ECO mode JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 1213 of 1784

GOVERNOR DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove governor weights and spring from body
(Fig. 13).
(2) Remove snap ring and separate inner weight
and outer weight and spring (Fig 13).
(3) Remove bolts attaching governor to park gear
(Fig. 13).
(4) Remove park gear from governor body.
(5) Remove filter screen from park gear or gover-
nor body (Fig. 13).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Thoroughly clean all the governor parts in a suit-
able cleaning solution but do not use any type of
caustic cleaning agents.
The weights and valves should fall freely in their
bores when clean and dry. Minor surface scratches
and burrs can be removed with crocus cloth.
Inspect the governor weight spring for distortion.
Replace the spring, if damaged. Clean the filter in
solvent and dry it with compressed air. Replace the
filter, if damaged. Inspect the park gear for chipped
or worn gear teeth or damaged ring grooves. Replace
the gear, if damaged.
GOVERNOR ASSEMBLY
The governor valve used in 30RH/31RH/32RH
transmissions built since the 1992 model year, is
made of aluminum. In addition, the output shaft
has been spotfaced to accept the new aluminum
valve. The aluminum valve must not be used in
previous transmissions. The valve can only be
used with an output shaft that has been spot-
faced for valve end clearance. In addition, thegovernor body and output shaft must be prop-
erly indexed during reassembly. Be sure to in-
dex these components as described in the
Transmission Assembly and Adjustment proce-
dures.
(1) Install filter screen in park gear.
(2) Assemble governor body and park gear. Be sure
oil passages in body and gear are aligned.
(3) Install governor-to-park gear bolts finger tight
only at this time.
(4) Install governor weight snap ring in governor
body. Then install governor weight and spring assem-
bly in governor body.
GOVERNOR INSTALLATION
(1) Align and install park gear/governor assembly
on output shaft.
(2) Align valve shaft bore in governor body with
bore in output shaft.Be sure hole in output shaft
for governor valve shaft is aligned with gover-
nor valve bore in governor body. Valve shaft
will bind if misalignment occurs. Remove and
reposition governor body if necessary.
(3) Install governor valve and shaft. Be sure shaft
slides freely in bore before installing E-clip on shaft.
(4) Install governor valve on shaft and in governor
body. Then install remaining shaft retaining snap
ring.
(5) Install components that retain governor body
and park gear on output shaft as follows:
(a) On models with single snap ring, install snap
ring (Fig. 12). Be sure ring is seated in shaft.
(b) On models with thrust washer and two snap
rings, install thin snap ring first. Then install
thrust washer second and thick snap ring last (Fig.
12).
16(c) Verify correct position of snap rings.Be
sure flat side of each snap ring is toward gov-
ernor body.
(6) Tighten governor-to-park gear bolts to 11 Nzm
(95 in. lbs.).
(7) Install adapter and gasket on transmission.
Tighten adapter bolts to 32 Nzm (24 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install transfer case and rear crossmember.
(9) Connect speedometer cable, or vehicle speed
sensor wires exhaust pipe brackets and brake cable,
if removed.
(10) Align and connect propeller shafts. Tighten
clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
(12) Check and adjust transmission fluid level.
PARK LOCK COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
COMPONENT REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove transfer case and
adapter housing from transmission.
Fig. 13 Governor Components
21 - 102 30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICEJ
Page 1217 of 1784

condenser. The auxiliary cooler is a serviceable com-
ponent and can be repaired if necessary.
The main and auxiliary coolers should be thor-
oughly reverse flushed if a transmission failure
contaminates the fluid. Reverse flushing the cooler
and lines will prevent sludge and particles from
flowing back into the transmission after repair.
The same flushing procedure is used for main and
auxiliary coolers. Pressure equipment is preferred for
reverse flushing. However, reverse flushing can be
performed using hand operated equipment as de-
scribed in the following procedure.
REVERSE FLUSHING PROCEDURE
(1) Disconnect cooler lines at transmission. Refer
to Figure 21 for cooler line fitting identification.
Front fitting is outlet to cooler and rear fitting is in-
let from cooler.
(2) Position drain pan under cooler outlet line to
material flushed through cooler and lines.
(3) Reverse flush cooler using hand operated suc-
tion gun filled with mineral spirits. Insert gun nozzle
(or hose) into cooler inlet (return) line. Then force
mineral spirits through Line and cooler.
(4) Continue reverse flushing until fluid exiting in-
let (pressure) line is clear and free of debris/residue.
Replace radiator if fluid cannot be pumped
through cooler.
(5) Clear flushing materials from cooler and lines
with short pulses of compressed air. Insert air gun
nozzle into cooler inlet (return) line and continue
short pulses of air until all fluid is cleared from
cooler and lines.
(6) Pump one quart of fresh automatic transmis-
sion fluid through cooler and lines before reconnect-
ing cooler lines.
TRANSMISSION COOLER FLOW TESTING
The transmission main and auxiliary coolers
should be flow tested whenever a fluid overheat con-
dition is suspected. An overheat condition is indi-
cated when the fluid changes from the normal red, to
a dark orange, or brown color.
The same method of flow testing is used for both
coolers.Cooler flow is checked by measuring the amount of
fluid flow through the cooler in a 20 second time pe-
riod. The test is performed with the engine running
and transmission in neutral. Fluid is then pumped
through the cooler by the transmission oil pump.
(1) Disconnect cooler inlet line at transmission fitting.
(2) Securely attach hose to end of inlet line and po-
sition line in a one quart test container.
(3) Add extra quart of fluid to transmission.
(4) Use stopwatch to check flow test time.
(5) Shift transmission into neutral and set parking
brake.
(6) Start and run engine at curb idle speed and im-
mediately note cooler flow. Approximately one quart of
fluid should flow into test container in 20 second period.
(7) If cooler flow is intermittent, flows less than
one quart in 20 seconds, or does not flow at all,
cooler is faulty and must be replaced.
SERVICING TRANSMISSION COOLER LINES AND
FITTINGS
Fitting Types
The transmission cooler lines are attached with
quick disconnect fittings.
A flange on the cooler line serves as the sealing
mechanism. The wire retainer clip (Fig. 22), secures
the cooler line in the fitting by this flange. The clip
fits behind the flange to hold the line in place.
Three different fitting styles may be used. Type 1
fittings have the retainer clip exposed (Fig. 22). Type
2 fittings have the retainer clip and fitting body en-
cased in a shrink wrap material (Fig. 23). Type 3 fit-
tings have the retainer clip encased in a metal sleeve
crimped onto the fitting body (Fig. 24).
Fitting Release Tool
A release tool isrequiredto disconnect each of the
fitting types. A plastic tool is clipped directly to one
of the cooler lines on models with the type 2 and 3
fittings. This tool can also be used to disconnect type
1 fittings. The tool is needed to spread the wire re-
tainer clip in each fitting. The clip must be opened in
order to release the cooler line from the fitting.
Fig. 21 Identifying Transmission Cooler Lines
Fig. 22 Type 1 Quick Disconnect Fitting
21 - 106 30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICEJ
Page 1231 of 1784
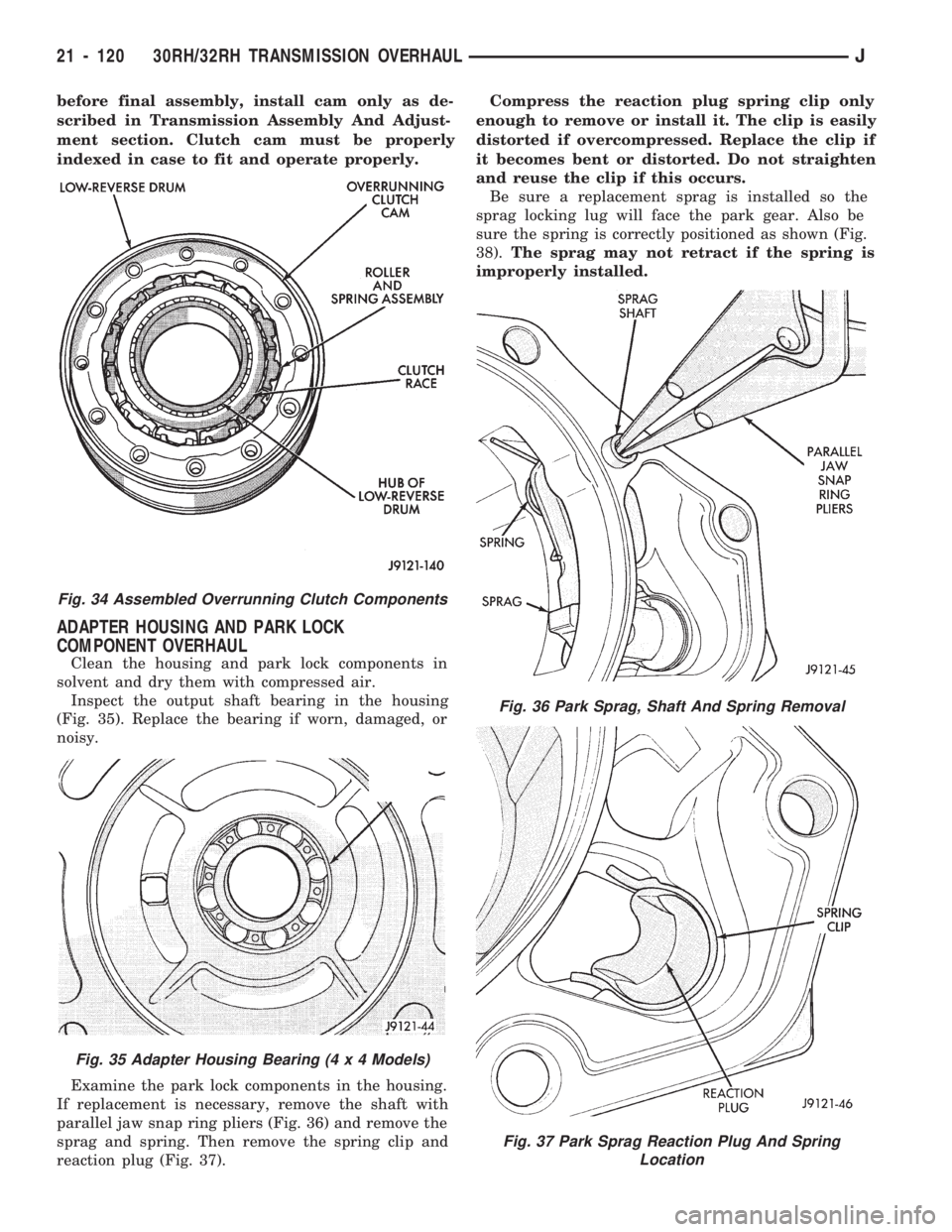
before final assembly, install cam only as de-
scribed in Transmission Assembly And Adjust-
ment section. Clutch cam must be properly
indexed in case to fit and operate properly.
ADAPTER HOUSING AND PARK LOCK
COMPONENT OVERHAUL
Clean the housing and park lock components in
solvent and dry them with compressed air.
Inspect the output shaft bearing in the housing
(Fig. 35). Replace the bearing if worn, damaged, or
noisy.
Examine the park lock components in the housing.
If replacement is necessary, remove the shaft with
parallel jaw snap ring pliers (Fig. 36) and remove the
sprag and spring. Then remove the spring clip and
reaction plug (Fig. 37).Compress the reaction plug spring clip only
enough to remove or install it. The clip is easily
distorted if overcompressed. Replace the clip if
it becomes bent or distorted. Do not straighten
and reuse the clip if this occurs.
Be sure a replacement sprag is installed so the
sprag locking lug will face the park gear. Also be
sure the spring is correctly positioned as shown (Fig.
38).The sprag may not retract if the spring is
improperly installed.
Fig. 34 Assembled Overrunning Clutch Components
Fig. 35 Adapter Housing Bearing (4 x 4 Models)
Fig. 36 Park Sprag, Shaft And Spring Removal
Fig. 37 Park Sprag Reaction Plug And Spring
Location
21 - 120 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION OVERHAULJ
Page 1268 of 1784

The valve body solenoids are controlled by signals
from the transmission control module (TCM). Signal
sequence is determined by vehicle speed and throttle
position.
Fourth gear is an 0.75:1 ratio overdrive range.
First, second, third and reverse gear are conventional
ranges. Third gear ratio is 1:1. A separate planetary
gear set provides overdrive operation in fourth gear.
TRANSMISSION RANGES AND SHIFT LEVER
POSITIONS
The AW-4 transmission has six ranges and shift le-
ver positions. Park, Reverse and Neutral are conven-
tional and mechanically operated. The 1-2, 3 and D
ranges provide electronically controlled shifting.
The 1-2 position provides first and second gear
only. The 3 position provides first, second and third
gear.
The D range provides first through fourth gear.
Overdrive fourth gear range is available only when
the shift lever is in D position (Fig. 2).
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The transmission I.D. plate is attached to the case
(Fig. 3). The plate contains the transmission serial
and model numbers. Refer to the information on this
plate when ordering service parts.
COMPONENTS AND OPERATION
ELECTRONIC CONTROLS
The AW-4 is electronically controlled in the 1, 2, 3
and D ranges. Controls consist of the transmission
control module (TCM), valve body solenoids and var-ious sensors. The sensors monitor vehicle speed,
throttle opening, shift lever position and brake pedal
application.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
The module determines shift and converter clutch
engagement timing based on signals from the sen-
sors. The valve body solenoids are activated, or deac-
tivated accordingly.
The module has a self diagnostic program. Compo-
nent and circuitry malfunctions can be diagnosed
with the DRB II scan tool. Once a malfunction is
noted and stored in control module memory, it is re-
tained even after the problem has been corrected. To
cancel a stored malfunction, simply disconnect and
reconnect the9Trans.9fuse in the module harness.
TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY SOLENOIDS
The solenoids are mounted on the valve body and
operated by the transmission control module. The so-
lenoids control operation of the converter clutch and
shift valves in response to input signals from the
module.
SENSORS
The sensors include the throttle position sensor
(TPS), transmission output speed sensor, vehicle
speed sensor, park/neutral position switch and brake
switch.
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the
throttle body. It electronically determines throttle po-
sition and relays this information to the transmission
control module to determine shift points and con-
verter clutch engagement.
The transmission speed sensor consists of a rotor
and magnet on the transmission output shaft and a
switch in the extension housing or adapter. The sen-
sor switch is activated each time the rotor and mag-
Fig. 2 AW-4 Shift Lever Positions And Transmission
Ranges
Fig. 3 Transmission Identification
JAW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 21 - 157
Page 1280 of 1784

PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS
If pressures in D and Reverse are higher than
specified, check for the following:
²throttle cable loose, worn, binding or out of adjust-
ment
²throttle valve, downshift plug, throttle cam, or pri-
mary regulator valve are sticking, worn or damaged
If pressures in D and Reverse are lower than spec-
ified, check for following:
²throttle cable loose, worn, binding or out of adjust-
ment
²throttle valve, downshift plug, throttle cam stick-
ing, worn or damaged
²primary regulator valve sticking, worn, or dam-
aged
²oil pump gears or housing worn or damaged
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
If pressures are low in D range only, check for fol-
lowing:
²forward clutch worn or damaged
²fluid leakage in D range circuit (component seal
and O-rings)
If pressures are low in Reverse only, check for fol-
lowing:
²shift cable and manual valve out of adjustment
²fluid leakage in reverse circuit (component seal
and O-rings)
²direct clutch worn or damaged
²first/reverse brake worn or damaged
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TEST
Stall testing checks the holding ability of the trans-
mission clutches and brakes and of the torque con-
verter stator overrunning clutch.
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature.
(2) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be viewed from drivers seat.
(3) Apply parking brakes and block wheels.
(4) Apply and hold service brakes.
(5) Shift transfer case into 2H position. On models
with NP249 transfer case, leave transfer case in 4H
position.
(6) Start engine.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW ANYONE TO STAND AT
THE FRONT OR REAR OF THE VEHICLE DURING
THE TEST.
(7) Shift transmission into D range.
(8) Press accelerator pedal to wide open throttle
position and note maximum engine rpm. Stall speed
should be 2100 to 2400 rpm in D range.
CAUTION: Do not maintain wide open throttle for
more than 3-4 seconds at a time.(9) Release throttle and shift transmission into
Neutral. Allow transmission fluid to cool for 15-20
seconds.
(10) Shift transmission into Reverse.
(11) Press accelerator down to wide open throttle
position and note maximum engine rpm. Stall speed
should be 2100-to-2400 rpm in Reverse.
STALL SPEED TEST ANALYSIS
If engine rpm is lower than specified in D and Re-
verse, check for the following:
²engine output/performance insufficient
²stator overrunning clutch in torque converter not
holding if engine speed was 1500 rpm or less.
If stall speed in D range is higher than specified,
check for the following:
²line pressure low
²forward clutch slipping
²No. 2 one-way clutch not holding
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
If stall speed in Reverse was higher than specified,
check for the following:
²line pressure low
²direct clutch slipping
²first/ reverse brake slipping
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
If stall speeds were higher than specified in both D
and Reverse, check for the following:
²low fluid level
²line pressure low
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
TIME LAG TEST
This test checks general condition of the overdrive
clutch, forward clutch, rear clutch and first/reverse
brake. Condition is indicated by the amount of time
required for clutch/brake engagement with the en-
gine at curb idle speed. Engagement time is mea-
sured for D and Reverse positions. A stop watch is
recommended for test accuracy.
TEST PROCEDURE
(1) Check and adjust transmission fluid level if
necessary.
(2) Bring transmission to normal operating tem-
perature.
(3) Apply parking brakes and turn off air condi-
tioning unit.
(4) Shift transfer case into 2H range. On models
with NP249 transfer case, leave transfer case in 4H
range.
(5) Start engine and check curb idle speed. Adjust
speed if necessary. Curb idle must be correct to en-
sure accurate test results.
(6) Shift transmission into Neutral and set stop
watch.
(7) During following test steps, start stop watch as
soon as shift lever reaches D and Reverse ranges.
JAW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 169
Page 1284 of 1784

AW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Accumulator Pistons and Springs........... 179
Adapter Housing Seal Replacement.......... 182
Checking Fluid Level and Condition.......... 173
Manual Valve Shaft Seal Replacement....... 178
Park Interlock Cable Adjustment............ 186
Park Rod and Pawl Service................ 181
Park/Neutral Position Switch............... 173
Second Coast Brake Servo................ 181
Shift Cable Adjustment................... 186
Speed Sensor.......................... 182Speed Sensor RotorÐSpeedometer Drive Gear . 183
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Service....... 184
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Service . . . 173
Transmission Cooler Line Fittings........... 187
Transmission Cooler Service............... 187
Transmission Throttle Cable Adjustment....... 185
Transmission Throttle Cable Replacement..... 184
Transmission Valve Body Installation......... 177
Transmission Valve Body Removal.......... 176
Transmission Valve Body Solenoids.......... 175
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
Recommended fluid for AW-4 transmissions is Mo-
par Dexron IIE/Mercon. Mopar Dexron II may be
used if Mercon fluid is not readily available.
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature. Normal operating temperature is
reached after approximately 15 miles (25 km) of op-
eration.
(2) Position vehicle on level surface. This is impor-
tant for an accurate fluid level check.
(3) Shift transmission through all gear ranges and
back to Park.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Verify that transmission is in Park.
(6) Wipe off dipstick handle to prevent dirt from
entering fill tube. Then remove dipstick and check
fluid level and condition.
(7) Correct fluid level isto FULL mark on dip-
stick when fluid is at normal operating temper-
ature(Fig. 1).
(8) If fluid level is low, top off level with Mopar
Dexron IIE/Mercon. Mopar Dexron II may also be
used if Mercon is not available.Do not overfill
transmission. Add only enough fluid to bring
level to Full mark.
CHECKING FLUID CONDITION
Inspect the appearance of the fluid during the fluid
level check. The fluid should be clear and free of for-eign material or particles. If the fluid is dark brown
or black in color and smells burnt, the fluid has been
overheated and should be replaced.
Transmission operation should also be checked if
the fluid is severely discolored and contains quanti-
ties of foreign material, metal particles, or clutch disc
friction material.
A small quantity of friction material or metal
particles in the oil pan is normal. The particles
are usually generated during the break-in pe-
riod and indicate normal seating of the various
transmission components.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
SERVICE
Use the DRB II scan tool to diagnose transmission
control module function whenever a fault is sus-
pected. Replace the module only when actually faulty.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
REPLACEMENT
The transmission control module is mounted under
the instrument panel. On left hand drive models, it is
at the driver side of the lower finish panel (Fig. 2).
On right hand drive models, it is at the passenger
side of the lower finish panel (Fig. 3).
To remove the module, disconnect the wire harness,
remove the mounting screws and remove the module
from the finish panel. Tighten the module mounting
screws securely after installation. Also be sure the
wire harness is not twisted, kinked or touching any
body panels.
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
SWITCH TESTING
Test switch continuity with an ohmmeter. Discon-
nect the switch and check continuity at the connector
terminal positions and in the gear ranges indicated
in Figure 3. Switch continuity should be as follows:Fig. 1 Transmission Fluid Level
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 173
Page 1384 of 1784

OPERATING RANGES
NP231 operating ranges are: 2-wheel drive high; 4-
wheel drive high and 4-wheel drive low (Fig. 2).
2-wheel drive range is for use on all surfaces. The
4-wheel drive high and low ranges are undifferenti-
ated and should only be used on unpaved, low trac-
tion surfaces only.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a floor mounted
shift lever. The shift lever is connected to the trans-
fer case range lever by an adjustable linkage rod. A
straight line shift pattern is used (Fig. 2). Range po-
sitions are marked on the shifter bezel cover plate. A
front axle disconnect mechanism is only used on cer-
tain models.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each NP231 transfer case (Fig. 3). The ID tag pro-vides the transfer case model number, assembly
number, serial number and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents the
date of build. For example, a serial number of 8-
10-92 would represent August 10, 1992.
TRANSFER CASE LUBRICANT
Recommended Lubricant
Use Mopar Dexron II, or ATF Plus, type 7176 au-
tomatic transmission fluid in the NP231 transfer
case.
Lubricant Capacity
Approximate refill lubricant capacity is 1.54 liters
(3.25 pints) for YJ and 1.04 liters (2.2 pints) for XJ.
Fill Level
The correct fill level is to the bottom edge of the fill
plug hole. The vehicle must be level in order to en-
sure an accurate fluid level check.
Fig. 2 NP231 Shift Pattern
Fig. 3 Transfer Case Identification Tag
JNP231 TRANSFER CASE 21 - 273
Page 1405 of 1784

The transfer case serial number also represents the
date of build. For example, a serial number of 10-
5-91 would represent October 5, 1991.
TRANSFER CASE LUBRICANT
Recommended fluid for the NP242 transfer case is
Mopar Dexron II, or ATF Plus, Type 7176 automatic
transmission fluid.
Lubricant capacity of the Model 242 transfer case
is: 1.4 liters (1.48 qts.).
TRANSFER CASE FILL LEVEL
Correct fill level for the NP242 transfer case is to
the bottom edge of the fill plug hole.
Fig. 3 Transfer Case I.D. Tag
21 - 294 NP242 TRANSFER CASEJ
Page 1445 of 1784
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used on certain models.
Refer to Owner's Manual for more information.
CLEANING OF TIRES
Steam cleaning may be used for cleaning.
DO NOT use gasoline or wire brush for cleaning.
DO NOT use mineral oil or an oil-based solvent.
PRESSURE GAUGES
High-quality, dial-type, air-pressure gauges are
recommended. After checking with the gauge, re-
place valve cap and finger tight.
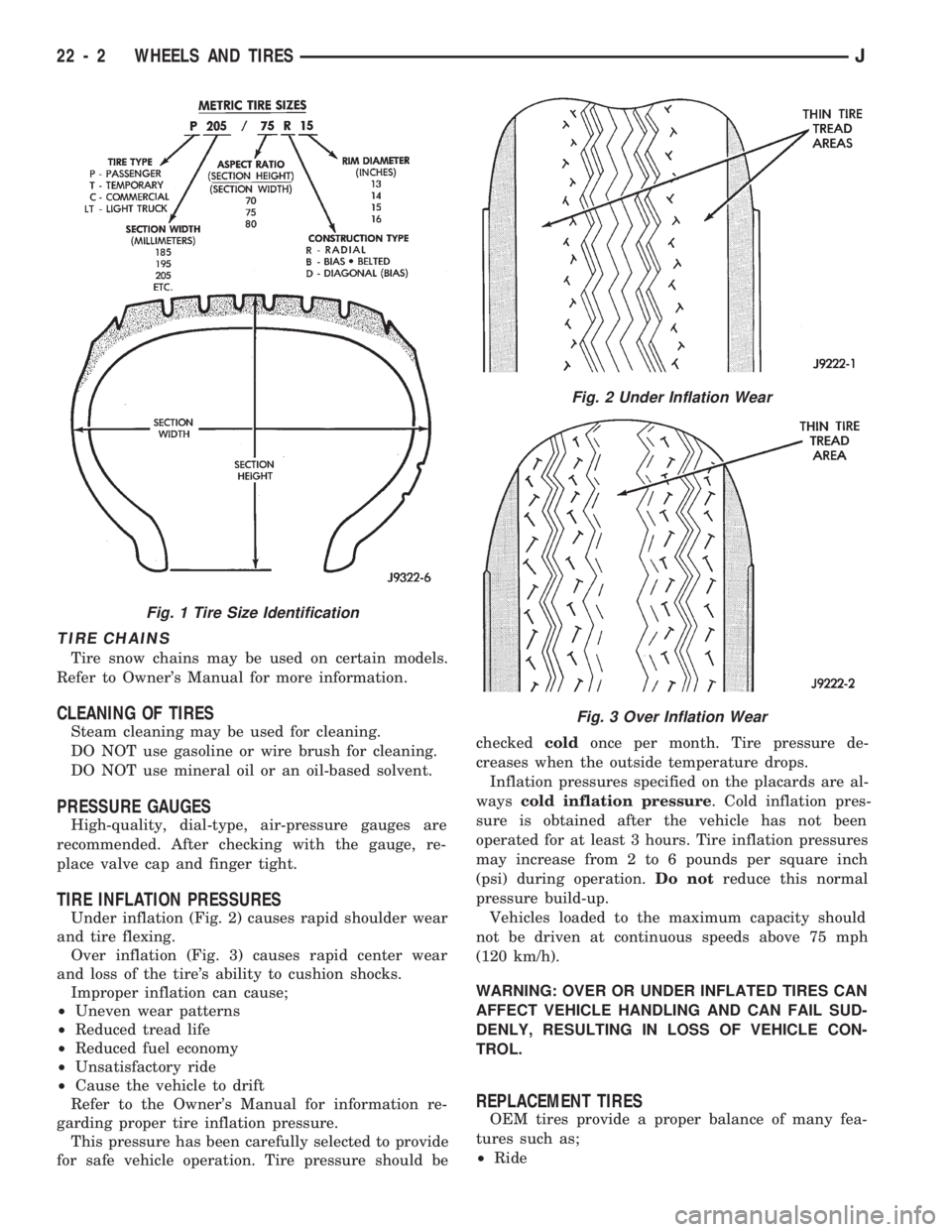
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation (Fig. 2) causes rapid shoulder wear
and tire flexing.
Over inflation (Fig. 3) causes rapid center wear
and loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks.
Improper inflation can cause;
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride
²Cause the vehicle to drift
Refer to the Owner's Manual for information re-
garding proper tire inflation pressure.
This pressure has been carefully selected to provide
for safe vehicle operation. Tire pressure should becheckedcoldonce per month. Tire pressure de-
creases when the outside temperature drops.
Inflation pressures specified on the placards are al-
wayscold inflation pressure. Cold inflation pres-
sure is obtained after the vehicle has not been
operated for at least 3 hours. Tire inflation pressures
may increase from 2 to 6 pounds per square inch
(psi) during operation.Do notreduce this normal
pressure build-up.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES CAN
AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING AND CAN FAIL SUD-
DENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE CON-
TROL.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
OEM tires provide a proper balance of many fea-
tures such as;
²Ride
Fig. 1 Tire Size Identification
Fig. 2 Under Inflation Wear
Fig. 3 Over Inflation Wear
22 - 2 WHEELS AND TIRESJ
Page 1449 of 1784

WHEELS
GENERAL INFORMATION
Original equipment wheels are designed for the
specified Maximum Vehicle Capacity.
All models use steel or cast aluminum drop center
wheels. The safety rim wheel (Fig. 1) has raised sec-
tions between the rim flanges and the rim well.
Initial inflation of the tire forces the bead over
these raised sections. In case of tire failure, the
raised sections hold the tire in position on the wheel
until the vehicle can be brought to a safe stop.
Cast aluminum wheels require special balance
weights and alignment equipment.
WHEEL INSTALLATION
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. They must be replaced with equivalent
parts. Do not use replacement parts of lesser quality
or a substitute design. All aluminum and some steel
wheels have wheel stud nuts which feature an en-
larged nose. This enlarged nose is necessary to en-
sure proper retention of the aluminum wheels.
Before installing the wheel, be sure to remove any
build up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surfaces.
Ensure wheels are installed with good metal-to-metal
contact. Improper installation could cause loosening
of wheel nuts. This could affect the safety and han-
dling of your vehicle.
To install the wheel, first position it properly on
the mounting surface. All wheel nuts should then be
tightened just snug. Gradually tighten them in se-
quence to 129 Nzm (95 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 2).Never
use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
WHEEL REPLACEMENT
Wheels must be replaced if they have:
²Excessive runout²Bent or dented
²Leak air through welds
²Have damaged bolt holes
Wheel repairs employing hammering, heating, or
welding are not allowed.
Original equipment wheels are available through
your dealer. Replacement wheels from any other
source should be equivalent in:
²Load carrying capacity
²Diameter
²Width
²Offset
²Mounting configuration
Failure to use equivalent replacement wheels may
affect the safety and handling of your vehicle. Re-
placement withusedwheels is not recommended.
Their service history may have included severe treat-
ment.
Refer to the Specifications Chart for informa-
tion regarding above requirements.
WHEEL ORNAMENTATION
WARNING: HANDLE ALL WHEEL ORNAMENTATION
WITH EXTREME CARE DURING REMOVAL AND IN-
STALLATION. SHARP EDGES ON THE COVERS OR
CAPS CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE
It is recommended that a two plane dynamic bal-
ancer be used when a wheel and tire assembly re-
quire balancing. Static should be used only when a
two plane balancer is not available.
For static imbalance, find location of heavy spot
causing imbalance. Counter balance wheel directly
opposite the heavy spot. Determine weight required
to counterbalance the area of imbalance. Place half
of this weight on theinnerrim flange and the other
Fig. 2 Lug Nut Tightening Pattern
Fig. 1 Wheel Safety Rim
22 - 6 WHEELS AND TIRESJ