wheel LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1996Pages: 455, PDF Size: 6.44 MB
Page 295 of 455

70BRAKES
14
REPAIRREV: 05/99 15.Coat a new wiper seal with brake fluid and fit to
new seal retainer. Slide assembly, seal first, over
protruding piston into bore recess.
16.Using special toolLRT-70-500- piston clamp,
press home seal retainer and piston.
Mounting inboard piston
17.Carry out same procedure as for removing and
fitting outboard piston and seals, instructions 8 to
16.
Fit calipers and pads to vehicle
18.Fit caliper to axle, tighten 2 bolts evenly to
82
Nm (60 lbf/ft).
19.Connect brake pipe to caliper. Tighten to15 Nm
(11 lbf/ft).
20.Remove clamp from flexible brake hose.
21.Insert pads and retaining springs, secure in
position with new retaining pins and spread ends
or fit new split pins, depending on vehicle model.
Note correct position of retaining springs on 90
models.
22.Bleed brake system
See Brake System Bleed.
23.Press brake pedal firmly several times to locate
pads.
24.Fit road wheels, remove axle stands. Finally
tighten road wheel nuts to correct torque:
Alloy wheels -
130 Nm (96 lbf/ft)
Steel wheels -100 Nm (80 lbf/ft)
Heavy duty wheels -170 Nm (125 lbf/ft)
25.Road test vehicle. Note new brake pads require
'bedding-in', for several hundred miles before
brakes are at maximum efficiency.REAR BRAKE DISC
Service repair no - 70.10.11.
Remove
1.Remove rear hub assembly
See REAR AXLE
AND FINAL DRIVE, Repair, Rear hub
assembly
.
2.Remove disc bolts.
3.Remove disc from rear hub.
Refit
4.Fit disc to rear hub.
5.Fit disc bolts. Tighten to
73 Nm (54 lbf/ft).
6.Check total disc run out, this must not exceed
0,15 mm (0.006 in). If necessary reposition disc.
7.Fit rear hub assembly
See REAR AXLE AND
FINAL DRIVE, Repair, Rear Hub Assembly
.
Disc reclamation
8.Check disc thickness. This dimension may be
machined to minimum thickness of 12 mm.
Machine equal amounts off each face.
NOTE: The brake disc MUST BE renewed if
the minimum running thickness stamped
on the disc is recorded.
Page 297 of 455

70BRAKES
16
REPAIRREV: 05/99 TRANSMISSION BRAKE SHOES
Service repair no - 70.45.18
Remove
1.Park vehicle on level ground, chock road wheels
and release handbrake. Alternatively, raise
vehicle on a ramp.
2.Disconnect rear propeller shaft from
transmission output flange at brake drum.
3.Slacken off transmission brake drum adjustment
bolt.
4.Remove single screw securing brake drum to
output flange.
5.Withdraw drum to expose brake assembly.
6.Release top and bottom springs from brake
shoes, see J6337.
7.Grip dished washer with a pair of pliers, depress
washer and turn through 90°.
8.Remove dished washer, complete with hold
down spring and pin from both shoes.
9.Move brake shoes out from adjuster slides,
release from abutment plate and remove from
backplate.
10.Check that springs are satisfactory for continued
use. If new brake shoes are to be fitted, the
srings should also be renewed.Refit
11.Locate RH brake shoe in slide and secure brake
shoe and lever assembly to backplate with hold
down pin, spring and dished washer.
12.Locate LH brake shoe in slide and fit abutment
plate between both brake shoes. Secure LH
shoe with hold down pin, spring and dished
washer.
13.Fit pull-off springs to brake shoes.
14.Fit brake drum. Tighten screw to
25 Nm (18
lbf/ft).
15.Check that hand brake lever is released.
16.Screw in and tighten adjuster bolt until brake
drum will not rotate by hand.
17.Tighten adjuster bolt to
25 Nm (18 lbf/ft)to
ensure brake drum is locked.
18.Slacken off adjuster bolt by 1.5 turns to give
shoes a running clearance. Check that the drum
is free to rotate.
19.Fit propeller shaft to output flange. Tighten
fixings to
46 Nm (34 lbf/ft).
20.Remove wheel chocks and check operation of
handbrake.
Page 298 of 455

BRAKES
17
REPAIR HANDBRAKE CABLE
Service repair no - 70.35.25
Remove
1.Park vehicle on level ground, chock road wheels
and release handbrake. Alternatively, raise
vehicle on ramp.
2.Remove 3 trim studs and lift up handbrake
gaiter.
3.Remove split pin, clevis pin, washer and
disconnect cable from handbrake lever.
4.Slacken off transmission brake drum adjusting
screw.
5.Disconnect propeller shaft from output flange.
6.Remove retaining screw and withdraw brake
drum.
7.Release handbrake cable clevis from abutment
on cable lever, see J6337, and pull through
aperture in back plate.
8.Pull cable from heelboard and remove from
vehicle.
Refit
9.Feed new cable through heelboard ensuring
rubber grommet is correctly located.
10.Position cable over guide plate, insert through
backplate and connect to cable lever.
11.Fit cable to handbrake lever and secure with
clevis pin and split pin.
12.Fit handbrake gaiter.
13.Fit brake drum. Tighten screw to
25 Nm (18
lbf/ft).
14.Screw in and tighten adjuster bolt until brake
drum will not rotate by hand.
15.Tighten adjuster bolt further to
25 Nm (18 lbf/ft)
to ensure brake drum is locked.
16.Slacken off adjuster bolt by 1.5 turns to give
brake shoes running clearance. Check that the
drum is free to rotate.
17.Slacken locknut and adjust cable to give the
handbrake pawl two notches free movement on
the rachet before being fully operational on third
notch (brake shoes are fully expanded against
drum).
NOTE: Cable adjustment is for a new cable
or to compensate for cable stretch. Cable
adjustment must not be used to take up
brake shoe wear.
18.Fit propeller shaft to output flange. Tighten
fixings to
46 Nm (34 lbf/ft).
19.Remove wheel chocks and check operation of
handbrake.
Page 304 of 455

WHEELS AND TYRES
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION TYPES OF WHEEL RIMS AND TYRES
Description
Dependent on specification and model type, the
vehicle is equipped with pressed steel or alloy wheel
rims, both using tubeless radial ply tyres.
Tyre codes
The text, codes and numbers moulded into the tyre
wall vary between tyre manufacturers, however most
tyres are marked with the information shown in the
illustrated example.
NOTE: The illustration is an example of the
type of markings moulded into tyres and is
for guidance only. For specific tyre
specifications
See GENERAL SPECIFICATION
DATA, Information, Tyre size and pressures
.1.Type of tyre construction -Radial Ply
2.Load index -104
3.Speed symbol -SorT
4.USA Tyre quality grading -Tread wear 160
Traction A temperature B
5.Tread wear indicators moulded into tread pattern
are located at intervals around the tyre and
marked by a code -E66 103S6
6.Tyres with 'Mud Snow' type tread pattern are
marked -M&S
7.Tyre reinforcing mark -Reinforced
8.USA Load and pressure secification -
(900Kg(1984LBS) at 340KA (50PSI) MACS
PRESS
9.Tyre size -205 16 ot 235/70 R16
10.Type of tyre -TUBELESS
11.Country of manufacture -MADE IN GREAT
BRITAIN
12.USA Compliance symbol and identification -
DOT AB7C DOFF 267
13.European type approval identification -E11
01234
14.Tyre construction -SIDE WALL 2 PLIES
RAYON. TREAD 2 RAYON 2 STEEL
15.Manufacturers brand name/type -TRACTION
PLUS mzx M
Page 305 of 455

WHEELS AND TYRES
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS TYRE WEAR CHART
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
Rapid wear at Tyres under-inflated Inflate to correct pressure
shoulders Worn suspension components Replace worn components
i.e. ball joints, panhard
rod bushes, steering damper
Excessive cornering speeds
Rapid wear at
centreTyres over-inflated Inflate to correct pressure
of tread
Wear at one
shoulderTrack out of adjustment Adjust track to correct figure
Bent panhard rod Check and replace worn or damaged
components
Bald spots or tyre Wheel out of balance Balance wheel and tyre
cupping assembly
Excessive radial runout Check runout and replace tyre
if necessary
Shock absorber worn Replace shock absorber
Excessive braking
Tyre scalloped Track out of adjustment Adjust toe to correct figure
Worn suspension components Replace tyre as necessary
Excessive cornering speeds
CAUTION: This diagnosis chart is for general guidance only and does not necessarily include
every cause of abnormal tyre wear.
Page 306 of 455
74WHEELS AND TYRES
2
FAULT DIAGNOSIS FAULT - SYMPTOMS
Vibration through steering wheel
1.Check tyre pressures
See Repair, Tyre
Pressures
.
2.Check condition of tyres
See Tyre Wear Chart.
3.Check front wheel alignment
See STEERING,
Adjustment, Front Wheel Alignment
.
4.Check wheel balance
See Repair, Wheel
Balancing
.
NOTE: In the event that any apparent
vibration is not eliminated at this stage
See PROPELLER SHAFTS, Fault
diagnosis, Vibration Harshness
.
NOTE: In the event that any apparent
vibration is not eliminated at this stage, go
to steering Fault Diagnosis, Fault -
Symptom (Steering vibration, road wheel
shimmy/wobble)
See STEERING, Fault diagnosis,
Steering Faults
.
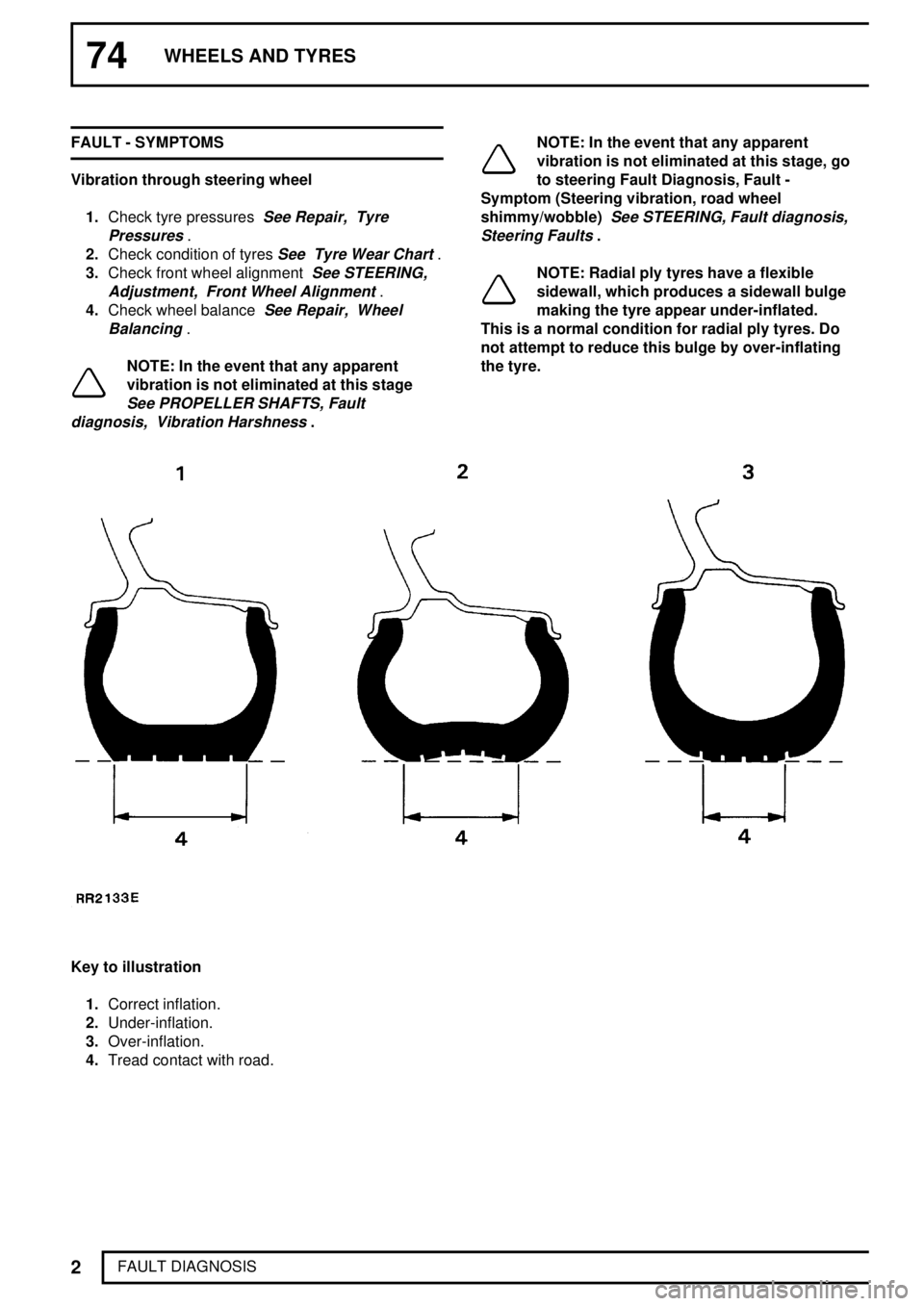
NOTE: Radial ply tyres have a flexible
sidewall, which produces a sidewall bulge
making the tyre appear under-inflated.
This is a normal condition for radial ply tyres. Do
not attempt to reduce this bulge by over-inflating
the tyre.
Key to illustration
1.Correct inflation.
2.Under-inflation.
3.Over-inflation.
4.Tread contact with road.
Page 307 of 455
WHEELS AND TYRES
1
REPAIR REV: 05/99 GENERAL INFORMATION
WARNING: This is a multi-purpose vehicle
with wheels and tyres designed for both
on and off road usage. Only use wheels
and tyres specified for use on the vehicle.
The vehicle is equipped with tubeless 'S','T' or 'H'
rated radial ply tyres as standard equipment. The
tyres are of European metric size and must not be
confused with the "P" size metric tyres available in
North America.
Vehicle wheel sets, including spare wheel, must be
fitted with the same make and type of tyre to the
correct specification and tread pattern. Under no
circumstances must cross-ply or bias-belted tyres be
used.
For tyre specification and pressures
See GENERAL
SPECIFICATION DATA, Information, Wheels and
Tyres
.
Steel wheels
Tubeless tyres are mounted on 7.0 inch wide by 16
inch diameter steel wheels.
Alloy Wheels
Tubeless tyres are mounted on 7.0 inch wide by 16
inch diameter cast aluminium alloy wheels. The
surface has a paint finish covered with a clear
polyurethane lacquer. Care must be taken when
handling the wheel to avoid scratching or chipping the
finish.
The alloy wheel rim is of the asymmetric hump
type incorporating a safety hump to improve
location of the tyre bead in its seat. If difficulty is
experienced in fitting tyres to this type of rim
See
Tyre Fitting
.
WARNING: DO NOT fit an inner tube to an
alloy wheel.TYRE INSPECTION
Inspect tyres at weekly intervals to obtain maximum
tyre life and performance and to ensure compliance
with legal requirements. Check for signs of incorrect
inflation and uneven wear, which may indicate a need
for balancing or front wheel alignment,
See Fault
diagnosis, Tyre Wear Chart
, if the tyres have
abnormal or uneven wear patterns.
Check tyres at least weekly for cuts, abrasions, bulges
and for objects embedded in the tread. More frequent
inspections are recommended when the vehicle is
regularly used in off road conditions.
To assist tyre inspection, tread wear indicators are
moulded into the bottom of the tread grooves, as
shown in the illustration above.
When the tread has worn to a depth of 1.6 mm the
indicators appear at the surface as bars which
connect the tread pattern across the width of the tread
as shown in the illustration above.
Page 308 of 455

74WHEELS AND TYRES
2
REPAIRREV: 05/99 When the indicators appear in two or more adjacent
grooves, at three locations around the tyre, a new tyre
must be fitted.
NOTE: DO NOT attempt to interchange
tyres, e.g. from front to rear, as tyre wear
produces characteristic patterns
depending on their position. If tyre position is
changed after wear has occured, the performance
of the tyre will be adversely affected.
NOTE: Territorial vehicle regulations
governing tyre wear MUST be adhered to.
WHEELS INSPECTION
Regularly check the condition of the wheels. Replace
any wheel that is bent, cracked, dented or has
excessive runout.
VALVES INSPECTION
Check condition of inflation valve. Replace any valve
that is worn, cracked, loose, or leaking air.TYRE PRESSURES
Maximum tyre life and performance will be
obtained only if tyres are maintained at the correct
pressures.
Tyre pressures must be checked at least once a week
and preferably daily, if the vehicle is used off road.
The tyre inflation pressure is calculated to give the
vehicle satisfactory ride and steering characteristics
without compromising tyre tread life. For
recommended tyre pressures in all conditions
See
GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA, Information,
Wheels and Tyres
.
Always check tyre inflation pressures using an
accurate gauge and inflate tyres to the
recommended pressures only.
Check and adjust tyre pressuresONLYwhen the
tyres are cold, vehicle parked for three hours or more,
or driven for less than 3.2 km (2 miles) at speeds
below 64 km/h (40 mph). Do not reduce inflation
pressures if the tyres are hot or the vehicle has been
driven for more than 3.2 km (2 miles) at speeds over
64 km/h (40 mph), as pressures can increase by 0.41
bars (6 lb/in
2) over cold inflation pressures.
CheckALLtyre pressures including the spare. Refit
the valve caps as they form a positive seal and keep
dust out of the valve.
Page 309 of 455

WHEELS AND TYRES
3
REPAIR WHEEL BALANCING
CAUTION: It is essential that all wheel
balancing is carried out off the vehicle.
The use of on the vehicle balancing could
cause component damage or personal injury and
MUST NOT be attempted.
NOTE: Before attempting to balance a
wheel and tyre assembly clean all mud and
dirt deposits from both inside and outside
rims and remove existing balance weights.
Remove stones from the tyre tread in order to avoid
operator injury during dynamic balancing and to obtain
the correct balance.
Inspect tyres for damage and correct tyre pressures
and balance according to the equipment
manufacturer's instructions.
Steel wheels
Clean area of wheel rim and attach balance weights in
position shown.
Alloy wheels
Clean area of wheel rim and attach adhesive balance
weights in position shown. Cut through rear face of
weight strip to detach required weights.
CAUTION: Use only correct adhesive
balance weights to avoid damage to
aluminium wheel rim. DO NOT attempt to
use a steel wheel weight on an aluminium wheel.
Page 310 of 455

74WHEELS AND TYRES
4
REPAIR Static balance
Wheel tramp
A- Heavy spot.
B- Add balance weights here.
C- Centre line of spindle.
Static balance is the equal distribution of weight
around the wheel. A statically unbalanced wheel will
cause a bouncing action called wheel tramp. This
condition will eventually cause uneven tyre wear.Dynamic balance
Wheel shimmyA- Heavy spot.
B- Add balance weights here.
C- Centre line of spindle.
Dynamic balance is the equal distribution of weight on
each side of the centre line so that when the wheel
spins there is no tendency for side to side movement.
A dynamically unbalanced wheel will cause wheel
shimmy.