JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 241 of 1784

SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (CONT.)
7 - 8 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 242 of 1784

SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Coolant................................ 15
Coolant Reserve/Overflow System............ 19
Cooling System Cleaning/Reverse Flushing..... 17
Cooling System Fans..................... 26
Cooling System Hoses.................... 26
Draining Cooling System................... 16
Radiator Pressure Cap.................... 20
Radiators............................... 22Refilling Cooling System................... 17
Testing Cooling System for Leaks............ 18
Thermostat............................. 13
Transmission Oil Coolers................... 29
Water Pump Tests........................ 9
Water PumpsÐGeneral Information............ 9
Water PumpsÐRemoval/Installation........... 10
WATER PUMPSÐGENERAL INFORMATION
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
radiator core, cooling system hoses and heater core.
The pump is driven from the engine crankshaft by a
drive belt on all engines.
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in bearings pressed into the
housing. The housing has a small hole to allow seep-
age to escape. The water pump seals are lubricated
by the antifreeze in the coolant mixture. No addi-
tional lubrication is necessary.
CAUTION: All engines are equipped with a reverse
(counter-clockwise) rotating water pump and vis-
cous fan drive assembly. REVERSE is stamped or
imprinted on the cover of the viscous fan drive and
inner side of the fan. The letter R is stamped into
the back of the water pump impeller (Fig. 1).Engines from previous model years, depending
upon application, may have been equipped with a
forward (clockwise) rotating water pump. Installation
of the wrong water pump will cause engine overheat-
ing.
A quick test to determine if the pump is working is
to check if the heater warms properly. A defective
water pump will not be able to circulate heated cool-
ant through the long heater hose to the heater core.
WATER PUMP TESTS
LOOSE IMPELLER
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain the cooling system.
(2) Loosen the fan belt(s).
(3) Disconnect the lower radiator hose from the
water pump.
(4) Bend a stiff clothes hanger or welding rod as
shown in (Fig. 2).
(5) Position the rod in the water pump inlet and
attempt to hold the impeller while turning the fan
blades. If equipped with a viscous fan drive, turn the
water pump shaft with a breaker bar and socket at-
tached to a mounting flange nut. If the impeller is
loose and can be held with the rod while the fan
blades are turning, the pump is defective. If the im-
peller turns, the pump is OK.
Connect the hose and install the coolant, or proceed
with repairs.
INSPECTING FOR INLET RESTRICTIONS
Inadequate heater performance may be caused by a
metal casting restriction in the water pump heater
hose inlet.Fig. 1 Reverse Rotating Water PumpÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 9
Page 243 of 1784

DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to de-
crease the level below the water pump heater hose
inlet.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
Remove the pump from engine before remov-
ing restriction to prevent contamination of the
coolant with debris. Refer to Water Pump Re-
moval.
WATER PUMPSÐREMOVAL/INSTALLATION
REMOVALÐALL MODELS
The water pump on all models can be removed
without discharging the air conditioning system (if
equipped).
CAUTION: All engines have a reverse (counter-
clockwise) rotating water pump. The letter R is
stamped into the back of the water pump impeller
(Fig. 1) to identify. Engines from previous model
years, depending upon application, may be
equipped with a forward (clockwise) rotating water
pump. Installation of the wrong water pump will
cause engine over heating.The water pump impeller is pressed on the rear of
the pump shaft and bearing assembly. The water
pump is serviced only as a complete assembly.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE BLOCK DRAIN
PLUG(S) OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain coolant into a clean container for re-
use.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system. Refer to Draining
Cooling System in this group.
(3)XJ models with 4.0L engine equipped with
A/C or heavy duty cooling system:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
water pump pulley-to-water pump hub mounting
bolts (Fig. 3).
XJ models with 4.0L engine without A/C or
heavy duty cooling system; or any 2.5L engines;
or any YJ models:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
fan hub-to-water pump pulley mounting nuts (Fig.
4).
The engine accessory drive belt must be removed
prior to removing the fan (if installed at pump) or
fan pulley.
(4) Remove engine drive belt as follows:
(a) Loosen two rear power steering pump mount-
ing bolts A (Fig. 5).
(b) Loosen upper pump pivot bolt B and lower
lock nut C (Figs. 6 or 7).
(c) Loosen pump adjusting bolt D (Fig. 5) until
belt can be removed.
(d) Remove belt.
(5) Check condition of all pulleys.
(6) The power steering pump must be removed
from its cast mounting bracket to gain access to bolt
Fig. 2 Impeller TestÐTypical
Fig. 3 Water Pump Pulley Bolts
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 244 of 1784
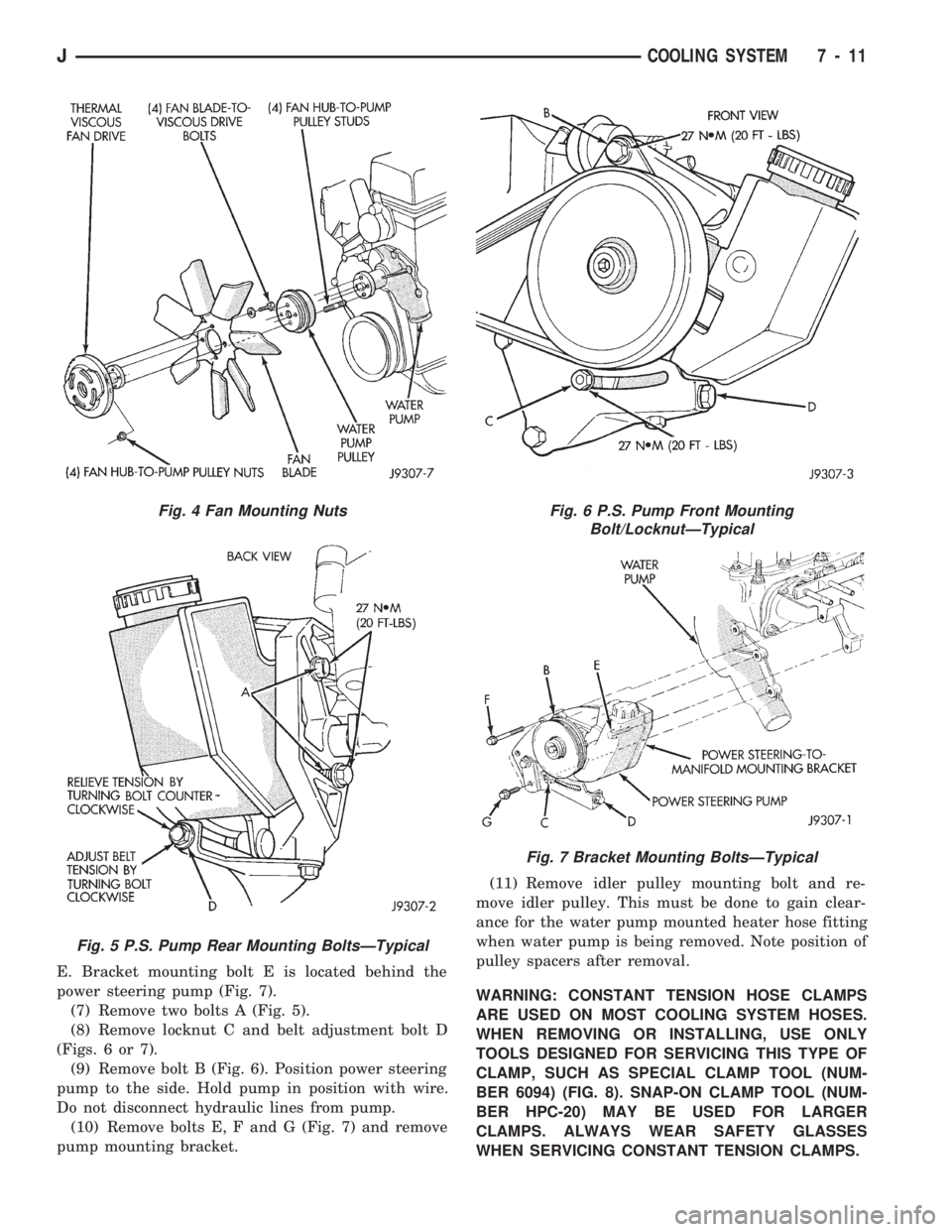
E. Bracket mounting bolt E is located behind the
power steering pump (Fig. 7).
(7) Remove two bolts A (Fig. 5).
(8) Remove locknut C and belt adjustment bolt D
(Figs. 6 or 7).
(9) Remove bolt B (Fig. 6). Position power steering
pump to the side. Hold pump in position with wire.
Do not disconnect hydraulic lines from pump.
(10) Remove bolts E, F and G (Fig. 7) and remove
pump mounting bracket.(11) Remove idler pulley mounting bolt and re-
move idler pulley. This must be done to gain clear-
ance for the water pump mounted heater hose fitting
when water pump is being removed. Note position of
pulley spacers after removal.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER 6094) (FIG. 8). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER
CLAMPS. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES
WHEN SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
Fig. 4 Fan Mounting Nuts
Fig. 5 P.S. Pump Rear Mounting BoltsÐTypical
Fig. 6 P.S. Pump Front Mounting
Bolt/LocknutÐTypical
Fig. 7 Bracket Mounting BoltsÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 11
Page 245 of 1784

CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.
(12) Remove lower radiator hose from water pump.
Remove heater hose from water pump fitting.
(13) Remove four nuts or bolts (refer to the previ-
ous step #3).
(14) Remove the fan assembly and pulley (if fan is
installed at pump), or remove the pulley from the ve-
hicle.
(15) Remove the four pump mounting bolts (Fig. 9)
and remove pump from vehicle. Discard old gasket.
Note that one of the four bolts is longer than the
other bolts.
(16) If pump is to be replaced, the heater hose fit-
ting must be removed. Note position of fitting before
removal.
INSTALLATIONÐALL MODELS
(1) If pump is being replaced, install the heater
hose fitting to the pump. Use a sealant on the fitting
such as MoparŸ Thread Sealant With Teflon. Refer
to the directions on the package.
(2) Clean the gasket mating surfaces. If the origi-
nal pump is used, remove any deposits or other for-
eign material. Inspect the cylinder block and water
pump mating surfaces for erosion or damage from
cavitation.
(3) Install the gasket and water pump (the gasket
is installed dry). Tighten mounting bolts to 30 Nzm
(22 ft. lbs.) torque. Rotate the shaft by hand to be
sure it turns freely.
(4) Connect the radiator and heater hoses to the
water pump.
(5) Position water pump pulley to water pump hub.
(6) If equipped with a water pump mounted fan,
install fan and four nuts to water pump hub. If notequipped with a water pump mounted fan, install
four pump hub bolts. Tighten bolts (or nuts) to 27
Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Position power steering pump bracket to en-
gine. Install bolts E, F and G (Fig. 7). Tighten bolts
FandGto38Nzm (28 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten bolt E
to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Position power steering pump to mounting
bracket. Install pivot bolt B (Fig. 6) finger tight. In-
stall locknut C and adjustment bolt D (Figs. 6 or 7)
finger tight.
(9) Install two adjustment bolts A (Fig. 6) finger
tight.
(10) Install idler pulley.
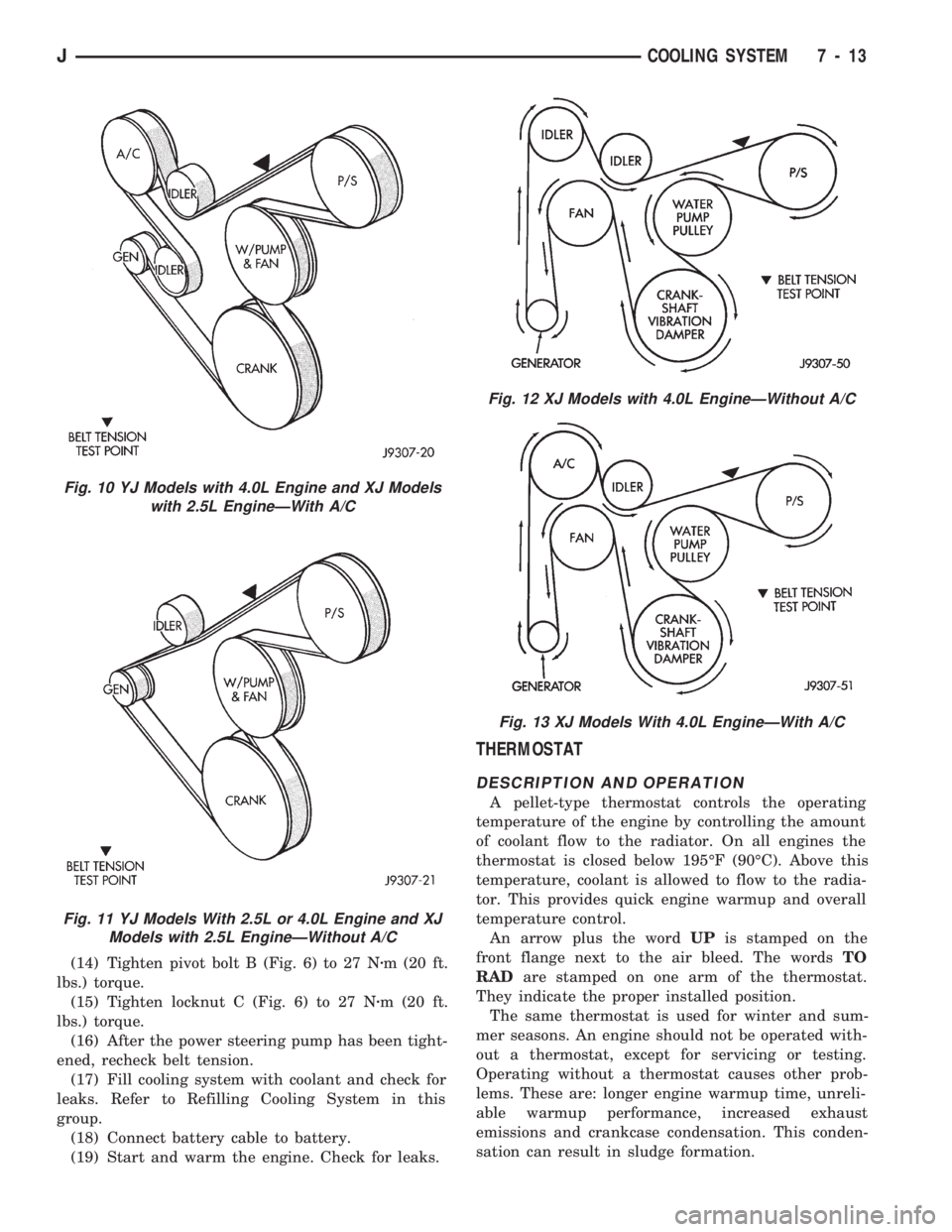
CAUTION: When installing the serpentine engine
accessory drive belt, the belt MUST be routed cor-
rectly. If not, the engine may overheat due to the
water pump rotating in the wrong direction. Refer to
Figs. 10, 11, 12 or 13 for appropriate belt routing.
You may also refer to the Belt Routing Label in the ve-
hicle engine compartment.
(11) Position drive belt to pulleys.
(12) Tighten belt adjustment bolt D (Fig. 5) to the
proper tension. Refer to the Specifications section at
the end of this group for belt tension.
(13) Tighten bolts A (Fig. 5) to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
Fig. 8 Hose Clamp ToolÐTypical
Fig. 9 Water Pump Remove/InstallÐTypical
7 - 12 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 246 of 1784
(14) Tighten pivot bolt B (Fig. 6) to 27 Nzm (20 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(15) Tighten locknut C (Fig. 6) to 27 Nzm (20 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(16) After the power steering pump has been tight-
ened, recheck belt tension.
(17) Fill cooling system with coolant and check for
leaks. Refer to Refilling Cooling System in this
group.
(18) Connect battery cable to battery.
(19) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator. On all engines the
thermostat is closed below 195ÉF (90ÉC). Above this
temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to the radia-
tor. This provides quick engine warmup and overall
temperature control.
An arrow plus the wordUPis stamped on the
front flange next to the air bleed. The wordsTO
RADare stamped on one arm of the thermostat.
They indicate the proper installed position.
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
Fig. 10 YJ Models with 4.0L Engine and XJ Models
with 2.5L EngineÐWith A/C
Fig. 11 YJ Models With 2.5L or 4.0L Engine and XJ
Models with 2.5L EngineÐWithout A/C
Fig. 12 XJ Models with 4.0L EngineÐWithout A/C
Fig. 13 XJ Models With 4.0L EngineÐWith A/C
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 13
Page 247 of 1784

CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
XJ and YJ models are equipped with On-Board Di-
agnostics for certain cooling system components. Re-
fer to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) in the Diagnosis
section of this group for additional information. If the
powertrain control module (PCM) detects low engine
coolant temperature, it will record a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) in the PCM memory. The DTC num-
ber for low coolant temperature is 17. Do not change
a thermostat for lack of heat as indicated by the in-
strument panel gauge or heater performance unless a
DTC number 17 is present. Refer to the Diagnosis
section of this group for other probable causes. For
other DTC numbers, refer to On-Board Diagnostics
in the General Diagnosis section of group 14, Fuel
Systems.
The DTC can also be accessed through the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures manual for diagnostic information
and operation of the DRB scan tool.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
(1) Drain the coolant from the radiator until the
level is below the thermostat housing.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER 6094) (FIG. 14). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER
CLAMPS. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES
WHEN SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.
(2) Remove radiator upper hose and heater hose at
thermostat housing.
(3) Disconnect wiring connector at engine coolant
temperature sensor.(4) Remove thermostat housing mounting bolts,
thermostat housing, gasket and thermostat (Fig. 15).
Discard old gasket.
(5) Clean the gasket mating surfaces.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the replacement thermostat so that the
pellet, which is encircled by a coil spring, faces the
engine. All thermostats are marked on the outer
flange to indicate the proper installed position.
(a) Observe the recess groove in the engine cyl-
inder head (Fig. 16).
(b) Position thermostat in groove with arrow and
air bleed hole on outer flange pointing up.
(2) Install replacement gasket and thermostat
housing.
Fig. 14 Hose Clamp ToolÐTypical
Fig. 15 Thermostat Removal/Installation
7 - 14 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 248 of 1784

CAUTION: Tightening the thermostat housing un-
evenly or with the thermostat out of its recess, may
result in a cracked housing.
(3) Tighten the housing bolts to 20 Nzm (15 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install hoses to thermostat housing.
(5) Install electrical connector to coolant tempera-
ture sensor.
(6) Be sure that the radiator draincock is tightly
closed. Fill the cooling system to the correct level
with the required coolant mixture. Refer to Refilling
Cooling System in this group.
(7) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
COOLANT
GENERAL INFORMATION
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
Coolant flows through the engine water jackets ab-
sorbing heat produced during engine operation. The
coolant carries heat to the radiator and heater core.
Here it is transferred to the ambient air passing
through the radiator and heater core fins. The cool-
ant also removes heat from the automatic transmis-
sion fluid in vehicles equipped with an automatic
transmission.
COOLANT PERFORMANCE
The required ethylene-glycol (antifreeze) and water
mixture depends upon climate and vehicle operating
conditions. The coolant performance of various mix-
tures follows:
Pure Water-Water can absorb more heat than a
mixture of water and ethylene-glycol. This is for pur-pose of heat transfer only. Water also freezes at a
higher temperature and allows corrosion.
100 percent Ethylene-Glycol-The corrosion inhib-
iting additives in ethylene-glycol need the presence
of water to dissolve. Without water, additives form
deposits in system. These act as insulation causing
temperature to rise to as high as 149ÉC (300ÉF). This
temperature is hot enough to melt plastic and soften
solder. The increased temperature can result in en-
gine detonation. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-
glycol freezes at -22ÉC (-8ÉF).
50/50 Ethylene-Glycol and Water-Is the recom-
mended mixture, it provides protection against freez-
ing to -37ÉC (-35ÉF). The antifreeze concentration
must alwaysbe a minimum of 44 percent, year-
round in all climates. If percentage is lower, engine
parts may be eroded by cavitation. Maximum protec-
tion against freezing is provided with a 68 percent
antifreeze concentration, which prevents freezing
down to -67.7ÉC (-90ÉF). A higher percentage will
freeze at a warmer temperature. Also, a higher per-
centage of antifreeze can cause the engine to over-
heat because specific heat of antifreeze is lower than
that of water.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.
COOLANT SELECTION-ADDITIVES
Coolant should be maintained at the specified level
with a mixture of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze
and low mineral content water. Only use an anti-
freeze containing ALUGARD 340-2 Ÿ.
CAUTION: Do not use coolant additives that are
claimed to improve engine cooling.
COOLANT SERVICE
It is recommended that the cooling system be
drained and flushed at 84,000 kilometers (52,500
miles), or 3 years, whichever occurs first. Then every
two years, or 48,000 kilometers (30,000 miles),
whichever occurs first.
COOLANT LEVEL CHECKÐROUTINE
Do not remove radiator cap for routine coolant
level inspections. The coolant level can be
checked at coolant reserve/overflow tank.
The coolant reserve/overflow system provides a
quick visual method for determining coolant level
without removing radiator pressure cap. With engine
idling and at normal operating temperature, observe
coolant level in reserve/overflow tank. The coolant
level should be between ADD and FULL marks.
Fig. 16 Thermostat Recess
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 15
Page 249 of 1784

ADDING ADDITIONAL COOLANTÐROUTINE
Do not remove radiator cap to add coolant to
system.When adding coolant to maintain correct
level, do so at coolant reserve/overflow tank. Use a
50/50 mixture of ethylene-glycol antifreeze contain-
ing Alugard 340-2 Ÿ and low mineral content water.
Remove radiator cap only for testing or when refill-
ing system after service. Removing cap unnecessarily
can cause loss of coolant and allow air to enter sys-
tem, which produces corrosion.
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK-SERVICE
The cooling system is closed and designed to main-
tain coolant level to top of radiator.
WARNING: DO NOT OPEN RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH ENGINE RUNNING OR WHILE ENGINE IS HOT
AND COOLING SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
When vehicle servicing requires a coolant level
check in radiator, drain several ounces of coolant
from radiator drain cock. Do this while observing
coolant reserve/overflow system tank. The coolant
level in reserve/overflow tank should drop slightly. If
not, inspect for a leak between radiator and coolant
reserve/overflow system connection. Remove radiator
cap. The coolant level should be to top of radiator. If
not and if coolant level in reserve/overflow tank is at
ADD mark, check for:
²An air leak in coolant reserve/overflow tank or its
hose
²An air leak in radiator filler neck
²Leak in pressure cap seal to radiator filler neck
LOW COOLANT LEVEL-AERATION
If the coolant level in radiator drops below top of
radiator core tubes, air will enter cooling system.
Low coolant level can cause thermostat pellet to be
suspended in air instead of coolant. This will cause
thermostat to open later, which in turn causes higher
coolant temperature. Air trapped in cooling system
also reduces amount of coolant circulating in heater
core resulting in low heat output.
DEAERATION
As the engine operates, any air trapped in cooling
system gathers under the radiator cap. The next time
the engine is operated, thermal expansion of coolant
will push any trapped air past radiator cap into the
coolant reserve/overflow tank. Here it escapes to the
atmosphere into the tank. When the engine cools
down the coolant, it will be drawn from the reserve/
overflow tank into the radiator to replace any re-
moved air.
DRAINING COOLING SYSTEM
ALL MODELSÐEXCEPT XJ WITH 4.0L ENGINE
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
DO NOT remove the radiator cap when draining
the coolant from the reserve/overflow tank. Open the
radiator draincock and when the tank is empty, re-
move the radiator cap. The coolant does not have to
be removed from the tank unless the system is being
refilled with a fresh mixture.
(1) Drain the coolant from the radiator by loosen-
ing the draincock.
(2) Drain coolant from engine as follows:
(a) On 2.5L engines (all models) by removing
drain plug at left rear side of block.
(b) On 4.0L engines by removing the drain plug
or coolant temperature sensor on the left side of
the block (Fig. 17).
XJ MODELS WITH 4.0L ENGINE
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 17 Draining CoolantÐ4.0L Engine
7 - 16 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 250 of 1784

DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
(1) Remove radiator pressure cap.
(2) For access to radiator draincock, remove radia-
tor grille (Fig. 18).
(3) Attach one end of a 24 inch long X 1/4 inch ID
hose to the radiator draincock. Put the other end into
a clean container. Open draincock and drain coolant
from radiator.
(4) Drain coolant from engine by removing the
drain plug and coolant temperature sensor on left
side of block (Fig. 17).
REFILLING COOLING SYSTEM
YJ MODELS
(1) Remove draining hose. Tighten the radiator
draincock and the cylinder block drain plug(s).
(2) Fill system using a 50/50 mixture of water and
antifreeze. This is described in the Coolant section of
this group. Fill the radiator to the top and install the
radiator cap. Add sufficient coolant to the reserve/
overflow tank to raise the level to the FULL mark.
(3) Operate the engine with the radiator cap and
reserve/overflow tank cap in place. After the engine
has reached the normal operating temperature, shut
the engine off and allow it to cool.
(4) Add coolant to the reserve/overflow tank as
necessary.Only add coolant when the engine is
cold. Coolant level in a warm engine will be
higher due to thermal expansion.
XJ MODELS
(1) Tighten the radiator draincock and the cylinder
block drain plug(s). If removed, install coolant tem-
perature sensor (4.0L engine).
(2) Fill system using a 50/50 mixture of water and
antifreeze as described in the Coolant section of this
group. Fill radiator to top and install radiator cap.
Add sufficient coolant to reserve/overflow tank to
raise level to FULL mark.
(3) With heater control unit in the HEAT position,
operate engine with radiator cap in place.
(4) After engine has reached normal operating
temperature, shut engine off and allow it to cool.
(5) Add coolant to reserve/overflow tank as neces-
sary.Only add coolant when the engine is cold.
Coolant level in a warm engine will be higher
due to thermal expansion.
COOLING SYSTEM CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14-to-18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
CLEANING
Drain cooling system and refill with water. Run
engine with radiator cap installed until upper radia-
tor hose is hot. Stop engine and drain water from
system. If water is dirty, fill system with water, run
engine and drain system. Repeat until water drains
clean.
REVERSE FLUSHING
Reverse flushing of the cooling system is the forc-
ing of water through the cooling system. This is done
using air pressure in the opposite direction of normal
coolant flow. It is usually only necessary with very
dirty systems with evidence of partial plugging.
REVERSE FLUSHING RADIATOR
Disconnect the radiator hoses from the radiator fit-
tings. Attach a section of radiator hose to the radia-
tor bottom outlet fitting and insert the flushing gun.
Connect a water supply hose and air supply hose to
the flushing gun.
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14-to-18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
Allow the radiator to fill with water. When radia-
tor is filled, apply air in short blasts allowing radia-
tor to refill between blasts. Continue this reverse
flushing until clean water flows out through rear of
radiator cooling tube passages. For more information,
refer to operating instructions supplied with flushing
equipment. Have radiator cleaned more extensively
by a radiator repair shop.
Fig. 18 Draincock AccessÐXJ Models with 4.0L
Engine
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 17