automatic transmission MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 8 of 1146
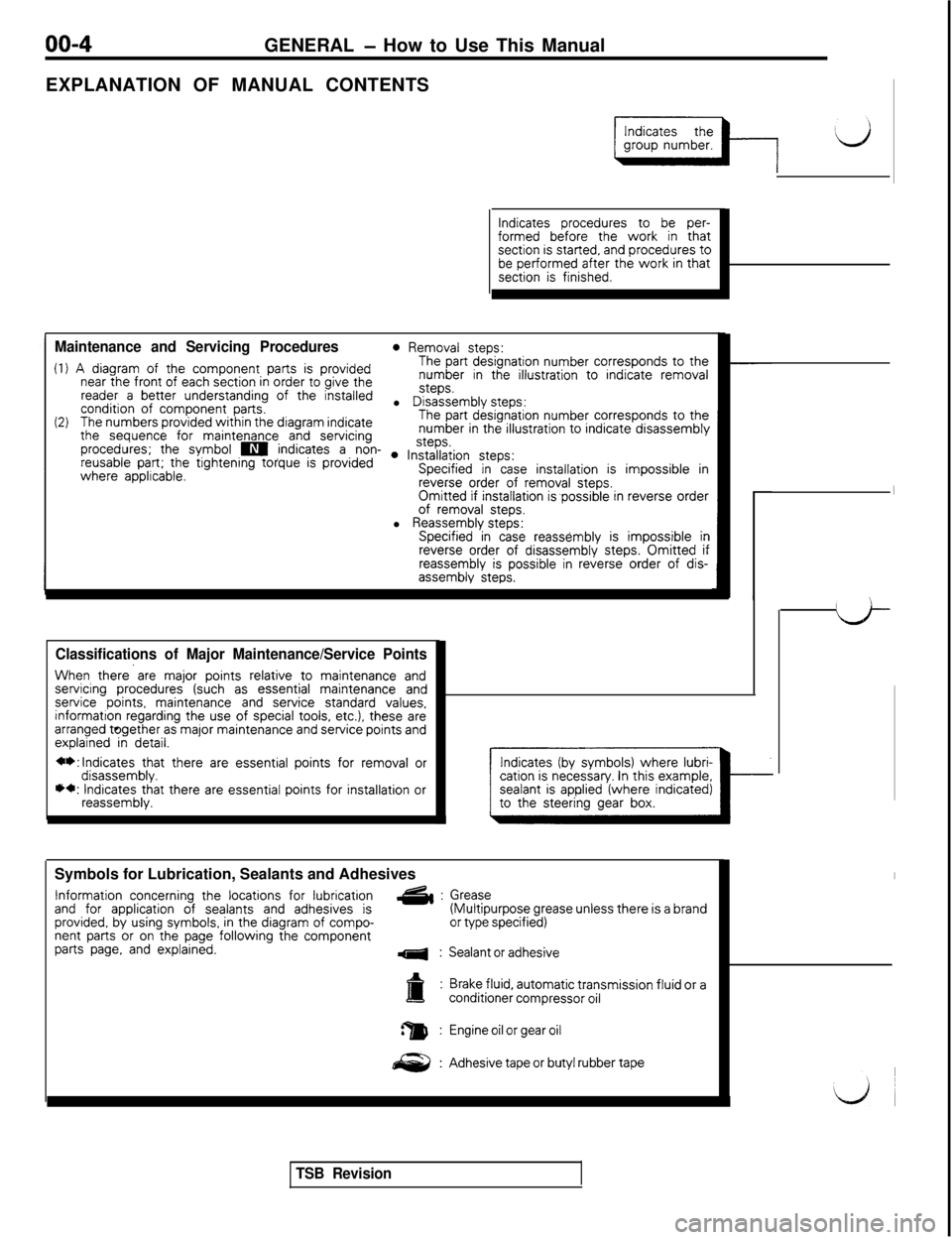
GENERAL - How to Use This Manual
EXPLANATION OF MANUAL CONTENTS
Indicates procedures to be per-formed before the work in thatsection is started, and procedures tobe performed after the work in thatsection is finished.
Maintenance and Servicing Procedures0 Removal steps:
(1) A diagram of the component parts is providedThe part designation number corresponds to the
near the front of each section in order to give thenumber in the illustration to indicate removal
reader a better understanding of the installedsteps.
condition of component parts.l Disassembly steps:
(2)The numbers provided within the diagram indicateThe part designation number corresponds to the
the sequence for maintenance and servicingnumber in the illustration to indicate disassembly
procedures; the symbol m indicates a non- . ln~~~~iion steps:reusable part; the tightening torque is providedwhere applicable.Specified in case installation is impossible inreverse order of removal steps.Omitted if installation is,possible in reverse orderof removal steps.l Reassembly steps:Specified in case reassembly is impossible inreverse order of disassembly steps. Omitted ifreassembly is possible in reverse order of dis-assembly steps.
Classifications of Major Maintenance/Service Points
When there’are major points relative to maintenance andservicing procedures (such as essential maintenance andservice points, maintenance and service standard values,informatton regarding the use of special toois, etc.), these arearranged together as major maintenance and service points andexplained in detail.
**:lndicates that there are essential points for removal ordisassembly.*+: Indicates that there are essential points for installation orreassembly.Symbols for Lubrication, Sealants and Adhesives
Information concerning the locations for lubricationand for application of sealants and adhesives isG&:
provided, by using symbols, in the diagram of compo-nent parts or on the page following the componentparts page, and explained.4:
Indicates (by symbols) where lubri-cation is necessary. In this example,
Grease(Multipurpose grease unless there is a brandor type specified)
Sealant or adhesive
Brake fluid, automatic transmission fluid or aconditioner compressor oil
Engine oil or gear oil
Adhesive tape or butyl rubber tape
TSB Revision
Page 44 of 1146

00-40
GENERAL - Maintenance Service
(2) Check that the transaxle oil level is at the lower portion of
the filler plug hole. For AWD-vehicles, check that the
transfer oil level is at the portion shown in the illustration.
(3) Check to be sure that the transmission oil is not noticeably
‘ddirty, and that it has a suitable viscosity.
10. AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
(Inspect fluid level)
MOOSEDL
1.Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual tempera-
ture
[70 - 80°C (160 - 18O”F)I.2. Place vehicle on level floor.
3. Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic circuit with fluid, then place
lever in “N” Neutral position. This operation is necessary to
be sure that fluid level check is accurate.
4. Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area around
dipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the condition
of the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.
l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
lIf there is a noticeably great amount of metal particles in
the fluid.
5. Check to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick. If
fluid level is low, add ATF until level reaches “HOT” range.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions because it
allows pump to take in air along with fluid. Air trapped in
hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make fluid spongy.
Therefore, pressures will be erratic.
Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. When
transaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam and
cause same conditions which occur with low fluid level,
resulting in accelerated deterioration of ATF transmission
fluid.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch, and
servo operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for a leak.
6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely.
L/(Change fluid)
Drain the fluid and check whether there is any evidence of
contamination.
Replenish with new fluid after the cause of any contamination
has been corrected.
(1) Remove drain plug at transaxle case bottom to let fluid
drain.(2) Place a drain container with large opening under the
transaxle oil pan.
(3) Loosen oil pan bolts and tap pan at one corner to break it
loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove oil pan.
d
TSB Revision
Page 137 of 1146
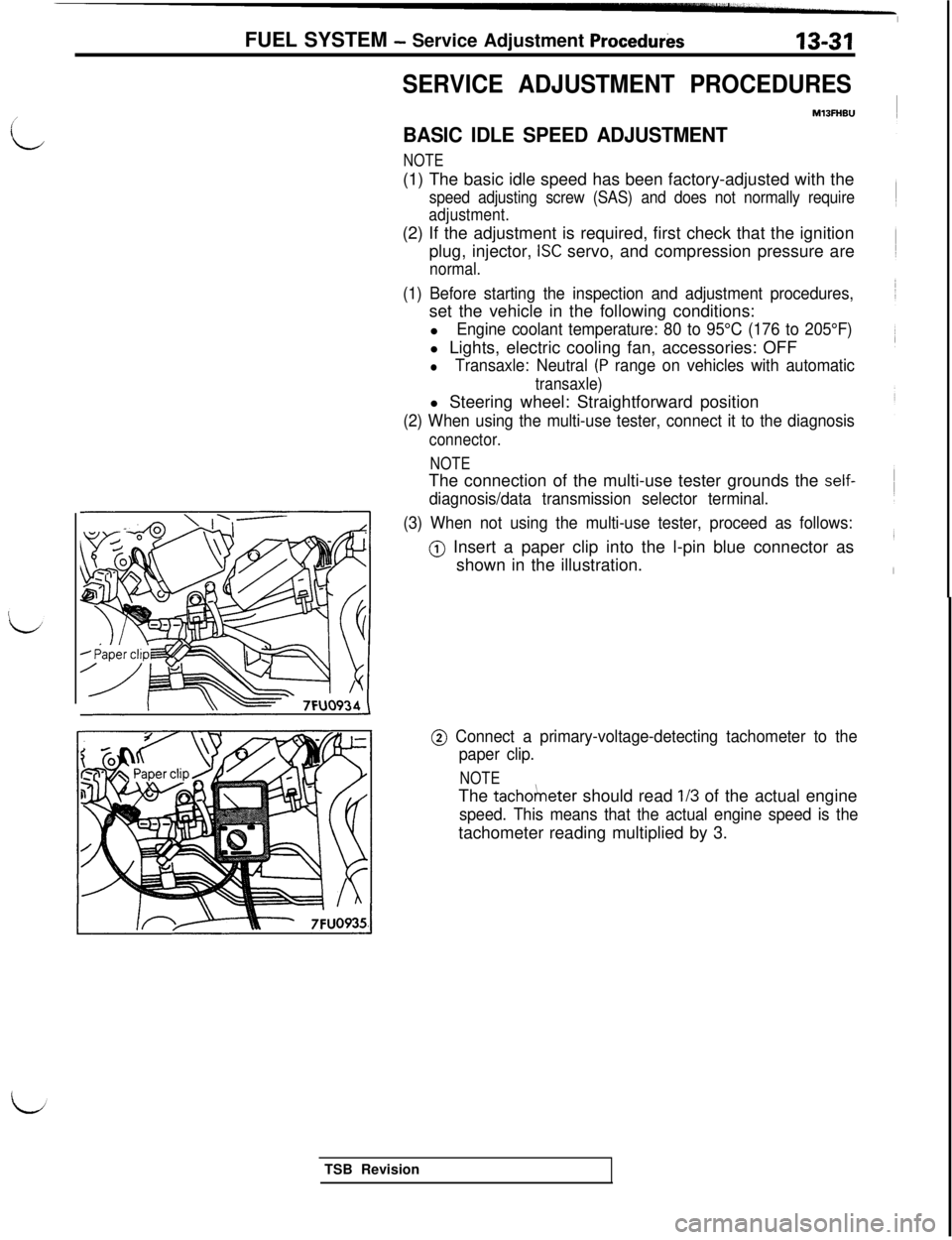
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
MlBFHSU
BASIC IDLE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
NOTE(1) The basic idle speed has been factory-adjusted with the
speed adjusting screw (SAS) and does not normally require
adjustment.(2) If the adjustment is required, first check that the ignition
plug, injector,
ISC servo, and compression pressure are
normal.
(1) Before starting the inspection and adjustment procedures,set the vehicle in the following conditions:
l
Engine coolant temperature: 80 to 95°C (176 to 205°F)l Lights, electric cooling fan, accessories: OFF
lTransaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with automatic
transaxle)l Steering wheel: Straightforward position
(2) When using the multi-use tester, connect it to the diagnosis
connector.
NOTEThe connection of the multi-use tester grounds the
self-
diagnosis/data transmission selector terminal.
(3) When not using the multi-use tester, proceed as follows:
@) Insert a paper clip into the l-pin blue connector as
shown in the illustration. FUEL SYSTEM
- Service Adjustment Procedurks13-31
i
@ Connect a primary-voltage-detecting tachometer to the
paper clip.
NOTEThe
tacho/neter should read l/3 of the actual engine
speed. This means that the actual engine speed is thetachometer reading multiplied by 3.
TSB Revision
Page 272 of 1146
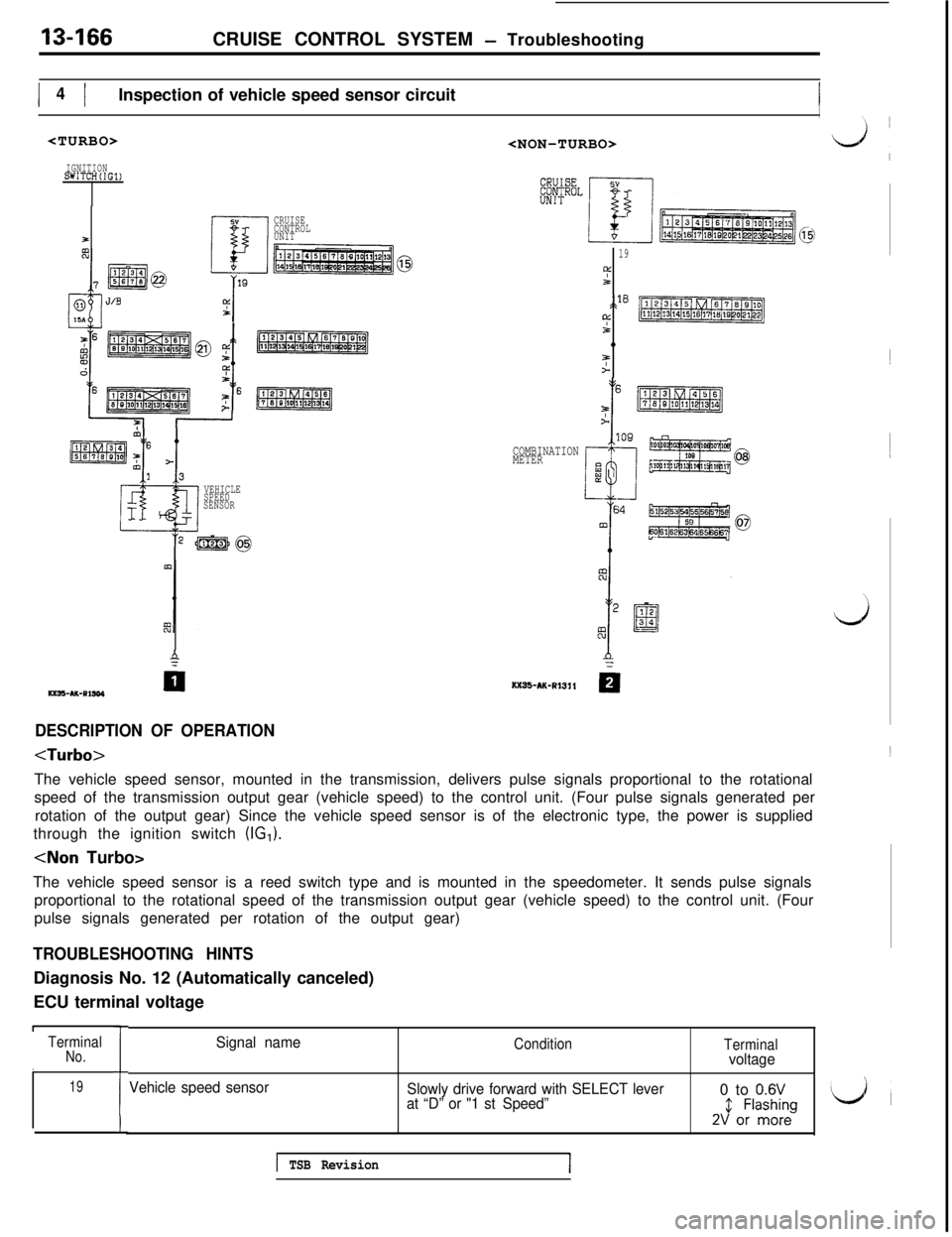
13466CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
I I4Inspection of vehicle speed sensor circuitI
IGNITIONSWITCH(IG1)
5”
El
CRUISE
CONTROL
3UNIT
cl!AI
g6pl!Ezq@zla
;i
d
“m ;ygmq%q
?
VEHICLE
SPEED
SENSOR
xX35-AR-RI304P
19Y
*
$
&
~E$iJ
0z
L
COMBINATION
METER
KX35-AK-Rl3Yla
DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION
The vehicle speed sensor, mounted in the transmission, delivers pulse signals proportional to the rotational
speed of the transmission output gear (vehicle speed) to the control unit. (Four pulse signals generated per
rotation of the output gear) Since the vehicle speed sensor is of the electronic type, the power is supplied
through the ignition switch (IG,).
The vehicle speed sensor is a reed switch type and is mounted in the speedometer. It sends pulse signals
proportional to the rotational speed of the transmission output gear (vehicle speed) to the control unit. (Four
pulse signals generated per rotation of the output gear)
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTSDiagnosis No. 12 (Automatically canceled)
ECU terminal voltage
1TerminalNo.I19
i
Signal nameCondition
Terminalvoltage
Vehicle speed sensor
Slowly drive forward with SELECT lever0 to
0.6Vat “D” or "1 st Speed”2J &l;;:neg
1 TSB RevisionI
LjlI~~
\
J1
l/j,
Page 443 of 1146

23-1
AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
CONTENTSMZJAA- _
ANNULUS GEAR AND TRANSFER DRIVE GEARTransmission Fluid Level Inspection................................46SET................................................................................................
102Transmission Fluid Replacement........................................
46
DIFFERENTIAL........................................................................104SPECIAL TOOLS........................................................................
16
:......................................... 12IEND CLUTCH ASSEMBLY....................................................99SPECIFICATIONS..........................
FRONT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY................................................95
GENERAL INFORMATlON....................................................2
KICKDOWN SERVO................................................................
107
LOW-REVERSE BRAKE............................................................
107
OIL PUMP....................................................................................93
PLANETARY GEAR................................................................
100
REAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY....................................................97
SELECTOR LEVER ASSEMBLY............................................58
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES............................46
Accelerator Switch
Inspection and Adjustment................
50Drive Shaft Oil Seals Replacement....................................
52Inhibitor Switch and Control Cable Adjustment................
52Key Interlock Mechanism Check........................................50KickdownServo Adjustment................................................
47Line Pressure Adjustment....................................................
48Reducing Pressure Adjustment........................................
49Selector Lever Operation Check........................................
50Shift Lock Mechanism Check............................................51Speedometer Cable Replacement....................................53
General Specifications........................................................12Lubricants............................................................................15Service Specifications........................................................12Spacer and Snap Ring........................................................13Valve Body Spring Identification Chart............................13
SPEEDOMETER DRIVEN GEAR ASSEMBLY....................106
TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY........................................................62
TRANSAXLE CONTROL*........................................................54
TRANSAXLE OIL COOLER, HOSES, TUBES
....................66
TRANSFER SHAFT....................................................................92
TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................
19
A/T Safety-lock System Troubleshooting........................44Converter Stall Test............................................................
43
Diagnosis and Test
................................................................
22
Element in Use at Each Position of Selector Lever........31Inspection
of ControlSystem............................................
28Inspection of Electronic Control System Components....32Oil Pressure Tests................................................................
39ShiftPatterns....................................................................
31,42Troubleshooting Guide........................................................
20
VALVE BODY. . . .._._.................................................................... 108
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS)
(1)A Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), which uses a driver-side air bag, has been installed in the 3668GT.(2)The SRS includes the following components: impact sensors, SRS diagnosis unit: SRS warning light, air bagmodule, clock spring, interconnecting wiring. Other SRS-related components (that may have to beremoved/installed in connection with SRS service or maintenance) are indicated in the table of contents byan asterisk (*).
WARNING!(1)Improper service or maintenance of any component of the SRS, or any SRS-related component, can lead topersonal injury or death to service personnel (from inadvertent firing of the air bag) or to the driver (from
rendering the SRS inoperative).
(2) Service or maintenance of any SRS component or SRS-related component must be performed only at an
authorized MITSUBISHI dealer.
(3) MlTSUBISHI dealer personnel must thoroughly review this manual, and especially its GROUP 52B -Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), before beginning any service or maintenance of any component of the
ISRS or any SRS-related component.
Page 481 of 1146
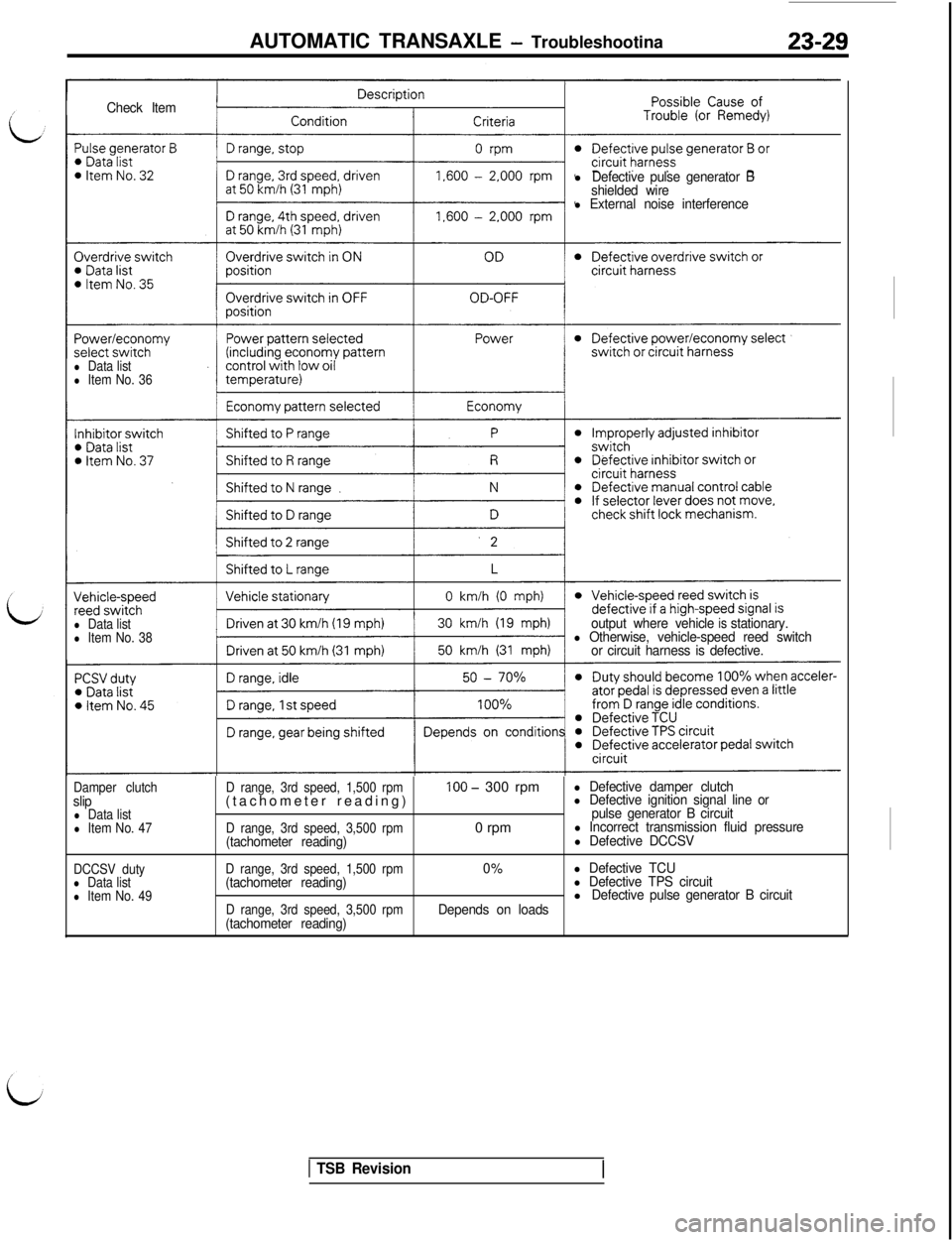
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshootina23-29
Check Iteml
Defective pulse generator B
shielded wire
l External noise interference
l Data listl Item No. 36
l Data listl Item No. 38output where vehicleisstationary.l Otherwise, vehicle-speed reed switch
or circuit harness is defective.
Damper clutchslipl Data listl Item No. 47
DCCSV duty
l Data listl Item No. 49D range, 3rd speed, 1,500 rpm(tachometer reading)
D range, 3rd speed, 3,500 rpm(tachometer reading)
D range, 3rd speed, 1,500 rpm(tachometer reading)
D range, 3rd speed, 3,500 rpm(tachometer reading)
100 - 300 rpm
0 rpm
0%
Depends on loads
l Defective damper clutchl Defective ignition signal line or
pulse generator B circuit
l Incorrect transmission fluid pressurel Defective DCCSV
l Defective TCUl Defective TPS circuitlDefective pulse generator B circuit
1 TSB Revision
Page 482 of 1146
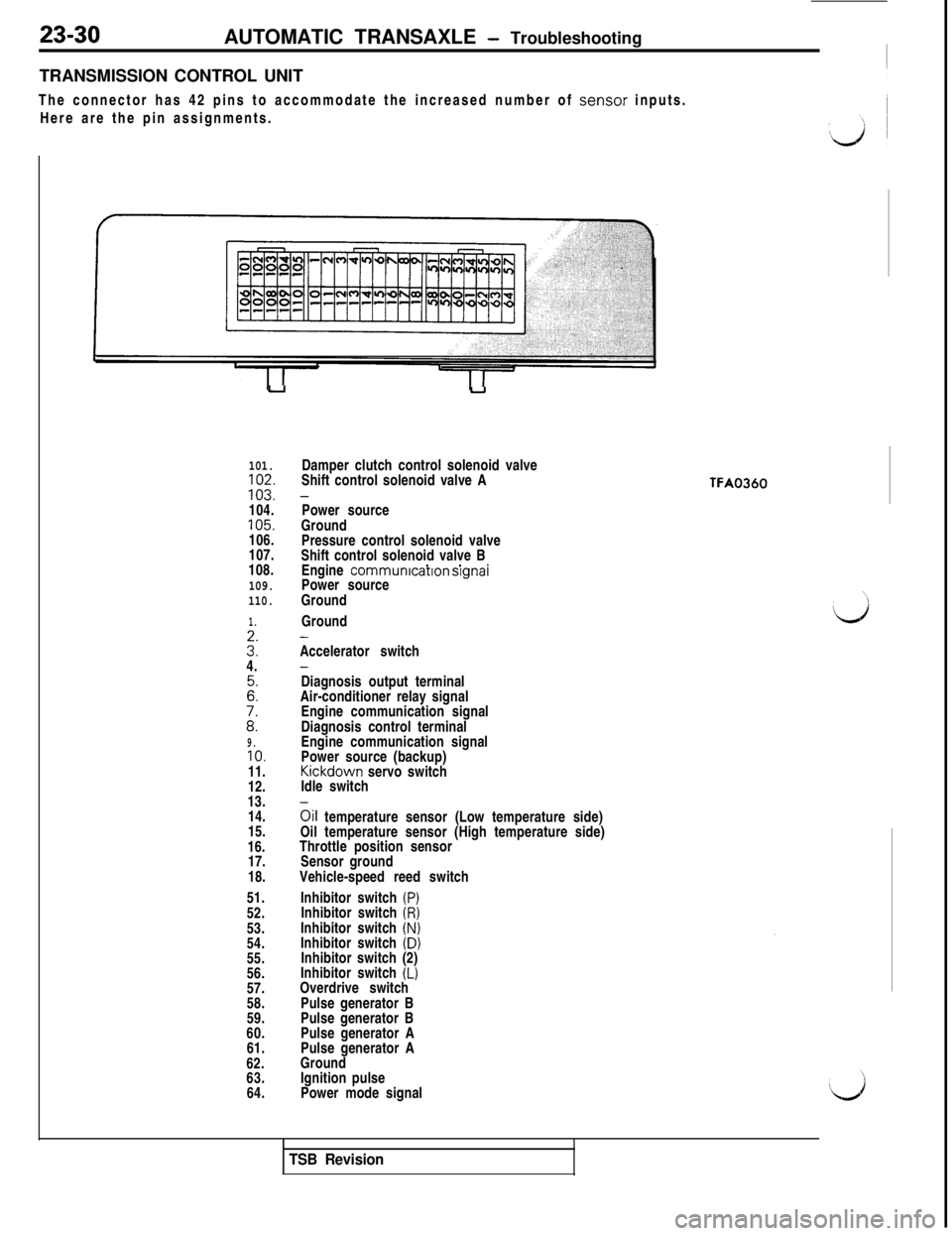
23-30AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshooting
TRANSMISSION CONTROL UNIT
The connector has 42 pins to accommodate the increased number of senso.r inputs.
Here are the pin assignments.
uu
101.102.103.
104.105.
106.
107.
108.
109.
110.
1.
3':4.
Z:
i:9.10.11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.Damper clutch control solenoid valve
Shift control solenoid valve A
-Power source
Ground
Pressure control solenoid valve
Shift control solenoid valve B
. .
*Engine communrcatron srgnaiPower source
Ground
Ground
-Accelerator switch
-Diagnosis output terminal
Air-conditioner relay signal
Engine communication signal
Diagnosis control terminal
Engine communication signal
Power source (backup)Kickdown servo switch
Idle switch
oil temperature sensor (Low temperature side)
Oil temperature sensor (High temperature side)
Throttle position sensor
Sensor ground
Vehicle-speed reed switch
Inhibitor switch
(P)Inhibitor switch (R)Inhibitor switch (N)Inhibitor switch (D)
Inhibitor switch (2)
Inhibitor switch
(L)Overdrive switch
Pulse generator B
Pulse generator B
Pulse generator A
Pulse generator A
Ground
Ignition pulse
Power mode signal
TFA0360
TSB Revision
Page 488 of 1146
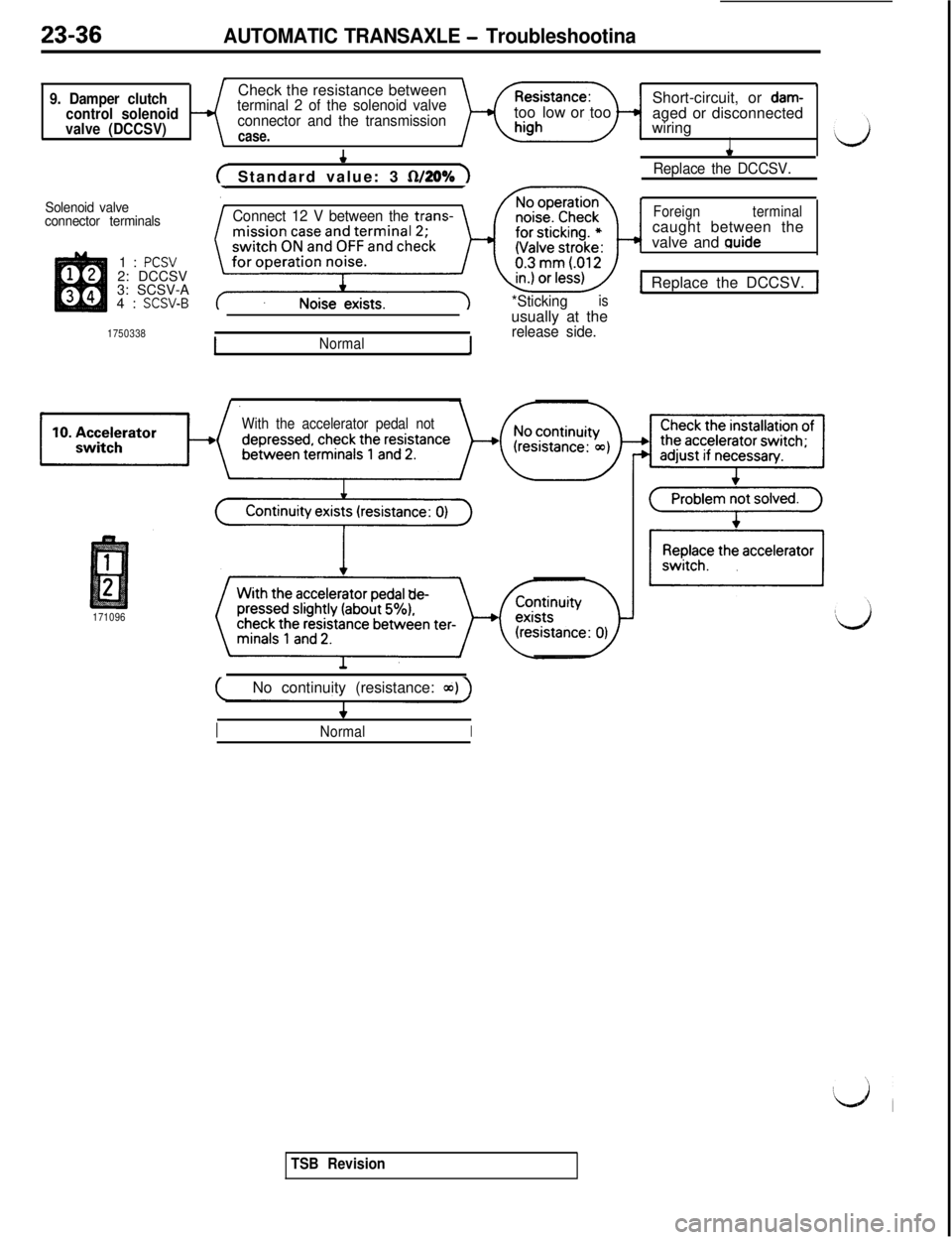
23-36AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshootina
9. Damper clutch
control solenoid
valve (DCCSV)Check the resistance betweenterminal 2 of the solenoid valve
connector and the transmission
case.
?Short-circuit, or
dam-toolow or too
aged or disconnected
wiring
I
Solenoid valve
connector terminals1:
PCSV2: DCCSV
3: SCSV-A
4:
SCSV-B
1750338
( Standard value: 3 fWO% 1
Connect 12 V between the trans-
*Sticking
isusually at the
release side.
*
Replace the DCCSV.
Foreignterminalcaught between the
valve and
guide
1 Replace the DCCSV. J
INormal1
With the accelerator pedal not
171096
(No continuity (resistance: a~) )
INormalI
TSB Revision
Page 492 of 1146

23-40AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshooting
REMEDIAL ACTION TO TAKE FOR INADEQUATE OIL PRESSURESymptom
Possible cause
Remedy
1. All line pressuresa. Plugged oil filter
are low (or high).b. Improperly adjusted regulatora. Visually check oil filter and replace it if plugged.
valve line pressure
b. Measure line pressure (2) (KID brake pres-
NOTE:sure) and readjust line pressure if it is
Line pressures areout of specifications.
@.@.@).@.@and @shown onc. Defective valve body assemblyOr, replace valve body assembly.
the Standard Oil
Pressure Table
on the preceding
paw.
d. Valve body left loose
e. Improper oil pump delivery.
pressurec. Replace valve body assembly.d. Torque valve body clamp bolt and mounting
bolt to specification.
e. Check oil pump gear side clearance and
replace oil pump assembly as necessary.
2. Improper reducing
a. Plugged reducing pressure
a. Disassemble valve body assembly to check
pressurecircuit filter (L-shaped)
b. Improperly adjusted reducingfilter and replace filter if it is plugged.
b. Measure reducing pressure @and readjust
pressure
c. Defective valve body assemblyas necessary.
c. Replace valve body assembly.
3. Improper K/D
brake pressure
(application)a. Defective seal ring
@ and D-ring @of K/D servo piston and seal ringa. Disassemble K/D servo and check seal ring
@of sleeveand D-ring for damage. Replace seal ringb. Defective valve body assemblyor D-ring if damaged or scratched.
b. Replace valve body assembly.
4. Improper KIDbrake pressure
(release)
J. Improper front
clutch pressurea. Defective seal ring
@ and D-ring @of K/D servo piston and seal ringa. Disassemble KID servo and check seal ring
@ of sleeveand D-ring for damage. Replace seal ring
b. Defective valve body assemblyor D-ring if damaged or scratched.b. Replace valve body assembly.
a. Defective seal ring @and D-ring
@of K/D servo piston and seal ringa. Disassemble K/D servo and check seal ring
@ of sleeveand D-ring for damage. Replace seal ringb. Defective valve body assemblyor D-ring if damaged or scratched.
c. Worn front clutch piston andb. Replace valve body assembly.c. Disassemble transaxle and check front clutch
retainer or defective D-ring @or seal ring @piston and retainer for wear and D-ring and
seal ring for damage. Replace piston, retainer,
D-ring, or seal ring as necessary.
3. Improper
rear clutch
pressure
7. Improper
end clutch
pressurea. Defective D-ring
@ of piston,
seal ring @ of retainer,
and seal ring @and D-ring @of input shaft
b. Defectrve valve body assembly
a. Defective seal ring
0. D-ring 0,and oil seal (iJ of end clutch
b. Defective valve body assemblya. Disassemble rear clutch and check input shaft
D-ring, center support seal ring, and piston
D-ring; replace if damaged or scratched.
b. Replace valve body assembly.
a. Disassemble the end clutch and check piston oil
seal, D-ring, and center support seal ring;
replace if damage or scratches are evident.
b. Replace valve body assembly.
8. Improper
low-reverse
brake pressurea. Damaged O-ring between valve
body and transmission
b. Defective valve body assemblyc. Defective D-ring @of piston
or O-ring
@I of center supporta. Remove valve body assembly and check O-ring
on top of upper valve body; replace if damage
or scratches are evident.
b. Replace valve body assembly.
c. Disassemble transaxle and check D-ring and
O-ring; replace if damage or scratches are eviden
3. Improper
torque converter
pressurea. Sticking damper clutch controla. Check damper clutch system and DCCSV
solenoid valve (DCCSV) or damper
for operation.
clutch control valve
b. Plugged or leaky oil cooler and
pipingsb. Repair or replace cooler or pipings.
c. Damaged seal ring @of input shaftc. Disassemble transaxle and check seal ring;
d. Defective torque converterreplace if it is damaged.
d. Replace torque converter.
TSB Revision
d
‘\
d
Page 498 of 1146
23-46AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Service Adjustment Procedures
Fluid level must be
within this range.
TFA038:
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE!5
MZ3FElBJ
TRANSMISSION FLUID LEVEL INSPECTION
1.Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual tempera-
ture
170 - 80°C (160 - 18O”F)].2. Place vehicle on level floor.
3. Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic circuit with fluid, then place
lever in “N” Neutral position.
4. Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area
arouniddipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the condition
of the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.
’ l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
lIf there is a noticeably great amount of metal particles in
the fluid.
5.Check to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick. If
fluid level is low, add automatic transmission fluid until level
reaches “HOT” range.
Transmission fluid: MITSUBISHI PLUS ATF/Automatictransmission fluid “DEXRON”
abr“DEXRON II”
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions because it
allows pump to take in air along with fluid. Air trapped in
hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make fluid spongy.
Therefore, pressures will be erratic, causing delayed shift,
slippy clutch and brakes, etc.
Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. When
transaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam
anldcause the same conditions which occur with low fluid level,
resulting in accelerated deterioration of automatic
transaxllefluid.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch, and
servo operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for a leak.
6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely.
TRANSMISSION FLUID REPLACEMENTM23FCBHRefer to GROUP 00
- Maintenance Service.
TSB Revision