fuel type MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 22 of 1146
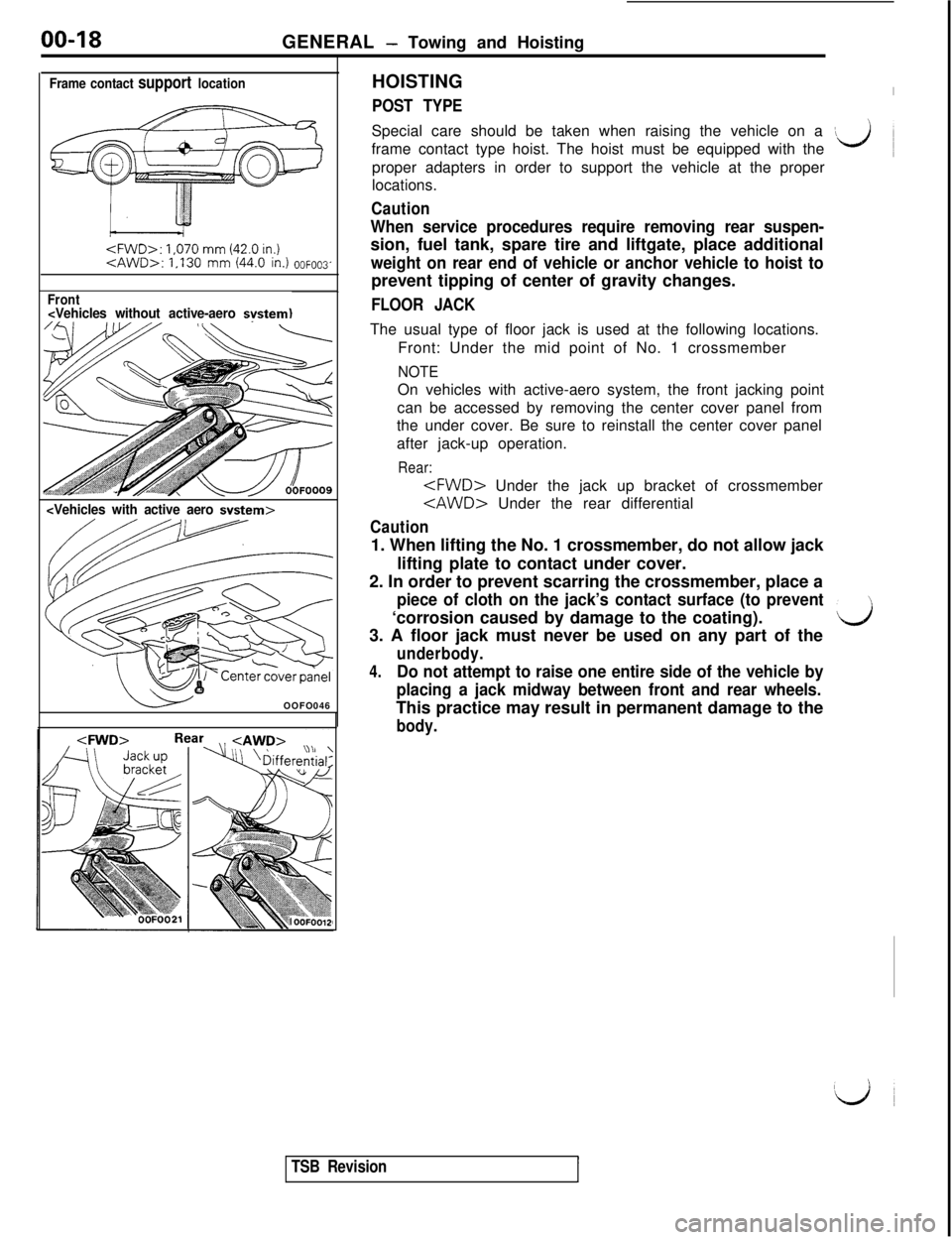
00-18
GENERAL - Towing and Hoisting
Frame contact support location
1,070 mm (42.0 in.)
Front
POST TYPESpecial care should be taken when raising the vehicle on a
\frame contact type hoist. The hoist must be equipped with theL)proper adapters in order to support the vehicle at the proper
locations.
Caution
When service procedures require removing rear suspen-sion, fuel tank, spare tire and liftgate, place additional
weight on rear end of vehicle or anchor vehicle to hoist toprevent tipping of center of gravity changes.
FLOOR JACKThe usual type of floor jack is used at the following locations.
Front: Under the mid point of No. 1 crossmember
NOTEOn vehicles with active-aero system, the front jacking point
can be accessed by removing the center cover panel from
the under cover. Be sure to reinstall the center cover panel
after jack-up operation.
Rear:
Caution1. When lifting the No. 1 crossmember, do not allow jack
lifting plate to contact under cover.
2. In order to prevent scarring the crossmember, place a
piece of cloth on the jack’s contact surface (to prevent‘corrosion caused by damage to the coating).
d3. A floor jack must never be used on any part of the
underbody.
4.Do not attempt to raise one entire side of the vehicle by
placing a jack midway between front and rear wheels.This practice may result in permanent damage to the
body.
TSB Revision
Page 26 of 1146
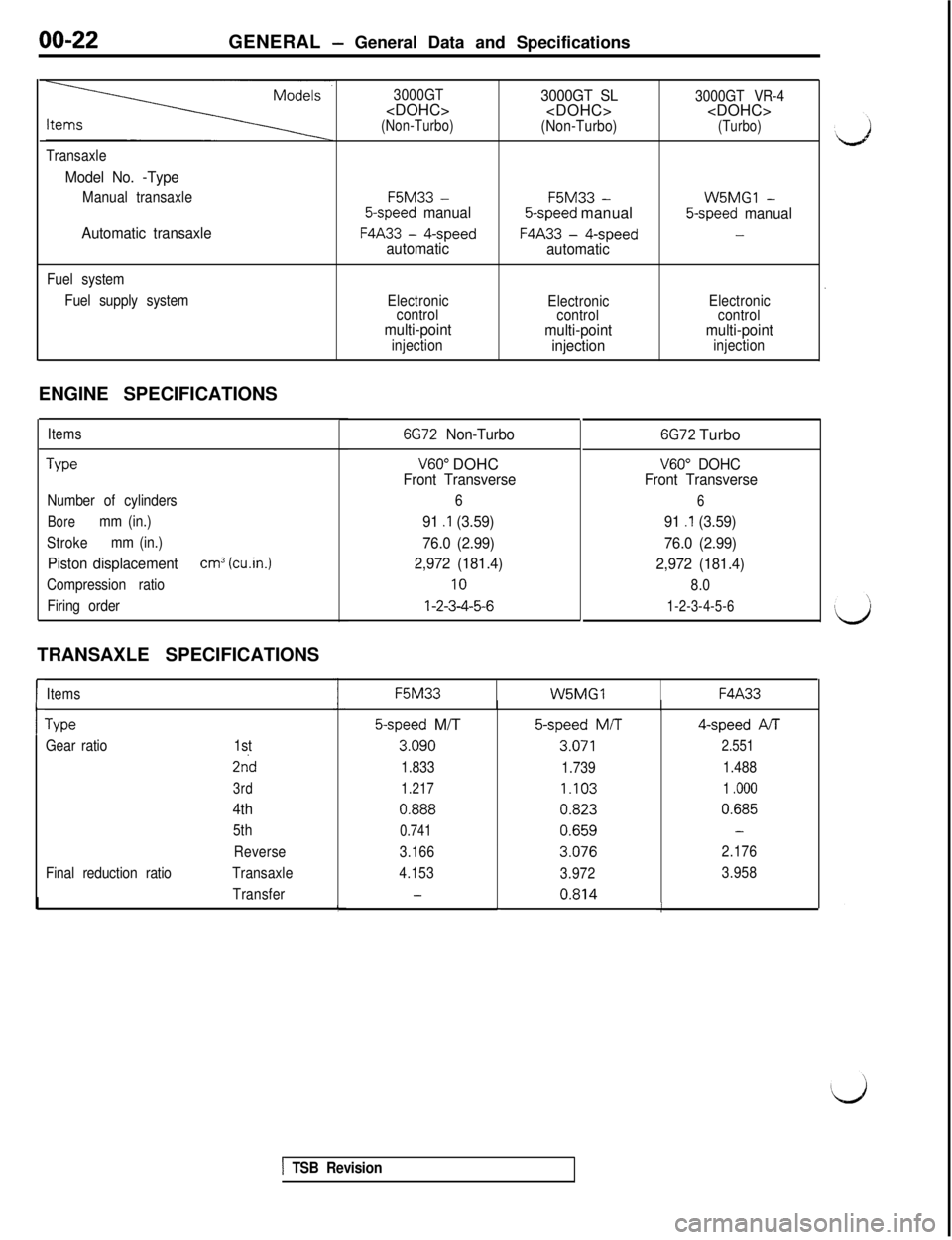
00-22GENERAL - General Data and Specifications
Transaxle
Model No. -Type
Manual transaxle
Automatic transaxle
Fuel system
Fuel supply system3000GT
(Non-Turbo)
F5M33 -5speed manual
F4A33 - 4-speedautomatic
Electronic
control
multi-pointinjection
3000GT SL
(Non-Turbo)
F5M33 -5-speed manual
F4A33 - 4-speedautomatic
Electronic
control
multi-point
injection
3000GT VR-4
(Turbo)W5MGl
-5-speed manual
-
Electronic
control
multi-pointinjectionENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Items
Type
Number of cylinders
Boremm (in.)
Strokemm (in.)
Piston displacementcm3 (cu.in.)
Compression ratio
Firing orderTRANSAXLE SPECIFICATIONS
FL
Items
Type
Gear ratio
Final reduction ratio1st
2n’d
3rd
4th
5th
Reverse
Transaxle
Transfer
L
6672 Non-Turbo
V60” DOHCFront Transverse
6
91 .I (3.59)
76.0 (2.99)
2,972 (181.4)
10
1-2-3-4-5-6
6672 Turbo
V60” DOHC
Front Transverse
6
91 .I (3.59)
76.0 (2.99)
2,972 (181.4)
8.0
1-2-3-4-5-6
F5M33W5MGlF4A33
5-speed M/T
3.090
1.833
1.217
0.888
0.741
3.166
4.153
-
5-speed MIT
3.071
1.739
1.103
0.823
0.659
3.076
3.972
0.814i
4-speed AlT
2.551
1.488
1 .ooo
0.685
-
2.176
3.958
1 TSB Revision
Page 35 of 1146

GENERAL - Lubrication and Maintenance00-31LUBRICATION AND MAINTE-
NANCEMOOPA- -
iiMaintenance and lubrication service recommenda-
tions have been compiled to provide maximum
protection for the vehicle owner’s investment
against all reasonable types of driving conditions.
Since these conditions vary with the individual
vehicle owner’s driving habits, the area in which the
vehicle is operated and the type of driving to which
the vehicle is subjected, it is necessary to prescribe
lubrication and maintenance service on a time
frequency as well as mileage interval basis.
Oils, lubricants and greases are classified and
graded according to standards recommended by the
Society of Automotive Engineers
(SAE), the Amer-
ican Petroleum Institute (API) and the National
Lubricating Grease Institute
(NLGI).MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
Information for service maintenance is provided
under “SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE TABLE”.
Three schedules are provided; one for “Required
Maintenance”, one for “General Maintenance” and
one for “Severe Usage Service”.
Item numbers in the “SCHEDULED MAINTE-
NANCE TABLE” correspond to the item numbers in
the “MAINTENANCE SERVICE” section.
LSEVERE SERVICE
Vehicles operating under severe service conditions
will require more frequent service.
Component service information is included in
appropriate units for vehicles operating under one or
more of the following conditions:
1. Police, taxi, or commercial type operation
2. Operation of Vehicle
(1) Short-trip operation at freezing temperature
(engine not thoroughly warmed up)
(2) More than 50% operation in heavy city
traffic during hot weather above 32°C
(90°F)(3) Extensive idling
(4) Driving in sandy areas
(5) Driving in salty areas
(6) Driving in dusty conditions
ENGINE OIL
The SAE grade number indicates the viscosity of
engine oils, for example, SAE 30, which is a single
grade oil. Engine oils are also identified by a dual
number, for example, SAE 1 OW-30, which indicates
a multigrade oil.
The API classification system defines oil perform-
ance in terms of engine usage. Only engine oil
idesigned “For Service SG” or “For Service
SGXD”,when available, should be used. These oils contain
sufficient chemical additives to provide maximumengine protection. Both the SAE grade and the API
designation can be found on the container.
Caution
Test results submitted to EPA have shown thatlaboratory animals develop skin cancer after
prolonged contact with used engine oil. Accor-dingly, the potential exists for humans to de-
velop a number of skin disorders, including
cancer, from such exposure to used engine oil.
Care should be taken, therefore, when changing
engine oil, to minimize the amount and length ofexposure time to used engine oil on your skin.
Protective clothing and gloves, that cannot be
penetrated by oil, should be worn. The skin
should be thoroughly washed with soap and
water, or use waterless hand cleaner, to removeany used engine oil. Do not use gasoline,
thinners, or solvents.GEAR
LUEiRlCANTSThe SAE grade number also indicates the viscosity
of Multi-Purpose Gear Lubricants.
The API classification system defines gear lubri-
cants in terms of usage. Typically gear lubricants
conforming to API GL-4 or GL-5 with a viscosity of
SAE
75W-85W are recommended for manual trans-
axle.
LUBRICANTS
- GREASES
Semi-solid lubricants, bear the
NLGI designation and
are further classified as grades 0, 1, 2, 3 etc.
Whenever “Chassis Lubricant” is specified,
Multi-Purpose Grease,
NLGI grade 2, should be used.
FUEL USAGE STATEMENT
Use premium unleaded gasoline having a minimum
octane rating of 91,
(R + M)/2. However, it is also
possible to use unleaded gasoline with an octane
rating of at least 87.
Unleaded gasolines only must be used in vehicles
equipped with catalyst emission control systems.
All vehicles, so equipped, have labels located on the
instrument panel and on the back of fuel filler lid that
state, “UNLEADED GASOLINE ONLY”. These vehi-
cles also have fuel filler tubes especially designed to
accept the smaller diameter unleaded gasoline
dispensing nozzles only.
MATERIALS ADDED TO FUEL
Indiscriminate use of fuel system cleaning agents
should be avoided. Many of these materials in-
tended for gum and varnish removal may contain
highly active solvents or similar ingredients that can
be harmful to gasket and diaphragm materials used
in fuel system component parts.
1 TSB Revision
Page 40 of 1146

00-36GENERAL - Scheduled Maintenance Table / Maintenance Service
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE UNDER SEVERE USAGE CONDITIONS
The maintenance items should be performed according to the following table:
Mileage Intervals Kilometers in ThousandsSevere Usage
MaintenanceService to be(Miles in Thousands)Conditions
itemPerformed
(6 (15) (22.5) (30) (37.5) (45) (50) (52.5) (60)24 36 48 60 72 80 84 96 A B C D E F G
Air Cleaner ElementReplaceMore FrequentlyXX
Spark PlugsReplaceXXXXXX
Engine OilChange Every Or3 MonthsEvery 4,800 Km (3,000 Miles)x x x xX
Engine Oil FilterReplace Every or6 MonthsEvery 9,600 Km (6.000 Miles)x x x xX
Disc Brake PadsInspect for WearMore FrequentlyXX
Severe usage conditions
A-Driving in dusty conditionsE -B -Police, taxi, or commercial type operationF -Driving in sandy areas
C -Extensive idlingG -Driving in salty areas
D -Short trip operation at freezing temperaturesMore than 50% operation in heavy city traffic during
(engine not thoroughly warmed up)hot weather above 32°C (90°F)MAINTENANCE SERVICE
1. FUEL SYSTEM (TANK, LINES, CONNECTIONS
AND FUEL FILLER CAP) (Check for leaks)
/ 2.
FUEL HOSES (Check for leaks or damage)MWShGC
1. Check for damage or leakage in the fuel lines and
connections and looseness of the fuel filler cap.
2.Inspect the surface of fuel hoses for heat and mechanical
damage. Hard and brittle rubber, cracking, checking, tears,
cuts, abrasions and excessive swelling indicate deteriora-
tion of the rubber.
3.If the fabric casing of the rubber hose is exposed by cracks
and abrasions in the fuel system, the hoses should be
changed.
TSB Revision
Page 108 of 1146

13-2
Boost Meter
Components Location........................................................36
Crank Angle Sensor
............................................................72Detonation Sensor................................................................84EGR Control Solenoid Valve
EGR Temperature Sensor
Fuel Pump Operation Check................................................137Fuel Pump Relay No. 2........................................................53Fuel Pump Resistor............................................................53
Idle Position Switch............................................................68Idle Speed Control Servo (Stepper Motor Type)............1 IOIgnition Coil and Power Transistor....................................115Ignition Switch-ST and Inhibitor Switch ................76Ignition Switch-ST
Injectors
94
Oxygen Sensor
Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch................................80Power Supply and Ignition Switch-IG................................41
Purge Control Solenord Valve............................................1 19Release of Residual Pressure from High
Pressure Fuel Hose............................................................137Throttle Position Sensor....................................................65Top Dead Center Sensor....................................................70Variable Induction Control Servo (DC Motor)
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES............................31
Adjustment of Fixed SAS....................................................35Adjustment of Idle Position Switch and
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)............................................33Basic Idle Speed Adjustment............................................31Throttle Body (Throttle Valve Area) Cleaning....................33
SPECIAL TOOLS........................................................................8
SPECIFICATIONS
....................................................................6
General Specifications........................................................6Sealant....................................................................................7Service Specifications........................................................7
THROlTLE BODY....................................................................143
TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................9
Check Chart Classified by Problem Symptoms................16Circuit Diagram....................................................................18Engine Warning Light (Malfunction Indicator Light)........11Explanation and Cautions about Harness Check............10Explanation of Troubleshooting Procedures....................9Fuel Tank and Fuel Line........................................................30
Problem Symptoms Table (For Your Information)............17Self-diagnosis........................................................................12)
I
Page 112 of 1146

Tank capacityliter (gal.)
Return system
Filter
High pressure type
Electrical, in-tank type
Driven by
Throttle position sensor
idle speed control servoVariable resistor type
Stepper motor typeThe stepper motor type by-pass air controlsystem with the first idle air valve
Engine control unit
Identification model No.
Federal
California
Karman vortex type
Barometric pressure
sensorSemiconductor diffusion type
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Oxygen sensor
Vehicle speed sensor
Detonation sensor
Top dead center sensor
Crank angle sensor
Induction control valve position sensor
EGRtemperature sensor
Piezoelectric device type
Photo interrupter type
Photo interrupter type
Variable’resistor type
13-6FUEL SYSTEM - Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
TSB Revision
Page 113 of 1146

FUEL SYSTEM - SDecifications
L
Items
Actuators
Control relay type
Injector type and number
Injector identification mark
Variable induction control servo
Purge control solenoid valve
EGR control solenoid valve
Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
Waste gate solenoid valve
Fuel pressure regulator
Regulated pressure
kPa (psi)
Specifications
Contact switch type
Electromagnetic, 6
BDH210
BDL360
Electric motor
ON/OFF type solenoid valve
Duty cycle solenoid valve
ON/OFF type solenoid valve
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
335 (47.6)
300 (43.5)
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
i
ternsSpecifications
3asic ignition timing5” -t 2”BTDC at curb idle
3urb idle speedrpm700 * 100
dle speed when air conditioner is on
rpm
3asic idle speedrpm700 + 50
Throttle position sensor adjusting voltageV0.4- 1 .o
Throttle position sensor resistancek03.5 - 6.5
dle speed control servo (stepper motor) coil resistance028 - 33 [at 20°C (68”F)I
ntake air temperature sensor resistancekfi2.7 [at 20°C (68”F)I
Engine coolant temperature sensor resistancekQ
20°C (68°F)
2.4
80°C (176°F)0.3
%el pressurekPa (psi)
Vacuum hose disconnection
295 - 315 (43 - 45) at curb idle
Vacuum hose connection
Sz
2 - 3 [at 20°C (68”F)I
SEALANTMlXE-A
IItems1 Specified sealantI
/
L
Engine coolant temperature sensor threaded portion3M NUT Locking Part No. 4171 or equivalent
Fuel tank hole cover3M ATD Part No. 8509 or equivalent
1 TSB Revision
Page 122 of 1146
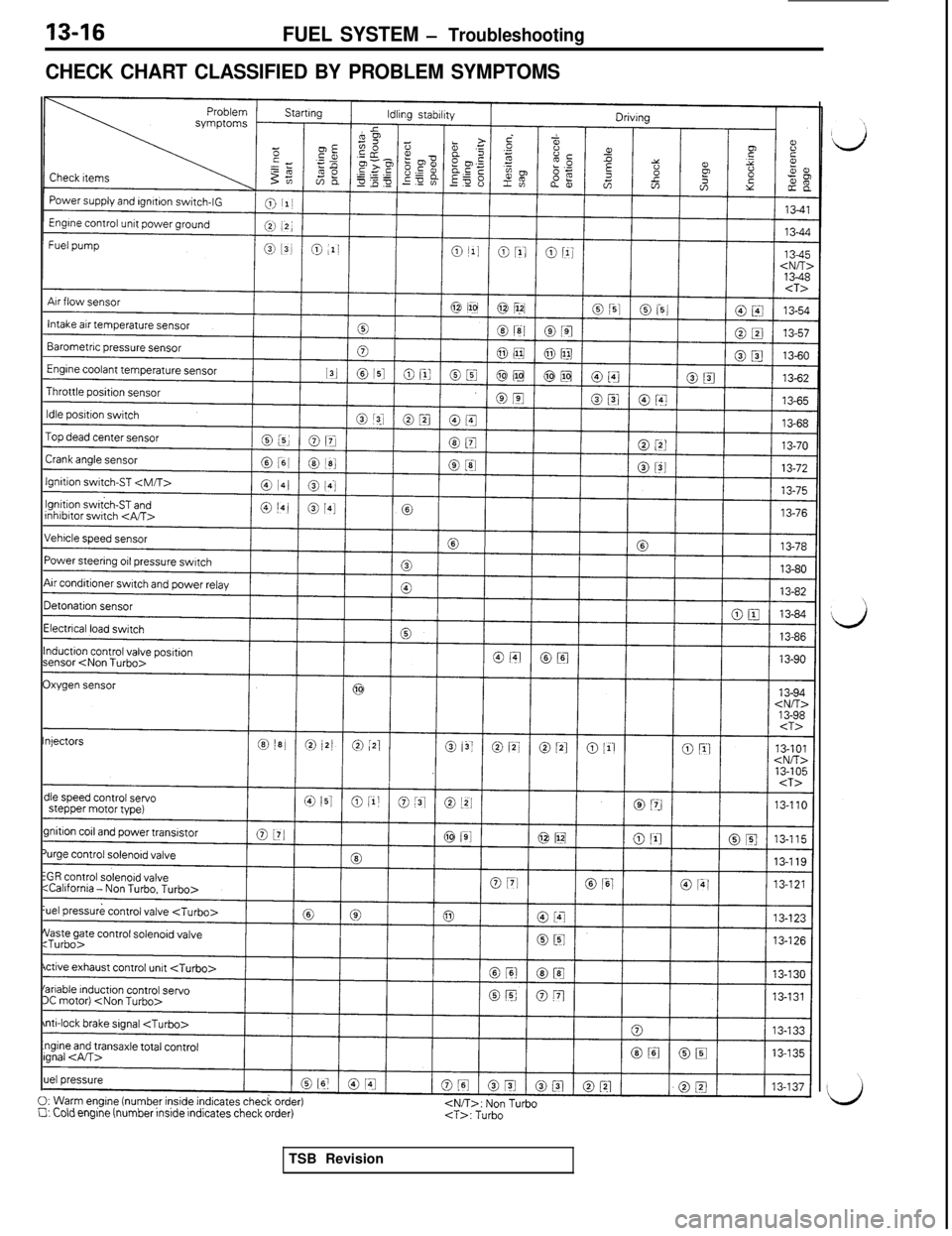
13-16FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
CHECK CHART CLASSIFIED BY PROBLEM SYMPTOMSstepper motor type)
0:Warmen,gine (number inside indicates check order)Cl: Cold engine (number inside indicates check order)
Page 173 of 1146
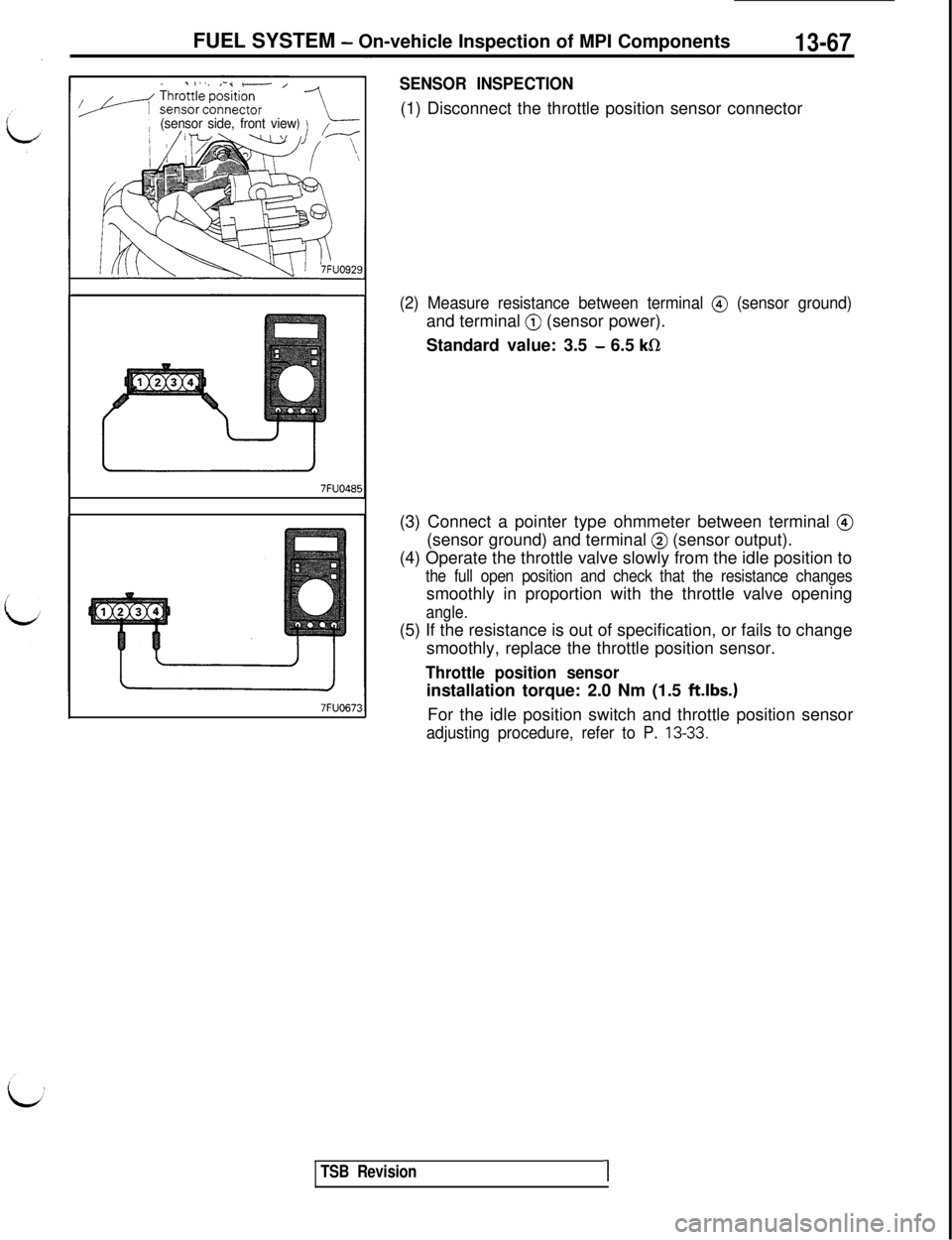
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-67
(sensor side, front view7FU048t7FUO67:
SENSOR INSPECTION(1) Disconnect the throttle position sensor connector
(2) Measure resistance between terminal @ (sensor ground)and terminal
@ (sensor power).
Standard value: 3.5
- 6.5 kR(3) Connect a pointer type ohmmeter between terminal
@(sensor ground) and terminal
@ (sensor output).
(4) Operate the throttle valve slowly from the idle position to
the full open position and check that the resistance changessmoothly in proportion with the throttle valve opening
angle.(5) If the resistance is out of specification, or fails to change
smoothly, replace the throttle position sensor.
Throttle position sensorinstallation torque: 2.0 Nm (1.5
ft.lbs.)For the idle position switch and throttle position sensor
adjusting procedure, refer to P. 13-33.
TSB Revision1
Page 216 of 1146
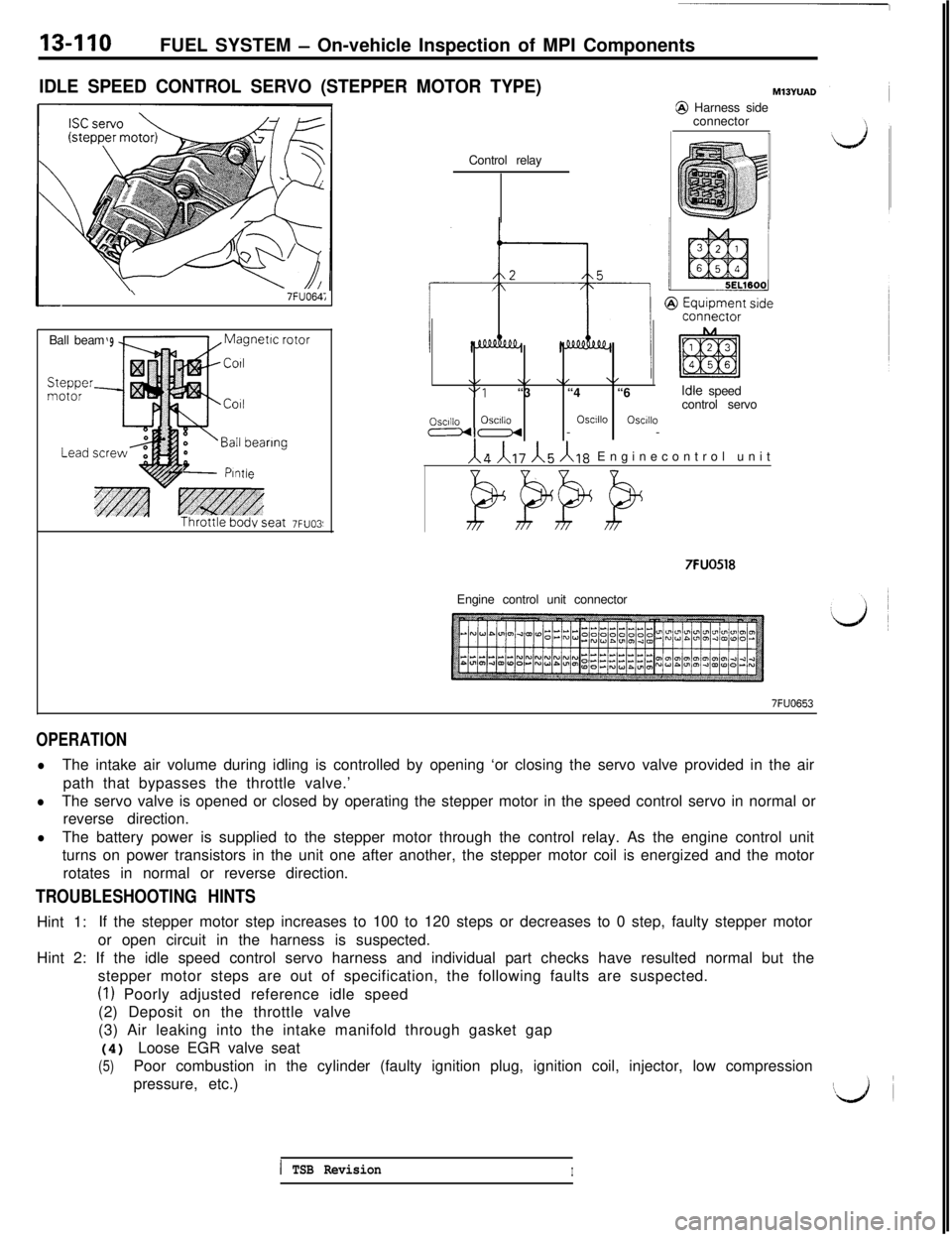
13-110FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
IDLE SPEED CONTROL SERVO (STEPPER MOTOR TYPE)\
7FUO64;Ball beam
‘9
L PlntleControl relay
@ Harness side
connector
\/1, \,\/“1“3 “4 “6Idle speed
control servo
OSCIIIOOSCIIIOOSClllOosclllomu--
/(a /(IT ),!j /I,, Enginecontrol unit
BPPP
7FUO518Engine control unit connector
7FUO653
OPERATION
lThe intake air volume during idling is controlled by opening ‘or closing the servo valve provided in the air
path that bypasses the throttle valve.’
lThe servo valve is opened or closed by operating the stepper motor in the speed control servo in normal or
reverse direction.
lThe battery power is supplied to the stepper motor through the control relay. As the engine control unit
turns on power transistors in the unit one after another, the stepper motor coil is energized and the motor
rotates in normal or reverse direction.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTSHint 1:If the stepper motor step increases to 100 to 120 steps or decreases to 0 step, faulty stepper motor
or open circuit in the harness is suspected.
Hint 2: If the idle speed control servo harness and individual part checks have resulted normal but the
stepper motor steps are out of specification, the following faults are suspected.
(I) Poorly adjusted reference idle speed
(2) Deposit on the throttle valve
(3) Air leaking into the intake manifold through gasket gap
(4) Loose EGR valve seat
(5)Poor combustion in the cylinder (faulty ignition plug, ignition coil, injector, low compression
pressure, etc.)
\L.J
1 TSB RevisionI