display JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 332 of 1784

With the ignition key in the ON position and en-
gine not running, check the sensor output voltage at
the center terminal wire of the connector. Check this
at idle (throttle plate closed) and at wide open throt-
tle (WOT). At idle, sensor output voltage should be
greater than 200 millivolts. At wide open throttle,
sensor output voltage must be less than 4.8 volts.
The output voltage should increase gradually as the
throttle plate is slowly opened from idle to WOT.
OXYGEN SENSOR TESTS
For diagnosis, removal or installation, refer to
Group 14, Fuel Systems in this manual.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
FOR IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor certain ignition system cir-
cuits:
EXAMPLE:
If a reference signal is not being detected during
engine cranking from the crankshaft position sensor,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) number 11 can be
observed at the Check Engine Lamp.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit of-
ten enough to indicate an actual problem, a DTC is
stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory
for eventual display to the service technician. If the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the DTC after 51 engine starts.
Certain criteria must be met for a DTC to be en-
tered into PCM memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine rpm, engine temperature and/or
input voltage to the PCM.
A DTC indicates that the PCM has recognized an
abnormal signal in a circuit or the system. A DTC
may indicate the result of a failure, but never iden-
tify the failed component directly.
It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit
may not be entered into memory even though a mal-
function has occurred. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) in Group 14, Fuel Systems for additional in-
formation.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be dis-
played by cycling the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On
within three seconds and observing the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp. This lamp was formerly referred to
as the Check Engine Lamp. The lamp is located on
the instrument panel.
They can also be displayed through the use of the
Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB) scan tool. The DRB
connects to the data link connector in the enginecompartment (Figs. 32 or 33). For operation of the
DRB, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
EXAMPLES:
²If the lamp flashes 1 time, pauses and flashes 1
more time, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
number 11 is indicated.
²If the lamp flashes 3 times, pauses and flashes 5
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 35 is indicated.
After any stored DTC information has been ob-
served, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored
information.
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, the DRB scan
tool must be used to erase a DTC. Refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
Fig. 32 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 33 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 19
Page 349 of 1784

other side. When coolant temperature is too high the
switch closes providing a path to ground, and the indi-
cator bulb lights.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer displays the engine speed (RPM).
With the engine running, the tachometer receives an
engine speed signal from the Powertrain Control
Module pin 43 (values shown in Specifications chart).
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER SYSTEM
The speedometer/odometer system consists of an elec-
tric speedometer and pushbutton reset odometer
mounted in the cluster. The system also includes the
wire harness from the cluster to the vehicle speed sen-
sor at the transmission, and the adapter and pinion in
the transmission. A signal is sent from a transmission
mounted vehicle speed sensor to the speedometer/odom-
eter circuitry through the wiring harness. Refer to
Group 21 - Transmission for selecting the proper pinion,
and selecting and indexing the proper adapter.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge pointer position is controlled by a
magnetic field created by electrical current flow through
the coils within the gauge. A change in current flow will
change the magnetic field which changes the pointer po-
sition. The fuel level sender is a variable resistor that
changes electrical resistance with a change of the level
of fuel in the tank (values shown in Specifications
chart).
LOW FUEL WARNING LAMP
The low fuel warning lamp will light when the fuel
level falls below approximately 4 gallons. A low fuel
warning module controls when the lamp will light.
When the module senses 66.5 ohms or less from the
fuel level sender for 10 continuous seconds, the lamp
will light. The lamp will remain on until the module
senses 63.5 ohms or more from the fuel level sender
for 20 continuous seconds.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have an
optional upshift indicator lamp. The lamp is controlled
by the Powertrain Control Module. The lamp lights to
indicate when the driver should shift to the next high-
est gear for best fuel economy. The Powertrain Control
Module will turn the lamp off after 3 to 5 seconds if the
upshift is not performed. The lamp will remain off until
the vehicle stops accelerating and is brought back to the
range of lamp operation or shifted into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally illuminated when
the ignition switch is turned ON and is turned off
when the engine is started. The lamp will be lighted
during engine operation according to engine speed
and load.
BRAKE INDICATOR LAMP
The brake indicator lamp warns the driver that the
parking brake is applied or that hydraulic pressure in
the split brake system is unequal.
Voltage is supplied through the brake indicator
bulb to 3 switches. A path to ground for the current
is available if:
²The brake warning switch is closed (with unequal
brake system hydraulic pressures), or
²
The ignition switch is in the START position (to test
the bulb), or
²The park brake switch is closed (with the parking
brake applied).
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) INDICATOR
LAMP
The anti-lock brake system (ABS) lamp lights to in-
dicate a system self-check is in process at vehicle
start-up. If light remains on after start-up or comes
on and stays on while driving, it may indicate that
the ABS system has detected a malfunction or has
become inoperative.
4WD INDICATOR LAMP
COMMAND-TRAC 4WD
The PART TIME lamp lights when the vehicle is en-
gaged in four-wheel drive mode. Voltage is supplied to
one side of the indicator bulb. A switch in the transfer
case area is connected to the other side of the indicator
bulb. When the switch is closed, a path to ground is pro-
vided and the indicator bulb lights.
SELECT-TRAC 4WD
The four-wheel drive icon or FULL TIME lamp
lights when the vehicle is engaged in full time four-
wheel drive mode. The PART TIME lamp lights when
the vehicle is in part time four-wheel drive mode.
Voltage is supplied to one side of the indicators.
Switches in the transfer case area are connected to
the other side of the indicator bulbs. When a switch
is closed, a path to ground is provided and the indi-
cator bulb lights.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)
lights each time the ignition switch is turned ON and
stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.
If the PCM receives an incorrect signal or no signal
from certain sensors or emission related systems the
lamp is turned on (pin 32 of PCM). This is a warning
that the PCM has recorded a system or sensor mal-
function. In some cases when a diagnostic trouble
code is declared the PCM will go into a limp-in mode
in an attempt to keep the system operating. It sig-
nals an immediate need for service.
The lamp also can be used to display diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC). Cycle the ignition switch ON,
OFF, ON, OFF, ON within 5 seconds. This will allow
any trouble codes stored in the PCM memory to be
displayed in a series of flashes representing digits.
8E - 2 XJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 351 of 1784

(3) Connect a jumper between terminal A and B on
the body half of the fuel gauge sender connector. The
gauge should move to F. If gauge is OK, replace
sender. If not, go to step 4.
(4) Measure resistance of sender. Meter should
read 105 to 5 ohms. If OK, go to step 5. If not, re-
place sender.
(5) Check for an open between sender connector
and gauge. If OK, replace gauge. If not, repair open
to gauge.
LOW FUEL WARNING INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Disconnect terminal B1 of the instrument clus-
ter connector. Wait at least 10 seconds. Lamp (LED)
should light. If OK, replace sender. If not, replace
low fuel warning module.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Ground pin 7 of connector B. Lamp should
light. If not, replace bulb. If OK, continue with
step 3.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Check for conti-
nuity between connector B pin 2 and pin 54 of the
Powertrain Control Module. If OK, replace PCM. If
not, repair open.
BRAKE INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Apply parking
brake, brake warning switch connector unplugged.
(2) Jumper brake warning switch connector termi-
nal B to ground. Lamp should light. If bulb is OK,
repair open to indicator.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Measure resis-
tance between brake warning switch connector ter-
minal A and ground. Meter should read zero ohms. If
OK, check switch and/or brake system. If not, repair
open to park brake switch ground.
4WD INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Apply parking brake, start engine, vehicle in
4WD Lock or 4WD.
(2) Unplug switch and touch harness side of wire
to ground. Lamp should light. If OK, check switch
operation, replace if bad. If bulb is OK, repair open
to indicator.
LOW WASHER INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Jumper 12 volts to fluid level switch connector
terminal B. Lamp should light. If not, go to step 3.
(3) Measure resistance between terminal B and
ground. Meter should read zero ohms. If not, repair
open to bulb. If OK, go to step 4.
(4) Measure voltage at fluid level switch connector
terminal A. Meter should read battery voltage. If
OK, replace switch. If not, repair open to fuse.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE)
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Jumper Powertrain Control Module terminal 2
to ground. Lamp should light. If bulb is OK, check
for open to instrument cluster connector terminal 2.
ANTI-LOCK INDICATOR
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Jumper instrument cluster connector terminal
6 to ground. Lamp should light. If bulb is OK, check
wiring for an open to module. Refer to Group 5 -
Brakes.
SEAT BELT INDICATOR
Jumper instrument cluster connector terminal 15
to 12 volts. Lamp should light. If not, replace bulb. If
OK, check wiring for an open to buzzer module. Re-
fer to Group 8U - Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems.
RADIO/CLOCK ILLUMINATION
With the ignition switch in ACCESSORY or ON,
power comes from the radio fuse. It then goes
through the normally closed contacts of the radio il-
lumination relay to the radio at connector terminal
11.
Pulling the headlamp switch to ON energizes the
radio illumination relay. This closes the normally
open contacts of the relay, and the brightness for the
radio display is controlled by the headlamp switch
rheostat. The back-lighting for the radio is also con-
trolled by the headlamp rheostat through radio con-
nector terminal 10.
Refer to Group 8F - Audio Systems, for radio illu-
mination relay diagnosis.
INSTRUMENT PANEL LAMPS
Voltage is supplied at all times from the 40 amp
Maxi fuse (located in the Power Distribution Center)
through the park lamps fuse to the headlamp switch.
The circuit continues through the instrument lamps
fuse to the individual instrument panel lamps to
ground. Lamp brightness is controlled by turning the
headlamp switch knob.
DIAGNOSIS
(1) Turn parking lamps ON.
(2) Check park lamps fuse. Replace as required.
(3) Check instrument lamps fuse. Replace as re-
quired.
(4) Measure voltage at battery side of instrument
lamps fuse with rheostat turned counterclockwise to
clockwise (LO to HI). Meter should read zero volts to
battery voltage. If not, replace headlamp switch.
(5) Measure resistance at ground side of instru-
ment lamps fuse with parking lamps OFF. Meter
should read almost zero ohms (except bulb filament).
If not, repair open to ground. If zero ohms, 12 volt
supply wire from fuse is shorted to ground, repair short.
8E - 4 XJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 361 of 1784

INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJE
CONTENTS
page page
GAUGE PACKAGE DIAGNOSIS............ 22
GAUGE PACKAGE GENERAL INFORMATION . 22
GAUGE PACKAGE SERVICE PROCEDURES . . 24
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS....... 14INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GENERAL INFORMATION.14
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SERVICE PROCEDURES.. 17
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 27
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GENERAL INFORMATION
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER SYSTEM
The speedometer/odometer system consists of an
electric speedometer and pushbutton reset odometer
mounted in the cluster. The system also includes the
wire harness from the cluster to the vehicle speed
sensor at the transmission, and the adapter and pin-
ion in the transmission. A signal is sent from a
transmission mounted vehicle speed sensor to the
speedometer/odometer circuitry through the wiring
harness. Refer to Group 21 - Transmission for select-
ing the proper pinion, and selecting and indexing the
proper adapter.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer displays the engine speed (RPM).
With the engine running, the tachometer receives anengine speed signal from the Powertrain Control
Module pin 43 (values shown in Specifications chart).
INDICATOR LAMPS
The Brake, Upshift (2.5L with 5 speed transmis-
sion except California), and Malfunction Indicator
(Check Engine) lamps are located in the indicator
lamp panel above the steering column. The lamps
share a common battery feed connection through the
ignition switch and fuse #9.
The turn signals, high beam indicator, seat belt re-
minder, hazard lamp, master lighting and illumina-
tion bulbs are supplied battery voltage through
various switches and share a common ground.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Brake Indicator Lamp...................... 16
DiagnosingÐAll Lamps Out................. 16
Instrument Panel Illumination Lamps.......... 16
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)..... 16Seat Belt Reminder Lamp................... 16
Speedometer............................ 14
Tachometer............................. 14
Upshift Indicator Lamp..................... 16
SPEEDOMETER
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the vehicle speed sensor connector.
(3) Connect a voltmeter between the black wire
pin of the connector and ground.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(5) Check for approximately 5 volts. If OK, per-
form vehicle speed sensor test. Refer to the appropri-
ate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual. If not
OK, continue with step 6.
(6) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.(7) Check continuity between vehicle speed sensor
connector and terminal 13 of instrument cluster con-
nector. If OK, replace speedometer. If not OK, repair
open circuit.
TACHOMETER
(1) Tachometer input is from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) pin 43. Use the DRB scan tool to
perform actuator test. If OK, continue with step 2. If
not, replace PCM.
(2) Check for continuity between cluster connector
pin 12 and PCM pin 43. If OK, replace tachometer. If
not, repair open circuit.
8E - 14 YJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 363 of 1784

DIAGNOSINGÐALL LAMPS OUT
(1) Inspect fuse #9. Replace as required.
(2) Measure voltage at instrument cluster connec-
tor terminal 20. Meter should read zero ohms. If not,
repair open to ground.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have
an optional upshift indicator lamp. The lamp is con-
trolled by the PCM. The lamp lights to indicate when
the driver should shift to the next highest gear for best
fuel economy. The PCM will turn the lamp off after 3 to
5 seconds if the upshift is not performed. The lamp will
remain off until the vehicle stops accelerating and is
brought back to the range of lamp operation or shifted
into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally illuminated when
the ignition switch is turned ON and it is turned off
when the engine is started. The lamp will be lighted
during engine operation according to engine speed
and load.
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Ground pin 2 of cluster connector. Lamp should
light. If not, replace bulb. If OK, continue with step 3.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Check for conti-
nuity between cluster connector pin 2 and pin 54 of
the PCM. If not, repair open. If OK, refer to DRB
scan tool actuator test of upshift indicator.
BRAKE INDICATOR LAMP
The brake indicator is a dual function lamp. It will in-
dicate an unequal pressure condition in the split brake
hydraulic system and it also will indicate when the park-
ing brake is engaged. Separate switches are used for each
indicator lamp function. A switch mounted on the brake
pedal assembly will close a ground circuit whenever the
parking brakes are applied. A second switch is installed
in the brake hydraulic lines near the master cylinder. If
the switch is balanced by equal pressure on both ends of
the switch valve, the valve remains centered and the
lamp remains off. If the valve is shifted by unequal pres-
sure between the front or rear brake hydraulic systems,
the lamp circuit is connected to ground. To make sure
the brake lamp is functional before the vehicle is driven,
it is illuminated through a ground circuit when the igni-
tion switch is turned to the START position.
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Ground pin 1 of the cluster connector. Lamp
should light. If not, replace bulb. If OK, continue
with step 3.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Check for continuity to
park brake switch and brake warning switch.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine) il-
luminates each time the ignition switch is turned
ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.If the PCM receives an incorrect signal or no signal
from certain sensors or emission related systems the
lamp is turned on (pin 32 of PCM). This is a warning
that the PCM has recorded a system or sensor mal-
function. In some cases when a diagnostic fault is de-
clared the PCM will go into a limp-in mode in an
attempt to keep the system operating. It signals an
immediate need for service.
The lamp also can be used to display diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC). Cycle the ignition switch ON,
OFF, ON, OFF, ON within 5 seconds. This will allow
any DTC's stored in the PCM memory to be dis-
played in a series of flashes representing digits.
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Ground pin 4 of cluster connector. Lamp should
light. If not, replace bulb. If OK, continue with step 3.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Check for conti-
nuity between cluster connector pin 4 and PCM cav-
ity 32. If OK, replace PCM. If not, repair open.
SEAT BELT REMINDER LAMP
Apply 12 volts to terminal 16 of cluster connector.
Lamp should light. If not, replace bulb. If OK, check
wiring for an open to buzzer module. Refer to Group
8U - Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems.
INSTRUMENT PANEL ILLUMINATION LAMPS
The instrument panel illumination lamps share
two common connections. There is a splice after fuse
#10 that connects the lamps to battery feed. There is
also a splice that connects all lamps to ground. Be-
cause they share these common connection points in
a parallel circuit, the illumination lamps will all
come on at the same time. It also means one or more
lamps can be out without affecting the operation of
the other lamps.
On the battery side of the circuit, the headlamp
switch illumination rheostat/switch and panel lamps
fuse receive battery feed in series from the park/tail
fuse. In the park lamp position, the headlamp switch
completes the circuit from the park/tail fuse to the il-
lumination rheostat/switch and panel lamps fuse.
The illumination rheostat contains a variable resis-
tor that allows the driver to vary illumination inten-
sity from off to full brightness.
DIAGNOSIS
(1) Turn parking lamps ON.
(2) Check fuse #10. Replace as required.
(3) Measure voltage at battery side of fuse #10
with rheostat turned counterclockwise to clockwise
(LO to HI). Meter should read zero volts to battery
voltage. If not, replace headlamp switch.
(4) Measure resistance at ground side of fuse #10
with parking lamps OFF. Meter should read almost
zero ohms (except bulb filament). If not, repair open
to ground. If zero ohms, 12 volt supply wire from fuse
is shorted to ground, repair short.
8E - 16 YJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 376 of 1784

AUDIO SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
RADIO ANTENNA........................ 8XJ SERVICE PROCEDURES................ 4
YJ SERVICE PROCEDURES................ 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
Each radio receives ignition feed from an ignition
switch controlled fuse. There is an additional in-line
fuse in the back of the radio chassis. The in-line fuse
will blow in the event an internal short occurs.
The electronically tuned radio (ETR)/cassette
models protect the vehicle from a radio failure
with an in-line fuse located in the rear of the ra-
dio chassis (Fig. 1).
XJ/YJ vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse that is removed when the vehicles
are shipped from the factory. This fuse is in the
Power Distribution Center to prevent battery dis-
charge during storage. For specific location refer to
Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
The IOD fuse is in the radio memory circuitry and
should be checked if the memory (time or radio sta-
tion programming) is inoperative.
All radios are connected to the radio illumination
relay. When the ignition switch is in ON or ACCES-
SORY and the radio illumination relay remains de-
energized, the radio receives battery voltage via the
relay from the:
²(20 amp #7 fuse YJ)
²(15 amp #2 fuse XJ).
The radio illumination relay is energized when the
headlamp switch is used to turn on the parklamps or
headlamps. Battery voltage is switched to the dimdisplay input of the radio through the relay contacts.
The radio panel illumination is dimmed for night
driving.
The ETR models require an additional battery feed
connection to the (10 amp #F16 fuse-YJ), (10 amp
#9 fuse-XJ) to retain the radio's memory when the
ignition switch is turned OFF.
ETR models are self-compensating. A radio
trimmer adjustment is not required.
DIAGNOSIS
RADIO INOPERATIVE
Turn ignition switch to ON
²Inspect the (#7-YJ), (#2-XJ) fuse and replace if
necessary.
²Measure voltage at battery side of the fuse. There
should be 12 volts. If not, repair open from ignition
switch.
²Inspect in-line fuse at rear of radio and replace if
necessary.
Turn ignition switch to OFF.
²Disconnect radio connector. Measure resistance
from radio ground pin to a clean chassis ground.
There should be zero ohms. If not, repair open be-
tween radio connector and ground.
NO AUDIO OUTPUT ON ONE OR MORE
SPEAKERS
Refer to Radio Connector Pins.
FRONT SPEAKERS
²Radio OFF, radio connector disconnected. Measure
resistance between radio left front feed and return
connector pins. Measure between right front feed and
return connector pins. The meter should read 5 to 8
ohms. If the meter reading is correct, remove radio
for service. If not, repair wiring or replace speakers
as required.
Fig. 1 In-Line Fuse Location
JAUDIO SYSTEMS 8F - 1
Page 377 of 1784
REAR SPEAKERS
²Radio OFF, radio connector disconnected. Measure
resistance between radio left rear feed and return
connector pins. Measure between right rear feed and
return connector pins. The meter should read 5 to 8
ohms. If meter reading is correct remove radio for
service. If not, repair wiring or replace speakers as
required.
DISTORTED AUDIO OUTPUT ON ONE OR
MORE SPEAKERS
²With the radio ON, substitute known good speaker
or speakers. If the sound is still distorted, remove ra-
dio for service.
WEAK OR NO RECEPTION; NO AUDIO
OUTPUT; BACKGROUND NOISE PRESENT
Ignition switch in ON, radio ON.
²Inspect antenna cable and connector at radio and
tighten or repair as necessary.
²Unplug coax cable and connectors from radio. Mea-
sure resistance from center conductor to coaxial
shield. The meter should read infinite resistance
(open). If it does not, replace antenna assembly.
²Measure resistance of antenna mast to tip of cen-
ter conductor at radio end of cable. The meter should
read 0 to 0.5 ohms. If it does not, replace lead-in ca-
ble or antenna assembly.
²Measure resistance from coaxial shield to chassis
ground (vehicle body). The meter should read zero
ohms. If it does not, ground antenna base to vehicle
body, or replace antenna assembly as required
For all problems with no or low audio output
not resolved by these tests, remove radio for ser-
vice.
MEMORY DOES NOT OPERATE
²Inspect (F16 in Power Distribution Center-YJ),
(#9 in Fuse Panel-XJ) fuse and replace if necessary.
²Measure voltage at battery side of previously ref-
erenced fuse. There should be 12 volts at battery side
of fuse. If not, check the Maxi fuse.
Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
²Measure voltage at radio connector pin 4. There
should be 12 volts. If meter reading is correct, re-
move radio for service. If not, repair open from fuse.
RADIO DISPLAY ILLUMINATION (PARKLAMPS
AND HEADLAMPS OPERATING NORMALLY)
Headlamp switch OFF, radio ON.
²Measure voltage at radio connector pin 10. There
should be 12 volts. If not, go to next step. If OK, re-
move radio for repair by authorized outlet.
²Measure voltage at illumination relay pin 3. There
should be 12 volts. If 12 volts present, replace illumi-
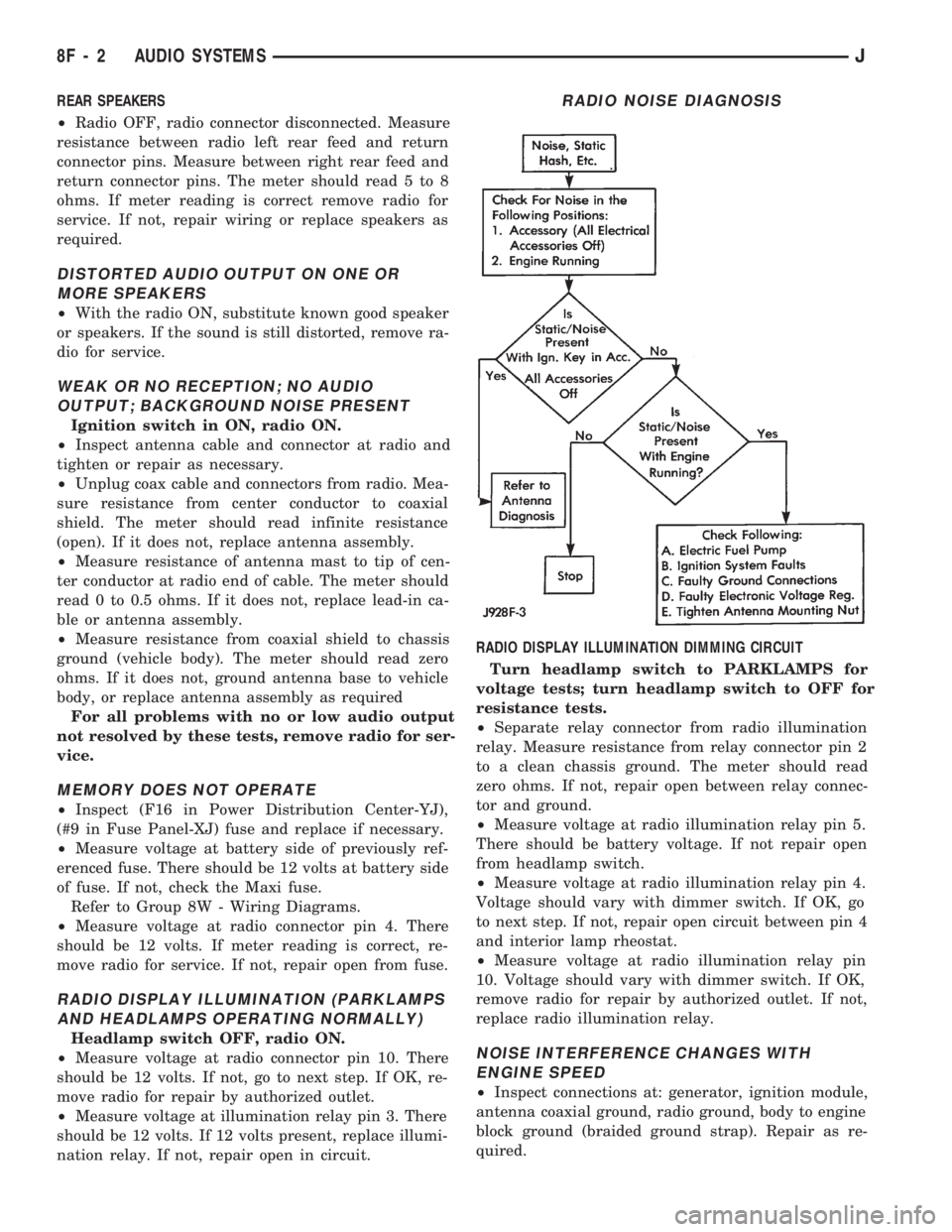
nation relay. If not, repair open in circuit.RADIO DISPLAY ILLUMINATION DIMMING CIRCUIT
Turn headlamp switch to PARKLAMPS for
voltage tests; turn headlamp switch to OFF for
resistance tests.
²Separate relay connector from radio illumination
relay. Measure resistance from relay connector pin 2
to a clean chassis ground. The meter should read
zero ohms. If not, repair open between relay connec-
tor and ground.
²Measure voltage at radio illumination relay pin 5.
There should be battery voltage. If not repair open
from headlamp switch.
²Measure voltage at radio illumination relay pin 4.
Voltage should vary with dimmer switch. If OK, go
to next step. If not, repair open circuit between pin 4
and interior lamp rheostat.
²Measure voltage at radio illumination relay pin
10. Voltage should vary with dimmer switch. If OK,
remove radio for repair by authorized outlet. If not,
replace radio illumination relay.NOISE INTERFERENCE CHANGES WITH
ENGINE SPEED
²Inspect connections at: generator, ignition module,
antenna coaxial ground, radio ground, body to engine
block ground (braided ground strap). Repair as re-
quired.
RADIO NOISE DIAGNOSIS
8F - 2 AUDIO SYSTEMSJ
Page 394 of 1784

TEST PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Checking for Diagnostic Trouble Code......... 5
Electrical Tests at Powertrain Control Module.... 6
Electrical Tests at Servo.................... 5
Inoperative System........................ 5
Operational Check (Road Test)............... 7
Road Test............................... 5Speed Control Switch (Turn Signal Lever) Test . . . 7
Stop Lamp Speed Control Switch Test......... 7
Vacuum Supply Test....................... 7
Vehicle Speed Control System Electrical Tests . . . 5
Vehicle Speed Sensor Test.................. 5
ROAD TEST
Refer to Operational Check (Road Test) section to
verify reports of speed control system malfunction.
INOPERATIVE SYSTEM
Road test vehicle to verify reports of speed control
system malfunction. An inspection should be made
for loose electrical and vacuum connections at the
servo.
Check for correct installation of the vacuum check
valve in the hose from servo to vacuum source. The
word VAC on the valve must point toward the vac-
uum source.
Corrosion should be removed from electrical termi-
nals and a light coating of Mopar MultiPurpose
Grease, or equivalent, applied.
Inspection also should be made to verify that both
ends of the speed control cable are securely attached.
CHECKING FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
(1) When trying to verify a speed control system
electronic malfunction use a DRB scan tool to find
the cause (refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual).
If DRB is not available, the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) may be determined with the following
method:
(a) With key inserted in ignition switch, cycle
switch to ON position 3 times. On third cycle, leave
switch in ON position.
(b) After switch has been cycled 3 times, observe
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (CHECK ENGINE)
on instrument cluster. If a DTC is present, the code
will be displayed in a series of flashes representing
digits. Three flashes in rapid succession, a slight
pause, then 4 flashes in rapid succession would in-
dicate DTC 34.
(2) If a DTC 34 is observed, perform tests in the
sections Electrical Tests at Servo and Electrical Tests
at Powertrain Control Module.
If a DTC 15 is observed, perform test for a faulty
vehicle speed sensor.
(3) Correct any problems found when performing
these tests and recheck for DTC if changes were
made.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR TEST
For testing of the vehicle speed sensor and related
components, refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual.
VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL
TESTS
Vehicle speed control systems may be tested using
two different methods. One involves use of a DRB
scan tool. If this test method is desired, refer to Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual.
The other test method uses a voltmeter. The volt-
meter method is described in the following tests.
If any information is needed concerning wiring, re-
fer to Section 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals, or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
ELECTRICAL TESTS AT SERVO
(1) Turn ignition switch to the ON position. With
speed control switch in the ON position, setup a volt-
meter to read battery voltage and connect negative
lead to a good chassis ground.
(2) Disconnect 4-way connector going to servo
(Figs. 2 and 3). Blue wire with red tracer of main
harness 4-way connector should read approximately
battery voltage. If not, check for loose connections,
brake switch adjustment or, repair main harness as
necessary.
(3) Connect a jumper wire between male and fe-
male terminals of blue wire with red tracer. The
other 3 male terminals from servo should show bat-
tery voltage. If not, replace servo.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, connect one lead to a good
body ground. Touch other lead to black wire terminal
in 4-way connector of main harness. Meter should
show continuity. If not, repair ground circuit as nec-
essary.
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 5
Page 439 of 1784

FOG LAMP SERVICE INFORMATION
Fog lamps can be operatedONLYwhen the head-
lamps are on LOW beam. If the headlamps are
switched to HIGH beam, the fog lamps will not oper-
ate.
Also, the fog lamps ON display on the switch will:
²be illuminated when the headlamps are switched
to LOW beam; and
²be extinguished when the headlamps are switched
to HIGH beam.
FOG LAMP TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
ONE FOG LAMP INOPERATIVE
(1) Place the headlamp switch in the full ON posi-
tion, the dimmer switch in the LOW beam position
and the fog lamp switch in the ON position.
(2) Disconnect the applicable fog lamp wire har-
ness connector (Fig. 33).
(3) Measure the resistance between the lamp con-
nector terminals. The ohmmeter should indicate zero
ohms. If not OK, replace the bulb.
(4) Measure the resistance between the wire har-
ness connector ground terminal and vehicle body
ground. The ohmmeter should indicate zero ohms. If
not OK, repair the open circuit in the wire harness
to vehicle body ground.
(5) Measure the voltage between the wire harness
connector voltage supply terminal and body ground.
The voltmeter should indicate battery voltage. If not
OK, repair the open circuit in the wire harness that
leads to the source of battery voltage.
BOTH FOG LAMPS INOPERATIVE
(1) Place headlamp switch in the full ON position.The dimmer switch in the LOW beam position. The
fog lamp switch in the ON position.
(2) Measure the voltage between the fog lamp
switch wire harness connector terminal B and vehi-
cle body ground. The voltmeter should indicate bat-
tery voltage. If not OK, repair the open circuit in the
wire harness that leads to the headlamp dimmer
switch circuit.
(3) Measure the voltage between the fog lamp
switch connector terminal C and vehicle body
ground. The voltmeter should indicate battery volt-
age. If not OK, replace the fog lamp switch.
(4) Measure the voltage between the fog lamp re-
lay connector terminal 1 and vehicle body ground.
The voltmeter should indicate battery voltage. If not
OK, repair the open circuit in the wire harness that
leads to the power distribution center/PDC.
(5) Measure the voltage between the fog lamp re-
lay connector terminal 5 and vehicle body ground.
The voltmeter should indicate battery voltage. If not
OK, repair the open circuit in the wire harness that
leads to the fog lamp switch.
(6) Measure the voltage between the fog lamp re-
lay connector terminal 2 and vehicle body ground.
The voltmeter should indicate battery voltage. If not
OK, repair the open circuit in the wire harness that
leads to vehicle body ground.
(7) Measure the voltage between the fog lamp re-
lay connector terminal 4 and vehicle body ground.
The voltmeter should indicate battery voltage. If not
OK, replace the relay.
FOG LAMP BEAM ADJUSTMENT
Use an ``aiming'' screen for fog lamp beam aim ad-
justment.
PREPARATION
Prior to adjustment, the following preparation is
required.
Fig. 32 Replacing CHMSL Bulb
Fig. 33 Fog Lamp & Wire Harness ConnectorÐXJ
Vehicles
8L - 12 LAMPSJ
Page 864 of 1784

INSPECTION
Inspect for cracks in the combustion chambers and
valve ports.
Inspect for cracks on the exhaust seat.
Inspect for cracks in the gasket surface at each
coolant passage.
Inspect valves for burned, cracked or warped heads.
Inspect for scuffed or bent valve stems.
Replace valves displaying any damage.
VALVE REFACING
(1) Use a valve refacing machine to reface the in-
take and exhaust valves to the specified angle.
(2) After refacing, a margin of at least 0.787 mm
(0.031 inch) must remain (Fig. 8). If the margin is
less than 0.787 mm (0.031 inch), the valve must be
replaced.
VALVE SEAT REFACING
(1) Install a pilot of the correct size in the valve
guide bore. Reface the valve seat to the specified an-
gle with a good dressing stone. Remove only enough
metal to provide a smooth finish.
(2) Use tapered stones to obtain the specified seat
width when required.
(3) Control valve seat runout to a maximum of
0.0635 mm (0.0025 in.)Ð(Fig. 9).
VALVE STEM OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT
Valve stem oil seals are installed on each valve
stem to prevent rocker arm lubricating oil from en-
tering the combustion chamber through the valve
guide bores. One seal is marked INT (intake valve)
and the other is marked EXH (exhaust valve).Replace the oil seals whenever valve service is per-
formed or if the seals have deteriorated.
VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are an integral part of the engine
cylinder head and are not replaceable.
When the valve stem guide clearance is excessive,
the valve guide bores must be reamed oversize. Ser-
vice valves with oversize stems are available in 0.076
mm (0.003 inch) and 0.381 mm (0.015 inch) incre-
ments.
Corresponding oversize valve stem seals are also
available and must be used with valves having 0.381
mm (0.015 inch) oversize stems.
If the valve guides are reamed oversize, the
valve seats must be ground to ensure that the
valve seat is concentric to the valve guide.
VALVE STEM-TO-GUIDE CLEARANCE
MEASUREMENT
Valve stem-to-guide clearance may be measured by
either of the following two methods.
PREFERRED METHOD:
(1) Remove the valve from the head.
(2) Clean the valve stem guide bore with solvent
and a bristle brush.
(3) Insert a telescoping gauge into the valve stem
guide bore approximately 9.525 mm (.375 inch) from
the valve spring side of the head (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove and measure telescoping gauge with a
micrometer.
(5) Repeat the measurement with contacts length-
wise to engine cylinder head.
(6) Compare the crosswise to lengthwise measure-
ments to determine out-of-roundness. If the measure-
ments differ by more than 0.0635 mm (0.0025 in.),
ream the guide bore to accommodate an oversize
valve stem.
Fig. 8 Valve Facing Margin
Fig. 9 Measurement of Valve Seat Runout
J2.5L ENGINE 9 - 23