engine LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 647 of 1529
AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22 - 24
44-50 REPAIRS
Cooler - fluid - V8
$% 44.24.10
Remove
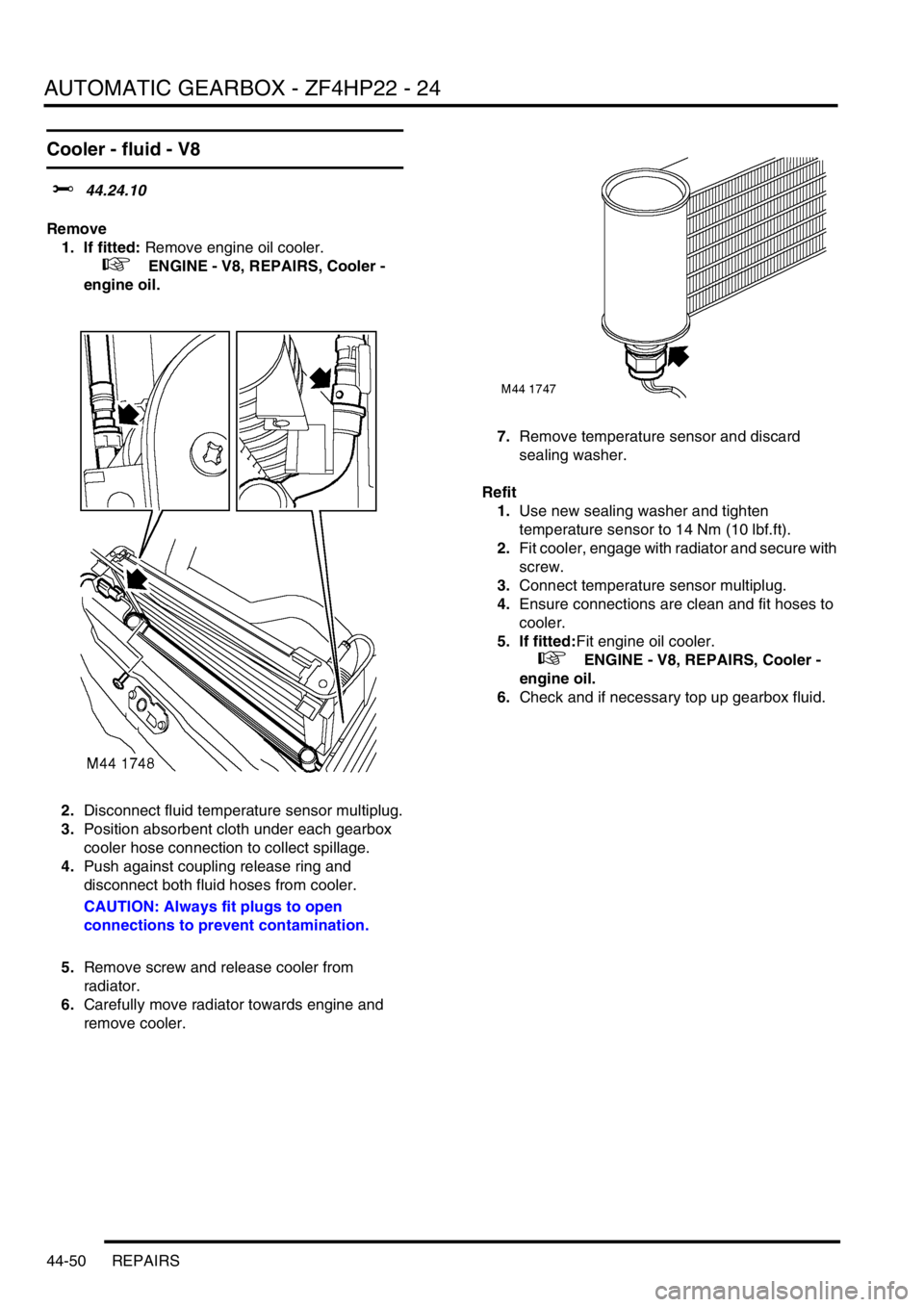
1. If fitted: Remove engine oil cooler.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Cooler -
engine oil.
2.Disconnect fluid temperature sensor multiplug.
3.Position absorbent cloth under each gearbox
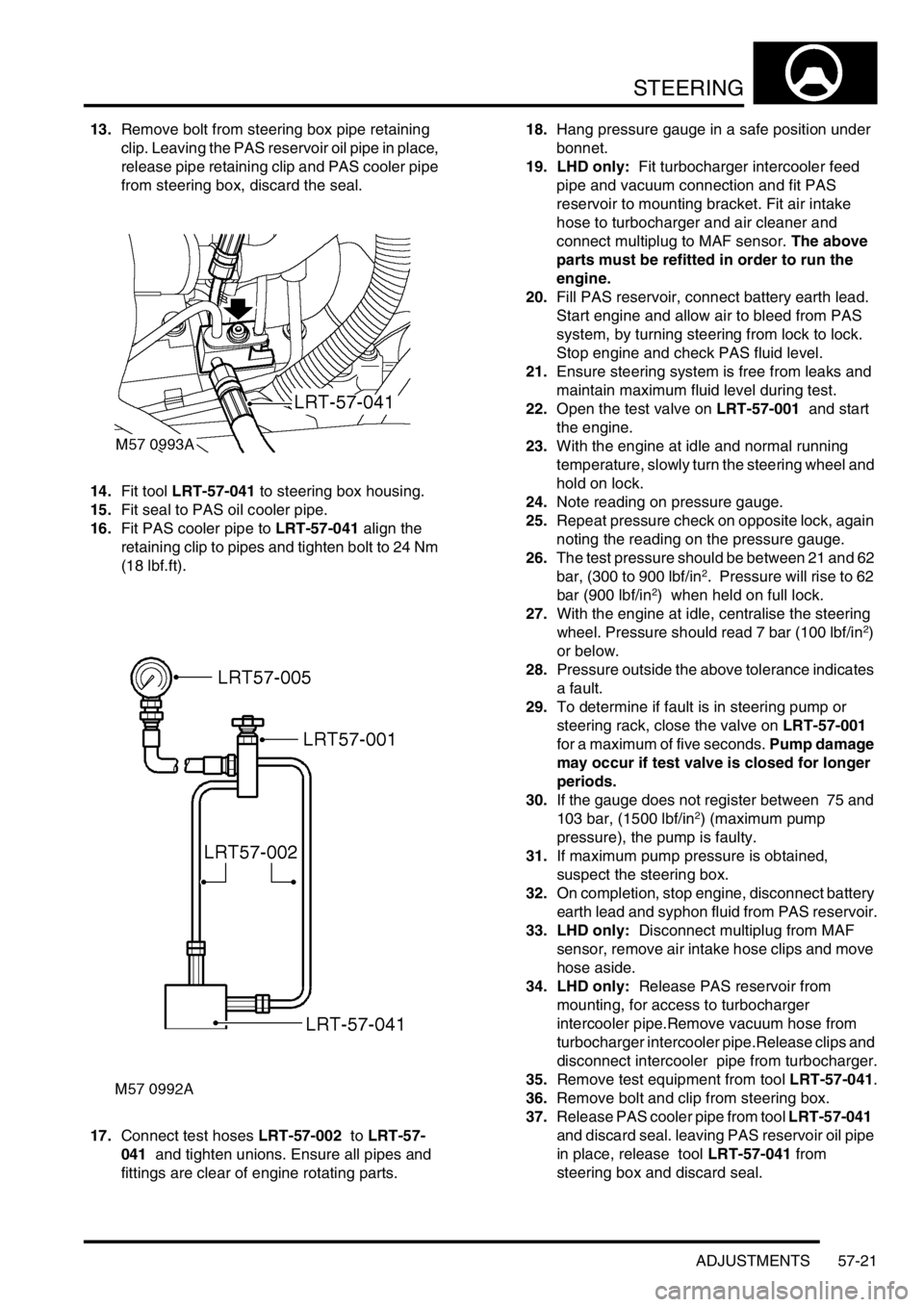
cooler hose connection to collect spillage.
4.Push against coupling release ring and
disconnect both fluid hoses from cooler.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
5.Remove screw and release cooler from
radiator.
6.Carefully move radiator towards engine and
remove cooler.7.Remove temperature sensor and discard
sealing washer.
Refit
1.Use new sealing washer and tighten
temperature sensor to 14 Nm (10 lbf.ft).
2.Fit cooler, engage with radiator and secure with
screw.
3.Connect temperature sensor multiplug.
4.Ensure connections are clean and fit hoses to
cooler.
5. If fitted:Fit engine oil cooler.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Cooler -
engine oil.
6.Check and if necessary top up gearbox fluid.
Page 657 of 1529

PROPELLER SHAFTS
47-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
Front and rear propeller shafts transmit the drive from the transfer box to the axles.
On vehicles from 03 model year fitted with the 4.6l V8 engine and 4HP24 transmission, the front propeller shaft is 15
mm (0.6 in) longer and the rear propeller shaft is 15mm (0.6 in) shorter than those used on vehicles with the 4.0l V8
and Td5 engines. This is to accomodate an increase in length of the 4HP24 transmission.
Page 681 of 1529

FRONT AXLE
54-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The front axle consists of an axle casing with a differential unit attached to the right of the vehicle centre line. A wheel
hub is installed in a steering knuckle at each end of the axle casing and connected to the differential unit by a drive
shaft.
Axle casing
The axle casing is of welded construction, with brackets on the casing exterior for attachment to the front suspension.
Yokes at each end of the casing incorporate upper and lower ball joints for attachment of the steering knuckles.
A differential cover on the front of the axle casing contains an oil level plug for checking and replenishment of the
differential lubricating oil. A magnetic drain plug is installed on the underside of the casing. An oil seal is installed in
each end of the axle casing to prevent leakage past the drive shafts.
The interior of the axle casing is ventilated through a breather tube inserted in a red plastic sleeve in the top of the
casing. The open end of the breather tube is located in the left rear corner of the engine compartment.
Differential unit
The differential unit is of the spiral bevel type, lubricated by splash oil. The unit consists of a differential carrier
attached to a pinion housing. In the pinion housing, the pinion is splined to a drive flange which is secured with a bolt
and washer. An oil seal prevents leakage past the drive flange.
Steering knuckle
The steering knuckles are mounted on upper and lower ball joints in the yokes at the end of the axle casing. A tension
collet, in the lower mounting point of each steering knuckle, accommodates manufacturing tolerances to enable the
correct tightening of both ball joints. Lugs are incorporated on the steering knuckles for attachment of the steering
system drag link and track rod.
Page 698 of 1529

STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-5
Description
General
The major steering components comprise an impact absorbing telescopic steering column, a Power Assisted Steering
(PAS) box, a PAS pump, and fluid reservoir. Hydraulic fluid from the fluid reservoir is filtered and then supplied
through the suction line to the inlet on the PAS pump. The PAS pump supplies fluid to the steering box through a
pressure line routed above the front cross member. Fluid returns to the reservoir along the same route through a
return line. On LH drive vehicles the pipe route above the front cross member is still used, the length of pipe acting
as an oil cooler.
To minimise driver's injury in the event of an accident the steering system has a number of safety features including
a collapsible steering column. An additional safety feature is an air bag located in the steering wheel.
+ RESTRAINT SYSTEMS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SRS.
Steering column assembly and intermediate shaft
The steering column central shaft comprises of two shafts, the upper shaft is splined to accept the steering wheel and
located in bearings in the column tube. A universal joint is located on the bottom of the upper shaft, the joint allows
for angular movement between the upper and lower shafts. The lower shaft is made in two parts, the top section of
the lower shaft is located outside of the lower section. The two sections of the lower shaft are connected by two nylon
injection moulded shear pins. The lower shaft goes through a lower bearing attached to the bulkhead, the lower shaft
is connected by a universal joint to the intermediate shaft in the engine compartment.
Steering column
An upper column tube provides for the location of the steering lock and ignition switch and also the steering switch
gear and a rotary coupler. The rotary coupler provides the electrical connection for the steering wheel mounted airbag,
switches and horn. The upper mounting bracket has two slots, a slotted metal bracket is held in each slot by four resin
shear pins.
The column is mounted on four captive studs which are located on a column mounting bracket. The captive studs
pass through the metal brackets, locknuts secure the steering column to the bulkhead. The two lower mountings are
fixed and cannot move when loads are applied to them. The upper mounting is designed to disengage or deform when
a load is applied, allowing the column to collapse in the event of an accident. The steering column must be replaced
as a complete assembly if necessary.
When an axial load is applied to the upper column tube, energy absorption is achieved by the following mechanism:
lthe mounting bracket deforms,
lthe resin shear pins holding the slotted metal brackets shear,
lthe top mounting bracket slides out of the slotted metal brackets.
The slotted metal brackets remain on the captive studs on the bulkhead. If the column mounting moves, injection
moulded shear pins retaining the two sections of the lower column shaft will shear. This allows the two sections of the
lower shaft to 'telescope' together.
In the event of a collision where the steering box itself moves, two universal joints in the column allow the intermediate
shaft to articulate, minimising movement of the column towards the driver. If movement continues energy absorption
is achieved by the following mechanism:
lthe decouple joint in the intermediate shaft will disengage,
lthe lower section of the steering column shaft will move through the lower bearing,
lthe injection moulded shear pins retaining the two sections of the lower column shaft will shear.
This allows the two sections of the lower shaft to 'telescope' together reducing further column intrusion. Protection to
the drivers face and upper torso is provided by an SRS airbag module located in the centre of the steering wheel.
+ RESTRAINT SYSTEMS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SRS.
Page 700 of 1529
STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-7
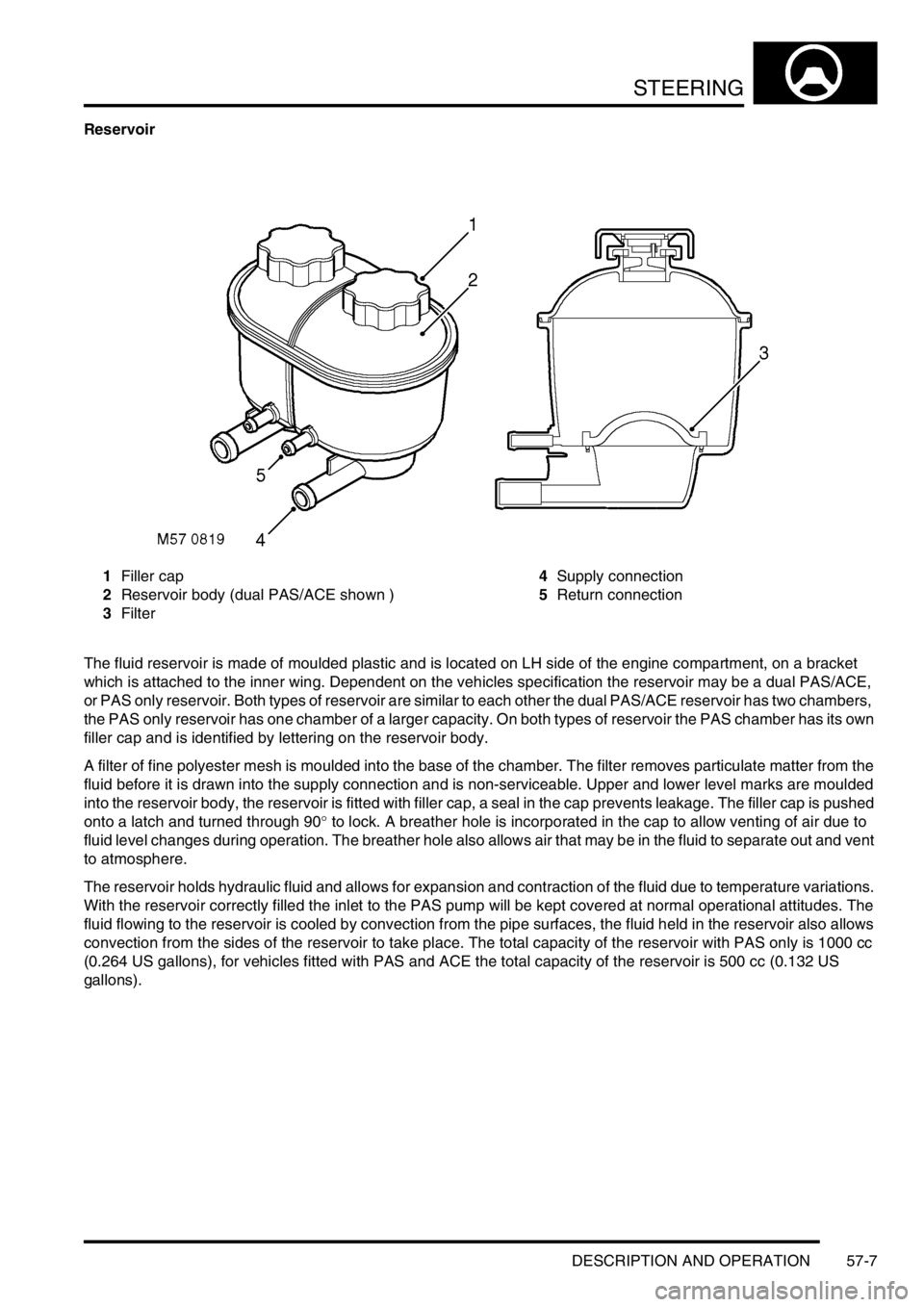
Reservoir
1Filler cap
2Reservoir body (dual PAS/ACE shown )
3Filter4Supply connection
5Return connection
The fluid reservoir is made of moulded plastic and is located on LH side of the engine compartment, on a bracket
which is attached to the inner wing. Dependent on the vehicles specification the reservoir may be a dual PAS/ACE,
or PAS only reservoir. Both types of reservoir are similar to each other the dual PAS/ACE reservoir has two chambers,
the PAS only reservoir has one chamber of a larger capacity. On both types of reservoir the PAS chamber has its own
filler cap and is identified by lettering on the reservoir body.
A filter of fine polyester mesh is moulded into the base of the chamber. The filter removes particulate matter from the
fluid before it is drawn into the supply connection and is non-serviceable. Upper and lower level marks are moulded
into the reservoir body, the reservoir is fitted with filler cap, a seal in the cap prevents leakage. The filler cap is pushed
onto a latch and turned through 90° to lock. A breather hole is incorporated in the cap to allow venting of air due to
fluid level changes during operation. The breather hole also allows air that may be in the fluid to separate out and vent
to atmosphere.
The reservoir holds hydraulic fluid and allows for expansion and contraction of the fluid due to temperature variations.
With the reservoir correctly filled the inlet to the PAS pump will be kept covered at normal operational attitudes. The
fluid flowing to the reservoir is cooled by convection from the pipe surfaces, the fluid held in the reservoir also allows
convection from the sides of the reservoir to take place. The total capacity of the reservoir with PAS only is 1000 cc
(0.264 US gallons), for vehicles fitted with PAS and ACE the total capacity of the reservoir is 500 cc (0.132 US
gallons).
Page 706 of 1529

STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-13
The internal 'cam' shape of the pump housing causes the rollers to move closer together as the pump rotor rotates
towards the outlet port. The reduced volume of the chamber between the roller vanes causes the fluid to become
pressurised. When the chamber is opened to the outlet port of the pump the fluid escapes at high pressure. The roller
vanes continue turning and go past the outlet port, closing off the chamber between the two roller vanes.
As rotation continues the inlet sequence begins again. The inlet and pressurisation/outlet sequences continue as the
pump rotates, and is repeated between each two roller vanes. The pump is a positive displacement type and the
potential pump output increases with engine (drive pulley) speed. The pressure relief and flow control valve regulates
flow/pressure by diverting fluid back to the pump inlet through internal recirculation passages in the pump body.
Page 708 of 1529

STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 57-15
As the pump rotor rotates towards the pump inlet the volume between the roller vanes and the pump housing
increases, this action causes a depression in the chamber between the pump roller vanes and the housing. As the
rotation continues the chamber is opened to the pump inlet, and the depression in the chamber causes fluid to be
drawn in. The roller vanes continue past the inlet port, closing off the inlet port and trapping the fluid in the chamber
between the rollers and the pump housing.
The internal 'cam' shape of the pump housing causes the rollers to move closer together as the pump rotor rotates
towards the outlet port. The reduced volume of the chamber between the roller vanes causes the fluid to become
pressurised. When the chamber is opened to the outlet port of the pump the fluid escapes at high pressure. The roller
vanes continue turning and go past the outlet port, closing off the chamber between the two roller vanes.
As rotation continues the inlet sequence begins again. The inlet and pressurisation/outlet sequences continue as the
pump rotates, and is repeated between each two roller vanes. The pump is a positive displacement type and the
potential pump output increases with engine (drive pulley) speed. The pressure relief and flow control valve regulates
flow/pressure by diverting fluid back to the pump inlet through internal recirculation passages in the pump body.
Steering damper
The steering damper is located behind and just below the first cross member of the chassis. The ends of the steering
damper have steel 'eyes' welded on, rubber bushes are installed in each 'eye'. The steering damper is attached
between brackets on the chassis rail and the drag link. Each end of the steering damper is secured by a bolt and
locknut. The hydraulic damper absorbs shocks in the steering, caused by road wheel deflections when operating on
rough terrain.
Page 711 of 1529
STEERING
57-18 ADJUSTMENTS
Hydraulic system - bleed
$% 57.15.02
Bleed
1.Clean PAS fluid reservoir around filler cap and
fluid level indicators.
2.Remove filler cap from PAS fluid reservoir. If
necessary, fill PAS fluid reservoir to upper level
indicator with recommended fluid.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS,
LUBRICANTS AND SEALANTS, Fluids.
CAUTION: Ensure no dirt is allowed to enter
the steering reservoir when the cap is
removed.
3.Start engine and run to normal operating
temperature.
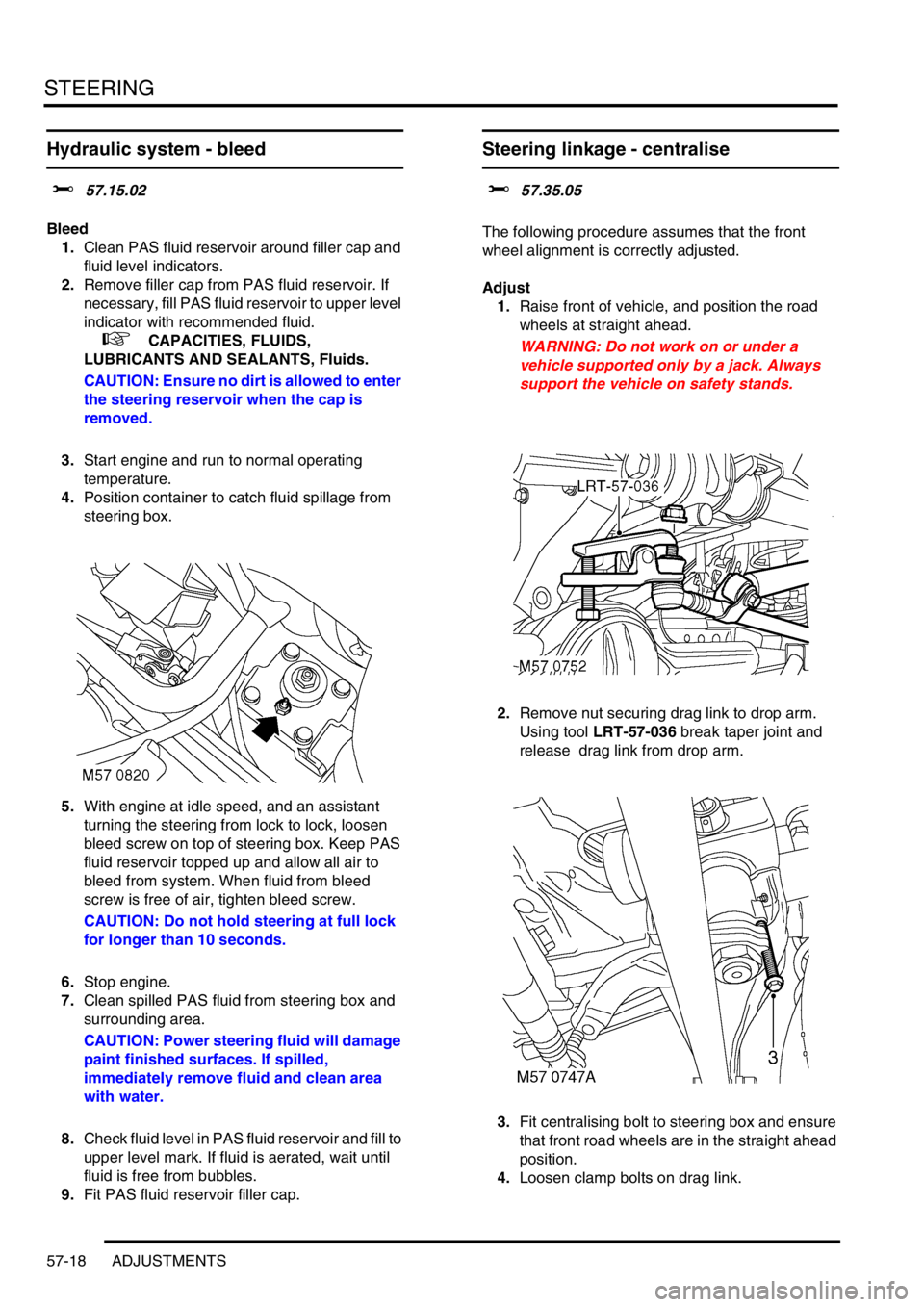
4.Position container to catch fluid spillage from
steering box.
5.With engine at idle speed, and an assistant
turning the steering from lock to lock, loosen
bleed screw on top of steering box. Keep PAS
fluid reservoir topped up and allow all air to
bleed from system. When fluid from bleed
screw is free of air, tighten bleed screw.
CAUTION: Do not hold steering at full lock
for longer than 10 seconds.
6.Stop engine.
7.Clean spilled PAS fluid from steering box and
surrounding area.
CAUTION: Power steering fluid will damage
paint finished surfaces. If spilled,
immediately remove fluid and clean area
with water.
8.Check fluid level in PAS fluid reservoir and fill to
upper level mark. If fluid is aerated, wait until
fluid is free from bubbles.
9.Fit PAS fluid reservoir filler cap.
Steering linkage - centralise
$% 57.35.05
The following procedure assumes that the front
wheel alignment is correctly adjusted.
Adjust
1.Raise front of vehicle, and position the road
wheels at straight ahead.
WARNING: Do not work on or under a
vehicle supported only by a jack. Always
support the vehicle on safety stands.
2.Remove nut securing drag link to drop arm.
Using tool LRT-57-036 break taper joint and
release drag link from drop arm.
3.Fit centralising bolt to steering box and ensure
that front road wheels are in the straight ahead
position.
4.Loosen clamp bolts on drag link.
Page 713 of 1529
STEERING
57-20 ADJUSTMENTS
Power steering pressure check - diesel
models
$% 57.90.10.01
Check
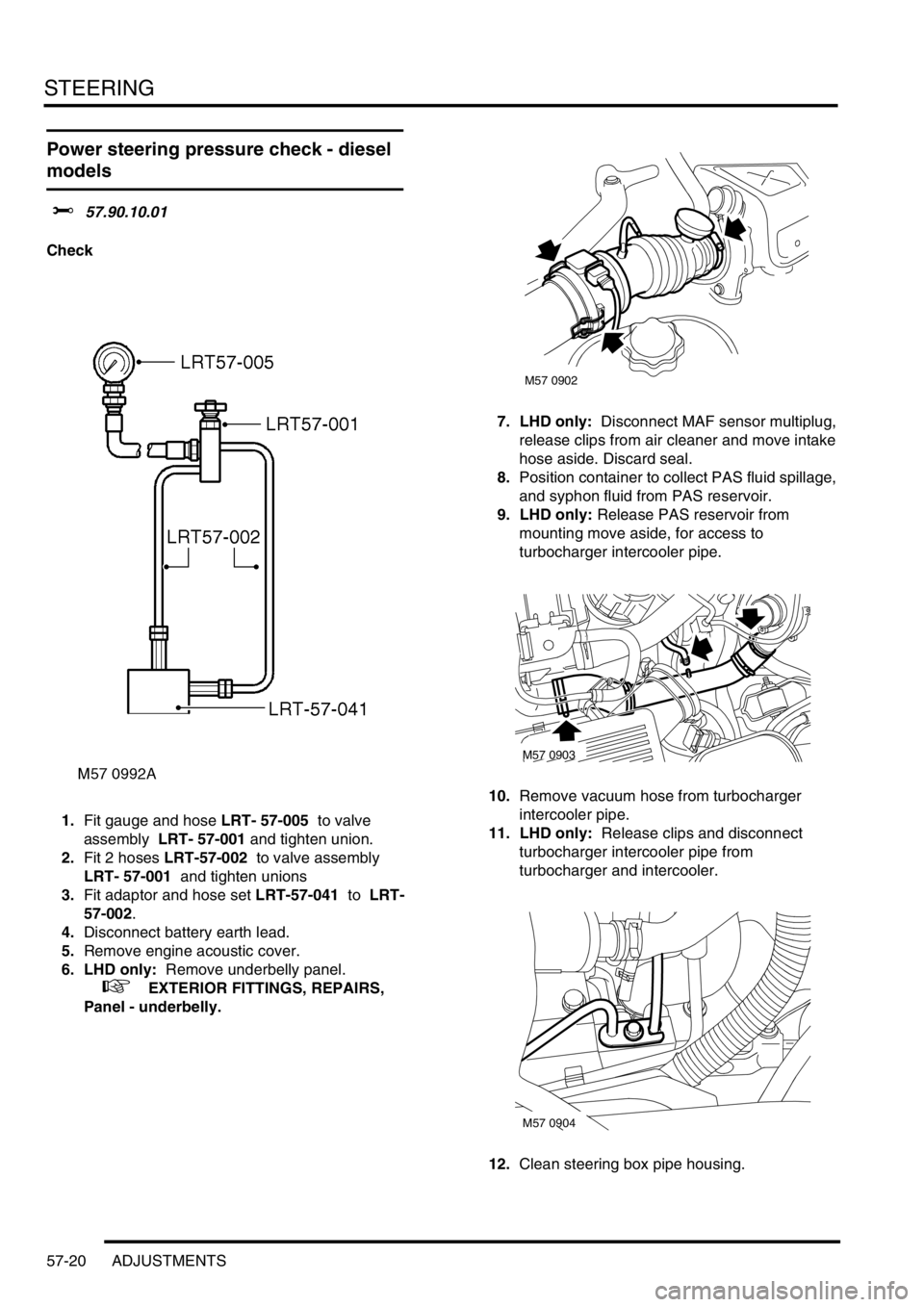
1.Fit gauge and hose LRT- 57-005 to valve
assembly LRT- 57-001 and tighten union.
2.Fit 2 hoses LRT-57-002 to valve assembly
LRT- 57-001 and tighten unions
3.Fit adaptor and hose set LRT-57-041 to LRT-
57-002.
4.Disconnect battery earth lead.
5.Remove engine acoustic cover.
6. LHD only: Remove underbelly panel.
+ EXTERIOR FITTINGS, REPAIRS,
Panel - underbelly.7. LHD only: Disconnect MAF sensor multiplug,
release clips from air cleaner and move intake
hose aside. Discard seal.
8.Position container to collect PAS fluid spillage,
and syphon fluid from PAS reservoir.
9. LHD only: Release PAS reservoir from
mounting move aside, for access to
turbocharger intercooler pipe.
10.Remove vacuum hose from turbocharger
intercooler pipe.
11. LHD only: Release clips and disconnect
turbocharger intercooler pipe from
turbocharger and intercooler.
12.Clean steering box pipe housing.
M57 0902
M57 0903
M57 0904
Page 714 of 1529
STEERING
ADJUSTMENTS 57-21
13.Remove bolt from steering box pipe retaining
clip. Leaving the PAS reservoir oil pipe in place,
release pipe retaining clip and PAS cooler pipe
from steering box, discard the seal.
14.Fit tool LRT-57-041 to steering box housing.
15.Fit seal to PAS oil cooler pipe.
16.Fit PAS cooler pipe to LRT-57-041 align the
retaining clip to pipes and tighten bolt to 24 Nm
(18 lbf.ft).
17.Connect test hoses LRT-57-002 to LRT-57-
041 and tighten unions. Ensure all pipes and
fittings are clear of engine rotating parts.18.Hang pressure gauge in a safe position under
bonnet.
19. LHD only: Fit turbocharger intercooler feed
pipe and vacuum connection and fit PAS
reservoir to mounting bracket. Fit air intake
hose to turbocharger and air cleaner and
connect multiplug to MAF sensor. The above
parts must be refitted in order to run the
engine.
20.Fill PAS reservoir, connect battery earth lead.
Start engine and allow air to bleed from PAS
system, by turning steering from lock to lock.
Stop engine and check PAS fluid level.
21.Ensure steering system is free from leaks and
maintain maximum fluid level during test.
22.Open the test valve on LRT-57-001 and start
the engine.
23.With the engine at idle and normal running
temperature, slowly turn the steering wheel and
hold on lock.
24.Note reading on pressure gauge.
25.Repeat pressure check on opposite lock, again
noting the reading on the pressure gauge.
26.The test pressure should be between 21 and 62
bar, (300 to 900 lbf/in
2. Pressure will rise to 62
bar (900 lbf/in2) when held on full lock.
27.With the engine at idle, centralise the steering
wheel. Pressure should read 7 bar (100 lbf/in
2)
or below.
28.Pressure outside the above tolerance indicates
a fault.
29.To determine if fault is in steering pump or
steering rack, close the valve on LRT-57-001
for a maximum of five seconds. Pump damage
may occur if test valve is closed for longer
periods.
30.If the gauge does not register between 75 and
103 bar, (1500 lbf/in
2) (maximum pump
pressure), the pump is faulty.
31.If maximum pump pressure is obtained,
suspect the steering box.
32.On completion, stop engine, disconnect battery
earth lead and syphon fluid from PAS reservoir.
33. LHD only: Disconnect multiplug from MAF
sensor, remove air intake hose clips and move
hose aside.
34. LHD only: Release PAS reservoir from
mounting, for access to turbocharger
intercooler pipe.Remove vacuum hose from
turbocharger intercooler pipe.Release clips and
disconnect intercooler pipe from turbocharger.
35.Remove test equipment from tool LRT-57-041.
36.Remove bolt and clip from steering box.
37.Release PAS cooler pipe from tool LRT-57-041
and discard seal. leaving PAS reservoir oil pipe
in place, release tool LRT-57-041 from
steering box and discard seal.