ECO mode LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 280 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-47
The following table shows the components itemised on the above illustration and the test applicable to each
component.
Test 1– Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Pump
Power Supply and Relay
Check all wiring and connections.
Functional Check of SAI Pump
The ECM checks the engine coolant temperature when the engine is started in addition to checking the elapsed time
since the last engine start. The engine coolant temperature must be below 55°C (131°F) and the ambient temperature
above 8°C (46°F) for the SAI pump to run. Also, depending on the long term 'modelled' ambient temperature
determined by the ECM, the minimum time elapsed required since the last engine start can be up to 8.25 hours. The
period of time that the SAI pump runs for depends on the starting temperature of the engine and varies from
approximately 95 seconds for a start at 8°C (46°F) to 30 seconds for a start at 55°C (131°F).
With a warm engine which is switched off and the SAI pump relay removed, the SAI pump can be supplied with power
by bridging terminals 87 and 30 at the relay socket.
CAUTION: Ensure that terminals 87 and 87a are not connected or bridged in any way, a short circuit will
occur.
NOTE: TestBook/T4 can also be used to force the SAI system to perform an SAI active diagnostic routine. During this
routine the SAI pump will run for approximately 10 seconds.
When the terminals are bridged or the diagnostic routine initiated, the pump must run when requested which will be
noticeable by the running noise of the pump. Only allow the SAI pump to run for a maximum of 90 seconds and allow
sufficient time for the pump to cool down before running again.
If the SAI pump does not run or makes a scraping noise, it must be replaced. In this case, all other system components
must also be checked.
Noise Complaints
If the SAI pump runs but the operating noise is excessively loud, the external components of the pump, cable, hose
line, and decoupling segments, must be checked. Check the decoupling segments and hose line for distortion and
the cable and hose line for contact with the pump body.
If excessive noise still occurs, the SAI pump must be replaced.
NOTE: Before a new SAI pump is fitted, the SAI control valves must checked for correct function and tightness – Refer
to Test 2 – Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Control Valves.
When fitting a new SAI pump, ensure that the hose lines, the cable and the decoupling segments are fitted without
tension and contact with the pump body.
Item No. Component Description Applicable Test
1 SAI Pump Test 1 – Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Pump
2 SAI control valves (1 per engine bank) Test 2 – Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Control
Valves
3 Vacuum solenoid valve Test 3 – Vacuum Solenoid Valve
4 Delivery hoses to SAI control valves Test 4 – Delivery Hoses to Secondary air
Injection (SAI) Control Valves
5 Connection to air manifold (SAI rail) Test 5 – Connection to Air Manifold
6 Vacuum line (intake manifold to vacuum solenoid valve) Test 6 – Vacuum Lines
7 Vacuum lines (vacuum solenoid valve to SAI control valves) Test 6 – Vacuum Lines
Page 319 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
There are three types of ECT sensor diagnostic checks:
lThe ECT sensor signal is within limits, but is inaccurate – the engine has to be running and the signal indicates
a coolant temperature below 40°C (104°F). The signal differs too much from the coolant temperature model for
longer than 2.53 seconds.
lThe ECT sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold value – the ECM has to be powered up to perform
the diagnostic, but the engine does not need to be running.
lThe ECT sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold value – the ECM has to be powered up to perform
the diagnostic, but the engine does not need to be running.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0116 Engine coolant temperature circuit/range
performance problemSignal differs too much from temperature model for
longer than 2.53s
P0117 Engine coolant temperature circuit low input Open circuit or short circuit to battery supply
P0118 Engine coolant temperature circuit high input Short circuit to earth
Page 326 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-27
There are two types of IAT sensor diagnostic checks:
lThe IAT sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine has to have been running for longer than
180 seconds, and idle speed control must have been operational for longer than 10 seconds. No fuel cut off is
active. The IAT sensor signal must be less than -35°C (-31°F) for longer than 200 ms.
lThe IAT sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold – the ECM has to be powered up (engine does not
need to be running), and the signal must be greater than 140°C (284°F) for longer than 200 ms.
If the IAT sensor fails the following fault codes will be produced and can be retrieved by TestBook:
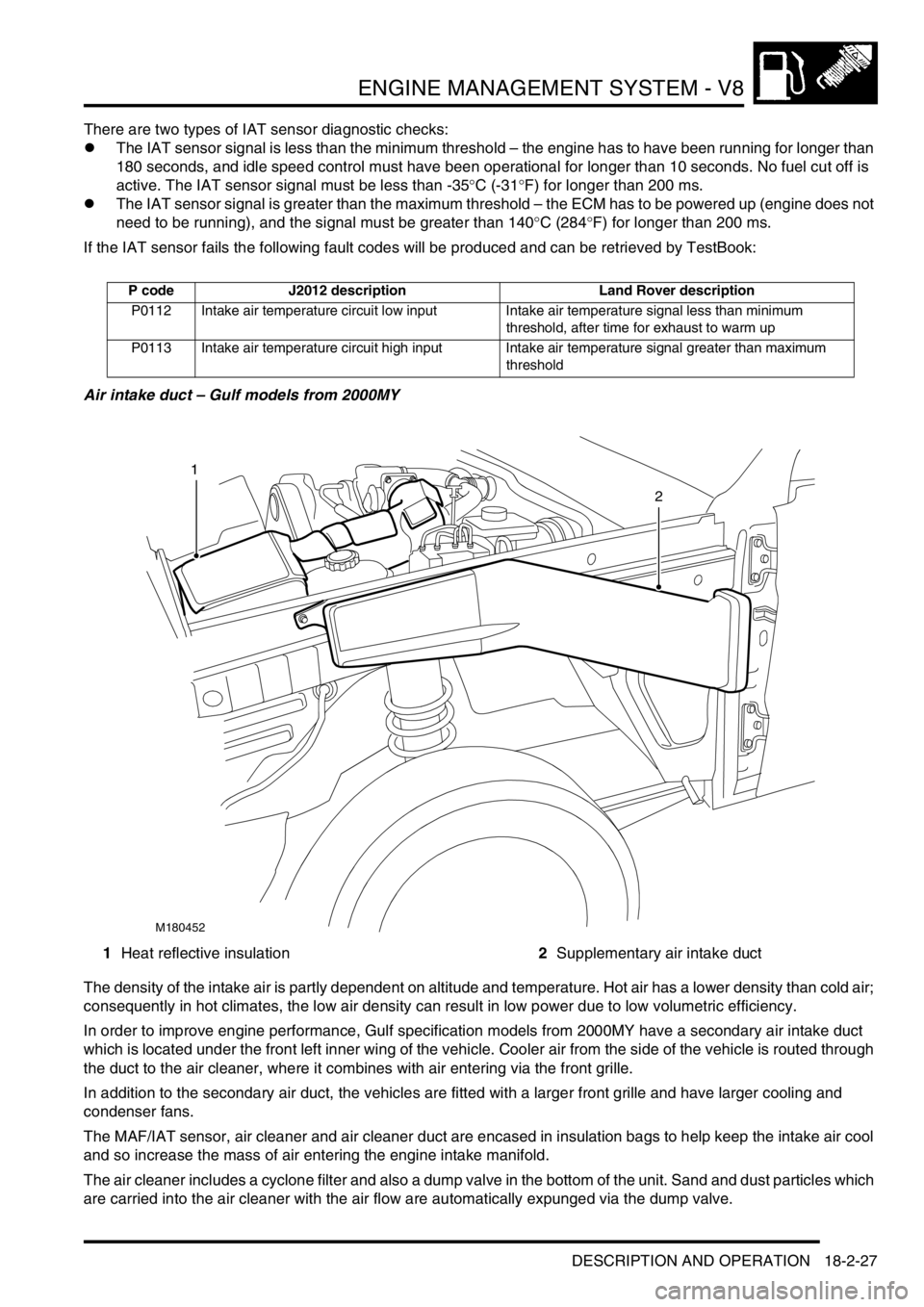
Air intake duct – Gulf models from 2000MY
1Heat reflective insulation2Supplementary air intake duct
The density of the intake air is partly dependent on altitude and temperature. Hot air has a lower density than cold air;
consequently in hot climates, the low air density can result in low power due to low volumetric efficiency.
In order to improve engine performance, Gulf specification models from 2000MY have a secondary air intake duct
which is located under the front left inner wing of the vehicle. Cooler air from the side of the vehicle is routed through
the duct to the air cleaner, where it combines with air entering via the front grille.
In addition to the secondary air duct, the vehicles are fitted with a larger front grille and have larger cooling and
condenser fans.
The MAF/IAT sensor, air cleaner and air cleaner duct are encased in insulation bags to help keep the intake air cool
and so increase the mass of air entering the engine intake manifold.
The air cleaner includes a cyclone filter and also a dump valve in the bottom of the unit. Sand and dust particles which
are carried into the air cleaner with the air flow are automatically expunged via the dump valve.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0112 Intake air temperature circuit low input Intake air temperature signal less than minimum
threshold, after time for exhaust to warm up
P0113 Intake air temperature circuit high input Intake air temperature signal greater than maximum
threshold
M180452
1
2
Page 342 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-43
The ECM performs the following diagnostic checks to confirm correct knock sensor operation:
lKS signal level is less than the minimum threshold (dependent on engine speed) – the engine must be running,
coolant temperature above 60°C (140°F), number of camshaft revolutions since start greater than 50 and the KS
signal profile must be less than the threshold value at a given engine speed for a fault condition to be flagged
lKS signal is greater than the maximum threshold (dependent on engine speed) – the engine must be running,
coolant temperature above 60°C (140°F), number of camshaft revolutions since start greater than 50 and the KS
signal profile must be greater than the threshold value at a given engine speed for a fault condition to be flagged
lError counter for verification of knock internal circuitry exceeded – the engine must be running, coolant
temperature above 60°C (140°F), number of camshaft revolutions since start greater than 50 and the error
counter greater than the threshold value at a given engine speed for a fault condition to be flagged
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
Spark plugs
The spark plugs are platinum tipped on both centre and earth electrodes. The platinum tips give a long maintenance
free life.
Cleaning or resetting the spark plug gap is not recommended as this could result in damaging the platinum tips and
thereby reducing reliability.
The misfire detection system will malfunction and store erroneous codes if the incorrect spark plugs are used.
Input/Output
The ignition coils provide a voltage to the spark plugs via the ht leads. The cylinder head via the individual thread of
each spark plug provides the earth path.
The spark plugs can fail in the following ways:
lFaulty component.
lConnector or wiring fault.
lBreakdown of high tension lead causing tracking to chassis earth.
lIncorrect spark plugs fitted.
In the event of a spark plug failure, misfire on specific cylinder may be observed:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0327 Knock sensor 1 circuit low input (bank 1 or single
sensor)LH bank signal less than threshold determined from
ECM model above 2200 rev/min
P0328 Knock sensor 1 circuit high input (bank 1 or
single sensor)LH bank signal greater than threshold determined from
ECM model above 2200 rev/min
P0332 Knock sensor 2 circuit low input (bank 2) RH bank signal less than threshold determined from
ECM model above 2200 rev/min
P0333 Knock sensor 2 circuit high input (bank 2) RH bank signal greater than threshold determined from
ECM model above 2200 rev/min
Page 357 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-58 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Conditions
The CAN system is used by the EAT ECU and the ECM for transmission of the following information:
lGearshift torque control information.
lEAT OBD information.
lMIL request.
lVehicle speed signal.
lEngine temperature.
lEngine torque and speed.
lGear selected.
lGear change information.
lAltitude adaptation factor
lAir intake temperature
lThrottle angle / pedal position
Function
The CAN system uses a twisted pair of wires to form the 'data bus' to minimise electrical interference. This method of
serial interface is very reliable and very fast. The information messages are structured so that each of the receivers
(ECM or EAT ECU) is able to interpret and react to the messages sent.
The CAN 'data bus' is directly connected between pin 36 of connector C0637 of the ECM and pin 16 of connector
C0193 at the EAT ECU, and pin 37 of connector C0637 of the ECM and pin 44 of connector C0193 at the EAT ECU.
The CAN system can fail in the following ways:
lCAN data bus wiring open circuit.
lCAN data bus wiring short circuit.
In the event of a CAN data bus failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lMIL illuminated after 2 drive cycles (NAS only).
lEAT defaults to 3rd gear only.
lHarsh gearshifts.
l'Sport' and 'manual' lights flash alternately.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Drive cycles
The following are the TestBook drive cycles:
⇒ Drive cycle A:
1Switch on the ignition for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle B:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
8Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0600 Serial communication link malfunction CAN time out
P1776 Transmission control system torque interface
malfunctionEAT torque interface error
Page 358 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-59
⇒ Drive cycle C:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 8 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 3 minutes.
9Allow engine to idle for 3 minutes.
10Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
NOTE: The following areas have an associated readiness test which must be flagged as complete, before a problem
resolution can be verified:
lcatalytic converter fault;
lEvaporative loss system fault;
lHO
2 sensor fault;
lHO
2 sensor heater fault.
When carrying out a drive cycle C to determine a fault in any of the above areas, select the readiness test icon to
verify that the test has been flagged as complete.
⇒ Drive cycle D:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 35°C (95°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 5 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 5 minutes.
9Cruise at 35 mph (60 km/h) for 5 minutes.
10Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
11Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle E:
1Ensure fuel tank is at least a quarter full.
2Carry out Drive Cycle A.
3Switch off ignition.
4Leave vehicle undisturbed for 20 minutes.
5Switch on ignition.
6Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
Page 371 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-72 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Several fault codes can be generated:
Fault codes
1"Output power LOW when HIGH is expected" is flagged when Pin C0239-11 is shorted to earth.
This could be due to an external fault or an internal ECU fault and will be set if pin C0239-11 is LOW for longer
than 240 milliseconds, while in cruise mode.
2"Output power HIGH when LOW is expected" is flagged when Pin C0239-11 is shorted to battery voltage.
This could be due to an external fault or internal ECU fault and will be set if pin C0239-11 is HIGH for longer than
250 milliseconds while not in cruise mode.
3"Output pump LOW, when High is expected" is flagged when Pin C0239-7 is shorted to earth.
This could be due to an external fault or an internal ECU fault. This fault will be set if pin C0239-11 is HIGH for
longer than 7.5 milliseconds while pin C0239-7 is LOW for longer than 2.5 milliseconds while decelerating under
control of cruise.
4"Output pump HIGH, when LOW is expected" is flagged when Pin C0239-7 is shorted to battery voltage.
This could be due to an external fault or an internal ECU fault. This fault will be set if pin C0239-7 is LOW for
longer than 7.5 milliseconds of the last 8 pulses when the pump is switched on while accelerating under the
control of cruise.
5Output valve LOW, when HIGH is expected is flagged when Pin C0239-7 is shorted to battery voltage.
This could be due to an external fault or an internal ECU fault and will be set if pin C0239-17 is LOW for longer
than 2.5 milliseconds while pin C0239-7 is HIGH for longer than 2.5 milliseconds and pin C0239-11 is also HIGH
for longer than 7.5 milliseconds, while decelerating under control of the cruise control ECU.
6Output valve HIGH, when LOW is expected is flagged when Pin C0239-17 is shorted to battery voltage.
This could be an external fault or an internal ECU fault. The fault will be set if pin C0239-17 remains HIGH for
longer than 35 milliseconds after the vacuum control valve is switched on, while accelerating under control of
the cruise control ECU.
TestBook can be used to determine the fault codes present as well as the general status of the system.
Page 540 of 1529

TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 41-15
Functionality – Vehicles up to 03 model year only
The function of the differential lock used in previous applications is performed on this vehicle by the Electronic Traction
Control System. However, for the purposes of 2 wheel rolling road testing , the differential lock components are
retained. For all driving conditions however, the differential lock must be set in the unlocked position.
Up to 03 model year specification shown
The differential lock must only be engaged for 2 wheel rolling road testing as engagement of the lock disables the
traction control feature and inhibits correct operation of the electronic brake distribution and hill descent features. It
will also be necessary to disconnect the propeller shaft from the transfer box output shaft driving the axle whose
wheels are NOT on the rolling road. The lock may be engaged/disengaged by using a 10 mm open ended spanner
on the flats (arrowed) machined on the differential lock selector shaft.
Vehicles not fitted with a differential lock may be identified by there being no cover or selector shaft (arrowed) on the
front output housing.
WARNING: VEHICLES NOT FITTED WITH A DIFFERENTIAL LOCK MUST NOT BE TESTED ON A ROLLING
ROAD WHERE THE ROLLERS ARE DRIVEN BY THE VEHICLE.
Functionality – Vehicles from 03 model year only
The differential lock must be engaged for 2 wheel rolling road testing. It will also be necessary to disconnect the
propeller shaft from the transfer box output shaft driving the axle whose wheels are NOT on the rolling road. In
addition, the ETC system must be deactivated by either, removing a fuse (10A fuse 28 in the passenger compartment
fusebox, labelled ABS) or disconnecting the ABS modulator pump. This must be done with the ignition switched off.
Note that the SLABS ECU may record a system fault.
The lock can be engaged or disengaged using the selector lever.
WARNING: VEHICLES NOT FITTED WITH A DIFFERENTIAL LOCK MUST NOT BE TESTED ON A ROLLING
ROAD WHERE THE ROLLERS ARE DRIVEN BY THE VEHICLE.
Page 541 of 1529

TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
41-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Differential lock warning lamp switch - if fitted - Vehicles up to 03 model year
A differential lock warning lamp switch connected to the SLABS ECU and operated by movement of the selector fork
and shaft is screwed into the top of the output housing. The switch connects to earth when the differential lock is
engaged.
Differential lock warning lamp switches - Vehicles from 03 model year
Vehicles from 03 model year are fitted with two differential lock warning lamp switches.
Both switches are of a new design and are fitted into the top of the front output housing. The switches are connected
to the SLABS ECU and are operated by movement of the selector shaft.
Both switches have an aluminium washer which seals the switch to the casing and also sets the switch position,
removing the requirement for a setting procedure.
Both switches are connected in parallel to earth when the differential lock is engaged. This earth is sensed by the
SLABS ECU which illuminates the differential lock warning lamp in the instrument pack.
Differential lock warning lamp - Vehicles up to 03 model year – if fitted
The differential lock warning lamp is located in the instrument pack and provides a warning to the driver when the
ignition is switched on that the differential lock is engaged. The warning lamp illuminates in a Red colour.
With the lock engaged, the traction control and electronic brake distribution warning lamps will also be illuminated.
Disengagement of the differential lock should be carried out with the ignition switched off. The warning lamps must
be extinguished when the ignition is switched on again.
Differential lock warning lamp – vehicles from 03 model year
The differential lock warning lamp is amber coloured and is located in the instrument pack.
When the lock is engaged, the warning lamp is illuminated and the instrument pack sounder emits three audible
chimes. When the lock is disengaged, the warning lamp is extinguished and the instrument pack sounder emits three
audible chimes.
Rear output housing
The rear output housing carries the output shaft and flange. A cable operated transmission brake is attached to the
housing, the brake drum being attached to the output flange.
The rear output shaft is supported in the housing by a single bearing and is splined into the differential rear sun gear.
Lubrication
Lubrication is by splash, oil filler/level and drain plugs being located in the main casing.
Internal pressures caused by thermal expansion and contraction are avoided by the use of a plastic breather pipe
venting the interior of the box to atmosphere. The pipe is attached to the top of the high/low selector housing by a
banjo bolt and is then routed in a continuously rising path into the engine compartment where the open end is secured
by a clip attached to the engine cylinder block.
Oil temperature warning lamp switch
An oil temperature switch is fitted to V8 engine models up to 03 Model Year. In the event of the transfer box oil
approaching maximum recommended working temperature of 145°C (293°F), the switch will close and a warning
lamp in the instrument pack will be illuminated.
Page 542 of 1529

TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 41-17
High/Low range and differential lock selector lever assembly – Vehicles from 03 model year
1Selector lever
2High/Low range cable
3Differential lock cable4Interlock solenoid - North America and Japan
only
On vehicles fitted with a differential lock, the high/low range selector lever as fitted on previous models also
incorporates the differential lock selector on vehicles from 03 model year.
The lever can be moved forwards or backwards to select high, neutral or low range or sideways to select differential
lock engaged or disengaged, on vehicles with differential lock fitted.
The selector lever assembly comprises an aluminium casting with bosses for location of the two cables, the selector
lever mechanism and a housing for the interlock solenoid (if fitted). The upper face of the casting has threaded holes
which allow for the attachment of the casting to the mounting plate which is attached to the transmission tunnel.
A boss at the front provides location for the differential lock cable. The cable is attached to a lever which in turn is
attached to the selector lever. Movement of the selector lever is passed via the lever to the cable which moves the
differential lock selector shaft.
A second boss provides for the location of the high/low range cable. The cable is attached to a plate which moves in
a forward or rearward direction with the selector lever. On North American and Japanese specification models, plate
movement is prevented by an interlock solenoid when the ignition key is not in the ignition.
When fitted, the interlock solenoid is located on the right hand side of the selector lever casting. The solenoid is fitted
into a cast housing in the casting and retained with a circlip. Sealant is applied over the circlip to seal the solenoid in
the housing to prevent the ingress of dirt and moisture. The solenoid performs the same function as on previous
models, preventing the selection of neutral on the transfer box when the ignition key is not in the ignition.
A setting procedure is required for both the differential lock cable and the high/low range cable.