Specifications JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 2179 of 2199

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................24
DESCRIPTION - CCV SYSTEM...........25
DESCRIPTION - PCV SYSTEM...........25
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM.........26
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM.........26
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAPORATION SYSTEM.......27
CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L................................28
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING........28
INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING....29
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29REMOVAL.............................29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENABLING
CONDITIONS TO RUN EVAP LEAK
DETECTION TEST.....................32
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
P C V VA LV E
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L.......................37
REMOVAL - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.............39
INSTALLATION - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.........39
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................39
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through the control valve, through the fuel manage-
ment valve, and through vent hoses and tubes to a
charcoal filled evaporative canister. The canister tem-
porarily holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum todraw vapors into the combustion chambers during
certain operating conditions.
Gas powered engines use a duty cycle purge sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Duty Cycle
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system for OBD II requirements.
Also refer to Leak Detection Pump.
Vehicles powered with gasoline engines are also
equipped with ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery). Refer to ORVR for additional information.
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
Page 2182 of 2199
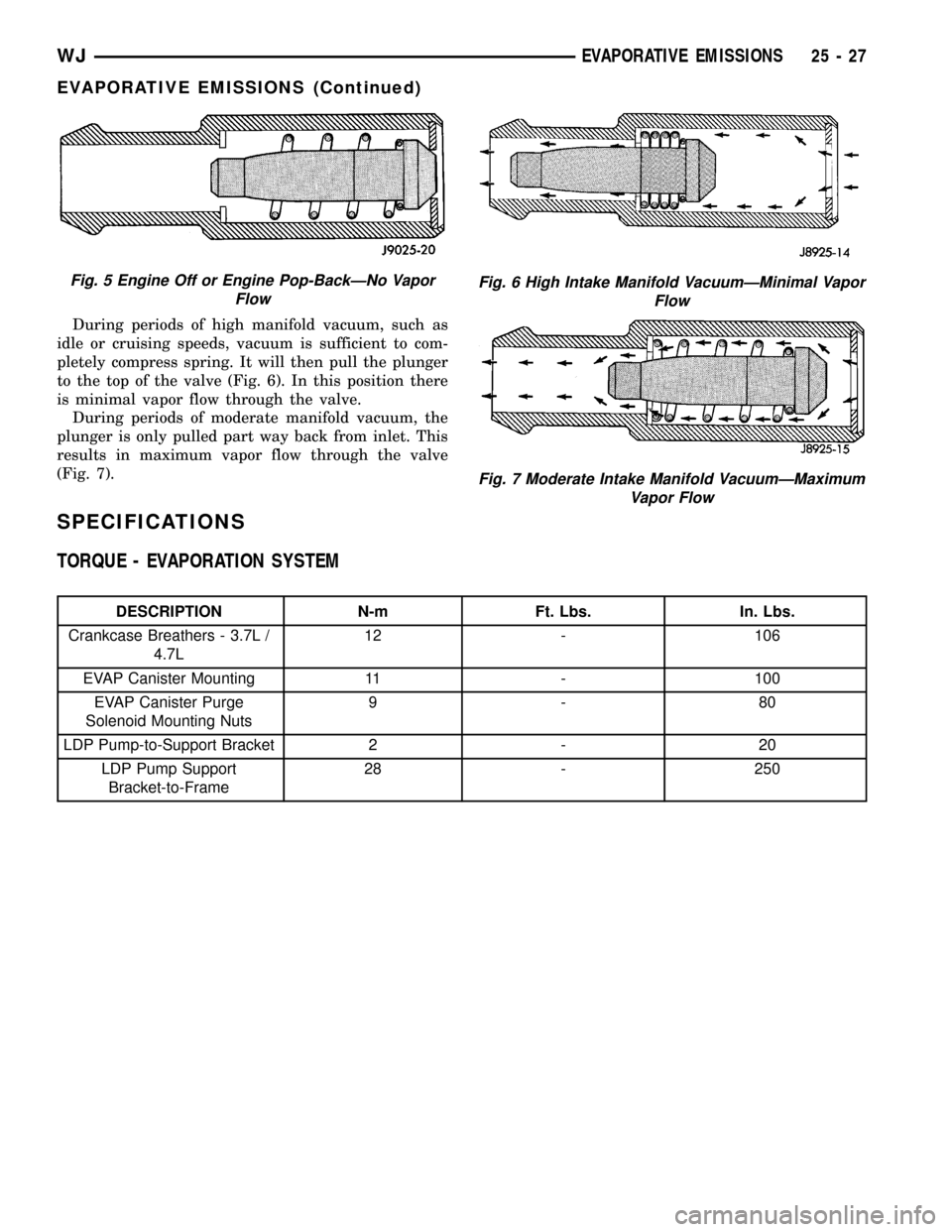
During periods of high manifold vacuum, such as
idle or cruising speeds, vacuum is sufficient to com-
pletely compress spring. It will then pull the plunger
to the top of the valve (Fig. 6). In this position there
is minimal vapor flow through the valve.
During periods of moderate manifold vacuum, the
plunger is only pulled part way back from inlet. This
results in maximum vapor flow through the valve
(Fig. 7).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAPORATION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Crankcase Breathers - 3.7L /
4.7L12 - 106
EVAP Canister Mounting 11 - 100
EVAP Canister Purge
Solenoid Mounting Nuts9- 80
LDP Pump-to-Support Bracket 2 - 20
LDP Pump Support
Bracket-to-Frame28 - 250
Fig. 5 Engine Off or Engine Pop-BackÐNo Vapor
FlowFig. 6 High Intake Manifold VacuumÐMinimal Vapor
Flow
Fig. 7 Moderate Intake Manifold VacuumÐMaximum
Vapor Flow
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 27
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 2192 of 2199

Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister purge solenoid for
damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
(2) Connect electrical connector to LDP.
(3) While raising front section of support bracket,
connect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(4) Install 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19). Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(5) Join front and rear sections of two-piece sup-
port bracket by installing 3 bolts on bottom of sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). Do not tighten bolts at this
time.
(6) Install support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17). Do
not tighten bolt at this time.
(7) Tighten 2 support bracket nuts at frame rail
(Fig. 19). Refer to Torque Specifications.
(8) Tighten 3 support bracket bolts and brace bolt.
Refer to Torque Specifications.
(9) Position stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Install new plastic rivets.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister. Certain ORVR components can be
found in (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled. Cer-
tain ORVR components can be found in (Fig. 1).
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,
the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 21) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 21). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 21). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 37
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2195 of 2199

REMOVAL
The EVAP canister is located behind the left-rear
wheel (Fig. 24). It is attached to a two-piece support
bracket (Fig. 25).
(1) Remove rear bumper facia. Refer to Rear Facia
Removal / Installation in Frame & Bumpers section.
(2) Remove 1 support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 25).
(3) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts (Fig. 26).
(4) Remove upper/rear support bracket mounting
bolt (Fig. 27).
(5) Carefully lower support bracket assembly to
gain access to vapor / vacuum lines. To prevent dam-
age to lines, suspend bracket assembly with rope or
string.
(6) Disconnect necessary vacuum / vapor lines at
EVAP canister.
(7) Remove EVAP canister mounting bolt (Fig. 28).
(8) Lift canister from support bracket (2 pins are
used to align canister into support bracket)
INSTALLATION
The EVAP canister is located behind the left-rear
wheel (Fig. 24). It is attached to a two-piece support
bracket (Fig. 25).
(1) Position canister to support bracket. Guide 2
alignment pins into support bracket.
(2) Install EVAP canister mounting bolt (Fig. 28).
Refer to Torque Specifications.
(3) Carefully install vapor / vacuum lines to canis-
ter.The vapor/vacuum lines and hoses must be
firmly connected. Check the vapor/vacuum
lines at the LDP, LDP filter and EVAP canister
purge solenoid for damage or leaks. If a leak is
present, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may
be set.
Fig. 24 LOCATION, LDP / EVAP CANISTER
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
2 - EVAP CANISTER
Fig. 25 TWO-PIECE SUPPORT BRACKET
1 - TWO-PIECE SUPPORT BRACKET (FRONT)
2 - SUPPORT BRACKET BRACE
3 - TWO-PIECE SUPPORT BRACKET (REAR)
4 - SUPPORT BRACKET ATTACHING BOLTS (3)
5 - SUPPORT BRACKET BRACE BOLT
25 - 40 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
VAPOR CANISTER (Continued)
Page 2196 of 2199

(4) Carefully raise support bracket assembly to
frame rail. Install 1 support bracket brace bolt (Fig.
25) and 2 support bracket nuts (Fig. 26).
(5) Install upper/rear support bracket mounting
bolt (Fig. 27). Refer to Torque Specifications.
(6) Install rear bumper facia. Refer to Rear Facia
Removal / Installation in Frame & Bumpers section.
Fig. 27 SUPPORT BRACKET BOLT
1 - EVAP CANISTER
2 - UPPER / REAR SUPPORT BRACKET BOLT
3 - SLOTTED HOLE
4 - ALIGNMENT PINS (2)
5 - TWO-PIECE SUPPORT BRACKET
Fig. 28 EVAP CANISTER REMOVE / INSTALL
1 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BOLT
2 - SLOTTED HOLE
3 - EVAP CANISTER (LOWERED)
Fig. 26 SUPPORT BRACKET NUTS
1 - SUPPORT BRACKET NUTS (2)
2 - SUPPORT BRACKET (FRONT)
3 - SUPPORT BRACKET BRACE BOLT
4 - LDP MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 41
VAPOR CANISTER (Continued)