sensor LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 1479 of 1529

NAVIGATION SYSTEM
87-26 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
GPS Tracking Menu
Sensor Check
Selecting Sensor Test from the service mode menu causes the sensor check menu to be displayed. The sensor
check menu is used to confirm that all the input sensors are working. Some of the tests below involve driving the
vehicle for short distances. Before starting these tests ensure that an appropriate location, away from public roads
and obstructions, is chosen. The system-input sensors can be tested as follows:
lWheel Sensors - When the vehicle is stationary the values in the wheel sensor boxes should both be zero. Drive
the vehicle for a short distance. While driving, a number should be displayed in the left wheel sensor box. The
value in the box should be proportional to the speed of the vehicle, and increase as the speed increases.
lGPS Satellites – Indicates the number of satellites being received
lGPS Status – Indicates the status of the GPS system by displaying one of the following messages:
lPosition Known – The system has a current position fix. This indicates that the GPS system is functioning
normally.
lSatellite Contact – The system is tracking a number of satellites. This indicates that the system is working
correctly but does not have enough information to determine the position of the vehicle. Check that there is
nothing obstructing GPS antenna's 'view' of the sky. It may take several minutes for the GPS system to
acquire enough satellites to determine the vehicle's position (Position Known).
lSatellite Search – The system is searching for satellites. If this is displayed it may mean that there is a failure
in the GPS system. First check that the GPS antenna's 'view' of the sky is not blocked in any way. Check
harness connections between the navigation computer and the GPS antenna.
lGPS Error – There is a communication error between the GPS receiver and the navigation computer.
lGYRO – Drive the vehicle forwards, in a straight line and making left and right turns. When the vehicle is moving
in a straight line the direction arrow should be pointing to the top of the screen and the gyro value beside the
direction arrow should remain relatively constant. When the vehicle turns to the right, the direction arrow should
turn clockwise and the gyro value should increase. The size of the angle through which the direction icon turns
depends on the tightness of the turn. When the vehicle turns to the left, the direction arrow should turn anti-
clockwise and the gyro value should decrease.
lDirection of Travel – When the gear lever is in any position other than reverse, the display should show
Forwards. When reverse is selected, the display should change to Backwards.
Selecting
GPS Tracking Info
1
2
3
4
Visible Satellites
Almanac
< Return
08
Yes
Functions 5.3 21
7.4 05
5.9
13
12.3
04CHPRN
S/N
CHPRN
S/N
4.3
27
3.9 19
18.2 02
14.3 10 5
6
7
8
Page 1480 of 1529

NAVIGATION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 87-27
Sensor Check Menu
TestBook/T4 Diagnostics
No serial diagnostic link is provided with the CARiN III navigation system, so TestBook/T4 cannot interact with the
system.
Vehicle Position
If the vehicle’s battery has been disconnected, or if the vehicle has been transported to a new location on another
vehicle (e.g. by trailer or train), the navigation system will require up to 15 minutes to identify the new position. Entering
the vehicle’s position manually, reduces this delay. To enter the vehicle's position manually:
1Highlight and select Information.
2From the information menu, scroll down to the next screen and highlight and select Vehicle position.
NOTE: If the correct CD is in the navigation computer, the country is automatically entered. If you have travelled
to a new country, a new CD may be needed.
3From the vehicle position menu, highlight and select City, then use the typewriter menu to enter the vehicle’s
position (town, road, etc.) in the same way that you would enter a destination.
4Once the town and road names are entered, the navigation computer asks for a junction. This is the name of the
road that forms the next junction ahead of the vehicle.
5Highlight and select Junction, then enter the name using the typewriter, or select the correct road name if a list
of names is displayed. Crossing the junction will be highlighted. Drive the vehicle in the direction of the junction
and press the rotary controller when you reach the junction.
NOTE: The vehicle position menu provides a street map facility which enables you to check your vehicle’s current
position and assists in identifying the name of the next road junction.
Provided that the information entered into the computer is correct, the navigation system requires approximately 1
minute to determine the vehicle's position.
Navigation and Trafficmaster
Road navigation and off-road navigation are accessed from the main menu by highlighting and selecting the
appropriate title with the rotary controller. In both modes of navigation, this brings up a safety notice on the display
unit. Pushing the rotary controller again accepts the safety notice and replaces it with a menu screen, which is the
entry point for operation of the navigation function. The Trafficmaster function only operates in the road navigation
mode, and is activated and de-activated by pushing and holding the menu switch for more than 0.5 second. When
activating the Trafficmaster function, the system returns to the navigation mode if the menu switch is not released
within 1.5 seconds.
Refer to the Owner Handbook: Navigation, CARiN III & Traffic Master, Publication Part No. LRL 0586ENG for full
details of how to operate the road navigation, off-road navigation and Trafficmaster functions.
M86 6074
Sensor Check
Wheel Sensors
GPS Satellites
GPS Status
GYRO
Direction of Travel
< Return0
0
08
Position known
0285
Forward
Page 1485 of 1529
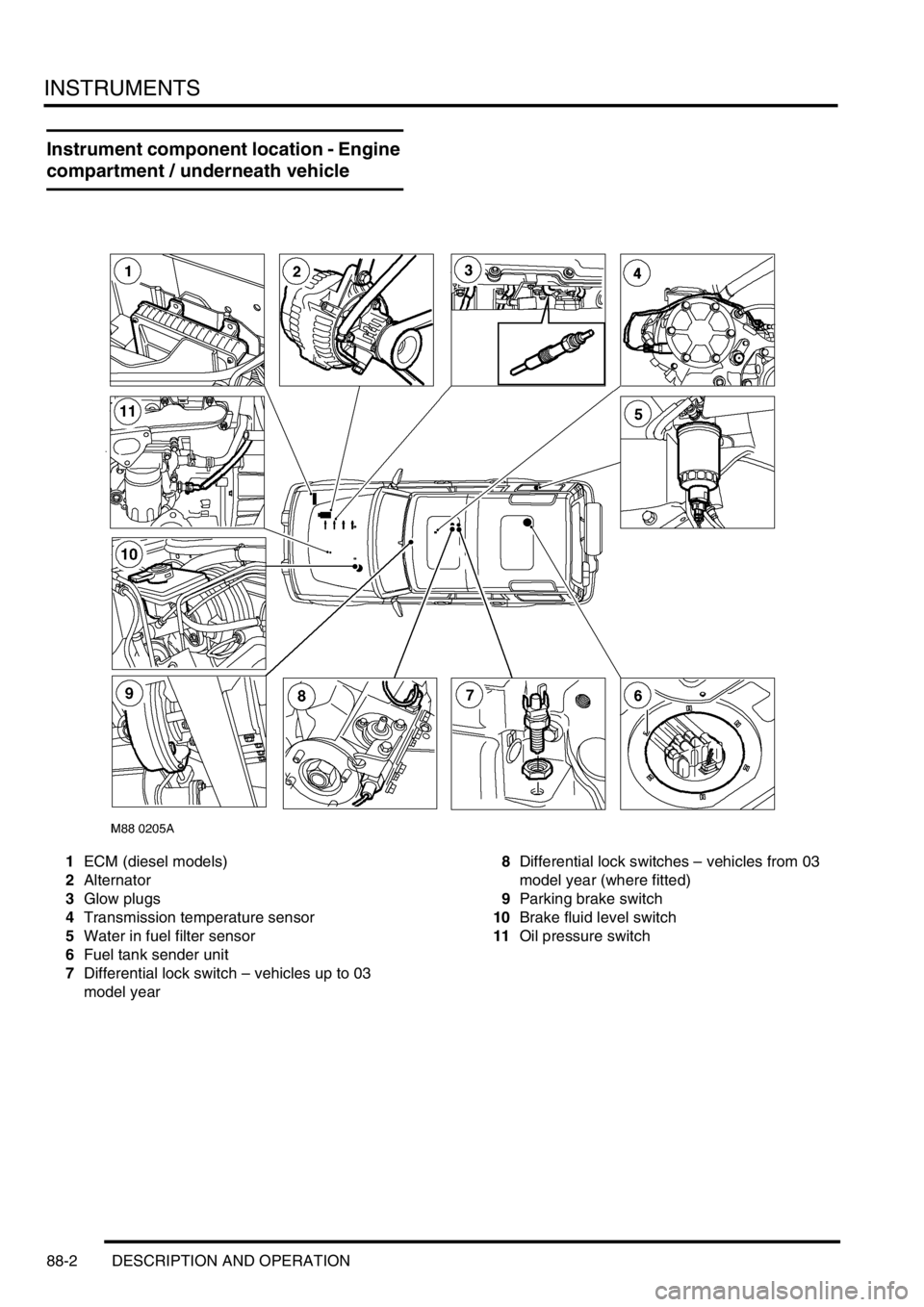
INSTRUMENTS
88-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Instrument component location - Engine
compartment / underneath vehicle
1ECM (diesel models)
2Alternator
3Glow plugs
4Transmission temperature sensor
5Water in fuel filter sensor
6Fuel tank sender unit
7Differential lock switch – vehicles up to 03
model year8Differential lock switches – vehicles from 03
model year (where fitted)
9Parking brake switch
10Brake fluid level switch
11Oil pressure switch
Page 1487 of 1529
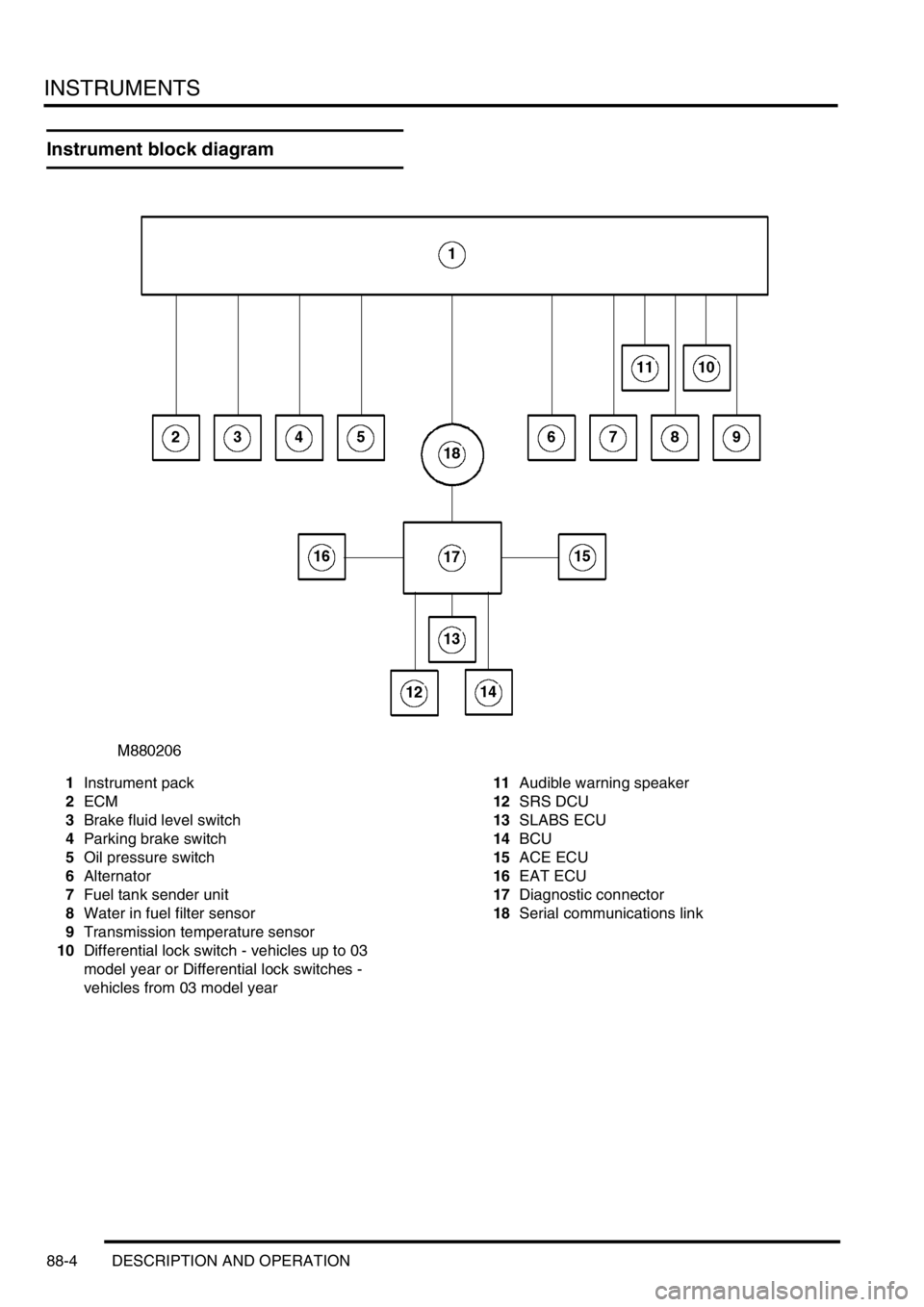
INSTRUMENTS
88-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Instrument block diagram
1Instrument pack
2ECM
3Brake fluid level switch
4Parking brake switch
5Oil pressure switch
6Alternator
7Fuel tank sender unit
8Water in fuel filter sensor
9Transmission temperature sensor
10Differential lock switch - vehicles up to 03
model year or Differential lock switches -
vehicles from 03 model year11Audible warning speaker
12SRS DCU
13SLABS ECU
14BCU
15ACE ECU
16EAT ECU
17Diagnostic connector
18Serial communications link
Page 1494 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-11
Engine coolant temperature gauge
The engine coolant temperature gauge is an analogue gauge with three sections: cold temperature; normal operating
temperature; high temperature. Under normal engine operating temperatures the engine coolant temperature gauge
will display in the centre of the gauge. When the engine is cold e.g. from first start-up, the coolant temperature gauge
will display in the cold band. When the engine is over heating the temperature gauge will display in the high
temperature band. If the engine coolant temperature gauge receives no input or the input is out of range the
temperature gauge will read cold and the high coolant temperature warning lamp will be illuminated.
The input signal is a PWM signal from the engine coolant temperature sensor via the ECM. The power input for the
high coolant temperature warning lamp is supplied by the instrument pack via fuse 27. The ECM controls the earth
path to illuminate the high coolant temperature warning lamp.
Page 1512 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-29
Water in fuel filter warning lamp
The water in fuel filter warning lamp within the instrument pack utilises an amber LED and a clear legend. On vehicles
with diesel engines the LED is illuminated when the water sensor detects water is present in the fuel filter, providing
the driver with a visible warning.
When the ignition is switched on, the instrument pack illuminates the LED to provide a self-check, providing there is
no water present in the fuel filter it will remain illuminated for 3 seconds or until the ignition is switched off.
The power input for the LED is supplied by the instrument pack via fuse 27. The water sensor provides the earth path
to illuminate the warning lamp. The voltage on the earth path from the sensor to the instrument pack is as follows:
l< 1.8 volts = warning lamp on.
l> 7.7 volts = warning lamp off.
Page 1513 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
88-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Water sensor
On vehicles with diesel engines a water sensor is located in the bottom of the fuel filter. The sensor utilises the
different resistance properties between water and diesel fuel to determines the presence of water in the fuel.
The sensor receives a battery voltage supply from the fuel pump relay. The sensor output is supplied to the instrument
pack. The water sensor provides the earth path to illuminate the warning lamp.
l< 1.8 volts = warning lamp on.
l> 7.7 volts = warning lamp off.
Page 1515 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
88-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Transmission high temperature warning lamp
The transmission high temperature warning lamp within the instrument pack utilises a red LED and a clear legend.
On vehicles fitted with automatic gearboxes, the transmission high temperature warning lamp is utilised to provide the
driver with a visible warning that the automatic gearbox oil has exceeded a normal operating temperature. The
warning lamp will extinguish if the gearbox oil returns back to normal operating temperature.
When the ignition is switched on, the instrument pack illuminates the LED to provide a self-check, providing there is
no fault it will remain illuminated for 3 seconds or until the ignition is switched off.
The power input for the LED is supplied by the instrument pack via fuse 13. The temperature sensor provides the
earth path to illuminate the transmission high temperature warning lamp.
The transmission high temperature warning lamp is controlled according to the voltage present on the temperature
sensor to instrument panel earth path:
l< 1.8 volts = warning lamp on.
l> 7.7 volts = warning lamp off.
Page 1525 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
88-42 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Interior rear view mirror with compass
(where fitted)
1Cover
2Electrical connector
3Mounting bracket
4Light sensor5Compass LED display
6Compass calibration switch
7Compass printed circuit board
Certain vehicles have an interior rear view mirror that features an automatic photochromatic dimming function and an
electronic compass with LED display.
The compass mirror is a self-contained unit and does not interface with any other vehicle system or electronic control
unit. The mirror is fixed to a metal bracket attached to the windscreen.
A three pin connector provides the electrical connection to the mirror's internal circuit board. Pin-1 of the connector
provides the 12V power supply to the board via the auxiliary relay located in the engine compartment fusebox. When
the ignition switch is turned to the 'II' position, a 12V supply is provided to energise the coil of the auxiliary relay via
fuse 26 in the passenger compartment fusebox. The auxiliary relay's contact supply voltage is provided from the
vehicle battery through fusible links 1 & 7. When the relay's contacts close, a 12V supply is fed to the compass mirror
circuit board via fuse 15 in the passenger compartment fusebox. This is the supply voltage feed for the mirror's internal
compass.
Pin-2 of the electrical connector provides the path to earth.
Pin-3 of the electrical connector is a 12V ignition switched supply voltage (position 'II' of the ignition switch). The
supply voltage is provided to the mirror's circuit board via fuse 25 in the passenger compartment fusebox, and the
reverse lamp switch (normally closed) for vehicles with manual transmission or the starter inhibitor / reverse light
switch (normally closed) for vehicles with automatic transmission. This is the supply voltage feed for the mirror's
photochromatic dimming function.
M88 0297
3
2
7
616
45
Page 1526 of 1529

INSTRUMENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 88-43
Compass
The mirror's compass display is activated when the ignition switch is turned to position 'II'. If the compass has been
previously calibrated, the current direction of the vehicle will be shown in the LED display at the upper RH side of the
mirror's reflective surface. The display is able to indicate one of eight compass points (i.e. N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W or
NW).
The compass mirror circuit board contains a microchip which is able to determine changes in vehicle direction due to
the changes in the earth's magnetic field. The circuit board is located in the stem of the mirror so that it follows the
changes in the vehicles direction and is not affected by adjustment of the mirror itself.
Because of changes in the lines of magnetic influence, the compass is set for operation in one of fifteen different zones
depending on the current location of the vehicle. If the vehicle is to be driven in a different zone, the compass will have
to be reset for operation in that zone. To determine the correct zone for a particular location on the planet, refer
to the maps provided in the Owner's Handbook. The mirror's default setting is zone 8 which is suitable for central
European countries (Germany, Austria, Italy etc.).
The compass should be set to the correct zone using the following procedure:
1Switch the ignition to position 'II'.
aIf the compass displays one of the eight compass point directions, proceed to step '3'.
bIf the compass displays 'C' then proceed to step '2'.
cIf the display does not show either of the above, then the calibration button on the underside of the mirror
should be pressed and held for approximately 6 seconds, using a small probe (e.g. paper clip or ballpoint
pen). The compass should now enter the set mode and 'C' should be shown in the display.
2To calibrate the compass, the vehicle must be driven slowly (5 mph (8 km/h) or less) in a circle until the display
shows a direction (usually 1 or 2 revolutions). The mirror can calibrate itself during normal driving, but this will
take considerably longer.
3Set the compass to the relevant zone of magnetic influence by pressing the calibration button on the underside
of the mirror for approximately 3 seconds, using a small probe, until a number is shown in the display. If the zone
is being entered for the first time, the default zone setting '8' should be displayed. If the zone is being reset from
a previous entry, the previous zone setting number will be displayed.
The calibration button should now be pressed and released with single presses, using a small probe, until the
desired zone number appears in the display.
After approximately 10 seconds, the compass display should return correctly set to the required zone.
Note the degree of magnetic variation from one zone to another is only very slight. Recalibration of the compass is
not normally necessary unless several zone changes are undertaken.
Automatic dimming
The mirror's automatic dimming function operates when the ignition switch is turned to the 'II' position.
A light sensor is contained at the upper centre of the mirror which detects the intensity of light from the headlights of
following vehicles in dark or low light conditions. When the light intensity is sufficiently high, the mirror automatically
adjusts the brightness of the reflected light by photochromatically changing the mirror's reflective properties and so
preventing glare affecting the driver.
When reverse gear is selected, the power supply for the mirror's photochromatic function is opened so that the mirror
defaults to its normal reflective properties while the reversing operation is in progress.
Another light sensor is located on the rear of the mirror so that the unit can detect the difference between strong
ambient light and that attributable to following vehicle headlights. To check operation of the light dimming function of
the mirror, use the following procedure:
1Turn ignition switch to position 'II', and ensure reverse gear is not selected.
2Cover the sensor on the back of the mirror.
3Shine a bright light on the front (reflective side) of the mirror; the mirror should darken.