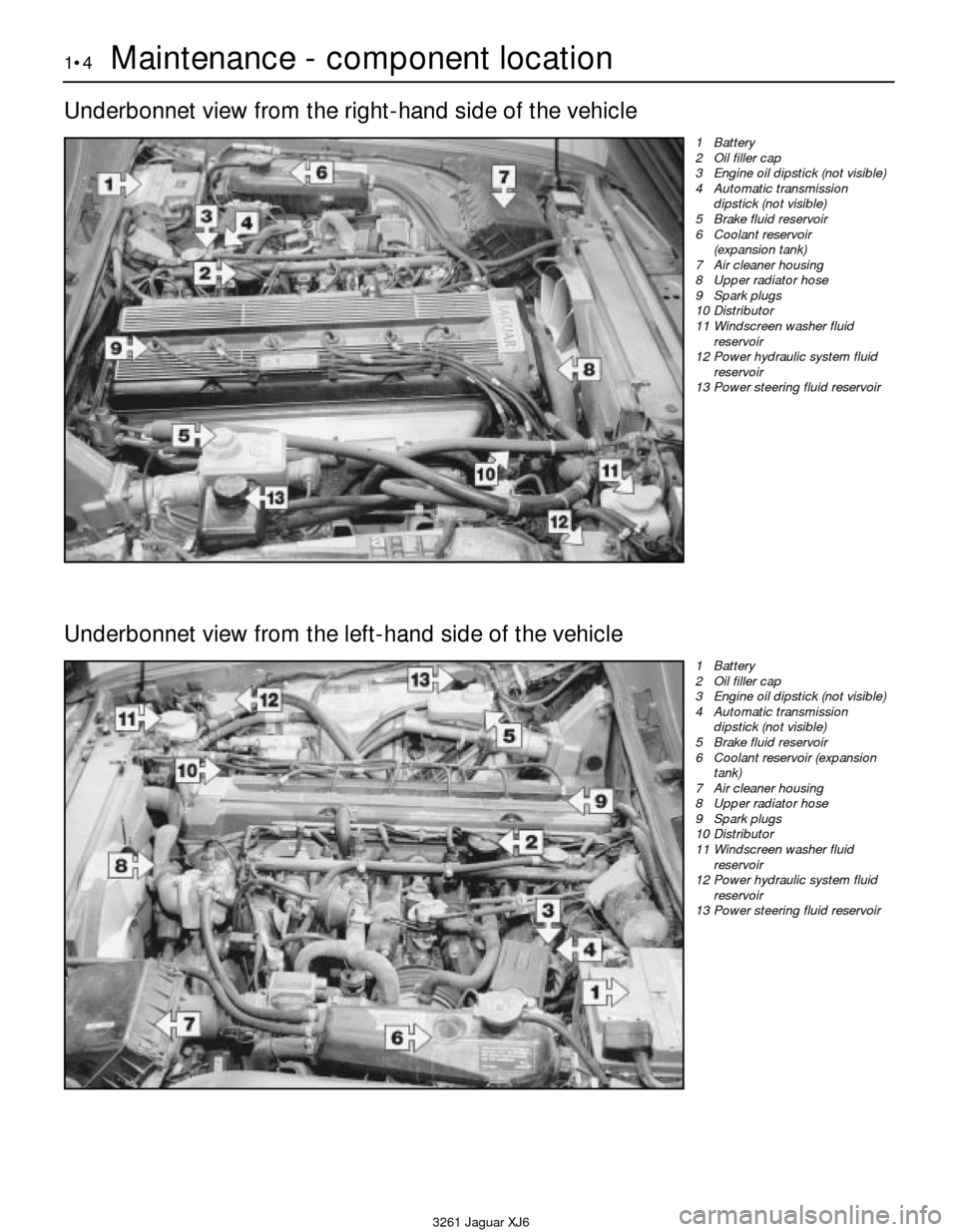
1•4Maintenance - component location
3261 Jaguar XJ6
1 Battery
2 Oil filler cap
3 Engine oil dipstick (not visible)
4 Automatic transmission
dipstick (not visible)
5 Brake fluid reservoir
6 Coolant reservoir
(expansion tank)
7 Air cleaner housing
8 Upper radiator hose
9 Spark plugs
10 Distributor
11 Windscreen washer fluid
reservoir
12 Power hydraulic system fluid
reservoir
13 Power steering fluid reservoir
Underbonnet view from the left-hand side of the vehicle Underbonnet view from the right-hand side of the vehicle
1 Battery
2 Oil filler cap
3 Engine oil dipstick (not visible)
4 Automatic transmission
dipstick (not visible)
5 Brake fluid reservoir
6 Coolant reservoir (expansion
tank)
7 Air cleaner housing
8 Upper radiator hose
9 Spark plugs
10 Distributor
11 Windscreen washer fluid
reservoir
12 Power hydraulic system fluid
reservoir
13 Power steering fluid reservoir
Page 21 of 227
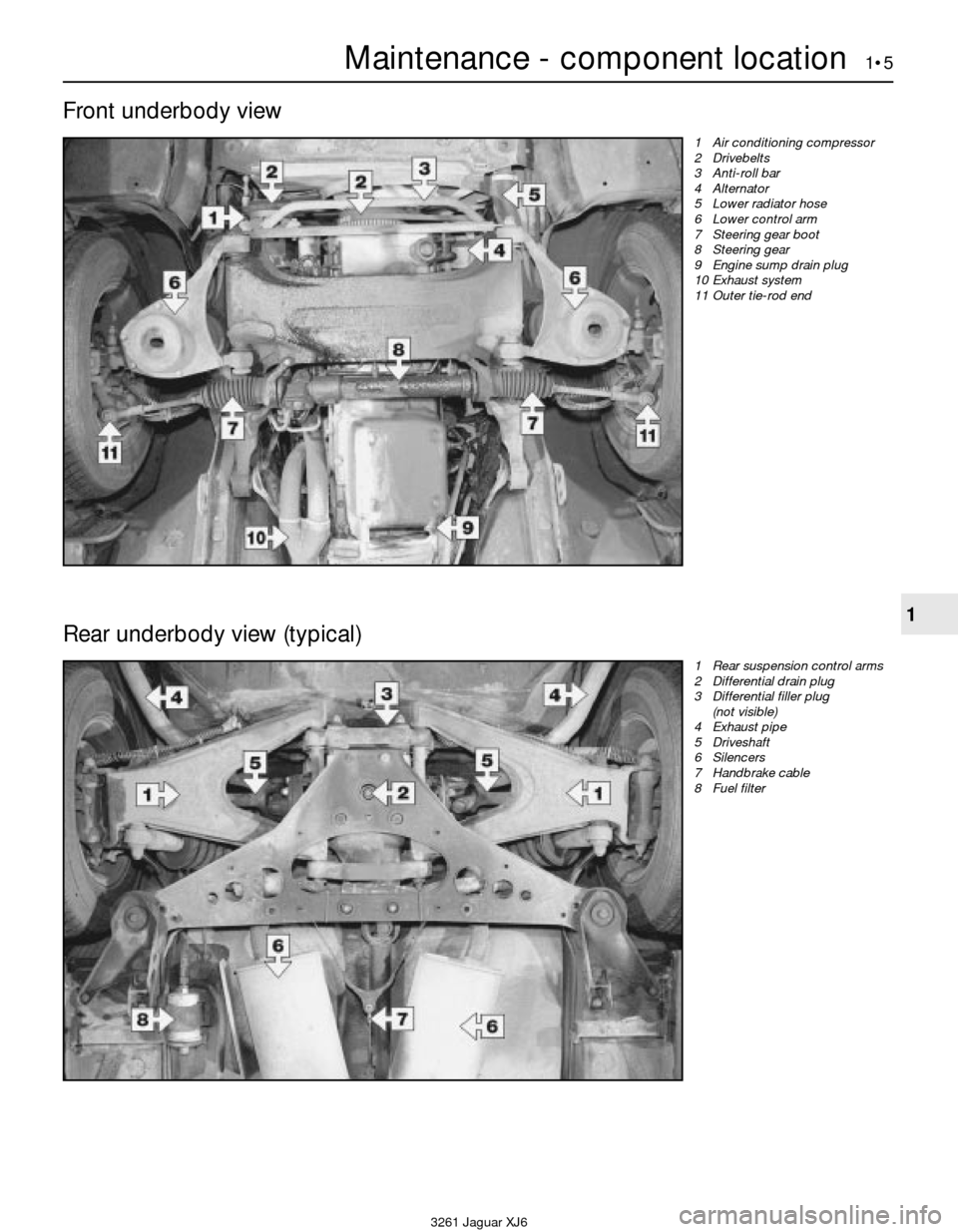
Maintenance - component location 1•5
1
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Front underbody view
1 Air conditioning compressor
2 Drivebelts
3 Anti-roll bar
4 Alternator
5 Lower radiator hose
6 Lower control arm
7 Steering gear boot
8 Steering gear
9 Engine sump drain plug
10 Exhaust system
11 Outer tie-rod end
Rear underbody view (typical)
1 Rear suspension control arms
2 Differential drain plug
3 Differential filler plug
(not visible)
4 Exhaust pipe
5 Driveshaft
6 Silencers
7 Handbrake cable
8 Fuel filter
Page 22 of 227
1 General information
1This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain his/her vehicle for safety,
economy, long life and peak performance.
2The Chapter contains a master
maintenance schedule, followed by Sections
dealing specifically with each task in the
schedule. Visual checks, adjustments,
component renewal and other helpful items
are included. Refer to the accompanying
illustrations of the engine compartment and
the underside of the vehicle for the locations
of the various components.
3Servicing your vehicle in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide a planned
maintenance programme, which should result
in a long and reliable service life. This is a
comprehensive plan, so maintaining some
items but not others at the specified service
intervals, will not produce the same results.
4As you service your vehicle, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the particular procedure being performed, or
because of the proximity of two otherwise-
unrelated components to one another. For
example, if the vehicle is raised for any
reason, the exhaust can be inspected at the
same time as the suspension and steering
components.
5The first step in this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all theSections relevant to the work to be carried out,
then make a list and gather all the parts and
tools required. If a problem is encountered,
seek advice from a parts specialist, or a dealer
service department.
2 Intensive maintenance
1If, from the time the vehicle is new, the
routine maintenance schedule is followed
closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid
levels and high-wear items, as suggested
throughout this manual, the engine will be
kept in relatively good running condition, and
the need for additional work will be minimised.
2It is possible that there will be times when
the engine is running poorly due to the lack of
regular maintenance. This is even more likely
if a used vehicle, which has not received
regular and frequent maintenance checks, is
purchased. In such cases, additional work
may need to be carried out, outside of the
regular maintenance intervals.
3If engine wear is suspected, a compression
test (refer to Chapter 2) will provide valuable
information regarding the overall performance
of the main internal components. Such a test
can be used as a basis to decide on the extent
of the work to be carried out. If, for example, a
compression test indicates serious internal
engine wear, conventional maintenance as
described in this Chapter will not greatly
improve the performance of the engine, and
may prove a waste of time and money, unless
extensive overhaul work is carried out first.4The following series of operations are those
which are most often required to improve the
performance of a generally poor-running
engine:
Primary operations
a) Clean, inspect and test the battery
(Section 6).
b) Check all the engine-related fluids (refer
to “Weekly checks”).
c) Check the condition and tension of the
auxiliary drivebelt (Section 21).
d) Renew the spark plugs (Section 16).
e) Inspect the distributor cap and rotor arm
(Section 19).
f) Check the condition of the air filter, and
renew if necessary (Section 17).
g) Renew the fuel filter (Section 18).
h) Check the condition of all hoses, and
check for fluid leaks (Section 7).
i) Check the exhaust gas emissions (see
Chapter 6).
5If the above operations do not prove fully
effective, carry out the following secondary
operations:
Secondary operations
All items listed under “Primary operations”,
plus the following:
a) Check the charging system (refer to
Chapter 5).
b) Check the ignition system (refer to
Chapter 5).
c) Check the fuel system (refer to Chapter 4).
d) Renew the distributor cap and rotor arm
(Section 19).
e) Renew the ignition HT leads (Section 19).
1•6Maintenance procedures
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Every 7500 miles (12 000 km) or 6 months
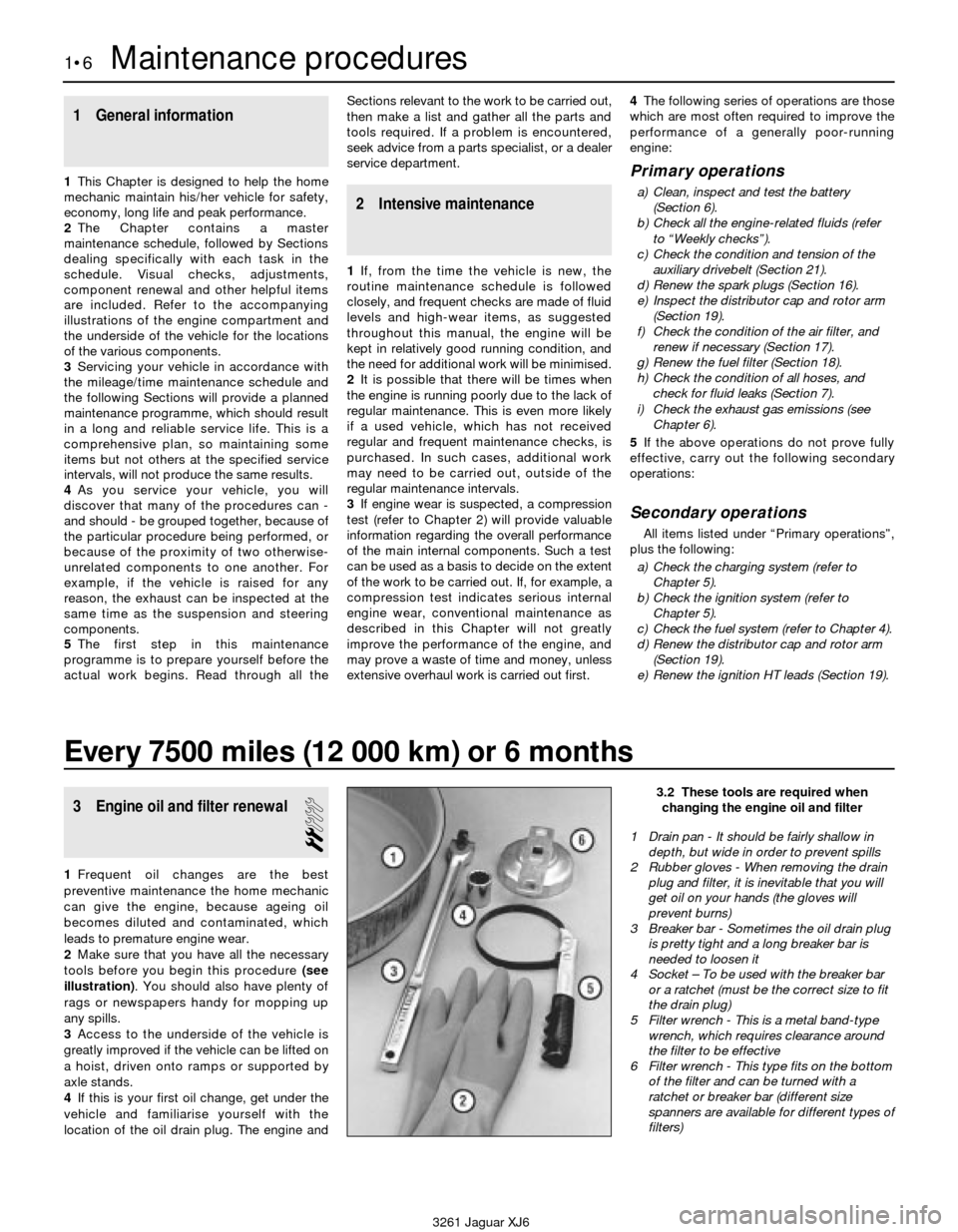
3 Engine oil and filter renewal
2
1Frequent oil changes are the best
preventive maintenance the home mechanic
can give the engine, because ageing oil
becomes diluted and contaminated, which
leads to premature engine wear.
2Make sure that you have all the necessary
tools before you begin this procedure (see
illustration). You should also have plenty of
rags or newspapers handy for mopping up
any spills.
3Access to the underside of the vehicle is
greatly improved if the vehicle can be lifted on
a hoist, driven onto ramps or supported by
axle stands.
4If this is your first oil change, get under the
vehicle and familiarise yourself with the
location of the oil drain plug. The engine and
3.2 These tools are required when
changing the engine oil and filter
1 Drain pan - It should be fairly shallow in
depth, but wide in order to prevent spills
2 Rubber gloves - When removing the drain
plug and filter, it is inevitable that you will
get oil on your hands (the gloves will
prevent burns)
3 Breaker bar - Sometimes the oil drain plug
is pretty tight and a long breaker bar is
needed to loosen it
4 Socket – To be used with the breaker bar
or a ratchet (must be the correct size to fit
the drain plug)
5 Filter wrench - This is a metal band-type
wrench, which requires clearance around
the filter to be effective
6 Filter wrench - This type fits on the bottom
of the filter and can be turned with a
ratchet or breaker bar (different size
spanners are available for different types of
filters)
Page 25 of 227
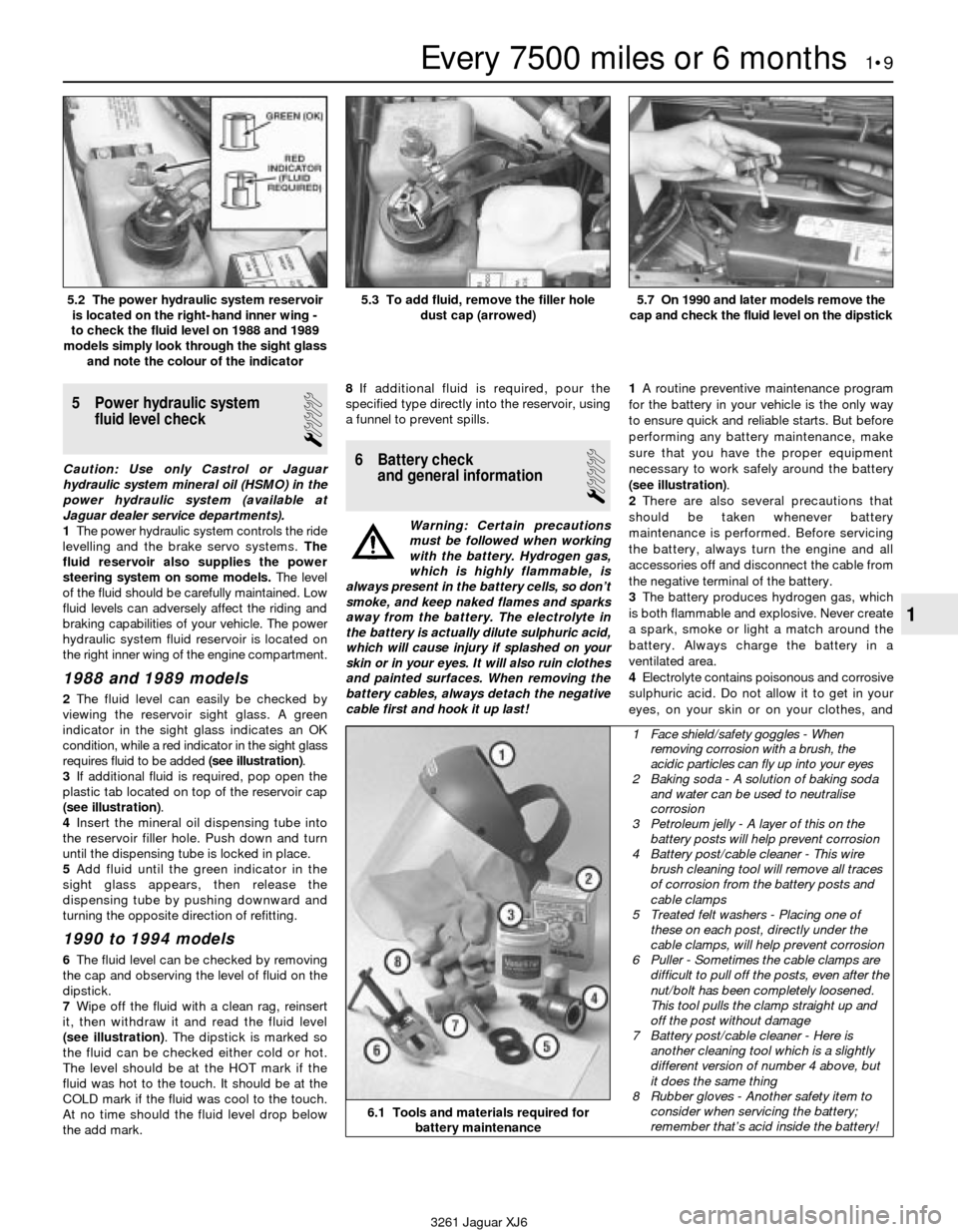
5 Power hydraulic system
fluid level check
1
Caution: Use only Castrol or Jaguar
hydraulic system mineral oil (HSMO) in the
power hydraulic system (available at
Jaguar dealer service departments).
1The power hydraulic system controls the ride
levelling and the brake servo systems. The
fluid reservoir also supplies the power
steering system on some models. The level
of the fluid should be carefully maintained. Low
fluid levels can adversely affect the riding and
braking capabilities of your vehicle. The power
hydraulic system fluid reservoir is located on
the right inner wing of the engine compartment.
1988 and 1989 models
2The fluid level can easily be checked by
viewing the reservoir sight glass. A green
indicator in the sight glass indicates an OK
condition, while a red indicator in the sight glass
requires fluid to be added (see illustration).
3If additional fluid is required, pop open the
plastic tab located on top of the reservoir cap
(see illustration).
4Insert the mineral oil dispensing tube into
the reservoir filler hole. Push down and turn
until the dispensing tube is locked in place.
5Add fluid until the green indicator in the
sight glass appears, then release the
dispensing tube by pushing downward and
turning the opposite direction of refitting.
1990 to 1994 models
6The fluid level can be checked by removing
the cap and observing the level of fluid on the
dipstick.
7Wipe off the fluid with a clean rag, reinsert
it, then withdraw it and read the fluid level
(see illustration). The dipstick is marked so
the fluid can be checked either cold or hot.
The level should be at the HOT mark if the
fluid was hot to the touch. It should be at the
COLD mark if the fluid was cool to the touch.
At no time should the fluid level drop below
the add mark.8If additional fluid is required, pour the
specified type directly into the reservoir, using
a funnel to prevent spills.
6 Battery check
and general information
1
Warning: Certain precautions
must be followed when working
with the battery. Hydrogen gas,
which is highly flammable, is
always present in the battery cells, so don’t
smoke, and keep naked flames and sparks
away from the battery. The electrolyte in
the battery is actually dilute sulphuric acid,
which will cause injury if splashed on your
skin or in your eyes. It will also ruin clothes
and painted surfaces. When removing the
battery cables, always detach the negative
cable first and hook it up last!1A routine preventive maintenance program
for the battery in your vehicle is the only way
to ensure quick and reliable starts. But before
performing any battery maintenance, make
sure that you have the proper equipment
necessary to work safely around the battery
(see illustration).
2There are also several precautions that
should be taken whenever battery
maintenance is performed. Before servicing
the battery, always turn the engine and all
accessories off and disconnect the cable from
the negative terminal of the battery.
3The battery produces hydrogen gas, which
is both flammable and explosive. Never create
a spark, smoke or light a match around the
battery. Always charge the battery in a
ventilated area.
4Electrolyte contains poisonous and corrosive
sulphuric acid. Do not allow it to get in your
eyes, on your skin or on your clothes, and
Every 7500 miles or 6 months 1•9
1
5.2 The power hydraulic system reservoir
is located on the right-hand inner wing -
to check the fluid level on 1988 and 1989
models simply look through the sight glass
and note the colour of the indicator5.3 To add fluid, remove the filler hole
dust cap (arrowed)5.7 On 1990 and later models remove the
cap and check the fluid level on the dipstick
6.1 Tools and materials required for
battery maintenance
1 Face shield/safety goggles - When
removing corrosion with a brush, the
acidic particles can fly up into your eyes
2 Baking soda - A solution of baking soda
and water can be used to neutralise
corrosion
3 Petroleum jelly - A layer of this on the
battery posts will help prevent corrosion
4 Battery post/cable cleaner - This wire
brush cleaning tool will remove all traces
of corrosion from the battery posts and
cable clamps
5 Treated felt washers - Placing one of
these on each post, directly under the
cable clamps, will help prevent corrosion
6 Puller - Sometimes the cable clamps are
difficult to pull off the posts, even after the
nut/bolt has been completely loosened.
This tool pulls the clamp straight up and
off the post without damage
7 Battery post/cable cleaner - Here is
another cleaning tool which is a slightly
different version of number 4 above, but
it does the same thing
8 Rubber gloves - Another safety item to
consider when servicing the battery;
remember that’s acid inside the battery!
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 33 of 227
compressor belt first because of the way they
are arranged on the crankshaft pulley.
Because of this and because belts tend to
wear out more or less together, it is a good
idea to replace both belts at the same time.
Mark each belt and its appropriate pulley
groove so the new belts can be installed in
their proper positions.
10Take the old belts to the parts store in
order to make a direct comparison for length,
width and design.
11After replacing a ribbed drivebelt, make
sure that it fits properly in the ribbed grooves
in the pulleys (see illustration). It is essential
that the belt be properly centred.
12Adjust the belt(s) in accordance with the
procedure outlined above.
22 Front wheel bearing check
and adjustment
3
Check and repack
1In most cases the front wheel bearings will
not need servicing until the brake pads are
changed. However, the bearings should be
checked whenever the front of the vehicle is
raised for any reason. Several items, including
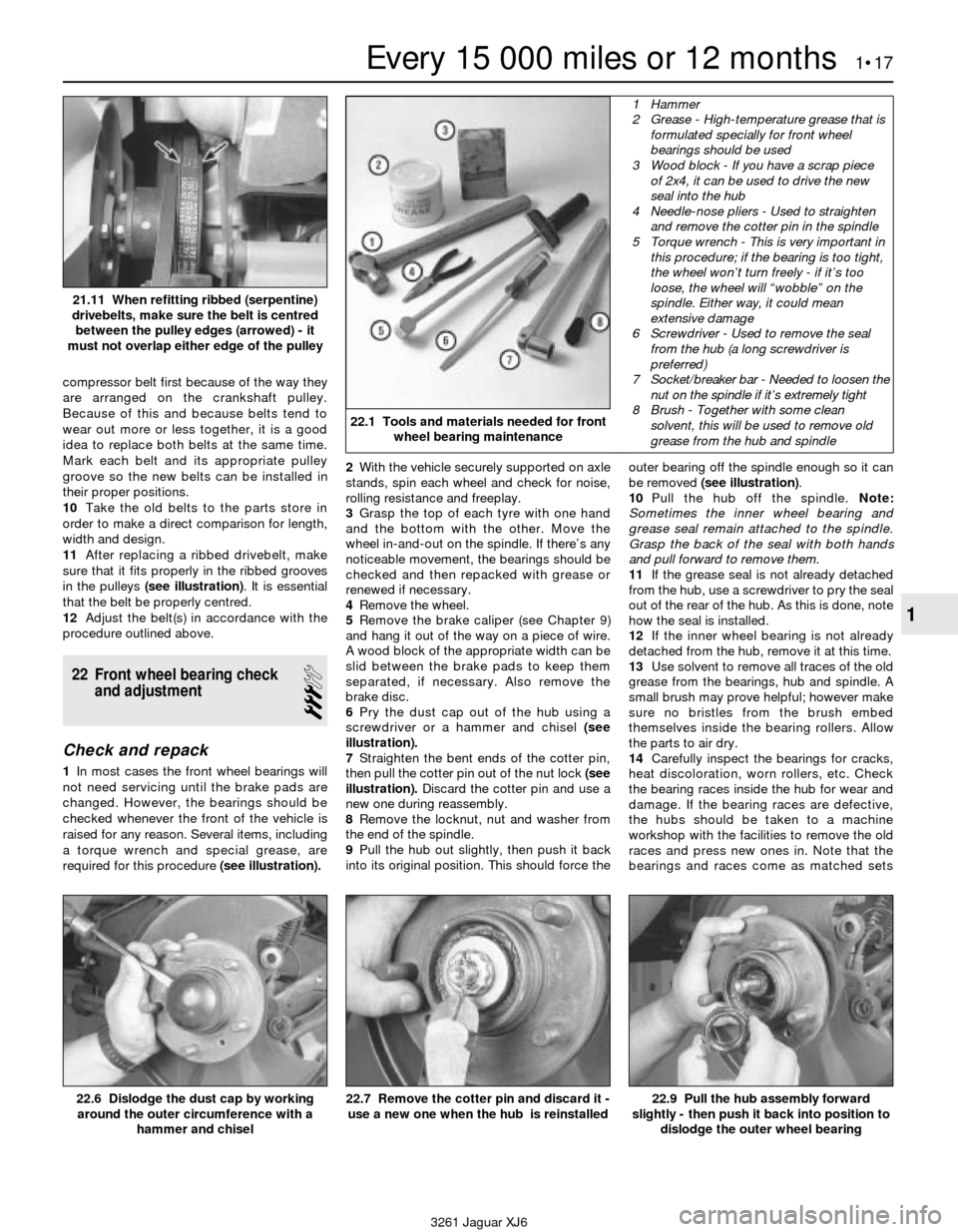
a torque wrench and special grease, are
required for this procedure (see illustration).2With the vehicle securely supported on axle
stands, spin each wheel and check for noise,
rolling resistance and freeplay.
3Grasp the top of each tyre with one hand
and the bottom with the other. Move the
wheel in-and-out on the spindle. If there’s any
noticeable movement, the bearings should be
checked and then repacked with grease or
renewed if necessary.
4Remove the wheel.
5Remove the brake caliper (see Chapter 9)
and hang it out of the way on a piece of wire.
A wood block of the appropriate width can be
slid between the brake pads to keep them
separated, if necessary. Also remove the
brake disc.
6Pry the dust cap out of the hub using a
screwdriver or a hammer and chisel (see
illustration).
7Straighten the bent ends of the cotter pin,
then pull the cotter pin out of the nut lock (see
illustration).Discard the cotter pin and use a
new one during reassembly.
8Remove the locknut, nut and washer from
the end of the spindle.
9Pull the hub out slightly, then push it back
into its original position. This should force theouter bearing off the spindle enough so it can
be removed (see illustration).
10Pull the hub off the spindle. Note:
Sometimes the inner wheel bearing and
grease seal remain attached to the spindle.
Grasp the back of the seal with both hands
and pull forward to remove them.
11If the grease seal is not already detached
from the hub, use a screwdriver to pry the seal
out of the rear of the hub. As this is done, note
how the seal is installed.
12If the inner wheel bearing is not already
detached from the hub, remove it at this time.
13Use solvent to remove all traces of the old
grease from the bearings, hub and spindle. A
small brush may prove helpful; however make
sure no bristles from the brush embed
themselves inside the bearing rollers. Allow
the parts to air dry.
14Carefully inspect the bearings for cracks,
heat discoloration, worn rollers, etc. Check
the bearing races inside the hub for wear and
damage. If the bearing races are defective,
the hubs should be taken to a machine
workshop with the facilities to remove the old
races and press new ones in. Note that the
bearings and races come as matched sets
Every 15 000 miles or 12 months 1•17
1
22.1 Tools and materials needed for front
wheel bearing maintenance
1 Hammer
2 Grease - High-temperature grease that is
formulated specially for front wheel
bearings should be used
3 Wood block - If you have a scrap piece
of 2x4, it can be used to drive the new
seal into the hub
4 Needle-nose pliers - Used to straighten
and remove the cotter pin in the spindle
5 Torque wrench - This is very important in
this procedure; if the bearing is too tight,
the wheel won’t turn freely - if it’s too
loose, the wheel will “wobble” on the
spindle. Either way, it could mean
extensive damage
6 Screwdriver - Used to remove the seal
from the hub (a long screwdriver is
preferred)
7 Socket/breaker bar - Needed to loosen the
nut on the spindle if it’s extremely tight
8 Brush - Together with some clean
solvent, this will be used to remove old
grease from the hub and spindle
22.6 Dislodge the dust cap by working
around the outer circumference with a
hammer and chisel
22.7 Remove the cotter pin and discard it -
use a new one when the hub is reinstalled22.9 Pull the hub assembly forward
slightly - then push it back into position to
dislodge the outer wheel bearing
3261 Jaguar XJ6 21.11 When refitting ribbed (serpentine)
drivebelts, make sure the belt is centred
between the pulley edges (arrowed) - it
must not overlap either edge of the pulley
Page 57 of 227

Engine block
Deck warpage limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.076 mm (0.003 inch)
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard
Size group A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90.990 to 91.003 mm (3.5823 to 3.5828 inches)
Size group B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.005 to 91.018 mm (3.5829 to 3.5834 inches)
Oversize
0.25 mm (0.010 inch) OS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.259 to 91.272 mm (3.5929 to 3.5934 inches)
0.50 mm (0.020 inch) OS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.513 to 91.526 mm (3.6029 to 3.6034 inches)
Pistons and rings
Piston-to-bore clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.017 to 0.043 mm (0.0007 to 0.0017 inch)
Piston ring end gap
No.1 (top) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 to 0.66 mm (0.016 to 0.026 inch)
No.2 (middle) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 to 0.66 mm (0.016 to 0.026 inch)
Oil ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.30 to 0.55 mm (0.012 to 0.022 inch)
Piston ring groove clearance
No. 1 (top) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.040 to 0.076 mm (0.0016 to 0.0030 inch)
No. 2 (middle) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.040 to 0.076 mm (0.0016 to 0.0030 inch)
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Main bearing cap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136 to 142 100 to 105
Connecting rod cap nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 to 60 37 to 44
* Note:Refer to Part A for additional torque specifications.
2B•2 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
3261 Jaguar XJ6
1 General information
Included in this portion of Chapter 2 are the
general overhaul procedures for the cylinder
head and internal engine components.
The information ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of replacement parts to detailed,
step-by-step procedures covering removal
and refitting of internal engine components
and the inspection of parts.
The following Sections have been written
based on the assumption that the engine has
been removed from the vehicle. For
information concerning in-vehicle engine
repair, as well as removal and refitting of the
external components necessary for the
overhaul, see Part A of this Chapter.
The Specifications included in this Part are
only those necessary for the inspection and
overhaul procedures which follow. Refer to
Part A for additional Specifications.
2 Engine overhaul-
general information
It’s not always easy to determine when, or if,
an engine should be completely overhauled,
as a number of factors must be considered.
High mileage is not necessarily an indication
that an overhaul is needed, while low mileage
doesn’t preclude the need for an overhaul.
Frequency of servicing is probably the most
important consideration. An engine that’s had
regular and frequent oil and filter changes, as
well as other required maintenance, will most
likely give many thousands of miles of reliableservice. Conversely, a neglected engine may
require an overhaul very early in its life.
Excessive oil consumption is an indication
that piston rings, valve seals and/or valve
guides are in need of attention. Make sure that
oil leaks aren’t responsible before deciding
that the rings and/or guides are bad. Perform a
cylinder compression check to determine the
extent of the work required (see Section 4).
Also check the vacuum readings under various
conditions (see Section 3).
Check the oil pressure with a gauge
installed in place of the oil pressure sender
unit (see illustrations)and compare it to this
Chapter’s Specifications. If it’s extremely low,
the bearings and/or oil pump are probably
worn out.
Loss of power, rough running, knocking or
metallic engine noises, excessive valve train
noise and high fuel consumption rates may
also point to the need for an overhaul,
especially if they’re all present at the same
time. If a complete tune-up doesn’t remedy
the situation, major mechanical work is the
only solution.An engine overhaul involves restoring the
internal parts to the specifications of a new
engine. During an overhaul, the piston rings
are replaced and the cylinder walls are
reconditioned (rebored and/or honed). If a
rebore is done by an automotive machine
workshop, new oversize pistons will also be
installed. The main bearings, big-end bearings
and camshaft bearings are generally replaced
with new ones and, if necessary, the
crankshaft may be reground to restore the
journals. Generally, the valves are serviced as
well, since they’re usually in less-than-perfect
condition at this point. While the engine is
being overhauled, other components, such as
the distributor, starter and alternator, can be
rebuilt as well. The end result should be a like
new engine that will give many trouble free
miles. Note:Critical cooling system
components such as the hoses, drivebelts,
thermostat and water pump should be
replaced with new parts when an engine is
overhauled. The radiator should be checked
carefully to ensure that it isn’t clogged or
leaking (see Chapter 3).If you purchase a
2.4a The oil pressure sender unit (arrowed)
is located in the right front corner of the
engine block, near the oil filter2.4b The oil pressure can be checked by
removing the sender unit and refitting a
pressure gauge in its place