electrical JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 1357 of 2198
STEERING COLUMNÐYJ
INDEX
page page
Assembly............................... 63
Assembly............................... 71
Column Replacement...................... 58
Disassembly............................. 66DisassemblyÐColumn or Console Shift......... 60
Non-Tilt Steering Column................... 60
Steering Wheel........................... 58
Tilt Steering Column....................... 66
The column may be disassembled and reassembled.
Also most steering column components can be serviced
without removing the column from the vehicle. For ad-
ditional information, refer to Group 8H, Electrical.
CAUTION: Bumping, jolting and hammering on the
steering column shaft and gear shift tube must be
avoided during all service procedures.
CAUTION: Disconnect negative (ground) cable from the
battery before servicing any component on the column.
Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when involved with steering column service.
STEERING WHEEL
REMOVAL
(1) Make sure the front wheels are in thestraight
aheadposition.
(2) Disconnect the negative (ground) cable from the
battery.
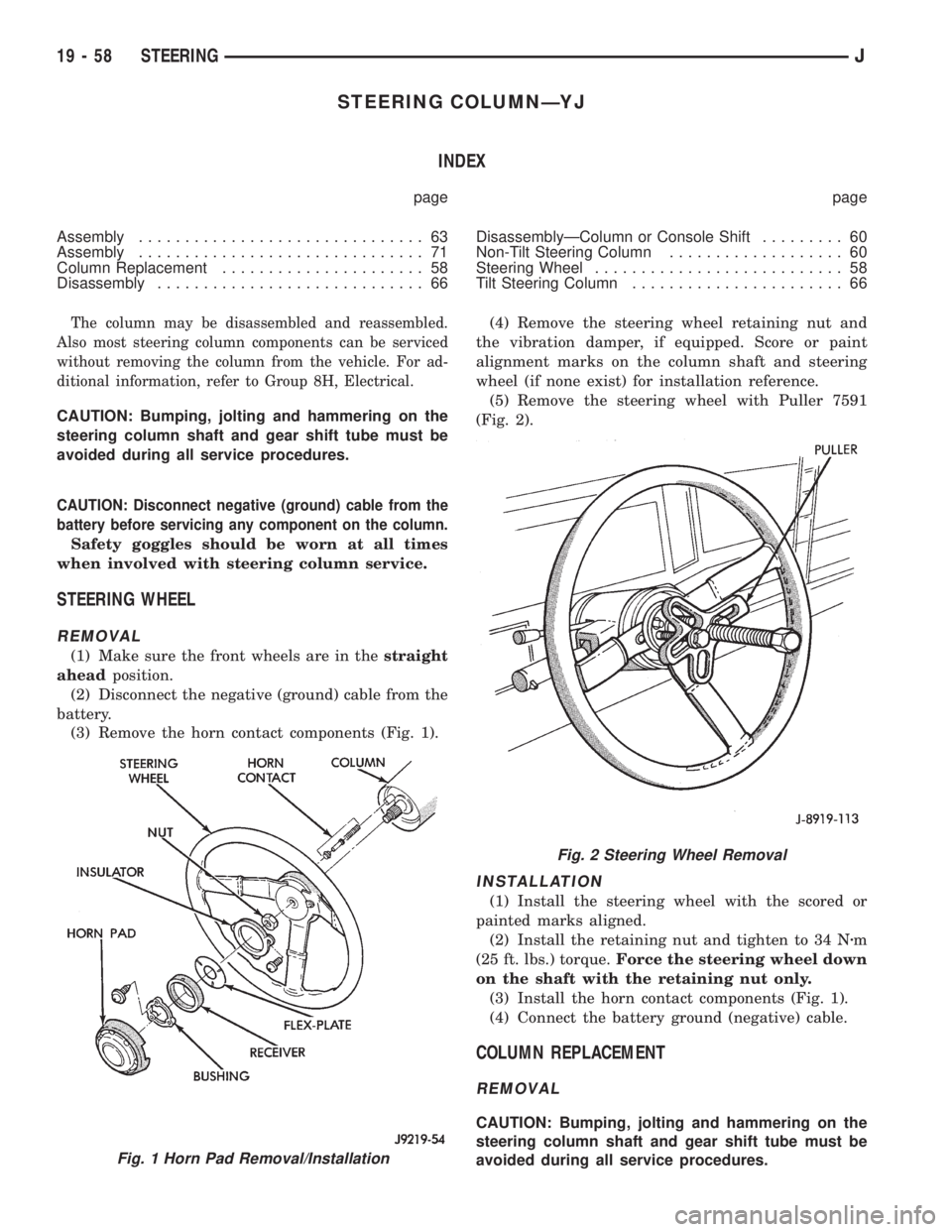
(3) Remove the horn contact components (Fig. 1).(4) Remove the steering wheel retaining nut and
the vibration damper, if equipped. Score or paint
alignment marks on the column shaft and steering
wheel (if none exist) for installation reference.
(5) Remove the steering wheel with Puller 7591
(Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the steering wheel with the scored or
painted marks aligned.
(2) Install the retaining nut and tighten to 34 Nzm
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.Force the steering wheel down
on the shaft with the retaining nut only.
(3) Install the horn contact components (Fig. 1).
(4) Connect the battery ground (negative) cable.
COLUMN REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Bumping, jolting and hammering on the
steering column shaft and gear shift tube must be
avoided during all service procedures.
Fig. 1 Horn Pad Removal/Installation
Fig. 2 Steering Wheel Removal
19 - 58 STEERINGJ
Page 1379 of 2198
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The AX 4/5 identification code is on the bottom sur-
face of the transmission case near the fill plug (Fig. 2).
The first number is year of manufacture. The second
and third numbers indicate month of manufacture. The
next series of numbers is the transmission serial num-
ber.
GEAR RATIOS
Gear ratios for the AX 4 and AX 5 are as follows:
²First gear: 3.93:1
²Second gear: 2.33:1
²Third gear: 1.45:1
²Fourth gear: 1.00:1
²Fifth gear (AX 5): 0.85:1
²Reverse gear: 4.74:1
SHIFT PATTERN
The AX 4/5 first through fourth gear shift pattern
is in a conventional H configuration. On the AX 5,
fifth gear is up and to the right and reverse gear is
down and to the right (Fig. 3).
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANT
Recommended lubricant for AX 4/5 transmissions is
Mopar 75W-90, API Grade GL-5 gear lubricant, or
equivalent.
Correct lubricant level is from the bottom edge, to
no more than 6 mm (1/4 in.) below the bottom edge of
the fill plug hole.
The fill plug is at the passenger side of the adapter
housing Fig. 4). The drain plug is at the bottom of
the case.
Approximate dry fill lubricant capacity is 3.3 liters
(3.5 qts.).
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill, or an incor-
rect lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, intermediate plate and adaptor or extension
housing, or from the front/rear seals. A suspected
leak could also be the result of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening, or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal. Lu-
bricant may be seen dripping from the clutch housing
after extended operation. If the leak is severe, it may
also contaminate the clutch disc causing slip, grab
and chatter.
Transmissions filled from air or electrically powered
lubricant containers can be underfilled. This generally
Fig. 2 Transmission Identification
Fig. 3 AX 4/5 Shift Pattern
Fig. 4 Fill Plug Location
21 - 2 AX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1411 of 2198

The first number is year of manufacture. The sec-
ond and third numbers indicate month of manufac-
ture. The next series of numbers is the transmission
serial number.
TRANSMISSION SHIFT PATTERN
The AX 15 shift pattern is shown in Figure 3. First
and second and third and fourth gear ranges are in
line for improved shifting. Fifth and reverse gear
ranges are also in line at the extreme right of the
pattern (Fig. 3).
The AX 15 is equipped with a reverse lockout
mechanism. The shift lever must be moved through
the Neutral detent before making a shift to reverse.
TRANSMISSION LUBRICANT
Recommended lubricant for AX 15 transmissions is
Mopar 75W-90, API Grade GL-5 gear lubricant, or
equivalent.
Correct lubricant level is from the bottom edge, to
no more than 6 mm (1/4 in.) below the bottom edge of
the fill plug hole.
Approximate dry fill lubricant capacity is:
²3.10 liters (3.27 qts.) in 4-wheel drive models
²3.15 liters (3.32 qts.) in 2-wheel drive models
TRANSMISSION SWITCH AND PLUG LOCATIONS
The fill plug is at the driver side of the gear case
(Fig. 4).
The drain plug and backup light switch are on the
passenger side of the gear case (Fig. 5).
TRANSMISSION GEAR RATIOS
AX 15 gear ratios are:
First gear - 3.83:1
Second gear - 2.33:1
Third gear - 1.44:1
Fourth gear - 1.00:1
Fifth gear - 0.79:1
Reverse - 4.22:1
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill, or an incor-
rect lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, intermediate plate and adapter or extension
housing, or from the front/rear seals. A suspected
leak could also be the result of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will usually be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening, or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal. Lu-
bricant may be seen dripping from the clutch housing
after extended operation. If the leak is severe, it may
also contaminate the clutch disc causing slip, grab
and chatter.
Transmissions filled from air or electrically pow-
ered lubricant containers can be underfilled. This
Fig. 3 AX 15 Shift Pattern
Fig. 4 Fill Plug Location
Fig. 5 Drain Plug/Backup Light Switch Location
21 - 34 AX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1444 of 2198

30RH/32RH AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
Recommended Fluid....................... 67
Torque Converter......................... 67
Transmission Application.................... 67
Transmission Changes and Parts Interchangeability.. 67
Transmission Controls and Components........ 67
Transmission Identification.................. 67
TRANSMISSION APPLICATION
Chrysler 30RH and 32RH automatic transmissions
are used in XJ/YJ models. Both are 3-speed auto-
matic transmissions with a gear-type oil pump, two
clutches and bands and a planetary gear system (Fig.
1).
The 30RH is used in XJ/YJ models with a 2.5L en-
gine. The 32RH is used in YJ models with a 4.0L en-
gine.
TORQUE CONVERTER
A three element, torque converter is used for all
applications. The converter consists of an impeller,
stator, and turbine.
The converter used with 30RH/32RH transmissions
has a converter clutch. The clutch is engaged by an
electrical solenoid and mechanical module on the
valve body. The solenoid is operated by the power-
train control module.
The torque converter is a welded assembly and is
not a repairable component. The converter is serviced
as an assembly.
RECOMMENDED FLUID
The recommended and preferred fluid for 30RH/
32RH transmissions is Mopar ATF Plus, Type 7176.
Dexron II is not really recommended and should
only be used when ATF Plus is not available.
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The transmission identification numbers are
stamped on the left side of the case just above the oil
pan gasket surface (Fig. 2). The first set of numbers
is the transmission part number. The next set of code
numbers set is the date of build. The final set of code
numbers represents the transmission serial number.
TRANSMISSION CHANGES AND PARTS
INTERCHANGEABILITY
1995 transmissions are similar to previous models
but only in appearance. Current transmissions are
dimensionally different. Do not interchange new/oldparts. Different dimensions, fluid passages, input/
output shafts, cases, bands, valve bodies and gover-
nor assemblies are just a few of the changed items.
CAUTION: Special bolts are used to attach the
driveplate to the crankshaft on models with a 2.5L
engine and 30RH transmission,. These bolts have a
smaller hex head for torque converter clearance.
DO NOT interchange these bolts with similar size
bolts for any reason.
Different governor weight assemblies are used in
30RH/32RH transmissions. The 30RH weight assem-
bly is much the same as in previous years. However,
the 32RH has a three stage governor weight assem-
bly consisting of the outer weight, a smaller weight
spring, and a new intermediate weight. Refer to the
overhaul and in-vehicle service sections for more de-
tailed information.
Plastic check balls are now used in many 30RH/
32RH valve bodies. The new check balls entered pro-
duction as a running change. Plastic and steel check
balls are not interchangeable.
A converter drainback check valve has been added
to the fluid cooler system. The one-way valve is lo-
cated in the transmission outlet (pressure) line. The
valve prevents fluid drainback when the vehicle is
parked for lengthy periods.
TRANSMISSION CONTROLS AND COMPONENTS
The transmission hydraulic control system per-
forms five basic functions, which are:
²pressure supply
²pressure regulation
²flow control
²clutch/band apply and release
²lubrication
Pressure Supply And Regulation
The oil pump generates the fluid working pressure
needed for operation and lubrication. The pump is
J30RH/32RH AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 21 - 67
Page 1487 of 2198
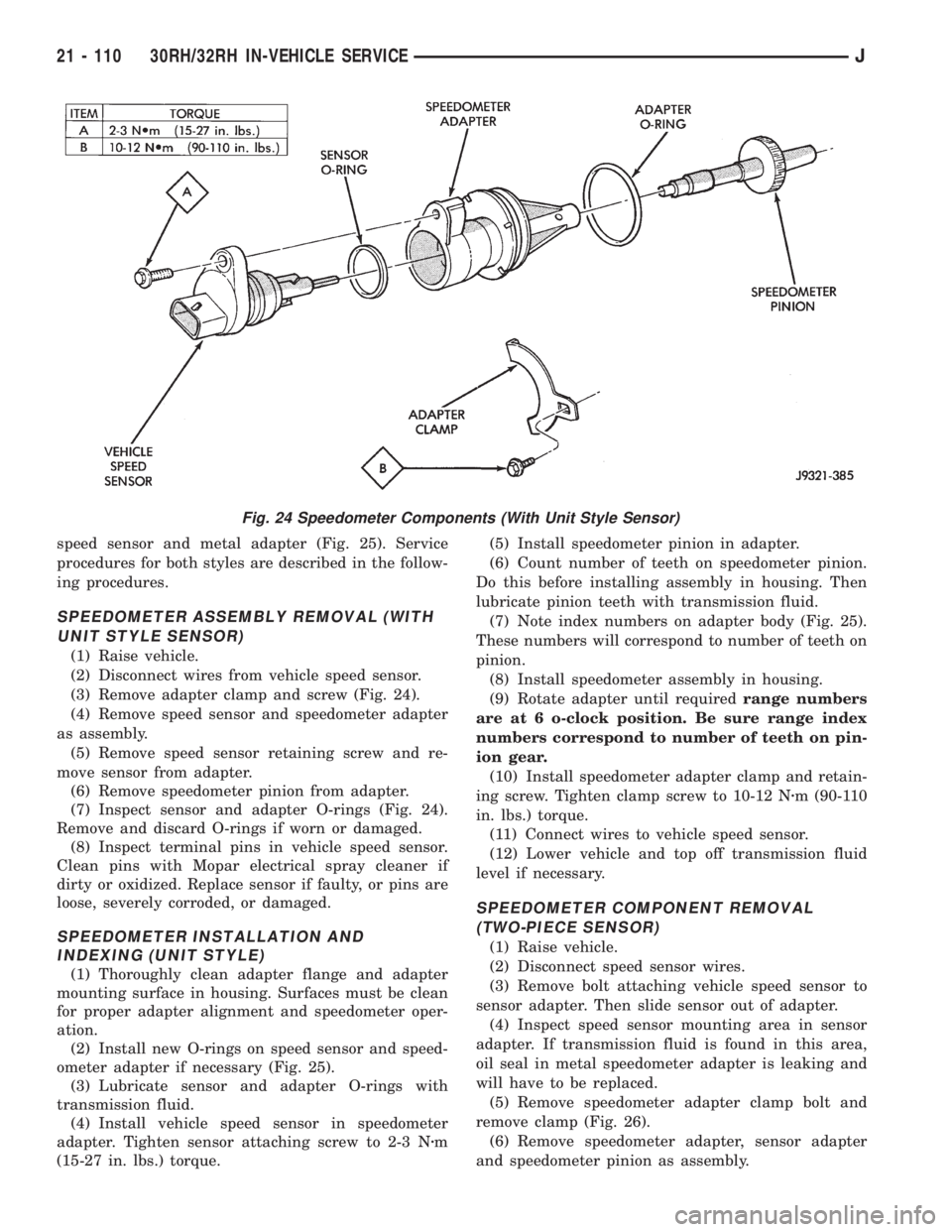
speed sensor and metal adapter (Fig. 25). Service
procedures for both styles are described in the follow-
ing procedures.
SPEEDOMETER ASSEMBLY REMOVAL (WITH
UNIT STYLE SENSOR)
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect wires from vehicle speed sensor.
(3) Remove adapter clamp and screw (Fig. 24).
(4) Remove speed sensor and speedometer adapter
as assembly.
(5) Remove speed sensor retaining screw and re-
move sensor from adapter.
(6) Remove speedometer pinion from adapter.
(7) Inspect sensor and adapter O-rings (Fig. 24).
Remove and discard O-rings if worn or damaged.
(8) Inspect terminal pins in vehicle speed sensor.
Clean pins with Mopar electrical spray cleaner if
dirty or oxidized. Replace sensor if faulty, or pins are
loose, severely corroded, or damaged.
SPEEDOMETER INSTALLATION AND
INDEXING (UNIT STYLE)
(1) Thoroughly clean adapter flange and adapter
mounting surface in housing. Surfaces must be clean
for proper adapter alignment and speedometer oper-
ation.
(2) Install new O-rings on speed sensor and speed-
ometer adapter if necessary (Fig. 25).
(3) Lubricate sensor and adapter O-rings with
transmission fluid.
(4) Install vehicle speed sensor in speedometer
adapter. Tighten sensor attaching screw to 2-3 Nzm
(15-27 in. lbs.) torque.(5) Install speedometer pinion in adapter.
(6) Count number of teeth on speedometer pinion.
Do this before installing assembly in housing. Then
lubricate pinion teeth with transmission fluid.
(7) Note index numbers on adapter body (Fig. 25).
These numbers will correspond to number of teeth on
pinion.
(8) Install speedometer assembly in housing.
(9) Rotate adapter until requiredrange numbers
are at 6 o-clock position. Be sure range index
numbers correspond to number of teeth on pin-
ion gear.
(10) Install speedometer adapter clamp and retain-
ing screw. Tighten clamp screw to 10-12 Nzm (90-110
in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect wires to vehicle speed sensor.
(12) Lower vehicle and top off transmission fluid
level if necessary.
SPEEDOMETER COMPONENT REMOVAL
(TWO-PIECE SENSOR)
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect speed sensor wires.
(3) Remove bolt attaching vehicle speed sensor to
sensor adapter. Then slide sensor out of adapter.
(4) Inspect speed sensor mounting area in sensor
adapter. If transmission fluid is found in this area,
oil seal in metal speedometer adapter is leaking and
will have to be replaced.
(5) Remove speedometer adapter clamp bolt and
remove clamp (Fig. 26).
(6) Remove speedometer adapter, sensor adapter
and speedometer pinion as assembly.
Fig. 24 Speedometer Components (With Unit Style Sensor)
21 - 110 30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICEJ
Page 1542 of 2198

AW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
CONTENTS
page page
AW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION........ 165
AW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE.............. 182
AW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS......... 176
AW-4 TRANSMISSION OVERHAUL......... 201AW-4 TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION....................... 198
GENERAL INFORMATION................ 165
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
Components and Operation................. 166
Description............................. 165
First/Second/Third/Reverse Components....... 168
Fourth Gear Overdrive Components.......... 167
Geartrain Operation and Application Charts..... 169Hydraulic System........................ 169
Recommended Fluid and Capacity........... 166
Torque Converter........................ 167
Transmission Identification.................. 166
Transmission Ranges and Shift Lever Positions . . 166
DESCRIPTION
AW-4 Transmission Overhaul
The AW-4 is a 4-speed, electronically controlled au-
tomatic transmission (Fig. 1). The AW-4 is used in XJ
models with a 4.0L engine.
Running gear consists of an oil pump, planetary
gear sets, clutch and brake units, hydraulic accumu-
lators, a valve body with electrical solenoids and a
transmission control module (TCM). Cables are usedfor shift and throttle pressure control. A park/neutral
position switch permits engine starting in Park and
Neutral range only.
The valve body solenoids are controlled by signals
from the transmission control module (TCM). Signal
sequence is determined by vehicle speed and throttle
position.
Fourth gear is an 0.75:1 ratio overdrive range.
First, second, third and reverse gear are conventional
Fig. 1 AW-4 Automatic Transmission
JAW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 21 - 165
Page 1553 of 2198
AW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
General Diagnosis Information............... 176
Hydraulic Pressure Test.................... 177
Manual Shifting Test...................... 177Preliminary Inspection and Adjustment......... 176
TimeLagTest ........................... 178
Torque Converter Stall Test................. 178
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS INFORMATION
Shift points are controlled by the transmission con-
trol module (TCM). Before attempting repair, deter-
mine if a malfunction is electrical or mechanical.
The TCM used with the AW-4 transmission has a
self-diagnostic program compatible with the DRB
scan tool. The tester will identify faults in the elec-
trical control system.
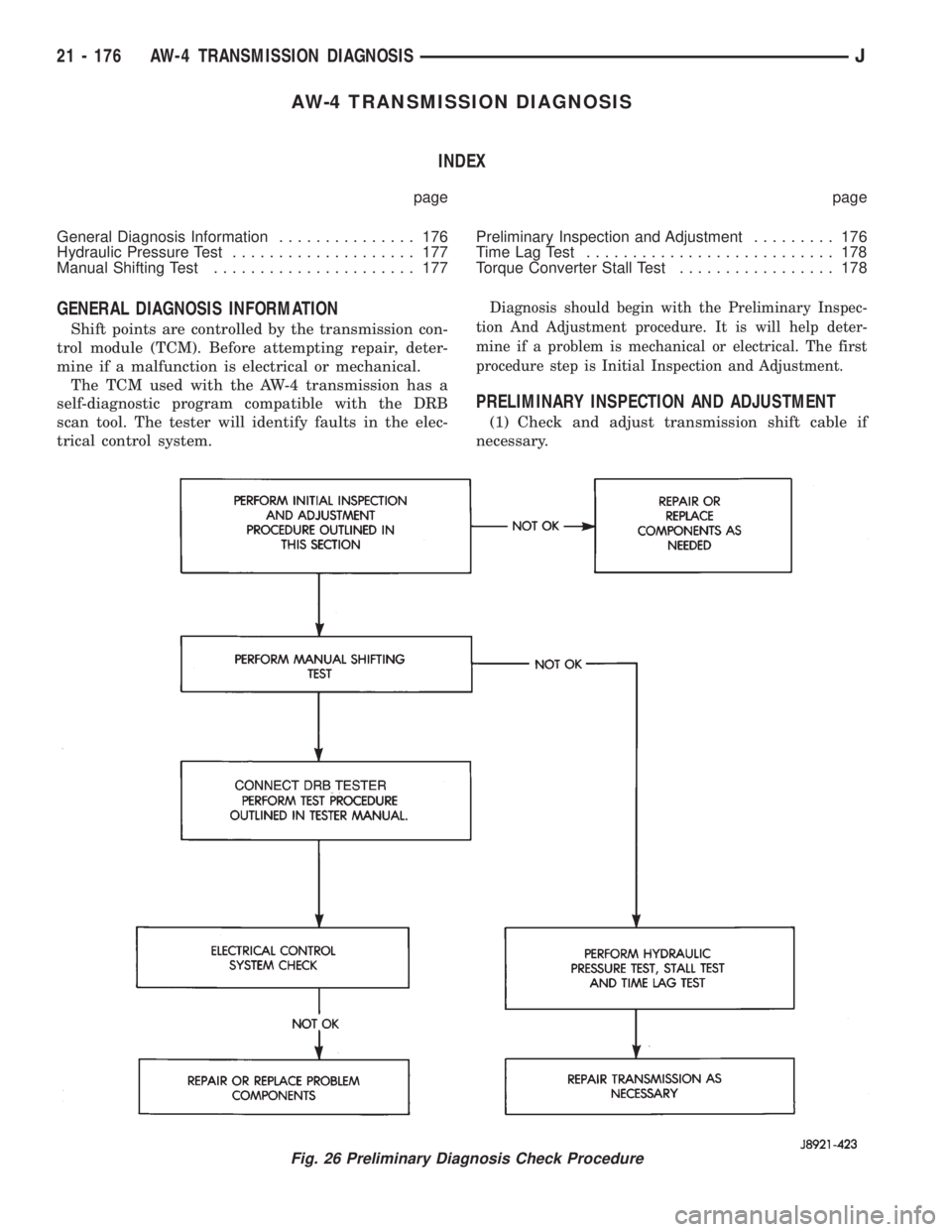
Diagnosis should begin with the Preliminary Inspec-
tion And Adjustment procedure. It is will help deter-
mine if a problem is mechanical or electrical. The first
procedure step is Initial Inspection and Adjustment.
PRELIMINARY INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
(1) Check and adjust transmission shift cable if
necessary.
Fig. 26 Preliminary Diagnosis Check Procedure
21 - 176 AW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1554 of 2198

(2) Verify transmission throttle cable operation.
Repair or replace cable if necessary.
(3) Check engine throttle operation. Operate accel-
erator pedal and observe injector throttle plate move-
ment. Adjust linkage if throttle plate does not reach
wide open position.
(4) Check transmission fluid level when fluid is at
normal operating temperature. Start engine. Shift
transmission through all gear ranges then back to
Neutral. Correct level is to Full or Add mark on dip-
stick with engine at curb idle speed.
(5) Check and adjust park/neutral position switch
if necessary.
(6) Check throttle position sensor adjustment and
operation. Adjust the sensor if necessary.
MANUAL SHIFTING TEST
(1) This test determines if problem is related to
mechanical or electrical component.
(2) Stop engine and disconnect transmission con-
trol module or module fuse.
(3) Road test vehicle. Shift transmission into each
gear range. Transmission should operate as follows:
²lock in Park
²back up in Reverse
²not move in Neutral
²provide first gear only with shift lever in 1-2 posi-
tion
²operate in third gear only with shift lever in 3 po-
sition
²operate in overdrive fourth gear in D position
(4) If transmission operates as described, proceed
to next step. However, if forward gear ranges were
difficult to distinguish (all feel the same), or vehicle
would not back up, refer to diagnosis charts. Do not
perform stall or time lag tests.
CAUTION: Do not overspeed the engine during the
next test step. Ease off the throttle and allow the
vehicle to slow before downshifting.
(5) Continue road test. Manually downshift trans-
mission from D to 3, and from 3 to 1-2 position. Then
manually upshift transmission through forward
ranges again.
(6) If transmission operation is OK, perform stall,
time lag and pressure tests. If transmission shifting
problem is encountered, refer to diagnosis charts.
(7) If a problem still exists, continue testing with
DRB scan tool.
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST
PRESSURE TEST PROCEDURE
(1) Connect pressure test gauge to test port on pas-
senger side of transmission. Use Adapter 7554 to con-
nect gauge. Be sure test gauge has minimum
capacity of 300 psi (2100 kPa).(2) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature.
(3) Apply parking brakes and block wheels.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW ANYONE TO STAND
AT THE FRONT OR REAR OF THE VEHICLE WHILE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING STEPS IN THE
PRESSURE TEST.
(4) Check and adjust engine curb idle speed.
(5) Apply (and hold) service brakes.
(6) Shift transmission into D range and note line
pressure with engine at curb idle speed. Pressure
should be 61-to-70 psi (421-to-481 kPa).
(7) Press accelerator pedal to wide open throttle
position and note line pressure. Pressure should be
173-to-209 psi (1196-to-1442 kPa).
CAUTION: Do not hold wide open throttle for more
than 3-4 seconds at a time.
(8) Shift transmission into Reverse and note line
pressure with engine at curb idle speed. Pressure
should be 75-to-90 psi (519-to-618 kPa).
(9) Press accelerator to wide open throttle position
and note line pressure in Reverse. Pressure should
be 213-to-263 psi (1471-to-1814 kPa).
CAUTION: Do not hold wide open throttle for more
than 4 seconds.
(10) If line pressure is not within specifications,
adjust transmission throttle cable and repeat pres-
sure test.
Fig. 27 Pressure Test Gauge Connection
JAW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 177
Page 1687 of 2198
(6) Install vehicle speed sensor and adapter, if re-
moved. Then connect vehicle speed sensor wires, vent
hoses and electrical switch connector.
(7) Align and connect propeller shafts. Tighten
shaft U-joint clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Fill transfer case with Mopar Dexron II. Cor-
rect fill level is to bottom edge of fill plug hole.
(9) Install rear crossmember. Tighten crossmember
bolts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Remove transmission jack and transmission
support stand.
(11) Move transfer case range lever to 4L position.
(12) Connect shift rod to transfer case range lever.
(13) Adjust transfer case shift linkage as described
in this section.
(14) Lower vehicle.
TRANSFER CASE DISASSEMBLY AND OVERHAUL
(1) Remove fill and drain plugs.
(2) Remove front yoke. Discard yoke seal washer
and nut.
(3) Place transfer case range lever in 4L position.
(4) Remove extension housing attaching bolts.
(5) Tap extension housing in a clockwise direction
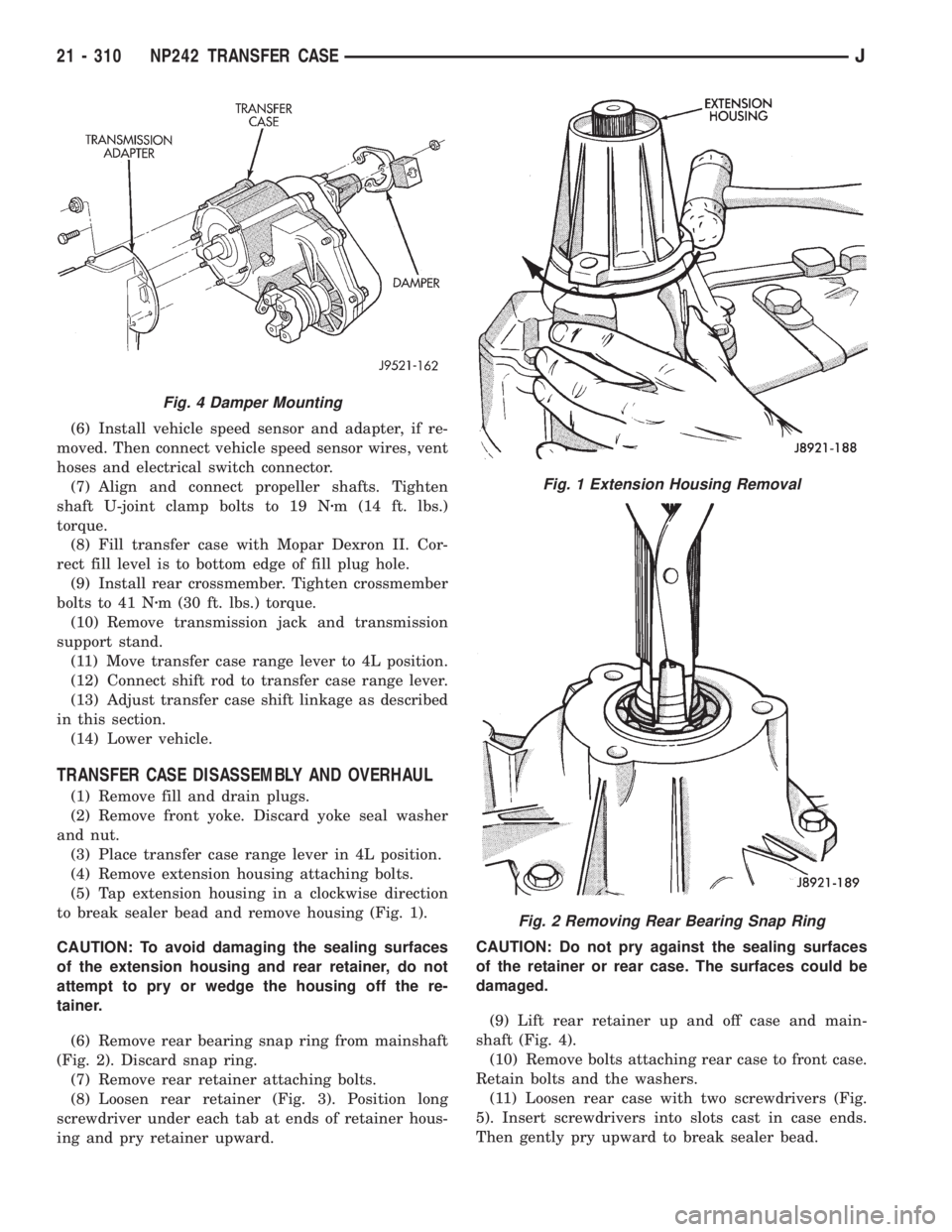
to break sealer bead and remove housing (Fig. 1).
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the sealing surfaces
of the extension housing and rear retainer, do not
attempt to pry or wedge the housing off the re-
tainer.
(6) Remove rear bearing snap ring from mainshaft
(Fig. 2). Discard snap ring.
(7) Remove rear retainer attaching bolts.
(8) Loosen rear retainer (Fig. 3). Position long
screwdriver under each tab at ends of retainer hous-
ing and pry retainer upward.CAUTION: Do not pry against the sealing surfaces
of the retainer or rear case. The surfaces could be
damaged.
(9) Lift rear retainer up and off case and main-
shaft (Fig. 4).
(10) Remove bolts attaching rear case to front case.
Retain bolts and the washers.
(11) Loosen rear case with two screwdrivers (Fig.
5). Insert screwdrivers into slots cast in case ends.
Then gently pry upward to break sealer bead.
Fig. 4 Damper Mounting
Fig. 1 Extension Housing Removal
Fig. 2 Removing Rear Bearing Snap Ring
21 - 310 NP242 TRANSFER CASEJ
Page 1761 of 2198
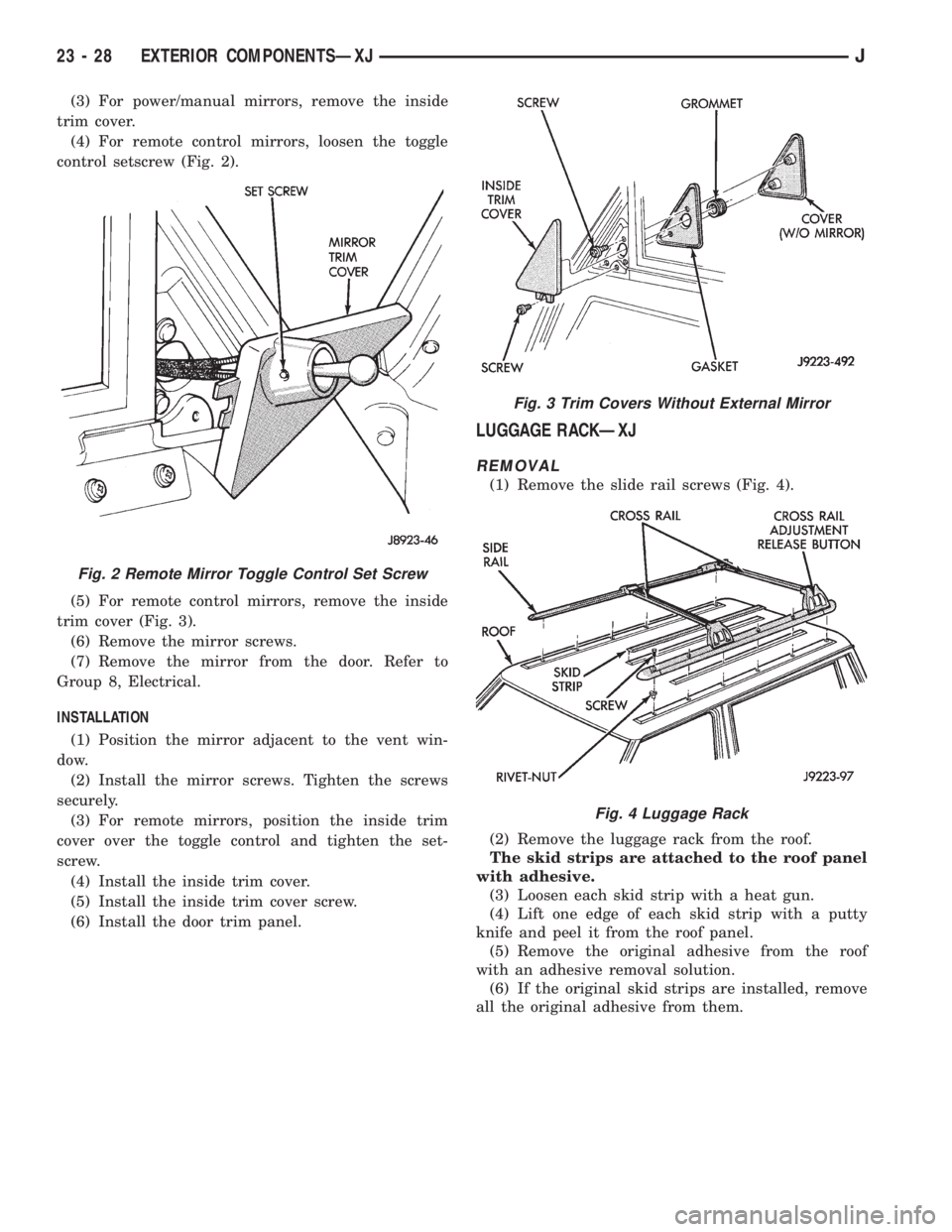
(3) For power/manual mirrors, remove the inside
trim cover.
(4) For remote control mirrors, loosen the toggle
control setscrew (Fig. 2).
(5) For remote control mirrors, remove the inside
trim cover (Fig. 3).
(6) Remove the mirror screws.
(7) Remove the mirror from the door. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the mirror adjacent to the vent win-
dow.
(2) Install the mirror screws. Tighten the screws
securely.
(3) For remote mirrors, position the inside trim
cover over the toggle control and tighten the set-
screw.
(4) Install the inside trim cover.
(5) Install the inside trim cover screw.
(6) Install the door trim panel.
LUGGAGE RACKÐXJ
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the slide rail screws (Fig. 4).
(2) Remove the luggage rack from the roof.
The skid strips are attached to the roof panel
with adhesive.
(3) Loosen each skid strip with a heat gun.
(4) Lift one edge of each skid strip with a putty
knife and peel it from the roof panel.
(5) Remove the original adhesive from the roof
with an adhesive removal solution.
(6) If the original skid strips are installed, remove
all the original adhesive from them.
Fig. 2 Remote Mirror Toggle Control Set Screw
Fig. 3 Trim Covers Without External Mirror
Fig. 4 Luggage Rack
23 - 28 EXTERIOR COMPONENTSÐXJJ