engine oil LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 490 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
In the event of an IACV signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEither low or high idle speed.
lEngine stalls.
lDifficult starting.
lIdle speed in default condition.
There are eight IACV diagnostic checks performed by the ECM:
lOutput short circuit to earth – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to battery supply – opening coil
lOutput open circuit – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to earth – closing coil
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage – closing coil
lOutput open circuit – closing coil
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error low (engine speed must be 100 rev/min less than the target speed, engine load
less than 2.5 and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h less than the expected air flow for a fault condition to
be flagged).
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error high (the engine speed must be more than 180 rev/min greater than the target
speed and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h greater than the expected air flow for a fault condition to be
flagged).
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a 4 pin normally open relay. Input from the
ECM allows the fuel pump relay to control the electrical input to the fuel pump, regulating the fuel supply to the fuel
injectors. When the ignition is switched on and the engine is cranked, the fuel pump relay is activated by the ECM,
allowing the fuel system to be pressurised to 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2). The ECM then deactivates the relay until the engine
has started.
If the fuel pump runs, but the fuel pressure is out of limits, adaptive fuel faults will be stored.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1510 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - opening winding
P1513 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - opening winding
P1514 IACV opening coil malfunction Open circuit - opening winding
P1553 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - closing winding
P1552 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - closing winding
P1551 IACV closing coil malfunction Open circuit - closing winding
P0505 Idle control system malfunction Blocked IACV - high or low rev/min error
Page 492 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-35
Ignition coils
Two double ended ignition coils are located at the rear of the engine, below the inlet plenum camber mounted on a
bracket. The ignition system operates on the wasted spark principle. When the ECM triggers an ignition coil to spark,
current from the coil travels to one spark plug jumping the gap at the spark plug electrodes igniting the mixture in the
cylinder. Current continues to travel along the earth path (via the cylinder head) to the spark plug negative electrode
at the cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke. The current jumps across the spark plug electrodes and back to the coil
completing the circuit. Since it has sparked simultaneously in a cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke it has not done
any work, therefore it is wasted.
The coils are paired in the following cylinder order:
l1 and 6.
l8 and 5.
l4 and 7.
l3 and 2.
The ECM calculates the dwell timing from battery voltage, and engine speed to ensure constant secondary energy.
This ensures sufficient spark energy is always available without excessive primary current flow and thus avoiding
overheating or damage to the coils. Individual cylinder spark timing is calculated from the following signals:
lEngine speed.
lEngine load.
lEngine temperature.
lKnock control.
lAutomatic gearbox shift control.
lIdle speed control.
During engine warm up ignition timing should be an expected value of 12
° BTDC.
TestBook can not directly carry out diagnostics on the high-tension side of the ignition system. Ignition related faults
are monitored indirectly by the misfire detection system.
Input/Output
Input to the low tension side of the ignition coils comes from Fuse 14 located in the passenger compartment fuse box.
This fuse provides battery power for two ignition coils.
Page 493 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-36 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
It is possible to test both primary and secondary coils of the ignition coils for resistance using a multimeter as follows:
lExpected primary coil resistance: 0.5
± 0.05 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F).
lExpected secondary coil resistance: 13.3
± 1.3 kΩ at 20 °C (68 °F).
The ECM provides the earth control for each coil on separate pins as follows:
LH Bank (cylinders 1, 3, 5, 7)
lCylinder 1 - pin 6 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder 3 - pin 2 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder 5 - pin 8 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder 7 - pin 7 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
RH Bank (cylinders 2, 4, 6, 8)
lCylinder 2 - pin 2 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder 4 - pin 7 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder 6 - pin 6 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
lCylinder 8 - pin 8 of connector C0638 of the ECM multiplug.
The ignition coil can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lCoil open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lFaulty component.
In the event of ignition coil failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine misfire on specific cylinders.
lEngine will not start.
Knock Sensor (KS)
The ECM uses two knock sensors located between the centre two cylinders of each bank to detect pre-ignition. The
knock sensors consist of piezo ceramic crystals that oscillate to create a voltage signal. During pre-ignition the
frequency of crystal oscillation increases, which alters the signal output to the ECM. The ECM compares the signal
to known signal profiles in its memory. If pre-ignition is detected the ECM retards ignition timing for a number of cycles.
If no more pre-ignition is detected, the timing is gradually advanced to the original setting.
Page 495 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-38 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Spark plugs
The spark plugs are platinum tipped on both centre and earth electrodes. The platinum tips give a long maintenance
free life.
Cleaning or resetting the spark plug gap is not recommended as this could result in damaging the platinum tips and
thereby reducing reliability.
The misfire detection system will malfunction and store erroneous codes if the incorrect spark plugs are used.
Input/Output
The ignition coils provide a voltage to the spark plugs via the ht leads. The cylinder head via the individual thread of
each spark plug provides the earth path.
The spark plugs can fail in the following ways:
lFaulty component.
lConnector or wiring fault.
lBreakdown of high tension lead causing tracking to chassis earth.
lIncorrect spark plugs fitted.
In the event of a spark plug failure, misfire on specific cylinder may be observed:
High tension (ht) leads
The ht leads are located on top of the engine, below the plenum chamber. Their function is to transfer the ht voltage
generated by the ignition coils to the spark plugs in the engine.
Input/Output
The input to the ht lead is ht voltage from the ignition coil pack. The ht lead then supplies this voltage to the spark
plug. Output ht voltage is used by the spark plugs to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
The ht leads can fail in the following ways:
lConnector/ Wiring fault.
lFaulty component causing spark tracking to chassis earth.
lDamage to ht leads during component removal.
In the event of a ht lead failure the following symptom may be observed:
lMisfire on specific cylinder.
All ignition system related faults are diagnosed by the misfire detection system and its fault codes.
Page 498 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-41
Input/Output
The ECM provides the earth for the relay coil to allow the relay contacts to close and the ATC clutch drive to receive
battery voltage. The ECM uses a transistor as a switch to generate an open circuit in the earth path of the relay coil.
When the ECM opens the earth path, the return spring in the relay will pull the contacts apart to shut down the ATC
clutch drive.
Input to the ATC clutch relay switching contacts is via fuse 6 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The relay
coils are supplied with battery voltage from the main relay, also located in the engine compartment fuse box. The earth
path for the relay coil is via pin 29 of the ECM C0657 connector. When the relay is energised the output from the
switching contacts goes directly to the ATC compressor clutch.
The ATC clutch relay can fail in the following ways:
lRelay open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBroken return spring.
In the event of an ATC clutch relay failure, the ATC does not work.
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1536 Air conditioning compressor request range/
performanceATC compressor clutch relay open circuit
P1537 Air conditioning compressor request low input ATC compressor clutch relay short to earth
P1538 Air conditioning compressor request high input ATC compressor clutch relay short to battery supply
Page 499 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-42 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Cooling fan relay
The cooling fan relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a four pin normally open relay. The relay
must be energised to drive the cooling fan.
The cooling fan is used to cool both the condenser in which the ATC refrigerant is held and the radiator. This fan is
used especially when the engine is operating at excessively high temperatures. It is also used as a part of the ECM
backup strategy if the ECT fails.
Input/Output
The ECM provides the earth for the relay coils to allow the relay contacts to close and the cooling fan motor to receive
battery voltage. The ECM uses a transistor as a switch to generate an open circuit in the earth path of the relay
windings. When the ECM opens the earth path, the return spring in the relay will pull the contacts apart to shut down
the cooling fan motor drive.
Input to the cooling fan relay switching contacts is via fuse 5 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The relay
coils are supplied with battery voltage from the main relay, also located in the engine compartment fuse box. The earth
path for the relay coils is via pin 31 of the ECM connector C0636. When the relay is energised the output from the
switching contacts is directly to the cooling fan motor.
The cooling fan relay can fail in the following ways:
lRelay open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle battery supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBroken return spring.
In the event of a cooling fan relay failure, the cooling fan does not work.
Page 502 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-45
Ignition timing
The ignition timing is an important part of the ECM adaptive strategy. Ignition is controlled by a direct ignition system
using two four-ended coils operating on the wasted spark principle.
When the ECM triggers an ignition coil to spark, current from the coil travels to one spark plug, then jumps the gap at
the spark plug electrodes, igniting the mixture in the cylinder in the process. Current continues to travel along the earth
path (via the cylinder head) to the spark plug negative electrode at the cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke. The
current jumps across the spark plug electrodes and back to the coil completing the circuit. Since it has simultaneously
sparked in a cylinder that is on the exhaust stroke, it has not provided an ignition source there and is consequently
termed 'wasted'.
Conditions
The ECM calculates ignition timing using input from the following:
lCKP sensor.
lKnock sensors (KS).
lMAF sensor.
lTP sensor (idle only).
lECT sensor.
Function
At engine start up, the ECM sets ignition timing dependent on ECT information and starting rev/min from the CKP. As
the running characteristics of the engine change, the ignition timing changes. The ECM compares the CKP signal to
stored values in its memory, and if necessary advances or retards the spark via the ignition coils.
Ignition timing is used by the ECM for knock control.
Knock control
The ECM uses active knock control to prevent possible engine damage due to pre-ignition. This is achieved by
converting engine block noise into a suitable electrical signal that can be processed by the ECM. A major contributing
factor to engine 'knock' is fuel quality, the ECM can function satisfactorily on 91 RON fuel as well as the 95 RON fuel
that it is calibrated for.
Conditions
The ECM knock control system operates as follows:
lHot running engine.
l91 or 95 RON fuel.
Function
The ECM knock control uses two sensors located one between the centre two cylinders of each bank. The knock
sensors consist of piezo ceramic crystals that oscillate to create a voltage signal. During pre-ignition, the frequency
of crystal oscillation increases which alters the signal output to the ECM.
If the knock sensors detect pre-ignition in any of the cylinders, the ECM retards the ignition timing by 3
° for that
particular cylinder. If this action stops the engine knock, the ignition timing is restored to its previous figure in
increments of 0.75
°. If this action does not stop engine knock then the ECM retards the ignition timing a further 3° up
to a maximum of -15
° and then restores it by 0.75° and so on until the engine knock is eliminated.
The ECM also counteracts engine knock at high intake air temperatures by retarding the ignition as above. The ECM
uses the IAT signal to determine air temperature.
Page 503 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-46 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Idle speed control
The ECM regulates the engine speed at idling. The ECM uses the idle air control valve (IACV) to compensate for the
idle speed drop that occurs when the engine is placed under greater load than usual. When the throttle is in the rest
position i.e. it has not been pressed, the majority of intake air that the engine consumes comes from the idle air control
valve.
IACV control idle speed
Conditions in which the ECM operates the IACV control idle speed is as follows:
lIf any automatic transmission gears other than P or N are selected.
lIf air conditioning is switched on.
lIf cooling fans are switched on.
lAny electrical loads activated by the driver.
Function
The idle air control valve utilises two coils that use opposing pulse width modulated (PWM) signals to control the
position of a rotary valve. If one of the circuits that supplies the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining
signal preventing the idle air control valve from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the idle
air control valve assumes a default idle position at which the engine idle speed is raised to 1200 rev/min with no load
placed on the engine.
Evaporative emission control
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to limit evaporative emissions (fuel vapour) from the fuel
tank.
The ECM controls the emission control system using the following components:
lEVAP canister.
lPurge valve.
lCanister vent solenoid (CVS) valve – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lFuel tank pressure sensor – (NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability only)
lFuel leak detection pump – (NAS vehicles with positive pressure type EVAP system leak detection capability
only)
lInterconnecting pipe work.
Refer to Emissions section for operating conditions of evaporative emission systems.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Evaporative emission control operation.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) - North American Specification vehicles only
The ECM monitors performance of the engine for misfires, catalyst efficiency, exhaust leaks and evaporative control
loss. If a fault occurs, the ECM stores the relevant fault code and warns the driver of component failure by illuminating
the Malfunction Indicator Light in the instrument pack.
On vehicles fitted with automatic gearbox, the ECM combines with the Electronic Automatic Transmission (EAT) ECU
to provide the OBD strategy.
Conditions
If the OBD function of the ECM flags a fault during its operation, it falls into one of the following categories:
lmin = minimum value of the signal exceeded.
lmax = maximum value of the signal exceeded.
lsignal = signal not present.
lplaus = an implausible condition has been diagnosed.
Page 528 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
REPAIRS 18-2-71
REPAIRS
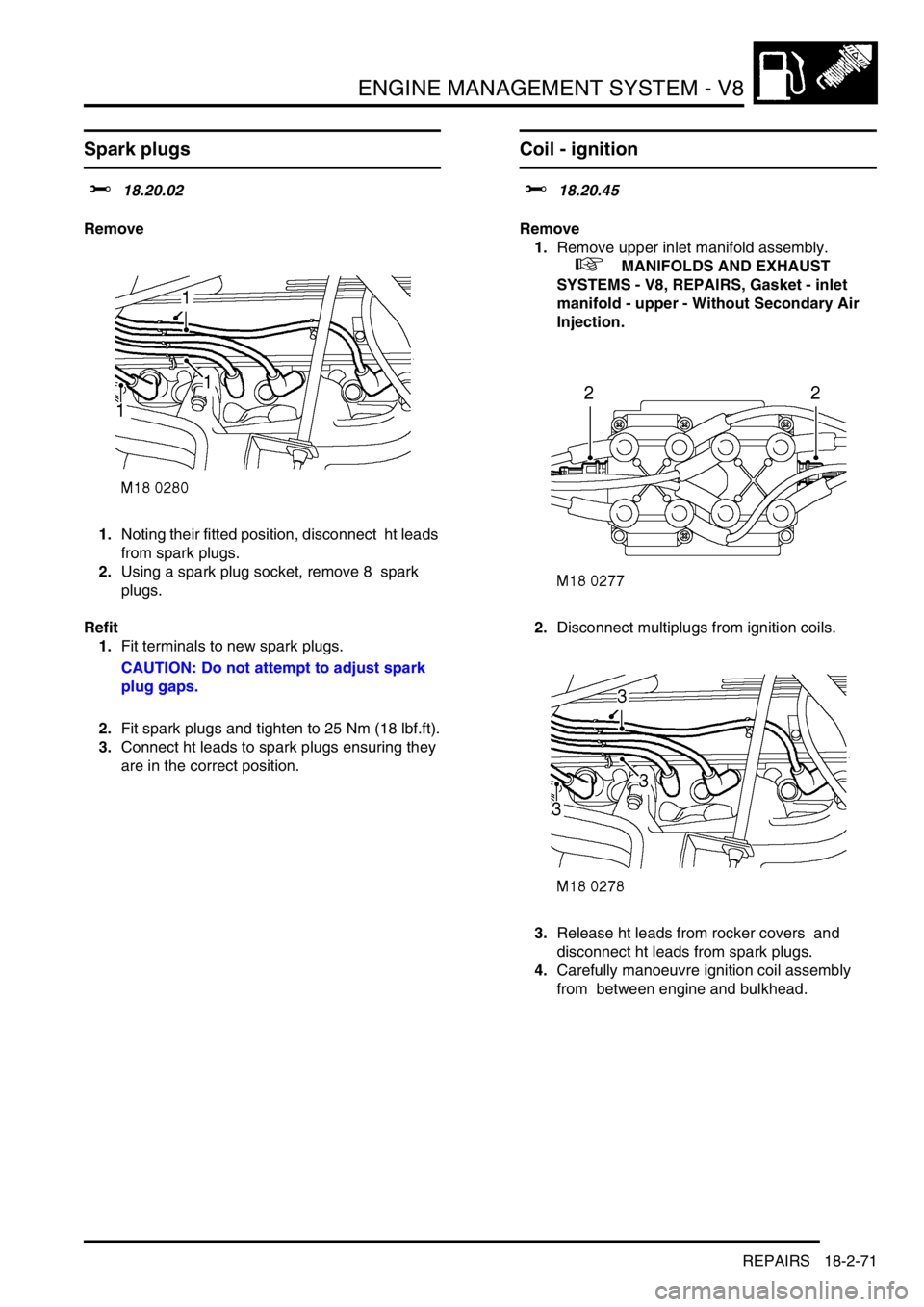
Spark plugs
$% 18.20.02
Remove
1.Noting their fitted position, disconnect ht leads
from spark plugs.
2.Using a spark plug socket, remove 8 spark
plugs.
Refit
1.Fit terminals to new spark plugs.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to adjust spark
plug gaps.
2.Fit spark plugs and tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
3.Connect ht leads to spark plugs ensuring they
are in the correct position.
Coil - ignition
$% 18.20.45
Remove
1.Remove upper inlet manifold assembly.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket - inlet
manifold - upper - Without Secondary Air
Injection.
2.Disconnect multiplugs from ignition coils.
3.Release ht leads from rocker covers and
disconnect ht leads from spark plugs.
4.Carefully manoeuvre ignition coil assembly
from between engine and bulkhead.
Page 529 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-72 REPAIRS
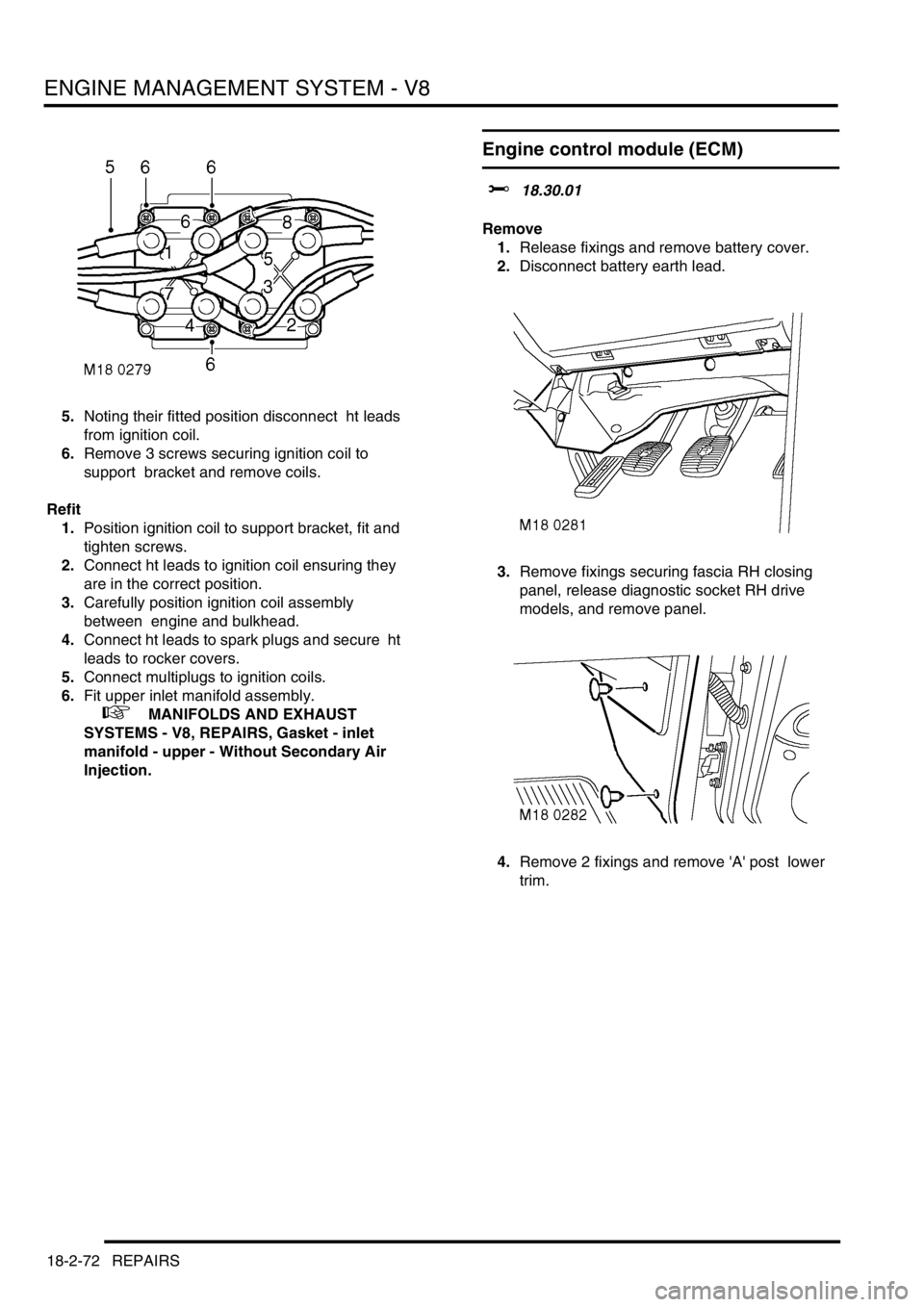
5.Noting their fitted position disconnect ht leads
from ignition coil.
6.Remove 3 screws securing ignition coil to
support bracket and remove coils.
Refit
1.Position ignition coil to support bracket, fit and
tighten screws.
2.Connect ht leads to ignition coil ensuring they
are in the correct position.
3.Carefully position ignition coil assembly
between engine and bulkhead.
4.Connect ht leads to spark plugs and secure ht
leads to rocker covers.
5.Connect multiplugs to ignition coils.
6.Fit upper inlet manifold assembly.
+ MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST
SYSTEMS - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket - inlet
manifold - upper - Without Secondary Air
Injection.
Engine control module (ECM)
$% 18.30.01
Remove
1.Release fixings and remove battery cover.
2.Disconnect battery earth lead.
3.Remove fixings securing fascia RH closing
panel, release diagnostic socket RH drive
models, and remove panel.
4.Remove 2 fixings and remove 'A' post lower
trim.