flywheel LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 277 of 1672
ENGINE - V8
12-2-34 REPAIRS
4.Ensure ring gear is correctly seated around the
complete circumference of flywheel and allow
to cool.
5.Fit flywheel.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Flywheel.
Filter - oil
$% 12.60.04
Remove
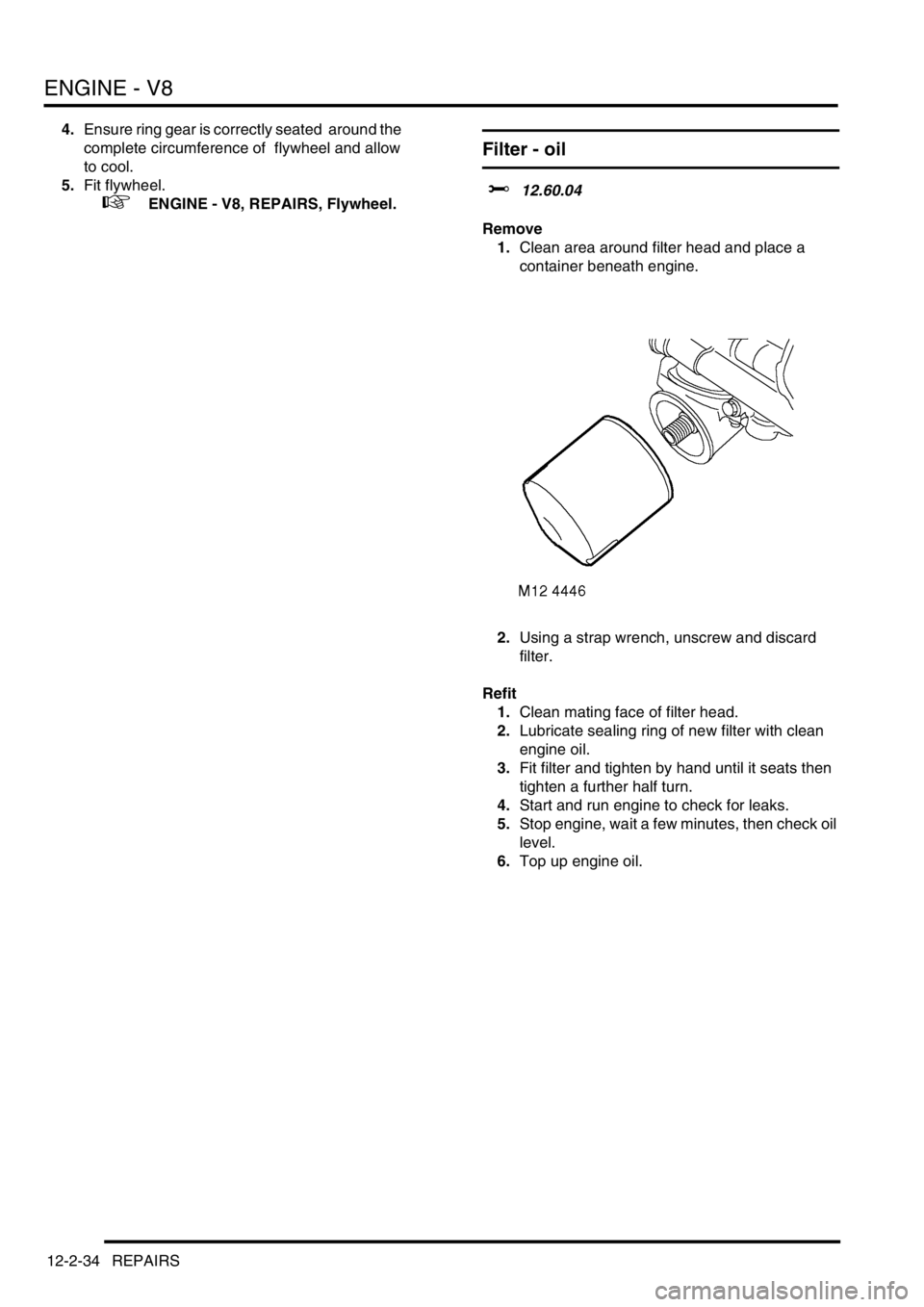
1.Clean area around filter head and place a
container beneath engine.
2.Using a strap wrench, unscrew and discard
filter.
Refit
1.Clean mating face of filter head.
2.Lubricate sealing ring of new filter with clean
engine oil.
3.Fit filter and tighten by hand until it seats then
tighten a further half turn.
4.Start and run engine to check for leaks.
5.Stop engine, wait a few minutes, then check oil
level.
6.Top up engine oil.
Page 293 of 1672
ENGINE - V8
12-2-50 OVERHAUL
5.Clean hub and mating face, spacer and clamp
ring.
6.Clean drive plate and ensure free from cracks
and distortion.
7.Fit spacer and hub to crankshaft, tighten Allen
screws to 78 Nm (58 lbf.ft).
8.Fit drive plate and clamp ring, tighten bolts to
45 Nm (35 lbf.ft).
9.Fit CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
Seal - crankshaft - rear - manual models
$% 12.21.20.01
Disassembly
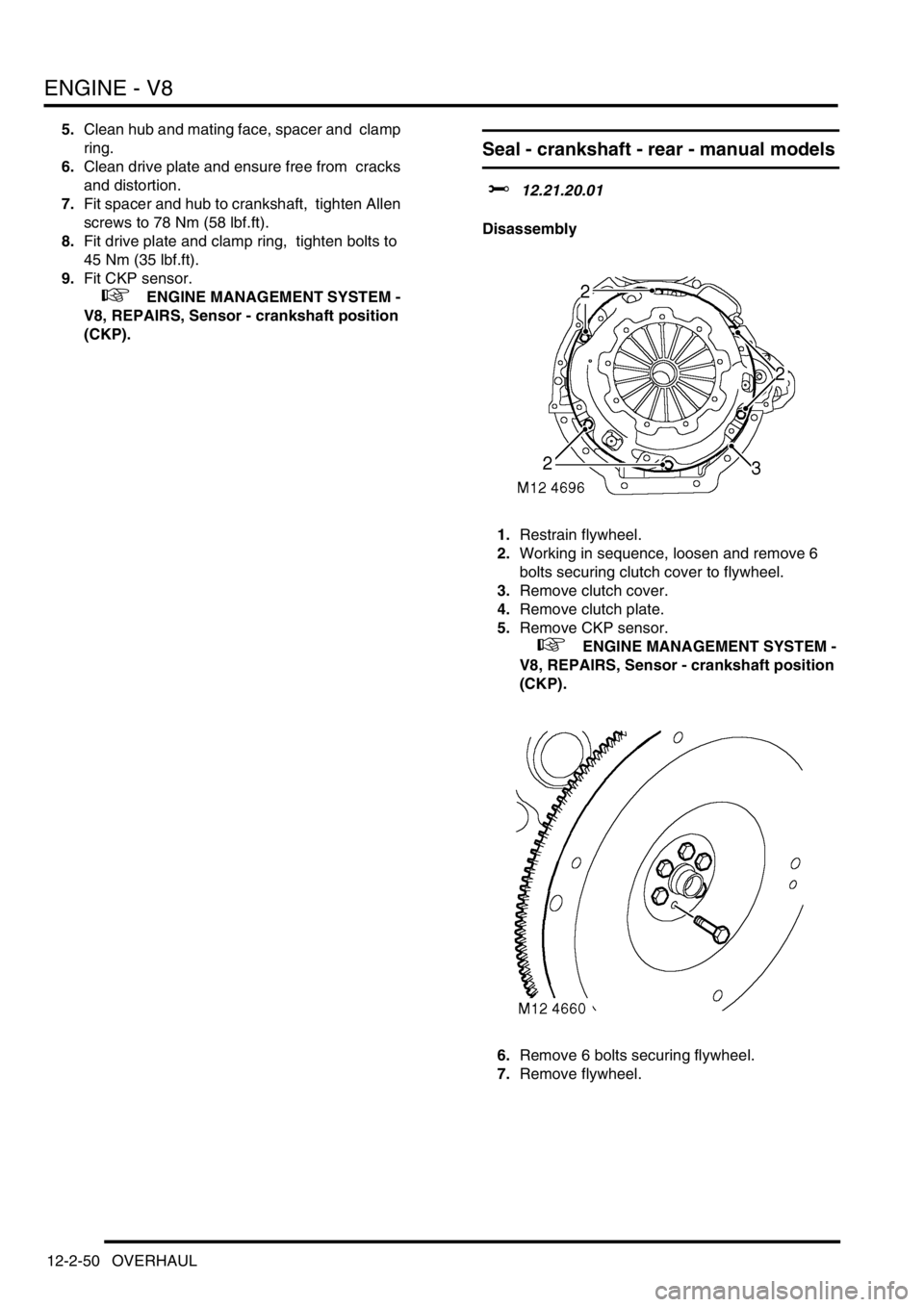
1.Restrain flywheel.
2.Working in sequence, loosen and remove 6
bolts securing clutch cover to flywheel.
3.Remove clutch cover.
4.Remove clutch plate.
5.Remove CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
6.Remove 6 bolts securing flywheel.
7.Remove flywheel.
Page 294 of 1672
ENGINE - V8
OVERHAUL 12-2-51
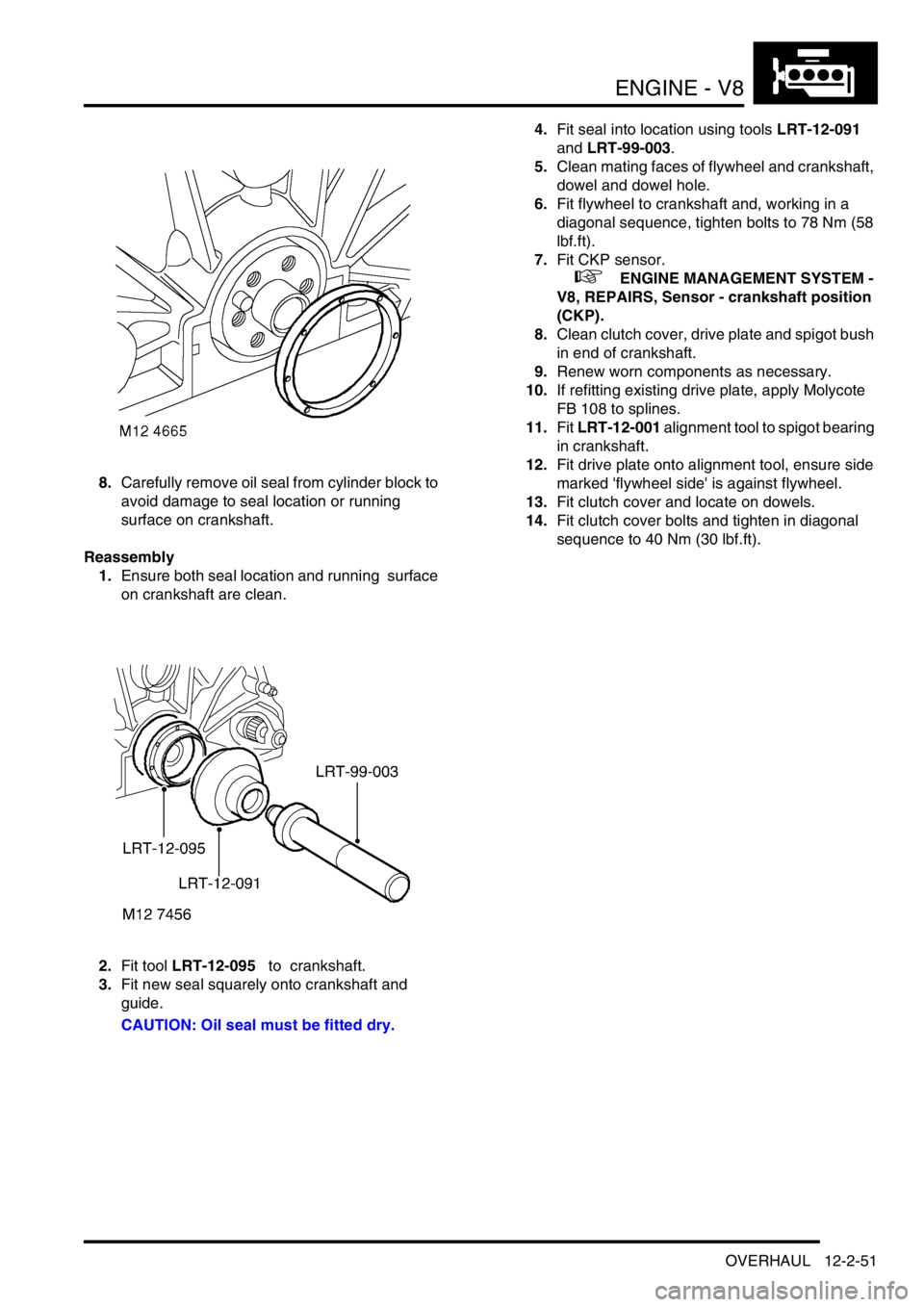
8.Carefully remove oil seal from cylinder block to
avoid damage to seal location or running
surface on crankshaft.
Reassembly
1.Ensure both seal location and running surface
on crankshaft are clean.
2.Fit tool LRT-12-095 to crankshaft.
3.Fit new seal squarely onto crankshaft and
guide.
CAUTION: Oil seal must be fitted dry.4.Fit seal into location using tools LRT-12-091
and LRT-99-003.
5.Clean mating faces of flywheel and crankshaft,
dowel and dowel hole.
6.Fit flywheel to crankshaft and, working in a
diagonal sequence, tighten bolts to 78 Nm (58
lbf.ft).
7.Fit CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
8.Clean clutch cover, drive plate and spigot bush
in end of crankshaft.
9.Renew worn components as necessary.
10.If refitting existing drive plate, apply Molycote
FB 108 to splines.
11.Fit LRT-12-001 alignment tool to spigot bearing
in crankshaft.
12.Fit drive plate onto alignment tool, ensure side
marked 'flywheel side' is against flywheel.
13.Fit clutch cover and locate on dowels.
14.Fit clutch cover bolts and tighten in diagonal
sequence to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
Page 295 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-52 OVERHAUL
Bearing - spigot - crankshaft
$% 12.21.45.01
Disassembly
1.Remove 6 bolts securing clutch cover.
2.Remove clutch cover.
3.Tap a thread in spigot bush to accommodate a
suitable impulse extractor.
4.Fit extractor to bush.
5.Remove bush from crankshaft. Reassembly
1.Clean bush register in rear of crankshaft.
2.Using a suitable drift, fit new bush to crankshaft
so that it is flush with or up to a maximum of 1.6
mm (0.06 in) below the end of the crankshaft.
3.Ream spigot bush to 19.117 + 0.025
− 0.00 mm
(0.75 + 0.001
− 0.00 in) .
4.Remove all traces of swarf on completion.
5.Clean mating faces of flywheel and crankshaft,
dowel and dowel hole.
6.Fit clutch cover to flywheel and tighten bolts by
diagonal slection to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
Page 409 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Crankshaft speed and Position (CKP) sensor
The CKP is located in the transmission housing with its tip adjacent to the outer circumference of the flywheel. The
CKP sensor works on the variable reluctance principle, which sends a signal back to the ECM in the form of an ac
voltage.
The ECM uses the signal from the CKP for the following functions:
lTo calculate engine speed.
lTo determine engine crank position.
lTo determine fuel injection timing.
The CKP sensor works as a Variable Reluctance Sensor (VRS). It uses an electromagnet and a target ring to generate
a signal. As the target ring passes the tip of the CKP sensor the magnetic field produced by the sensor is cut and then
re-instated. The ECM measures the signal as an ac voltage.
The outer circumference of the flywheel acts as the target ring for the sensor. The flywheel is divided into 36 segments
each of 10
°. 31 segments have drilled holes and 5 segments are spaces. This equals 360° or one engine revolution.
The 5 spaces correspond to the TDC position of the 5 cylinders, this allows the ECM to control fuel injection timing
for each of the cylinders.
Input/Output
The two pins on the sensor are both outputs. The ECM processes the outputs of the sensor. To protect the integrity
of the CKP signal an earth shield or screen is used.
The ECM measures the outputs from the CKP. The ECM measures the positive signal from the CKP at pin 13 of ECM
connector C0158. The ECM measures the negative signal from the CKP at pin 36 of ECM connector C0158. The earth
path is via pin 16 of ECM connector C0158.
Voltage generation from the CKP sensor is relative to engine speed. The values expected from a good CKP sensor
are as follows:
l2 to 3 volts with engine cranking.
lRising to 6 to 6.5 volts from 1000 rev/min upwards.
The above readings are dependent upon correct air gap between the tip of the CKP sensor and the passing teeth of
the reluctor ring.
Page 469 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Connector 5 (C0638): This connector contains 9 pins and is used to control the ignition system. The ignition coils are
supplied with power and a switching earth completes the circuit.
Pin out details connector C0638
Crankshaft speed and Position (CKP) sensor (C0168)
The CKP sensor is located towards the rear of the engine below cylinder number 7, with its tip adjacent to the outer
circumference of the flywheel. The CKP sensor is the most important sensor on the vehicle and without its signal the
engine will not run. The signal produced by the CKP sensor allows the ECM to determine crankshaft angle and speed
of rotation. The ECM uses this information to calculate ignition timing and fuel injection timing.
The CKP sensor works as a variable reluctance sensor. It uses an electromagnet and a reluctor ring to generate a
signal. As the reluctor ring passes the tip of the CKP sensor the magnetic field produced by the sensor is cut and then
re-instated. The ECM measures the signal as an ac voltage.
The output voltage varies in proportion to engine speed. The reluctor ring has a set tooth pattern, 60 teeth are spaced
at 6
° intervals and are 3° wide, two teeth are removed to provide a reference mark at 60° BTDC for number 1 cylinder.
There is no back up strategy or limp home facility if this sensor fails, the engine does not run.
Pin No. Function Signal type Reading
1 Not used - -
2 Ignition , Cylinders 2 and 3 Output Switch to earth
3 Not used - -
4 Not used - -
5 Ignition coil earth Earth 0V
6 Ignition , Cylinders 1 and 6 Output Switch to earth
7 Ignition , Cylinders 4 and 7 Output Switch to earth
8 Ignition , Cylinders 5 and 8 Output Switch to earth
9 Not used - -
Page 471 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-14 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
In the event of a CKP sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine cranks but fails to start.
lMIL remains on at all times.
lEngine misfires (CKP sensor incorrectly fitted).
lEngine runs roughly or even stalls (CKP sensor incorrectly fitted).
lTachometer fails to work.
lFlywheel adaption reset – ferrous contamination
If the CKP sensor fails while the engine is running the engine will suddenly stall, this is because the CKP sensor has
no backup strategy. If this happens the ECM will produce a fault code that it can store in its memory. If the engine is
not running when the CKP sensor fails, the vehicle will crank but will be unlikely to start, and no fault code will be
generated. In this instance the MIL lamp will remain illuminated and the tachometer will fail to read.
It is vital that the CKP sensor output wires are not reversed (i.e. the connector is fitted incorrectly) as this will cause
a 3
° advance in ignition timing. This happens because the ECM uses the falling edge of the signal waveform as its
reference or timing point for each passing tooth on the reluctor.
Whenever a new crankshaft position sensor is fitted or the flywheel is removed, the adaptive values will have to be
reset, using TestBook.
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor (C0176)
The CMP sensor is located on the front of the engine, above and behind the crankshaft pulley. The CMP sensor is a
Hall effect sensor producing four pulses for every two crankshaft revolutions. The sensor is positioned close to the
camshaft gear wheel, the gear wheel has four slots machined at 90
° intervals. This allows the ECM to recognise 4
individual cylinders every camshaft revolution or all 8 cylinders every crankshaft revolution.
The CMP sensor Hall effect works as a magnetic switch. It switches battery voltage on or off depending on the position
of the camshaft gear wheel in relationship to the sensor.
The ECM uses this signal for cylinder recognition to control sequential fuel injection, engine knock and diagnostic
purposes.
P Code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0335 Crankshaft position sensor a circuit malfunction Reference mark outside search window for more than
two revs, with engine speed above 500 rev/min
P0336 Crankshaft position sensor a circuit range/
performanceIncorrect number of teeth detected ±1 tooth between
reference marks with engine speed above 500 rpm
Page 505 of 1672
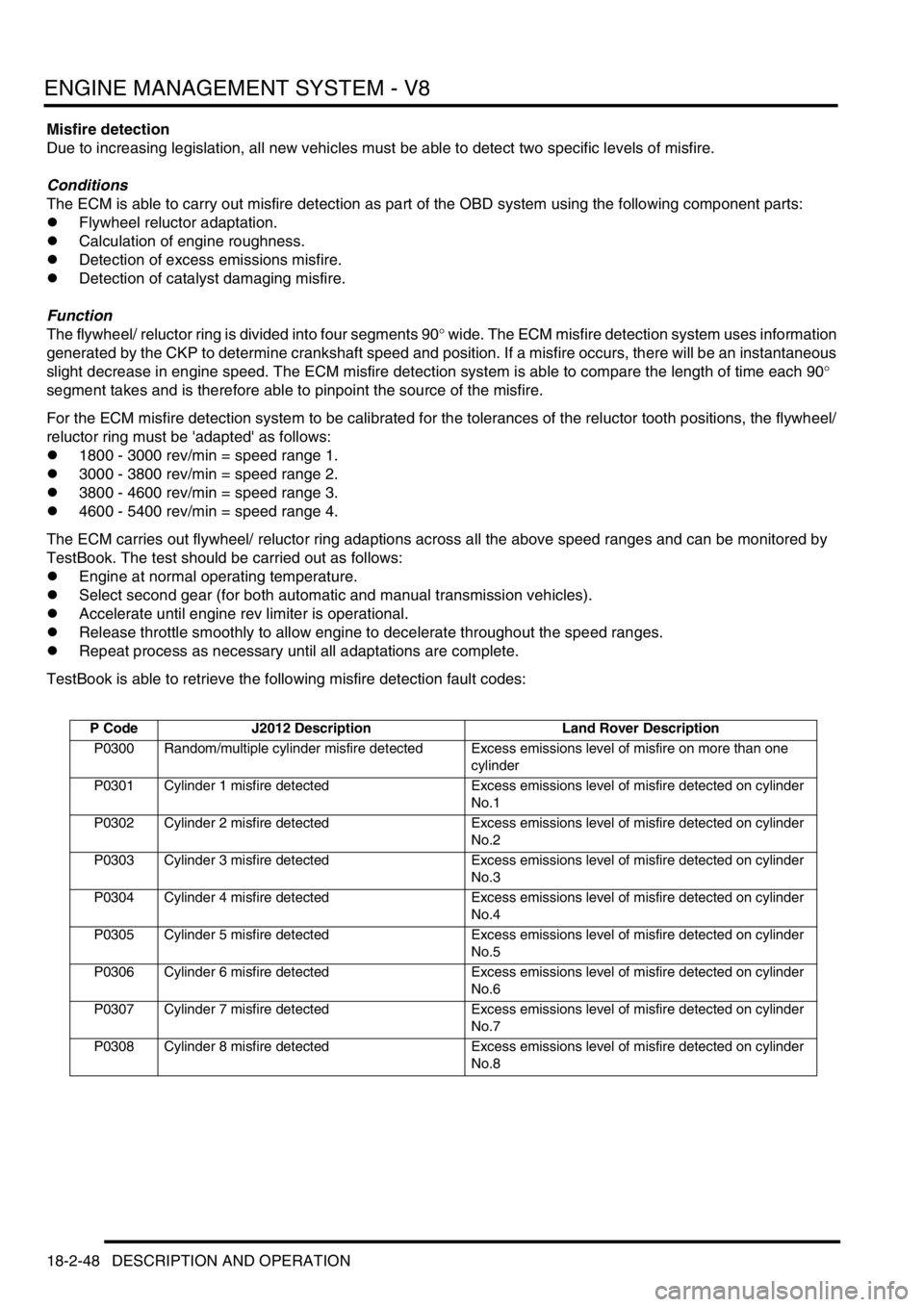
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-48 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Misfire detection
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to detect two specific levels of misfire.
Conditions
The ECM is able to carry out misfire detection as part of the OBD system using the following component parts:
lFlywheel reluctor adaptation.
lCalculation of engine roughness.
lDetection of excess emissions misfire.
lDetection of catalyst damaging misfire.
Function
The flywheel/ reluctor ring is divided into four segments 90
° wide. The ECM misfire detection system uses information
generated by the CKP to determine crankshaft speed and position. If a misfire occurs, there will be an instantaneous
slight decrease in engine speed. The ECM misfire detection system is able to compare the length of time each 90
°
segment takes and is therefore able to pinpoint the source of the misfire.
For the ECM misfire detection system to be calibrated for the tolerances of the reluctor tooth positions, the flywheel/
reluctor ring must be 'adapted' as follows:
l1800 - 3000 rev/min = speed range 1.
l3000 - 3800 rev/min = speed range 2.
l3800 - 4600 rev/min = speed range 3.
l4600 - 5400 rev/min = speed range 4.
The ECM carries out flywheel/ reluctor ring adaptions across all the above speed ranges and can be monitored by
TestBook. The test should be carried out as follows:
lEngine at normal operating temperature.
lSelect second gear (for both automatic and manual transmission vehicles).
lAccelerate until engine rev limiter is operational.
lRelease throttle smoothly to allow engine to decelerate throughout the speed ranges.
lRepeat process as necessary until all adaptations are complete.
TestBook is able to retrieve the following misfire detection fault codes:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0300 Random/multiple cylinder misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire on more than one
cylinder
P0301 Cylinder 1 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.1
P0302 Cylinder 2 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.2
P0303 Cylinder 3 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.3
P0304 Cylinder 4 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.4
P0305 Cylinder 5 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.5
P0306 Cylinder 6 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.6
P0307 Cylinder 7 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.7
P0308 Cylinder 8 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.8
Page 506 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-49
TestBook is able to retrieve the following Catalyst damage fault codes:
The flywheel/ reluctor ring adaptions must be reset if the CKP sensor or the flywheel are changed.
Vehicle Speed Signal (VSS)
The VSS is used, by the ECM, to control idle speed and overrun cut off. The ECM receives the signal through a hard
wired connection direct from the SLABS ECU.
For vehicles fitted with an automatic gearbox, two vehicle speed signals are received by the ECM. The second signal
is derived from the main gearbox output shaft speed, and is sent to the ECM by the Electronic Automatic Transmission
(EAT) ECU though the Controller Area Network (CAN). The ECM compares the vehicle speed signal generated by
the SLABS ECU with that supplied via the CAN.
The ECM also receives transfer box information. This allows the ECM to take in to account the vehicle being driven
using low range gearing and compensate as necessary.
On vehicles with manual transmission, the SLABS signal is checked against a threshold value stored in ECM memory.
If other engine parameters indicate the engine is at high load and the VSS is below the threshold, a fault condition is
registered in the diagnostic memory.
The vehicle speed signal generated by the SLABS ECU is in the form of a pulse width modulated signal (PWM).
Pulses are generated at 8000 per mile, and the frequency of the signal changes in accordance with road speed. At
zero road speed the ECU outputs a reference signal at a frequency of 2Hz for diagnostic purposes.
Function
The input signal for the SLABS ECU is measured via pin 22 of connector C0637 of the ECM. The SLABS ECU
generates a PWM signal switching between 0 and 12 volts at a frequency of 8000 pulses per mile. For vehicles with
automatic gearbox the input signal for the EAT ECU is measured via pins 36 and 37 of connector C0637 of the ECM.
These pin numbers provide a bi-directional communications link using the CAN data bus.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1300 Misfire detected sufficient to cause catalyst
damageCatalyst damaging level of misfire on more than one
cylinder
P1301 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.1
P1302 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.2
P1303 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.3
P1304 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.4
P1305 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.5
P1306 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.6
P1307 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.7
P1308 No description Catalyst damaging level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.8
Page 654 of 1672

CLUTCH - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 33-1-3
1Brake/clutch reservoir
2Connecting hose
3Bolt 2 off
4Master cylinder
5Clutch pedal
6Gearbox housing
7Primary driveshaft
8Bolt 2 off
9Slave cylinder
10Bleed nipple
11Pressure plate
12Drive plate
13Dual mass flywheel
14Metal hydraulic pipe
15Ball spigot
16Clutch release bearing sleeve
17Bolt 2 off
18Pivot washer
19Release lever
20Release bearing
21Retaining clip
22Bolt
23Plastic hydraulic pipe