Actuator KIA CARNIVAL 2007 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: KIA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: CARNIVAL, Model: KIA CARNIVAL 2007Pages: 1575, PDF Size: 44.86 MB
Page 928 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
DESCRIPTION
This specification applies to HCU(Hydraulic Control Unit) and ECU(Electronic Control Unit) of the HECU.(Hydraulic and
Electronic Control Unit)
This specification is for the wiring design and installation of ABS/TCS/ESC ECU.
This unit has the functions as follows.
a. Input of signal from Pressure sensor, Steering angle sensor, Yaw & Lateral G sensor, the wheel speed sensors
attached to each wheel.
b. Control of braking force / traction force/ yaw moment.
c. Failsafe function.
d. Self diagnosis function.
e. Interface with the external diagnosis tester.
Installation position : engine compartment a. Brake tube length from Master cylinder port to HECU inlet port should be max. 1m
b. The position should not be close to the engine block and not lower than the wheel.
OPERATION
The ECU shall be put into operation by switching on the operating voltage (IGN).
On completion of the initialization phase, the ECU shall be ready for operation.
In the operating condition, the ECU shall be ready, within the specified limits (voltage and temperature), to process the
signals offered by the various sensors and switches in accordance with the control algorithm defined by the software
and to control the hydraulic and electrical actuators.
Wheel Sensor signal processing
The ECU shall receive wheel speed signal from the four active wheel sensors.
The wheel signals are converted to voltage signal by the signal conditioning circuit after receiving current signal from
active wheel sensors and given as input to the MCU.
Solenoid Valve Control
When one side of the valve coil is connected to the positive voltage that is provided through the valve relay and the
other side is connected to the ground by the semiconductor circuit, the solenoid valve goes into operation.
The electrical function of the coils are always monitored by the valve test pulse under normal operation conditions.
Voltage limits
a.Overvoltage
When overvoltage is detected(above 16.8 V), the ECU switches off the valve relay and shuts down the system.
When voltage is returned to operating range, the system goes back to the normal condition after the initialization
phase.
b. Undervoltage
In the event of undervoltage(below 9.3 V), ABS control shall be inhibited and the warning lamp shall be turned on.
When voltage is returned to operating range, the warning lamp is switched off and ECU returns to normal operating
mode.
Pump Motor Checking
The ECU performs a pump motor test at a speed of 15km/h once after IGN is switched on.
Diagnostic Interface
Failures detected by the ECU are encoded on the ECU, stored in a EEPROM and read out by diagnostic equipment
when the ignition switch is turned on.
The diagnosis interface can also be used for testing the ECU during production of the ECU and for actuating the HCU
(Air - bleeding line or Roll and Brake Test line).
Warning Lamp module
Page 936 of 1575

PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
SymptomSuspect Area
ABS does not operate. Only when 1. - 4. are all normal and the problem is still
occurring, replace the HECU.
a. Check the DTC reconfirming that the normal code is
output.
b. Power source circuit.
c. Speed sensor circuit.
d. Check the hydraulic circuit for leakage.
ABS does not operate intermittently. Only when 1. - 4. are all normal and the problem is still
occurring, replace the ABS actuator assembly.
a. Check the DTC reconfirming that the system is
operating to specifications.
b. Wheel speed sensor circuit.
Page 967 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
description of ESP
Optimum driving safety now has a name : ESP, the Electronic Stability Control.
ESP recognizes critical driving conditions, such as panic reactions in dangerous situations, and stabilizes the vehicle
by wheel- individual braking and engine control intervention with no needfor actuating the brake or the gas pedal.
ESP adds a further function known as Active Yaw Control (AYC) to the ABS, TCS, EBD and ESP functions. Whereas
the ABS/TCS function controls wheel slip during braking and acceleration and, thus, mainly intervenes in the
longitudinal dynamics of the vehicle, active yaw control stabilizes the vehicle about its vertical axis.
This is achieved by wheel individual brake intervention and adaptation of the momentary engine torque with no need
for any action to be taken by the driver.
ESC essentially consists of three assemblies : the sensors, the electronic control unit and the actuators.
Of course, the stability control feature works under all driving and operating conditions. Under certain driving
conditions, the ABS/TCS function can be activated simultaneously with the ESP function in response to a command
by the driver.
In the event of a failure of the stability control function, the basic safety function, ABS, is still maintained.
DESCRIPTION OF ESP CONTROL
ESP system includes ABS/EBD, TCS and AYC (Active yaw control) function.
ABS/EBD function : The ECU changes the active sensor signal (current shift) coming from the four wheel sensors to
the square waveform.By using the input of above signals, the ECU calculates the vehicle speed and the acceleration
& deceleration of the four wheels.And, the ECU judges whether the ABS/EBD should be actuated or not.
TCS function prevents the wheel slip of drive direction by adding the brake pressure and engine torque reduction via
CAN communication.TCS function uses the wheel speed sensor signal to determine the wheel slip as far as ABS
function.
AYC function prevents unstable maneuver of the vehicle. To determine the vehicle maneuver, AYC function uses the
maneuver sensor signals(Yaw Rate Sensor, Lateral Acceleration Sensor, Steering Wheel Angle Sensor).If vehicle
maneuver is unstable (Over Steer or Under Steer), AYC function applies the brake pressure on certain wheel, and
send engine torque reduction signal by CAN.
After the key - on, the ECU continually diagnoses the system failure. (self- diagnosis)If the system failure is detected,
the ECU informs driver of the system failure through the BRAKE/ABS/ESP warning lamp. (fail- safe warning)
Page 1011 of 1575

2.Installation is the reverse of removal.
LATCH ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENT
1.Remove the tailgate trim.
2. Disconnect the outside handle rod (A), connector (B).
3.After loosening the mounting screws, then remove the latch assembly (A).
4.Installation is the reverse of removal.
a. Make sure the connector is connected properly and the connecting rod is connected properly.
b. Make sure the tailgate opens properly and locks securely.
ACTUATOR ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENT
1.Remove the tailgate trim.
2. Disconnect the outside handle rod (A), actuator rod (B), key cylinder rod (C) and connector.
3. After loosening the mounting bolt and nuts, then remove the actuator assembly (D).
Page 1038 of 1575

2.After disconnecting the connector (B), remove the power window motor (A).
3.Installation is the reverse of removal.
a.Roll the glass up and down to see if it move will freely without binding.
OUT SIDE HANDLE REPLACEMENT
1.Remove the following items.
a. Door trim.
b. Door trim seal.
c. Actuator.
2. Loosen the mounting bolt, then remove the outside handle bracket (A).
3.Remove the outside handle (A).
Page 1041 of 1575

4.Installation is the reverse of removal.
DOOR ACTUATOR REPLACEMENT
1.Remove the inside handle.
2. Remove the door trim.
3. Remove the door trim seal.
4. Disconnect the connector (A) and cable (B).
5.After loosening the mounting bolts and nuts, then remove the actuator assembly (A).
Page 1202 of 1575
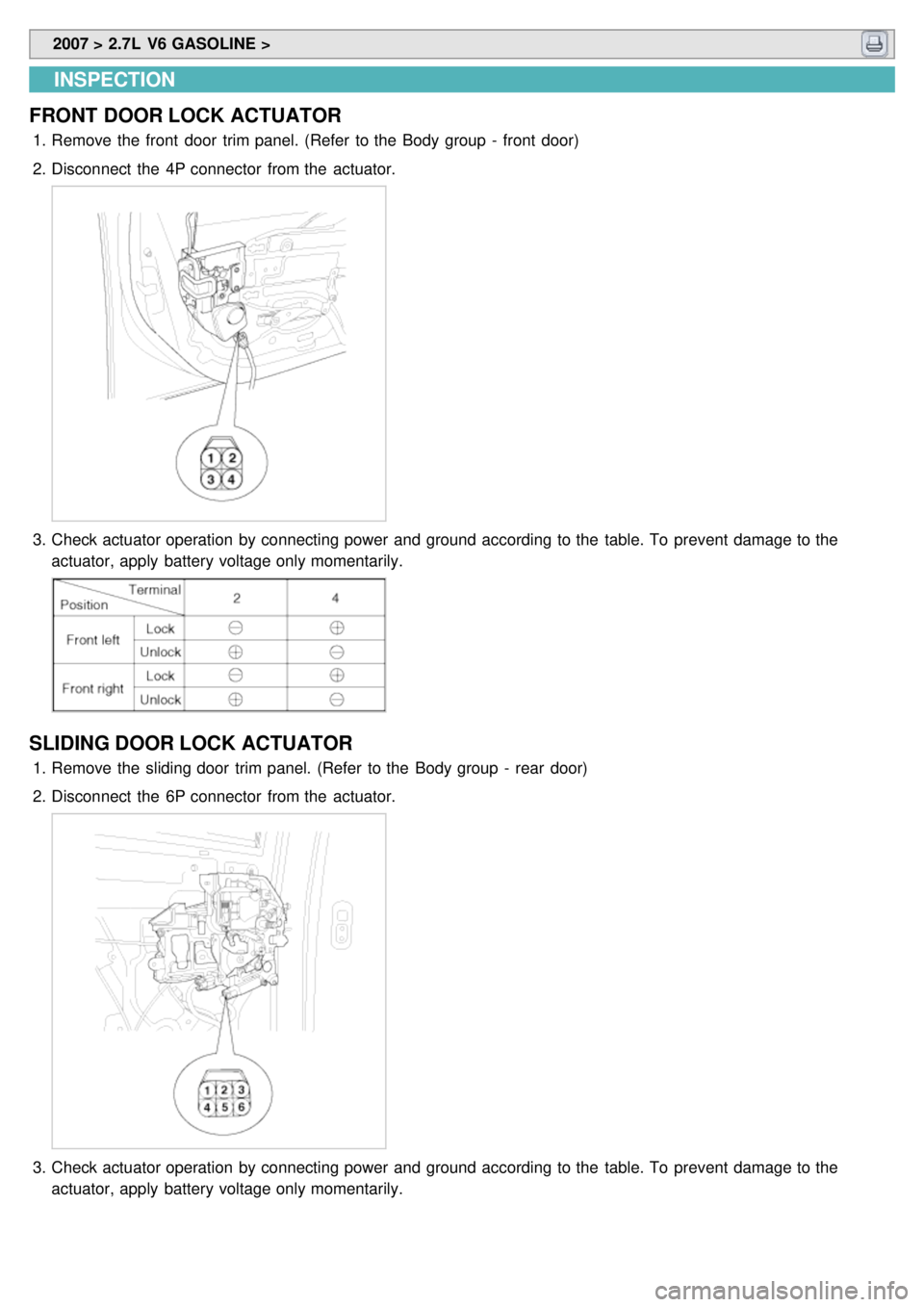
2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
INSPECTION
FRONT DOOR LOCK ACTUATOR
1. Remove the front door trim panel. (Refer to the Body group - front door)
2. Disconnect the 4P connector from the actuator.
3.Check actuator operation by connecting power and ground according to the table. To prevent damage to the
actuator, apply battery voltage only momentarily.
SLIDING DOOR LOCK ACTUATOR
1.Remove the sliding door trim panel. (Refer to the Body group - rear door)
2. Disconnect the 6P connector from the actuator.
3.Check actuator operation by connecting power and ground according to the table. To prevent damage to the
actuator, apply battery voltage only momentarily.
Page 1203 of 1575

TAILGATE LOCK ACTUATOR (5DOORS)
1.Remove the tailgate trim panel. (Refer to the Body group - tailgate)
2. Disconnect the 6P connector from the actuator.
3.Check actuator operation by connecting power and ground according to the table. To prevent damage to the
actuator, apply battery voltage only momentarily.
FRONT DOOR LOCK SWITCH
1.Remove the front door trim panel. (Refer to the Body group - front door)
2. Disconnect the 4P connector from the actuator.
3.Check for continuity between the terminals in each switch position according to the table.
Page 1204 of 1575

SLIDING DOOR LOCK SWITCH
1.Remove the sliding door trim panel. (Refer to the Body group - rear door)
2. Disconnect the 6P connector from the actuator.
3.Check for continuity between the terminals in each switch position according to the table.
TAILGATE LOCK SWITCH
1.Remove the tailgate trim panel. (Refer to the Body group - tailgate)
2. Disconnect the 6P connector from the actuator.
3.Check for continuity between the terminals in each switch position according to the table.
Page 1211 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
DESCRIPTION
All modules are linked a low speed CAN network.
The input information for the modules is coming from both the CAN network and the hardware components
(actuatorsand sensors).
a. FAM (Front Area Module)
a. Headlamp low/high beam control (with DRL)
b. Park lamp control
c. Front fog lamp control
d. Front turn signal lamp control
e. Windshield wiper control
f. Windshield deicer
g. Diagnostics
b. IPM (In - Panel Module)
a. RKE (Remote Keyless Control)
b. VAS (Voice Alarm System)
c. Ignition key hole illumination
d. Switch indicators control
e. Panel light control
f. Seat belt warning
g. Auto light/DRL control (Logic)
h. Windshield/Rear wiper control (Logic)
i. Turn and Hazard lamp control (Logic)
j. Central door lock (Logic)
k. Windshield deicer timer
l. Rear glass defog timer
m. Gateway for ISO- 9141 (K- Line)
c. RAM (Rear Area Module)
a. Tail lamp control
b. Turn and Hazard lamp control
c. Back up lamp control
d. Rea fog lamp control
e. Stop lamp outage detection
f. Sliding door power window/Quarter glass control
g. Room lamp control
h. Rear wiper control
i. Rear glass defog
j. Fuel filler door open solenoid control
d. ADM (Assist Drive Module)
e. DDM (Driver Drive Module)
MODULE INTRODUCTION
FAM/IPM/RAM consists of a power board and an electronic board. The power board contains circuit protection devices
and switching devices. The electronic board uses Intelligent Power Switching (IPS) for HS/LS load control, logic
functions and CAN/K- Line communication. The power board and electronic board are connected with pin blocks for
the Front Area Module (FAM) and VCD (Variable Connection Displacement) for the In- Panel Module (IPM) and the
Rear Area Module (RAM).