sensor LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1995, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995Pages: 873, PDF Size: 12.89 MB
Page 511 of 873
FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
9
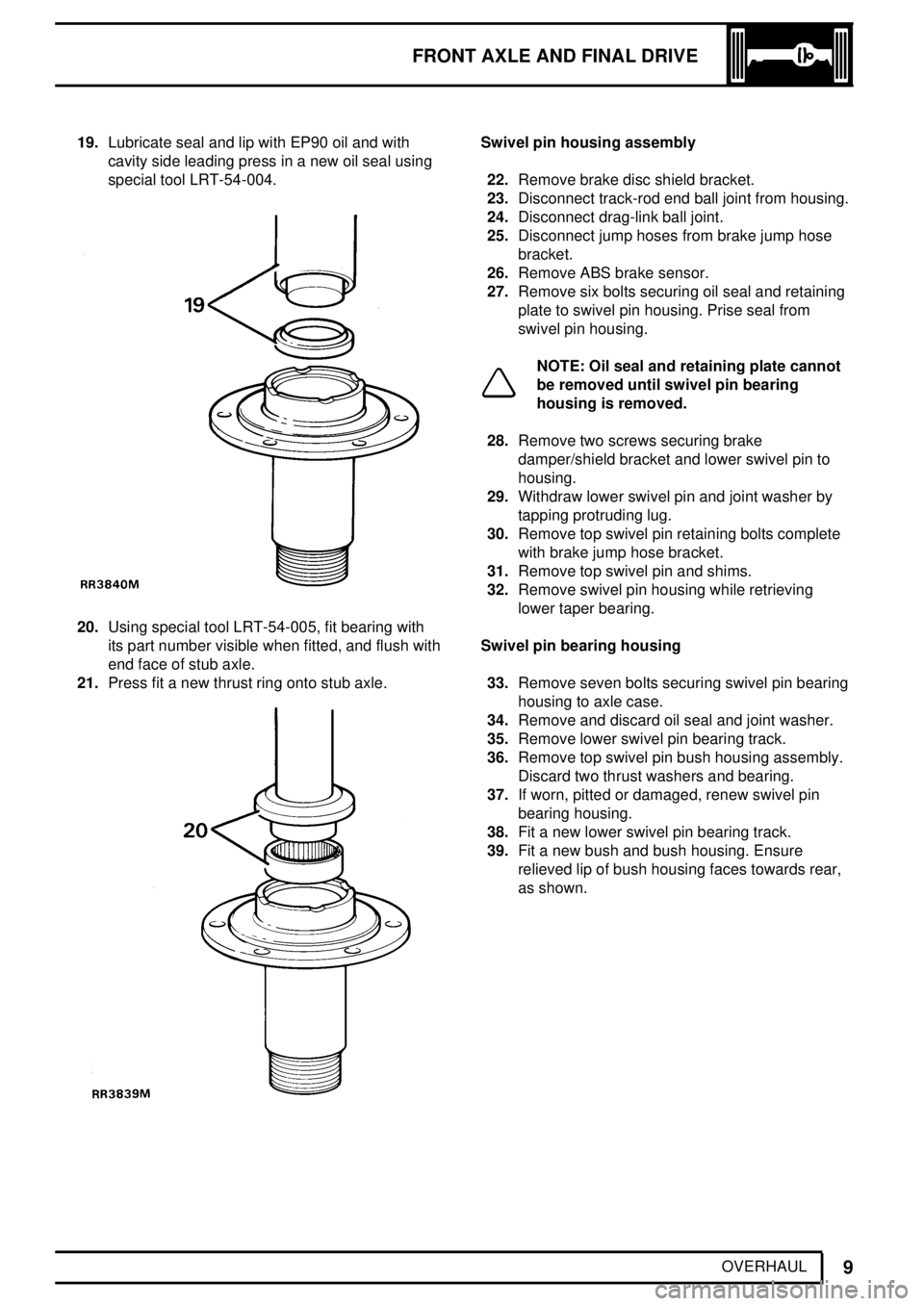
OVERHAUL 19.Lubricate seal and lip with EP90 oil and with
cavity side leading press in a new oil seal using
special tool LRT-54-004.
20.Using special tool LRT-54-005, fit bearing with
its part number visible when fitted, and flush with
end face of stub axle.
21.Press fit a new thrust ring onto stub axle.
Swivel pin housing assembly
22.Remove brake disc shield bracket.
23.Disconnect track-rod end ball joint from housing.
24.Disconnect drag-link ball joint.
25.Disconnect jump hoses from brake jump hose
bracket.
26.Remove ABS brake sensor.
27.Remove six bolts securing oil seal and retaining
plate to swivel pin housing. Prise seal from
swivel pin housing.
NOTE: Oil seal and retaining plate cannot
be removed until swivel pin bearing
housing is removed.
28.Remove two screws securing brake
damper/shield bracket and lower swivel pin to
housing.
29.Withdraw lower swivel pin and joint washer by
tapping protruding lug.
30.Remove top swivel pin retaining bolts complete
with brake jump hose bracket.
31.Remove top swivel pin and shims.
32.Remove swivel pin housing while retrieving
lower taper bearing.
Swivel pin bearing housing
33.Remove seven bolts securing swivel pin bearing
housing to axle case.
34.Remove and discard oil seal and joint washer.
35.Remove lower swivel pin bearing track.
36.Remove top swivel pin bush housing assembly.
Discard two thrust washers and bearing.
37.If worn, pitted or damaged, renew swivel pin
bearing housing.
38.Fit a new lower swivel pin bearing track.
39.Fit a new bush and bush housing. Ensure
relieved lip of bush housing faces towards rear,
as shown.
Page 512 of 873
54FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
10
OVERHAUL
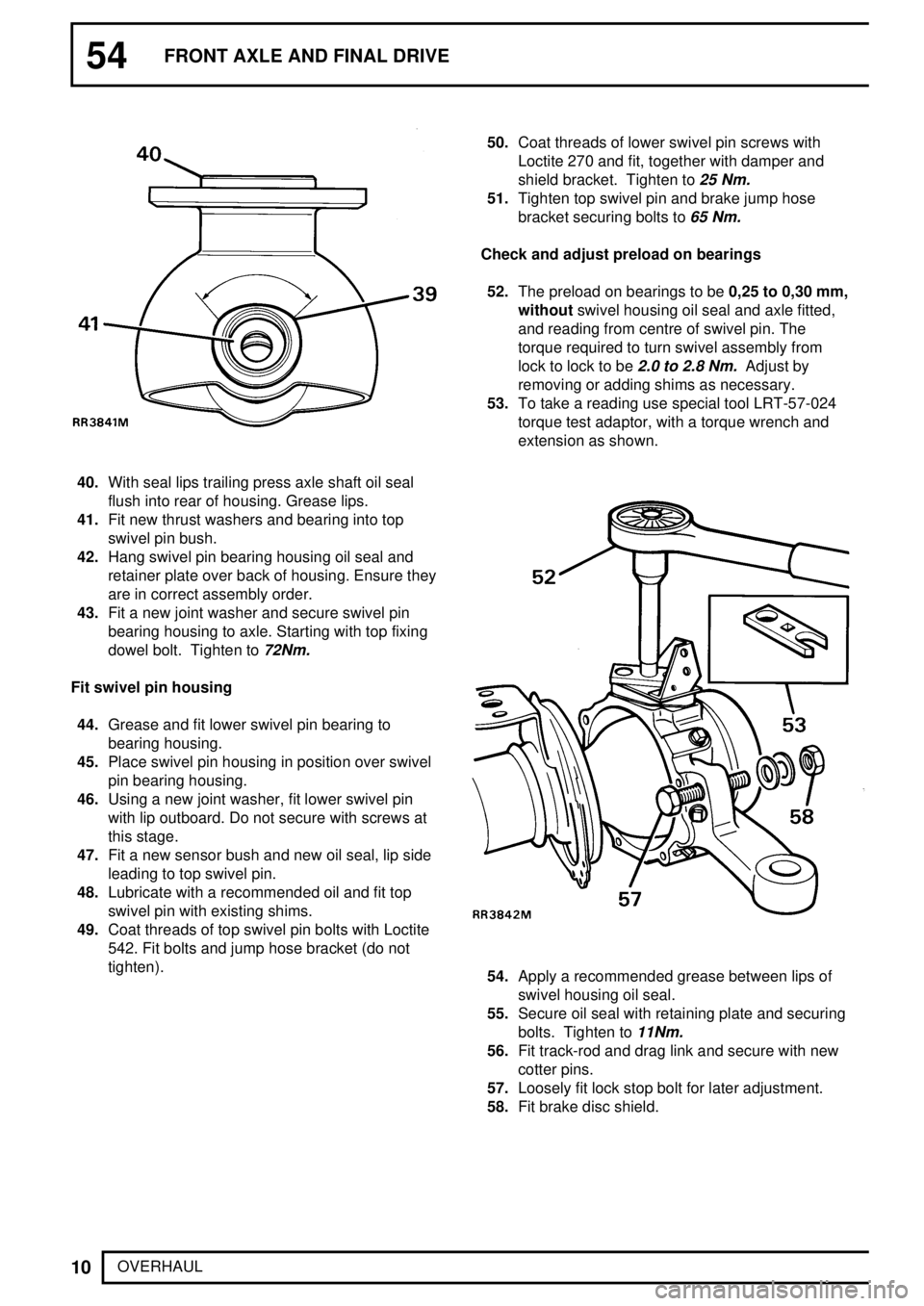
40.With seal lips trailing press axle shaft oil seal
flush into rear of housing. Grease lips.
41.Fit new thrust washers and bearing into top
swivel pin bush.
42.Hang swivel pin bearing housing oil seal and
retainer plate over back of housing. Ensure they
are in correct assembly order.
43.Fit a new joint washer and secure swivel pin
bearing housing to axle. Starting with top fixing
dowel bolt. Tighten to
72Nm.
Fit swivel pin housing
44.Grease and fit lower swivel pin bearing to
bearing housing.
45.Place swivel pin housing in position over swivel
pin bearing housing.
46.Using a new joint washer, fit lower swivel pin
with lip outboard. Do not secure with screws at
this stage.
47.Fit a new sensor bush and new oil seal, lip side
leading to top swivel pin.
48.Lubricate with a recommended oil and fit top
swivel pin with existing shims.
49.Coat threads of top swivel pin bolts with Loctite
542. Fit bolts and jump hose bracket (do not
tighten).50.Coat threads of lower swivel pin screws with
Loctite 270 and fit, together with damper and
shield bracket. Tighten to
25 Nm.
51.Tighten top swivel pin and brake jump hose
bracket securing bolts to
65 Nm.
Check and adjust preload on bearings
52.The preload on bearings to be0,25 to 0,30 mm,
withoutswivel housing oil seal and axle fitted,
and reading from centre of swivel pin. The
torque required to turn swivel assembly from
lock to lock to be
2.0 to 2.8 Nm.Adjust by
removing or adding shims as necessary.
53.To take a reading use special tool LRT-57-024
torque test adaptor, with a torque wrench and
extension as shown.
54.Apply a recommended grease between lips of
swivel housing oil seal.
55.Secure oil seal with retaining plate and securing
bolts. Tighten to
11Nm.
56.Fit track-rod and drag link and secure with new
cotter pins.
57.Loosely fit lock stop bolt for later adjustment.
58.Fit brake disc shield.
Page 513 of 873

FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
11
OVERHAUL Fit driveshaft and stub axle
59.Insert axle shaft, and when differential splines
are engaged, push assembly in fully.
CAUTION: Take care not to damage axle
shaft oil seals.
60.Place a new joint washer in position on swivelpin
housing to stub axle mating face. Coat threads
of stub axle bolts with Loctite 270.
61.Fit stub axle with flat at 12 o'clock position.
CAUTION: Ensure that constant velocity
joint bearing journal is butted against
thrust ring on stub axle. Before stub axle
is secured.
62.Place mud shield in position and secure stub
axle to swivel pin housing with six bolts and
tighten evenly to
65 Nm.
63.Fit brake jump hoses to brake jump hose
bracket.
64.Fit front hub complete assembly.
See Repair,
Front Hub Assembly
65.Check swivel pin housing oil drain plug is fitted.
66.Fill swivel assembly to correct level, with new oil.
See SECTION 10, Maintenance, Under
Vehicle Maintenance
67.Set steering lock stop bolts to provide a
clearance of 20mm.
See STEERING,
Adjustment, Steering Lock Stops
68.Fit ABS brake sensor.See BRAKES, Repair,
Sensors - Front
Page 514 of 873
54FRONT AXLE AND FINAL DRIVE
12
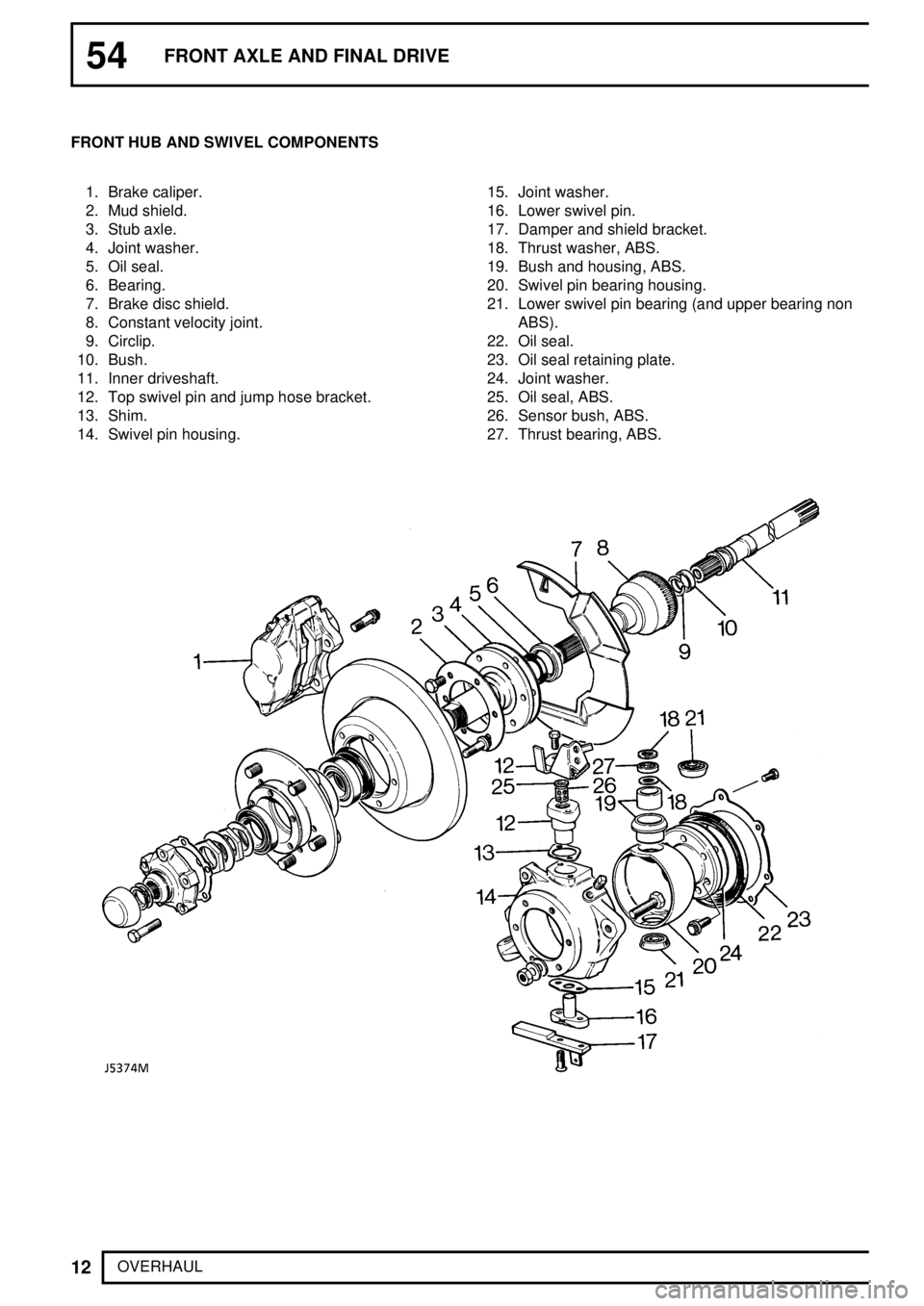
OVERHAUL FRONT HUB AND SWIVEL COMPONENTS
1. Brake caliper.
2. Mud shield.
3. Stub axle.
4. Joint washer.
5. Oil seal.
6. Bearing.
7. Brake disc shield.
8. Constant velocity joint.
9. Circlip.
10. Bush.
11. Inner driveshaft.
12. Top swivel pin and jump hose bracket.
13. Shim.
14. Swivel pin housing.15. Joint washer.
16. Lower swivel pin.
17. Damper and shield bracket.
18. Thrust washer, ABS.
19. Bush and housing, ABS.
20. Swivel pin bearing housing.
21. Lower swivel pin bearing (and upper bearing non
ABS).
22. Oil seal.
23. Oil seal retaining plate.
24. Joint washer.
25. Oil seal, ABS.
26. Sensor bush, ABS.
27. Thrust bearing, ABS.
Page 538 of 873

57STEERING
12
FAULT DIAGNOSIS Steering column alignment
1.Place vehicle on level ground. Measure the
angle of lower steering shaft using a Pernumeter
placed on the shaft between the universal joints.
The angle should measure a minimum of 12Ê.
2.If necessary, realign the shaft. Release the five
fixings securing the steering column. Position
column as required. Tighten the fixings evenly,
27 Nm.
3.Loosen the three screws securing lower steering
column shroud to upper shroud ensure lower
shroud is clipped to upper shroud. Reposition
shroud, tighten screws.
4.Recheck steering column angle.
Steering box adjustment
1.Check steering box adjustment.
See
Adjustment, Power Steering Box
Steering damper check
1.Check condition of steering damper
See
Steering Damper
VISUAL CHECK AND BASIC ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE: It is important that the following
instructions are carried out in the
sequence shown and the results recorded.
1.Road springs - check that road springs are
correctly seated and are to correct specification
for vehicle. For spring specification.
See
GENERAL SPECIFICATION DATA,
Information, Road Springs Data
2.Ride height - measure trim height from wheel
centre to wheelarch eyebrow. Record results on
data sheet.
3.Check/top up power steering fluid
See Repair,
Power Steering Fluid Reservoir
4.Check tension and condition of drive belt.See
ENGINE, Repair, Drive Belt
5.Track rod/drag link - check condition of track rod,
drag link and ball joints.
See Repair, Drag Link
and Drag Link Ends
If either component is damaged, check operation
of steering damper and steering box for
smoothness. Replace all damaged or worn
components that impair the operation of the
steering system.
6.Suspension bushes - examine all steering and
suspension bushes for signs of wear and
deterioration. Also check all fixings for torque
relaxation. Tighten to correct torque value.
See
FRONT SUSPENSION, Specifications, torque,
Torque Values
7.Oil leaks - check front and rear axle hubs for
leak and repair as necessary.
8.Brake system - check brake system for leaks,
pipe condition, pad wear/contamination, disc
wear/condition and ABS sensors for correct
fitting.
9.Hub end float - check movement in the hubs by
rocking the wheels.
10.Check front wheel alignment. Vehicles displaying
a tendency to veer more than considered
allowable, it is permissible to set the front track
to parallel.
11.Having completed all the above checks and
adjustments, road test vehicle.
See Road Test
Procedure
Attempting to reproduce the symptoms
established earlier. If symptoms still exist refer to
relevant Diagnostic Chart.
Page 593 of 873
70BRAKES
2
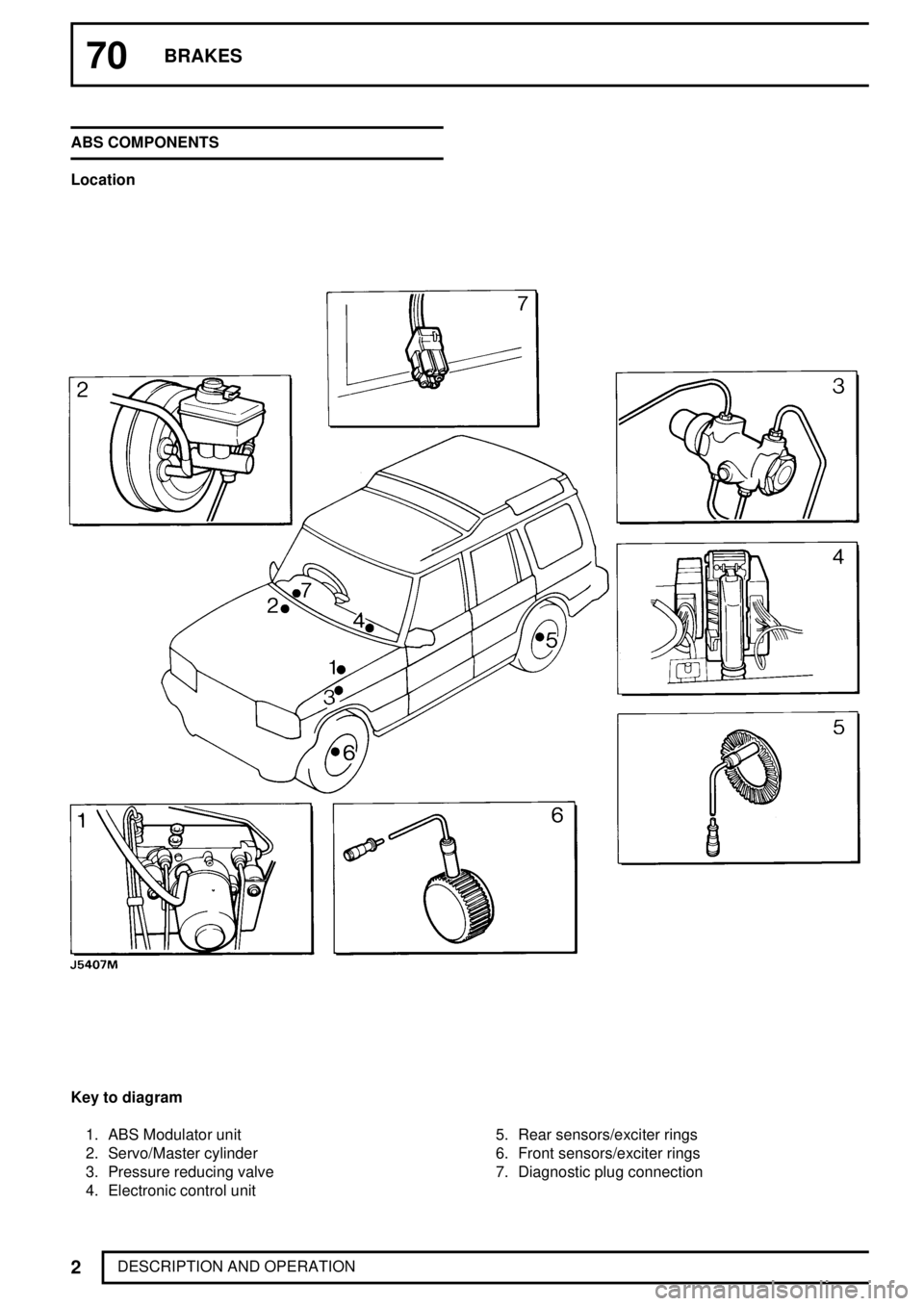
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ABS COMPONENTS
Location
Key to diagram
1. ABS Modulator unit
2. Servo/Master cylinder
3. Pressure reducing valve
4. Electronic control unit5. Rear sensors/exciter rings
6. Front sensors/exciter rings
7. Diagnostic plug connection
Page 594 of 873

BRAKES
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Description of components
1. ABS Modulator unit
To provide the ABS function a Modulator is positioned
within the system between the master cylinder and the
calipers. On both LHD and RHD vehicles it is sited on
the left inner wing [fender]. The Modulator has 8
solenoid valves, 2 for each wheel, 2 expanders and a
recirculation pump. It is non serviceable.
2. Servo/master cylinder
Actuation of the system is provided by a combined
master cylinder and servo assembly attached to the
pedal box, this provides pressure to opposed piston
calipers at each brake pad Twin piston at the front
axle, single piston at the rear.
3. Pressure reducing valve
To maintain the braking balance, pressure to the rear
axle is regulated by a Pressure Reducing Valve (PRV)
This PRV is of the failure bypass type, allowing full
system pressure to the rear axle in the event of a front
circuit failure. It is sited on the left inner wing [fender].
4. Electronic control unit - ECU
ABS control is provided by an electronic control unit
which is positioned on the passenger side of the
vehicle behind the dash panel/glove box.
The ECU, which is non-serviceable, is connected to
the ABS harness by a 35 way connector. non
serviceable.
The ECU continually monitors the brake system,
providing diagnostics in the event of a system
malfunction. Details of how to access the ECU
diagnostics are provided in the Electrical
Troubleshooting Manual.
5.& 6. Front and rear sensors/exciter rings - 4 off
A sensor is sited at each wheel, sensing a 60 tooth
exciter ring. When vehicle is in motion inductive
sensors send signals to ECU. Front exciter ring is
fitted to outside diameter of constant velocity joint
inside each front hub assembly. The rear exciter ring
is bolted to the rear of each brake disc bell.7. Diagnostic plug connection
A diagnostic plug is located behind the dash. To the
left of the steering column on LHD vehicles. To the
right of the steering column on RHD vehicles. It is a 5
way blue connector.
The location and identification of ABS electrical relays
are given in the Electrical Troubleshooting Manual.
For location and identification of ABS electrical fuses.
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Fuse Box - Interioror.
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Fuse Box - Engine
Compartment
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - ABS
Manufactured by WABCO
Introduction
The purpose of ABS is to prevent vehicle wheels
locking during brake application, thus maintaining
vehicle steerability and stability. This allows vehicle to
be steered whilst brakes are applied, even under
emergency conditions, and to avoid obstacles where
there is sufficient space to redirect the vehicle.
WARNING: ABS is an aid to retaining
steering control and stability while
braking.
·ABS cannot defy the natural laws of physics
acting on the vehicle.
·ABS will not prevent accidents resulting from
excessive cornering speeds, following
another vehicle too closely or aquaplaning,
i.e. where a layer of water prevents adequate
contact between tyre and road surface.
·The additional control provided by ABS must
never be exploited in a dangerous or
reckless manner which could jeopardise the
safety of driver or other road users.
·The fitting of ABS does not imply that the
vehicle will always stop in a shorter stopping
distance.
Page 595 of 873
70BRAKES
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION System description
The brake system consists of dual hydraulic circuits in
a front - rear split. That is individual circuits to front
and rear axles.
Wheelspeed signals are provided by the fitting of
exciter rings to axles and speed sensors.
An ABS stop light switch is fitted to provide a braking
signal to the ECU as well as operate the stop lights.
Electrical wiring is provided as necessary with system
relays and fuses. Discovery Electrical Troubleshooting
Manual gives the location and wiring circuits of these
components.
Visual warning of system malfunction is provided via a
warning light in the instrument panel.
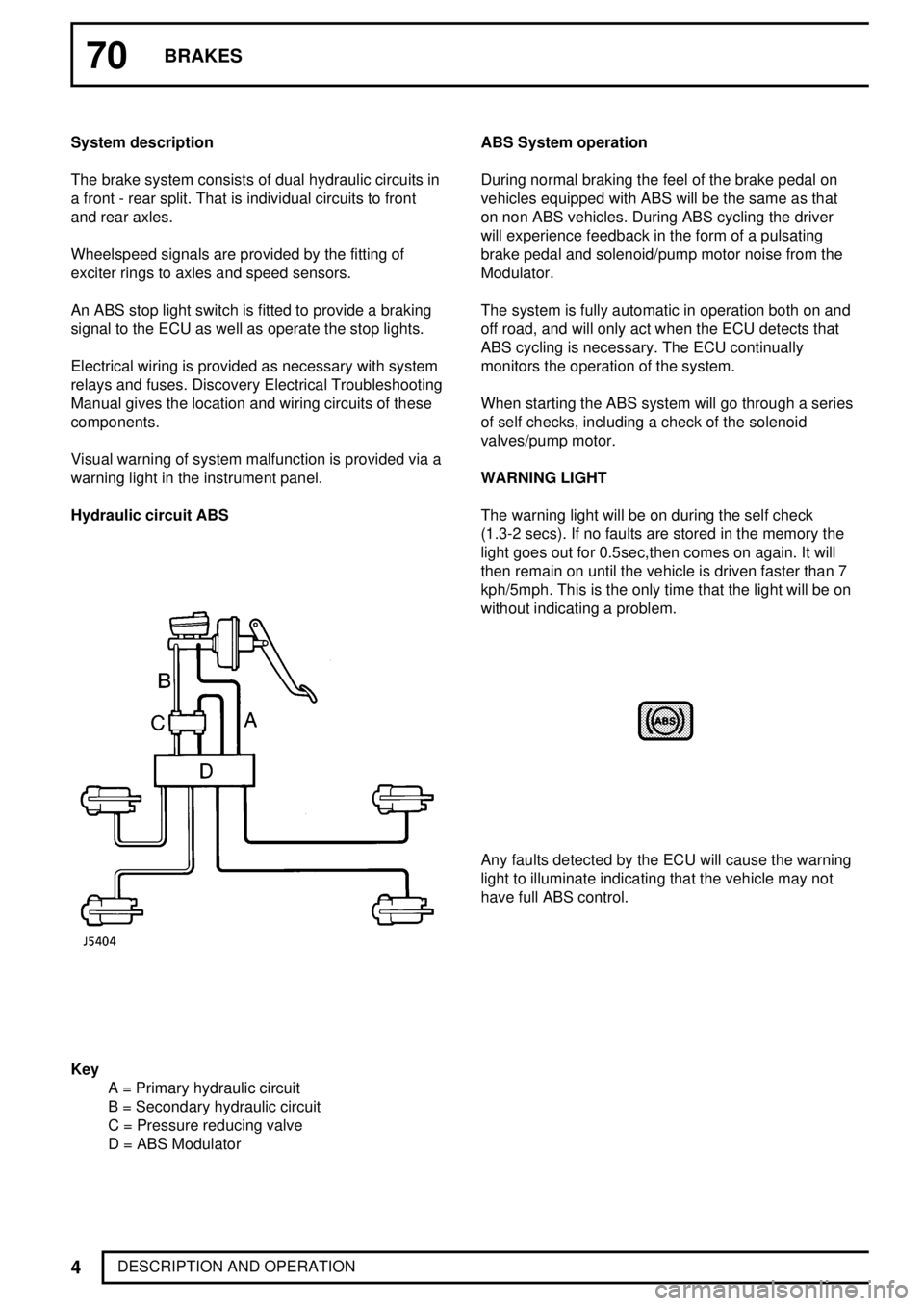
Hydraulic circuit ABS
Key
A = Primary hydraulic circuit
B = Secondary hydraulic circuit
C = Pressure reducing valve
D = ABS ModulatorABS System operation
During normal braking the feel of the brake pedal on
vehicles equipped with ABS will be the same as that
on non ABS vehicles. During ABS cycling the driver
will experience feedback in the form of a pulsating
brake pedal and solenoid/pump motor noise from the
Modulator.
The system is fully automatic in operation both on and
off road, and will only act when the ECU detects that
ABS cycling is necessary. The ECU continually
monitors the operation of the system.
When starting the ABS system will go through a series
of self checks, including a check of the solenoid
valves/pump motor.
WARNING LIGHT
The warning light will be on during the self check
(1.3-2 secs). If no faults are stored in the memory the
light goes out for 0.5sec,then comes on again. It will
then remain on until the vehicle is driven faster than 7
kph/5mph. This is the only time that the light will be on
without indicating a problem.
Any faults detected by the ECU will cause the warning
light to illuminate indicating that the vehicle may not
have full ABS control.
Page 601 of 873

BRAKES
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ABS FAULT DIAGNOSIS
If a fault has occurred, or has been identified by ECU
self diagnostic function and ABS warning light is
illuminated. The system and components must be
checked to locate and rectify fault, using Testbook
diagnostics.
NOTE: If warning lamp has indicated a
fault in system, and no fault code has been
stored in memory, cause of fault is:
a) Failure in electrical supply
b) Bad ECU ground
c) Faulty warning light relay
d) ECU not connected
Before commencing fault diagnosis procedure
following items must be checked:
1.Inspect all exposed cables for damage or
abrasion.
2.Check ground on ABS system.
3.Battery - state of charge.
4.Check hub end-float.
5.All ABS fuses and electrical connections.
Fault rectification
1.Complete harness should be replaced if faults
are found in wiring harness.
2.DO NOT use unspecified cables or connectors,
as this could jeopardise safe function of ABS.
3.DO NOT attempt to open sealed 35 way
connector to ECU.FAULT DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE
NOTE: If ABS warning light illuminates due
to large sensor air gap, fault will be
retained by the ECU memory. Where wheel
sensors have been pushed fully home prior to
test, The ECU will indicate a fault that has been
rectified.
NOTE: After any steering adjustment,
bearing replacement/adjustment, brake
disc replacement: Check hub end-float and
sensor clearance.
RELAYS AND FUSES ABS
The location and identification of ABS electrical relays
are given in the Electrical Troubleshooting Manual
For location and identification of ABS electrical fuses.
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Fuse Box - Interioror.
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Fuse Box - Engine
Compartment
Page 602 of 873
70BRAKES
2
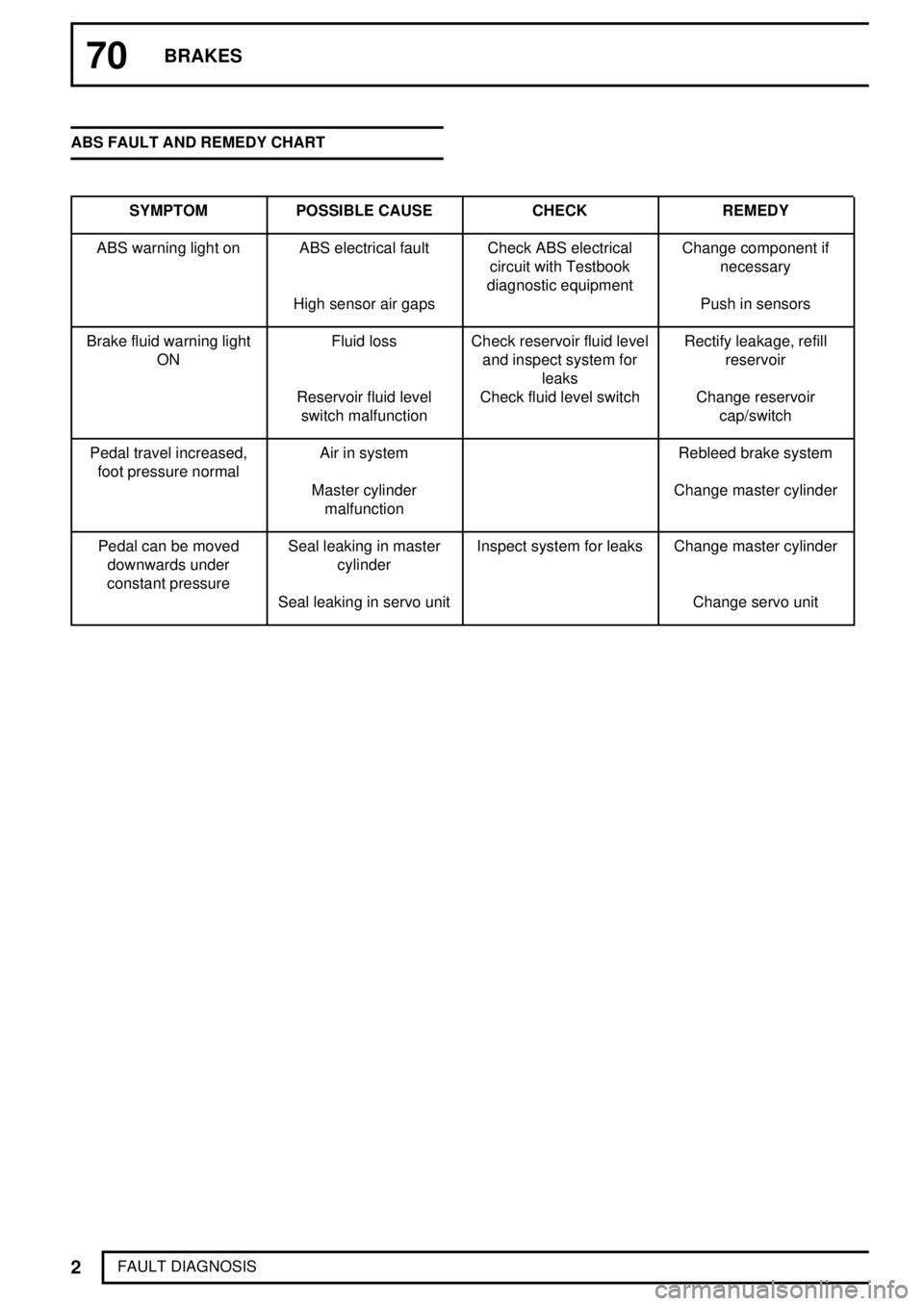
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ABS FAULT AND REMEDY CHART
SYMPTOM POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK REMEDY
ABS warning light on ABS electrical fault Check ABS electrical
circuit with Testbook
diagnostic equipmentChange component if
necessary
High sensor air gaps Push in sensors
Brake fluid warning light
ONFluid loss Check reservoir fluid level
and inspect system for
leaksRectify leakage, refill
reservoir
Reservoir fluid level
switch malfunctionCheck fluid level switch Change reservoir
cap/switch
Pedal travel increased,
foot pressure normalAir in system Rebleed brake system
Master cylinder
malfunctionChange master cylinder
Pedal can be moved
downwards under
constant pressureSeal leaking in master
cylinderInspect system for leaks Change master cylinder
Seal leaking in servo unit Change servo unit