oil level LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 126 of 1672
MAINTENANCE
PROCEDURES 10-17
Automatic gearbox
WARNING: Avoid excessive skin contact with
mineral oil. Mineral oils remove the natural fats
from the skin, leading to dryness, irritation and
dermatitis.
Replace oil filter
1.Replace oil filter.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22
- 24, REPAIRS, Filter - oil.
Replace oil
1. Ensure that gearbox is cool. Apply
handbrake and securely chock front and rear
wheels.
2.Place a suitable container beneath gearbox.
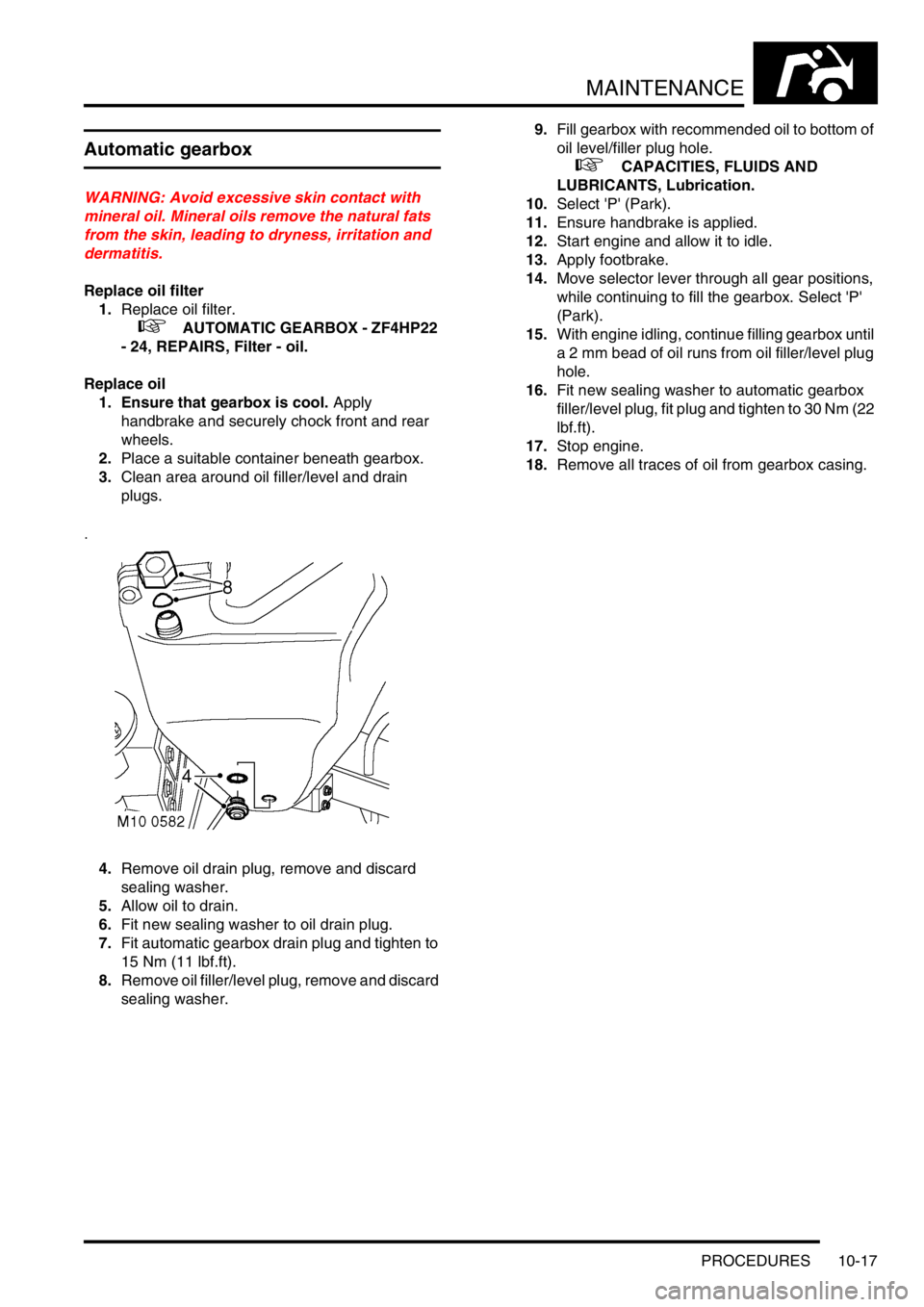
3.Clean area around oil filler/level and drain
plugs.
4.Remove oil drain plug, remove and discard
sealing washer.
5.Allow oil to drain.
6.Fit new sealing washer to oil drain plug.
7.Fit automatic gearbox drain plug and tighten to
15 Nm (11 lbf.ft).
8.Remove oil filler/level plug, remove and discard
sealing washer.9.Fill gearbox with recommended oil to bottom of
oil level/filler plug hole.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Lubrication.
10.Select 'P' (Park).
11.Ensure handbrake is applied.
12.Start engine and allow it to idle.
13.Apply footbrake.
14.Move selector lever through all gear positions,
while continuing to fill the gearbox. Select 'P'
(Park).
15.With engine idling, continue filling gearbox until
a 2 mm bead of oil runs from oil filler/level plug
hole.
16.Fit new sealing washer to automatic gearbox
filler/level plug, fit plug and tighten to 30 Nm (22
l b f . f t ) .
17.Stop engine.
18.Remove all traces of oil from gearbox casing.
Page 127 of 1672

MAINTENANCE
10-18 PROCEDURES
Transfer box
WARNING: Avoid excessive skin contact with
mineral oil. Mineral oils remove the natural fats
from the skin, leading to dryness, irritation and
dermatitis.
Check/top-up oil level
1.Release fixings, remove rear underbelly panel.
2.Clean area around oil filler/level plug.
3.Remove oil filler/level plug.
4.Check that oil level is to bottom of filler/level
plug hole.
5.Top-up level (if required) with recommended oil
to bottom of oil filler/level plug hole.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Lubrication.
6.Remove all traces of sealant from threads of oil
filler/level plug.
7.Apply Loctite 290 to threads of oil filler/level
plug.
8. Fit transfer box filler/level plug and tighten to 25
Nm (18 lbf.ft).
9.Remove all traces of oil from main casing.
10.Fit rear underbelly panel (if fitted), secure
fixings.Replace oil
1. Release fixings, remove rear underbelly panel.
2.Place a suitable container beneath transfer box
drain plug.
3.Clean area around oil filler/level and drain
plugs.
4.Remove oil filler/level plug.
5.Remove oil drain plug.
6.Allow oil to drain.
7.Apply Loctite 290 to threads of oil drain plug.
8. Fit transfer box drain plug and tighten to 30
Nm (22 lbf.ft).
9.Fill transfer box with recommended oil to
bottom of oil filler/level plug hole.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Lubrication.
10.Remove all traces of sealant from threads of oil
filler/level plug.
11.Apply Loctite 290 to threads of oil filler/level
plug.
12. Fit transfer box filler/level plug and tighten to 25
Nm (18 lbf.ft).
13. Remove all traces of oil from transfer box.
14.Fit rear underbelly panel (if fitted), secure
fixings.
Page 128 of 1672

MAINTENANCE
PROCEDURES 10-19
Front and rear axle
WARNING: Avoid excessive skin contact with
mineral oil. Mineral oils remove the natural fats
from the skin, leading to dryness, irritation and
dermatitis.
Replace oil
1.Place a suitable container beneath differential
housing of axle to be drained.
2.Clean area around oil filler/level and drain
plugs.
3.Remove oil filler/level plug.
4.Remove and discard 'O' ring from oil filler/level
plug.
5.Remove oil drain plug, allow oil to drain.
6.Remove all traces of Loctite from threads of oil
drain plug.
7.Apply Loctite 290 to threads of oil drain plug.
8. Fit axle drain plug and tighten to 64 Nm (47
lbf.ft).
9.Fill differential housing with recommended oil to
bottom of oil filler/level plug hole.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Lubrication.
10.Lubricate a new 'O' ring with recommended oil
and fit to oil filler/level plug.
11.Fit axle filler/level plug and tighten to 10 Nm (7
lbf.ft).
12.Remove all traces of oil from differential
housing.
Propeller shafts
Lubricate
Rear shaft
1.Clean area around front universal joint grease
nipple.
2.Apply recommended grease to the grease
nipple.
+ CAPACITIES, FLUIDS AND
LUBRICANTS, Lubrication.
Front shaft
3.Remove blanking plug adjacent to sliding joint
from propeller shaft.
4.Screw a 1/4in UNF grease nipple into blanking
plug hole.
Page 169 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Oil from the sump is drawn up through a two-piece plastic pick-up which contains a mesh to siphon any relatively large
pieces of material which could cause damage to the pump. The head of the pick-up is centrally immersed in the sump
oil and oil is delivered to the inlet side of the eccentric rotor pump through a gallery in the stiffener plate.
Pressurised oil from the pump is passed through to the cylinder block where it is delivered to the centrifuge filter and
full-flow filter via a port in the RH cylinder block which interfaces with a port in the centre gallery of the oil cooler
housing. The oil pump contains an oil pressure relief valve which opens to allow oil to be recirculated back around the
pump if the oil pressure increases to a high enough level.
10% of the oil flow from the pump is diverted through the centrifuge filter and returned to the sump via the centrifuge
filter drain tube. The remaining 90% of the oil passes through the standard full-flow filter to the main oil gallery in the
cylinder block.
Page 171 of 1672

ENGINE - TD5
12-1-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
When the engine temperature is below 74° C, the thermostat in the full-flow filter housing is closed and a proportion
of the oil flow to the main oil gallery is diverted to the oil cooler to supply an oil feed to the turbocharger bearings. Oil
passes through the oil cooler to the front gallery in the oil cooler housing where there is a tapping to connect the feed
pipe to the turbocharger. Oil used by the turbocharger bearings is returned to the sump through an oil drain pipe which
connects to a port in the LH side of the cylinder block.
The remainder of the oil flow leaving the full-flow filter outlet is passed into the cylinder block via a port at the rear of
oil cooler rear gallery.
When the oil temperature rises above 74
° C the thermostat in the full-flow filter adaptor housing begins to open to
allow a proportion of the oil from the full-flow filter to pass through the oil cooler before it reaches the main oil gallery
in the cylinder block. In this instance, oil supply to the turbocharger bearings is fed directly from the full-flow filter
without first passing through the oil cooler. Between 74
° C and 88° C the thermostat valve plunger opens by about
9mm to allow proportionally more oil to flow through the oil cooler before being passed to the cylinder block main oil
delivery gallery. Above 88
°C the thermostat valve continues to open by about 1mm for every 10° C increase in
temperature until the valve is fully open, when all the oil flow to the cylinder block is forced to pass to the cylinder block
via the oil cooler.
An oil pressure switch is located in a port in the rear gallery of the oil cooler housing to sense the oil pressure level
before flow enters the main oil gallery in the engine block. A warning lamp in the instrument cluster is switched on if
the oil pressure is detected as being too low.
+ INSTRUMENTS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Drillings from the cylinder block main oil gallery direct oil to the crankshaft main bearings and cross drillings in the
crankshaft direct oil to the big-end bearings. An additional five drillings in the cylinder block supply oil at reduced
pressure to the oil squirt jets for piston cooling and gudgeon pin lubrication.
Oil supply from the cylinder block is then passed to the cylinder head galleries through a non-return valve which is
included as an integral item in the lower face of the cylinder head.
Page 196 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
REPAIRS 12-1-57
Filter - oil
$% 12.60.04
Remove
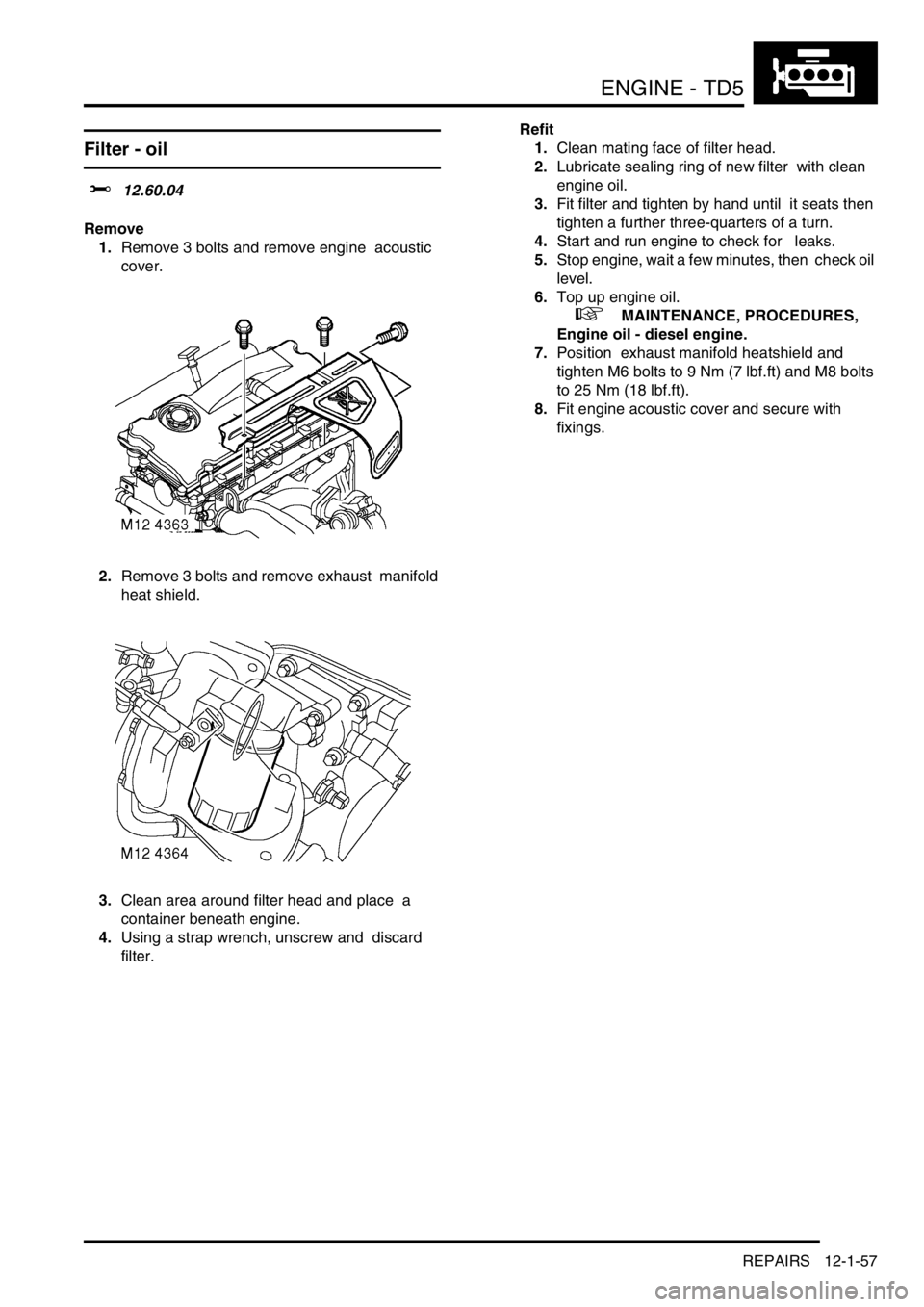
1.Remove 3 bolts and remove engine acoustic
cover.
2.Remove 3 bolts and remove exhaust manifold
heat shield.
3.Clean area around filter head and place a
container beneath engine.
4.Using a strap wrench, unscrew and discard
filter. Refit
1.Clean mating face of filter head.
2.Lubricate sealing ring of new filter with clean
engine oil.
3.Fit filter and tighten by hand until it seats then
tighten a further three-quarters of a turn.
4.Start and run engine to check for leaks.
5.Stop engine, wait a few minutes, then check oil
level.
6.Top up engine oil.
+ MAINTENANCE, PROCEDURES,
Engine oil - diesel engine.
7.Position exhaust manifold heatshield and
tighten M6 bolts to 9 Nm (7 lbf.ft) and M8 bolts
to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
8.Fit engine acoustic cover and secure with
fixings.
Page 201 of 1672
ENGINE - TD5
12-1-62 REPAIRS
Valve - relief - oil pressure
$% 12.60.56
Remove
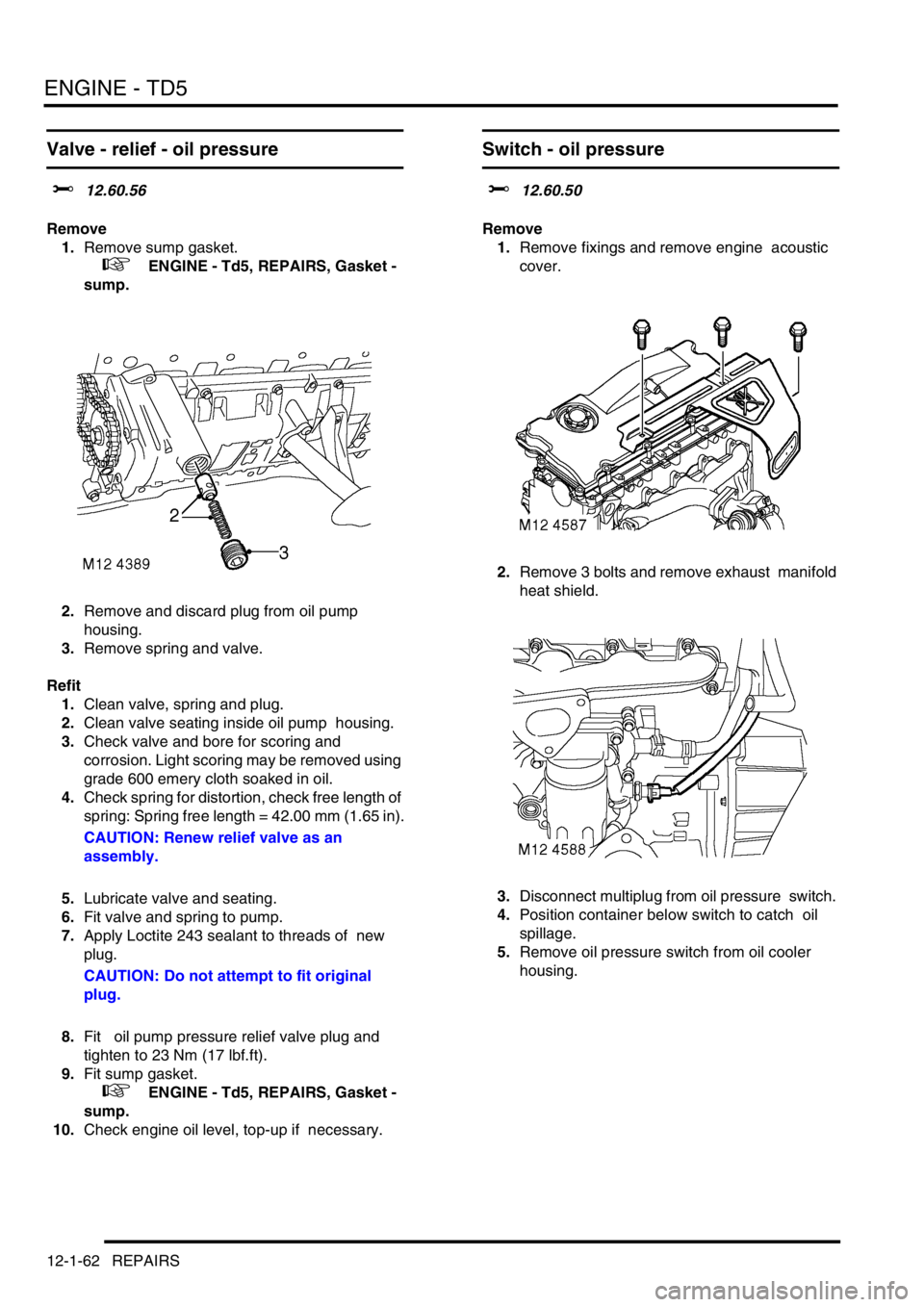
1.Remove sump gasket.
+ ENGINE - Td5, REPAIRS, Gasket -
sump.
2.Remove and discard plug from oil pump
housing.
3.Remove spring and valve.
Refit
1.Clean valve, spring and plug.
2.Clean valve seating inside oil pump housing.
3.Check valve and bore for scoring and
corrosion. Light scoring may be removed using
grade 600 emery cloth soaked in oil.
4.Check spring for distortion, check free length of
spring: Spring free length = 42.00 mm (1.65 in).
CAUTION: Renew relief valve as an
assembly.
5.Lubricate valve and seating.
6.Fit valve and spring to pump.
7.Apply Loctite 243 sealant to threads of new
plug.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to fit original
plug.
8.Fit oil pump pressure relief valve plug and
tighten to 23 Nm (17 lbf.ft).
9.Fit sump gasket.
+ ENGINE - Td5, REPAIRS, Gasket -
sump.
10.Check engine oil level, top-up if necessary.
Switch - oil pressure
$% 12.60.50
Remove
1.Remove fixings and remove engine acoustic
cover.
2.Remove 3 bolts and remove exhaust manifold
heat shield.
3.Disconnect multiplug from oil pressure switch.
4.Position container below switch to catch oil
spillage.
5.Remove oil pressure switch from oil cooler
housing.
Page 277 of 1672
ENGINE - V8
12-2-34 REPAIRS
4.Ensure ring gear is correctly seated around the
complete circumference of flywheel and allow
to cool.
5.Fit flywheel.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Flywheel.
Filter - oil
$% 12.60.04
Remove
1.Clean area around filter head and place a
container beneath engine.
2.Using a strap wrench, unscrew and discard
filter.
Refit
1.Clean mating face of filter head.
2.Lubricate sealing ring of new filter with clean
engine oil.
3.Fit filter and tighten by hand until it seats then
tighten a further half turn.
4.Start and run engine to check for leaks.
5.Stop engine, wait a few minutes, then check oil
level.
6.Top up engine oil.
Page 325 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - TD5
17-1-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Emission Control Systems
Engine design has evolved in order to minimise the emission of harmful by-products. Emission control systems fitted
to Land Rover vehicles are designed to maintain the emission levels within the legal limits pertaining for the specified
market.
Despite the utilisation of specialised emission control equipment, it is still necessary to ensure that the engine is
correctly maintained and is in good mechanical order, so that it operates at its optimum condition.
In addition to emissions improvements through engine design and the application of electronic engine management
systems, special emission control systems are used to limit the pollutant levels developed under certain conditions.
Two main types of additional emission control system are utilised with the Td5 engine to reduce the levels of harmful
emissions released into the atmosphere. These are as follows:
1Crankcase emission control – also known as blow-by gas emissions from the engine crankcase.
2Exhaust gas recirculation – to reduce NO
2 emissions.
Crankcase emission control
All internal combustion engines generate oil vapour and smoke in the crankcase as a result of high crankcase
temperatures and piston ring and valve stem blow-by, a closed crankcase ventilation system is used to vent
crankcase gases back to the air induction system and so reduce the emission of hydrocarbons.
Gases from the crankcase are drawn into the inlet manifold to be burnt in the combustion chambers with the fresh air/
fuel mixture. The system provides effective emission control under all engine operating conditions.
Crankcase gases are drawn through the breather port in the top of the camshaft cover and routed through the breather
hose and breather valve on the flexible air intake duct to be drawn into the turbocharger intake for delivery to the air
inlet manifold via an intercooler.
An oil separator plate is included in the camshaft cover which removes the heavy particles of oil before the crankcase
gas leaves via the camshaft cover port. The rocker cover features circular chambers which promote swirl in the oil
mist emanating from the cylinder head and camshaft carrier. As the mist passes through the series of chambers
between the rocker cover and oil separator plate, oil particles are thrown against the separator walls where they
condense and fall back into the cylinder head via two air inlet holes located at each end of the rocker cover.
The breather valve is a depression limiting valve which progressively closes as engine speed increases, thereby
limiting the depression in the crankcase. The valve is of moulded plastic construction and has a port on the underside
which plugs into a port in the flexible air intake duct. A port on the side of the breather valve connects to the camshaft
cover port by means of a breather hose which is constructed from a heavy-duty braided rubber hose which is held in
place by hose clips. A corrugated plastic sleeve is used to give further protection to the breather hose. The breather
valve is orientation sensitive, and “TOP” is marked on the upper surface to ensure it is mounted correctly.
It is important that the system is airtight so hose connections to ports should be checked and the condition of the
breather hose should be periodically inspected to ensure it is in good condition.
Page 346 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-9
Emission Control Systems
Engine design has evolved in order to minimise the emission of harmful by-products. Emission control systems are
fitted to Land Rover vehicles which are designed to maintain the emission levels within the legal limits pertaining for
the specified market.
Despite the utilisation of specialised emission control equipment, it is still necessary to ensure that the engine is
correctly maintained and is in good mechanical order so that it operates at its optimal condition. In particular, ignition
timing has an effect on the production of HC and NO
x emissions, with the harmful emissions rising as the ignition
timing is advanced.
CAUTION: In many countries it is against the law for a vehicle owner or an unauthorised dealer to modify or
tamper with emission control equipment. In some cases, the vehicle owner and/or the dealer may even be
liable for prosecution.
The engine management ECM is fundamental for controlling the emission control systems. In addition to controlling
normal operation, the system complies with On Board Diagnostic (OBD) system strategies. The system monitors and
reports on faults detected with ignition, fuelling and exhaust systems which cause an excessive increase in tailpipe
emissions. This includes component failures, engine misfire, catalyst damage, catalyst efficiency, fuel evaporative
loss and exhaust leaks.
When an emission relevant fault is determined, the fault condition is stored in the ECM memory. For NAS vehicles,
the MIL warning light on the instrument pack will be illuminated when the fault is confirmed. Confirmation of a fault
condition occurs if the fault is still found to be present during the driving cycle subsequent to the one when the fault
was first detected.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
The following types of supplementary control system are used to reduce harmful emissions released into the
atmosphere from the vehicle:
1Crankcase emission control – also known as blow-by gas emissions from the engine crankcase.
2Exhaust emission control – to limit the undesirable by-products of combustion.
3Fuel vapour evaporative loss control – to restrict the emission of fuel through evaporation from the fuel
system.
4Fuel leak detection system (NAS only) – there are two types of system which may be used to check the
evaporative emission system for the presence of leaks from the fuel tank to purge valve.
aVacuum leak detection test – checks for leaks down to 1 mm (0.04 in.) in diameter.
bPositive pressure leak detection test – utilises a leak detection pump to check for leaks down to 0.5 mm (0.02
in.) in diameter.
5Secondary air injection system (NAS only) – to reduce emissions experienced during cold starting.
Crankcase emission control system
The concentration of hydrocarbons in the crankcase of an engine is much greater than that in the vehicle's exhaust
system. In order to prevent the emission of these hydrocarbons into the atmosphere, crankcase emission control
systems are employed and are a standard legal requirement.
The crankcase ventilation system is an integral part of the air supply to the engine combustion chambers and it is
often overlooked when diagnosing problems associated with engine performance. A blocked ventilation pipe or filter
or excessive air leak into the inlet system through a damaged pipe or a leaking gasket can affect the air:fuel mixture,
performance and efficiency of the engine. Periodically check the ventilation hoses are not cracked and that they are
securely fitted to form airtight connections at their relevant ports.
The purpose of the crankcase ventilation system is to ensure that any noxious gas generated in the engine crankcase
is rendered harmless by complete burning of the fuel in the combustion chamber. Burning the crankcase vapours in
a controlled manner decreases the HC pollutants that could be emitted and helps to prevent the development of
sludge in the engine oil as well as increasing fuel economy.