JEEP YJ 1995 Service And Repair Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: YJ, Model: JEEP YJ 1995Pages: 2158, PDF Size: 81.9 MB
Page 411 of 2158

HORNS
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1SERVICE PROCEDURES................... 3
SPECIFICATIONS......................... 5
GENERAL INFORMATION
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the XJ (Cherokee)/YJ (Wrangler) horn
systems. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for
complete circuit descriptions and diagrams.
HORN SWITCH
XJ
Two horn switches are installed in the steering
wheel, one on each side of the center-mounted driv-
er's airbag module. When either switch is depressed
it completes a circuit to ground for the coil side of the
horn relay. The steering wheel and steering column
must be properly grounded for the horn switches to
function. The horn switches are only serviced as a set
with their wiring. If either switch should fail, both
switches must be replaced.
YJ
A single switch is installed in the center of the
steering wheel, directly under the horn button. When
the horn button is depressed the switch completes a
circuit to ground for the coil side of the horn relay.
The steering wheel and steering column must be
properly grounded for the horn switch to function.
The horn switch is available for service.
HORN RELAY
On XJ models, the horn relay is a mini-relay in-
stalled in the relay center, which is mounted to the
lower instrument panel reinforcement inboard of thesteering column. On YJ models, the horn relay is a
ISO relay installed in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) near the battery tray. Refer to underside of
PDC cover for relay identification.
One side of the horn relay electromagnetic coil re-
ceives battery voltage at all times. When a horn
switch is depressed, the other side of the relay coil is
grounded. The energized relay coil causes the nor-
mally open relay contacts to close, providing battery
voltage to the horn.
If a problem is encountered with a continuously
sounding horn, it can usually be quickly resolved by
removing the horn relay until further diagnosis is
completed.
HORNS
On YJ models, a standard single, low-note, dia-
phragm-type horn is mounted and grounded to the
left inner fender shield under the hood. Dual horns
are standard equipment on XJ models. The high-note
diaphragm-type horn is mounted and grounded to
the left radiator closure panel brace behind the front
bumper. The low-note diaphragm-type horn is con-
nected in parallel with the high-note horn and is
mounted and grounded to the right radiator closure
panel brace behind the front bumper.
On XJ models, a cadmium-plated screw is
used to attach the horns to the body. Do not
substitute other types of screws as they may be-
come corroded and cause a loss of ground.
JHORNS 8G - 1
Page 412 of 2158

DIAGNOSIS
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AN AIR-
BAG, REFER TO GROUP 8M - RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING STEERING WHEEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT
IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POS-
SIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Inspect fuses (F8 and F16 in PDC on YJ)(11 in
fuseblock module and F14 in PDC on XJ). Replace
fuses, as required.
(2) Remove the horn relay (in the PDC on YJ)(in
the relay center on XJ). See Horn Relay Connec-
tions-XJ (Fig. 1) or Horn Relay Connections-YJ (Fig.
2) and perform the following tests.
²The common feed terminal (30) is connected to
battery voltage and should be hot at all times. If bat-
tery voltage is not present at relay cavity 30, check
circuit to fuse (F16 on YJ)(11 on XJ). Repair as re-
quired.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is connected to
terminal 30 in the de-energized position, but is not
used for this application.
²The normally open terminal (87) is connected to
the common feed terminal (30) in the energized posi-
tion. This terminal supplies battery voltage to the
horn. There should be continuity between relay cav-
ity 87 and the horn terminal at all times. If not, re-
pair wiring or connections as required.
²The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to the
electromagnet in the relay, and battery voltage
should be present at all times. If battery voltage is
not present at relay cavity 86, check circuit to fuse
(F16 on YJ)(11 on XJ). Repair as required.
²The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to the
electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded when the
horn switch is depressed. Check for continuity to
ground at relay cavity 85 with the horn switch de-
pressed. If no continuity is found with horn switch
depressed or, if continuity is found with horn switch
released, repair horn switch or wiring as required.
See Horn Switch Remove/Install in this group for ser-
vice procedures.
If all relay connections check OK, proceed to next
step.
(3) With the horn relay still removed, check the
horn relay by performing the following tests.
²A relay in the de-energized position should have
continuity between terminal 87A and terminal 30,
and no continuity between terminal 87 and terminal
30.
²Resistance value between terminals 85 and 86
(electromagnet) is 7565 ohms.²Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86. There
should now be continuity between terminal 87 and
terminal 30.
If relay fails any of the above tests, replace faulty
relay. If relay checks OK, reinstall and proceed to
next step.
(4) Disconnect wiring at horn terminal. Depress
horn switch. There should be battery voltage at the
horn wiring connector. If not, repair wiring to relay.
If OK, proceed to next step.
(5) Measure the resistance between the horn
bracket and a good chassis ground. The meter should
read zero ohms. If not, clean and tighten ground con-
nection between horn mounting screw and bracket. If
OK, replace faulty horn(s).
Fig. 1 Horn Relay Connections-XJ
Fig. 2 Horn Relay Connections-YJ
8G - 2 HORNSJ
Page 413 of 2158
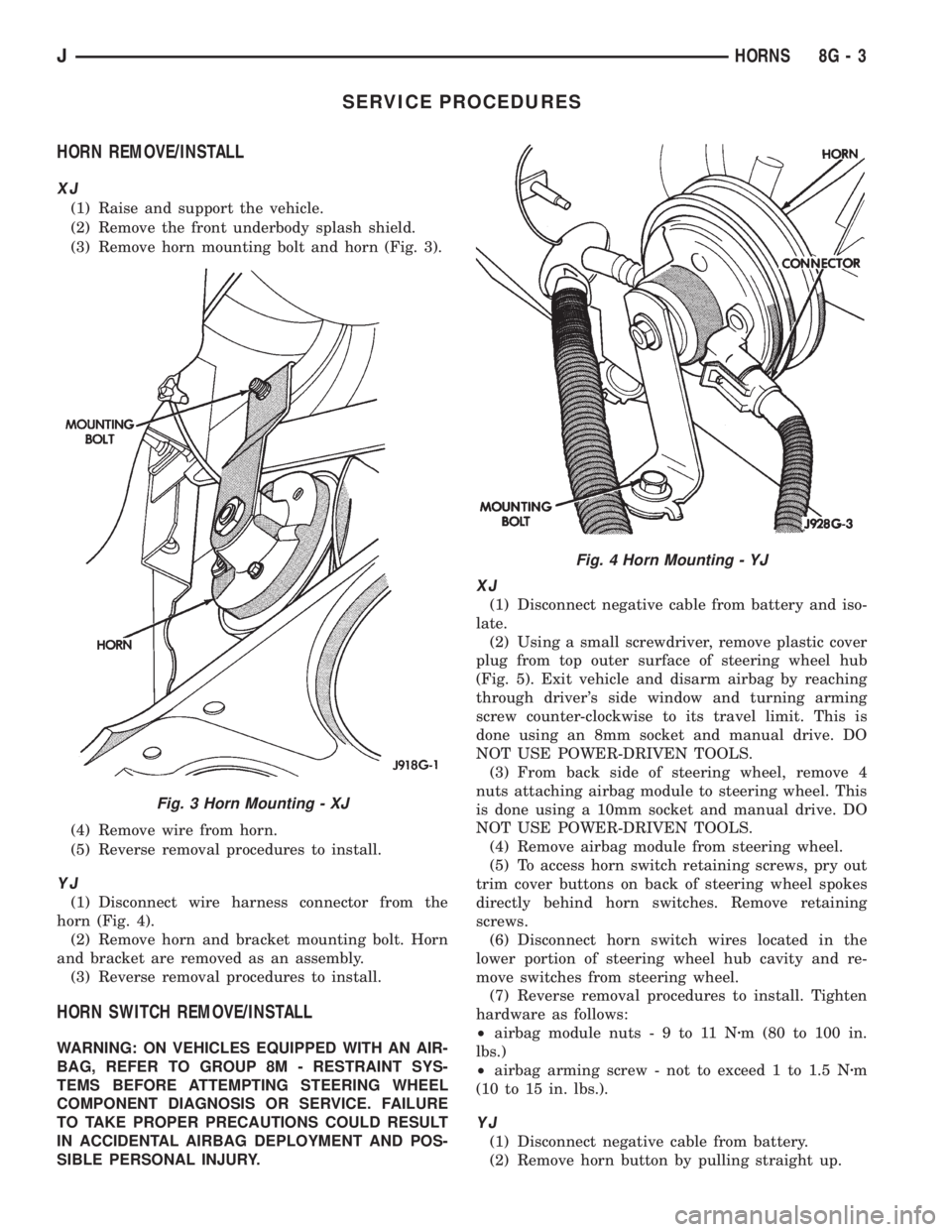
SERVICE PROCEDURES
HORN REMOVE/INSTALL
XJ
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front underbody splash shield.
(3) Remove horn mounting bolt and horn (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove wire from horn.
(5) Reverse removal procedures to install.
YJ
(1) Disconnect wire harness connector from the
horn (Fig. 4).
(2) Remove horn and bracket mounting bolt. Horn
and bracket are removed as an assembly.
(3) Reverse removal procedures to install.
HORN SWITCH REMOVE/INSTALL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AN AIR-
BAG, REFER TO GROUP 8M - RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING STEERING WHEEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT
IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POS-
SIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
XJ
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery and iso-
late.
(2) Using a small screwdriver, remove plastic cover
plug from top outer surface of steering wheel hub
(Fig. 5). Exit vehicle and disarm airbag by reaching
through driver's side window and turning arming
screw counter-clockwise to its travel limit. This is
done using an 8mm socket and manual drive. DO
NOT USE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS.
(3) From back side of steering wheel, remove 4
nuts attaching airbag module to steering wheel. This
is done using a 10mm socket and manual drive. DO
NOT USE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS.
(4) Remove airbag module from steering wheel.
(5) To access horn switch retaining screws, pry out
trim cover buttons on back of steering wheel spokes
directly behind horn switches. Remove retaining
screws.
(6) Disconnect horn switch wires located in the
lower portion of steering wheel hub cavity and re-
move switches from steering wheel.
(7) Reverse removal procedures to install. Tighten
hardware as follows:
²airbag module nuts-9to11Nzm (80 to 100 in.
lbs.)
²airbag arming screw - not to exceed 1 to 1.5 Nzm
(10 to 15 in. lbs.).
YJ
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove horn button by pulling straight up.
Fig. 3 Horn Mounting - XJ
Fig. 4 Horn Mounting - YJ
JHORNS 8G - 3
Page 414 of 2158
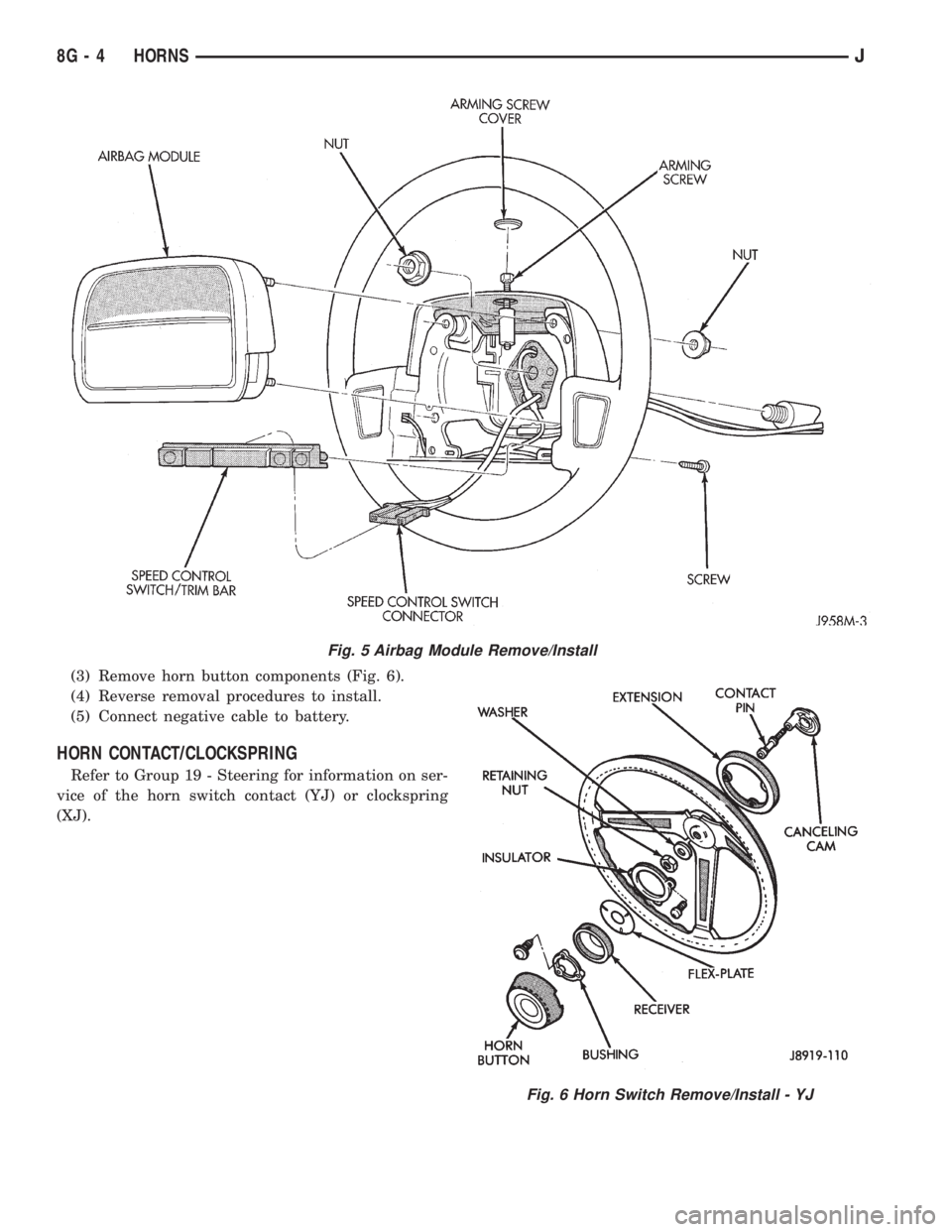
(3) Remove horn button components (Fig. 6).
(4) Reverse removal procedures to install.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery.
HORN CONTACT/CLOCKSPRING
Refer to Group 19 - Steering for information on ser-
vice of the horn switch contact (YJ) or clockspring
(XJ).
Fig. 5 Airbag Module Remove/Install
Fig. 6 Horn Switch Remove/Install - YJ
8G - 4 HORNSJ
Page 415 of 2158

SPECIFICATIONS
JHORNS 8G - 5
Page 416 of 2158

Page 417 of 2158

VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1SERVICE PROCEDURES................... 9
GENERAL INFORMATION
The vehicle speed control system (Fig. 1) is an
available option on all XJ (Cherokee) models. The
system is electronically controlled and vacuum oper-
ated. Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the vehicle speed control system. Re-
fer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for complete cir-
cuit descriptions and diagrams.
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
The speed control servo is mounted to a bracket on
the right side inner fender shield in the engine com-
partment. The servo unit consists of a solenoid valve
body, a vacuum servo and the mounting bracket. The
PCM controls the solenoid valve body. The solenoid
valve body controls the application and release of
vacuum to the diaphragm of the vacuum servo. The
servo unit cannot be repaired and is serviced only as
a complete assembly.
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
The speed control switch module is mounted to the
center of the steering wheel below the driver's airbag
module. The PCM monitors the state of the speed
control switches. The individual switches are labeled:
OFF/ON, RESUME/ACCEL, SET/COAST. Refer to
the owner's manual for more information on speed
control switch functions and setting procedures. The
individual switches cannot be repaired. If one switch
fails, the entire switch module must be replaced.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
Vehicles with the speed control option use a dual
function stop lamp switch. The switch is mounted in
the same location as the conventional stop lamp
switch, on the brake pedal mounting bracket under
the instrument panel. The PCM monitors the state of
the dual function stop lamp switch. Refer to Group 5
- Brakes for more information on stop lamp switch
service and adjustment procedures.
SERVO CABLE
The speed control servo cable is connected betweenthe speed control vacuum servo diaphragm and the
throttle control linkage. This cable causes the throt-
tle control linkage to open or close the throttle valve
in response to movement of the vacuum servo dia-
phragm.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The speed control electronic control circuitry is in-
tegrated into the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The PCM is located in the engine compartment on
the left side inner fender shield. The PCM speed con-
trol functions are monitored by the On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems are
monitored by the PCM. Each monitored circuit is as-
signed a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM
will store a DTC in electronic memory for any failure
it detects. See Using On-Board Diagnostic System in
this group for more information. The PCM cannot be
repaired and must be replaced if faulty.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
The vacuum reservoir is mounted behind the left
end of the front bumper bar. The reservoir contains a
one-way check valve to trap engine vacuum in the
reservoir. When engine vacuum drops, as in climbing
a grade while driving, the reservoir supplies the vac-
uum needed to maintain proper speed control opera-
tion. The vacuum reservoir cannot be repaired and
must be replaced if faulty.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) is a pulse genera-
tor mounted to an adapter near the transmission
(two-wheel drive) or transfer case (four-wheel drive)
output shaft. The sensor is driven through the
adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The VSS pulse
signal to the speedometer/odometer is monitored by
the PCM speed control circuitry to determine vehicle
speed and to maintain speed control set speed. Refer
to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for testing of this component. Refer to Group
14 - Fuel System for service of this component.
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1
Page 418 of 2158

WARNING: THE USE OF VEHICLE SPEED CON-
TROL IS NOT RECOMMENDED WHEN DRIVING
CONDITIONS DO NOT PERMIT MAINTAINING ACONSTANT SPEED, SUCH AS IN HEAVY TRAFFIC
OR ON ROADS THAT ARE WINDING, ICY, SNOW
COVERED, OR SLIPPERY.
DIAGNOSIS
Before beginning diagnosis, perform a vehicle road
test to verify reports of speed control system mal-
function. The road test should include attention to
the speedometer. Speedometer operation should be
smooth and without flutter at all speeds.
Flutter in the speedometer indicates a problem
which might cause surging in the speed control sys-
tem. The cause of any speedometer problems should
be corrected before proceeding. Refer to Group 8E -
Instrument Panel and Gauges for speedometer diag-
nosis.
If a road test verifies a system problem and the
speedometer operates properly, check for:
(1) Loose or corroded electrical connections at the
servo. Corrosion should be removed from electricalterminals and a light coating of Mopar MultiPurpose
Grease, or equivalent, applied.
(2) Correct installation of the vacuum check valve
in the hose from servo to vacuum source. The word
VAC on the valve must point toward the vacuum
source.
(3) Loose or leaking vacuum hoses or connections.
(4) Secure attachment of both ends of the speed
control servo cable.
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals, or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
Fig. 1 Vehicle Speed Control System
8H - 2 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMJ
Page 419 of 2158
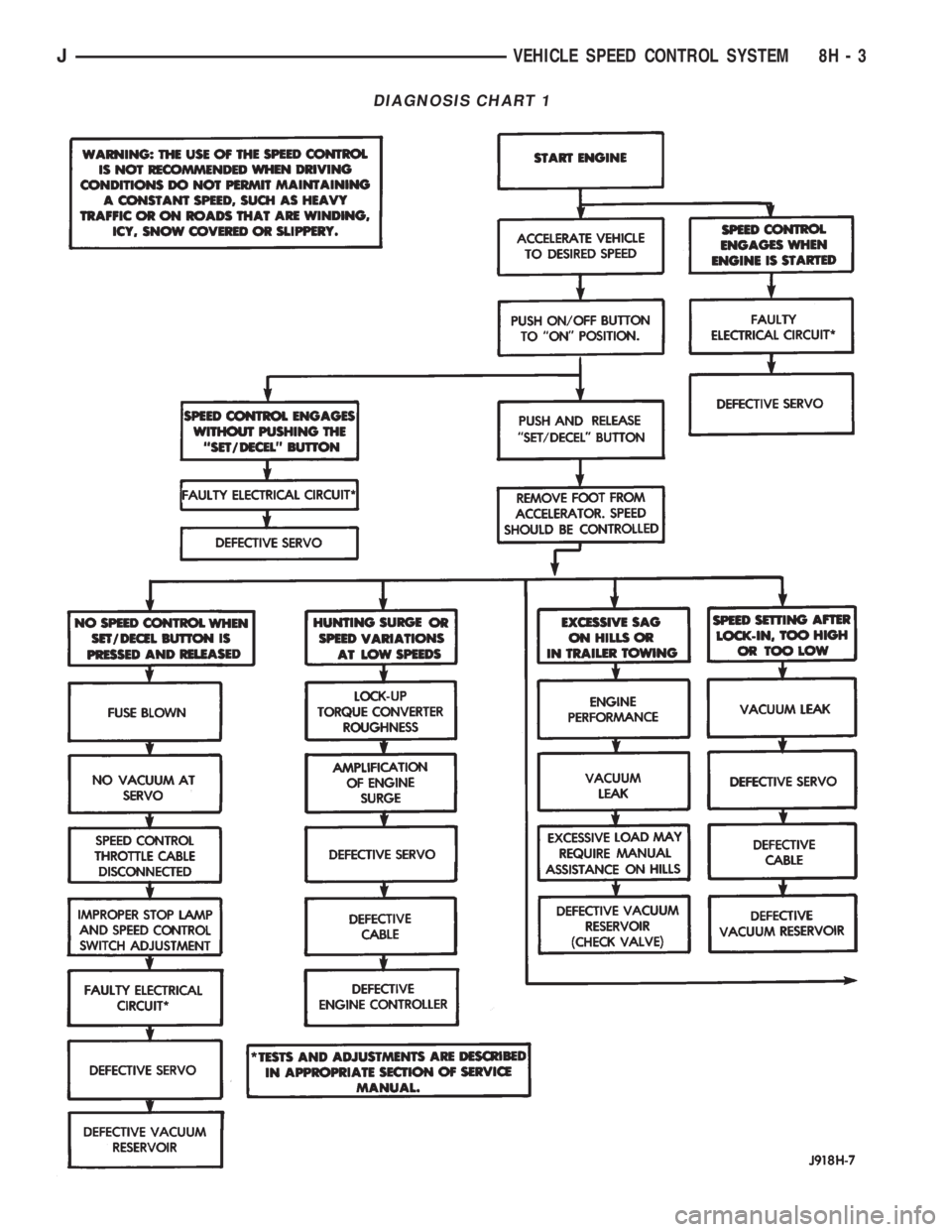
DIAGNOSIS CHART 1
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 3
Page 420 of 2158
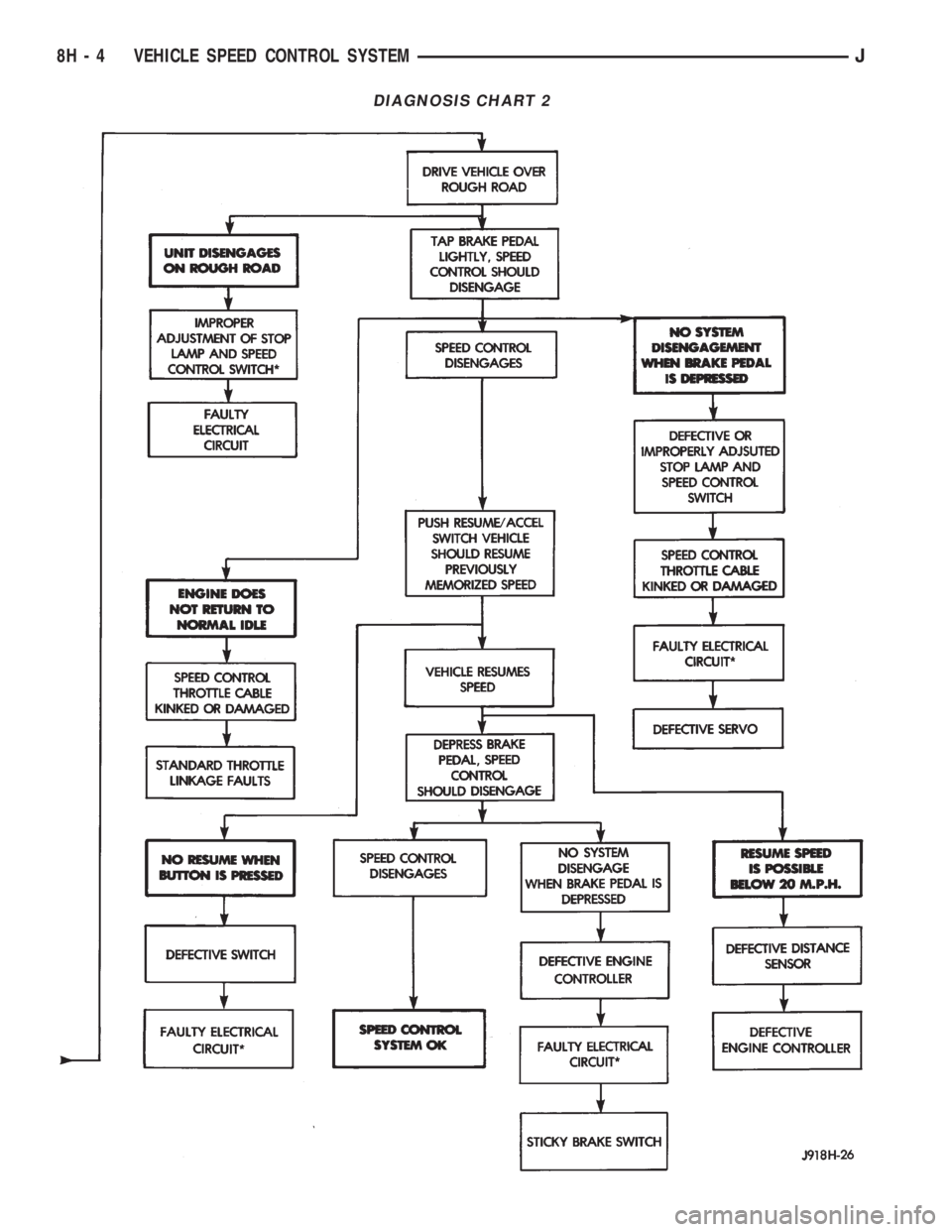
DIAGNOSIS CHART 2
8H - 4 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMJ