service JEEP CJ 1953 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: CJ, Model: JEEP CJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 163 of 376
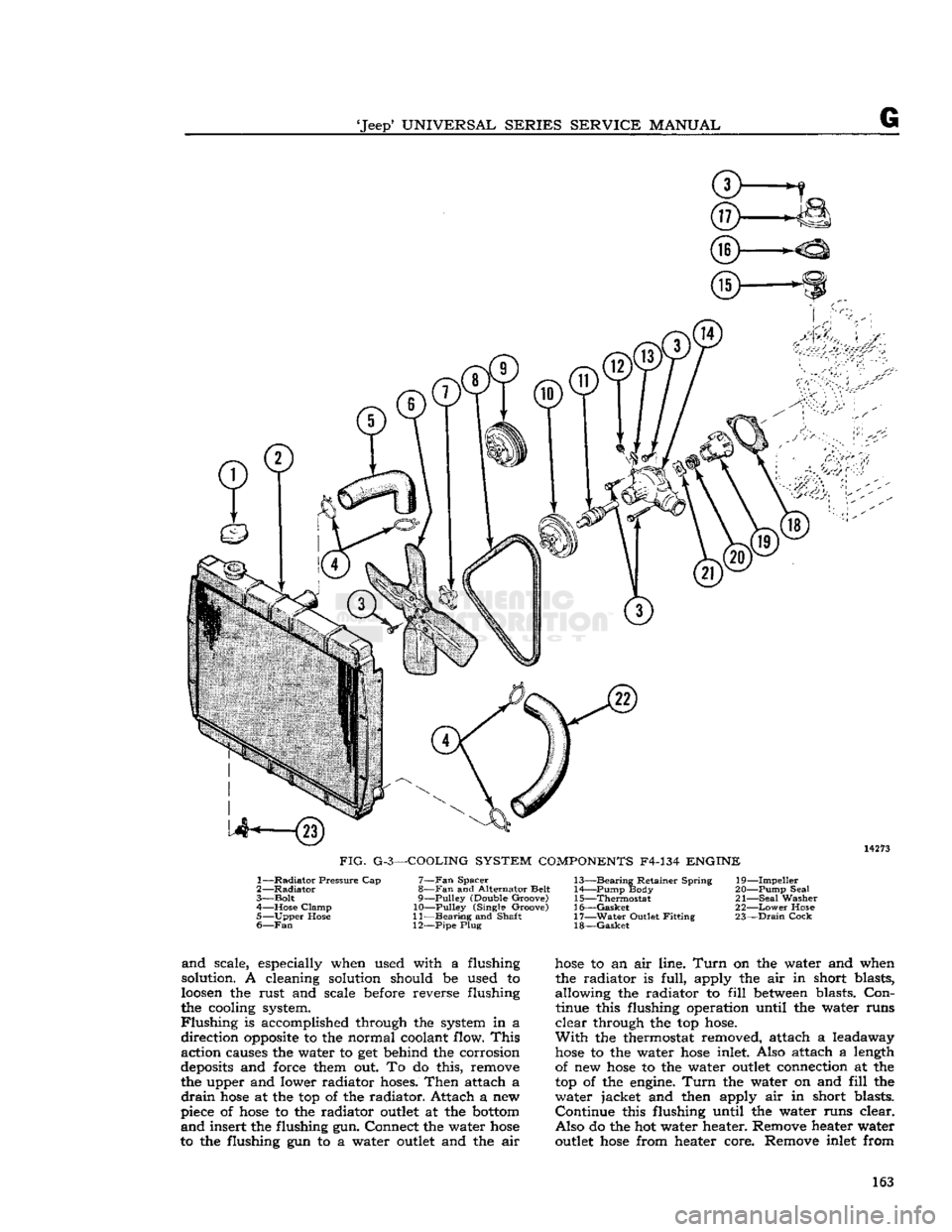
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
G and
scale, especially when used with a flushing
solution. A cleaning solution should be used to
loosen
the rust and scale before reverse flushing
the cooling system.
Flushing
is accomplished through the system in a direction
opposite
to the normal coolant flow.
This
action causes the water to get behind the corrosion
deposits
and force them out. To do this, remove
the upper and lower radiator
hoses.
Then
attach a
drain
hose
at the top of the radiator. Attach a new
piece of
hose
to the radiator
outlet
at the
bottom
and
insert the flushing gun. Connect the water
hose
to the flushing gun to a water
outlet
and the air
hose
to an air line.
Turn
on the water and when
the radiator is
full,
apply the air in short blasts,
allowing the radiator to
fill
between
blasts.
Con
tinue this flushing operation until the water runs
clear
through the top
hose.
With
the thermostat removed, attach a leadaway
hose
to the water
hose
inlet. Also attach a length
of new
hose
to the water
outlet
connection at the
top of the engine.
Turn
the water on and
fill
the
water jacket and then apply air in short blasts.
Continue
this flushing until the water runs clear.
Also
do the hot water heater. Remove heater water
outlet
hose
from heater core. Remove inlet from 163
Page 164 of 376

G
COOLING SYSTEM
engine
connections. Insert flushing gun and flush
heater core.
Care
must be taken when applying air
pressure to prevent damage to the heater core.
G-2.
Filling
Cooling System
To
fill
the cooling system, remove the
fill
cap and
fill
the tank to the top. Replace the cap and run
the
engine
at medium speed for approximately one
minute. Remove the cap and recheck the coolant level. Add more coolant if necessary to bring the level back to the top of the tank. If the cooling system is filled when the
engine
is cold, recheck the coolant level after the
engine
has warmed up.
This
will
ensure that the thermostat has opened allow ing complete cooling system circulation.
Always
correct any cooling system leaks before installing antifreeze. A corrosion inhibitor should be used in the cooling system to prevent the forma
tion of rust and scale. A quality brand antifreeze containing a corrosion inhibitor should be used.
When
the antifreeze is drained in the spring, a
corrosion inhibitor should be added with the water.
Note:
Cooling system components for both V6 and
F4
engines
are shown in
Figs.
G-2 and G-3.
G-3. Draining
Cooling System
To
completely
drain
the cooling system, open the
drain
in the
bottom
of the radiator and also a
drain
on the right side of the cylinder block on the
Hurricane
F4 engine. The Dauntless V-6
engine
has two
drain
plugs, one located on each side of the cylinder block. Both plugs must be removed to
completely
drain
the cooling system.
Remove the radiator cap to break any vacuum
that may have developed.
Should
the cooling solution be lost from the system
and
the
engine
become
overheated do not
refill
the system immediately but allow the
engine
to cool or
refill
slowly while the
engine
is running. If
cold solution is poured into the radiator while the
engine
is overheated there is danger of cracking the
cylinder
block and/or cylinder head.
G-4.
Radiator Pressure
Cap
All
radiators are equipped with pressure caps which
reduce evaporation of cooling solution and make the
engines
more efficient by permitting slightly
higher operating temperatures. When operating
properly,
the pressure cap permits pressure build-up
in
the cooling system during periods of severe heat
load.
This
pressure increases the boiling point of the coolant and thus reduces overflow losses. The
effectiveness
of the cap is limited by its opening
pressure and the boiling point of the coolant (see
note
below). The pressure cap employs a spring-
loaded, rubber-faced pressure seal which presses against a seat in the radiator top tank. Spring pres
sure
determines the opening pressure of the valve.
A
typical pressure cap is shown in Fig. G-5.
Note:
Refer to cooling system specifications (Par.
G-21)
for opening (relief) pressure when the ve
hicle is equipped with either the
Hurricane
F4
or
Dauntless V-6 engine. If a new cap is required, always install a cap of the same type and pressure
rating
specified. It should never be altered or re
placed by a plain cap.
A
vacuum release valve (Fig. G-5) is employed to
prevent undesirable vacuum build-up when the system
cools
down. The vacuum release valve is
held against its seat under light spring pressure.
Vacuum
in the system is relieved by the valve
which
opens
at V2 to 1 psi. [0,035 a 0,07 kg-cm2]
vacuum.
A pressure tester can be used to check and
test
the vacuum pressure rate (see Fig. G-6).
Although the mechanism of the pressure cap re quires no maintenance, the cap should be inspected
periodically for cleanliness and freedom of opera tion. The pressure cap gasket and radiator filler neck seat should also be inspected to be sure they
are
providing a proper seal. If the rubber face of
the valve is defective, a new cap should be installed.
Filler
neck reseating
tools
are commercially
avail
able to correct minor
defects
at the surface of the seat. Follow instructions of the reseating tool manu
facturer.
To
remove the radiator pressure cap when the
engine
coolant temperature is high or boiling, place
a
cloth over the pressure cap and
turn
counter clockwise about Vi
turn
until the first (pressure release)
stop
is reached. Keep the cap in this posi
tion until all pressure is released.
Then
push cap
down and
turn
still
further until cap can be re moved. To install the pressure cap, place it in posi
tion and
turn
it clockwise as far as it
will
go.
Caution:
Use extreme care in removing the radiator
pressure cap. In overheated systems, the sudden release of pressure can cause a steam flash and this
flash,
or the
loosened
cap can cause serious personal
injury.
G-5.
RADIATOR
Maintenance of the radiator consists of keeping
the exterior of the radiator core clean, the interior free from rust and scale, and the radiator free from
leaks.
Check
the cooling system fluid level and for
leaks each
2000
miles
[3.200
km.] or every 30
days, whichever occurs first.
This
exterior of the
radiator
core should be cleaned and the radiator inspected for leaks each
6000
miles
[9.600
km.]
of normal service of the vehicle. Cleaning should be performed by blowing out with air stream or water stream directed from the
rear
of the radiator.
Visual
inspection is not sufficient as the accumula tion of small particles of foreign material on core
surfaces can restrict cooling without closing the core openings.
Radiator
leakage occasionally results from cor
rosion perforation of the metal but most leakage results from mechanical failure of soldered joints
when too much strain has been put on the joint.
Fractures
occur most
often
at the joint where the
radiator
inlet and
outlet
pipes are attached to the
tanks.
When the seams break, the entire soldered
joint
is
exposed
and can corrode, but breakage
rather
than corrosion is the
primary
cause of seam
leakage. Examine the radiator carefully for leaks before and after cleaning. Cleaning may uncover points of leakage already existing but plugged with
rust.
White, rusty, or colored leakage stains indicate 164
Page 165 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
G
FIG.
G-4—PRESSURE TESTING COOLING SYSTEM
1—Pressure Tester C-3499 previous radiator leakage. These
spots
may not be
damp if water only or methyl-alcohol-base anti freeze is in the cooling system since such coolants
evaporate readily. An ethylene-glycol-base anti freeze shows up existing leaks as it
does
not evapo
rate.
The radiator may be tested for leaks by using
a
Pressure Tester Tool C-4080, as shown in Fig.
G-2.
When
the pressure cap opens, the sudden surge of
vapor
or liquid must blow out through the overflow
pipe. If the overflow pipe is dented or clogged,
the pressure caused by obstruction may cause dam
age to the radiator or
hose
connections in the cool-
1
FIG.
G-5—RADIATOR PRESSURE
CAP
1—
Pressure
Cap
2—
Overflow
Tube
3—
Pressure
Seal 4—
Vacuum
Release Valve
5—
Radiator
Neck
FIG.
G-6—TESTING RADIATOR PRESSURE
CAP
1—
Radiator
Pressure Cap
2—
Adapter
3—
Pressure
Tester C-3499 ing system. To remove clogging material, run a
flexible wire through the overflow pipe.
G-6.
Radiator Removal
and
Replacement
a.
Drain
the radiator by opening the
drain
cock
and
removing the radiator pressure cap.
b.
Remove the upper and lower
hose
clamps and
hoses
at the radiator.
c.
Remove the four cap screws, lock washers and
flat washers that secure the radiator to the radiator
body support. Remove the radiator.
d.
To replace the radiator, reverse the removal
procedure.
G-7.
Radiator
Hoses
and
Heater Hoses
Air,
heat, and water deteriorate radiator and heater
hoses
in two ways: by hardening or cracking which
destroys flexibility and causes leaks; by softening
and
swelling which produces lining failure and
hose
rupture
and clogging. Examine
hoses
spring and
fall
for possible need of replacement or tightening.
If
hoses
are collapsed, cracked, or indicate a
soft
condition on the inside they should be replaced.
Correct
installation of a new heater
hose
is impor
tant to prevent contact between the
hose
and the
exhaust manifold. On the
Hurricane
F4 engine the
molded curved end of the
hose
connects to the
hot water intake of the heater; the flexible end to the hot water valve on top of the cylinder head.
On
the Dauntless V-6 engine the heater inlet
hose
is connected to the
rear
of the intake manifold 165
Page 167 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
FIG.
G-8—TEMPERATURE SENDING UNIT- HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
1—Temperature
Sending Unit
b.
Dauntless V-6 Engine.
The
thermo-couple coolant sending unit is mounted
in
the left
rear
area of the intake manifold and is
connected by a single wire to the dash unit of
the instrument cluster.
G-ll.
WATER PUMP
a.
Hurricane
F4 Engine.
The
water pump on the
Hurricane
F4
engine
is a
centrifugal
impeller type of large capacity to
cir
culate water in the entire cooling system. The double row
ball
bearing (Fig. G-9), is integral with
the shaft and is packed at assembly with a special
high melting point grease which
will
last the life of
the bearing. The bearing is sealed to retain the
lubricant
and prevent
dirt
and dust from entering.
The
bearing and shaft are retained in the water
pump body by the bearing retaining wire. The
water
seal bears against the ground seat on the
pump body and the inside of the impeller, maintain
ing a constant pressure against both and preventing
water
leakage. A
drain
hole
in the
bottom
of the
pump body precludes any water
seepage
past the
seal
from entering the bearing.
The
impeller and the pulley hub are pressed on
the shaft under high pressure,
b.
Dauntless V-6 Engine.
A
centrifugal-type water pump, shown in
Fig.
G-10,
circulates
coolant through the Dauntless V-6
engine
and
its cooling system.
This
pump is mounted on
the timing chain cover.
Similar
to the
engine
cooling
fan
mounted on its hub, the pump is driven through
a
V-belt from the crankshaft pulley.
Coolant
enters the water pump at its center.
Centri
fugal force then forces coolant radially outward, through vanes of the pump impeller, and backward
through two discharge passages in the timing chain cover. These passages conduct an equal amount of
coolant to each cylinder bank water jacket.
This
water
pump has a sealed double row
ball
bearing
and
a ceramic water seal, neither of which can be
serviced.
In
event
of bearing or water seal failure, the entire water pump assembly must be replaced.
G-l2.
Water
Pump Inspection
Check
the water pump for leaks, and excessive end play or
looseness
of the shaft in the pump. A
quick
way to check is to work the fan blades up
and
down by hand. If any play is noticed, this
indicates that the bearings are rough. Rough bearings should be checked to see if the water pump
should be replaced or rebuilt.
G-13.
Water Pump
Disassembly
—
Hurricane
F4
Engine
•
Refer to Fig. G-9.
a.
Remove the fan belt, fan blades, and fan pulley.
b.
Remove the
bolts
attaching the water pump
to the block. Remove the pump.
c.
Remove the bearing retainer spring.
d.
Remove the pump impeller and pulley with a suitable puller.
e.
Remove the pump seal, bearing and shaft, and
bearing
slinger.
G-l4.
Water Pump Reassembly
—
Hurricane
F4
Engine
•
Refer to Fig. G-9.
Before assembling the water pump, examine water
seal
seat in the pump body and should it be rough,
install
a new pump body.
To
reassemble the unit, insert the long end of the shaft into the pump body from the front end until
the outer end of the bearing is flush against the
FIG.
G-9—WATER
PUMP-
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
1—
Fan
and Pump Pulley
2—
Bearing
and Shaft
3—
Bearing
Retainer Spring
A—Pipe
Plug 5—
Pump
Body
6—
Seal
Washer 7—
Pump
Seal
8—
Impeller
9—
Gasket
167
Page 168 of 376

G
COOLING SYSTEM
12761
FIG.
G-10—WATER
PUMP—
CROSS-SECTIONAL
VIEW
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
1—
Hub
2—
—Shaft
and Bearing
3—
Cover
4—
Impeller
5—
Ceramic
Seal
6—
Seal
Assembly front end of the pump body. Position the seal,
washer,
and pump seal on shaft flush against the ground seat in the water pump body. Place the
impeller
on an arbor press and press the long end
of the shaft into the impeller until the end of the shaft is flush with the hub of the impeller. Support
the assembly on the impeller end of the shaft and
press the pulley hub on the shaft until the shaft end is flush with the pulley hub. Move the shaft
in
the pump body to align the retaining wire
grooves
in the bearing and pump body and place
the bearing retaining wire in position.
G-l
5. Water Pump Removal and Replacement — Dauntless V-6 Engine
Drain
the cooling system. Remove the fan belt and remove the cooling fan and pulley from the hub on
the water pump. Disconnect the
hoses
from the
water
pump. Remove the cap screws that secure
the water pump to the timing chain cover; remove
the water pump. Do not disassemble the water
pump;
it is serviceable only as an assembly. When
replacing
the water pump, torque the water pump cap screws 6 to 8 lb-ft. [0,829 a 1,106 kg-m.].
G-16.
Antifreeze Solutions
When
water freezes it expands approximately 9%
in
volume. When water, confined in a cooling sys
tem, freezes it exerts tremendous pressures causing
serious damage. To prevent freezing, antifreeze can
be added to the water to lower its freezing point.
The
two
types
of antifreeze commonly used today have either a methanol or ethylene glycol base,
and
contain corrosion inhibitors. The only anti
freeze recommended for the cooling system of
'Jeep'
vehicles is ethylene glycol (permanent type).
Methanol
base antifreeze evaporates with the water
when the vehicle is operated at warmer tempera
tures and requires more attention to avoid
loss
of
protection. Ethylene glycol base antifreeze seldom
evaporates at normal operating temperatures.
Methanol
solution is injurious to vehicle finishes.
Should
any be spilled on the vehicle, it should be
washed off immediately with a
good
supply of cold water without wiping or rubbing. Under ordi
nary
conditions, ethylene glycol is not injurious to
vehicle finishes.
Warning.*
Drinking
ethylene glycol antifreeze or its
solutions can be harmful or fatal. Do not use anti
freeze containers for
food
or beverages.
A
table in Par.
G-2
2
gives
the protection obtained
by the addition of various amounts cf ethylene glycol.
Before installing antifreeze, inspect the cooling sys
tem to be sure it is clean, leak-proof, and otherwise
in
proper operating condition.
Drain
the cooling system, see Par. G-3. Pour in 3 quarts [3 ltr.] of
clean
water, add the required quantity of anti freeze, then add clean water to within 1" [2,54 cm.] of the top of the overflow pipe to allow for expan
sion when hot. Run the
engine
until it is
warm.
Then
recheck the solution level.
Check
the anti
freeze protection with a hydrometer reading.
G-l7.
Inhibited Coolant Solutions
All
'Jeep5 vehicles equipped with either the
Hur
ricane
F4 or Dauntless V-6
engine
should use only
inhibited
year-round, permanent-type
engine
cool
ant
solutions that are formulated to withstand two
full
calendar years of normal operation without
draining
or adding inhibitors. The
engine
cooling
system should be completely drained and the
rec
ommended coolant installed every two years. Be-
fo
a
installing the permanent-type solution, inspect the cooling system to be sure it is clean, leakproof,
and
in proper operating condition.
Note:
Water alone, methanol, or alcohol-type anti
freeze is definitely not recommended for 'Jeep*
Vehicles.
G-l8.
Fan Belt
The
fan, water pump, generator or alternator are
driven
by a V-belt. The drive of the V-belt is on
the side of the V. A fan belt that is too tight
will
cause
rapid
wear of the alternator or generator and
water
pump bearings. If the belt is too
loose,
it may
slip
preventing the water pump from properly cool
ing the
engine
or the generator or alternator from
properly
charging the electrical
circuit.
Use fan belt
tension
gauge
Tool W-283 to properly adjust belt.
The
fan belt is properly adjusted when it can be
deflected Vi" [13 mm.] with strong thumb pres
sure
applied midway
between
the fan and alter
nator
pulleys.
Check
this adjustment and inspect the condition of the fan belt at each
engine
lubri-
168
Page 169 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
G
cation period. It is
good
preventive maintenance to
replace a badly frayed, worn or cracked fan belt
before it breaks in operation.
To
replace the fan belt,
loosen
the attaching
bolts
at each generator or alternator brace-to-engine mounting and pivot the alternator or generator to
ward
the
engine
to gain slack needed to install the new belt Remove the old belt. Position the new
belt over the fan pulley, over the crankshaft pulley,
then over the generator or alternator pulley.
Pull
the generator or alternator away from the
engine
until
belt tension is
firm.
Then tighten the generator
or
alternator mounting
bolts
and check the tension
as indicated above. Reset the generator or alternator as necessary for correct belt tension.
Finally,
torque
the generator or alternator mounting
bolts
25 to 35 lb-ft. [3,4 a 4,8 kg-m.].
Note:
On the Dauntless V-6
engine
when adjusting
the fan belt tension, the alternator mounting
bolts
should be torqued 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,14 to 5,53
kg-m.].
If a fan belt tension
gauge
(W-283) is
avail
able, proper tension should be 80 pounds [36,2 kg.].
G-l
9. Engine Overheating
An
engine
will
not be damaged by high coolant
temperatures unless the coolant boils. The pres
surized
cooling system on the 'Jeep' vehicles raises the boiling point of the coolant solution. Should
overheating be encountered, and the fault is be
lieved to be in the cooling system check for the
following:
a.
Proper coolant level. See
Filling
Cooling Sys
tem Par. G-2.
b. Poor air flow.
Check
for dirty radiator core. (See Radiator Par. G-5).
Check
for faulty belt
pulley operation, worn or
loose
fan belt, or dam aged fan.
Clean,
repair, replace or adjust as neces
sary.
c. Foaming coolant.
Check
for air leaks at water
pump,
hose
connection and filler cap. Tighten, re
pair
or replace as necessary.
d.
Surging or "after boil".
Check
pressure cap and
replace if valves or gasket are faulty.
e.
External
leaks.
Check
the following for leaks:
Hoses and clamps, water pump, radiator, head gas
ket, core plugs and drain cocks, as well as the cylin der head or block for
cracks.
f.
Internal
leaks.
Check
for faulty head gasket,
cracked
cylinder head or block.
g. Poor coolant flow.
Check
hose
condition, water pump, fan belt, and repair or replace as necessary. Inspect block for rust or scale, and clean and flush
the system, if necessary.
h.
Check
the temperature
gauge.
169
Page 170 of 376
G
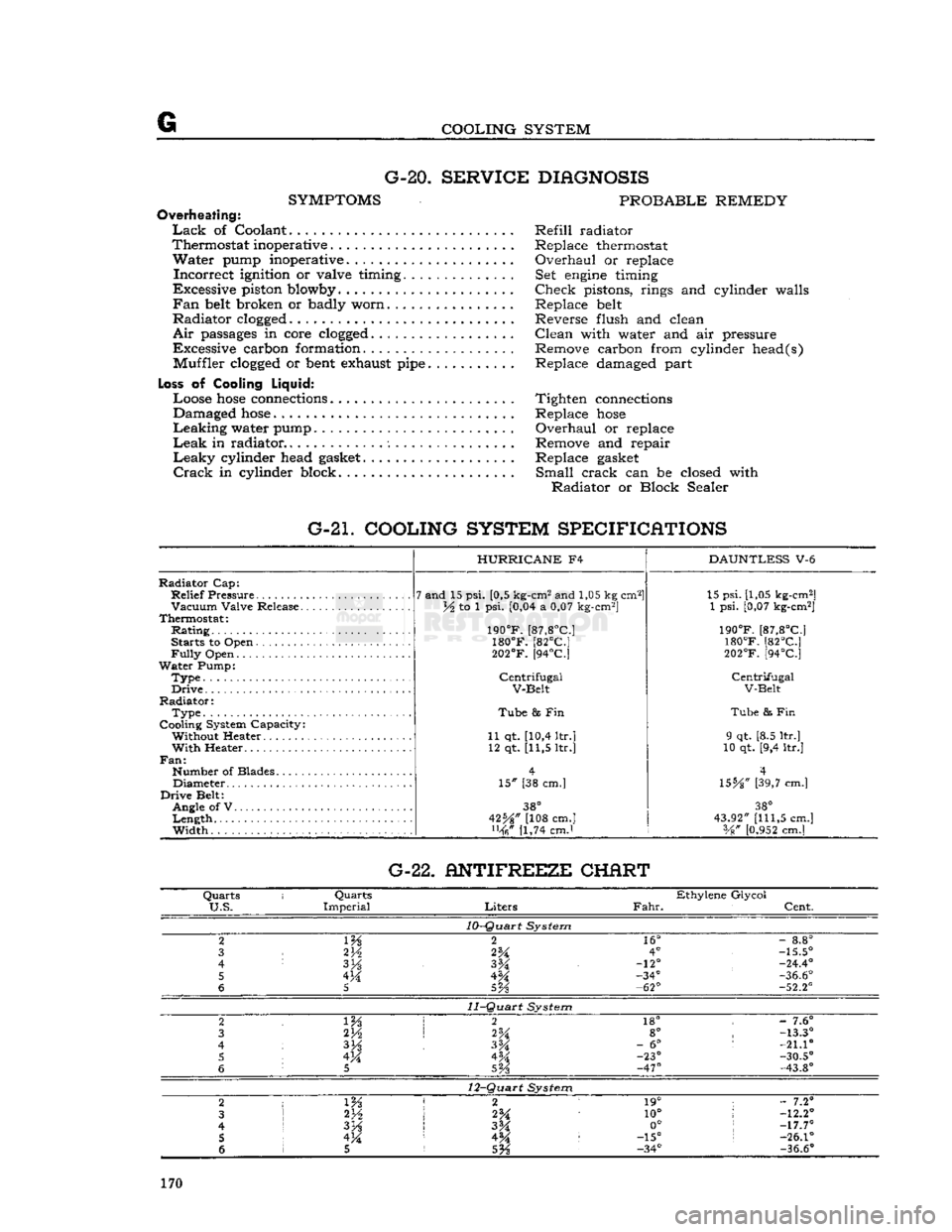
COOLING SYSTEM G-20.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
SYMPTOMS
PROBABLE REMEDY
Overheating:
Lack
of Coolant Refill radiator
Thermostat inoperative . Replace thermostat
Water
pump inoperative. Overhaul or replace
Incorrect
ignition or valve timing. Set
engine
timing
Excessive piston blowby Check pistons, rings and cylinder walls
Fan
belt
broken or badly worn Replace
belt
Radiator
clogged
Reverse flush and clean
Air
passages
in core
clogged
Clean with water and air pressure
Excessive carbon formation. Remove carbon from cylinder head(s) Muffler
clogged
or
bent
exhaust
pipe
Replace damaged part
Loss
of Cooling
Liquid:
Loose
hose
connections
Tighten
connections
Damaged
hose
Replace
hose
Leaking
water pump Overhaul or replace
Leak
in radiator Remove and repair
Leaky
cylinder head
gasket
Replace
gasket
Crack
in cylinder block. Small crack can be closed with
Radiator
or Block Sealer
G-21. COOLING SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS
Radiator
Cap:
Relief
Pressure
Vacuum
Valve Release.
Thermostat:
Rating
Starts to Open
Fully
Open
Water
Pump:
Type.
Drive
Radiator:
Type
Cooling System Capacity: Without Heater
With
Heater..
Fan:
Number of Blades Diameter
Drive
Belt: Angle of V
Length
Width
HURRICANE
F4
7 and 15 psi. [0,5 kg-cm2 and 1,05 kg cm2]
lA to 1 psi. [0,04 a 0,07 kg-cm2]
190°F.
[87,8°C]
180°F.
[82°C]
202°F.
[94°C]
Centrifugal
V-Belt
Tube
8s Fin
11 qt. [10,4 ltr.] 12 qt. [11,5 ltr.]
15" [38 cm.]
38°
42%" [108 cm.] [1,74 cmJ
DAUNTLESS
V-6 15 psi. [1,05 kg-cm2]
1 psi. [0,07 kg-cm2]
190°F.
[87,8°C]
180°F.
[82°C]
202°F.
[94°C]
Centrifugal
V-Belt
Tube
& Fin
9 qt. [8.5 ltr.]
10 qt. [9,4 ltr.]
4
\SbA"
[39,7 cm.]
38°
43.92"
[111,5
cm.] Vg"
[0.952
cm.] G-22. ANTIFREEZE CHERT
Quarts
i
Quarts
Ethylene Glycol
U.S.
Imperial
Liters
Fahr.
Cent.
10-Quart
System
2
m
2
16°
-
8.8°
3
2V2
2%
4°
-15.5°
4
3H
-12°
-24.4°
5 4M -34°
-36.6°
6
5
5Vs
-62°
-52.2°
11-Quart
System
2 2
18° -
7.6°
3 2H
2%
8°
-13.3°
4
3%
-
6°
:
-21.10
5 4M 4M -23°
-30.5°
6
5
SVs
-47°
-43.8°
12-Quart
System
2
1 m 2 1
19° ;
- 7.2°
3
2*A
10°
!
-12.2°
4
I
3H
3M 0°
;
-17.7°
5 !
4M 4^ :
-15°
s
-26.1°
6 1 5
5%
-34°
-36.6°
170
Page 171 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL
. -H-l Alternator Charging System H-6, 63 Battery. . . .H-2
Electrical
Instruments. H-l 11 Ignition System H-3
Lighting
System H-8, 125
Primary
Circuit.
.. H-4 Secondary
Circuit
H-5
SparkPlugs H-33
Starting System H-7, 88
DISTRIBUTOR
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
H-9
Coil
H-19 Condenser
.H-l
2
Disassembly.
.........................
.H-16
Distributor Cap H-10 Distributor
Points
H-13
Governor Mechanism H-l4
Inspection H-l
7
Installation and Timing H-18
Removal H-15
Rotor H-ll
DISTRIBUTOR
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
H-20
Ballast
Resistor. H-32
Centrifugal
Advance H-25
Cleaning and Inspection H-28
Coil
H-31
Condenser H-23
Disassembly. H-27
Distributor Cap H-21 Distributor
Points
H-24
Installation and Timing. . .H-30
Reassembly. H-29
Removal H-2 6
Rotor H-2
2
GENERATOR CHARGING SYSTEM SERVICE
H-34 Generator Armature H-3
7
Generator Assembly. H-40
Generator
Brush
Holders H-39
Generator Disassembly H-36
Generator
Field
Coils.
H-38
Generator Maintenance H-35 Generator -
Current
-
Voltage
Regulator. . .H-41
Generator Regulator Quick Checks...... .H-48
Generator Regulator Test Procedure H-47
ALTERNATOR PRECAUTIONS.
H-64
ALTERNATOR CHARGING SYSTEM.
. .H-63 Alternator On-Vehicle Tests. .H-67
Alternator Output Test. .H-70 Isolation
Diode
Test H-69
Regulator Test .H-71 Removal and Installation of
Voltage
Regulator. H-72
SUBJECT
PAR.
Service
Diagnosis
H-66 Test Equipment H-68
Alternator
Field
Circuit
Test H-73
Brush
Insulation and Continuity Test H-75
Brush
Removal and Inspection H-74
Rotor In-Vehicle Tests H-76
ALTERNATOR BENCH TESTS.
.H-77
ALTERNATOR REMOVAL
H-78 Alternator Disassembly H-80 Alternator Installation. H-87
Assembling Alternator H-86
General
Inspection H-81
Diode
Test H-85
Out-Of-Circuit
Rotor Test. .H-82
Out-Of-Circuit
Stator Leakage Test.. . H-83 Rotor Tests H-79
Stator
Coil
Leakage and Continuity Test. .H-84
STARTING
MOTOR
—
PRESTOLITE.
. .H-92
Armature
.H-l
00 Bench Test H-l04
Bendix
Folo-Thru
Drive H-105
Brush
Holder Inspection. .H-102
Brushes H-98
Commutator H-95, 99
Disassembly H-9 7
Field
Coils H-101
Lubrication
of
Folo-Thru
Drive H-l06
Maintenance Procedure H-93
Overhaul
Procedure H-96
Reassembly of Starting Motor. .
H-l
03
Starter
Solenoid
Switch H-10 7 Starter Ignition Switch. .H-89
Wiring.
. . . H-94
STARTING
MOTOR
—DELCO
H-108
Armature
H-101
Brush
Holder Inspection H-l 15 Brushes
H:lll
Commutator H-112
Field
Coils........
H-114
Locked
Armature Test. . . H-l20
Solenoid
Coils H-l 16
Starting Motor Reassembly H-l 17
Starting Motor Cleaning and Inspection.
.H-l
10
Starting Motor Disassembly .H-109 Starting Motor No-Load Test H-119
Starting Motor Test — General H-l 18 Starter Switch —
Solenoid
Type. H-l21
Starter Ignition Switch. .H-89
ELECTRICAL
INSTRUMENTS
H-122 Testing Instrument Gauges H-l24
LIGHTING
SYSTEM
H-l25 Aiming Head Lamps H-132
Backup
Lamps H-135
(continued
on
next
page)
171
Page 172 of 376

H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM SUBJECT
PAR.
Directional
Signal
Lamps
H-138
Hazard
Warning
Lamps
H-139
Head
Lamp
Replacement H-130
Head
Lamp
Aiming Procedure H-131 Headlight Dimmer Switch H-127
License
Plate
Lamp
H-136
Main
Light
Switch. H-126
Marker
Lights .H-l40
Parking
and
Turn
Signal
Light
H-133
Stop
Light
Switch. H-l28
Tail,
Stop and
Turn
Signal
Lamp
.H-134
H-1. GENERAL
All
'Jeep' Universal vehicles are equipped with 12- volt electrical systems. Use caution around the higher
voltage
of the 12-volt system as accidental
short
circuits are more capable of damaging electri
cal
units. Also, arcs around the 12-volt battery are
more apt to ignite any gas that may be escaping
from
it. In the following paragraphs
will
be found
information about the battery, distributor, coil,
generator, alternator,
voltage
regulator and start ing motor. These units with the connecting wires,
make
up the
engine
electrical system. The wiring
diagram
will
show the different circuits of the en
gine
electrical system and the various units which
make
up
those
circuits.
With
plastic-covered wiring harnesses use only
rubber-insulated
wiring clips.
Caution:
All current production vehicles are 12- volt, negative ground. Whenever servicing a 12-
volt electrical system, use caution, as an accidental
short
circuit is capable of damaging electrical units. Disconnect battery ground cable before changing
electrical
components.
H-2.
Battery
The
battery is a storage reservoir for electrical
energy produced by the alternator or generator.
The
battery should store sufficient energy for
operation of the entire electrical system when the
alternator
or generator is not pr 1,scing output,
such
as when the ignition is first turned on. Of
particular
importance is maintaining the electrolyte
at the correct level, regularly checking with a
hydrometer, and maintaining clean, tight cable connections.
Battery
service information is given in this section.
Caution:
Do not allow flames or sparks to be
brought near the vent
openings
of the battery since
hydrogen gas may be present in the battery and might explode.
Note:
The liquid in the battery (electrolyte) is a
solution of sulphuric acid which, on contact, can
injure
skin or
eyes,
or damage clothes. If it is spilled
on the skin or spattered in the
eyes,
promptly flush
it
away with quantities of clear water only. If the
acid
is spilled on clothes, wet it thoroughly with a
weak
solution of ammonia, or with a solution of sodium bicarbonate or baking soda.
SUBJECT
PAR.
HORN
H-137
ELECTRICAL
COMPONENT
REPLACEMENT
H-150
WINDSHIPLD
WIPER SYSTEM
H-141
thru
149
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS.
. .H-151
ELECTRICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
H-152
Caution:
When installing the battery, the nega
tive terminal must be grounded. Reverse polarity of the battery can cause severe damage to the charging system.
Battery
Inspection
a.
Check
the specific gravity of the electrolyte in
each cell of the battery. A hydrometer reading of 1.260 indicates that the battery is fully charged.
If
the reading is 1.225 or below, the battery
needs
recharging.
If one or more cells is 25 "points" (.025) or more lower than the other cells, this in
dicates that the cell is shorted, the cell is about to
fail,
or there is a
crack
in the battery partition in
the case. Unless the battery is repaired or replaced, battery trouble
will
soon
be experienced.
b.
Check
the electrolyte level in each cell, add
distilled
water to maintain the solution [9,5 mm.] above the plates. Avoid overfilling. Replace
the filler caps and tighten securely. It is important to keep the electrolyte level above the plates at all
times because plates that are
exposed
for any
length of time
will
be seriously damaged.
c.
Check
the wing nuts on the hold-down frame for tightness. Tighten them only with finger pres
sure,
never with pliers or a wrench. Excessive
pressure
could damage the battery case.
d.
Clean
the battery terminals and cable con nectors. Prepare a strong solution of baking soda
and
water and brush it around the terminals to
remove any corrosion that is present. The cell caps must be tight and their vents sealed to prevent
cleaning solution entering the cells. After cleaning,
connect cables to battery and coat the terminals
with
heavy grease.
e.
Inspect the battery cables and replace if badly
corroded
or frayed.
Check
tightness
of terminal
screws to ensure
good
electrical connections.
Check
the
tightness
of the negative ground cable connection at the frame to ensure a
good
ground
connection.
f.
Load
test
the battery. Connect a voltmeter across the battery. Run the starting motor for 15 seconds. If the
voltage
does
not drop below 10
volts the battery is satisfactory. If the
voltage
falls
below the figure given, yet the specific gravity is
above
1.225,
the condition of the battery is questionable.
g. Be sure the
engine
ground strap connection, 172
Page 173 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
H
FIG.
H-l—ENGINE
GROUND
STRAP—F4
ENGINE
Fig.
H-l, is tight at both connections. If
these
connections are
loose
-
or
dirty,
hard
starting or
failure
to start may result.
H-3.
Ignition System
The
ignition system consists of the battery, ignition
switch,
ignition coil ballast resistor (V-6 engine
only),
ignition coil, ignition distributor,
spark
plugs,
and
the low and high tension wiring.
Electrical
energy is obtained from the battery while cranking
and
from the alternator after the engine is running.
These
supply circuits must be considered part of
the ignition system.
The
ignition system furnishes the
spark
-for the
spark
plugs. The
spark
must occur in each cylinder
at exactly the proper time. To accomplish this, the following units are required.
a.
The battery, supplying the electrical energy.
Note: 'Jeep* vehicles equipped with Dauntless
V-6
engines have a ballast resistor connected be tween the ignition switch and the positive (+)
terminal
of the coil. The ballast resistor limits to
a
safe maximum the
primary
current flow through
the coil and the distributor contact points.
b.
The ignition coil, transforming the battery low
tension current to high tension current that jumps
the
spark
plug gap in the cylinders under com
pression.
c.
The distributor, delivering the
spark
to the
proper
cylinders and incorporates the mechanical
breaker,
that
opens
and closes the
primary
circuit at the exact time.
d.
The
spark
plugs, providing the gap in the engine
cylinders.
e. The wiring, connecting the various ignition
units.
f. The ignition switch controling the battery
current
when it is desired to start or
stop
the engine.
g. The firing order for the
Hurricane
F4 engine is
1-3-4-2.
Cylinder
No. 1 is the cylinder closest to the
radiator.
h.
The firing order for the Dauntless V-6 engine
is
1-6-5-4-3-2.
Cylinders
1-3-5 are on the left bank
and
cylinders 2-4-6 are on the right bank. H-4.
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
Before testing the
primary
circuit,
make certain
that the battery is satisfactory or install a fully
charged
battery for the
primary
circuit
tests. Also,
check
the starter motor for excessive voltage drop
and
check the starter motor itself for excessive
draw.
a.
Measure the voltage at the coil
primary
termi
nals
while cranking the engine with the starter
motor. If the voltage is less than 9 volts the trouble
will
be found in the
primary
circuit.
If there is no voltage at all, check for a break in the
primary
circuit,
possibly in the coil
primary
winding.
b.
To check the
primary
circuit,
turn
the ignition
on,
turn
the engine until the points are closed, and
then measure the voltage drop across each portion
of the circuit with a voltmeter.
Note: Most voltage drops
will
be found at the con
nections of wires to terminals as
dirt,
oxidation etc. can cause excessive resistance at
these
points.
Measure
voltage drops in wires to take this into
account.
c.
Connect the voltmeter from the battery cable
terminal
on the starter solenoid to the battery
terminal
of the coil
primary.
If the voltmeter reads more than 0.2 volt, perform the checks given in
steps, d, e, and f following.
d.
Connect the voltmeter from the solenoid termi
nal
to the battery terminal of the ignition switch.
If
the voltmeter reads more than .05 volt, check
and
clean the connections at solenoid, light switch,
and
ignition switch.
e. If the voltmeter reading in
step
d is less than .05 volt, connect the voltmeter from the battery
terminal
to the ignition terminal on the ignition
switch.
If the voltage drop is more than 0.1 volt,
repair
or replace the ignition switch.
f. If the voltage drop in
step
e is not more than 0.1 volt, connect the voltmeter from the ignition
terminal
of the ignition switch to the battery termi
nal
of the coil
primary.
If the voltmeter reads more
than
.05 volt, clean and tighten the connections
and
check again. If the voltmeter again reads more
than
.05 volt, replace the wire.
g. Connect the voltmeter from the distributor
primary
terminal on the coil to the coil terminal on
the distributor. Voltage drop should not exceed .05 volt.
Clean
and tighten connections if necessary.
h.
Connect the voltmeter from the coil terminal
on the distributor to a clean,
paint-
free spot on the
distributor
body. The reading should not exceed .05
volt. If more, it indicates excessive resistance
through the points or in the distributor internal connections.
Clean
and align the points and make
sure
the breaker arm connection to the
primary
terminal
as well as the stationary contact point mounting in the body is clean and tight.
i.
Open the points and check the voltmeter. It
should read close to peak voltage. Low voltage in dicates that a circuit through the distributor (a
short)
exists while the points are open.
j.
Disconnect the condenser lead and open the points. A jump to
full
voltage indicates a short in 173