sensor JEEP YJ 1995 Service And Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: YJ, Model: JEEP YJ 1995Pages: 2158, PDF Size: 81.9 MB
Page 349 of 2158
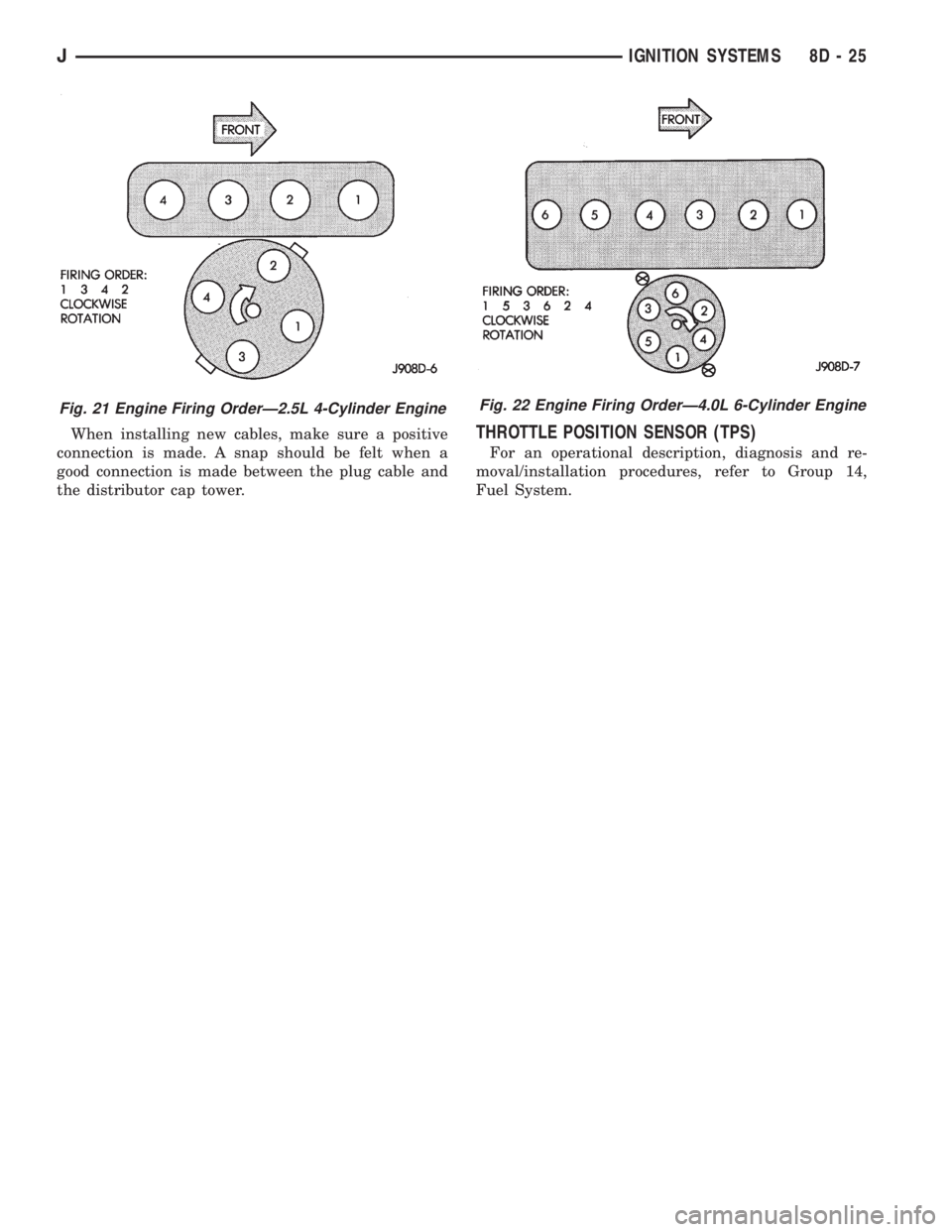
When installing new cables, make sure a positive
connection is made. A snap should be felt when a
good connection is made between the plug cable and
the distributor cap tower.THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
For an operational description, diagnosis and re-
moval/installation procedures, refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
Fig. 22 Engine Firing OrderÐ4.0L 6-Cylinder EngineFig. 21 Engine Firing OrderÐ2.5L 4-Cylinder Engine
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 25
Page 358 of 2158

The high-line cluster includes the following gauges:
²coolant temperature gauge
²fuel gauge
²oil pressure gauge
²speedometer/odometer
²tachometer
²trip odometer
²voltmeter.
The high-line cluster includes provisions for the fol-
lowing indicator lamps:
²anti-lock brake system lamp
²brake warning lamp
²four-wheel drive indicator lamps
²headlamp high beam indicator lamp
²low fuel warning lamp
²low washer fluid warning lamp
²malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp
²seat belt reminder lamp
²turn signal indicator lamps
²upshift indicator lamp.
GAUGES
With the ignition switch in the ON or START posi-
tion, voltage is supplied to all gauges through the in-
strument cluster gauge area printed circuit. With the
ignition switch in the OFF position, voltage is not
supplied to the gauges. A gauge pointer may remain
within the gauge scale after the ignition switch is
OFF. However, the gauges do not accurately indicate
any vehicle condition unless the ignition switch is
ON.
All gauges except the odometer are air core mag-
netic units. Two fixed electromagnetic coils are lo-
cated within the gauge. These coils are wrapped at
right angles to each other around a movable perma-
nent magnet. The movable magnet is suspended
within the coils on one end of a shaft. The gauge nee-
dle is attached to the other end of the shaft.
One of the coils has a fixed current flowing through
it to maintain a constant magnetic field strength.
Current flow through the second coil changes, which
causes changes in its magnetic field strength. The
current flowing through the second coil can be
changed by:
²a variable resistor-type sending unit (fuel level,
coolant temperature, or oil pressure)
²changes in electrical system voltage (voltmeter)
²electronic control circuitry (speedometer/odometer,
tachometer).
The gauge needle moves as the movable permanent
magnet aligns itself to the changing magnetic fields
created around it by the electromagnets.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE
The coolant temperature gauge gives an indication
of engine coolant temperature. The coolant tempera-
ture sending unit is a thermistor that changes elec-
trical resistance with changes in engine coolanttemperature. High sending unit resistance causes
low coolant temperature readings. Low resistance
causes high coolant temperature readings.
The gauge will read at the high end of the scale
when the ignition switch is turned to the START po-
sition. This is caused by the bulb test circuit wiring
provision. The same wiring is used for the high-line
cluster with a coolant temperature gauge and the
low-line cluster with a coolant temperature warning
lamp. Sending unit resistance values are shown in a
chart in Specifications.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge gives an indication of the level of
fuel in the fuel tank. The fuel gauge sending unit has
a float attached to a swing-arm in the fuel tank. The
float moves up or down within the fuel tank as fuel
level changes. As the float moves, an electrical con-
tact on the swing-arm wipes across a resistor coil,
which changes sending unit resistance. High sending
unit resistance causes low fuel level readings. Low
resistance causes high fuel level readings. Sending
unit resistance values are shown in a chart in Spec-
ifications.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The oil pressure gauge gives an indication of en-
gine oil pressure. The combination oil pressure send-
ing unit contains a flexible diaphragm. The
diaphragm moves in response to changes in engine
oil pressure. As the diaphragm moves, sending unit
resistance increases or decreases. High resistance on
the gauge side of the sending unit causes high oil
pressure readings. Low resistance causes low oil
pressure readings. Sending unit resistance values are
shown in a chart in Specifications.
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER
The speedometer/odometer gives an indication of
vehicle speed and travel distance. The speedometer
receives a vehicle speed pulse signal from the Vehicle
Speed Sensor (VSS). An electronic integrated circuit
contained within the speedometer reads and analyzes
the pulse signal. It then adjusts the ground path re-
sistance of one electromagnet in the gauge to control
needle movement. It also sends signals to an electric
stepper motor to control movement of the odometer
number rolls. Frequency values for the pulse signal
are shown in a chart in Specifications.
The VSS is mounted to an adapter near the trans-
mission (two-wheel drive) or transfer case (four-wheel
drive) output shaft. The sensor is driven through the
adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The adapter
and pinion vary with transmission, transfer case,
axle ratio and tire size. Refer to Group 21 - Trans-
mission and Transfer Case for more information.
8E - 2 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJJ
Page 360 of 2158

HEADLAMP HIGH BEAM INDICATOR LAMP
The high beam indicator lamp is controlled by the
headlamp dimmer (multi-function) switch. One side
of the indicator bulb is grounded at all times. The
other side of the bulb receives battery feed through
the contacts of the dimmer switch when the multi-
function switch stalk is actuated to turn the head-
lamp high beams on. Refer to Group 8L - Lamps for
more information.
LOW FUEL WARNING LAMP
A Light-Emitting Diode (LED) on the face of the
fuel gauge will light when the fuel level falls below
approximately 4 gallons. A low fuel warning module
attached to the rear of the fuel gauge controls when
the LED will light. When the module senses 66.5
ohms or more resistance from the fuel level sending
unit for 10 continuous seconds, the LED will light.
When the module senses 63.5 ohms or less resistance
from the fuel level sending unit for 20 continuous
seconds, the LED is turned off.
LOW OIL PRESSURE WARNING LAMP
The low oil pressure warning lamp lights with the
ignition switch in the ON position and the engine not
running. The lamp should be off when the engine is
running. Battery voltage is supplied to one side of
the indicator bulb when the ignition switch is turned
ON. The warning lamp side of the combination oil
pressure sending unit is connected to the other side
of the bulb. When normal engine oil pressure is ap-
plied to the sending unit, resistance on the warning
lamp side is high and the lamp goes off. When engine
oil pressure is too low, resistance on the warning
lamp side of the sending unit is low, which causes
the bulb to light.
LOW WASHER FLUID WARNING LAMP
The low washer fluid warning lamp indicates when
the fluid level in the washer reservoir is too low. The
washer fluid level sensor uses a float in the reservoir
to monitor fluid level. The action of the float opens or
closes the switch within the sensor that provides ig-
nition-switched battery voltage to the lamp bulb. Re-
fer to Group 8K - Wiper and Washer Systems for
more information.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
The CHECK ENGINE or Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) lights each time the ignition switch is
turned ON, and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.
If the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) receives an
incorrect signal or no signal from certain fuel oremission system related circuits or components, the
lamp is turned on. This will indicate that the PCM
has recorded a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in
electronic memory for a circuit or component mal-
function. Refer to Group 14 - Fuel System for more
information.
SEAT BELT REMINDER LAMP
The seat belt reminder lamp lights for 4 to 8 sec-
onds after the ignition switch is turned to the ON po-
sition. A timer in the chime/buzzer module controls
ignition-switched battery feed to the lamp. Refer to
Group 8U - Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems for more
information.
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR LAMPS
The left and right turn signal indicator lamps are
controlled by the turn signal and hazard warning
(multi-function) switches. One side of the bulb for
each lamp is grounded at all times. The other side of
the bulb receives battery feed through the contacts of
the multi-function switch when the turn signal lever
(multi-function switch stalk) or hazard warning but-
ton are actuated. Refer to Group 8J - Turn Signal
and Hazard Warning Systems for more information.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have
an optional upshift indicator lamp. Ground feed for
the lamp is switched by the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). The lamp lights to indicate when the
driver should shift to the next highest gear for best
fuel economy. The PCM will turn the lamp off after 3
to 5 seconds if the upshift is not performed. The lamp
will remain off until the vehicle stops accelerating
and is brought back to the range of lamp operation,
or until the transmission is shifted into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally on when the igni-
tion switch is turned ON and is turned off when the
engine is started. The lamp will be turned on during
vehicle operation according to engine speed and load.
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS
All cluster illumination lamps receive battery feed
from the instrument lamps fuse in the fuseblock
module through the panel dimmer rheostat of the
headlamp switch. When the park or headlamps are
on, the cluster illumination lamps light. Illumination
brightness can be adjusted by rotating the headlamp
switch knob (clockwise to dim, counterclockwise to
brighten).
8E - 4 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJJ
Page 362 of 2158

(5) Probe cavity B1 of cluster connector A. Check
for continuity to a good ground. There should be no
continuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair
short circuit as required.
(6) Still probing cavity B1 of cluster connector A,
check for continuity to cavity B of sending unit body
half connector. There should be continuity. If OK, re-
place gauge. If not OK, repair open circuit as re-
quired.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The diagnosis found here addresses an inoperative
gauge condition. If the problem being diagnosed is re-
lated to gauge accuracy, be certain to confirm that
problem is with gauge and not with engine oiling sys-
tem performance. Actual engine oil pressure should
be checked with a test gauge and compared to gauge
readings before you proceed with gauge diagnosis.
Refer to Group 9 - Engines for more information.
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Disconnect oil pres-
sure sending unit connector. The sending unit (Fig. 3)
is located on right side of engine block. On 2.5L en-
gine, it is just forward of ignition distributor and just
to the rear of generator mounting bracket. On 4.0L
engine, it is just to the rear of ignition distributor
and above oil filter adapter. The gauge needle should
move to high end of gauge scale. If OK, go to next
step. If not OK, go to step 3.
(2) Install a jumper wire from sending unit wiring
to ground. The gauge needle should move to low end
of gauge scale. If OK, replace sending unit. If not
OK, remove jumper wire and go to next step.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Disconnect battery
negative cable. Remove instrument cluster bezel and
cluster assembly. Disconnect instrument cluster con-
nector A.
(4) Probe cavity B7 (cavity B8 - RHD) of cluster
connector A. Check for continuity to a good ground.
There should be no continuity. If OK, go to next step.
If not OK, repair short circuit as required.(5) Still probing cavity B7 (cavity B8 - RHD) of
cluster connector A, check for continuity to sending
unit wire connector. There should be continuity. If
OK, replace gauge. If not OK, repair open circuit as
required.
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER
The diagnosis found here addresses an inoperative
gauge condition. If the problem being diagnosed is re-
lated to gauge accuracy, be certain to confirm that
problem is with gauge and not with incorrect speed-
ometer pinion, axle ratio or tire size. Refer to Group
21 - Transmission and Transfer Case for more infor-
mation.
(1) Perform vehicle speed sensor test as described
in the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, replace ve-
hicle speed sensor.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable. Unplug vehi-
cle speed sensor, PCM, and daytime running lamp
module connectors. Remove instrument cluster bezel
and cluster assembly. Disconnect instrument cluster
connector A.
(3) Probe cavity A5 (cavity B6 - RHD) of cluster
connector A. Check for continuity to a good ground.
There should be no continuity. If OK, go to next step.
If not OK, repair short circuit as required.
(4) Still probing cavity A5 (cavity B6 - RHD) of
cluster connector A, check for continuity to cavity 1 of
vehicle speed sensor connector (Fig. 4). There should
be continuity. If OK, replace speedometer/odometer. If
not OK, repair open circuit as required.
TACHOMETER
(1) With engine running, check for tachometer sig-
nal at pin 43 of PCM connector (Fig. 5). See Tachom-
eter Calibration chart in Specifications. If OK, go to
next step. If not OK, replace PCM.
Fig. 2 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit ConnectorFig. 3 Oil Pressure Switch/Sending Unit - Typical
8E - 6 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJJ
Page 363 of 2158
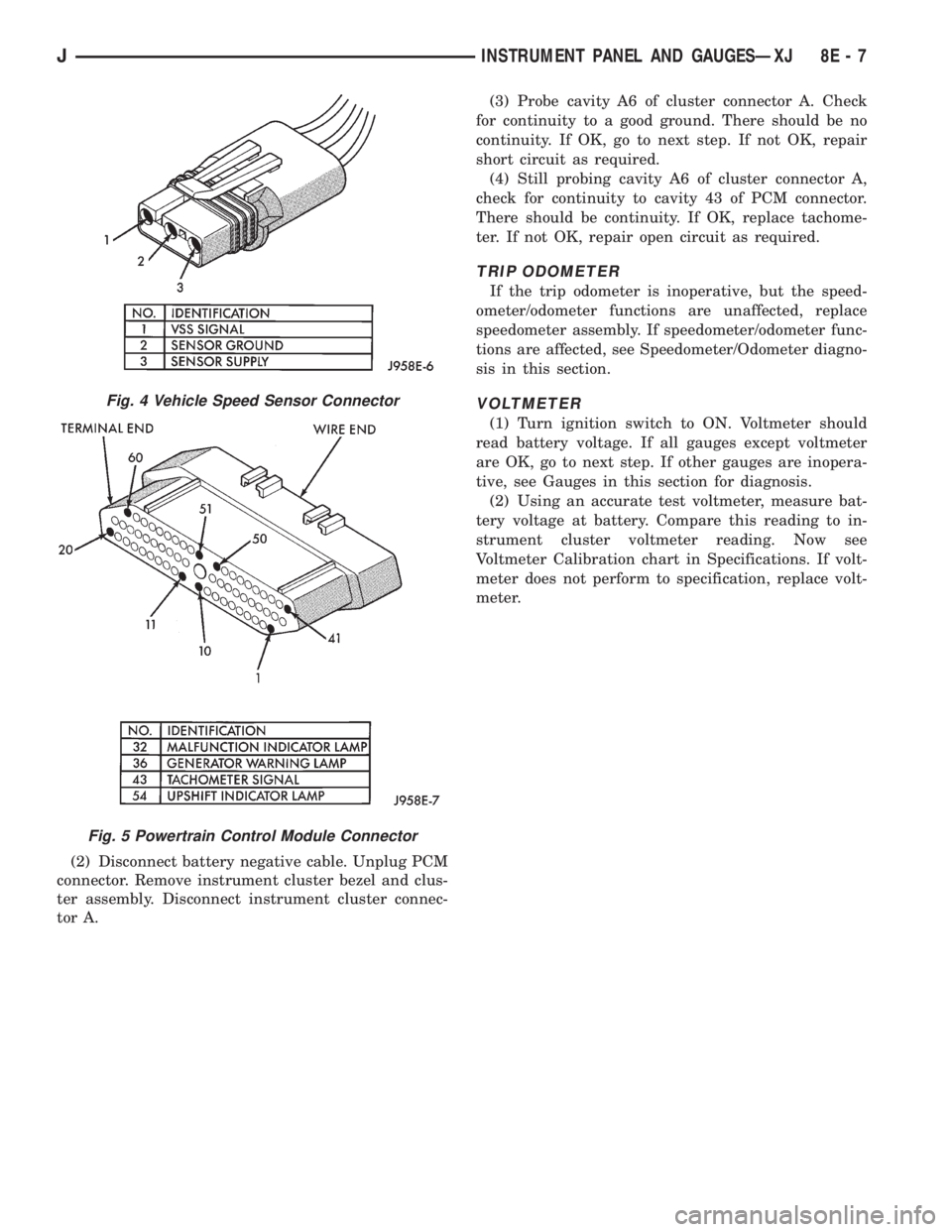
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable. Unplug PCM
connector. Remove instrument cluster bezel and clus-
ter assembly. Disconnect instrument cluster connec-
tor A.(3) Probe cavity A6 of cluster connector A. Check
for continuity to a good ground. There should be no
continuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair
short circuit as required.
(4) Still probing cavity A6 of cluster connector A,
check for continuity to cavity 43 of PCM connector.
There should be continuity. If OK, replace tachome-
ter. If not OK, repair open circuit as required.
TRIP ODOMETER
If the trip odometer is inoperative, but the speed-
ometer/odometer functions are unaffected, replace
speedometer assembly. If speedometer/odometer func-
tions are affected, see Speedometer/Odometer diagno-
sis in this section.
VOLTMETER
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Voltmeter should
read battery voltage. If all gauges except voltmeter
are OK, go to next step. If other gauges are inopera-
tive, see Gauges in this section for diagnosis.
(2) Using an accurate test voltmeter, measure bat-
tery voltage at battery. Compare this reading to in-
strument cluster voltmeter reading. Now see
Voltmeter Calibration chart in Specifications. If volt-
meter does not perform to specification, replace volt-
meter.
Fig. 4 Vehicle Speed Sensor Connector
Fig. 5 Powertrain Control Module Connector
JINSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJ 8E - 7
Page 381 of 2158

The gauge needle moves as the movable permanent
magnet aligns itself to the changing magnetic fields
created around it by the electromagnets.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE
The coolant temperature gauge gives an indication
of engine coolant temperature. The coolant tempera-
ture sending unit is a thermistor that changes elec-
trical resistance with changes in engine coolant
temperature. High sending unit resistance causes
low coolant temperature readings. Low resistance
causes high coolant temperature readings. Sending
unit resistance values are shown in a chart in Spec-
ifications.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge gives an indication of the level of
fuel in the fuel tank. The fuel gauge sending unit has
a float attached to a swing-arm in the fuel tank. The
float moves up or down within the fuel tank as fuel
level changes. As the float moves, an electrical con-
tact on the swing-arm wipes across a resistor coil,
which changes sending unit resistance. High sending
unit resistance causes high fuel level readings. Low
resistance causes low fuel level readings. Sending
unit resistance values are shown in a chart in Spec-
ifications.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The oil pressure gauge gives an indication of en-
gine oil pressure. The combination oil pressure send-
ing unit contains a flexible diaphragm. The
diaphragm moves in response to changes in engine
oil pressure. As the diaphragm moves, sending unit
resistance increases or decreases. High resistance on
the gauge side of the sending unit causes high oil
pressure readings. Low resistance causes low oil
pressure readings. Sending unit resistance values are
shown in a chart in Specifications.
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER
The speedometer/odometer give an indication of ve-
hicle speed and travel distance. The speedometer re-
ceives a vehicle speed pulse signal from the Vehicle
Speed Sensor (VSS). An electronic integrated circuit
contained within the speedometer reads and analyzes
the pulse signal. It then adjusts the ground path re-
sistance of one electromagnet in the gauge to control
needle movement. It also sends signals to an electric
stepper motor to control movement of the odometer
number rolls. Frequency values for the pulse signal
are shown in a chart in Specifications.
The VSS is mounted to an adapter near the trans-
fer case output shaft. The sensor is driven through
the adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The
adapter and pinion vary with transmission, axle ratio
and tire size. Refer to Group 21 - Transmission and
Transfer Case for more information.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer gives an indication of engine speed
in Revolutions-Per-Minute (RPM). With the engine
running, the tachometer receives an engine speed
pulse signal from the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). An electronic integrated circuit contained
within the tachometer reads and analyzes the pulse
signal. It then adjusts the ground path resistance of
one electromagnet in the gauge to control needle
movement. Frequency values for the pulse signal are
shown in a chart in Specifications.
TRIP ODOMETER
The trip odometer is driven by the same electronic
integrated circuit as the speedometer/odometer. How-
ever, by depressing the trip odometer reset knob on
the face of the speedometer, the trip odometer can be
reset to zero. The trip odometer is serviced only as a
part of the speedometer/odometer gauge assembly.
VOLTMETER
The voltmeter is connected in parallel with the bat-
tery. With the ignition switch ON, the voltmeter in-
dicates battery or generator output voltage,
whichever is greater.
INDICATOR LAMPS
All indicator lamps, except the four-wheel drive in-
dicator, are located in the main cluster tell-tale area
above the steering column opening. Each of the
lamps is served by the main cluster printed circuit
and cluster connector. The four-wheel drive indicator
lamp is located in the gauge package cluster and is
served by the gauge package printed circuit and clus-
ter connector.
Up to eleven indicator lamps can be found in the
tell-tale area of the main cluster. These lamps are ar-
ranged in two rows, with six lamps in the upper row
and five lamps in the lower row.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM LAMP
The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) lamp is
switched to ground by the ABS module. The module
lights the lamp when the ignition switch is turned to
the START position as a bulb test. The lamp will
stay on for 3 to 5 seconds after vehicle start-up to in-
dicate a system self-test is in process. If the lamp re-
mains on after start-up, or comes on and stays on
while driving, it may indicate that the ABS module
has detected a system malfunction or that the system
has become inoperative. Refer to Group 5 - Brakes
for more information.
BRAKE WARNING LAMP
The brake warning lamp warns the driver that the
parking brake is applied or that the pressures in the
two halves of the split brake hydraulic system are
unequal. With the ignition switch turned ON, battery
JINSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJ 8E - 25
Page 384 of 2158

continuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair
circuit to ground as required.
(4) Remove center instrument cluster bezel and
gauge package cluster assembly. Disconnect cluster
connector.
(5) Probe cavity 6 of cluster connector. Check for
continuity to a good ground. There should be no con-
tinuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair short
circuit as required.
(6) Still probing cavity 6 of cluster connector, check
for continuity to cavity 2 of sending unit wiring body
half connector. There should be continuity. If OK, re-
place gauge. If not OK, repair open circuit as re-
quired.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The diagnosis found here addresses an inoperative
gauge condition. If the problem being diagnosed is re-
lated to gauge accuracy, be certain to confirm that
problem is with gauge and not with engine oiling sys-
tem performance. Actual engine oil pressure should
be checked with a test gauge and compared to gauge
readings before you proceed with gauge diagnosis.
Refer to Group 9 - Engines for more information.
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Disconnect oil pres-
sure sending unit connector. The sending unit (Fig. 3)
is located on right side of engine block. On 2.5L en-
gine, it is just forward of ignition distributor and just
to the rear of generator mounting bracket. On 4.0L
engine, it is just to the rear of ignition distributor
and above oil filter adapter. The gauge needle should
move to high end of gauge scale. If OK, go to next
step. If not OK, go to step 3.
(2) Install a jumper wire from sending unit wiring
to ground. The gauge needle should move to low end
of gauge scale. If OK, replace sending unit. If not
OK, remove jumper wire and go to next step.(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Disconnect battery
negative cable. Remove center instrument cluster be-
zel and gauge package cluster assembly. Disconnect
cluster connector.
(4) Probe cavity 9 of cluster connector. Check for
continuity to a good ground. There should be no con-
tinuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair short
circuit as required.
(5) Still probing cavity 9 of cluster connector, check
for continuity to sending unit wire connector. There
should be continuity. If OK, replace gauge. If not OK,
repair open circuit as required.
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER
The diagnosis found here addresses an inoperative
gauge condition. If the problem being diagnosed is re-
lated to gauge accuracy, be certain to confirm that
problem is with gauge and not with incorrect speed-
ometer pinion, axle ratio or tire size. Refer to Group
21 - Transmission and Transfer Case for more infor-
mation.
(1) Perform vehicle speed sensor test as described
in the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, replace ve-
hicle speed sensor.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable. Unplug vehi-
cle speed sensor, PCM, and daytime running lamp
module connectors. Remove left instrument cluster
bezel and main cluster assembly. Disconnect cluster
connector.
(3) Probe cavity 13 of cluster connector. Check for
continuity to a good ground. There should be no con-
tinuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair short
circuit as required.
(4) Still probing cavity 13 of cluster connector,
check for continuity to cavity 1 of vehicle speed sen-
sor connector (Fig. 4). There should be continuity. If
OK, replace speedometer/odometer. If not OK, repair
open circuit as required.
Fig. 2 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit ConnectorFig. 3 Oil Pressure Sending Unit - Typical
8E - 28 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJJ
Page 385 of 2158

TACHOMETER
(1) With engine running, check for tachometer sig-
nal at pin 43 of PCM connector (Fig. 5). See Tachom-
eter Calibration chart in Specifications. If OK, go to
next step. If not OK, replace PCM.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable. Unplug PCM
connector. Remove left instrument cluster bezel and
main cluster assembly. Disconnect cluster connector.
(3) Probe cavity 12 of cluster connector. Check for
continuity to a good ground. There should be no con-
tinuity. If OK, go to next step. If not OK, repair short
circuit as required.
(4) Still probing cavity 12 of cluster connector,
check for continuity to cavity 43 of PCM connector.
There should be continuity. If OK, replace tachome-
ter. If not OK, repair open circuit as required.
TRIP ODOMETER
If the trip odometer is inoperative, but the speed-
ometer/odometer functions are unaffected, replace
speedometer assembly. If speedometer/odometer func-
tions are affected, see Speedometer/Odometer diagno-
sis in this section.
VOLTMETER
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Voltmeter should
read battery voltage. If all gauges except voltmeter
are OK, go to next step. If other gauges are inopera-
tive, see Gauges in this section for diagnosis.
(2) Using an accurate test voltmeter, measure bat-
tery voltage at battery. Compare this reading to in-
strument cluster voltmeter reading. Now see
Voltmeter Calibration chart in Specifications. If volt-
meter does not perform to specification, replace volt-
meter.
Fig. 4 Vehicle Speed Sensor Connector
Fig. 5 Powertrain Control Module Connector
JINSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJ 8E - 29
Page 417 of 2158

VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1SERVICE PROCEDURES................... 9
GENERAL INFORMATION
The vehicle speed control system (Fig. 1) is an
available option on all XJ (Cherokee) models. The
system is electronically controlled and vacuum oper-
ated. Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the vehicle speed control system. Re-
fer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams for complete cir-
cuit descriptions and diagrams.
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
The speed control servo is mounted to a bracket on
the right side inner fender shield in the engine com-
partment. The servo unit consists of a solenoid valve
body, a vacuum servo and the mounting bracket. The
PCM controls the solenoid valve body. The solenoid
valve body controls the application and release of
vacuum to the diaphragm of the vacuum servo. The
servo unit cannot be repaired and is serviced only as
a complete assembly.
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
The speed control switch module is mounted to the
center of the steering wheel below the driver's airbag
module. The PCM monitors the state of the speed
control switches. The individual switches are labeled:
OFF/ON, RESUME/ACCEL, SET/COAST. Refer to
the owner's manual for more information on speed
control switch functions and setting procedures. The
individual switches cannot be repaired. If one switch
fails, the entire switch module must be replaced.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
Vehicles with the speed control option use a dual
function stop lamp switch. The switch is mounted in
the same location as the conventional stop lamp
switch, on the brake pedal mounting bracket under
the instrument panel. The PCM monitors the state of
the dual function stop lamp switch. Refer to Group 5
- Brakes for more information on stop lamp switch
service and adjustment procedures.
SERVO CABLE
The speed control servo cable is connected betweenthe speed control vacuum servo diaphragm and the
throttle control linkage. This cable causes the throt-
tle control linkage to open or close the throttle valve
in response to movement of the vacuum servo dia-
phragm.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The speed control electronic control circuitry is in-
tegrated into the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The PCM is located in the engine compartment on
the left side inner fender shield. The PCM speed con-
trol functions are monitored by the On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems are
monitored by the PCM. Each monitored circuit is as-
signed a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM
will store a DTC in electronic memory for any failure
it detects. See Using On-Board Diagnostic System in
this group for more information. The PCM cannot be
repaired and must be replaced if faulty.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
The vacuum reservoir is mounted behind the left
end of the front bumper bar. The reservoir contains a
one-way check valve to trap engine vacuum in the
reservoir. When engine vacuum drops, as in climbing
a grade while driving, the reservoir supplies the vac-
uum needed to maintain proper speed control opera-
tion. The vacuum reservoir cannot be repaired and
must be replaced if faulty.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) is a pulse genera-
tor mounted to an adapter near the transmission
(two-wheel drive) or transfer case (four-wheel drive)
output shaft. The sensor is driven through the
adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The VSS pulse
signal to the speedometer/odometer is monitored by
the PCM speed control circuitry to determine vehicle
speed and to maintain speed control set speed. Refer
to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for testing of this component. Refer to Group
14 - Fuel System for service of this component.
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1
Page 421 of 2158

USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the speed control
system, making sure they are operational. A Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the OBD system. Some
circuits are checked continuously and some are
checked only under certain conditions.
If the OBD system senses that a monitored circuit
is bad, it will put a DTC into electronic memory. The
DTC will stay in electronic memory as long as the
circuit continues to be bad. The PCM is programmed
to clear the memory after 50 engine starts, if the
problem does not occur again.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) are two-digit num-
bers flashed on the malfunction indicator (Check En-
gine) lamp that identify which circuit is bad. A DTC
description can also be read using the DRB scan tool.
Refer to Group 14 - Fuel Systems for more informa-
tion.
A DTC does not identify which component in a cir-
cuit is bad. Thus, a DTC should be treated as a
symptom, not as the cause for the problem. In some
cases, because of the design of the diagnostic test
procedure, a DTC can be the reason for another DTC
to be set. Therefore, it is important that the test pro-
cedures be followed in sequence, to understand what
caused a DTC to be set.
See Speed Control Diagnostic Trouble Code chart
for DTC's which apply to the speed control system.Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures man-
ual to diagnose an on-board diagnostic system trou-
ble code.
RETRIEVING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To start this function, cycle the ignition switch ON-
OFF-ON-OFF-ON within 5 seconds. This will cause
any DTC stored in the PCM memory to be displayed.
The malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp will
display a DTC by flashing on and off. There is a
short pause between flashes and a longer pause be-
tween digits. All DTC's displayed are two-digit num-
bers, with a four-second pause between codes.
An example of a DTC is as follows:
(1) Lamp on for 2 seconds, then turns off.
(2) Lamp flashes 1 time pauses and then flashes 5
times.
(3) Lamp pauses for 4 seconds, flashes 3 times,
pauses, then flashes 4 times.
The two DTC's are 15 and 34. Any number of
DTC's can be displayed, as long as they are in mem-
ory. The lamp will flash until all stored DTC's are
displayed (55 = end of test).
If a DTC 15 is observed, see diagnosis for Vehicle
Speed Sensor in this group. If a DTC 34 is observed,
see diagnosis for Speed Control Servo and Power-
train Control Module in this group. Correct any prob-
lems found in your diagnosis, then recheck for DTC
after corrections are completed.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
For diagnosis of the VSS, refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual.
SPEED CONTROL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 5