engine LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1995, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995Pages: 873, PDF Size: 12.89 MB
Page 183 of 873

Mpi
1
SERVICE TOOLS ENGINE
LRT-12-056 Engine lifting bracket
18G 1644
LRT-12-058 Location pin valve timing
18G 1523
LRT-12-059 Crankshaft pulley locking tool
18G 1641
LRT-12-060 Locking tool crankshaft gear
18G 1524
Page 184 of 873

12ENGINE
2
SERVICE TOOLS
LRT-12-061 Protection sleeve crankshaft rear oil
18G 1108 seal
LRT-12-063 Remover camshaft oil seals
18G 1476
LRT-12-064 Replacer pilot camshaft front
18G 1475
LRT-12-069 Replacer crankshaft front oil seal
18G 1509
Page 186 of 873

12ENGINE
4
SERVICE TOOLS
LRT-12-076 Replacer needle crankshaft bearing
Page 187 of 873

EMISSION CONTROL
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 EMISSION CONTROL
Three systems are used to control the vehicle
atmospheric emissions these are:
Engine crankcase fume emissions.
Fuel tank Evaporative emissions
Engine exhaust gas emissions.
Crankcase ventilation system - 3.9 MFi models
only
The crankcase ventilation system which is an integral
part of the air supply to the engine combustion
chambers, is often overlooked when diagnosing
problems associated with engine performance. A
blocked ventilation pipe or filter or excessive air leak
into the inlet system through a damaged pipe or
leaking gasket can effect the mixture, performance
and economy of the engine.
1. Three way connector
2. Air filter
3. Oil separatorThe purpose of the crankcase ventilation system is to
ensure that any noxious gas generated in the engine
crankcase is rendered harmless by burning in the
combustion chambers as follows:
Oil laden noxious gas in the engine crankcase is
drawn through an oil separator 3 located on the right
cylinder head rocker cover, where the oil is separated
and returned to the sump. The gas flows through a
restrictor in the three way connection 1 and into the
inlet plenum chamber where it is drawn into the
combustion chambers and burned. The volume of
fresh air which is drawn from the atmospheric side of
the throttle butterfly to mix with the gas, depends on
the position of the throttle and the engine speed.
The air filter 2 fitted to the left cylinder head rocker
cover, must be maintained in clean condition to
ensure sufficient air enters the crankcase under
varying throttle openings and manifold depression, to
prevent excessive crankcase pressure or depression
developing.
Page 190 of 873

17EMISSION CONTROL
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 Evaporative emission control system - pre
advanced EVAPS.
The system is designed to prevent harmful fuel vapour
from escaping to the atmosphere. The system
consists of a vapour separator tank, connected to the
fuel tank and located between the body inner and
outer panels on the right hand side of the vehicle near
the rear wheel arch. An adsorbtion canister,
containing activated charcoal, is positioned in the
engine compartment attached to the front right
valance. The two components are connected by a
pipe running the length of the chassis.
A Pressure relief to atmosphere.
B From fuel tank to separator.
C To adsorbtion canister.
D Pressure relief valve.
E Pressure relief valve.
F Shut-off valve.
G "Speed Fit" connectors.A pressure relief valve is fitted in the hose which is
open to atmosphere. This valve acts as a safety valve
should a build-up of pressure occur in the system, for
example if a hose became blocked or kinked. The
volume of vapour emitted, in such an instance, would
be acceptable.
A pressure relief valve is also fitted in the hose
connected to the adsorbtion canister and releases
vapor to the canister when the pressure in the
separator reaches between 5 and 7 Kpa.
In the top of the separator a shut-off valve is
incorporated in the vapor exit port to prevent the
possible presence of any liquid fuel being transmitted
to the adsorbtion canister should the vehicle roll over.
The adsorbtion canister, which is connected by a hose
to the plenum chamber, absorbs and stores the fuel
vapour from the fuel tank while the engine is not
running. When the engine is started, the vapour is
purged from the canister by air drawn through an
orifice in the base of the canister and by the influence
of vacuum at the top. The vapour drawn into the
plenum chamber through a solenoid operated purge
valve is finally burnt in the combustion chambers.
The purge valve, which is attached to the adsorbtion
canister support bracket, is controlled by the Engine
Control Module ECM which determines the most
emission acceptable time at which purging should
take place. This will normally be at engine speeds
above idle and when the vehicle is in motion. A signal
from the ECM to the purge valve operates the
solenoid and opens the valve to purge the canister of
fuel vapour.
Page 194 of 873

17EMISSION CONTROL
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ADD: 09/95 System operation
The system is designed to prevent fuel vapour
escaping to atmosphere, and consists of four roll-over
valves fitted internally in the fuel tank, connected to
the liquid/vapour separator by a nylon line. The
separator is mounted to the side of the filler neck. An
EVAP canister is positioned in the engine
compartment mounted on the right front side valance.
The liquid/vapour separator and EVAP canister are
connected by a nylon line which runs the length of the
chassis.
Pressure/vacuum relief valves are incorporated into
the fuel filler cap and are designed to protect the fuel
tank from permanent deformation in the event of
system pressure or vacuum exceeding the system
operating parameters. There are no other relief or
one-way valves in the system.
A vent line flow restrictor known as an anti-trickle fill
valve is fitted to the filler pipe in the line between the
tank and EVAP canister. The function of this valve is
to prevent overfilling the tank by trickling fuel in,
thereby preserving the vapour space in the tank to
allow for fuel expansion during hot weather.
The valve achieves this by blocking the vent line
during the fuel filling process. The valve is operated
by the action of inserting the filler gun so that when
the fuel in the tank reaches the level of the filling
breather, flow cut off occurs due to fuel filling the filler
pipe.During normal vehicle operation and when the engine
is switched off, the venting system between the fuel
tank and EVAP canister is open to allow the free
passage of vapour.
The EVAP canister, which is connected by a nylon
hose to the plenum chamber, absorbs and stores the
fuel vapour from the fuel tank when the engine is not
running. With the engine running, vapour is purged
from the EVAP canister by allowing outside air to be
drawn through the EVAP canister vent solenoid and
link pipe by the influence of manifold vacuum to the
EVAP canister purge connection on the canister.
Filter pads are fitted above and below the charcoal
and in the EVAP canister vent solenoid to prevent the
ingress of foreign matter into the purge line.
The EVAP canister purge valve, which is fitted in the
line from the EVAP canister to the plenum, is
controlled by the ECM which determines the most
emission acceptable time at which purging should
take place. This will normally be at engine speeds
above idle and when the vehicle is in motion.
The EVAP canister vent solenoid is mounted on the
side of the EVAP canister bracket and is connected to
the EVAP canister by a length of large bore hose. The
ECVS is controlled by the ECM and is normally open.
The function of the ECVS is to block the air intake
side of the EVAP canister. When the system receives
an ECM signal the valve closes; this allows the
system leak check to take place. The leak check only
occurs when pre-determined vehicle operating
conditions are met.
Page 195 of 873

EMISSION CONTROL
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS REV: 09/95 TESTING EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL -
PRE ADVANCED EVAPS
The following pressure test procedure is intended to
provide a method for ensuring that the system does
not leak excessively and will effectively control
evaporative emissions.
Equipment required.
Nitrogen cylinder (compressed air may be used to
pressure the system when there has NEVER been
fuel present in the fuel or evaporative control
systems).
Water manometer (0 - 30" H2O or more).
Pipework and a "T" piece.
Method.
1.Ensure that there is at least two gallons of fuel in
the petrol tank unless there has never been any
fuel in the system.
2.Disconnect, at the adsorption canister, the pipe
to the vapour separator.
3.Connect this pipe to the nitrogen cylinder and
the water manometer using the "T" piece.
4.Pressurize the system to between 26.5 and 27.5
inches of water, allow the reading to stabilize,
then turn off the nitrogen supply.
5.Measure the pressure drop within a period of 2
minutes 30 seconds. If the drop is greater than
2.5 inches of water the system has failed the
test. Note that a fully sealed system will show a
slight increase in pressure.
6.Should the system fail the test, maintain the
pressure in the system and apply a soap
solution round all the joints and connections until
bubbles appear to reveal the source of the leak.
7.Repeat the test and if successful, dismantle the
test equipment and reconnect the pipe to the
adsorption canister.LEAK DETECTION PROCEDURE - ADVANCED
EVAPS
1.Connect TestBook to the vehicle and confirm
that the fault code(s) displayed relate to an
EVAP system fault.
2.Examine components in fuel and EVAP system
for damage or poorly connected joints.
3.Repair or replace components to rectify any
faults found, then reset the Check Engine light
using TestBook.
4.Carry out Drive Cycle,
See Drive Cycle -
Advanced EVAPS
5.Using TestBook confirm that the Evaporative
Loss Control (ELC) Inspection and Maintenance
(IM) flag has cleared. This procedure should
confirm that the ELC test was carried out during
the drive cycle and that the fault was cured.
6.If the IM flag is still shown, use TestBook to
interrogate the engine management system to
ascertain which of the following situations exists:
·If a fault code is shown then further investigation
is required, proceed to the next step.
·If the IM flag is still shown, but no faults are
indicated the conditions for the ELC check have
not been met and the drive cycle must be
repeated.
7.Connect the Leak Detection/EVAP Diagnostic
Station to the vehicle and carry out the
procedures given in the operating instructions
supplied with the equipment.
8.Rectify faults indicated by the Leak
Detection/EVAP Diagnostic Station and return to
step 4.
Page 196 of 873

17EMISSION CONTROL
2
FAULT DIAGNOSISADD: 09/95 DRIVE CYCLE - ADVANCED EVAPS
1.Switch on ignition for 30 seconds.
2.Ensure that coolant temperature is less than 140
°F (30°C).
3.Start engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4.Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph with
light pedal pressure).
5.Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph
with moderate pedal pressure).
6.Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph with
heavy pedal pressure).
7.Cruise at 60 mph for 5 minutes.
8.Cruise at 50 mph for 5 minutes.
9.Cruise at 35 mph for 5 minutes.
10.Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
11.Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
Page 198 of 873
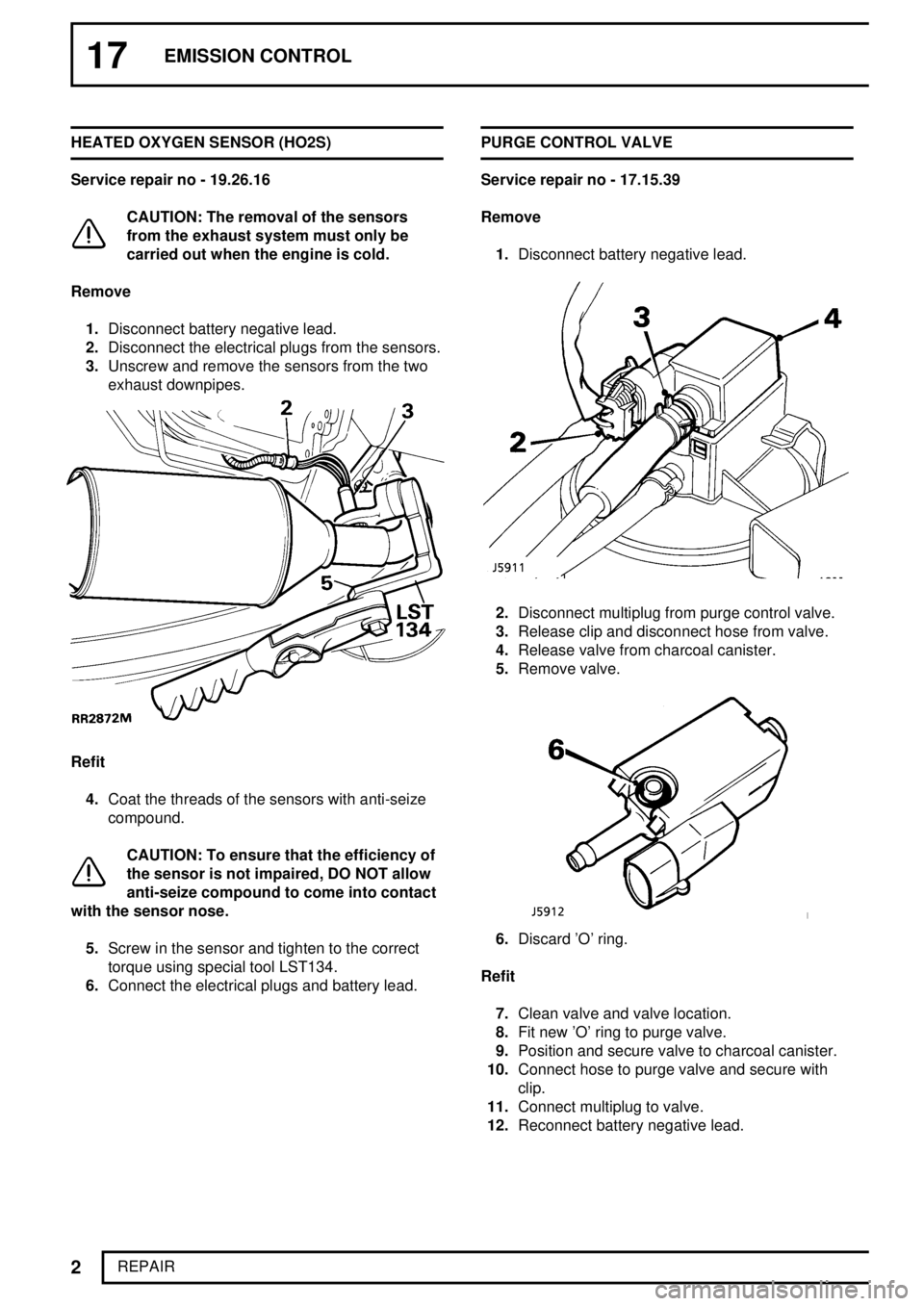
17EMISSION CONTROL
2
REPAIR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S)
Service repair no - 19.26.16
CAUTION: The removal of the sensors
from the exhaust system must only be
carried out when the engine is cold.
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect the electrical plugs from the sensors.
3.Unscrew and remove the sensors from the two
exhaust downpipes.
Refit
4.Coat the threads of the sensors with anti-seize
compound.
CAUTION: To ensure that the efficiency of
the sensor is not impaired, DO NOT allow
anti-seize compound to come into contact
with the sensor nose.
5.Screw in the sensor and tighten to the correct
torque using special tool LST134.
6.Connect the electrical plugs and battery lead.PURGE CONTROL VALVE
Service repair no - 17.15.39
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect multiplug from purge control valve.
3.Release clip and disconnect hose from valve.
4.Release valve from charcoal canister.
5.Remove valve.
6.Discard 'O' ring.
Refit
7.Clean valve and valve location.
8.Fit new 'O' ring to purge valve.
9.Position and secure valve to charcoal canister.
10.Connect hose to purge valve and secure with
clip.
11.Connect multiplug to valve.
12.Reconnect battery negative lead.
Page 201 of 873
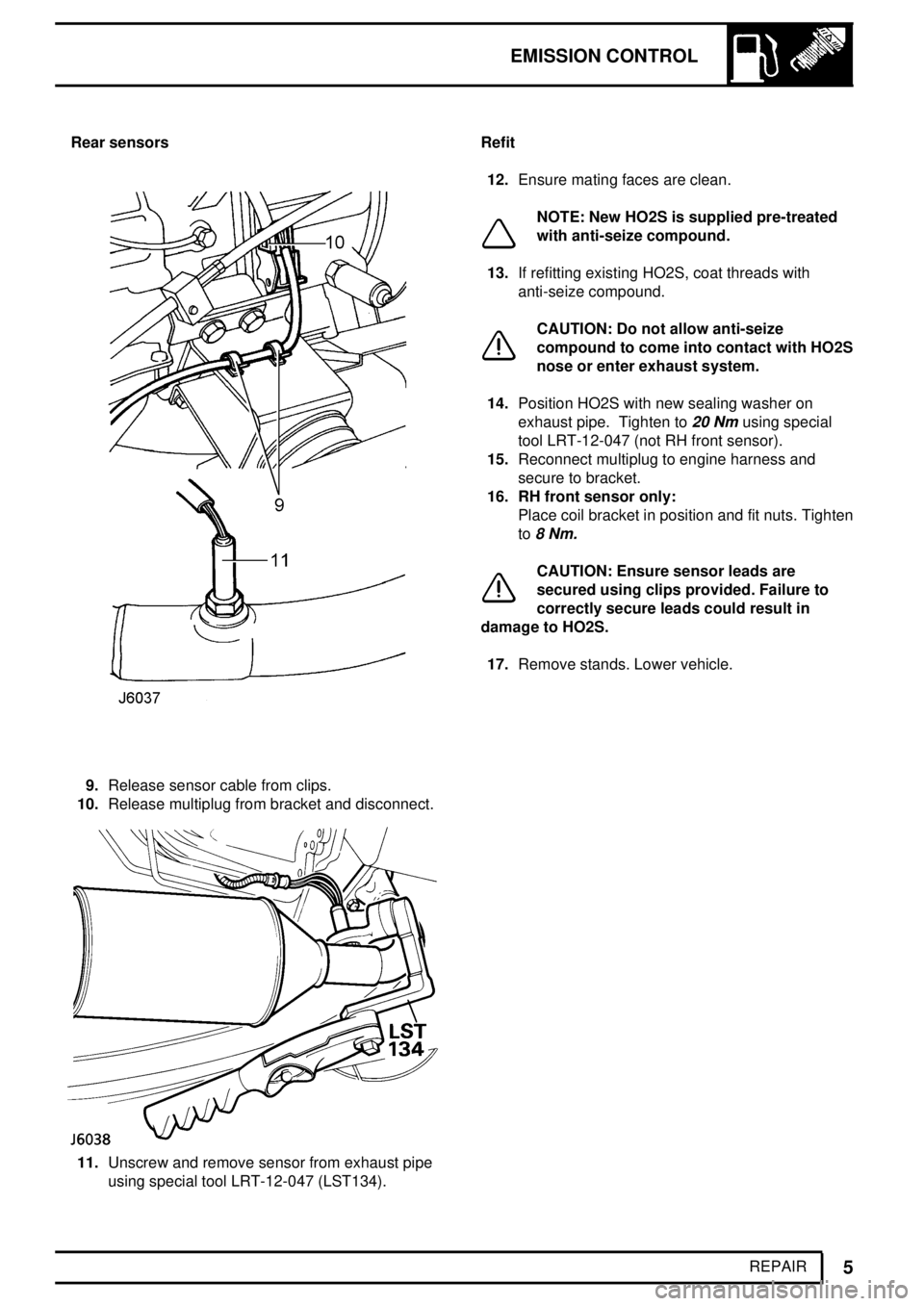
EMISSION CONTROL
5
REPAIR Rear sensors
9.Release sensor cable from clips.
10.Release multiplug from bracket and disconnect.
11.Unscrew and remove sensor from exhaust pipe
using special tool LRT-12-047 (LST134).Refit
12.Ensure mating faces are clean.
NOTE: New HO2S is supplied pre-treated
with anti-seize compound.
13.If refitting existing HO2S, coat threads with
anti-seize compound.
CAUTION: Do not allow anti-seize
compound to come into contact with HO2S
nose or enter exhaust system.
14.Position HO2S with new sealing washer on
exhaust pipe. Tighten to
20 Nmusing special
tool LRT-12-047 (not RH front sensor).
15.Reconnect multiplug to engine harness and
secure to bracket.
16. RH front sensor only:
Place coil bracket in position and fit nuts. Tighten
to
8 Nm.
CAUTION: Ensure sensor leads are
secured using clips provided. Failure to
correctly secure leads could result in
damage to HO2S.
17.Remove stands. Lower vehicle.