key JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 647 of 1803

(4) Disconnect the steering wheel wire harness
connector for the horn switch from the horn switch
feed pigtail wire connector, which is located on the
back of the driver airbag housing.
CAUTION: Do not pull on the clockspring pigtail
wires or pry on the connector insulator to disen-
gage the connector from the driver airbag inflator
connector receptacle. Improper removal of these
pigtail wires and their connector insulators can
result in damage to the airbag circuits or connector
insulators.
(5) The clockspring driver airbag pigtail wire con-
nectors are secured by integral latches to the airbag
inflator connector receptacles, which are located on
the back of the driver airbag housing. Depress the
latches on each side of each connector insulator and
pull the insulators straight out from the airbag infla-
tor to disconnect them from the connector recepta-
cles.
(6) Remove the driver airbag from the steering
wheel.
(7) If the driver airbag has been deployed, the
clockspring must be replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
The following procedure is for replacement of a
faulty or damaged driver airbag. If the driver airbag
has been deployed, the clockspring must also be
replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION).
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.WARNING: USE EXTREME CARE TO PREVENT ANY
FOREIGN MATERIAL FROM ENTERING THE DRIVER
AIRBAG, OR BECOMING ENTRAPPED BETWEEN
THE DRIVER AIRBAG CUSHION AND THE DRIVER
AIRBAG TRIM COVER. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS
WARNING COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT INJURIES
UPON AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.
WARNING: THE DRIVER AIRBAG TRIM COVER
MUST NEVER BE PAINTED. REPLACEMENT AIR-
BAGS ARE SERVICED IN THE ORIGINAL COLORS.
PAINT MAY CHANGE THE WAY IN WHICH THE
MATERIAL OF THE TRIM COVER RESPONDS TO AN
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT. FAILURE TO OBSERVE
THIS WARNING COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT
INJURIES UPON AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.
(1) Position the driver airbag close enough to the
steering wheel to reconnect all three electrical con-
nections on the back of the airbag housing.
(2) When installing the driver airbag, reconnect
the two clockspring driver airbag pigtail wire connec-
tors to the airbag inflator connector receptacles by
pressing straight in on the connectors (Fig. 16). Be
certain to engage each keyed and color-coded connec-
tor to the matching connector receptacle. You can be
certain that each connector is fully engaged in its
receptacle by listening carefully for a distinct, audi-
ble click as the connector latches snap into place.
(3) Reconnect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector for the horn switch to the horn switch feed
pigtail wire connector, which is located at the back of
the driver airbag housing.
(4) Carefully position the driver airbag in the
steering wheel. Be certain that the clockspring pig-
tail wires and steering wheel wire harness in the
steering wheel hub area are not pinched between the
driver airbag and the steering wheel armature.
(5) From the underside of the steering wheel,
install and tighten the two screws that secure the
driver airbag to the steering wheel armature.
Tighten the screws to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(6) Do not reconnect the battery negative cable at
this time. The airbag system verification test proce-
dure should be performed following service of any
supplemental restraint system component. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - VERIFICATION TEST).
8O - 20 RESTRAINTSKJ
DRIVER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 654 of 1803

PASSENGER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION
The rearward facing surface of the injection
molded, thermoplastic passenger airbag door is the
most visible part of the passenger airbag (Fig. 23).
The passenger airbag door is located above the glove
box opening in front of the front seat passenger seat-
ing position on the instrument panel. The integral
upper mounting flange is secured with five screws
and the lower mounting flange with six screws to the
instrument panel structural support. The passenger
airbag door includes an integral air conditioning
panel outlet housing and an integral side window
demister outlet. An integral stamped metal bracket
that reinforces the upper airbag door mounting
flange is secured to the back of the door unit with
heat stakes. The upper airbag door fasteners and
mounting flange are concealed beneath the instru-
ment panel top cover, while the lower fasteners and
mounting flange are concealed beneath a bezel on the
instrument panel above the glove box opening.
Located behind the passenger airbag door within
the instrument panel is the passenger airbag unit
(Fig. 24). The passenger airbag unit used in this
model is a multistage, Next Generation-type that
complies with revised federal airbag standards to
deploy with less force than those used in some prior
models. The passenger airbag unit consists of a
molded, glass-filled nylon plastic housing, a molded
plastic inner airbag cushion cover, the airbag cush-
ion, and the airbag inflator. The airbag housing con-tains the airbag inflator, while the inner cover
contains the folded airbag cushion. The inner cover
completely encloses the airbag cushion and is perma-
nently retained to the housing. The passenger airbag
unit is secured by two screws on each side to two
stamped metal mounting brackets that are fastened
with screws to the instrument panel structural sup-
port. The airbag cushion is constructed of a coated
nylon fabric. The airbag inflator is a dual-initiator,
hybrid-type unit that is secured to and sealed within
the airbag housing. A short four-wire pigtail harness
with a keyed, yellow connector insulator connects the
two inflator initiators to the vehicle electrical system
through a dedicated take out and connector of the
instrument panel wire harness.
The passenger airbag cannot be repaired, and must
be replaced if deployed, faulty, or in any way dam-
aged. The passenger airbag door and the passenger
airbag mounting brackets are available for separate
service replacement.
OPERATION
The multistage passenger airbag is deployed by
electrical signals generated by the Airbag Control
Module (ACM) through the passenger airbag squib 1
and squib 2 circuits to the two initiators in the air-
bag inflator. By using two initiators, the airbag can
be deployed at multiple levels of force. The force level
is controlled by the ACM to suit the monitored
impact conditions by providing one of three delay
intervals between the electrical signals provided to
the two initiators. The longer the delay between
these signals, the less forcefully the airbag will
deploy.
Fig. 23 Passenger Airbag Door
1 - PASSENGER AIRBAG DOOR
2 - DEMISTER OUTLET
3 - PANEL OUTLET
4 - BEZEL
5 - GLOVE BOX
Fig. 24 Passenger Airbag Unit
1 - PIGTAIL WIRE CONNECTOR
2 - RETAINER
3 - HOUSING
4 - INNER COVER
KJRESTRAINTS 8O - 27
Page 663 of 1803

in parallel with the IC where the two pigtail wire
leads connect to the IC pins.
The seat belt switch cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, the entire seat belt buckle-
half unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The seat belt switches are designed to provide a
status signal to the seat belt switch sense inputs of
the Airbag Control Module (ACM) indicating whether
the front seat belts are fastened. The ACM uses the
seat belt switch inputs as a factor in determining
what level of force with which it should deploy the
multistage driver and passenger airbags. In addition,
the ACM sends electronic messages to the ElectroMe-
chanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) to control the
seat belt indicator based upon the status of the
driver side front seat belt switch. A spring-loaded
plastic slide with a small, enclosed permanent mag-
net is integral to the buckle latch mechanism. When
a seat belt tip-half is inserted and latched into the
seat belt buckle, the slide is pushed downward and
into close proximity of the Hall Effect Integrated Cir-
cuit (IC) chip within the buckle, which induces a cur-
rent within the chip. The chip provides this induced
current as an output to the ACM, which monitors the
current to determine the status of the front seat
belts. When the seat belt is unbuckled, the spring-
loaded slide and permanent magnet move upward
and away from the IC, causing the output current
from the seat belt switch to be reduced.
The seat belt switch receives a supply current from
the ACM, and the ACM senses the status of the front
seat belts through its pigtail wire connection to the
seat wire harness. The ACM also monitors the condi-
tion of the seat belt switch circuits through circuit
resistance created by the diagnostic resistor. The
ACM will illuminate the airbag indicator in the
EMIC and store a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) for
any fault that is detected in either seat belt switch
circuit. For proper diagnosis of the seat belt switches,
a DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the appro-
priate diagnostic information.
SEAT BELT TENSIONER
DESCRIPTION
A driver side seat belt tensioner supplements the
driver airbag system for all versions of this model
(Fig. 34). The seat belt tensioner is integral to the
driver side front seat belt and retractor unit, which is
secured to the B-pillar on the left side of the vehicle.
The retractor is concealed beneath the molded plastic
B-pillar trim. The seat belt tensioner consists prima-
rily of a molded plastic tensioner housing, a tubularmetal piston housing, a piston, a short rack gear, a
set of pinion gears, a pyrotechnically activated gas
generator, and a short pigtail wire. All of these com-
ponents are located on one side of the retractor spool
on the outside of the retractor housing. The seat belt
tensioner is controlled by the Airbag Control Module
(ACM) and is connected to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a dedicated take out of the body wire
harness by a keyed and latching molded plastic con-
nector insulator to ensure a secure connection.
The seat belt tensioner cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire driver side front seat
belt and retractor unit must be replaced. The seat
belt tensioner is not intended for reuse and must be
replaced following a deployment. A locked retractor
that will not allow the seat belt webbing to be
retracted or extracted is a sure indication that the
seat belt tensioner has been deployed and requires
replacement. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/FRONT SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL).
OPERATION
The seat belt tensioner is deployed by a signal gen-
erated by the Airbag Control Module (ACM) through
the driver seat belt tensioner line 1 and line 2 (or
squib) circuits. When the ACM sends the proper elec-
trical signal to the tensioner, the electrical energy
generates enough heat to initiate a small pyrotechnic
gas generator. The gas generator is installed in one
end of the tubular metal piston housing, which con-
tains a piston and a small rack gear. As the gas
expands, it pushes the piston and the rack gear
Fig. 34 Seat Belt Tensioner
1 - RETRACTOR
2 - TENSIONER HOUSING
3 - PISTON HOUSING
4 - PIGTAIL WIRE
5 - GAS GENERATOR
8O - 36 RESTRAINTSKJ
SEAT BELT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 682 of 1803
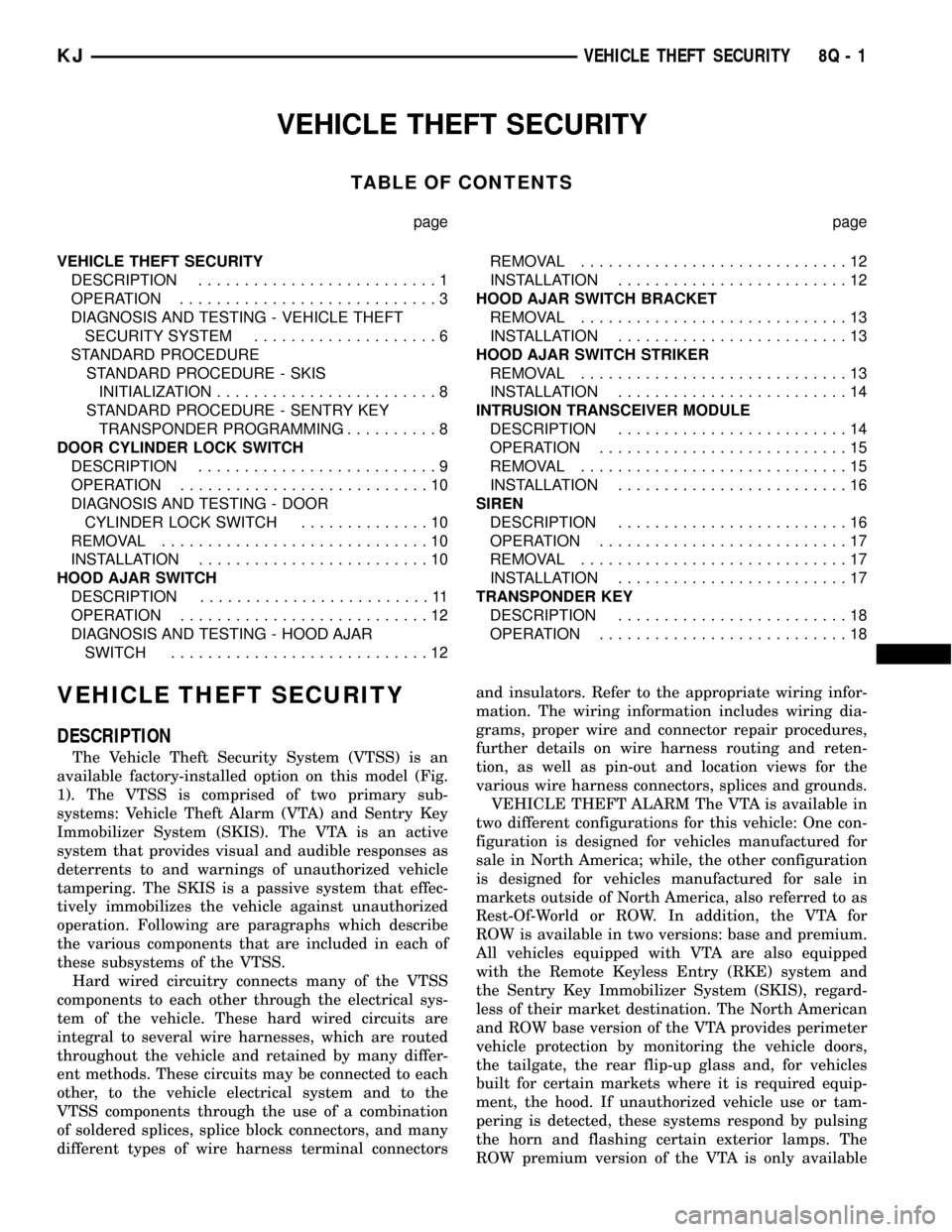
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY SYSTEM....................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SKIS
INITIALIZATION........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SENTRY KEY
TRANSPONDER PROGRAMMING..........8
DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR
CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH..............10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
HOOD AJAR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HOOD AJAR
SWITCH............................12REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
HOOD AJAR SWITCH BRACKET
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
HOOD AJAR SWITCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................14
INTRUSION TRANSCEIVER MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................15
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................16
SIREN
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
TRANSPONDER KEY
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY
DESCRIPTION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) is an
available factory-installed option on this model (Fig.
1). The VTSS is comprised of two primary sub-
systems: Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA) and Sentry Key
Immobilizer System (SKIS). The VTA is an active
system that provides visual and audible responses as
deterrents to and warnings of unauthorized vehicle
tampering. The SKIS is a passive system that effec-
tively immobilizes the vehicle against unauthorized
operation. Following are paragraphs which describe
the various components that are included in each of
these subsystems of the VTSS.
Hard wired circuitry connects many of the VTSS
components to each other through the electrical sys-
tem of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
VTSS components through the use of a combination
of soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectorsand insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
VEHICLE THEFT ALARM The VTA is available in
two different configurations for this vehicle: One con-
figuration is designed for vehicles manufactured for
sale in North America; while, the other configuration
is designed for vehicles manufactured for sale in
markets outside of North America, also referred to as
Rest-Of-World or ROW. In addition, the VTA for
ROW is available in two versions: base and premium.
All vehicles equipped with VTA are also equipped
with the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system and
the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS), regard-
less of their market destination. The North American
and ROW base version of the VTA provides perimeter
vehicle protection by monitoring the vehicle doors,
the tailgate, the rear flip-up glass and, for vehicles
built for certain markets where it is required equip-
ment, the hood. If unauthorized vehicle use or tam-
pering is detected, these systems respond by pulsing
the horn and flashing certain exterior lamps. The
ROW premium version of the VTA is only available
KJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 1
Page 683 of 1803

in vehicles manufactured for sale in certain markets
where it is required equipment. The ROW premium
version of the VTA provides the same perimeter pro-
tection features as the base version, but adds interior
vehicle intrusion protection. The ROW premium VTA
also replaces the pulsing horn feature of the base
version with an alarm siren as the audible deterrent,
while retaining the flashing exterior lamps visual
deterrent.The VTA includes the following major components,
which are described in further detail elsewhere in
this service information:
²Body Control Module- The Body Control
Module (BCM) is located on the Junction Block (JB)
under the driver side outboard end of the instrument
panel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/BODY CONTROL MODULE
- DESCRIPTION).
Fig. 1 Vehicle Theft Security System
1 - SIREN MODULE
2 - BODY CONTROL MODULE
3 - SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE4 - DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH (2)
5 - INTRUSION TRANSCEIVER MODULE
8Q - 2 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYKJ
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 684 of 1803

²Combination Flasher- An electronic combina-
tion flasher is integral to the hazard switch located
in the center of the instrument panel above the
radio. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHT-
ING - EXTERIOR/COMBINATION FLASHER -
DESCRIPTION).
²Door Ajar Switch- A door ajar switch is inte-
gral to the latch of each door in the vehicle. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR/
DOOR AJAR SWITCH - DESCRIPTION).
²Door Cylinder Lock Switch- For North
American vehicles only, a door cylinder lock switch is
located on the back of the lock cylinder of each front
door. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY/DOOR CYLINDER LOCK SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION).
²Flip-Up Glass Ajar Switch- A flip-up glass
ajar switch is integral to the rear flip-up glass latch,
located on the top of the tailgate near the center.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING -
INTERIOR/FLIP-UP GLASS AJAR SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION).
²Hood Ajar Switch- A hood ajar switch is
located beneath the hood panel on the right inner
fender side shield of vehicles built for sale in certain
markets where it is required equipment. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY/HOOD
AJAR SWITCH - DESCRIPTION).
²Horn Relay- A horn relay is located on the
Junction Block (JB) under the driver side outboard
end of the instrument panel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/HORN/HORN RELAY - DESCRIPTION).
²Intrusion Transceiver Module- An Intrusion
Transceiver Module (ITM) is located near the center
of the headliner in the passenger compartment of
vehicles built for sale in certain markets where it is
required equipment. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VE-
HICLE THEFT SECURITY/UK SECURITY SYSTEM
MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Security Indicator- A security indicator is
located in the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster
(EMIC) on the instrument panel in front of the driver
side front seat. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRU-
MENT CLUSTER/SECURITY INDICATOR -
DESCRIPTION).
²Siren- An alarm siren is located on the front
extension of the right front wheel house panel in the
engine compartment of vehicles built for sale in cer-
tain markets where it is required equipment. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY/
SIREN - DESCRIPTION).
²Tailgate Ajar Switch- A tailgate ajar switch is
integral to the latch for the tailgate in the vehicle.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING -
INTERIOR/TAILGATE AJAR SWITCH - DESCRIP-
TION).SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM The Sen-
try Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) is available as a
factory-installed option on this model. Vehicles
equipped with the Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA) are also
equipped with SKIS. The SKIS provides passive vehi-
cle protection by preventing the engine from operat-
ing unless a valid electronically encoded key is
detected in the ignition lock cylinder. The SKIS
includes the following major components, which are
described in further detail elsewhere in this service
information:
²Powertrain Control Module- The Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) is located on the left inner
fender shield in the engine compartment near the
dash panel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Sentry Key Immobilizer Module- The Sentry
Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) is located beneath
the steering column shrouds on the right side of the
steering column near the ignition lock cylinder hous-
ing. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Sentry Key Transponder- The Sentry Key
transponder is molded into the head of the ignition
key, and concealed by a gray molded rubber cap.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECU-
RITY/TRANSPONDER KEY - DESCRIPTION).
²SKIS Indicator- The SKIS indicator is located
in the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
on the instrument panel in front of the driver side
front seat. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRU-
MENT CLUSTER/SPEED CONTROL INDICATOR -
DESCRIPTION).
OPERATION
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) is
divided into two basic subsystems: Vehicle Theft
Alarm (VTA) and Sentry Key Immobilizer System
(SKIS). Following are paragraphs that briefly
describe the operation of each of these two sub-
systems.
VEHICLE THEFT ALARM The Body Control Mod-
ule (BCM) is used on this model to control and inte-
grate many of the electronic functions and features
included in the Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA). The BCM
receives hard wired inputs indicating the status of
the door ajar switches, the door cylinder lock
switches, the ignition switch, the tailgate ajar switch,
the tailgate cylinder lock switch, the flip-up glass
ajar switch, the power lock switches and, in vehicles
built for certain markets where it is required, the
hood ajar switch. The programming in the BCM
allows it to process the information from all of these
inputs and send control outputs to energize or de-en-
KJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 3
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 685 of 1803

ergize the combination flasher, the horn relay (except
vehicles with the Rest-Of-World or ROW premium
version of the VTA), and the security indicator. In
addition, in vehicles built for certain markets where
the ROW premium version of the VTA is required,
the BCM also exchanges electronic messages with
the Intrusion Transceiver Module (ITM) over the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus
network to provide the features found in this version
of the VTA.
The hard wired circuits and components of the
VTA may be diagnosed and tested using conventional
diagnostic tools and procedures. However, conven-
tional diagnostic methods may not prove conclusive
in the diagnosis of the Body Control Module (BCM),
the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC),
the Intrusion Transceiver Module (ITM), or the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus
network. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the BCM, the EMIC, the ITM,
and the PCI data bus network inputs and outputs
related to the VTA requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation. Following are paragraphs that briefly
describe the operation of each of the VTA features.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the VTA.
²ENABLING- The BCM must have the VTA
function electronically enabled in order for the VTA
to perform as designed. The logic in the BCM keeps
its VTA function dormant until it is enabled using a
DRBIIItscan tool. The VTA function of the BCM is
enabled on vehicles equipped with the VTA option at
the factory, but a service replacement BCM must be
VTA-enabled by the dealer using a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
²PRE-ARMING- The VTA has a pre-arming
sequence. Pre-arming occurs when a door, the tail-
gate, or the flip-up glass is open when the vehicle is
locked using a power lock switch, or when the ªLockº
button on the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmit-
ter is depressed. The power lock switch will not ini-
tiate the pre-arming sequence if the key is in the
ignition switch. When the VTA is pre-armed, the
arming sequence is delayed until all of the doors, the
tailgate, and the flip-up glass are closed.
²ARMING- Passive arming of the VTA occurs
when the vehicle is exited with the key removed from
the ignition switch and the doors are locked while
they are open using the power lock switch (see Pre-
Arming). Active arming of the VTA occurs when the
ªLockº button on the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
transmitter is depressed to lock the vehicle after all
of the doors, the tailgate, and the flip-up glass are
closed. The VTA will not arm if the doors are lockedusing the key in a lock cylinder or using a mechani-
cal lock button. Once the VTA begins the passive or
active arming sequence, the security indicator in the
instrument cluster will flash rapidly for about six-
teen seconds. This indicates that the VTA arming
sequence is in progress. If the ignition switch is
turned to the On position, if a door is unlocked with
the power lock switch or the RKE transmitter, or if
the tailgate is unlocked by any means during the six-
teen second arming sequence, the security indicator
will stop flashing and the VTA arming sequence will
abort. On vehicles equipped with the hood ajar
switch, the VTA arming sequence will occur regard-
less of whether the hood is open or closed, but the
underhood area will not be protected unless the hood
is closed when the VTA arming sequence begins.
Also, if the status of the hood ajar switch changes
from open (hood closed) to closed (hood open) during
the sixteen second arming sequence, the security
indicator will stop flashing and the VTA arming
sequence will abort. Once the sixteen second arming
sequence is successfully completed, the security indi-
cator will flash at a slower rate, indicating that the
VTA is armed.
²DISARMING- For vehicles built for the North
American market, disarming of the VTA occurs when
the vehicle is unlocked using the key to unlock a door
or the tailgate. Disarming of the VTA for any market
also occurs when the vehicle is unlocked by depress-
ing the ªUnlockº button of the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) transmitter, or by turning the ignition switch
to the On position using a valid Sentry Key Immobi-
lizer System (SKIS) key. Once the alarm has been
activated, any of these disarming methods will also
deactivate the alarm.
²POWER-UP MODE- When the armed VTA
senses that the battery has been disconnected and
reconnected, it enters its power-up mode. In the pow-
er-up mode the alarm system returns to the mode
that was last selected prior to the battery failure or
disconnect. If the VTA was armed prior to the battery
disconnect or failure, the technician or vehicle opera-
tor will have to actively or passively disarm the sys-
tem after the battery is reconnected. The power-up
mode will also apply if the battery goes dead while
the system is armed, and battery jump-starting is
then attempted. The VTA will remain armed until
the technician or vehicle operator has actively or pas-
sively disarmed the system. If the VTA is in the dis-
armed mode prior to a battery disconnect or failure,
it will remain disarmed after the battery is recon-
nected or replaced, or if jump-starting is attempted.
²ALARM- The VTA alarm output varies by the
version of the VTA with which the vehicle is
equipped. In all cases, the alarm provides both visual
and audible outputs; however, the time intervals of
8Q - 4 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYKJ
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 686 of 1803

these outputs vary by the requirements of the mar-
ket for which the vehicle is manufactured. In all
cases, the visual output will be a flashing on and off
of the exterior lamps. For vehicles equipped with the
North American or the ROW base version of the
VTA, the audible output will be a pulsing of the horn.
For vehicles with the ROW premium version of the
VTA, the audible output will be a cycling of the
alarm siren. See the owner's manual in the vehicle
glove box for details of the alarm output require-
ments of the specific market for which the vehicle
was manufactured. The inputs that will trigger the
alarm include the door ajar switches, the tailgate
ajar switch, the flip-up glass ajar switch, and in vehi-
cles built for certain markets where they are
required, the hood ajar switch and the Intrusion
Transceiver Module (ITM).
²TAMPER ALERT- The VTA tamper alert fea-
ture will pulse the horn (or the alarm siren for the
ROW premium version of the VTA) three times upon
VTA disarming, if the alarm was triggered and has
since timed-out. This feature alerts the vehicle oper-
ator that the VTA alarm was activated while the
vehicle was unattended.
²INTRUSION ALARM- The intrusion alarm is
an exclusive feature of the ROW premium version of
the VTA, which is only available in certain markets
where it is required. When the VTA is armed, a
motion sensor in the Intrusion Transceiver Module
(ITM) monitors the interior of the vehicle for move-
ment. If motion is detected, the ITM sends an elec-
tronic message to the BCM over the PCI data bus to
invoke the visual alarm feature, and sends an elec-
tronic message to the alarm siren in the engine com-
partment over a dedicated serial bus to invoke the
audible alarm feature. The motion detect feature of
the ITM can be disabled by depressing the ªLockº
button on the RKE transmitter three times within
fifteen seconds during VTA arming, while the secu-
rity indicator is still flashing rapidly. The VTA pro-
vides a single short siren ªchirpº as an audible
confirmation that the motion detect disable request
has been received. The ITM must be electronically
enabled in order for the intrusion alarm to perform
as designed. The logic in the ITM keeps its intrusion
alarm function dormant until it is enabled using a
DRBIIItscan tool. The intrusion alarm function of
the ITM is enabled on vehicles equipped with thisoption at the factory, but a service replacement ITM
must be configured and enabled by the dealer using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM The Sen-
try Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) is designed to
provide passive protection against unauthorized vehi-
cle use by disabling the engine after about two sec-
onds of running, whenever any method other than a
valid Sentry Key is used to start the vehicle. The
SKIS is considered a passive protection system
because it is always active when the ignition system
is energized and does not require any customer inter-
vention. The SKIS uses Radio Frequency (RF) com-
munication to obtain confirmation that the key in the
ignition switch is a valid key for operating the vehi-
cle. The microprocessor-based SKIS hardware and
software also use electronic messages to communi-
cate with other electronic modules in the vehicle over
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
data bus. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/COMMUNICATION - OPER-
ATION).
Pre-programmed Sentry Key transponders are pro-
vided with the vehicle from the factory. Each Sentry
Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) will recognize a
maximum of eight Sentry Keys. If the customer
would like additional keys other than those provided
with the vehicle, they may be purchased from any
authorized dealer. These additional keys must be pro-
grammed to the SKIM in the vehicle in order for the
system to recognize them as valid keys. This can be
done by the dealer using a DRBIIItscan tool or, if
Customer Learn programming is an available SKIS
feature in the market where the vehicle was pur-
chased, the customer can program the additional
keys, as long as at least two valid Sentry Keys are
already available. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHI-
CLE THEFT SECURITY - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - TRANSPONDER PROGRAMMING).
The SKIS performs a self-test each time the igni-
tion switch is turned to the On position, and will
store fault information in the form of Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTC's) if a system malfunction is
detected. The SKIS can be diagnosed, and any stored
DTC's can be retrieved using a DRBIIItscan tool.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
KJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 5
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 687 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY SYSTEM
The Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) is
divided into two basic subsystems: Vehicle Theft
Alarm (VTA) and Sentry Key Immobilizer System
(SKIS). Following are the recommended procedures
for diagnosis and testing of each of these two sub-
systems.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
VEHICLE THEFT ALARM
Models equipped with the Rest-Of-World (ROW)
premium version of the Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA)
provide some preliminary diagnostic feedback by illu-minating the security indicator located in the Elec-
troMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC). If the
security indicator illuminates with the ignition
switch in the On position, it indicates that there is a
communication problem between the Intrusion
Transceiver Module (ITM) and the Body Control
Module (BCM), or between the ITM and the siren
module. The BCM will also turn on the security indi-
cator if it receives a message from the ITM indicating
that the ITM has stored a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) for a siren module fault.
The hard wired circuits and components of the
VTA may be diagnosed and tested using conventional
diagnostic tools and procedures. However, conven-
tional diagnostic methods may not prove conclusive
in the diagnosis of the Body Control Module (BCM),
the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC),
the Intrusion Transceiver Module (ITM), or the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus
network. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the BCM, the EMIC, the ITM,
and the PCI data bus network inputs and outputs
related to the VTA requires the use of a DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
8Q - 6 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYKJ
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 688 of 1803

SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SKIS INDICATOR FAILS TO
LIGHT DURING BULB TEST1. SKIS indicator faulty. 1. Test and replace the instrument cluster as
required.
2. Fuse faulty. 2. Test and replace the SKIM fused B(+) and
fused ignition switch output (run-start) fuses in the
Junction Block (JB) as required.
3. Ground circuit faulty. 3. Test and repair the SKIM ground circuit as
required.
4. Fused B(+) circuit faulty. 4. Test and repair the SKIM fused B(+) circuit as
required.
5. Fused ignition switch
output circuit faulty.5. Test and repair the SKIM fused ignition switch
output (run-start) circuit as required.
SKIS INDICATOR FLASHES
WHEN IGNITION SWITCH IS
TURNED TO9ON9
POSITION1. Invalid key in ignition
switch lock cylinder.1. Replace the key with a known valid key.
2. Key-related fault. 2. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to diagnose the
key-related fault. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
SKIS INDICATOR LIGHTS
SOLID FOLLOWING BULB
TEST1. SKIS system malfunction/
fault detected.1. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to diagnose the SKIS.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
2. SKIS system inoperative. 2. Use a DRBIIITscan tool to diagnose the SKIS.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
SKIS INDICATOR FAILS TO LIGHT DURING BULB TEST
If the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) indi-
cator in the instrument cluster fails to illuminate for
about three seconds after the ignition switch is
turned to the On position (bulb test), perform the
instrument cluster actuator test. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). If the SKIS indicator still fails to
light during the bulb test, a wiring problem resulting
in the loss of battery current or ground to the Sentry
Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) should be sus-
pected, and the following procedure should be used
for diagnosis. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
details of wire harness routing and retention, connec-
tor pin-out information and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
NOTE: The following tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of this system. The most reli-
able, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose the
Sentry Key Immobilizer System requires the use of
a DRBIIITscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse (Fuse 33 - 10
ampere) in the Junction Block (JB). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
(Fuse 33 - 10 ampere) in the JB. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the open B(+) circuit between the
JB and the battery as required.
(3) Check the fused ignition switch output (run-
start) fuse (Fuse 15 - 10 ampere) in the JB. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or
component as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (run-start) fuse (Fuse 15 - 10 ampere) in the
JB. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open
fused ignition switch output (run-start) circuit
between the JB and the ignition switch as required.
(5) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector for the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
(SKIM) from the SKIM connector receptacle. Check
for continuity between each of the two ground circuit
cavities of the instrument panel wire harness connec-
tor for the SKIM and a good ground. There should be
KJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 7
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)