fuel filter LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1995, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1995Pages: 873, PDF Size: 12.89 MB
Page 116 of 873

V8i
3
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ENGINE STARTING PROBLEMS
Engine fails to crank in park or neutral (Automatic
Transmission)
1.Is battery in good state of charge?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Jump Starting
YES - Continue.
2.Is automatic transmission inhibitor switch faulty
or gear selection linkage incorrectly adjusted?
YES -
See AUTOMATIC GEARBOX, Repair,
Inhibitor Switch
,
NO -
See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 1.
Engine fails to crank (Manual Transmission)
1.Is battery in good state of charge?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Jump Starting
YES -See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 1.
Engine cranks but fails to start
1.Is the cranking speed fast enough (120 rpm)?
NO -
See INTRODUCTION, Information,
Jump Starting
If necessary also.See Electrical Trouble
Shooting Manual.
YES - Continue.
2.Is there combustion in any cylinder?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Fault diagnosis,
Lucas Constant Energy Ignition
System - V8i See Electrical Trouble
Shooting Manual.
YES - Continue.
3.Are the fuel supply, tank, pump, ventilation and
emission control systems in correct working
order or the fuel contaminated?
NO -
See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel
Filter See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Tank See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel pump and Sender Unit See
EMISSION CONTROL, Description and
operation, Emission control
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 2.ENGINE RUNNING PROBLEMS
Engine runs at high speed but will not idle (stops)
Engine idle speed erratic Engine starts but stops
immediately
Engine stalls Engine misfires/hesitation
1.Multiport fuel injection.
See Electrical Trouble
Shooting Manual. See ELECTRICAL, Fault
diagnosis, Lucas Constant Energy Ignition
System - V8i
Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation, Brake
Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum
connections.
See HEATING AND
VENTILATION, Description and operation,
Heating and Ventilation Unit
If problem is not diagnosed continue.
2.Are HT leads correctly routed and clipped?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor
- V8i
YES - Continue.
3.Is fuel supply, tank, pump, ventilation and
emission control systems in correct working
order or the fuel contaminated?
NO -
See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel
Filter See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Tank See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Pump and Sender Unit See
EMISSION CONTROL, Description and
operation, Emission Control
If problem is not diagnosed repeat tests, starting
at 1.
Engine lacks power/poor performance
1.Is throttle travel restricted or cable incorrectly
adjusted?
YES - Check thickness of carpets.
See FUEL
SYSTEM, Repair, Throttle Cable See
FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Accelerator
Pedal
NO - Continue.
2.Are the Ignition and Multiport Fuel Injection
systems in order?
NO -
See Electrical Trouble Shooting
Manual.A1 See ELECTRICAL, Fault
diagnosis, Lucas Constant Energy
Ignition System - V8i See
ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor - V8i
YES - Continue.
Page 117 of 873

12ENGINE
4
FAULT DIAGNOSIS 3.Are fuel supply, tank, pump, ventilation and
emission control systems in correct working
order or the fuel contaminated?
NO -
See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair, Fuel
Filter See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Tank See FUEL SYSTEM, Repair,
Fuel Pump and Sender Unit
YES - Suspect valves held open by hydraulic
tappets due to high oil pressure.
See
Engine Oil Pressure Test
4.Is oil pressure high?
YES - Remove oil filter and cooler adaptor and
check pressure relief valve strainer gauze
for blockage and that the relief valve is
not stuck closed.
See Description and
operation, Description
NO - Carry out cylinder compression tests to
determine condition of head gaskets and
valves.
See Cylinder Compression -
Test
5.Are cylinder compressions satisfactory?
NO -
See Repair, Cylinder Heads - Renew
YES - Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation,
Brake Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum connections.
See HEATING AND VENTILATION, Description and
operation, Heating and Ventilation Unit
If problem is not diagnosed: Continue.
6.Are the brakes binding?
YES - Investigate cause of binding.
NO - Continue.
7.Automatic Transmission only. Is the Torque
Converter and Transmission operating correctly?
Carry out Road test, Static tests and Stall tests
to determine condition of Automatic
transmission.
If problem is not diagnosed: repeat tests starting at 1.Engine backfires into exhaust system
1.Are there any leaking joints/connections or holes
in the exhaust system?
YES -
See MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST
SYSTEM, Repair, Exhaust System
Complete
NO - Continue.
2.Is distributor fitted correctly, HT leads in correct
firing order and routed correctly?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Repair, Distributor
- V8i
YES - Continue.
3.Is air fuel ratio correct?
NO - Check multiport fuel injection.
See
Electrical Trouble Shooting Manual.
Check brake vacuum connections.See
BRAKES, Description and operation, Brake
Servo Unit
Check heater/ventilation unit vacuum
connections.
See HEATING AND
VENTILATION, Description and operation,
Heating and Ventilation Unit
Check the crank case and fuel tank ventilation
system.
See EMISSION CONTROL,
Description and operation, Emission Control
YES - Continue.
4.Are cylinder compressions satisfactory?
NO - Carry out compression test to check for
leaking gaskets valves etc.
See
Cylinder Compression - Test
See Repair, Cylinder Heads - Renew
If problem is not diagnosed: repeat tests starting
at 1.
Page 187 of 873

EMISSION CONTROL
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 EMISSION CONTROL
Three systems are used to control the vehicle
atmospheric emissions these are:
Engine crankcase fume emissions.
Fuel tank Evaporative emissions
Engine exhaust gas emissions.
Crankcase ventilation system - 3.9 MFi models
only
The crankcase ventilation system which is an integral
part of the air supply to the engine combustion
chambers, is often overlooked when diagnosing
problems associated with engine performance. A
blocked ventilation pipe or filter or excessive air leak
into the inlet system through a damaged pipe or
leaking gasket can effect the mixture, performance
and economy of the engine.
1. Three way connector
2. Air filter
3. Oil separatorThe purpose of the crankcase ventilation system is to
ensure that any noxious gas generated in the engine
crankcase is rendered harmless by burning in the
combustion chambers as follows:
Oil laden noxious gas in the engine crankcase is
drawn through an oil separator 3 located on the right
cylinder head rocker cover, where the oil is separated
and returned to the sump. The gas flows through a
restrictor in the three way connection 1 and into the
inlet plenum chamber where it is drawn into the
combustion chambers and burned. The volume of
fresh air which is drawn from the atmospheric side of
the throttle butterfly to mix with the gas, depends on
the position of the throttle and the engine speed.
The air filter 2 fitted to the left cylinder head rocker
cover, must be maintained in clean condition to
ensure sufficient air enters the crankcase under
varying throttle openings and manifold depression, to
prevent excessive crankcase pressure or depression
developing.
Page 194 of 873

17EMISSION CONTROL
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ADD: 09/95 System operation
The system is designed to prevent fuel vapour
escaping to atmosphere, and consists of four roll-over
valves fitted internally in the fuel tank, connected to
the liquid/vapour separator by a nylon line. The
separator is mounted to the side of the filler neck. An
EVAP canister is positioned in the engine
compartment mounted on the right front side valance.
The liquid/vapour separator and EVAP canister are
connected by a nylon line which runs the length of the
chassis.
Pressure/vacuum relief valves are incorporated into
the fuel filler cap and are designed to protect the fuel
tank from permanent deformation in the event of
system pressure or vacuum exceeding the system
operating parameters. There are no other relief or
one-way valves in the system.
A vent line flow restrictor known as an anti-trickle fill
valve is fitted to the filler pipe in the line between the
tank and EVAP canister. The function of this valve is
to prevent overfilling the tank by trickling fuel in,
thereby preserving the vapour space in the tank to
allow for fuel expansion during hot weather.
The valve achieves this by blocking the vent line
during the fuel filling process. The valve is operated
by the action of inserting the filler gun so that when
the fuel in the tank reaches the level of the filling
breather, flow cut off occurs due to fuel filling the filler
pipe.During normal vehicle operation and when the engine
is switched off, the venting system between the fuel
tank and EVAP canister is open to allow the free
passage of vapour.
The EVAP canister, which is connected by a nylon
hose to the plenum chamber, absorbs and stores the
fuel vapour from the fuel tank when the engine is not
running. With the engine running, vapour is purged
from the EVAP canister by allowing outside air to be
drawn through the EVAP canister vent solenoid and
link pipe by the influence of manifold vacuum to the
EVAP canister purge connection on the canister.
Filter pads are fitted above and below the charcoal
and in the EVAP canister vent solenoid to prevent the
ingress of foreign matter into the purge line.
The EVAP canister purge valve, which is fitted in the
line from the EVAP canister to the plenum, is
controlled by the ECM which determines the most
emission acceptable time at which purging should
take place. This will normally be at engine speeds
above idle and when the vehicle is in motion.
The EVAP canister vent solenoid is mounted on the
side of the EVAP canister bracket and is connected to
the EVAP canister by a length of large bore hose. The
ECVS is controlled by the ECM and is normally open.
The function of the ECVS is to block the air intake
side of the EVAP canister. When the system receives
an ECM signal the valve closes; this allows the
system leak check to take place. The leak check only
occurs when pre-determined vehicle operating
conditions are met.
Page 206 of 873

Tdi
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
Air intake
The air cleaner is positioned to the right of the engine
and connected by hoses to a cold air intake duct and
the turbocharger inlet. A crankcase breather hose is
fitted between the air cleaner and the separator.
A single stage turbocharger, fitted between the
exhaust manifold and exhaust pipe, is connected by
hoses to the air cleaner and to an intercooler mounted
on the right of the radiator. The intercooler is
connected by a hose to the inlet manifold.
Fuel system
A 89 litre fuel tank is mounted at the rear of the
vehicle beneath the load space floor. The tank is
vented by a 2 way valve in the filler cap.
A mechanical lift pump, driven by the camshaft, is
mounted on the side of the engine.
A fuel filter, fitted with a replaceable element and
incorporating a water separator, is positioned on the
LH side of the bulkhead.
A Bosch Type injection pump, incorporating a cold
start advance unit and a high idle setting is mounted
on the LH side of the engine and is directly driven by
gears from the crankshaft. The pump meters and
distributes fuel to 4 pintle type injectors located in
pre-combustion chambers in the cylinder heads.
A return line passes excess fuel from the injection
pump and injectors back to the fuel tank.
Glow plugs
Four glow plugs are located in the cylinder head,
directly below each injector.Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
Exhaust gas recirculation is controlled by the EGR
control unit mounted in the passenger compartment
on the RH 'A' post behind the fascia and receives the
following inputs:
a. Engine temperature from coolant temperature
transmitter in No. 4 cylinder head.
b. Throttle position from the sensor on the injection
pump.
c. Engine speed from the tachometer.
d. EGR valve lift position.
When all correct signals are received, the EGR
solenoid allows vacuum to open the EGR valve and
recirculate a portion of the exhaust gas.
Page 207 of 873
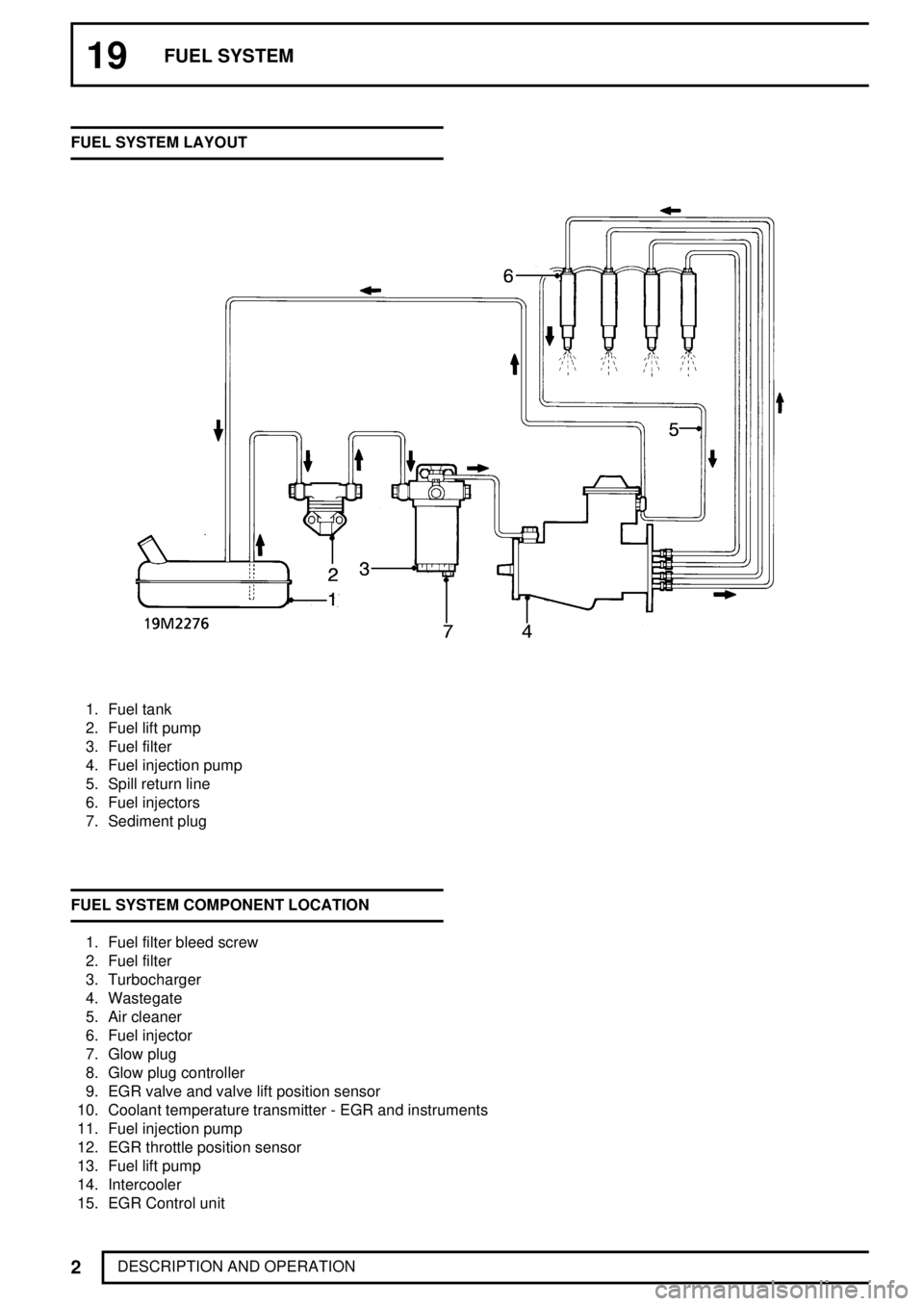
19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL SYSTEM LAYOUT
1. Fuel tank
2. Fuel lift pump
3. Fuel filter
4. Fuel injection pump
5. Spill return line
6. Fuel injectors
7. Sediment plug
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT LOCATION
1. Fuel filter bleed screw
2. Fuel filter
3. Turbocharger
4. Wastegate
5. Air cleaner
6. Fuel injector
7. Glow plug
8. Glow plug controller
9. EGR valve and valve lift position sensor
10. Coolant temperature transmitter - EGR and instruments
11. Fuel injection pump
12. EGR throttle position sensor
13. Fuel lift pump
14. Intercooler
15. EGR Control unit
Page 209 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
Diesel engines operate by compression ignition. The
rapid compression of air in the cylinder during the
compression cycle heats the injected fuel, causing it
to self ignite. During cold starting, automatically
controlled glow plugs assist in raising the temperature
of the compressed air to ignition point.
A cold start advance unit advances the injection timing
to further assist starting. Idle quality is improved by
the high idle setting.
The engine is supplied with pre-compressed air by a
single stage turbocharger.
Exhaust gases passing over a turbine cause it to
rotate, driving a compressor mounted on the turbine
shaft. Air drawn from the cold air intake passes, via
the air cleaner, to the turbocharger where it is
compressed. The compressed air passes to the
cylinders via an intercooler, which reduces the
temperature of the compressed air, increasing its
density.
Fuel is drawn from the tank by a mechanical lift pump
and passes to the injection pump via a filter. In
addition to removing particle contamination from the
fuel, the filter incorporates a water separator, which
removes and stores both bound and unbound water.
The injection pump meters a precisely timed, exact
quantity of fuel to the injectors in response to throttle
variations, injection timing varying with engine speed.
Any excess fuel delivered to the injection pump is not
injected, passing back to the tank via the fuel return
line.
Fuel is injected in a finely atomised form into a
pre-combustion chamber in the cylinder head where it
ignites. The burning fuel expands rapidly into the main
combustion chamber, creating extreme turbulence
which mixes the burning fuel thoroughly with the
compressed air, providing complete combustion.
Cold Starting is assisted by glow plugs, a cold start
advance unit and a high idle setting.Glow plugs
Glow plug operation is controlled by a timer unit, start
relay and resistor. When the ignition is turned on the
timer unit is energised, the glow plugs start to operate
and a warning light on the dashboard illuminates,
remaining illuminated until the glow plugs are
automatically switched off.
The length of time the glow plugs will operate is
dependent on under bonnet temperature, which is
monitored by a sensor located in the timer unit.
Starting the engine results in the power supply to the
glow plugs passing through the resistor, which
reduces their operating temperature. The glow plugs
are cut out either by the temperature sensor in the
timer, or by a microswitch on the injection pump which
operates when the throttle is depressed.
Cold start advance
The cold start advance unit is connected to the engine
cooling system via hoses. It contains a temperature
sensitive element which is retracted when cold and
pulls the advance lever, via cable, towards the rear of
the pump against spring pressure. As coolant
temperature rises, the cold start element expands
releasing tension on the cable and allowing spring
pressure to move the advance lever forwards.
Page 223 of 873
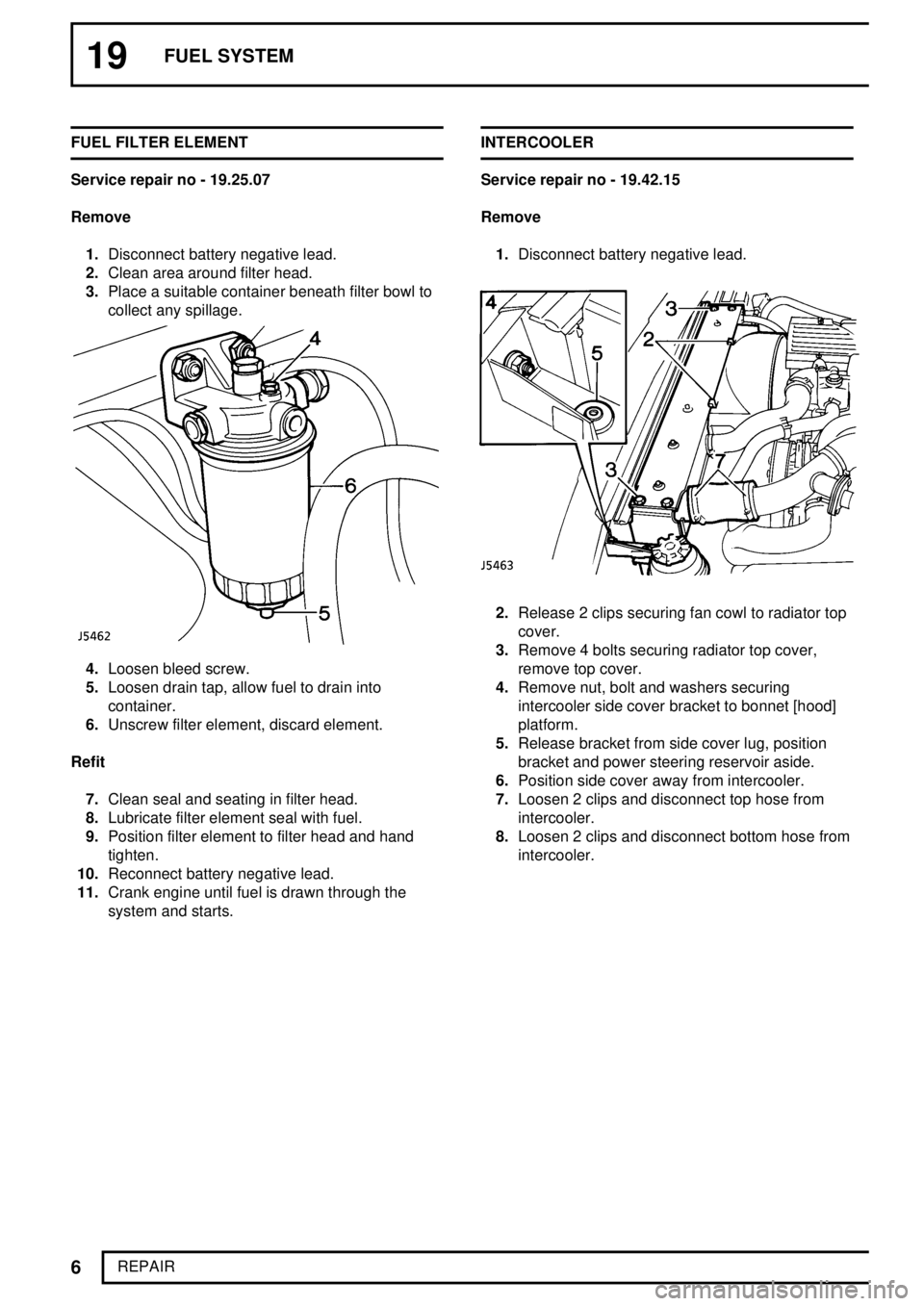
19FUEL SYSTEM
6
REPAIR FUEL FILTER ELEMENT
Service repair no - 19.25.07
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Clean area around filter head.
3.Place a suitable container beneath filter bowl to
collect any spillage.
4.Loosen bleed screw.
5.Loosen drain tap, allow fuel to drain into
container.
6.Unscrew filter element, discard element.
Refit
7.Clean seal and seating in filter head.
8.Lubricate filter element seal with fuel.
9.Position filter element to filter head and hand
tighten.
10.Reconnect battery negative lead.
11.Crank engine until fuel is drawn through the
system and starts.INTERCOOLER
Service repair no - 19.42.15
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Release 2 clips securing fan cowl to radiator top
cover.
3.Remove 4 bolts securing radiator top cover,
remove top cover.
4.Remove nut, bolt and washers securing
intercooler side cover bracket to bonnet [hood]
platform.
5.Release bracket from side cover lug, position
bracket and power steering reservoir aside.
6.Position side cover away from intercooler.
7.Loosen 2 clips and disconnect top hose from
intercooler.
8.Loosen 2 clips and disconnect bottom hose from
intercooler.
Page 241 of 873
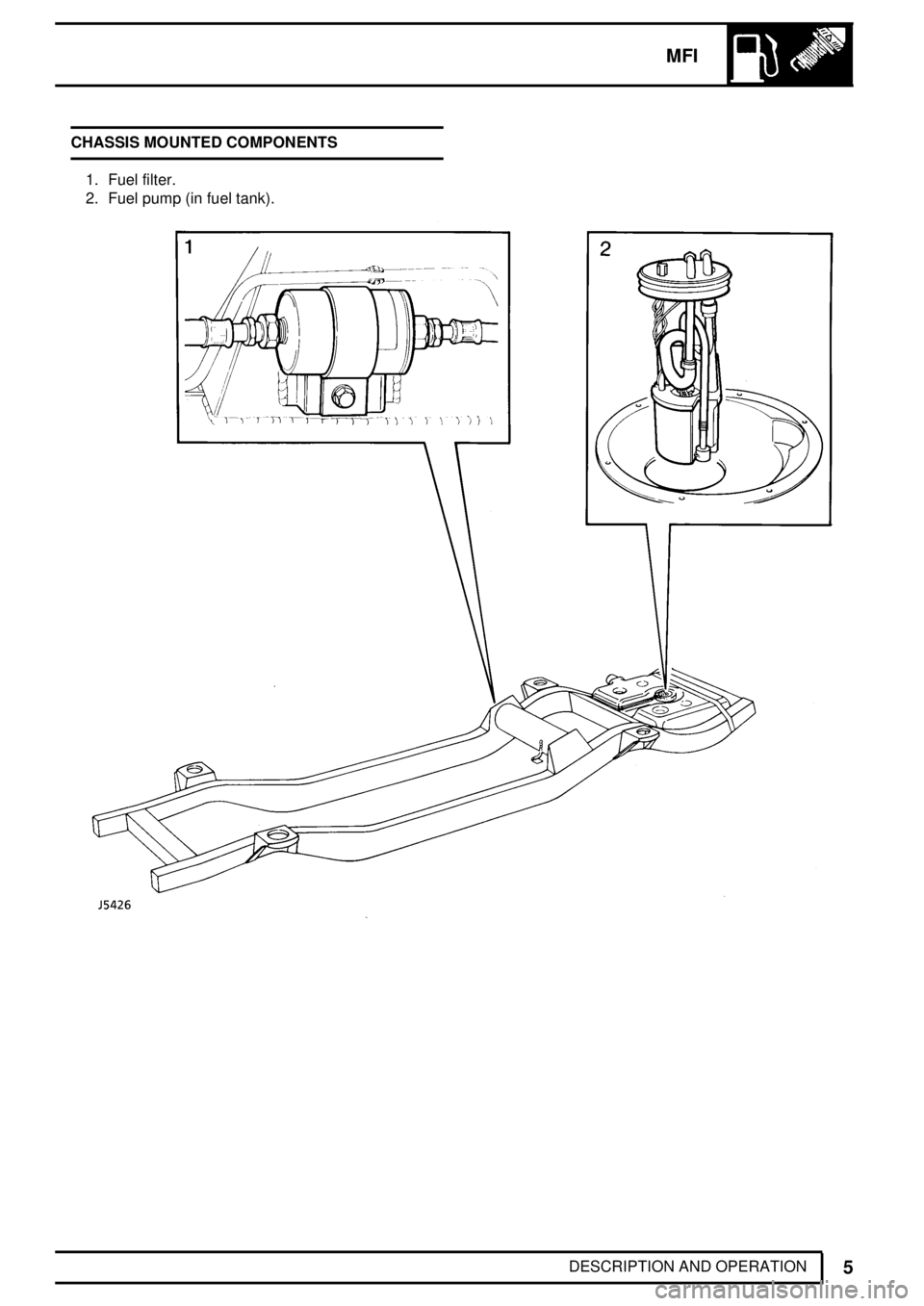
MFI
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION CHASSIS MOUNTED COMPONENTS
1. Fuel filter.
2. Fuel pump (in fuel tank).
Page 246 of 873
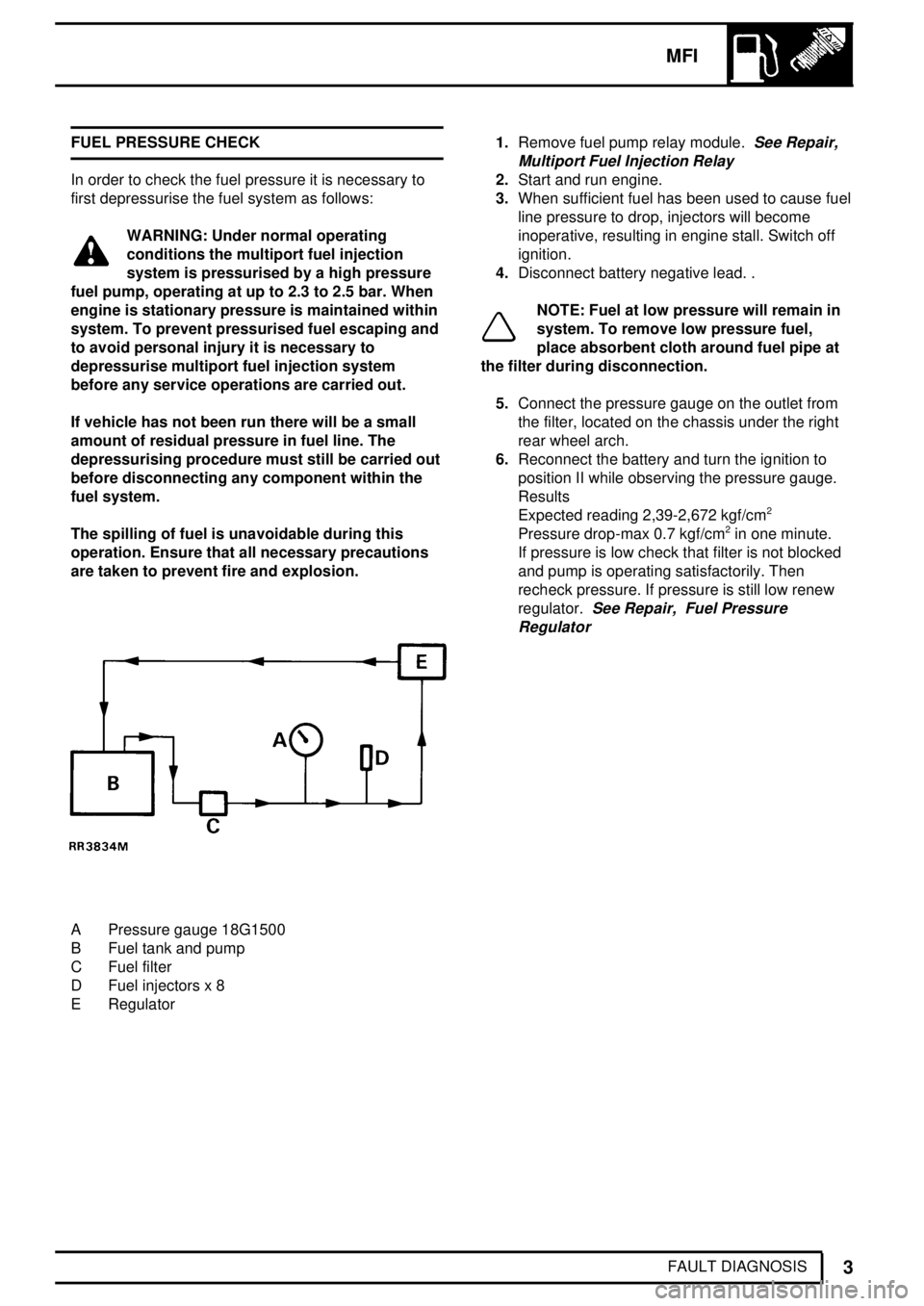
MFI
3
FAULT DIAGNOSIS FUEL PRESSURE CHECK
In order to check the fuel pressure it is necessary to
first depressurise the fuel system as follows:
WARNING: Under normal operating
conditions the multiport fuel injection
system is pressurised by a high pressure
fuel pump, operating at up to 2.3 to 2.5 bar. When
engine is stationary pressure is maintained within
system. To prevent pressurised fuel escaping and
to avoid personal injury it is necessary to
depressurise multiport fuel injection system
before any service operations are carried out.
If vehicle has not been run there will be a small
amount of residual pressure in fuel line. The
depressurising procedure must still be carried out
before disconnecting any component within the
fuel system.
The spilling of fuel is unavoidable during this
operation. Ensure that all necessary precautions
are taken to prevent fire and explosion.
A Pressure gauge 18G1500
B Fuel tank and pump
C Fuel filter
D Fuel injectors x 8
E Regulator1.Remove fuel pump relay module.
See Repair,
Multiport Fuel Injection Relay
2.Start and run engine.
3.When sufficient fuel has been used to cause fuel
line pressure to drop, injectors will become
inoperative, resulting in engine stall. Switch off
ignition.
4.Disconnect battery negative lead. .
NOTE: Fuel at low pressure will remain in
system. To remove low pressure fuel,
place absorbent cloth around fuel pipe at
the filter during disconnection.
5.Connect the pressure gauge on the outlet from
the filter, located on the chassis under the right
rear wheel arch.
6.Reconnect the battery and turn the ignition to
position II while observing the pressure gauge.
Results
Expected reading 2,39-2,672 kgf/cm
2
Pressure drop-max 0.7 kgf/cm2in one minute.
If pressure is low check that filter is not blocked
and pump is operating satisfactorily. Then
recheck pressure. If pressure is still low renew
regulator.
See Repair, Fuel Pressure
Regulator