rotate MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER 2005 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MERCEDES-BENZ, Model Year: 2005, Model line: SPRINTER, Model: MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER 2005Pages: 1232, PDF Size: 39.23 MB
Page 26 of 1232

(2) Install the lower ball joint nut (Fig. 6). Tighten
to 280 N´m (206 ft. lbs.)
(3) Install the strut to the steering knuckle (Fig.
6). Tighten to 185 N´m (136 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the outer tie rod end to the steering
knuckle (Fig. 6) and tighten the nut to 130 N´m (96
ft. lbs.).
(5) Install the ABS sensor by pushing the sensor
all the way into the knuckle and the sensor will self
adjust when the wheel is turned.
(6) Install the hub/bearing (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/HUB / BEARING - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the disc brake caliper adapter with the
brake caliper (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/
MECHANICAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER -
INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the front wheels (Refer to 22 - TIRES/
WHEELS/WHEELS - INSTALLATION).
(9) Lower the vehicle.
(10) Check and set toe if necessary (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
LOWER BALL JOINT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the front strut (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/STRUT - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the steering knuckle (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the lower ball joint using special tool
9294-1 (Driver) with 9294-2 (Reciever) and C-4212±F.
(Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the ball joint into the lower control arm
using special tool 9294-3 (Installer ring) inserted in
9294-2 (Reciever) and C-4212±F (Fig. 7).
(2) Install the front strut (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/STRUT - INSTALLATION).
(3) Install the steering knuckle (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the tire and wheel assembly (Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - INSTALLATION).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Check the front wheel alignment (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Insert spring blocks special tool 9288 between
the spring and the spring clamp plates, While the
vehicles wheels are on the ground.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the front wheels (Refer to 22 - TIRES/
WHEELS/WHEELS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the disc brake caliper adapter (Refer to
5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL).Hang
the caliper. Do not allow brake hose to support
the caliper weight.
(5) Remove the retaining nut holding the tie rod to
the steering knuckle (Fig. 8).
(6) Seperate the tie rod off the steering knuckle
(Fig. 8) using special tool C-3894±A.
NOTE: In order to remove tension from the strut,
Raise the lower control arm approximately 10 mm
with a jack.
(7) Remove the strut bolts from the steering
knuckle (Fig. 8).
(8) Remove the stop plate bolts and rotate the
plate upwards with the stabilizer link attached (Fig.
8).
(9) Lower the lower control arm.
(10) Remove the lower ball joint nut from the
steering knuckle (Fig. 8).
(11) Separate the lower ball joint from the knuckle
using special tool 9282.
(12) Remove the lower control arm nuts and bolts
from the frame (Fig. 8).
(13) Remove the lower control arm.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the lower control arm to the frame.
Hand tighten the nuts and bolts.
Fig. 7 LOWER BALL JOINT
1 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
2 - LOWER BALL JOINT
2 - 6 FRONTVA
KNUCKLE (Continued)
Page 27 of 1232

NOTE: In order to remove tension from the strut,
Raise the lower control arm approximately 10 mm
with a jack.
(2) Install the lower ball joint into the steering
knuckle. Tighten to 280 N´m (206 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install the strut bolts to the steering knuckle
(Fig. 8). Tighten to 185 N´m (136 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the stop plate (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/SPRING STOP PLATES - INSTALLA-
TION).
(5) Lower the lower control arm.
(6) Attach the tie rod to the steering knuckle (Fig.
8). Tighten the nut to 130 N´m (96 ft. lbs.)
(7) Install the disc brake caliper adapter (Refer to
5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - INSTALLATION)
(Fig. 8).
(8) Install the front tire & wheel assembly (Refer
to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(9) Lower the vehicle.
(10) Remove the spring blocks between the spring
and the spring clamp plates, While the vehicles
wheels are on the ground.
(11) Roll the vehicle approximately 1 mm forwards
and the backwards, and rock firmly.(12) Tighten the lower control arm nuts and bolts
to the frame to 150 N´m (110 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 8).
(13) Apply brake to actuate brake pressure.
SPRING
REMOVAL
(1)To do this next step the vehicle must be
on the ground.Remove the front and rear bolts on
the left and right spring clamp plates (Fig. 9).
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the front wheels.
(4) Remove the brake caliper adapter (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL).Do not
allow the caliper to hang by the hose, support
the caliper accordingly.
(5) Remove the ABS sensor from the mounting
bore in the steering knuckle (Fig. 9).
(6) Remove the outer tie rod retaining nut and
separate the tie rod from the knuckle (Fig. 9) using
special tool C-3894±A.
NOTE: In order to remove tension from the strut,
Raise the lower control arm approximately 10 mm
with a jack.
(7) Remove the strut bolts from the steering
knuckle.
(8) Remove both stop plate bolts and rotate the
plates upwards with the stabilizer link attached.
(9) Lower the lower control arm.
(10) Remove the lower ball joint nut from the
steering knuckle.
(11) Separate the lower ball joint from the knuckle
using special tool 9282.
(12) Remove the lower control arm nuts and bolts
from the frame.
(13) Remove the lower control arm from the frame
(Fig. 9).
NOTE: To avoid damaging the transverse leaf
spring, cushion the pad on the jack accordingly.
(14) Support the transverse leaf spring in the cen-
ter with a jack.
(15) Remove the left and right spring clamp plates
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/SPRING CLAMP
PLATES - REMOVAL) (Fig. 9).
NOTE: The upper spring blocks between the engine
cradle and the spring are color coded, Make sure
not to mix the blocks per sides. The blocks are dif-
ferent in sizes to accommodate the weight of the
vehicle and driver in order for the vehicle to sit
level.
Fig. 8 LOWER CONTROL ARM
1 - STRUT
2 - LOWER CONTROL ARM BOLT
3 - STOP PLATE BOLT
4 - STOP PLATE
5 - CALIPER ADPTER BOLT
6 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
7 - LOCKING BOLT
8 - DISC BRAKE ROTOR
9 - OUTER TIE ROD END RETAINING NUT
10 - OUTER TIE ROD END
11 - LOWER BALL JOINT NUT
12 - LOWER BALL JOINT
13 - LOWER CONTROL ARM NUTS
14 - STRUT BOLT
VAFRONT 2 - 7
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
Page 38 of 1232
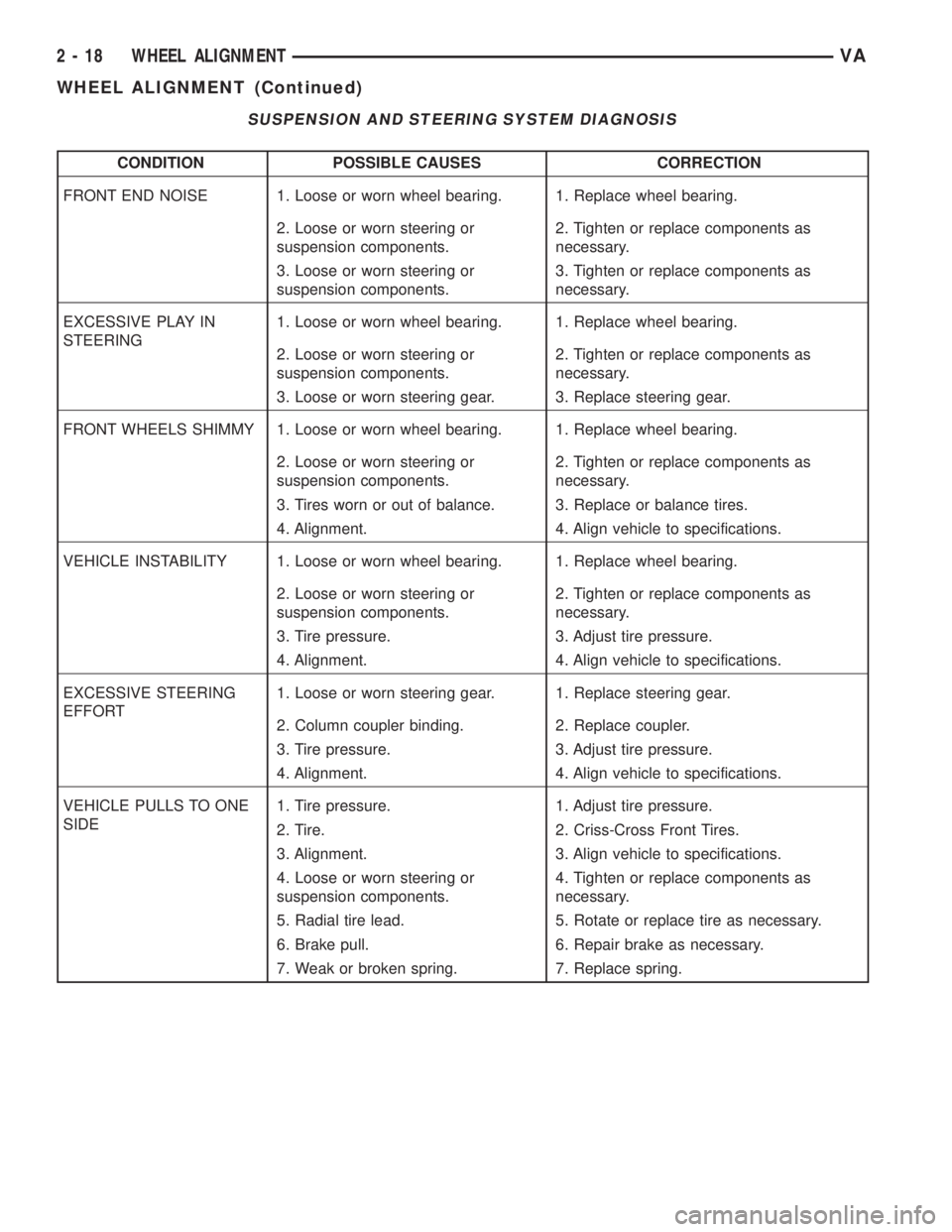
SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FRONT END NOISE 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.3. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN
STEERING1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Loose or worn steering gear. 3. Replace steering gear.
FRONT WHEELS SHIMMY 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Tires worn or out of balance. 3. Replace or balance tires.
4. Alignment. 4. Align vehicle to specifications.
VEHICLE INSTABILITY 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 1. Replace wheel bearing.
2. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.2. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
3. Tire pressure. 3. Adjust tire pressure.
4. Alignment. 4. Align vehicle to specifications.
EXCESSIVE STEERING
EFFORT1. Loose or worn steering gear. 1. Replace steering gear.
2. Column coupler binding. 2. Replace coupler.
3. Tire pressure. 3. Adjust tire pressure.
4. Alignment. 4. Align vehicle to specifications.
VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE
SIDE1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Tire. 2. Criss-Cross Front Tires.
3. Alignment. 3. Align vehicle to specifications.
4. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.4. Tighten or replace components as
necessary.
5. Radial tire lead. 5. Rotate or replace tire as necessary.
6. Brake pull. 6. Repair brake as necessary.
7. Weak or broken spring. 7. Replace spring.
2 - 18 WHEEL ALIGNMENTVA
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 43 of 1232

(15) If vibration remains unacceptable, preform
the procedure to the front end of the propeller shaft.
(16) Install the wheel and tires. Lower the vehicle.
PROPELLER SHAFT RUNOUT
(1) Clean the propeller shaft surface where the
dial indicator will contact the shaft.
(2) The dial indicator must be installed perpendic-
ular to the shaft surface.
(3) Measure runout at the center and ends of the
shaft away from weld areas, to ensure weld process
will not effect the measurements.
(4) Refer to Runout Specifications chart.
(5) If propeller shaft is out of specification, remove
propeller shaft and index the shaft 180É. Install the
propeller shaft and measure shaft runout again.
(6) If propeller shaft is now within specifications,
mark shaft and yokes for proper orientation.
(7) If propeller shaft runout is not within specifica-
tions, check runout of the transmission and axle.
Correct as necessary and repeat propeller shaft
runout measurement.
(8) Replace propeller shaft if the runout still
exceeds the limits.
RUNOUT SPECIFICATIONS
Front of Shaft 0.020 in. (0.50 mm)
Center of Shaft 0.025 in. (0.63 mm)
Rear of Shaft 0.020 in. (0.50 mm)
note:
Measure front/rear runout approximately 76 mm (3 in.)
from the weld seam at each end of the shaft tube for
tube lengths over 30 inches. For tube lengths under
30 inches, the maximum allowed runout is 0.50 mm
(0.020 in.) for the full length of the tube.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
PROPELLER SHAFT ANGLE
This procedure applies the front and rear propeller
shafts.
(1) Place vehicle in netural.
(2) Raise and support vehicle at the axles as level
as possible.
(3) Remove universal joint snap rings if equipped,
so Inclinometer 7663 base sits flat.
(4) Rotate shaft until transmission case output
yoke bearing is facing downward.
NOTE: Always make measurements from front to
rear and from the same side of the vehicle.
(5) Place Inclinometer 7663 on yoke bearing (A)
parallel to the shaft. Center bubble in sight glass and
record measurement.
Fig. 1 Clamp Screw At Position 1
1 - CLAMP
2 - SCREWDRIVER
Fig. 2 Two Clamp Screws At The Same Position
Fig. 3 Clamp Screws Separated
1-1¤2INCH
VAPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 3
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 44 of 1232

This measurement will give you the transmis-
sion yoke Output Angle (A).
(6) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place
inclinometer on yoke bearing parallel to the shaft.
Center bubble in sight glass and record measure-
ment. This measurement can also be taken at the
rear end of the shaft.
This measurement will give you the Propeller
Shaft Angle (C).
(7) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place
inclinometer on companion flange yoke bearing par-
allel to the shaft. Center bubble in sight glass and
record measurement.
This measurement will give you the Pinion
Flange Input Angle (B).
(8) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
A) to obtain TransmissionOutput Operating
Angle.(9) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
B) to obtain axleInput Operating Angle.
Refer to rules and example in (Fig. 4) for addi-
tional information.
RULES
²Good cancellation of U-joint operating angles
should be within 1degree.
²Operating angles should be less than 3 degrees.
²At least 1/2 of one degree continuous operating
(propeller shaft) angle.
TWO/THREE-PIECE PROPELLER SHAFT
The procedure to measure the propeller shaft
angles involved with a two/three-piece (Fig. 5) propel-
ler shaft is the same as those for a one-piece propel-
ler shaft.
Fig. 4 UNIVERSAL JOINT ANGLE EXAMPLE
1 - 4.9É Angle (C)
2 - 3.2É Angle (B)
3 - Input Yoke4 - 3.0É Angle (A)
5 - Output Yoke
3 - 4 PROPELLER SHAFTVA
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 50 of 1232

REAR AXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR AXLE
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAIN AND FILL . . 11
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
SPECIFICATIONS.......................13
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................14
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15AXLE BEARINGS/SEALS
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
AXLE SHAFTS - DUAL REAR WHEELS
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
AXLE HUB BEARINGS/SEALS
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................20
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
REAR AXLE
DESCRIPTION
The axle housings consist of a cast iron center sec-
tion with axle tubes extending from either side. The
tubes are pressed into and welded to the differential
housing to form a one-piece axle housing. The SRW
axle has semi-floating axle shafts, DRW has full-
floating axle shafts.
NOTE: Axle seals, axle bearings, pinion seal and
differential cover are the only serviceble compo-
nents. If differential is damaged/noisy the axle must
be replaced.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transmission
through the rear propeller shaft. The rear propeller
shaft is connected to the pinion gear which rotates
the differential through the gear mesh with the ring
gear bolted to the differential case. The engine power
is transmitted to the axle shafts through the pinion
mate and side gears. The side gears are splined to
the axle shafts.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
NOTE: Axle seals, axle bearings, pinion seals and
differential cover are the only serviceble compo-
nents. If differential is damaged/noisy the axle must
be replaced.
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, incorrect pinion depth, tooth
contact, worn/damaged gears, or the carrier housing
not having the proper offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion shaft can also cause a snap-
ping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearingshave a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
3 - 10 REAR AXLEVA
Page 51 of 1232

heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Differential bearings usually produce a low pitch
noise. Differential bearing noise is similar to pinion
bearing noise. The pitch of differential bearing noise
is also constant and varies only with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearingsproduce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
NOTE: All driveline components should be exam-
ined before starting any repair.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listenfor the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAIN AND FILL
NOTE: Drain oil when warm.
(1) Clean area around oil fill plug and drain plug.
(2) Remove oil drain plug and drain oil (Fig. 1).
(3) Install oil drain plug and tighten to N´m 100
(74 ft. lbs.).
(4) Remove oil fill plug and fill housing up to bot-
tom edge of oil fill hole (Fig. 1).
(5) Install oil fill plug and tighten to N´m 100 (74
ft. lbs.).
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the axle
and secure axle to device.
(3) Remove wheels and tires.
(4) Unplug wear indicator cable (Fig. 2) and (Fig.
3).
(5) Detach cable connector for brake pad wear
indicator.
(6) Remove ABS sensor and clamp bushing from
mounting bore.
NOTE: The right-hand ABS sensor cable is labeled
at the factory with a white tag.
(7) Remove cable ties from the park brake cables.
Release connection cable of brake pad wear indicator
and ABS sensor cable up to the relay unit of the
parking brake.
(8) Remove brake cables from adjuster.
(9) Remove brake calipers with adapters and lines.
Fig. 1 FILL PLUG
1 - FILL PLUG
2 - DRAIN PLUG
VAREAR AXLE 3 - 11
REAR AXLE (Continued)
Page 62 of 1232

PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wheels.
(2) Push back brake pads and release hand brake.
NOTE: If it is not possible to spin rear axle shafts
manually, detach rear brake cables.
(3) Drain rear axle oil.
(4) Remove propeller shaft.
(5) Spin pinion flange by hand and check axial
play of bearing.
CAUTION: There must not be any thrust bearing
play. If play excess or there are particles (shavings)
in the drained oil, replace gear assembly.
(6) Mark installation position of collared nut (Fig.
26) with respect to drive pinion.
(7) Unlock collared nut.
(8) Hold pinion flange with Flange Wrench C-3281
and remove nut.
(9) Remove pinion flange from pinion shaft with
Flange Puller 8992 (Fig. 27).
(10) Check sealing surfaces of joint flange for score
marks and replace joint flange if necessary.
(11) Remove both pinion radial seals (Fig. 28).
INSTALLATION
(1) Pack space between dust lip and sealing lip on
radial seal ring with multi-purpose grease.
(2) On radial seal rings without rubberized exter-
nal surface, coat outer circumference with sealant.CAUTION: Do not coat partially rubberized seals
with sealant.
(3) Drivenewpinion radial seals into rear axle
housing as far as the stop using Installer 9276 (Fig.
29).
(4) Fit coupling flange on drive pinion shaft.
NOTE: The groove in the drive pinion and the
groove in the joint flange must be in alignment.
(5) Hold pinion flange with Flange Wrench C-3281.
(6) Screw on the collared nut illustrated up to the
marking applied beforehand.
(7) Detach retainer wrench from joint flange.
(8) With a torque wrench, measure torque to
rotate pinion and record measurement.
Fig. 26 COLLARED NUT
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - COLLARED NUT
Fig. 27 FLANGE PULLER
1 - FLANGE PULLER
2 - PINION FLANGE
Fig. 28 PINION SEALS
1 - SEALS
2 - AXLE
3 - 22 REAR AXLEVA
Page 63 of 1232

(9) Unscrew the marked nut.
(10) Reattach retainer wrench to joint flange.
(11) Screw onnewcollared nut and tighten care-
fully in stages until the previously value of torque to
rotate is exceeded by 0.5 N´m. (4.4 in. lbs.).
CAUTION: The total friction moment must not be
obtained by slackening the collared nut. Avoid over-
tightening the collared nut otherwise the compres-
sion ring inside will be compressed and will have to
be replaced. This requires total disassembly of the
gear set.
(12) Cut the collar of the tightened collared nut
(Fig. 30).
(13) Bend collar so it touches the wall of the slot
in the pinion shaft (Fig. 31).(14) Connect propeller shaft to pinion flange.
(15) Pour in oil up to bottom edge of oil filler hole
(Fig. 32).
(16) Screw in oil filler plug and tighten to 100 N´m
(74 ft. lbs.).
(17) Install wheels at rear axle.
(18) Operate brake pedal several times until brake
pads contact brake discs (brake pressure built up).
(19) Attach rear brake cables if removed and
adjust parking brake.
Fig. 29 PINION SEAL INSTALLER
1 - AXLE
2 - INSTALLER
Fig. 30 COLLARED NUT
Fig. 31 BEND COLLAR OF NUT
1 - COLLARED NUT
2 - DRIFT
Fig. 32 FILL PLUG
1 - FILL PLUG
2 - DRAIN PLUG
VAREAR AXLE 3 - 23
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 91 of 1232

(7) Remove the adjuster (Fig. 37).
(8) Remove the pressure springs (Fig. 37). by
depressing with your fingers and twisting.
(9) Remove the rear park brake shoes (Fig. 37).
Pull the park brake shoes apart at the bottom
and remove them together with the adjuster.
CLEANING - REAR DRUM IN HAT BRAKE
Clean the individual brake components, including
the support plate exterior, with a water dampened
cloth or with brake cleaner. Do not use any other
cleaning agents. Remove light rust and scale from
the brake shoe contact pads on the support plate
with fine sandpaper.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - (SRW)
NOTE: Preassemble the retracting spring with the
short hook eye from the inside together with the
adjuster wheel at the bottom. Fit the preassembled
park brake shoes on the brake carrier.
(1)Ensure that the cable lock moves easily
before installing shoes.Install the park brake
shoes.(2) Install the lower retracting spring using special
tool 9280.
(3) Install the hold down springs using special tool
9281.
(4) Install the upper retracting spring using spe-
cial tool 9280.
(5) Install the adjuster.
(6) Install the front park brake cable to the pulley
unit.
(7) Install the disc brake rotor.
(8) Install the rear wheels.
(9) Adjust the parking brakes.
(10) Lower the vehicle.
(11) Pump the brake pedal several times to check
the operation of the brakes before moving vehicle.
INSTALLATION - (DRW)
NOTE: Preassemble the retracting spring with the
short hook eye from the inside together with the
adjuster wheel at the bottom. Fit the preassembled
park brake shoes on the brake carrier.
(1)Ensure that the cable lock moves easily
before installing shoes.Install the park brake
shoes.
(2) Install the lower retracting spring.
(3) Install the pressure hold down springs by
depressing with your fingers and twisting to lock in
place.
(4) Install the upper retracting spring.
(5) Install the adjuster.
(6) Install the front park brake cable to the pulley
unit.
(7) Install the disc brake rotor.
(8) Install the rear wheel flange ring. Tighten to
200 N´m (148 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the rear wheels.
(10) Adjust the parking brakes.
(11) Lower the vehicle.
(12) Pump the brake pedal several times to check
the operation of the brakes before moving vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the rear wheels.
(3) Turn the adjusting wheel through the hole of
the wheel lug bolt until it is no longer possible to
rotate the rear wheel (Fig. 38).
Fig. 37 PARK BRAKE SHOES WITH DUAL REAR
WHEELS
1 - HOLD DOWN PIN
2 - PRESSURE SPRING
3 - ADJUSTER
4 - UPPER RETRACTING SPRING
5 - LOWER RETRACTING SPRING
6 - CABLE LOCK
7 - LOCKING PIN
8 - BRAKE CABLE
9 - PARK BRAKE SHOE
VABRAKES - BASE 5 - 27
SHOES (Continued)