fuel LAND ROVER FREELANDER 2001 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: FREELANDER, Model: LAND ROVER FREELANDER 2001Pages: 1007, PDF Size: 23.47 MB
Page 35 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-4
Materials –
lkeep lids on containers of solvents;
lonly use the minimum quantity;
lconsider alternative materials;
lminimise over-spray when painting.
Gases –
luse the correct equipment for collecting
refrigerants;
ldon't burn rubbish on site.
Discharges to water
Most sites will have two systems for discharging
water: storm drains and foul drains. Storm drains
should only receive clean water, foul drains will take
dirty water.
The foul drain will accept many of the normal waste
waters such as washing water, detergents and
domestic type wastes, but oil, petrol, solvent, acids,
hydraulic oil, antifreeze and other such substances
should never be poured down the drain. If in any
doubt, speak to the local Water Company first.
Every precaution must be taken to prevent spillage of
oil, fuel, solvents etc. reaching the drains. All
handling of such materials must take place well away
from the drains and preferably in an area with a kerb
or wall around it, to prevent discharge into the drain.
If a spillage occurs, it should be soaked up
immediately. Having a spill kit available will make this
easier.
Additional precautions
Check whether the surface water drains are
connected to an oil/water separator, this could
reduce the pollution if an incident was to occur. Oil/
water separators require regular maintenance to
ensure effectiveness.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
Disposal –
lnever pour anything down a drain without first
checking that it is environmentally safe to do so,
and that it does not contravene any local
regulations or bye-laws;
lhave oil traps emptied regularly.
Spillage prevention –
lstore liquids in a walled area;
lmake sure the taps on liquid containers are
secure and cannot be accidentally turned on;
lprotect bulk storage tanks from vandalism by
locking the valves;
ltransfer liquids from one container to another in
an area away from open drains;
lensure lids are replaced securely on containers;
lhave spill kits available near to points of storage
and handling of liquids.Spill kits
Special materials are available to absorb a number of
different substances. They can be in granular form,
ready to use and bought in convenient containers for
storage. Disposal of used spill-absorbing material is
dealt with in the 'Waste Management' section.
Land contamination
Oils, fuels and solvents etc. can contaminate any soil
that they are allowed to contact. Such materials
should never be disposed of by pouring onto soil and
every precaution must be taken to prevent spillage
reaching soil. Waste materials stored on open
ground could also leak, or have polluting substances
washed off them that would contaminate the land.
Always store these materials in suitable skips or
other similarly robust containers.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
ldon't pour or spill anything onto the soil or bare
ground;
ldon't store waste materials on bare ground, see
'Spillage prevention' list.
Legal compliance
Some sites may have a discharge consent for
effluent discharge to the foul drain for a car wash etc.
It is important to know what materials are allowed in
the drain and to check the results of any monitoring
carried out by the Water Company.
Where paint spraying operations are carried out it
may be necessary to apply to the Local Authority for
an air emissions licence to operate the plant. If such
a licence is in operation, additional precautions will
be necessary to comply with the requirements, and
the results of any air quality monitoring must be
checked regularly.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
lknow what legal consents and licences apply to
the operations;
lcheck that the emissions and discharges
comply with legal requirements.
Page 36 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-5
Local issues
A number of environmental issues will be of
particular concern to residents and other neighbours
close to the site. The sensitivity of these issues will
depend on the proximity of the site and the layout
and amount of activity carried on at the site.
Noise is a major concern and therefore consideration
should be given to the time spent carrying out noisy
activities and the location of those activities that can
cause excessive noise.
Car alarm testing, panel beating, hammering and
other such noisy activities should, whenever
possible, be carried out indoors with doors and
windows shut, or as far away from houses as
possible.
Running vehicle engines may be an outside activity
which could cause nuisance to neighbours because
of both noise and smell.
Be sensitive to the time of day when these activities
are carried out and minimise the time of the noisy
operation, particularly in the early morning and late
evening.
Another local concern will be the smell from the
various materials used. Using less solvent, paint and
petrol could help prevent this annoyance.
Local residents and other business users will also be
concerned about traffic congestion, noise and
exhaust fumes, be sensitive to these concerns and
try to minimise inconvenience from deliveries,
customers and servicing operations.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
lidentify where the neighbours who are likely to
be affected are situated;
lminimise noise, smells and traffic nuisance;
lprevent litter by putting waste in the correct
containers;
lhave waste skips emptied regularly.Use of resource
Another environmental concern is the waste of
materials and energy that can occur in day to day
activities.
Electricity for heating, lighting and compressed air
uses resources and releases pollution during its
generation.
Fuel used for heating, running cars or vans and
mobile plant is another limited resource which
consumes large amounts of energy during its
extraction and refining processes.
Water has to be cleaned, piped to site and disposed
of, all of which creates more potential pollution;
Oil, spares, paint etc., have all produced pollution in
the process of manufacture and they become a
waste disposal problem if discarded.
Checklist
Always adhere to the following:
Electricity and heating –
lkeep doors and windows closed in the winter;
lswitch off machinery or lights when not needed;
luse energy efficient heating systems;
lswitch off computers and photocopiers when
not needed.
Fuel –
ldon't run engines unnecessarily;
lthink about whether journeys are necessary and
drive to conserve fuel.
Water –
ldon't leave taps and hose pipes running;
lmend leaks quickly, don't be wasteful.
Compressed air –
ldon't leave valves open;
lmend leaks quickly;
ldon't leave the compressor running when not
needed.
Use of environmentally damaging materials –
lcheck whether a less toxic material is available.
Handling and storage of materials –
lhave the correct facilities available for handling
liquids to prevent spillage and wastage as listed
above;
lprovide suitable locations for storage to prevent
frost damage or other deterioration.
Page 37 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-6
Waste Management
One of the major ways that pollution can be reduced
is by the careful handling, storage and disposal of all
waste materials that occur on sites. Legislation
makes it illegal to dispose of waste materials other
than to licensed waste carriers and disposal sites.
This means that it is necessary to not only know what
the waste materials are, but also to have the
necessary documentation and licenses.
Handling and storage of waste
Ensure that waste materials are not poured down the
drain or onto soils. They should be stored in such a
way as to prevent the escape of material to land,
water or air.
They must also be segregated into different types of
waste e.g. oil, metals, batteries, used vehicle
components. This will prevent any reaction between
different materials and assist in disposal.
Disposal of waste
Disposal of waste materials must only be to waste
carriers who are licensed to carry those particular
waste materials and all the necessary
documentation must be completed. The waste
carrier is responsible for ensuring that the waste is
taken to the correct disposal sites.Dispose of waste in accordance with the following
guidelines:
lFuel, hydraulic fluid, anti-freeze and oil –
keep separate and dispose of to specialist
contractor.
lRefrigerant – collect using specialist
equipment and containers, and reuse.
lDetergents – safe to pour down the foul drain
if diluted.
lPaint, thinners – keep separate and dispose of
to specialist contractor.
lComponents – send back to supplier for
refurbishment, or disassemble and reuse any
suitable parts. Dispose of the remainder in
ordinary waste.
lSmall parts – reuse any suitable parts, dispose
of the remainder in ordinary waste.
lMetals – can be sold if kept separate from
general waste.
lTyres – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lPackaging – compact as much as possible and
dispose of in ordinary waste.
lAsbestos-containing – keep separate and
dispose of to specialist contractor.
lOily and fuel wastes (e.g. rags, used spill kit
material) – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lAir filters – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lRubber/plastics – dispose of in ordinary
waste.
lHoses – dispose of in ordinary waste.
lBatteries – keep separate and dispose of to
specialist contractor.
lAirbags (explosives) – keep separate and
dispose of to specialist contractor.
lElectrical components – send back to
supplier for refurbishment, or disassemble and
reuse any suitable parts. Dispose of the
remainder in ordinary waste.
lElectronic components – send back to
supplier for refurbishment, or disassemble and
reuse any suitable parts. Dispose of the
remainder in ordinary waste.
lCatalysts – can be sold if kept separate from
general waste.
lUsed spill-absorbing material – keep
separate and dispose of to specialist contractor.
lOffice waste – recycle paper and toner/ink
cartridges, dispose of the remainder in ordinary
waste.
Page 38 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-7
General fitting instructions
Precautions against damage
To avoid damage to the vehicle when carrying out
repairs, always adhere to the following:
lAlways fit wing and seat covers before
commencing work. Avoid spilling brake fluid or
battery acid on paintwork; immediately wash off
with water if this occurs.
lDisconnect the battery earth lead before starting
work, see ELECTRICAL PRECAUTIONS.
lAlways use the recommended service tool or a
satisfactory equivalent where specified.
lProtect exposed bearing surfaces, sealing
surfaces and screw threads from damage.
Component removal
Whenever possible, clean components and
surrounding area before removal.
lBlank off openings exposed by component
removal.
lImmediately seal fuel, oil or hydraulic lines when
apertures are exposed; use plastic caps or
plugs to prevent loss of fluid and ingress of dirt.
lClose open ends of oilways exposed by
component removal with tapered hardwood
plugs or conspicuous plastic plugs.
lImmediately a component is removed, place it in
a suitable container; use a separate container
for each component and its associated parts.
lClean bench and provide marking materials,
labels, containers and locking wire before
dismantling a component.
Dismantling
Observe scrupulous cleanliness when dismantling
components, particularly when brake, fuel or
hydraulic system parts are being worked on. A
particle of dirt or a cloth fragment could cause a
serious malfunction if trapped in these systems.Use the following procedures:
lBlow out all tapped holes, crevices, oilways and
fluid passages with an air line. Ensure that any
O-rings used for sealing are correctly replaced
or renewed if disturbed during the process.
lUse marking ink to identify mating parts and
ensure correct reassembly. Do not use a centre
punch or scriber to mark parts, they could
initiate cracks or distortion in marked
components.
lWire together mating parts where necessary to
prevent accidental interchange (e.g. roller
bearing components).
lWire labels on to all parts which are to be
renewed, and to parts requiring further
inspection before being passed for reassembly;
place these parts in separate containers from
those containing parts for rebuild.
lDo not discard a part due for renewal until after
comparing it with a new part to ensure that its
correct replacement has been obtained.
Cleaning components
Always use the recommended cleaning agent or
equivalent. Ensure that adequate ventilation is
provided when volatile degreasing agents are being
used. Do not use degreasing equipment for
components containing items which could be
damaged by the use of this process.
When washing under bonnet, never direct water onto
ECM, as water ingress may occur resulting in
damage to electrical components inside.
General Inspection
All components should be inspected for wear or
damage before being reassembled.
lNever inspect a component for wear or
dimensional check unless it is absolutely clean;
a slight smear of grease can conceal an
incipient failure.
lWhen a component is to be checked
dimensionally against recommended values,
use the appropriate measuring equipment
(surface plates, micrometers, dial gauges etc.).
Ensure the measuring equipment is calibrated
and in good serviceable condition.
lReject a component if its dimensions are
outside the specified tolerances, or if it appears
to be damaged.
lA part may be refitted if its critical dimension is
exactly to its tolerance limit and it appears to be
in satisfactory condition.
lUse 'Plastigauge' 12 Type PG-1 for checking
bearing surface clearances.
Page 41 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-10
Joints and joint faces
General
Fit joints dry unless specified otherwise.
lAlways use the correct gaskets as specified.
lWhen joining compound is used, apply in a thin
uniform film to metal surfaces; take care to
prevent joining compound from entering
oilways, pipes or blind tapped holes.
lIf gaskets and/or joining compound is
recommended for use; remove all traces of old
joining material prior to reassembly. Do not use
a tool which will damage the joint faces and
smooth out any scratches or burrs using an oil
stone. Do not allow dirt or joining material to
enter any tapped holes or enclosed parts.
lPrior to reassembly, blow through any pipes,
channels or crevices with compressed air.
Locking devices
General
Always replace locking devices with one of the same
design.
Tab Washers
Always release locking tabs and fit new locking
washers, do not re-use locking tabs. Ensure the new
tab washer is the same design as that replaced.
Locking Nuts
Always use a backing spanner when loosening or
tightening locking nuts, brake and fuel pipe unions.
Roll Pins
Always fit new roll pins of an interference fit in the
hole.
Circlips
Always fit new circlips of the correct size for the
groove.
Locking wire
Always fit locking wire of the correct type. Arrange
wire so that its tension tends to tighten the bolt heads
or nuts to which it is fitted.
Keys and Keyways
Remove burrs from edges of keyways with a fine file
and clean thoroughly before attempting to refit key.
Clean and inspect key closely; keys are suitable for
refitting only if indistinguishable from new, as any
indentation may indicate the onset of wear.
Page 46 of 1007
GENERAL INFORMATION
03-15
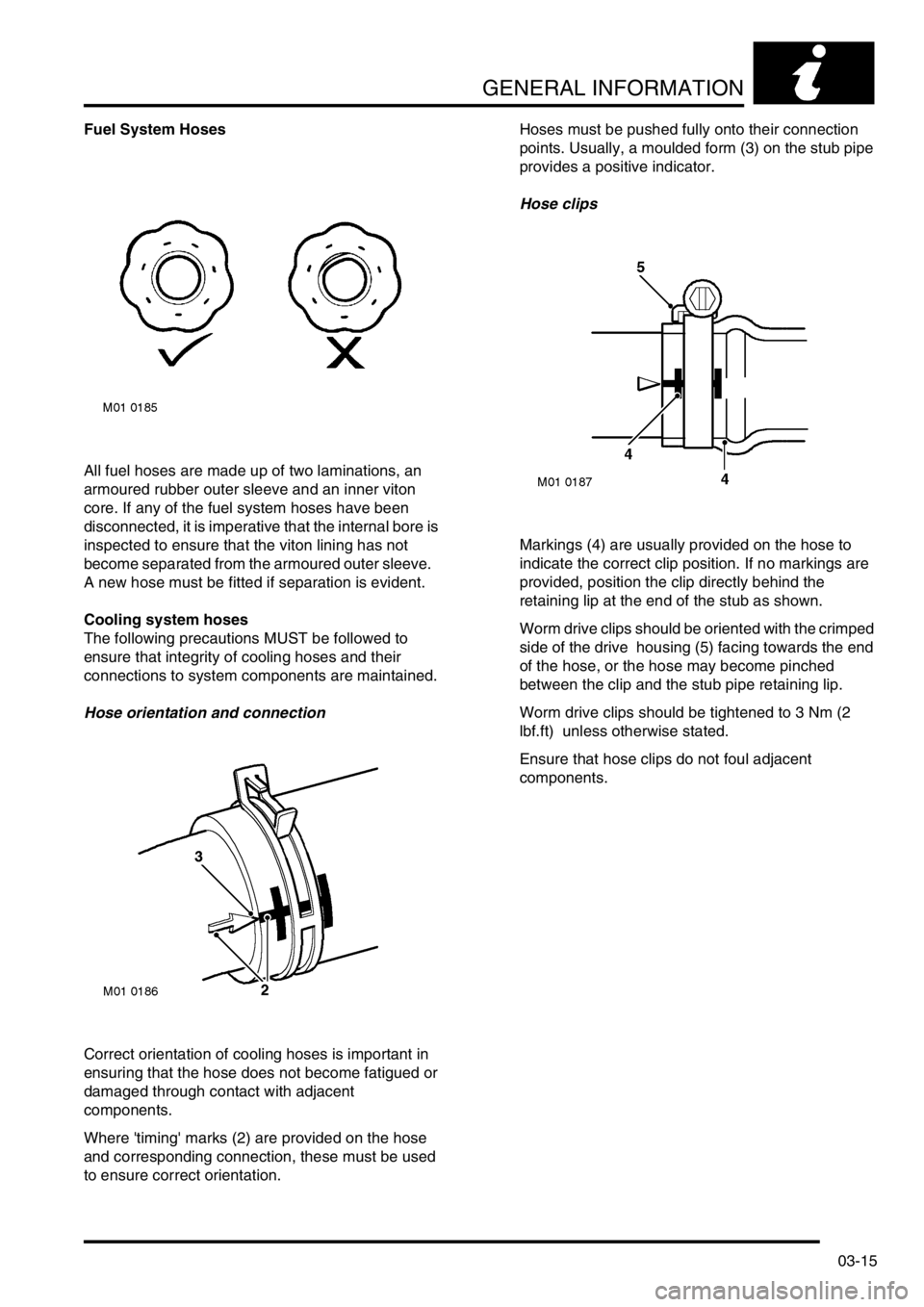
Fuel System Hoses
All fuel hoses are made up of two laminations, an
armoured rubber outer sleeve and an inner viton
core. If any of the fuel system hoses have been
disconnected, it is imperative that the internal bore is
inspected to ensure that the viton lining has not
become separated from the armoured outer sleeve.
A new hose must be fitted if separation is evident.
Cooling system hoses
The following precautions MUST be followed to
ensure that integrity of cooling hoses and their
connections to system components are maintained.
Hose orientation and connection
Correct orientation of cooling hoses is important in
ensuring that the hose does not become fatigued or
damaged through contact with adjacent
components.
Where 'timing' marks (2) are provided on the hose
and corresponding connection, these must be used
to ensure correct orientation.Hoses must be pushed fully onto their connection
points. Usually, a moulded form (3) on the stub pipe
provides a positive indicator.
Hose clips
Markings (4) are usually provided on the hose to
indicate the correct clip position. If no markings are
provided, position the clip directly behind the
retaining lip at the end of the stub as shown.
Worm drive clips should be oriented with the crimped
side of the drive housing (5) facing towards the end
of the hose, or the hose may become pinched
between the clip and the stub pipe retaining lip.
Worm drive clips should be tightened to 3 Nm (2
lbf.ft) unless otherwise stated.
Ensure that hose clips do not foul adjacent
components.
Page 49 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-18
Fuel handling precautions
Fuel vapour is highly inflammable and in confined
spaces is also explosive and toxic. The vapour is
heavier than air and will always fall to the lowest
level. The vapour can easily be distributed
throughout a workshop by air currents;
consequently, even a small spillage of fuel is
potentially very dangerous.
The following information provides basic precautions
which must be observed if petrol (gasoline) is to be
handled safely. It also outlines other areas of risk
which must not be ignored. This information is issued
for basic guidance only, if in doubt consult your local
Fire Officer.
General
Always have a fire extinguisher containing FOAM,
CO
2, GAS or POWDER close at hand when handling
or draining fuel or when dismantling fuel systems.
Fire extinguishers should also be located in areas
where fuel containers are stored.
Always disconnect the vehicle battery before
carrying out dismantling or draining work on a fuel
system.
Whenever fuel is being handled, drained or stored, or
when fuel systems are being dismantled, all forms of
ignition must be extinguished or removed; any
leadlamps must be flameproof and kept clear of
spillage.
WARNING: No one should be permitted to repair
components associated with fuel without first
having specialist training.
WARNING: Do not remove fuel system
components while the vehicle is over a pit.Fuel tank draining
Fuel tank draining should be carried out in
accordance with the procedure outlined in the FUEL
DELIVERY section of this manual and observing the
following precautions:
WARNING: Fuel must not be extracted or drained
from any vehicle while it is over a pit. Extraction
or draining of fuel must be carried out in a well
ventilated area.
The capacity of containers must be more than
adequate for the amount of fuel to be extracted or
drained. The container should be clearly marked
with its contents and placed in a safe storage
area which meets the requirements of local
authority regulations.
WARNING: When fuel has been drained from a
fuel tank the precautions governing naked lights
and ignition sources should be maintained.
Fuel tank removal
When the fuel line is secured to the fuel tank outlet by
a spring steel clip, the clip must be released before
the fuel line is disconnected or the fuel tank is
removed. This procedure will avoid the possibility of
residual petrol fumes in the fuel tank being ignited
when the clip is released.
As an added precaution, fuel tanks should have a
'FUEL VAPOUR' warning label attached to them as
soon as they are removed from the vehicle.
Fuel tank repairs
No attempt should be made to repair a plastic fuel
tank. If the structure of the tank is damaged, a new
tank must be fitted.
Body repairs
Plastic fuel pipes are particularly susceptible to heat,
even at relatively low temperature, and can be
melted by heat conducted from some distance away.
When body repairs involve the use of heat, all fuel
pipes which run in the vicinity of the repair area must
be removed, and the tank outlet plugged.
Page 64 of 1007
GENERAL DATA
04-1
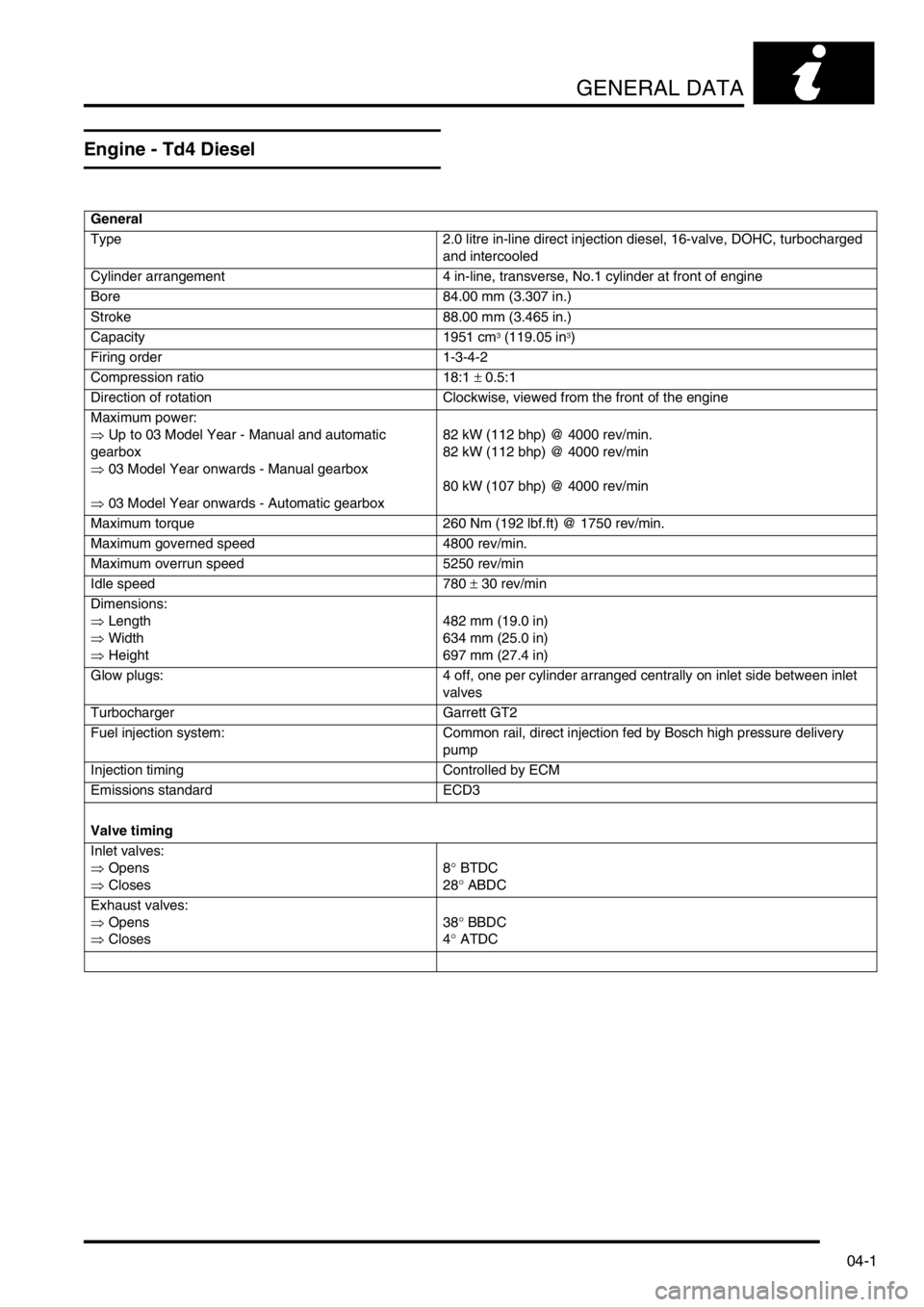
GENERAL DATA
Engine - Td4 Diesel
General
Type 2.0 litre in-line direct injection diesel, 16-valve, DOHC, turbocharged
and intercooled
Cylinder arrangement 4 in-line, transverse, No.1 cylinder at front of engine
Bore 84.00 mm (3.307 in.)
Stroke 88.00 mm (3.465 in.)
Capacity 1951 cm
3 (119.05 in3)
Firing order 1-3-4-2
Compression ratio 18:1 ± 0.5:1
Direction of rotation Clockwise, viewed from the front of the engine
Maximum power:
⇒ Up to 03 Model Year - Manual and automatic
gearbox
⇒ 03 Model Year onwards - Manual gearbox
⇒ 03 Model Year onwards - Automatic gearbox82 kW (112 bhp) @ 4000 rev/min.
82 kW (112 bhp) @ 4000 rev/min
80 kW (107 bhp) @ 4000 rev/min
Maximum torque 260 Nm (192 lbf.ft) @ 1750 rev/min.
Maximum governed speed 4800 rev/min.
Maximum overrun speed 5250 rev/min
Idle speed 780 ± 30 rev/min
Dimensions:
⇒ Length
⇒ Width
⇒ Height482 mm (19.0 in)
634 mm (25.0 in)
697 mm (27.4 in)
Glow plugs: 4 off, one per cylinder arranged centrally on inlet side between inlet
valves
Turbocharger Garrett GT2
Fuel injection system: Common rail, direct injection fed by Bosch high pressure delivery
pump
Injection timing Controlled by ECM
Emissions standard ECD3
Valve timing
Inlet valves:
⇒ Opens
⇒ Closes8° BTDC
28° ABDC
Exhaust valves:
⇒ Opens
⇒ Closes38° BBDC
4° ATDC
Page 69 of 1007
GENERAL DATA
04-6
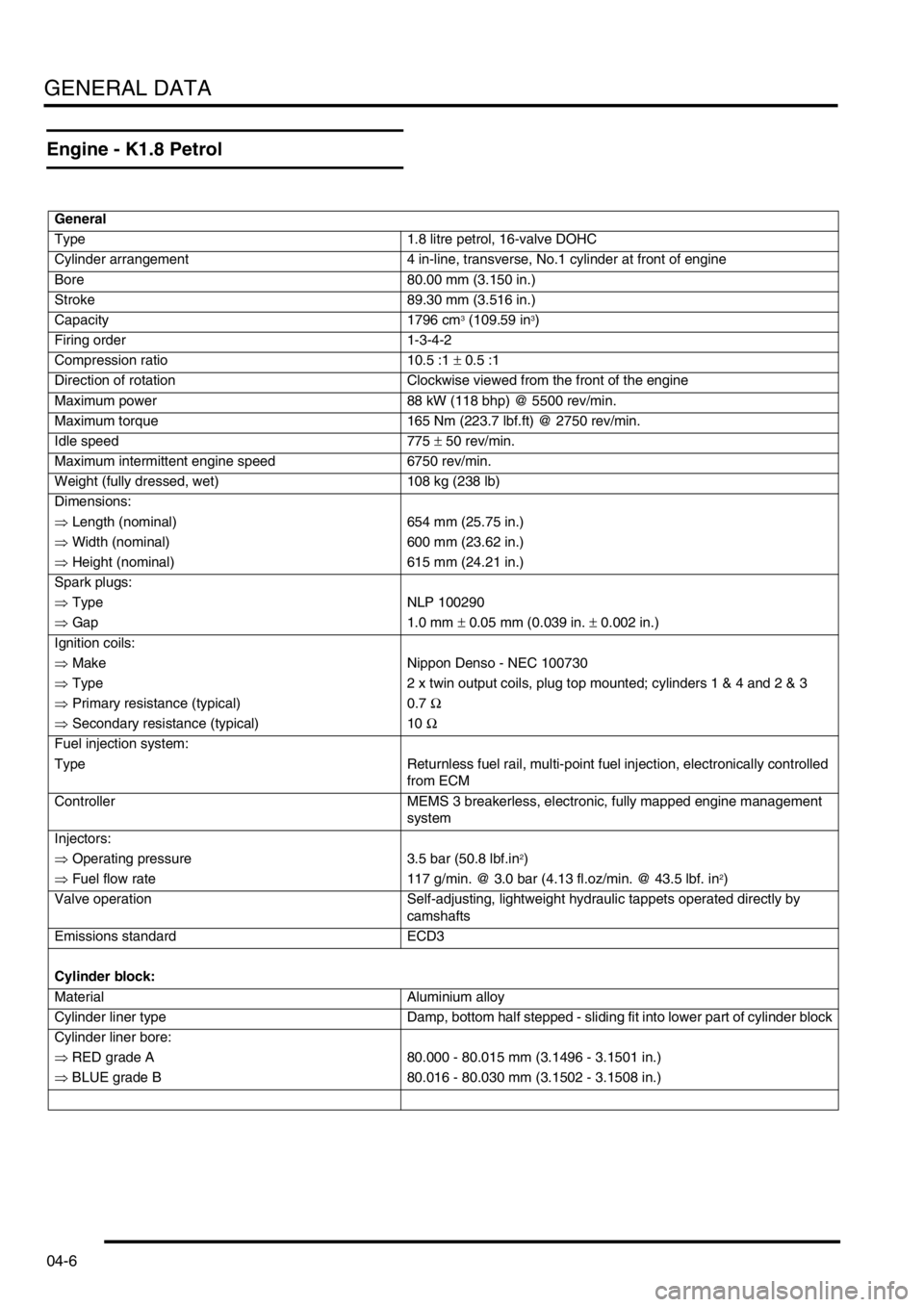
Engine - K1.8 Petrol
General
Type 1.8 litre petrol, 16-valve DOHC
Cylinder arrangement 4 in-line, transverse, No.1 cylinder at front of engine
Bore 80.00 mm (3.150 in.)
Stroke 89.30 mm (3.516 in.)
Capacity 1796 cm
3 (109.59 in3)
Firing order 1-3-4-2
Compression ratio 10.5 :1 ± 0.5 :1
Direction of rotation Clockwise viewed from the front of the engine
Maximum power 88 kW (118 bhp) @ 5500 rev/min.
Maximum torque 165 Nm (223.7 lbf.ft) @ 2750 rev/min.
Idle speed 775 ± 50 rev/min.
Maximum intermittent engine speed 6750 rev/min.
Weight (fully dressed, wet) 108 kg (238 lb)
Dimensions:
⇒ Length (nominal) 654 mm (25.75 in.)
⇒ Width (nominal) 600 mm (23.62 in.)
⇒ Height (nominal) 615 mm (24.21 in.)
Spark plugs:
⇒ Type NLP 100290
⇒ Gap 1.0 mm ± 0.05 mm (0.039 in. ± 0.002 in.)
Ignition coils:
⇒ Make Nippon Denso - NEC 100730
⇒ Type 2 x twin output coils, plug top mounted; cylinders 1 & 4 and 2 & 3
⇒ Primary resistance (typical) 0.7 Ω
⇒ Secondary resistance (typical) 10 Ω
Fuel injection system:
Type Returnless fuel rail, multi-point fuel injection, electronically controlled
from ECM
Controller MEMS 3 breakerless, electronic, fully mapped engine management
system
Injectors:
⇒ Operating pressure 3.5 bar (50.8 lbf.in
2)
⇒ Fuel flow rate 117 g/min. @ 3.0 bar (4.13 fl.oz/min. @ 43.5 lbf. in
2)
Valve operation Self-adjusting, lightweight hydraulic tappets operated directly by
camshafts
Emissions standard ECD3
Cylinder block:
Material Aluminium alloy
Cylinder liner type Damp, bottom half stepped - sliding fit into lower part of cylinder block
Cylinder liner bore:
⇒ RED grade A 80.000 - 80.015 mm (3.1496 - 3.1501 in.)
⇒ BLUE grade B 80.016 - 80.030 mm (3.1502 - 3.1508 in.)
Page 74 of 1007
GENERAL DATA
04-11
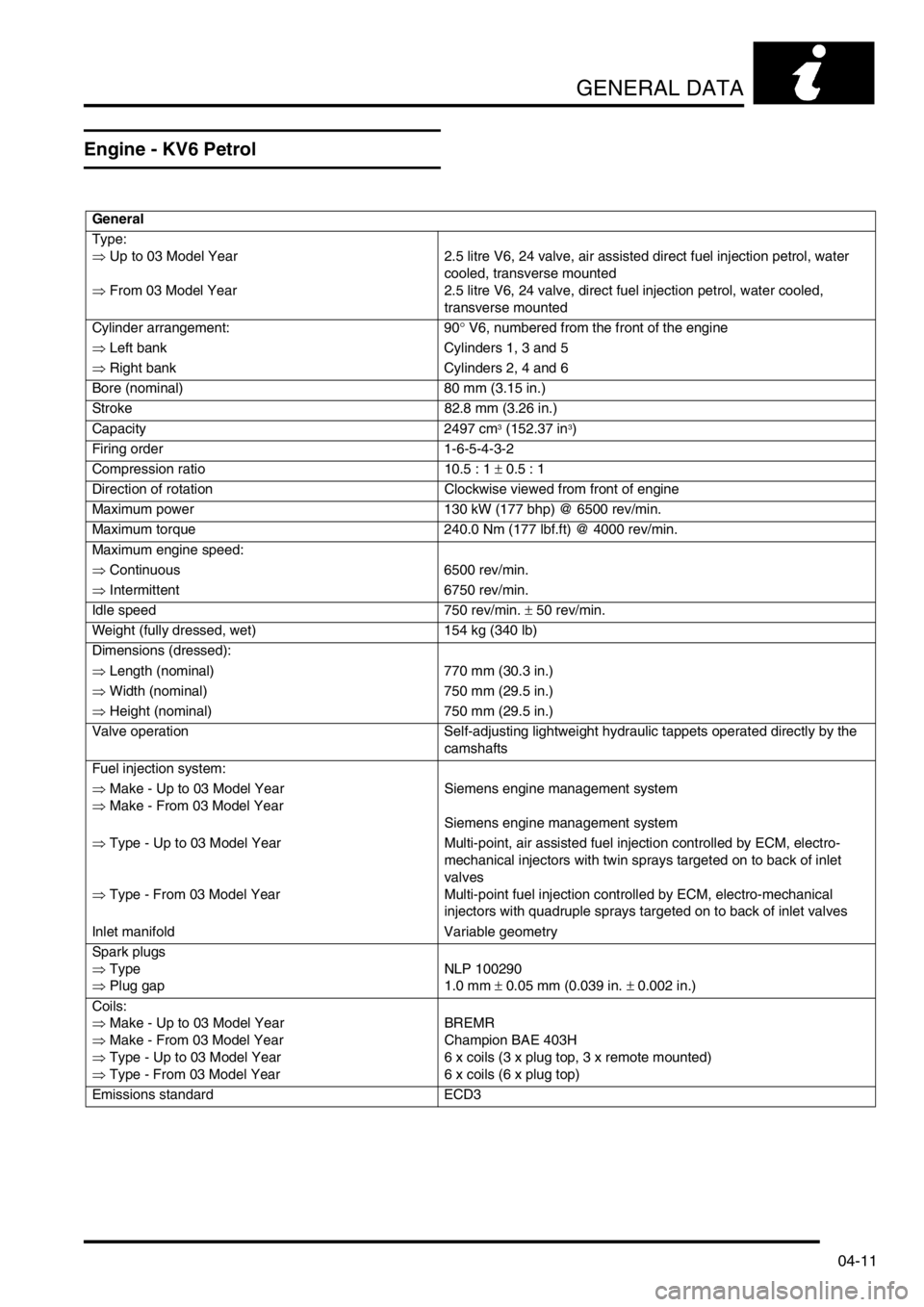
Engine - KV6 Petrol
General
Type:
⇒ Up to 03 Model Year
⇒ From 03 Model Year2.5 litre V6, 24 valve, air assisted direct fuel injection petrol, water
cooled, transverse mounted
2.5 litre V6, 24 valve, direct fuel injection petrol, water cooled,
transverse mounted
Cylinder arrangement: 90° V6, numbered from the front of the engine
⇒ Left bank Cylinders 1, 3 and 5
⇒ Right bank Cylinders 2, 4 and 6
Bore (nominal) 80 mm (3.15 in.)
Stroke 82.8 mm (3.26 in.)
Capacity 2497 cm
3 (152.37 in3)
Firing order 1-6-5-4-3-2
Compression ratio 10.5 : 1 ± 0.5 : 1
Direction of rotation Clockwise viewed from front of engine
Maximum power 130 kW (177 bhp) @ 6500 rev/min.
Maximum torque 240.0 Nm (177 lbf.ft) @ 4000 rev/min.
Maximum engine speed:
⇒ Continuous 6500 rev/min.
⇒ Intermittent 6750 rev/min.
Idle speed 750 rev/min. ± 50 rev/min.
Weight (fully dressed, wet) 154 kg (340 lb)
Dimensions (dressed):
⇒ Length (nominal) 770 mm (30.3 in.)
⇒ Width (nominal) 750 mm (29.5 in.)
⇒ Height (nominal) 750 mm (29.5 in.)
Valve operation Self-adjusting lightweight hydraulic tappets operated directly by the
camshafts
Fuel injection system:
⇒ Make - Up to 03 Model Year
⇒ Make - From 03 Model YearSiemens engine management system
Siemens engine management system
⇒ Type - Up to 03 Model Year
⇒ Type - From 03 Model YearMulti-point, air assisted fuel injection controlled by ECM, electro-
mechanical injectors with twin sprays targeted on to back of inlet
valves
Multi-point fuel injection controlled by ECM, electro-mechanical
injectors with quadruple sprays targeted on to back of inlet valves
Inlet manifold Variable geometry
Spark plugs
⇒ Type
⇒ Plug gapNLP 100290
1.0 mm ± 0.05 mm (0.039 in. ± 0.002 in.)
Coils:
⇒ Make - Up to 03 Model Year
⇒ Make - From 03 Model Year
⇒ Type - Up to 03 Model Year
⇒ Type - From 03 Model YearBREMR
Champion BAE 403H
6 x coils (3 x plug top, 3 x remote mounted)
6 x coils (6 x plug top)
Emissions standard ECD3