eco JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 346 of 1803

²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
INSPECTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) system. Some charging system circuits are
checked continuously, and some are checked only
under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Control Module; Electronic Control Modules for more
DTC information. This will include a complete list of
DTC's including DTC's for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBtscan tool. Per-form the following inspections before attaching the
scan tool.
(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to 8, Bat-
tery for procedures.
(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in 7, Cooling System.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EXCEPT DIESEL
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator Horizontal Mounting Bolts - 3.7L 57 42 -
Generator Vertical Mounting Bolt - 3.7L 40 29 -
Generator Mounting Bolts - 2.4L 57 42 -
B+ Terminal Nut at Top of Generator 13 - 115
Generator Decoupler 110 81 -
GENERATOR RATINGS - GAS ENGINES
TYPE PART NUMBER RATED SAE AMPS ENGINES MINIMUM TEST AMPS
DENSO 56044530AB 124 2.4L 88
DENSO 56044532AB 136 2.4L 96
DENSO 56041693AA 136 3.7L 96
DENSO 56029914AA 160 3.7L 112
KJCHARGING SYSTEM 8F - 23
CHARGING SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 347 of 1803

SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is attached
to the battery tray located under the battery.
OPERATION
The BTS is used to determine the battery temper-
ature and control battery charging rate. This temper-
ature data, along with data from monitored line
voltage, is used by the PCM to vary the battery
charging rate. System voltage will be higher at colder
temperatures and is gradually reduced at warmer
temperatures.
The PCM sends 5 volts to the sensor and is
grounded through the sensor return line. As temper-
ature increases, resistance in the sensor decreases
and the detection voltage at the PCM increases.The BTS is also used for OBD II diagnostics. Cer-
tain faults and OBD II monitors are either enabled
or disabled, depending upon BTS input (for example,
disable purge and enable Leak Detection Pump
(LDP) and O2 sensor heater tests). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20 degrees F.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery (Fig. 1) and is attached to a
mounting hole on battery tray.
(1) Remove battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
(2) Disconnect sensor pigtail harness from engine
wire harness electrical connector.
(3) Pry sensor straight up from battery tray
mounting hole.
INSTALLATION
The battery temperature sensor is located under
vehicle battery and is attached to a mounting hole on
battery tray.
(1) Feed pigtail harness through hole in top of bat-
tery tray and press sensor into top of battery tray.
(2) Connect pigtail harness.
(3) Install battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
GENERATOR DECOUPLER TOOL #8433
GENERATOR DECOUPLER TOOL #8823
Fig. 1 BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
1 - BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - BATTERY TRAY
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
8F - 24 CHARGING SYSTEMKJ
CHARGING SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 349 of 1803

INSTALLATION
Gasoline Powered Engines
(1) 2.4L Engine: Position generator to engine and
install 2 mounting bolts. Refer to torque specifica-
tions.
(2) 3.7L Engine: Position generator to engine and
install 3 mounting bolts. Tighten 2 horizontal mount-
ing bolts to specified torque. Tighten 1 verticle
mounting bolt to specified torque. Refer to torque
specifications.
(3) Snap field wire connector into rear of genera-
tor.
(4) Install B+ terminal and nut to generator
mounting stud. Refer to torque specifications.
(5) Snap plastic protective cover to B+ terminal.
CAUTION: Never force a belt over a pulley rim
using a screwdriver. The synthetic fiber of the belt
can be damaged.
CAUTION: When installing a serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. The
water pump will be rotating in the wrong direction if
the belt is installed incorrectly, causing the engine
to overheat. Refer to belt routing label in engine
compartment, or refer to Belt Schematics in 7, Cool-
ing System.
(6) Install drive belt Refer to 7, Cooling System for
belt routing, belt adjustment and bolt tightening pro-
cedures.
(7) Install negative battery cable to battery.
GENERATOR DECOUPLER
PULLEY
DESCRIPTION
The generator decoupler is used only with
certain engines.The decoupler is used in place of
the standard generator drive pulley (Fig. 5).
Fig. 3 GENERATOR - 2.4L
1 - UPPER MOUNTING BOLT
2 - GENERTOR
3 - LOWER MOUNTING BOLT
Fig. 4 GENERATOR - 3.7L
1 - GENERATOR
2 - VERTICAL MOUNTING BOLT
3 - HORIZONTAL MOUNTING BOLTS
8F - 26 CHARGING SYSTEMKJ
GENERATOR (Continued)
Page 350 of 1803
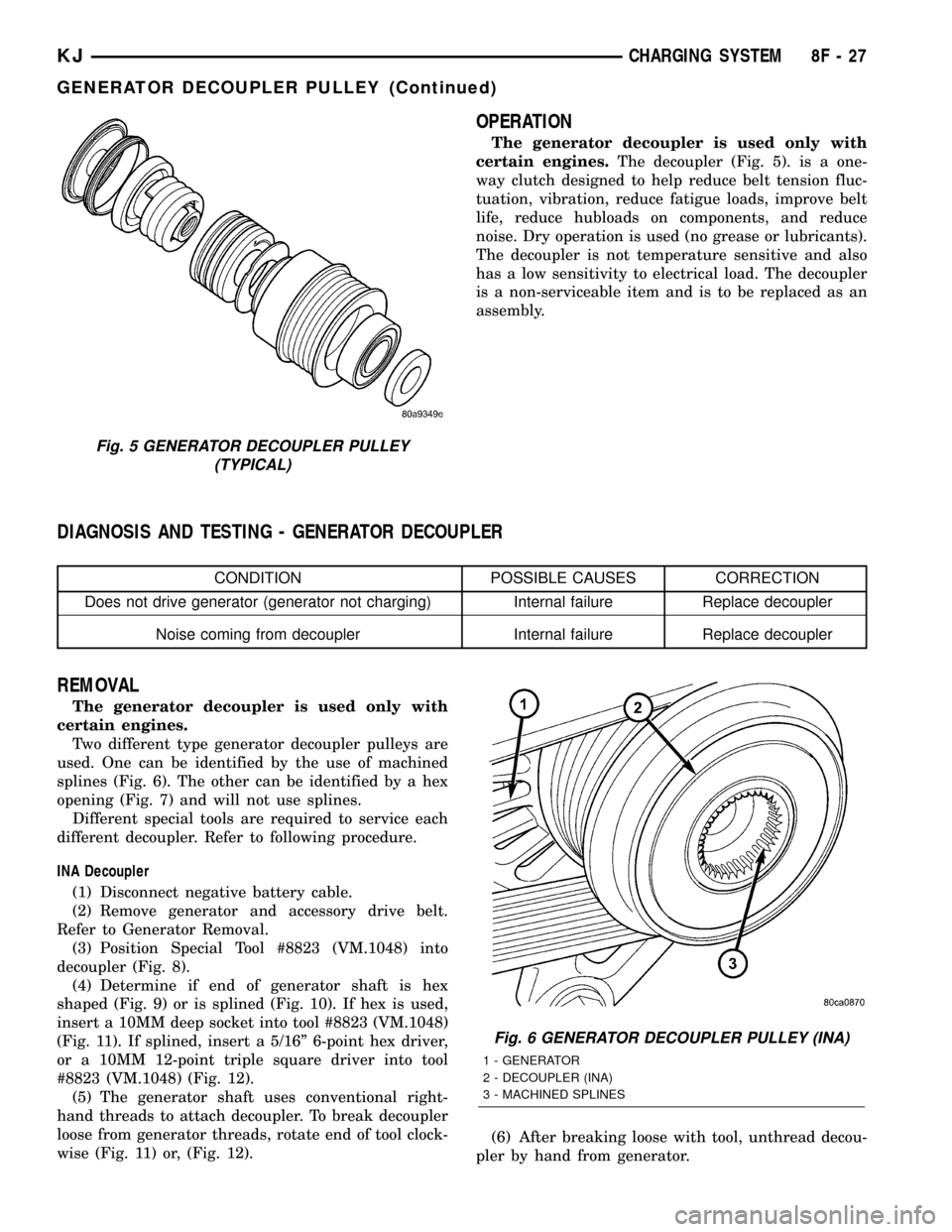

OPERATION
The generator decoupler is used only with
certain engines.The decoupler (Fig. 5). is a one-
way clutch designed to help reduce belt tension fluc-
tuation, vibration, reduce fatigue loads, improve belt
life, reduce hubloads on components, and reduce
noise. Dry operation is used (no grease or lubricants).
The decoupler is not temperature sensitive and also
has a low sensitivity to electrical load. The decoupler
is a non-serviceable item and is to be replaced as an
assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GENERATOR DECOUPLER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Does not drive generator (generator not charging) Internal failure Replace decoupler
Noise coming from decoupler Internal failure Replace decoupler
REMOVAL
The generator decoupler is used only with
certain engines.
Two different type generator decoupler pulleys are
used. One can be identified by the use of machined
splines (Fig. 6). The other can be identified by a hex
opening (Fig. 7) and will not use splines.
Different special tools are required to service each
different decoupler. Refer to following procedure.
INA Decoupler
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove generator and accessory drive belt.
Refer to Generator Removal.
(3) Position Special Tool #8823 (VM.1048) into
decoupler (Fig. 8).
(4) Determine if end of generator shaft is hex
shaped (Fig. 9) or is splined (Fig. 10). If hex is used,
insert a 10MM deep socket into tool #8823 (VM.1048)
(Fig. 11). If splined, insert a 5/16º 6-point hex driver,
or a 10MM 12-point triple square driver into tool
#8823 (VM.1048) (Fig. 12).
(5) The generator shaft uses conventional right-
hand threads to attach decoupler. To break decoupler
loose from generator threads, rotate end of tool clock-
wise (Fig. 11) or, (Fig. 12).(6) After breaking loose with tool, unthread decou-
pler by hand from generator.
Fig. 5 GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY
(TYPICAL)
Fig. 6 GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (INA)
1 - GENERATOR
2 - DECOUPLER (INA)
3 - MACHINED SPLINES
KJCHARGING SYSTEM 8F - 27
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (Continued)
Page 351 of 1803

Fig. 7 GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (LITENS)
1 - DECOUPLER (LITENS)
2 - HEX OPENING
Fig. 8 #8823 (VM.1048) TOOL AND INA DECOUPLER
1 - INA DECOUPLER
2 - TOOL #8823 (VM.1048)
Fig. 9 END OF GENERATOR SHAFT (HEX)
1 - GENERATOR SHAFT
2 - HEX
Fig. 10 END OF GENERATOR SHAFT (SPLINED)
1 - GENERATOR SHAFT
2 - SPLINES
8F - 28 CHARGING SYSTEMKJ
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (Continued)
Page 352 of 1803

Litens Decoupler
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.(2) Remove generator and accessory drive belt.
Refer to Generator Removal.
(3) Position Special Tool #8433 (Fig. 13) into
decoupler. Align to hex end of generator shaft.
(4) The generator shaft uses conventional right-
hand threads to attach decoupler. To break decoupler
loose from generator threads, rotate end of tool clock-
wise (Fig. 14).
(5) After breaking loose with tool, unthread decou-
pler by hand from generator.
Fig. 11 DECOUPLER REMOVAL (INA-HEX)
1 - DEEP 10 MM SOCKET
2 - TOOL #8823 (VM.1048)
Fig. 12 DECOUPLER REMOVAL (INA-SPLINED)
1 - DRIVER
2 - TOOL #8823 (VM.1048)
3 - 17 MM WRENCH
Fig. 13 # 8433 TOOL AND LITENS DECOUPLER
Fig. 14 DECOUPLER REMOVAL (LITENS)
KJCHARGING SYSTEM 8F - 29
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (Continued)
Page 353 of 1803

INSTALLATION
INA Decoupler
(1) Thread decoupler pulley onto generator shaft
by hand (right-hand threads).
(2) Position Special Tool #8823 (VM.1048) into
decoupler (Fig. 8).
(3) Determine if end of generator shaft is hex
shaped (Fig. 9) or is splined (Fig. 10). If hex is used,
insert a 10MM deep socket into tool #8823 (VM.1048)
(Fig. 15). If splined, insert a 5/16º 6-point hex driver,
or a 10MM 12-point triple square driver into tool
#8823 (VM.1048) (Fig. 16).
(4)Do not use an adjustable, ratcheting ªclick
typeº torque wrench. Most ªclick typeº
wrenches will only allow torque to be applied
in a clockwise rotation. Use a dial-type or
beam-type wrench.Tighten in counter-clockwise
rotation (Fig. 15) or, (Fig. 16). Refer to torque speci-
fications.
(5) Install accessory drive belt, and generator.
Refer to Generator Installation.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
Litens Decoupler
(1) Thread decoupler pulley onto generator shaft
by hand (right-hand threads).
(2) Position Special Tool 8433 (Fig. 13) into decou-
pler. Align tool to hex end of generator shaft.
(3)Do not use an adjustable, ratcheting ªclick
typeº torque wrench. Most ªclick typeº
wrenches will only allow torque to be applied
in a clockwise rotation. Use a dial-type orbeam-type wrench.Tighten in counter-clockwise
rotation (Fig. 17). Refer to torque specifications.
(4) Install accessory drive belt, and generator.
Refer to Generator Installation.
(5) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 15 DECOUPLER INSTALLATION (INA-HEX)
1 - 10MM DEEP SOCKET
2 - TOOL # 8823 (VM.1048)
Fig. 16 DECOUPLER INSTALLATION (INA SPLINED)
1 - DRIVER
2 - TOOL # 8823 (VM.1048)
Fig. 17 DECOUPLER INSTALLATION (Litens)
8F - 30 CHARGING SYSTEMKJ
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (Continued)
Page 354 of 1803

VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) is not a
separate component. It is actually a voltage regulat-
ing circuit located within the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The EVR is not serviced separately. If
replacement is necessary, the PCM must be replaced.
OPERATION
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by EVR circuitry contained within
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). This circuitry
is connected in series with the generators second
rotor field terminal and its ground.
Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. TheEVR circuitry monitors system line voltage (B+) and
battery temperature (refer to Battery Temperature
Sensor for more information). It then determines a
target charging voltage. If sensed battery voltage is
0.5 volts or lower than the target voltage, the PCM
grounds the field winding until sensed battery volt-
age is 0.5 volts above target voltage. A circuit in the
PCM cycles the ground side of the generator field up
to 100 times per second (100Hz), but has the capabil-
ity to ground the field control wire 100% of the time
(full field) to achieve the target voltage. If the charg-
ing rate cannot be monitored (limp-in), a duty cycle
of 25% is used by the PCM in order to have some
generator output. Also refer to Charging Operation
for additional information.
KJCHARGING SYSTEM 8F - 31
Page 368 of 1803
HEATED SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED MIRRORS......................... 1
WINDOW DEFOGGER....................... 3HEATED SEAT SYSTEM.................... 10
HEATED MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED
MIRRORS............................1
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the optional heated mirror
package have an electric heating grid located behind
the mirror glass of each outside rear view mirror.
The heated mirrors are controlled by the rear win-
dow defogger switch. Electrical current is directed to
the heating grid inside the mirror only when the rear
window defogger switch is in the On position.
If the outside mirror heating grids and the rear
window heating grid are all inoperative, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). If the outside mirror heating grids are
inoperative, but the rear window heating grid is
operating as designed, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
HEATED MIRRORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
The heating grid behind each outside mirror glass
cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
entire power mirror unit must be replaced(Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/POWER MIRRORS/SIDEVIEW MIR-
ROR - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
POWER MIRRORS/SIDEVIEW MIRROR -
INSTALLATION).
OPERATION
The heated mirror is controlled by the rear window
defogger switch. The only time that the heated mir-
ror is on is when the rear window defogger is on. The
mirror should become warm to the touch.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED MIRRORS
For circuit descriptions and diagrams (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Check the fuse in the junction block. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or
component as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the junction
block. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the ignition switch as required.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the front door trim panel on the side
of the vehicle with the inoperative mirror heating
grid. Unplug the wire harness connector at the mir-
ror. Check for continuity between the ground circuit
cavity in the body half of the power mirror wire har-
ness connector and a good ground. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to ground as
required.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Turn on the rear
window defogger system. Check for battery voltage at
the rear window defogger relay output circuit cavity
in the body half of the power mirror wire harness
connector. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
open circuit to the rear window defogger relay as
required.
KJHEATED SYSTEMS 8G - 1
Page 378 of 1803

The heated seat module monitors inputs from the
heated seat sensors and the heated seat switches. In
response to these inputs the heated seat module uses
its internal programming to control outputs to the
heated seat elements in both front seats and to con-
trol the heated seat LED indicator lamps located in
both of the heated seat switches. The heated seat
module is also programmed to provide self-diagnostic
capability. When the module detects certain failures
within the heated seat system, it will provide a
visual indication of the failure by flashing the indica-
tor lamps in the affected heated seat switch. The
heated seat module will automatically turn off the
heated seat elements if it detects a short or open in
the heated seat element circuit or a heated seat sen-
sor value that is out of range.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSIS
The heated seat system is capable of performing
some self-diagnostics. The following table depicts the
various monitored failures which will be reported to
the vehicle operator or technician by flashing the
individual heated seat switch Light Emitting Diode
(LED) indicator lamps. Refer to the Heated Seat Sys-
tem Self-Diagnosis table for failure identification.
The driver side heated seat switch indicator lamps
will flash if a failure occurs in the driver side heated
seat, and the passenger side heated seat switch indi-
cator lamps will flash for a passenger side heated
seat failure. If a monitored heated seat system fail-
ure occurs, the switch indicator lamps will flash at a
pulse rate of about one-half second on, followed by
about one-half second off for a duration of about one
minute after the switch for the faulty heated seat is
depressed in either the Low or High direction. This
process will repeat every time the faulty heated seat
switch is actuated until the problem has been cor-
rected.
Heated Seat System Self-Diagnosis
Monitored FailureSwitch High
Indicator LampSwitch Low
Indicator Lamp
Heated Seat
Element ShortedFlashing Flashing
Heated Seat
Element OpenFlashing Off
Heated Seat
Sensor Value Out
of RangeOff FlashingIf the heated seat system failure is identified by
flashing heated seat switch indicator lamps, go to the
appropriate diagnosis and testing procedure in this
section and confirm the condition, using the step by
step procedure. If the monitored failure is confirmed,
replace the component. If the monitored failure is not
confirmed, replace the heated seat module with a
known good unit and retest the system.
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM TESTING
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams. Before
testing the individual components in the heated seat
system, perform the following preliminary checks:
²If a single indicator lamp for one heated seat
switch does not operate and the heated seat elements
do heat, refer toDiagnosis and Testing the
Heated Seat Switchin this section for the location
of heated seat switch diagnosis and testing proce-
dures.
²If both indicator lamps for a heated seat switch
operate, but the heated seat elements do not heat,
refer toDiagnosis and Testing the Heated Seat
Modulein Electronic Control Modules for the loca-
tion of heated seat module diagnosis and testing pro-
cedures.
²If an indicator lamp on either heated seat switch
remains illuminated after the heated seat has been
turned Off, refer toDiagnosis and Testing the
Heated Seat Modulein Electronic Control Modules
for the location of heated seat module diagnosis and
testing procedures. Also refer to the Body Diagnostic
Manual for additional diagnosis and testing proce-
dures.
DRIVER SEAT HEATER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat switches are located on the out-
board cushion side shield of the driver and passenger
front seats (Fig. 1). The two, three-position rocker
type switches provide a resistor multiplexed signal to
the Heated Seat Module through separate hard wired
circuits. Each switch has an Off, Low and High set-
ting. Each switch contains two light emitting diodes
(LED), one for each High and Low setting to let the
occupant know that the seat heater system is on.
The heated seat switches and their LED's cannot
be repaired. If either switch is faulty or damaged the
entire switch must be replaced.
KJHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 11
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)