lock JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 173 of 2198

During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
ABS OPERATION IN ANTILOCK BRAKING MODE
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock ECU activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching zero (or lockup)
during braking. Periods of high wheel slip may occur
when brake stops involve high pedal pressure and
rate of deceleration.
The antilock system prevents lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the ECU for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem (Fig. 1). A speed sen-
sor input signal indicating a high slip condition acti-
vates the ECU antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel. The valves are all located within the
HCU valve body and work in pairs to either increase,
hold, or decrease apply pressure as needed in the in-
dividual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
HCU OPERATION
Normal Braking
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
Antilock Pressure Modulation
Solenoid valve pressure modulation occurs in three
stages which are: pressure increase, pressure hold,
and pressure decrease. The valves are all contained
in the valve body portion of the HCU.
Pressure Decrease
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle (Fig. 6).A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the ECU opens the outlet
valve, which also opens the return circuit to the ac-
cumulators. Fluid pressure is allowed to bleed off (de-
crease) as needed to prevent wheel lock.
Once the period of high wheel slip has ended, the
ECU closes the outlet valve and begins a pressure in-
crease or hold cycle as needed.
Pressure Hold
Both solenoid valves are closed in the pressure hold
cycle (Fig. 7). Fluid apply pressure in the control
channel is maintained at a constant rate. The ECU
maintains the hold cycle until sensor inputs indicate
a pressure change is necessary.
Pressure Increase
The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is
closed during the pressure increase cycle (Fig. 8). The
pressure increase cycle is used to counteract unequal
wheel speeds. This cycle controls re-application of
fluid apply pressure due to changing road surfaces or
wheel speed.
Fig. 6 Pressure Decrease Cycle
5 - 36 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 174 of 2198

WHEEL SPEED SENSOR OPERATION
Wheel speed input signals are generated by a sen-
sor and tone ring at each wheel. The sensors, which
are connected directly to the ECU, are mounted on
brackets attached to the front steering knuckles and
rear brake support plates.
The sensor triggering devices are the tone rings
which are similar in appearance to gears. The tone
rings are located on the outboard end of each front/rear axle shaft. The speed sensors generate a signal
whenever a tone ring tooth rotates past the sensor
pickup face.
The wheel speed sensors provide the input signal
to the ECU. If input signals indicate ABS mode brak-
ing, the ECU causes the HCU solenoids to decrease,
hold, or increase fluid apply pressure as needed.
The HCU solenoid valves are activated only when
wheel speed input signals indicate that a wheel is
approaching a high slip, or lockup condition. At this
point, the ECU will cycle the appropriate wheel con-
trol channel solenoid valves to prevent lockup.
The wheel sensors provide speed signals whenever
the vehicle wheels are rotating. The ECU examines
these signals for degree of deceleration and wheel
slip. If signals indicate normal braking, the solenoid
valves are not activated. However, when incoming
signals indicate the approach of wheel slip, or lockup,
the ECU cycles the solenoid valves as needed.
ACCELERATION SWITCH OPERATION
The ECU monitors the acceleration switch at all
times. The switch assembly contains three mercury
switches that monitor vehicle ride height and decel-
eration rates (G-force). Sudden, rapid changes in ve-
hicle and wheel deceleration rate, triggers the switch
sending a signal to the ECU. The switch assembly
provides three deceleration rates; two for forward
braking and one for rearward braking.
ECU OPERATION
The antilock ECU controls all phases of antilock
operation. It monitors and processes input signals
from the system sensors.
It is the ECU that activates the solenoid valves to
modulate apply pressure during antilock braking.
The ECU program is able to determine which wheel
control channel requires modulation and which fluid
pressure modulation cycle to use. The ECU cycles the
solenoid valves through the pressure decrease, hold
and increase phases.
ABS COMPONENT SERVICEABILITY
The ECU, acceleration sensor, wheel sensors, and
wire harnesses are serviced as assemblies only. The
axle shaft tone wheels are also not serviceable. If a
tone wheel becomes damaged, it will be necessary to
replace the axle shaft, or disc brake rotor and hub
assembly.
SPEED SENSOR AIR GAP
Front sensor air gap is fixed and not adjustable.
Only rear sensor air gap is adjustable.
Although front air gap is not adjustable, it can be
checked if diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Front
Fig. 7 Pressure Hold Cycle
Fig. 8 Pressure Increase Cycle
JABS OPERATION AND SERVICE 5 - 37
Page 175 of 2198

air gap should be 0.40 to 1.3 mm (0.0157 to 0.051
in.). If gap is incorrect, the sensor is either loose, or
damaged.
A rear sensor air gap adjustment is only needed
when reinstalling an original sensor. Replacement
sensors have an air gap spacer attached to the sensor
pickup face. The spacer establishes correct air gap
when pressed against the tone ring during installa-
tion. As the tone ring rotates, it peels the spacer off
the sensor to create the required air gap. Rear sensor
air gap is 0.92-1.45 mm (0.036-0.057 in.).
Sensor air gap measurement, or adjustment proce-
dures are provided in this section. Refer to the front,
or rear sensor removal and installation procedures as
required.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and turn wheel outward for easier
access to sensor.
(2) Remove sensor wire from mounting brackets.
(3) Clean sensor and surrounding area with shop
towel before removal.
(4) Remove bolt attaching sensor to steering
knuckle and remove sensor.
(5) remove sensor wire from brackets on body and
steering knuckle.
(6) Unseat sensor wire grommet in wheel house
panel.
(7) In engine compartment, disconnect sensor wire
connector at harness plug. Then remove sensor and
wire.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION
(1) Iforiginalsensor will be installed, wipe all
traces of old spacer material off sensor pickup face.
Use a dry shop towel for this purpose.
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to bolt
that secures sensor in steering knuckle. Use new
sensor bolt if original bolt is worn or damaged.
(3) Position sensor on steering knuckle. Seat sen-
sor locating tab in hole in knuckle and install sensor
attaching bolt finger tight.
(4) Tighten sensor attaching bolt to 14 Nzm (11 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(5) If original sensor has been installed, check sen-
sor air gap. Air gap should be 0.40 to 1.3 mm (0.0157
to 0.051 in.). If gap is incorrect, sensor is either loose,
or damaged.
(6) Secure sensor wire to steering knuckle and
body brackets.
(7) Route sensor wire forward and behind shock
absorber. Then attach sensor wire to spring seat
bracket with grommets on sensor wire.
(8) Route sensor wire to outer sill bracket. Remove
all twists or kinks from wire.
(9) Attach sensor wire to sill bracket with grom-
met. Be sure wire is free of twists and kinks.(10) Verify sensor wire routing. Wire should loop
forward and above sill bracket. Loose end of wire
should be below sill bracket and towards brake hose.
(11) Seat sensor wire grommet in body panel and
clip wire to brake line at grommet location.
(12) Connect sensor wire to harness in engine com-
partment.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) On XJ models, raise and fold rear seat forward
for access to rear sensor connectors (Fig. 9).
(2) Disconnect sensors at rear harness connectors.
(3) Push sensor grommets and sensor wires
through floorpan.
(4) Raise vehicle.
(5) Disconnect sensor wires at rear axle connectors.
(6) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(7) Remove brake drum.
(8) Remove clips securing sensor wires to brake-
lines, rear axle and, brake hose.
(9) Unseat sensor wire support plate grommet.
(10) Remove bolt attaching sensor to bracket and
remove sensor.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION AND
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Iforiginal sensoris being installed, remove
any remaining pieces of cardboard spacer from sen-
sor pickup face. Use dry shop towel only to remove
old spacer material.
(2) Insert sensor wire through support plate hole.
Then seat sensor grommet in support plate.
(3) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to
Fig. 9 Acceleration Switch And Rear Sensor
Connections (XJ)
5 - 38 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 177 of 2198
CAUTION: The mercury switch (inside the accelera-
tion switch), will not function properly if the switch
is mispositioned. Verify that the switch locating ar-
row is pointing to the front of the vehicle.
(2) Position switch in mounting bracket.
(3) Install and tighten switch attaching screws to
2-4 Nzm (17-32 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect harness to switch. Be sure harness
connecter is firmly seated.
(5) Move seat back to normal position.
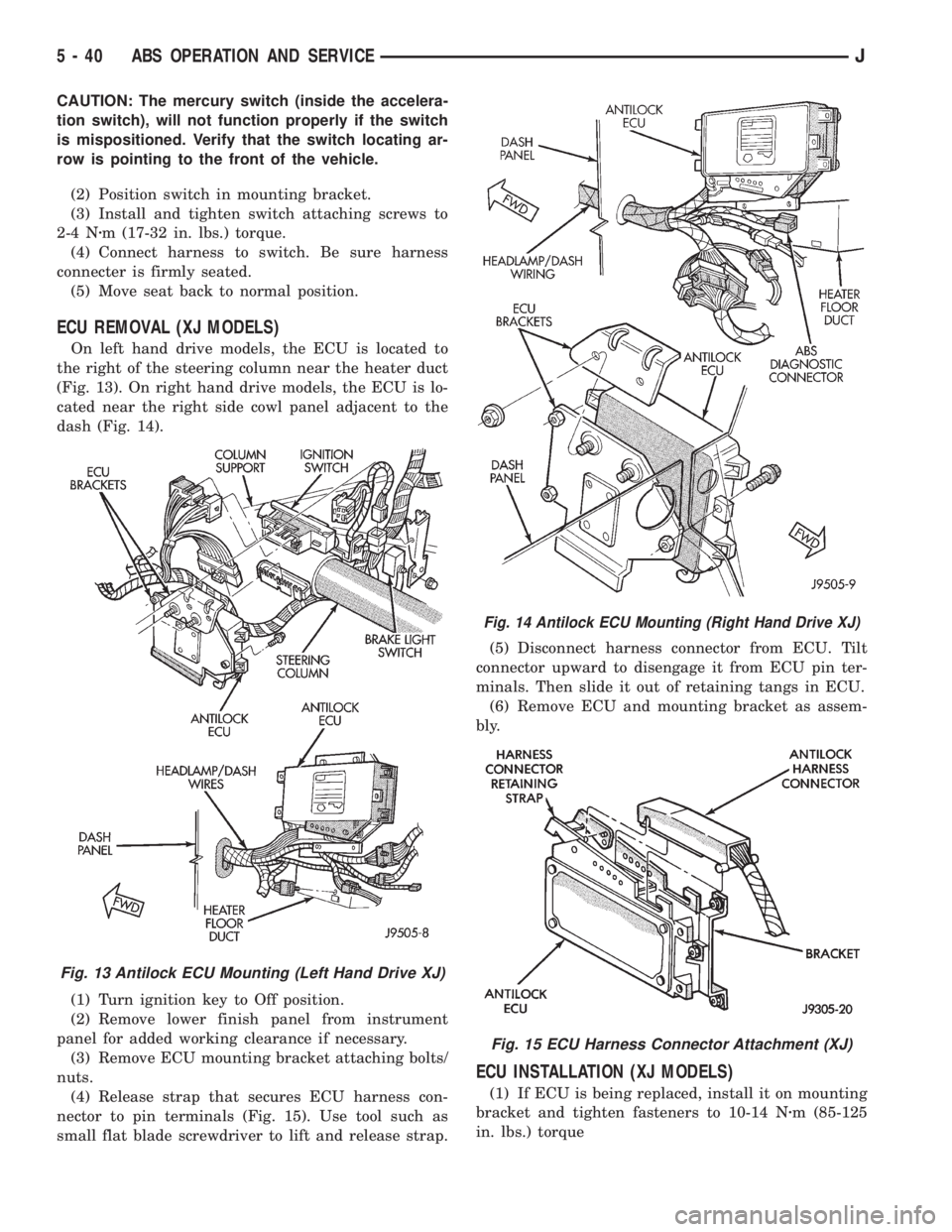
ECU REMOVAL (XJ MODELS)
On left hand drive models, the ECU is located to
the right of the steering column near the heater duct
(Fig. 13). On right hand drive models, the ECU is lo-
cated near the right side cowl panel adjacent to the
dash (Fig. 14).
(1) Turn ignition key to Off position.
(2) Remove lower finish panel from instrument
panel for added working clearance if necessary.
(3) Remove ECU mounting bracket attaching bolts/
nuts.
(4) Release strap that secures ECU harness con-
nector to pin terminals (Fig. 15). Use tool such as
small flat blade screwdriver to lift and release strap.(5) Disconnect harness connector from ECU. Tilt
connector upward to disengage it from ECU pin ter-
minals. Then slide it out of retaining tangs in ECU.
(6) Remove ECU and mounting bracket as assem-
bly.
ECU INSTALLATION (XJ MODELS)
(1) If ECU is being replaced, install it on mounting
bracket and tighten fasteners to 10-14 Nzm (85-125
in. lbs.) torque
Fig. 13 Antilock ECU Mounting (Left Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 14 Antilock ECU Mounting (Right Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 15 ECU Harness Connector Attachment (XJ)
5 - 40 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 178 of 2198

(2) Align and attach harness connector to ECU.
Slide connector into engagement with tangs on ECU.
Then tilt connector downward and into engagement
with ECU pin terminals. Exercise care as pin termi-
nals can be damaged if connector is forced into place.
(3) Connect harness to security alarm module, if
equipped.
(4) Position ECU bracket under instrument panel.
(5) Install and tighten ECU mounting bracket
bolts/nuts to 8-14 Nzm (75- 125 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install trim panel on instrument panel, if re-
moved.
ECU REMOVAL/INSTALLATION (YJ MODELS)
The antilock ECU is attached to the dash panel in-
side the passenger compartment. It is positioned just
above the heater/air conditioning plenum housing, in
line with the glove box (Fig. 16).
The ECU is attached to the dash panel by bolts
and nuts that are accessible from the engine com-
partment. The fasteners are located just to the right
of the battery.
On models with air conditioning, it will be neces-
sary to remove the air conditioning fascia panel and
ducts for access to the ECU and harness connecter.
HCU REMOVAL (XJ)
A new design HCU is used in 1995 models. The
new HCU has built-in accumulators that store the
extra fluid released for antilock mode operation. As a
result, the master cylinder and HCU are no longer
interconnected by hoses.The 1995 and prior hy-
draulic control units are NOT interchangeable.
(1) Disconnect vent hoses at air cleaner cover.
(2) Loosen clamp securing air cleaner hose to in-
take manifold. Use screwdriver to tap clamp loose.
(3) Remove air cleaner cover and hose. Then re-
move air filter from air cleaner shell (Fig. 17).
(4) Remove two bolts and one nut that secure air
cleaner housing to body panel (Fig. 17).
(5) Remove air cleaner housing from engine com-
partment.
Fig. 16 ECU Location (YJ)
Fig. 17 Air Cleaner Components
JABS OPERATION AND SERVICE 5 - 41
Page 194 of 2198

DRUM BRAKE ADJUSTMENT
Rear drum brakes are equipped with a self adjust-
ing mechanism. Under normal circumstances, the
only time adjustment is required is when the shoes
are replaced, removed for access to other parts, or
when one or both drums are replaced.
The only tool needed for adjustment is a standard
brake gauge.
Adjustment is performed with the brakeshoes in-
stalled on the support plate. Procedure is as follows:
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Raise and support vehicle rear end and remove
wheels and brake drums.
(2) Verify that left/right automatic adjuster lever
and cable are properly connected.
(3) Insert brake gauge in drum. Expand gauge un-
til gauge inner legs contact drum braking surface.
Then lock gauge in position (Fig. 6).
(4) Reverse gauge and install it on brakeshoes
(Fig. 6). Position gauge legs at shoe centers as
shown. If gauge does not fit (too loose or tight), ad-
just shoes.
(5) Pull shoe adjuster star wheel away from ad-
juster lever.(6) Turn adjuster star wheel (by hand) to expand
or retract brakeshoes. Continue adjustment until
gauge outside legs are light drag-fit on shoes (Fig. 7).
(7) Repeat adjustment at opposite brakeshoe as-
sembly.
(8) Install brake drums and wheels and lower ve-
hicle.
(9) Make final adjustment as follows:
(a) Drive vehicle and make one forward stop fol-
lowed by one reverse stop.
(b) Repeat procedure 8-10 times to actuate self
adjuster components and equalize adjustment.
(c)Bring vehicle to complete standstill at
each stop. Incomplete, rolling stops will NOT
activate adjuster mechanism.
WHEEL CYLINDER REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel.
(2) Disconnect brakeline at wheel cylinder.If cyl-
inder brakeline fitting is hard to break loose,
spray generous amount of Mopar Rust Pene-
trant between fitting and line and around fit-
ting threads in wheel cylinder. Note that it may
require a few minutes for penetrant to work.
(3) Remove brakeshoes.
(4) Remove bolts attaching wheel cylinder to sup-
port plate and remove cylinder.
WHEEL CYLINDER OVERHAUL (Figs. 8 and 9)
(1) Remove links.
(2) Remove dust boots.
(3) Remove cups and pistons. Discard cups.
(4) Remove and discard spring and expander.
(5) Remove bleed screw.
(6) Clean cylinder, pistons and links with Mopar
brake cleaner.
(7) Inspect cylinder bore and pistons. Light discol-
oration of bore is acceptable. However, replace cylin-
der if bore and pistons are scored, pitted, or corroded.
Fig. 5 Adjuster Screw Components (9-Inch Brake)
Fig. 6 Adjusting Gauge To Brake Drum
Fig. 7 Adjusting Brakeshoes To Gauge
JDRUM BRAKES 5 - 57
Page 195 of 2198

Do not hone cylinder bores or polish pistons.
Replace cylinder as an assembly if bore is dam-
aged.
(8) Install bleed screw.
(9) Coat cylinder bore, pistons, cups and expander
with brake fluid and reassemble cylinder compo-
nents. Be sure piston cup lips face expander.
WHEEL CYLINDER INSTALLATION
(1) Apply small bead of silicone sealer around cyl-
inder mounting surface of support plate.
(2) Start brakeline in wheel cylinder fitting by
hand.
(3) Align and seat wheel cylinder on support plate
(Fig. 10).
(4) Install cylinder mounting bolts (Fig. 10).
Tighten bolts to 10 Nzm (90 in. lbs.) torque.(5) Tighten brakeline fitting to 15 Nzm (132 in.
lbs.) torque.
(6) Install brakeshoes. Adjust shoes to drum with
brake gauge.
(7) Install brake drums and lower vehicle.
(8) Fill master cylinder and bleed brakes.
SUPPORT PLATE REPLACEMENT
The support plate should cleaned and inspected
whenever the drum brake components are being ser-
viced.
Check the support plate for wear, or rust through
at the contact pads and replace the plate if necessary.
Be sure to lubricate the contact pads with Mopar
multi-mileage grease before shoe installation. Lubri-
cation will avoid noisy operation and shoe bind.
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel/tire assembly.
(2) Remove brake drum, brakeshoes, and wheel
cylinder.
(3) Remove axle shaft as described in Group 3.
(4) Remove support plate attaching nuts and re-
move support plate.
(5) Clean axle tube flange. If gasket is not used on
flange, apply thin bead of silicone adhesive/sealer to
flange.
(6) Position new support plate on axle tube flange.
(7) Apply Mopar Lock N9Seal, or Loctite 242 to
support plate attaching nuts. Then install and
tighten nuts.
(8) Apply light coat of Mopar multi-mileage grease
to contact pads of new support plate.
(9) Install wheel cylinder and brakeshoes.
(10) Adjust brakeshoes to drums. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(11) Bleed brakes.
(12) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(13) Adjust parking brake cable tensioner. Refer to
procedure in Parking Brake section.
(14) Lower vehicle and verify proper service brake
and parking brake operation.
BRAKE DRUM REFINISHING
Brake drums can be machined to restore the brak-
ing surface. Use a brake lathe to clean up light scor-
ing and wear.
CAUTION: Never refinish a brake drum if machining
will cause the drum to exceed maximum allowable
brake surface diameter.
Brake drums that are warped, distorted, or se-
verely tapered should be replaced. Do not refinish
drums exhibiting these conditions. Brake drums that
are heat checked or have hard spots should also be
replaced.
Fig. 8 Wheel Cylinder (9-Inch Brake)
Fig. 9 Wheel Cylinder (10-Inch Brake)
Fig. 10 Wheel Cylinder Mounting
5 - 58 DRUM BRAKESJ
Page 200 of 2198
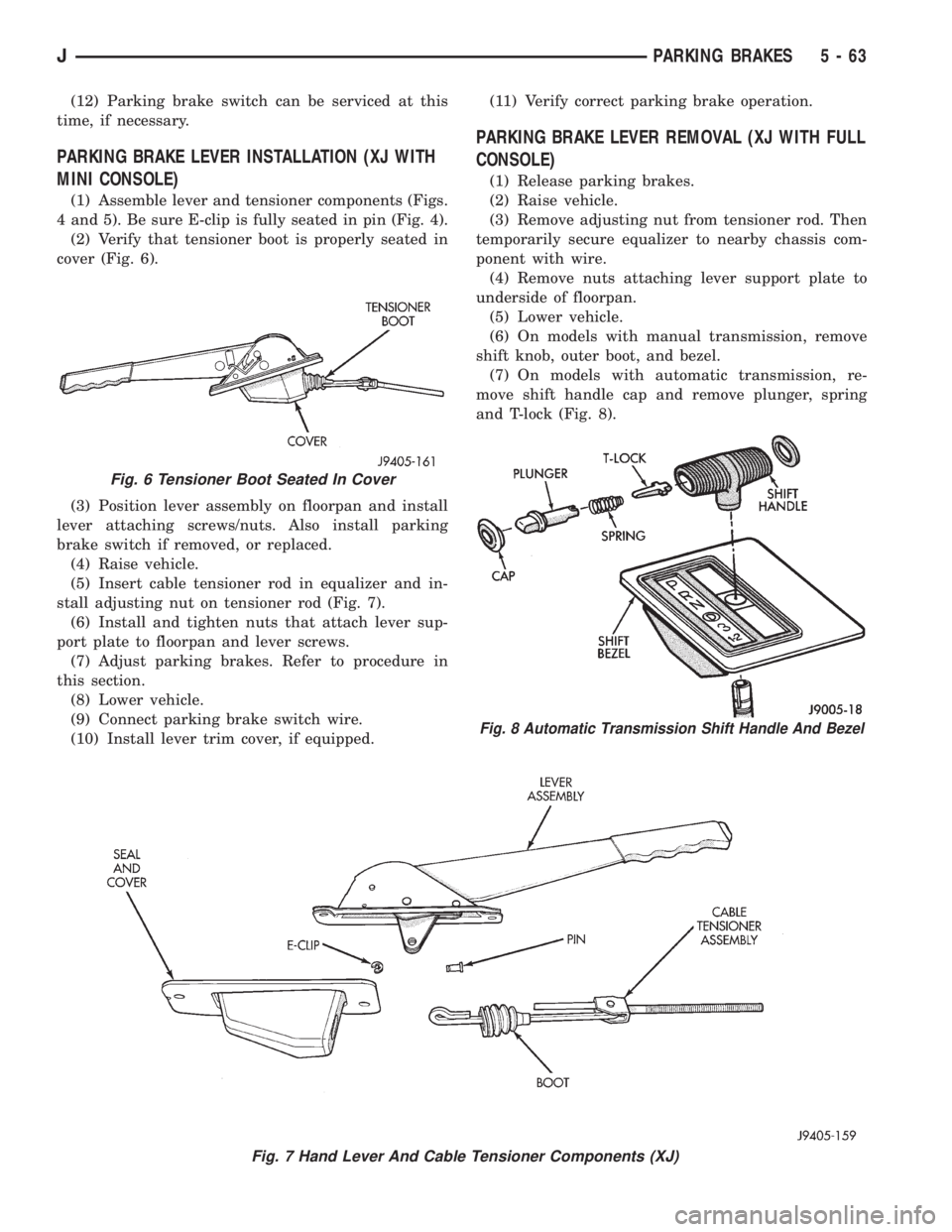
(12) Parking brake switch can be serviced at this
time, if necessary.
PARKING BRAKE LEVER INSTALLATION (XJ WITH
MINI CONSOLE)
(1) Assemble lever and tensioner components (Figs.
4 and 5). Be sure E-clip is fully seated in pin (Fig. 4).
(2) Verify that tensioner boot is properly seated in
cover (Fig. 6).
(3) Position lever assembly on floorpan and install
lever attaching screws/nuts. Also install parking
brake switch if removed, or replaced.
(4) Raise vehicle.
(5) Insert cable tensioner rod in equalizer and in-
stall adjusting nut on tensioner rod (Fig. 7).
(6) Install and tighten nuts that attach lever sup-
port plate to floorpan and lever screws.
(7) Adjust parking brakes. Refer to procedure in
this section.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Connect parking brake switch wire.
(10) Install lever trim cover, if equipped.(11) Verify correct parking brake operation.
PARKING BRAKE LEVER REMOVAL (XJ WITH FULL
CONSOLE)
(1) Release parking brakes.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove adjusting nut from tensioner rod. Then
temporarily secure equalizer to nearby chassis com-
ponent with wire.
(4) Remove nuts attaching lever support plate to
underside of floorpan.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) On models with manual transmission, remove
shift knob, outer boot, and bezel.
(7) On models with automatic transmission, re-
move shift handle cap and remove plunger, spring
and T-lock (Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Hand Lever And Cable Tensioner Components (XJ)
Fig. 6 Tensioner Boot Seated In Cover
Fig. 8 Automatic Transmission Shift Handle And Bezel
JPARKING BRAKES 5 - 63
Page 205 of 2198
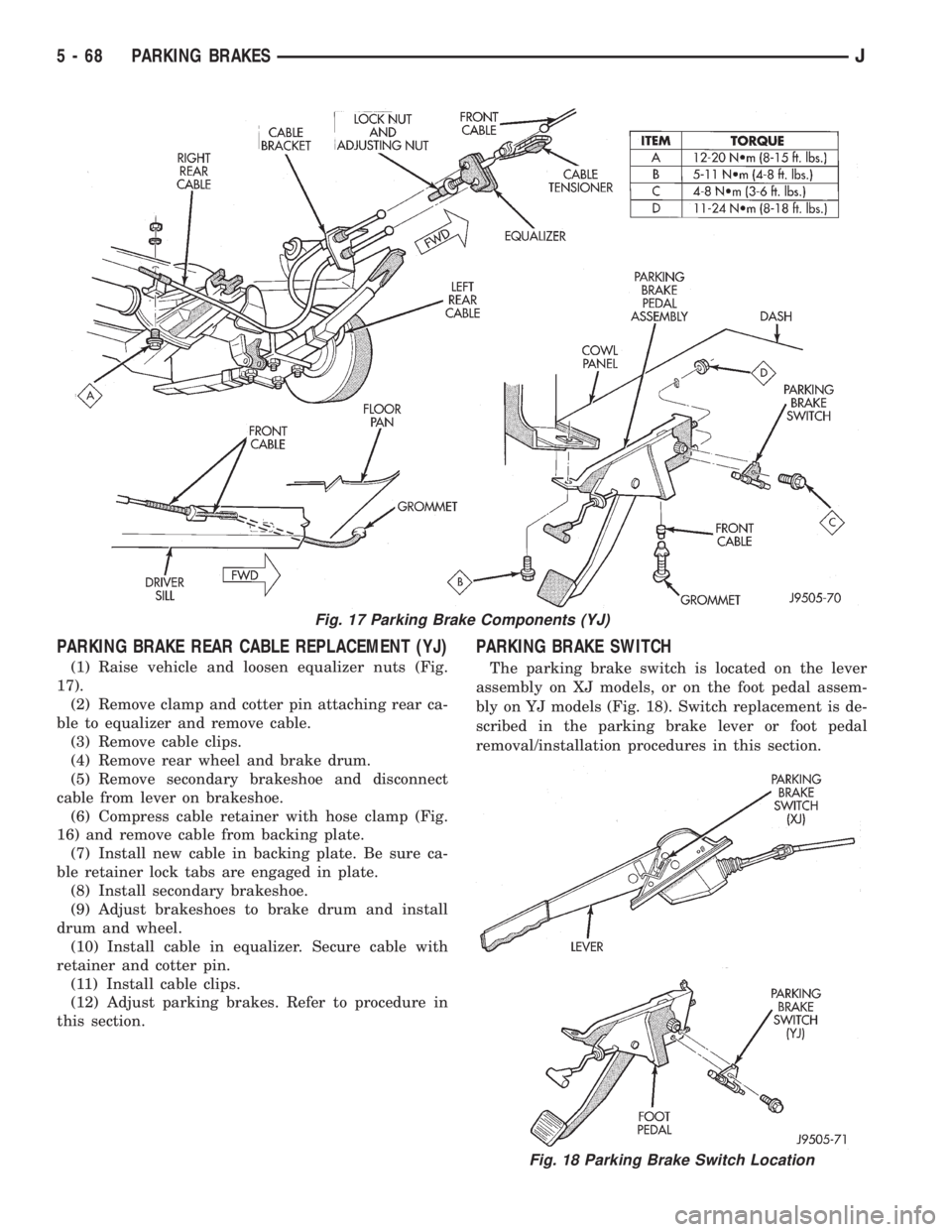
PARKING BRAKE REAR CABLE REPLACEMENT (YJ)
(1) Raise vehicle and loosen equalizer nuts (Fig.
17).
(2) Remove clamp and cotter pin attaching rear ca-
ble to equalizer and remove cable.
(3) Remove cable clips.
(4) Remove rear wheel and brake drum.
(5) Remove secondary brakeshoe and disconnect
cable from lever on brakeshoe.
(6) Compress cable retainer with hose clamp (Fig.
16) and remove cable from backing plate.
(7) Install new cable in backing plate. Be sure ca-
ble retainer lock tabs are engaged in plate.
(8) Install secondary brakeshoe.
(9) Adjust brakeshoes to brake drum and install
drum and wheel.
(10) Install cable in equalizer. Secure cable with
retainer and cotter pin.
(11) Install cable clips.
(12) Adjust parking brakes. Refer to procedure in
this section.
PARKING BRAKE SWITCH
The parking brake switch is located on the lever
assembly on XJ models, or on the foot pedal assem-
bly on YJ models (Fig. 18). Switch replacement is de-
scribed in the parking brake lever or foot pedal
removal/installation procedures in this section.
Fig. 17 Parking Brake Components (YJ)
Fig. 18 Parking Brake Switch Location
5 - 68 PARKING BRAKESJ
Page 210 of 2198

CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Clutch Contamination....................... 3
Clutch Cover and Disc Runout................ 3
Clutch Housing Misalignment................. 4
Clutch Misalignment........................ 3Flywheel Runout........................... 3
General Diagnosis Information................ 3
Inspection and Diagnosis Charts............... 4
Installation Methods and Parts Usage........... 4
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS INFORMATION
Unless the cause of a clutch problem is obvious, ac-
curate problem diagnosis will usually require a road
test to confirm a problem. Component inspection will
then be required to determine the actual problem
cause.
During a road test, drive the vehicle at normal
speeds. Shift the transmission through all gear
ranges and observe clutch action. If chatter, grab,
slip, or improper release is experienced, remove and
inspect the clutch components. However, if the prob-
lem is noise or hard shifting, further diagnosis may
be needed as the transmission or another driveline
component may be at fault. Careful observation dur-
ing the test will help narrow the problem area.
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION
Fluid contamination is a frequent cause of clutch
malfunctions. Oil, water, or clutch fluid on the clutch
disc and pressure plate surfaces will cause chatter,
slip and grab.
During inspection, note if any components are con-
taminated with oil, hydraulic fluid, or water/road
splash.
Oil contamination indicates a leak at either the
rear main seal or transmission input shaft. Oil leak-
age produces a residue of oil on the housing interior
and on the clutch cover and flywheel. Heat buildup
caused by slippage between the cover, disc and fly-
wheel, can sometimes bake the oil residue onto the
components. The glaze-like residue ranges in color
from amber to black.
Road splash contamination means dirt/water is en-
tering the clutch housing due to loose bolts, housing
cracks, or through hydraulic line openings. Driving
through deep water puddles can force water/road
splash into the housing through such openings.
Clutch fluid leaks are usually from damaged slave
cylinder push rod seals. This type of leak can only be
confirmed by visual inspection.
CLUTCH MISALIGNMENT
Clutch components must be in proper alignment
with the crankshaft and transmission input shaft.Misalignment caused by excessive runout or warpage
of any clutch component will cause grab, chatter and
improper clutch release.
FLYWHEEL RUNOUT
Check flywheel runout whenever misalignment is
suspected. Flywheel runout should not exceed 0.08
mm (0.003 in.). Measure runout at the outer edge of
the flywheel face with a dial indicator. Mount the in-
dicator on a stud installed in place of one of the fly-
wheel bolts.
Common causes of runout are:
²heat warpage
²improper machining
²incorrect bolt tightening
²improper seating on crankshaft flange shoulder
²foreign material on crankshaft flange
Flywheel machining is not recommended. The fly-
wheel clutch surface is machined to a unique contour
and machining will negate this feature. However, mi-
nor flywheel scoring can be cleaned up by hand with
180 grit emery, or with surface grinding equipment.
Remove only enough material to reduce scoring (ap-
proximately 0.001 - 0.003 in.). Heavy stock removal
isnot recommended.Replace the flywheel if scor-
ing is severe and deeper than 0.076 mm (0.003 in.).
Excessive stock removal can result in flywheel crack-
ing or warpage after installation; it can also weaken
the flywheel and interfere with proper clutch release.
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
flywheel. Dirt and grease on the flange surface may
cock the flywheel causing excessive runout. Use new
bolts when remounting a flywheel and secure the
bolts with Mopar Lock And Seal. Tighten flywheel
bolts to specified torque only. Overtightening can dis-
tort the flywheel hub causing runout.
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC RUNOUT
Check the clutch disc before installation. Axial
(face) runout of anewdisc should not exceed 0.50
mm (0.020 in.). Measure runout about 6 mm (1/4 in.)
from the outer edge of the disc facing. Obtain an-
other disc if runout is excessive.
Check condition of the clutch before installation. A
warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause grab
and incomplete release or engagement. Be careful
JCLUTCH DIAGNOSIS 6 - 3