brake JEEP DJ 1953 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: DJ, Model: JEEP DJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 71 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
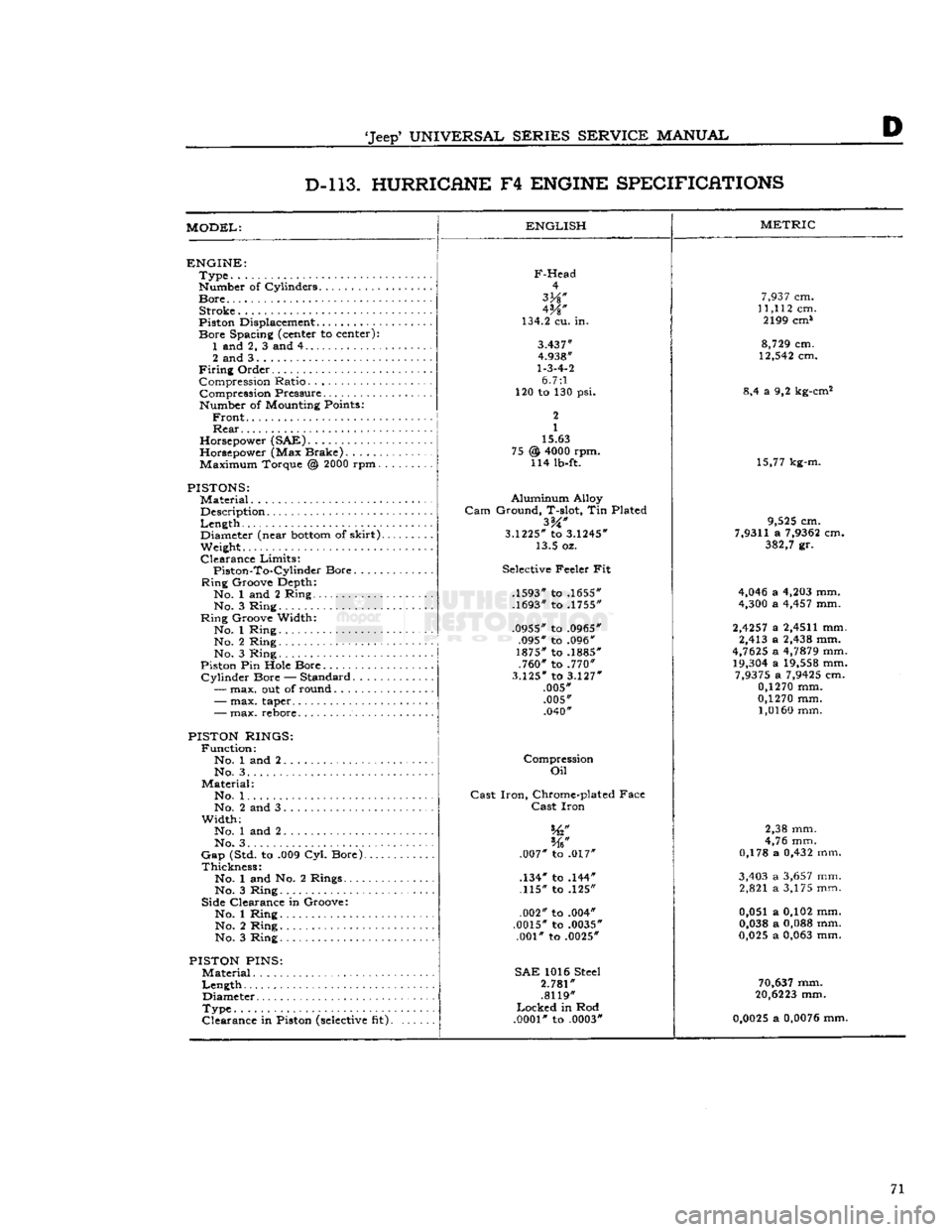
D D-l 13. HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL:
ENGLISH
ENGINE:
Type
Number of Cylinders
Bore
Stroke
Piston Displacement...........
Bore
Spacing (center to center): 1 and 2, 3 and 4
2 and 3
Firing
Order Compression Ratio Compression Pressure... .
Number of Mounting Points:
Front
Rear
Horsepower (SAE)
Horsepower (Max Brake) Maximum Torque @
2000
rpm.
PISTONS:
Material
Description
Length
,.
Diameter (near
bottom
of
skirt).
Weight.
Clearance
Limits:
Piston-To-Cylindcr
Bore
Ring
Groove Depth:
No. 1 and 2 Ring No. 3 Ring
Ring
Groove Width:
No. 1 Ring No. 2 Ring
No. 3 Ring
Piston Pin Hole Bore
Cylinder
Bore — Standard.....
—
max. out of round
F-Head
4
W
134.2 cu. in.
3.437"
4.938"
1-3-4-2
6.7:1
120 to 130 psi.
2
1
15.63
@
4000
rpm. 114 lb-ft. 75
-
max. taper..
-
max. rebore.
PISTON RINGS:
Function:
No. 1 and 2 No. 3. .
Material:
No. 1. .
No. 2 and 3
Width;
No. 1 and 2
No. 3. . . .
Gap
(Std. to .009 Cyl. Bore).
Thickness:
No. 1 and No. 2 Rings....
No. 3 Ring
Side Clearance in Groove:
No. 1 Ring No. 2 Ring
No. 3 Ring
PISTON
PINS:
Material
Length
Diameter
Type
Clearance
in Piston
(selective
fit).
Aluminum
Alloy
Gam
Ground, T-slot, Tin Plated
3.1225*
to
3.1245*
13.5 oz.
Selective Feeler Fit
.1593" to .1655"
.1693" to .1755"
.0955" to .0965" .095" to .096"
1875" to .1885" .760" to .770"
3.125"
to
3.127"
.005" .005" .040"
Compression
Oil
Cast
Iron,
Chrome-plated Face
Cast
Iron
.007" to .017"
.134" to .144" .115" to .125"
.002" to .004"
.0015" to .0035" .001" to .0025"
SAE
1016 Steel
2.781"
.8119"
Locked
in Rod
.0001"
to .0003"
METRIC
7,937
cm.
11,112
cm. 2199 cm*
8,729
cm.
12,542
cm.
8,4 a 9,2 kg-cm2
15,77 kg-m.
9,525
cm.
7,9311
a
7,9362
cm.
382,7
gr.
4,046
a
4,203
mm.
4,300
a
4,457
mm.
2,4257
a
2,4511
mm. 2,413 a
2,438
mm.
4,7625
a
4,7879
mm.
19,304
a
19,558
mm.
7,9375
a
7,9425
cm.
0,1270
mm.
0,1270
mm.
1,0160
mm.
2,38 mm.
4,76 mm.
0,178 a
0,432
mm.
3,403
a
3,657
mm. 2,821 a 3,175 mm.
0,051 a 0,102 mm.
0,038
a
0,088
mm.
0,025
a
0,063
mm.
70,637
mm.
20,6223
mm.
0,0025
a
0,0076
mm. 71
Page 105 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
Dl-104.
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
Poor Fuel Economy
Ignition Timing Late or Spark Advance Inoperative
Carburetor
Float Setting Too High
Accelerator Pump Improperly Adjusted
Fuel
Pump Pressure High
Fuel
Line
Leakage
Fuel
Pump Diaphragm Leakage
Cylinder
Compression Low
Valves Do Not Seat Properly
Spark
Plugs
Defective
Spark
Plug Cables
Defective
Ignition
Coil
or Capacitor
Defective
Carburetor
Air Cleaner Dirty
Brakes
Drag
Wheel Alignment Incorrect
Tire
Pressure Incorrect Odometer Inaccurate
Fuel
Tank
Cap Clogged or
Defective
Muffler or Exhaust Pipe Clogged or Bent
Lack
of
Power
Cylinder
Compression Low
Ingitdon Timing Late
Carburetor
or
Fuel
Pump Clogged or
Defective
Fuel
Lines Clogged
Air
Cleaner Restricted
Engine Temperature High Valves Do Not Seat Property
Valve
Timing Late Intake Manifold or Cylinder Head
Gasket Leaks
Muffler or Exhaust Pipe Clogged or Bent
Spark
Plugs Dirty or
Defective
Breaker
Point Gap Incorrect
Breaker
Points
Defective
Ignition
Coil
or Capacitor
Defective
Electrical
Connection Loose
Broken
Valve Spring
Broken
Piston Ring or Piston
Cylinder
Head Gasket
Defective
Distributor Cap Cracked
Low
Compression
Valves Not Seating Properly Piston Rings Seal Poorly
Valve
Spring Weak or Broken
Cylinder
Scored or Worn
Piston Clearance Too Great
Cylinder
Head Gasket Leaks
Burned
Valves and
Seats
Valves Stick or Are Too Loose in Guides
Valve
Timing Incorrect
Valve
Head and Seat Have Excessive Carbon
Engine Overheats
Valve
Spring Weak or Broken
Valve
Lifter Seized or Collapsed
Exhaust
System Clogged
Valves Sticking
Valve
Stem Warped
Valve
Stem Carbonized or Scored
Valve
Stem Clearance Insufficient in Guide
Valve
Spring Weak or Broken
Valve
Spring Distorted
Oil
Contaminated
Overheating
Cooling System Inoperative
Thermostat Inoperative Ignition Timing Incorrect
Valve
Timing Incorrect
Carbon
Accumulation Excessive
Fan
Belt Loose
Muffler or Exhaust Pipe Clogged or Bent
Oil
System Failure
Piston Rings Worn or Scored
Popping,
Spitting,
Detonation
Ignition Timing Incorrect
Carburetion
Improper
Carbon
Deposit
in Combustion
Chambers Excessive
Valves Not Seating Properly
Valve
Spring Broken
Spark
Plug Electrodes Burned
Water or Dirt in
Fuel
Fuel
Line
Clogged
Valve
Timing Incorrect
Excessive
Oil
Consumption
Piston Rings Stuck in Grooves, Weak,
Worn,
Broken, or Incorrectly Fitted
Crankshaft
Main Bearings or
Connecting Rod Bearings Have
Excessive Clearance
Gaskets or Oil Seals
Leak
Cylinder
Bores Worn, Scored,
Out-of-Round or Tapered
Pistons Have Too Great Clearance to Cylinder Bores
Connecting Rods Misaligned High Road Speed
High Temperature
Crankcase
Ventilation System Inoperative
Bearing Failure
Crankshaft
Bearing Journal Rough or Out-of-Round
Oil
Level Low
Oil
Leakage
Oil
Dirty
Oil
Pressure Low or Lacking
(Oil
Pump Failure)
Drilled
Passages
in Crankshaft or
Crankcase
Clogged
Oil
Screen Dirty
Connecting Rod Bent 105
Page 106 of 376
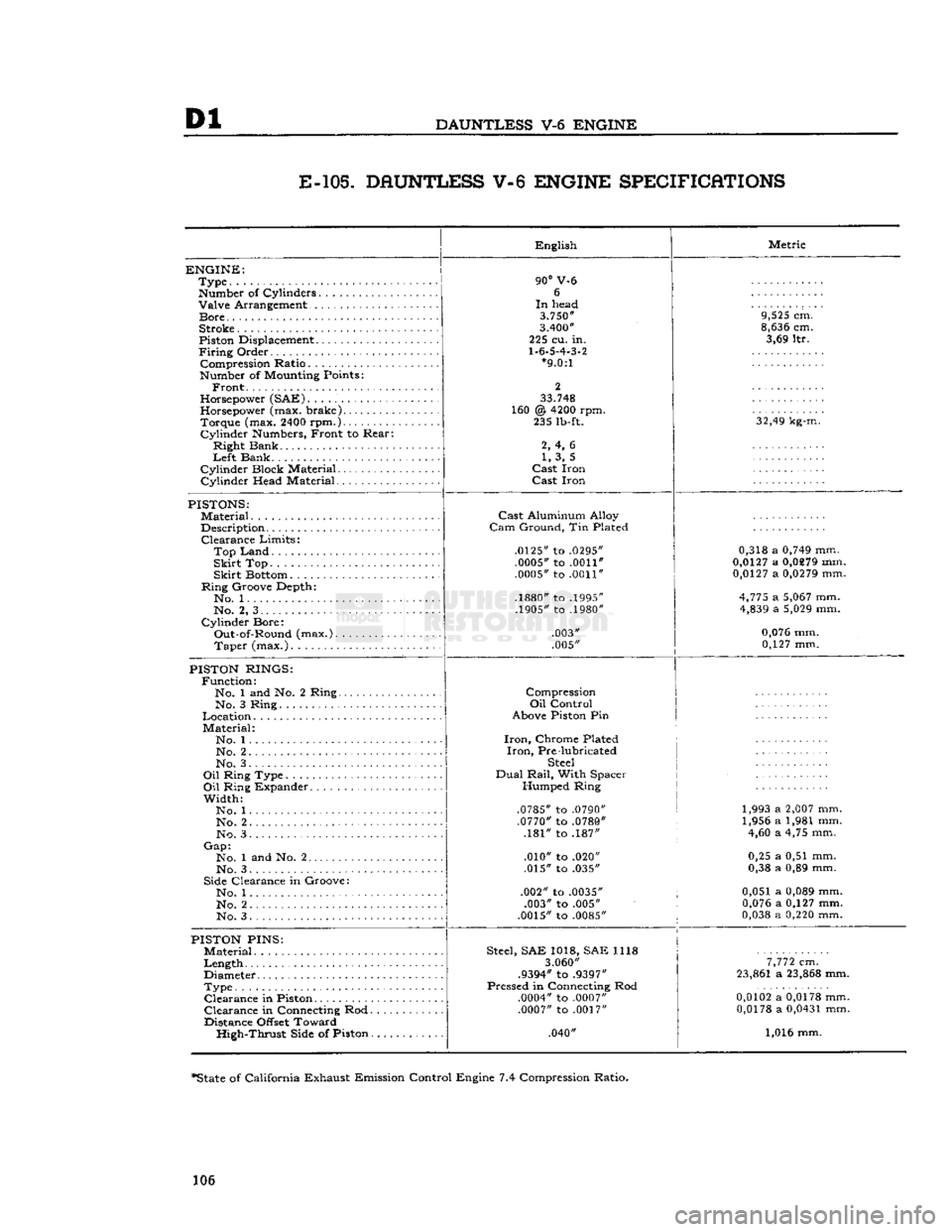
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
E-105.
DAUNTLESS V-6 ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE:
Type
Number
of Cylinders Valve Arrangement
Bore
Stroke
Piston
Displacement
Firing
Order Compression Ratio
Number
of
Mounting
Points:
Front.
Horsepower
(SAE)
Horsepower
(max. brake) Torque (max.
2400
rpm.)
Cylinder
Numbers,
Front to Rear:
Right Bank
Left
Bank
Cylinder Block Material
Cylinder Head Material English
90°
V-6 6
In
head
3.750"
3.400"
225 cu. in.
1.6.5.4.3.2
*9.0:1
2
33.748
160 @
4200
rpm. 235
lb-ft.
2, 4, 6 1, 3, 5
Cast
Iron
Cast
Iron Metric
9,525
cm.
8,636
cm. 3,69 ltr.
32,49
kg-m.
PISTONS:
Material
Description Clearance Limits:
Top
Land
Skirt
Top
Skirt
Bottom
Ring Groove Depth*. No. 1
No. 2, 3
Cylinder Bore: Out-of-Round (max.). Taper (max.)
Cast
Aluminum Alloy
Cam
Ground, Tin Plated
.0125"
to
.0295" .0005"
to
.0011"
.0005"
to
.0011"
.1880"
to
.1995"
.1905"
to
.1980"
.003"
.005" 0,318 a
0,749
mm.
0,0127
a
0,0279
mm.
0,0127
a
0,0279
mm.
4,775
a
5,067
mm.
4,839
a
5,029
mm.
0,076
mm. 0,127 mm.
PISTON
RINGS:
Function: No. 1 and No. 2 Ring.. No. 3 Ring
Location
Material: No. 1...
No. 2 No. 3.
Oil
Ring Type
Oil
Ring Expander
Width: No. 1
No. 2. .
No. 3
Gap:
No. 1 and No. 2
No. 3
Side
Clearance in Groove: No. 1
No. 2
No. 3 Compression
Oil
Control
Above
Piston
Pin
Iron,
Chrome Plated
Iron,
Pre lubricated
Steel
Dual
Rail,
With Spacer Humped Ring
.0785"
to
.0790" .0770"
to
.0780"
.181" to .187"
.010" to .020"
.015" to .035"
.002" to
.0035"
.003" to .005"
.0015"
to
.0085"
1,993 a
2,007
mm.
1,956 a 1,981 mm. 4,60 a 4,75 mm.
0,25 a 0,51 mm.
0,38 a 0,89 mm.
0,051 a
0,089
mm.
0,076
a 0,127 mm.
0,038
a
0,220
mm.
PISTON
PINS:
Material
Length
Diameter
Type Clearance in
Piston
Clearance in
Connecting
Rod.
Distance
Offset
Toward High-Thrust
Side
of Piston.
Steel,
SAE 1018, SAE 1118
3.060"
.9394"
to
.9397"
Pressed in
Connecting
Rod
.0004"
to
.0007" .0007"
to
.0017"
.040"
7,772
cm.
23,861
a
23,868
mm.
0,0102
a
0,0178
mm.
0,0178
a
0,0431
mm.
1,016 mm.
*State
of California Exhaust Emission Control Engine 7.4 Compression Ratio.
106
Page 134 of 376

E
FUEL
SYSTEM
E-78. SERVICE DIHGNOSIS
Symptoms Probable Remedy
Excessive
Fuel
Consumption:
Tires
improperly inflated Inflate
Brakes
drag Adjust
Engine
operates too cold Check thermostat
Heat control valve inoperative Check thermostatic spring
Leak
in fuel line Check all connections
Carburetor
float level high. See
"Carburetor"
section
Accelerator pump not properly adjusted Adjust
Leaky
fuel pump diaphragm Replace
Loose
engine
mountings causing high carburetor fuel level Tighten Ignition timing slow or spark advance stuck See "Distributor" section
Low
compression. Check valve tappet clearance
Air
cleaner dirty
.
Remove and clean
Engine
Hesitates on Acceleration: Accelerator pump
does
not function perfectly.
...................
.Replace piston and rod or adjust
Carburetor
float level. ... .Adjust
Spark
plugs Replace or clean and adjust
Low
compression Check valves
Distributor
points—dirty or pitted Replace
Weak
condenser or coil Replace
Carburetor
jets restricted Remove and clean
Excessive
engine
heat See "Engine" section
Engine
Stalls—Won't Idle:
Improper
condition of carburetor See
"Carburetor"
section
Low
speed
jet restricted Remove and clean
Dirty
fuel sediment bowl screen Remove and clean
Air
cleaner dirty Remove and clean
Leaky
manifold or gasket Replace
Fuel
pump diaphragm porous. Replace
Loose carburetor. Tighten
flange
nuts
Water
in fuel
Drain
and clean system
Improper
ignition. .See "Distributor" section
Spark
plugs Clean and adjust
Valves
sticking.
Grind
valves 134
Page 213 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
FIG.
H-52—MAIN
LIGHT SWITCH (LATE)
1—
Circuit
Breaker
2—
Light
Switch
3—
Rear
Lights
4—
Head
Lights
5—
Parking
Lights
The
light switch shown in
Fig.
H-51 was superseded
by the one shown in
Fig.
H-52.
H-127.
Headlight Dimmer Switch To
remove the headlight dimmer switch, first raise
the hood and disconnect the wires attached to the
switch.
Then
remove the two screws that hold the
dimmer
switch to the floor board. Remove the
switch.
Check
the operation of the dimmer switch
with
a
test
light. A
circuit
across two different pairs of contacts (one to headlights, the other to the
high-beam indicator light) should alternately light
the
test
lamp when the switch is operated.
H-128.
Stop Light Switch
The
stop
light switch is of the diaphragm type.
Should
the switch
become
inoperative, it is neces
sary
to install a new one.
Current
production vehicles are equipped with two
stop
light switches
that operate independently of each other. Both
switches are located along the
left
side of frame, in the front and
rear
brake lines.
Caution:
Do not apply the brakes while making
this exchange as air may enter the hydraulic line.
Bleed
the brakes after replacing the switch.
Fig.
H-54 shows the wiring of the
stop
light
circuit.
11500
FIG.
H-53—STOP
LIGHT SWITCH
FIG.
H-54—STOP
LIGHT CIRCUIT
1— Stop
Light
Switch
2—
Light
Switch
3—
Tail
Light
H-129. Head Lamp Service
H-130.
Head Lamp Replacement
Refer
to Fig. H-59.
Each
sealed beam head lamp can only be replaced as a
complete
unit.
A
sealed beam unit may be replaced by the fol lowing procedure:
a.
Remove door screw.
b.
Remove door.
c.
Remove retaining screws and retaining
ring.
d.
Remove sealed beam unit.
Installation
of sealed beam unit is the reverse of
above procedure. When replacing head lamps,
check
lamp aim following procedures described in
Par.
H-132.
FIG.
H-55—PARKING
LIGHT (EARLY)
1—
Bezel
2—
Lens
3—
Bulb
4—
Gasket
5—
Housing
and Cable
6—
Screw
213
Page 224 of 376
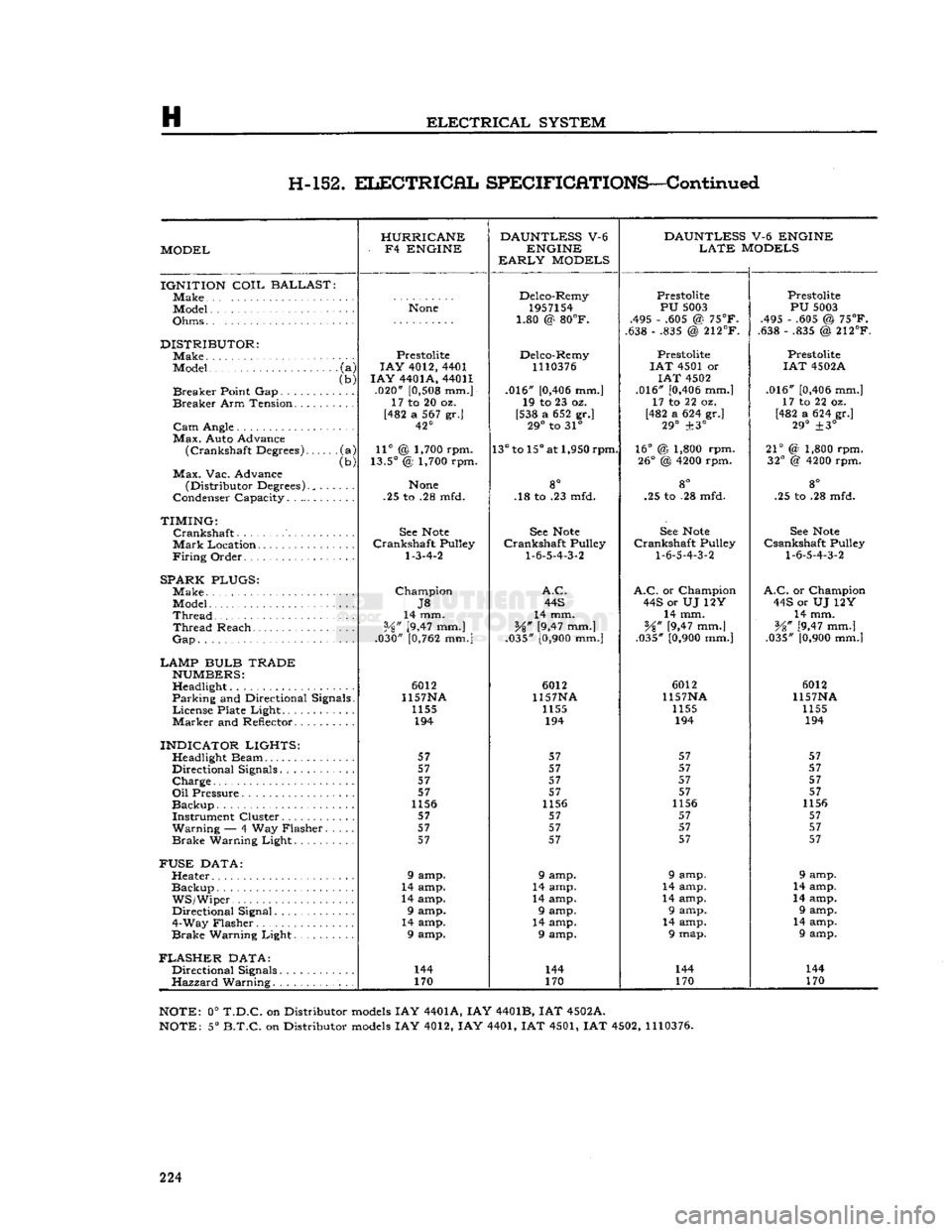
H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
H-152.
ELECTRICAL
SPECIFICATIONS—Continued
HURRICANE DAUNTLESS
V-6
DAUNTLESS
V-6 ENGINE
MODEL -
F4
ENGINE
ENGINE
LATE
MODELS
EARLY
MODELS
IGNITION
COIL
BALLAST
]Make Delco-Remy
Prestolite Prestolite
Model
None
1957154
PU
5003
PU
5003
Ohms • • 1.80 @
80°F.
.495 - .605 @
75°F.
.495 - .605 @
75°F.
1.80 @
80°F.
.638 - .835 @
212°F.
.638 - .835 @
212°F.
DISTRIBUTOR:
Prestolite Delco-Remy Prestolite Prestolite
Model
•
(a)
LAY
4012, 4401
1110376
I
AT
4501 or
IAT
4502A
(b)
I
AY
4401A, 44011
IAT
4502
Breaker
Point Gap (b)
.020"
[0,508
mm.] .016"
[0,406
mm.] .016"
[0,406
mm.]
.016"
[0,406
mm.]
Breaker
Arm Tension. ..... 17 to 20 oz.
19 to 23 oz. 17 to 22 oz. 17 to 22 oz.
[482 a 567 gr.] [538 a 652 gr.] [482 a 624 gr.]
[482 a 624 gr.]
42° 29°
to 31°
29°
±3°
29°
±3°
Max.
Auto Advance
(Crankshaft
Degrees) •(a)
11°
@ 1,700 rpm.
13°
to
15°
at 1,950 rpm.
16°
@ 1,800 rpm.
21°
(2 1,800 rpm.
(Crankshaft
Degrees)
(b)
13.5°
@ 1,700 rpm.
26°
@
4200
rpm.
32°
@
4200
rpm.
Max.
Vac. Advance go
(Distributor Degrees)., . .
None
8° 8°
go
Condenser Capacity. . .25 to .28 mfd. .18 to .23 mfd. .25 to .28 mfd. .25 to .28 mfd.
TIMING:
Crankshaft
See
Note
See
Note
See
Note
See
Note
Mark
Location............
Crankshaft
Pulley
Crankshaft
Pulley
Crankshaft
Pulley
Csankshaft
Pulley
Firing
Order
1-3-4-2
1-6-5-4-3-2
1-6-5-4-3-2 1-6-5-4-3-2
SPARK PLUGS:
Make
Champion
A.C. A.C.
or Champion
A.C.
or Champion
J8
44S
44S or UJ 12Y 44S or UJ 12Y
Thread
14 mm.
14 mm. 14 mm. 14 mm.
Thread
Reach
Vz"
[9,47 mm.]
%"
[9,47 mm.]
¥%"
[9,47 mm.]
V8" [9,47 mm.]
Gap
.030"
[0,762
mm.]
.035"
[0,900
mm.] .035"
[0,900
mm.] .035"
[0,900
mm.|
LAMP BULB TRADE
NUMBERS:
Headlight 6012
6012 6012 6012
Parking
and Directional Signals. 1157NA
1157NA 1157NA 1157NA
License
Plate Light........ 1155
1155 1155 1155
Marker
and Reflector 194
194 194 194
INDICATOR LIGHTS:
57 57 57 57
Directional Signals........ 57
57 57 57
Charge
57
57 57 57
57 57 57 57
1156 1156 1156 1156
Instrument Cluster 57 57 57 57
Warning
— 4 Way Flasher. . 57
57 57 57
Brake
Warning Light 57
57 57 57
FUSE
DATA:
Heater 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp.
Backup
14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp.
WS/Wiper.
14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp.
Directional Signal 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp.
4-Way Flasher 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp.
Brake
Warning Light 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 map. 9 amp.
FLASHER
DATA:
Directional Signals. 144
144 144 144
Hazzard
Warning. 170
170 170 170
NOTE:
0°
T.D.C.
on Distributor
models
IAY 4401A, IAY 4401B, IAT 4502A.
NOTE:
5°
B.T.C.
on Distributor
models
IAY 4012, IAY 4401, IAT 4501, IAT 4502,
1110376.
224
Page 227 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 User Guide
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
correct distance should be 10%"
[26,04
cm.].
If
the length of the clutch release pedal rod is
other than
10
W
[26,04
cm.], the vheicle is eq JEEP DJ 1953 User Guide
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
correct distance should be 10%"
[26,04
cm.].
If
the length of the clutch release pedal rod is
other than
10
W
[26,04
cm.], the vheicle is eq](/img/16/57041/w960_57041-226.png)
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
correct distance should be 10%"
[26,04
cm.].
If
the length of the clutch release pedal rod is
other than
10
W
[26,04
cm.], the vheicle is equipped with the early
type
Clutch
Control
Lever
and
Tube Assembly, which should be removed, and^trie latest
designed
parts should be installed.
The
free pedal clearance is adjusted by lengthening
or shortening the" clutch fork cable. To make this adjustment,
loosen
the jam nut on the cable clevis
and
lengthen or shorten the cable to obtain %"
[19,05
mm.] free travel at the pedal pad, then
tighten the jam unit.
•
Clutch
Control Cable Type
Refer
to Fig. 1-2.
a.
With the clutch pedal pad against the floor
panel, (pedal up, clutch
engaged)
adjust ball ad
justing nut until slack is removed from the cable
and
the clutch throwout bearing contacts the clutch
pressure plate, release levers or diaphragm plate.
b. Back-off ball adjusting nut 2
V2
turns to obtain
approximately %"
[19,05
mm.] free travel.
Lock
hex nut.
FIG.
1-3—AUBURN
CLUTCH
ASSEMBLY —
HURRICANE F4 ENGINE 1—
Driven
Plate and Hub
2—
Pressure
Plate
3—
Pivot Pin
4—
Bracket
5—
Spring
Cup 6—
Pressure
Spring 7— Release
Lever
8—
Return
Spring
9—
Adjusting
Screw
10—
Jam
Nut 11—
Washer
Note:
Some older 'Jeep' vehicles may
develop
side
movement
of the clutch and brake pedals resulting
from wear of the pedals, shafts, and bushings. One way to
compensate
for this wear is to install a pedal
slack
adjuster kit 1-4.
CLUTCH
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
•
Auburn
Vehicles equipped with the Hurricane F4
engine
have a 9.25" [23,4 cm.] driven plate. The auburn clutch driving (pressure) plate assembly (Fig. 1-3)
has three pressure springs and three levers or
fingers.
1-5.
Clutch
Removal
When
necessary to remove the clutch,
follow
the procedures outlined in Section J for the removal
of the transmission and transfer case from the vehicle. Then remove the flywheel housing and use
the following procedures for removing the clutch assembly.
Note:
The F4
engine
may be removed from the
vehicle when inspecting or replacing the clutch.
Refer
to Section D for Hurricane F4
engine
removal and then
follow
the instructions given
below
to remove the clutch assembly.
a.
Mark
the clutch pressure plate and
engine
fly
wheel with a center punch so the clutch assembly
may be installed in the same position after adjust
ments
or replacement are completed.
b. Remove the clutch pressure plate bracket
bolts
equally, a little at a time, to prevent distortion and
to relieve the clutch springs evenly.
c. Remove the pressure plate assembly and driven
plate from the flywheel.
1-6.
Clutch
Pressure Plate and Disc Inspection
Inspect the pressure plate face for
cracks,
chips,
and
warpage.
Check
the pressure plate levers for
excessive
wear and the springs for breaks. If any of the
above
conditions exist, the
complete
pressure
plate must be replaced.
Check
the clutch disc for
excessive
wear,
loose
or damaged facings, broken
vibration damper springs and evidence of grease
or oil. If any of the
above
conditions exist, replace
the clutch disc.
1-7.
Clutch
Pressure Plate Adjustment —
Auburn
The
clutch pressure plate must be checked
before
installing a new or reconditioned clutch. The proper 11339
FIG.
1-4—CHECKING
AUBURN
CLUTCH
LEVER
ADJUSTMENT
1— Adjustment Gauge
2—
Fixture
Mounting Bolt
3—
Clutch
Fixture
227
Page 241 of 376
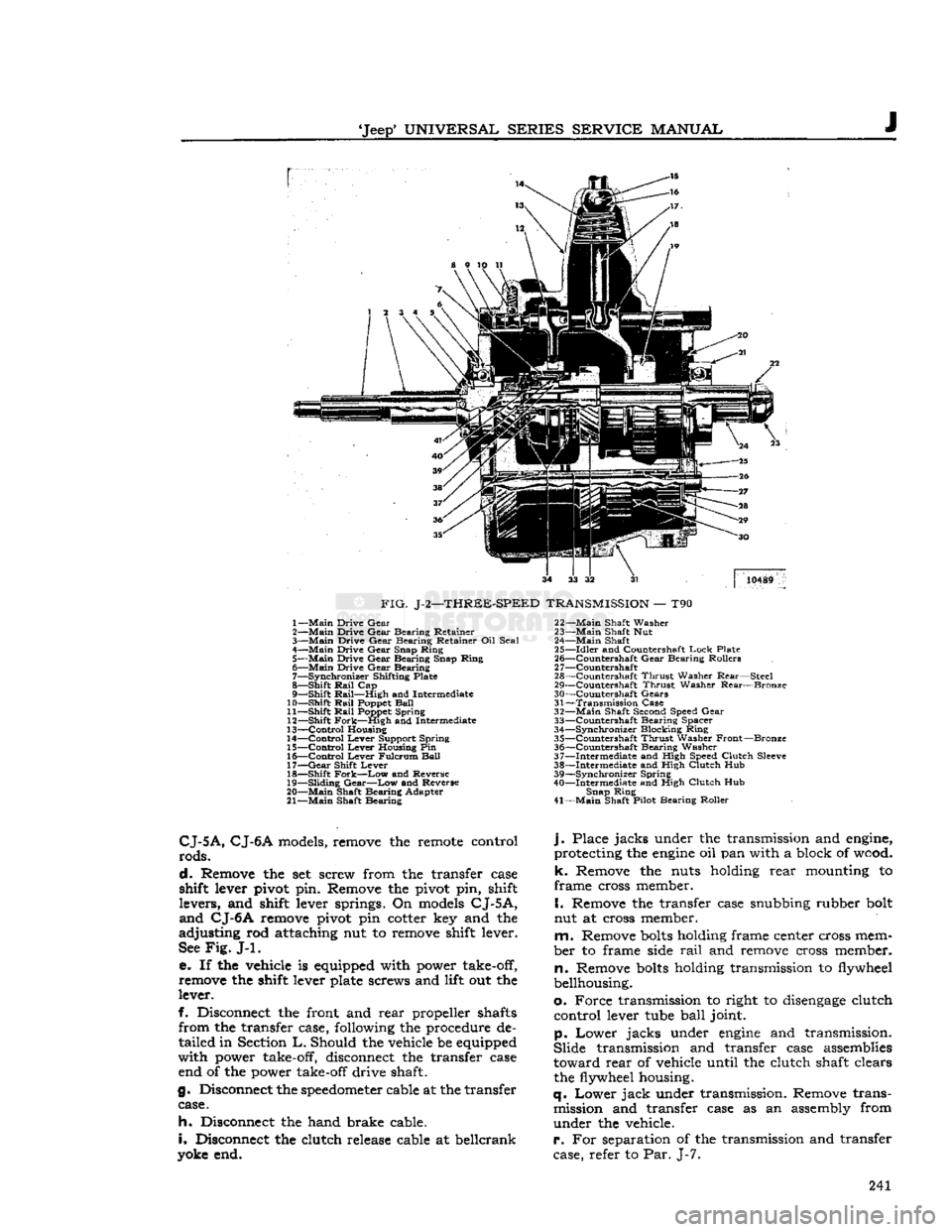
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
J
10489
FIG.
J-2—THREE-SPEED
TRANSMISSION
— T90 1—
Main
Drive
Gear
2—
Main
Drive
Gear
Bearing
Retainer
3—
Main
Drive
Gear
Bearing
Retainer Oil
Seal
4—
Main
Drive
Gear
Snap
Ring
5—
Main
Drive
Gear
Bearing
Snap
Ring
6—
Main
Drive
Gear
Bearing
7—
Synchronizer
Shifting Plate
8—
Shift
Rail
Cap
9—
Shift
Rail—High
and Intermediate
10—
Shift
Rail
Poppet
Ball
11—
Shift
Rail
Poppet
Spring
12—
Shift
Fork—High
and Intermediate
13—
Control
Housing
14—
Control
Lever
Support
Spring
15—
Control
Lever
Housing Pin
16—
Control
Lever
Fulcrum
Ball
17—
Gear
Shift
Lever
18—
Shift
Fork—Low
and Reverse
19—
Sliding
Gear—Low
and Reverse
20—
Main
Shaft
Bearing
Adapter
21—
Main
Shaft
Bearing
22—
Main
Shaft
Washer
23—
Main
Shaft Nut
24—
Main
Shaft
25—
Idler
and Countershaft
Lock
Plate
26—
^Countershaft
Gear
Bearing
Rollers
2
7—Countershaft
28—
Countershaft
Thrust
Washer
Rear—Steel
29—
Countershaft
Thrust
Washer
Rear—Bronze
30—
Countershaft
Gears
31—
Transmission
Case
32—
Main
Shaft Second Speed
Gear
33—
Countershaft
Bearing
Spacer
34—
Synchronizer
Blocking
Ring
35—
Countershaft
Thrust
Washer
Front—Bronze
36—
Countershaft
Bearing
Washer
37—
Intermediate
and High Speed
Clutch
Sleeve
38—
Intermediate
and High
Clutch
Hub
39—
Synchronizer
Spring
40—
Intermediate
and High
Clutch
Hub
Snap
Ring
41—
Main
Shaft Pilot
Bearing
Roller
CJ-5A,
CJ-6A
models, remove the remote control
rods.
d.
Remove the set screw from the transfer case
shift lever pivot pin. Remove the pivot pin, shift
levers,
and shift lever springs. On models
CJ-5A,
and
CJ-6A
remove pivot pin cotter key and the
adjusting
rod attaching nut to remove shift lever.
See
Fig.
J-l.
e. If the vehicle is equipped with power take-off,
remove the shift lever plate screws and lift out the
lever.
f. Disconnect the front and
rear
propeller shafts
from
the transfer case, following the procedure de
tailed
in Section
L.
Should the vehicle be equipped
with
power take-off, disconnect the transfer case end of the power take-off drive shaft.
g. Disconnect the
speedometer
cable at the transfer case.
h.
Disconnect the hand brake cable.
i.
Disconnect the clutch release cable at beilcrank
yoke end.
j.
Place
jacks
under the transmission and engine,
protecting the
engine
oil pan with a block of wood,
k.
Remove the nuts holding
rear
mounting to
frame
cross member.
I.
Remove the transfer case snubbing rubber bolt
nut at cross member.
m.
Remove
bolts
holding frame center cross mem
ber
to frame side
rail
and remove cross member,
n.
Remove
bolts
holding transmission to flywheel
bellhousing.
o.
Force
transmission to right to
disengage
clutch
control
lever tube
ball
joint.
p.
Lower
jacks
under
engine
and transmission.
Slide
transmission and transfer case assemblies
toward
rear
of vehicle until the clutch shaft clears the flywheel housing.
q.
Lower
jack
under transmission. Remove trans mission and transfer case as an assembly from
under
the vehicle.
r.
For separation of the transmission and transfer
case, refer to Par. J-7. 241
Page 267 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
ft
TRANSFER CASE
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL
. . .K-1
TRANSFER CASE REMOVAL
K-2
TRANSFER CASE DISASSEMBLY
K-3
Front
Bearing Cap K-4
Rear
Bearing Cap K-5
TRANSFER CASE REASSEMBLY.
. .K-6
TRANSFER CASE INSTALLATION
K-7
TRANSFER CASE LINKAGE
ADJUSTMENT
K-8
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
K-9
SPECIFICATIONS
.K-10
K-1. GENERAL
All
4-wheel-drive models are equipped with a
transfer
case to connect the power to the front
axle.
It is essentially a
two-speed
transmission
located at the
rear
of the standard transmission
and
provides a low and direct gear.
The
transfer case gears are controlled by the
driver
through
one shift lever.
Early
'Jeep'
Universal
Models with the F4-134
Hurricane
engine
are equipped with two transfer case shift control levers.
a.
On vehicles equipped with one transfer case
shift
lever, the transfer case shift lever has four
positions: 2WD
High,
4WD
High,
Neutral, and
4WD
low. The forward position of the lever 2WD
High
allows the
rear
wheels only to drive. The
first
rear
position (4WD High)
engages
the 4- wheel drive and provides high range 4-wheel drive.
The
second
rear
position (Neutral)
disengages
all power to the wheels and is used for stationary
power take-off operations. The last
rear
position
(4WD
Low) provides low range 4-wheel drive.
b.
On vehicles equipped with two transfer case
shift
levers, the transfer case front axle drive lever (left hand lever)
gives
a choice of 2-wheel or 4-
wheel drive. In the forward (out) position the
vehicle is in 2-wheel drive. Move the lever to the
rear
(in) position for 4-wheel drive operation.
The
4-wheel-drive
auxiliary-range
shift lever (right
hand
lever) has three positions; low, neutral, and
high.
The forward position (low)
gives
low-range
4-wheel drive. The center position (neutral) dis
engages
all power to the wheels and is used for
stationary
power take-off operations. A built-in in
terlock
prevents shifting into low range, 2-wheel
drive.
This
feature protects the
rear
axle from over
load.
K-2.
Removal of
Transfer
Case
The
transfer case may be removed from the vehicle
without removing the transmission. Where both
transmission
and transfer case are to be removed
together,
refer to Section J. To remove only the
transfer
case from the vehicle, proceed as follows:
a.
Drain
transmission
and transfer case and replace
drain
plugs.
b.
Disconnect the brake cable.
c.
Disconnect front and
rear
propeller shafts at
the transfer case. See "Propeller Shafts and
Uni
versal
Joints."
d.
Disconnect
speedometer
cable at transfer case. e. Disconnect the transfer case shift levers. On
vehicles equipped with two shift levers
loosen
set screw and remove pivot pin. Use a screw
driver
to pry shift lever springs away from shift levers.
Lift
levers from transfer case. On models equipped
with
a single shift lever remove pivot pin cotter
key,
and the adjusting rod attaching nut to remove
shift
lever. See Fig. K-4.
f. Remove cover plate on
rear
face of transfer case.
Remove
cotter key, nut and washer from trans
mission
main shaft.
g. If possible, at this point remove the transfer case main drive gear from the transmission main
shaft.
If not possible, see
step
j below.
h.
Remove transfer case torque reaction support
bracket
bolt and nut.
i.
Remove transmission to transfer case bolts.
j.
Remove transfer case. If the transfer case main
drive
gear has not been removed in
step
g above,
proceed as follows:
Brace
the end of the trans
mission
main shaft so that it cannot
move
in the
transmission,
pull
the transfer case to the
rear
to 267
Page 268 of 376
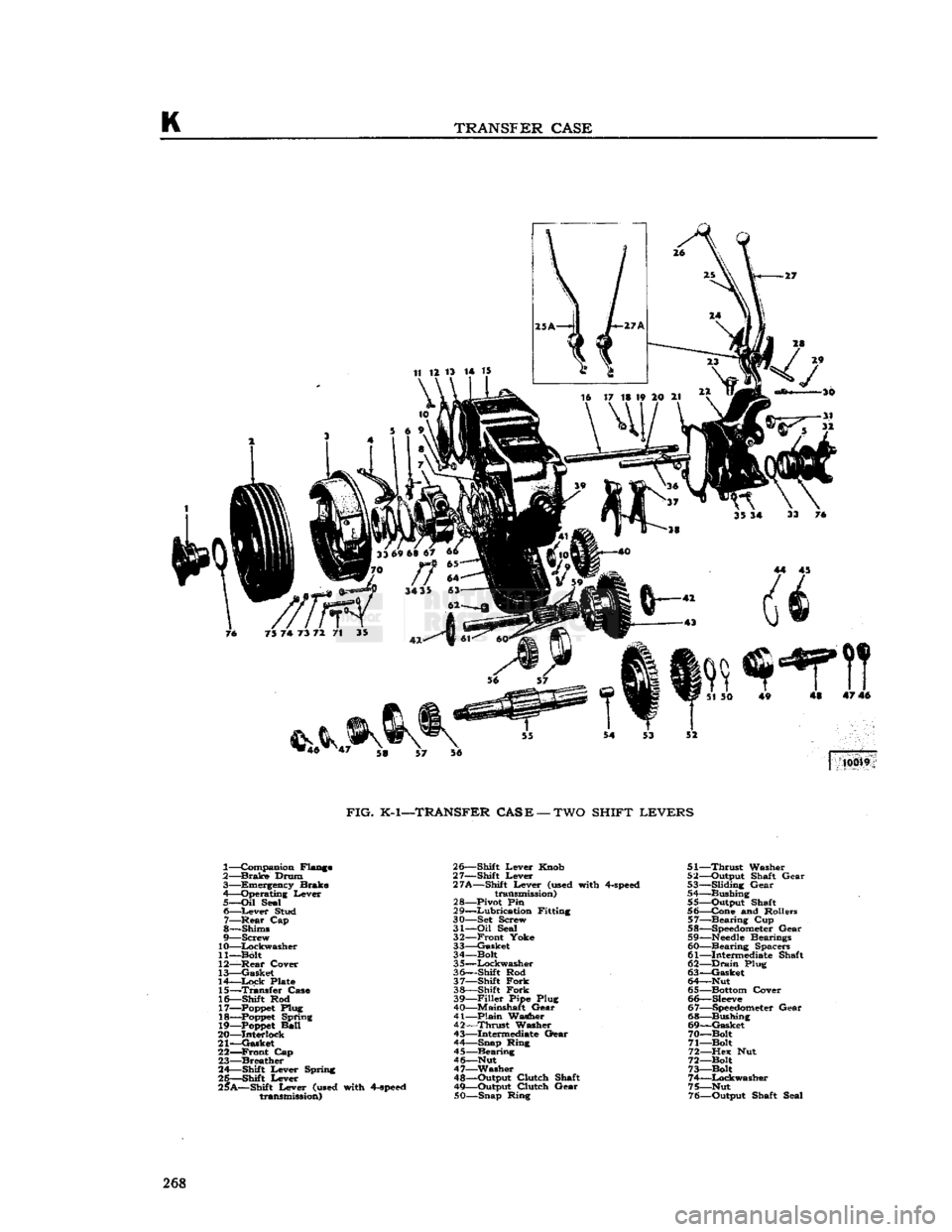
TRANSFER
CASE
FIG.
K-1—TRANSFER
CASE
—
TWO
SHIFT
LEVERS
1— Companion Flange
2—
Brake
Drum 3— Emergency Brake
4—Operating Lever
5—
Oil
Seal 6—
Lever
Stud 7—
-Rear
Cap
8— Shims
9—
Screw
10—
Lockwasher
11— Bolt
12—
-Rear
Cover
13—
Gasket
14—
Lock
Plate
15—
Transfer
Case
16— Shift Rod 17—
Poppet
Plug
18—Poppet
Spring 19—
Poppet
Ball
20— Interlock
21—Gasket 22—
Front
Cap
23—
Breather
24— Shift Lever Spring
26—Shift
Lever
25*A—Shift Lever
(used
with
4-speed
transmission) 26— Shift Lever Knob
27— Shift Lever
27A—Shift Lever
(used
with
4-speed
transmission)
28—
Pivot
Pin
29—
Lubrication
Fitting
30— Set Screw
31—
Oil
Seal 32—
Front
Yoke
33—
Gasket
34— Bolt
3
5—Lockwasher
36— Shift Rod
37—
Shift
Fork
38— Shift
Fork
39—
Filler
Pipe Plug
40—Mainshaft Gear 41— plain Washer
42—
Thrust
Washer
43—
Intermediate
Gear
44—
Snap Ring
45—
Bearing
46—
Nut 47— Washer
48— Output Clutch Shaft
49—
Output Clutch Gear
50— Snap Ring 51—
Thrust
Washer
52— Output Shaft Gear
53— Sliding Gear
54— Bushing
55— Output Shaft
56— Cone and Rollers
57—
Bearing
Cup
58—
Speedometer
Gear 59—
Needle
Bearings 60—Bearing Spacers
61—
Intermediate
Shaft
62—
Drain
Plug 63—
Gasket
64—Nut
65—
Bottom
Cover
66—
Sleeve
67—
Speedometer
Gear 68— Bushing
69—
Gasket
70— Bolt
71—Bolt
72—
Hex Nut
72— Bolt
73— Bolt
74—
Lockwasher
75— Nut
76— Output Shaft Seal 268