diagnostic MITSUBISHI 380 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: 380, Model: MITSUBISHI 380 2005Pages: 1500, PDF Size: 47.87 MB
Page 1090 of 1500

DOOR
BODY42-23
DOOR
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1423000100246
OPERATION
.
CENTRAL DOOR LOCKING SYSTEM
The central door locking system operates the door
lock actuator to lock or unlock the doors and the fuel
lid door using the door lock switch built into the front
power window (main or sub) switch or key cylinder
built into the driver's side door outside handle. The
system has the following operations and features:
All doors and fuel lid door can be locked using the
door lock switch built into the front power window
(main or sub
Insert the key into the driver's key cylinder and
turn once to the unlock side to unlock the driver's
door and fuel lid door. Turn the key once again to
the unlock side to unlock all doors and fuel lid
door.
The key reminder function automatically unlocks
all doors when door lock operation is performed
and the front doors are opened while the key is
inserted into the ignition switch.
.
POWER WINDOWS
When the power window (main or sub) switch is
operated, the door windows will open or close. This
system has the following operations and features:
A power window lock switch on the power win-
dow main switch prevents the door window glass
from opening/closing with the front passenger's
and rear power window sub switch.
The power window of the door window glass can
be opened/closed for 30 seconds with the timer
function after the ignition switch is turned OFF.
(The timer expires if the front door
opened when the timer is in operation).
The power window main switch contains a
one-touch down switch that will automatically
open the driver's side door window only.
CENTRAL DOOR LOCKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSISM1427000700217
The central door locking system is controlled by the
simplified wiring system (SWS). Refer to GROUP
54B, SWS Diagnosis P.54B-57.
POWER WINDOW DIAGNOSISM1429000700224
The power window is controlled by the simplified wir-
ing system (SWS). Refer to GROUP 54B, SWS
Diagnosis P.54B-57.
DOOR DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO GLASS AND DOOR DIAGNOSISM1423007300241
Glass and door faults include water leaks and
improper opening and closing. Causes for these
faults can include faults in the glass, weatherstrip,
drain hole, waterproof film or door installation.
GLASS AND DOOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1423006700246
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find a
glass and door fault.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the Symptom
Chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
Page 1127 of 1500
TRUNK LID
BODY42-60
TRUNK LID
TRUNK LID DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO TRUNK LID DIAGNOSISM1421005800374
Difficult locking and unlocking, uneven clearance and
height, and wind noise from the trunk lid may be
caused by improper adjustment of the trunk lid.
TRUNK LID DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1421005900348
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find a
trunk lid fault.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the Symptom
Chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
SYMPTOM CHARTM1421006000382
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: Difficult Locking and Unlocking
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the function of trunk lid opening
switch inside glove compartment.
Q: Can the latch unlocking mechanism noise "click"
be heard when operating the switch
YES :
Go to Step 2.
NO : Check switch circuit. Refer to P.42-65.
Then go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check the engagement of the trunk lid
latch and trunk lid striker.
Q: Are the trunk lid latch and trunk lid striker engaged
correctly?
YES :
Then go to Step 3.
NO : Adjust the trunk lid latch. Refer to P.42-61.
STEP 3. Retest the system.
Q: Does the trunk lid lock operate easily?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Return to Step 1.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 2: Uneven Body Clearance
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the clearance around the trunk
lid..
Q: Are the apertures between the trunk lid and the adjacent body panels aligned correctly?
YES :
Then go to Step 2.
NO : Adjust the trunk lid panel assembly. Refer to
P.42-61. SYMPTOM INSPECTION
PROCEDUREREFERENCE PAGE
Difficult locking and unlocking 1
P.42-60
Uneven body clearance 2
P.42-60
Uneven height 3
P.42-61
Page 1134 of 1500
KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM
BODY42-67
KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONBGBJABIE
Antenna and receiver are incorporated in the
ETACS-ECU.
ID code can be registered by using Diagnostic
tool (MUT-III).
Transmitter is a key holder type, which incorpo-
rates lock button, unlock button, trunk button and
panic button
When the transmitter unlock button is pressed
once, the driver's door will be unlocked. If the but-
ton is pressed twice, all the doors will be
unlocked. The adjustment function also allows
you to open all the doors by pressing the unlock
button only once. For further details on using the
multi-center display to adjust the unlock opera-
tion, refer to GROUP 54B, On-vehicle Service
P.54B-486.
When the transmitter is operated, the answer-
back function will work as follows:
The answerback operation can be altered as fol-
lows:NOTE: Enabling/disabling the hazard warning
light flashing, the horn sounding in accordance
with the answerback function. For further details
on using the transmitter to adjust answerback,
P.42-72 see the section below. For further details
on using the multi-center display to adjust
answerback, refer to GROUP 54B, On-vehicle
Service P.54B-486. ITEM OPERATION
DOORS LOCKED DOORS UNLOCKED
Dome light Flashes once Illuminates for 15 seconds
Turn-signal lights (RH and LH) Flashes once Flashes twice
Horn Sounds once when the lock button
is pressed with all the doors locked-
ITEM ADJUSTMENT ITEM ADJUSTMENT DETAIL
Keyless entry system
confirmation by turn
signal lightsAdjustment of hazard answerback
when the transmitter is used to
lock doorsWhen adjusting hazard answerback after the
doors are locked with the transmitter, the
following flashing conditions can be selected.
a. Flash (default)
b. No flash
Adjustment of hazard answerback
when the transmitter is used to
unlock doorsWhen adjusting hazard answerback after the
doors are unlocked with the transmitter, the
following flashing conditions can be selected.
a. Flash (default)
b. No flash
Keyless entry system
confirmation by hornAdjustment of horn answerback
when the transmitter is used to
lock doorsWhen adjusting horn answerback after the
doors are locked with the transmitter, the
following horn conditions can be selected.
a. Horn sounds
b. Horn sounds if doors are already locked
(default)
c. Horn does not sound
Page 1166 of 1500

35A-1
GROUP 35A
BASIC BRAKE
SYSTEM
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . .35A-2
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS35A-3
INTRODUCTION TO BASIC BRAKE
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-3
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY . . . . . . 35A-3
SYMPTOM CHART. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-3
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-3
SPECIAL TOOLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35A-12
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . .35A-13
BRAKE PEDAL CHECK AND
ADJUSTMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-13
BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATING TEST . . . 35A-14
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECK . . . . 35A-15
BLEEDING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-16
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR CHECK. . 35A-17
DISC BRAKE PAD CHECK AND
REPLACEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-17
DISC BRAKE ROTOR CHECK . . . . . . . . . . 35A-19
MASTER CYLINDER FUNCTION CHECK . 35A-23
BRAKE PEDAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35A-24
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 35A-24
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-25
MASTER CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
AND BRAKE BOOSTER . . . . . . . . . .35A-26
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 35A-26
MASTER CYLINDER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-28
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-29
DISC BRAKE ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . .35A-30
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 35A-30
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-32
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-38
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35A-40
FASTENER TIGHTENING
SPECIFICATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-40
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . 35A-40
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-41
LUBRICANTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35A-41
Page 1168 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-3
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSISM1351009700319
Hydraulic brakes are composed of the brake pedal,
master cylinder, brake booster and disc brakes. Mal-
functions such as insufficient braking power or the
generation of noise may occur due to wear, damage
or incorrect adjustment of these components.
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1351009800316
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find a
basic brake system fault.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the symptom
chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
SYMPTOM CHARTM1351009900324
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: Vehicle Pulls to One Side when Brakes are Applied
.DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check for oil, water, etc., on the pad
contact surface of all brakes.
Q: Is oil, water, etc., on the pad contact surface?
YES :
Replace the part and determine the
source/cause of foreign material. Then go to
St e p 5.
NO : Go to Step 2. SYMPTOM INSPECTION
PROCEDUREREFERENCE
PA G E
Vehicle pulls to one side when brakes are applied 1
P.35A-3
Insufficient braking power 2
P.35A-4
Increased pedal stroke (Reduced pedal-to-floor board clearance)3
P.35A-5
Brake drag 4
P.35A-6
Scraping or grinding noise when brake are applied 5
P.35A-7
Squealing, groaning or chattering noise when brake are applied 6
P.35A-8
Squealing noise when brakes are not applied 7
P.35A-9
Groaning, clicking or rattling noise when brakes are not applied8
P.35A-11
Page 1209 of 1500
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PARKING BRAKES36-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1361000100344
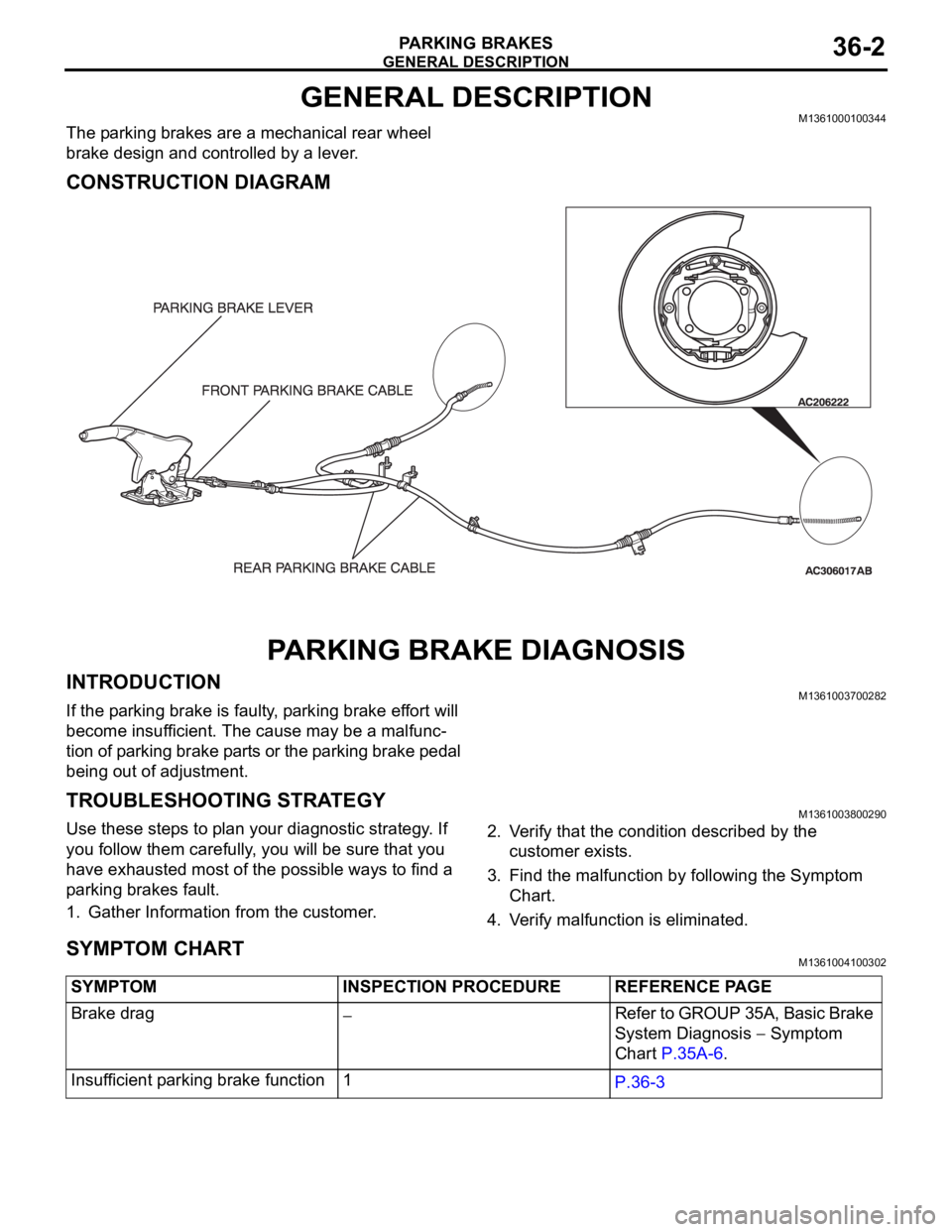
The parking brakes are a mechanical rear wheel
brake design and controlled by a lever.
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
PARKING BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTIONM1361003700282
If the parking brake is faulty, parking brake effort will
become insufficient. The cause may be a malfunc-
tion of parking brake parts or the parking brake pedal
being out of adjustment.
TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1361003800290
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find a
parking brakes fault.
1. Gather Information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the Symptom
Chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
SYMPTOM CHARTM1361004100302
SYMPTOM INSPECTION PROCEDURE REFERENCE PAGE
Brake drag
Refer to GROUP 35A, Basic Brake
System Diagnosis
Symptom
Chart P.35A-6.
Insufficient parking brake function 1
P.36-3
Page 1222 of 1500

00-1
GROUP 00
GENERAL
CONTENTS
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL . . . . . .00-3
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDELINES00-6
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING /
INSPECTION SERVICE POINTS. . . .00-7
TROUBLESHOOTING CONTENTS . . . . . . 00-7
HOW TO USE THE INSPECTION
PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-9
CONNECTOR MEASUREMENT SERVICE
POINTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-11
CONNECTOR INSPECTION SERVICE
POINTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-13
HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT
MALFUNCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-14
INSPECTION SERVICE POINTS
FOR A BLOWN FUSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-16
HOW TO TREAT CURRENT TROUBLE . . 00-16
HOW TO TREAT PAST TROUBLE . . . . . . 00-16
AFFILIATED DTC REFERENCE
TABLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .00-17
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION . . . . . . .00-18
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER . . . 00-18
VEHICLE INFORMATION NUMBER LIST 00-19
VEHICLE COMPLIANCE PLATE . . . . . . . . 00-19
VEHICLE DATA PLATE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-20
AUSTRALIAN DESIGN RULES . . . . . . . . . 00-20OPTION CODES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-21
EXPORT CODES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-21
TYRE AND LOADING PLACARD . . . . . . . . 00-21
ENGINE MODEL STAMPING . . . . . . . . . . . 00-22
PRECAUTIONS BEFORE SERVICE .00-22
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM (SRS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-22
HOW TO PERFORM VEHICLE
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) WRITING00-23
SERVICING ELECTRICAL SYSTEM . . . . . 00-24
VEHICLE WASHING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 00-24
APPLICATION OF ANTI-CORROSION
AGENTS AND UNDERCOATS . . . . . . . . . . 00-25
DIAGNOSTIC TOOL (MUT-III) . . . . . . . . . . 00-25
TOWING AND HOISTING. . . . . . . . . .00-26
GENERAL DATA AND
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .00-31
TIGHTENING TORQUE . . . . . . . . . . .00-32
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 00-34
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANTS AND
LUBRICANT CAPACITIES TABLE . .00-35
Continued on next page
Page 1227 of 1500

TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDELINES
GENERAL00-6
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDELINESM1001008800340
VERIFY THE COMPLAINT
Make sure the customer's complaint and the ser-
vice writer's work order description are under-
stood before starting work.
Make sure you understand the correct operation
of the system. Read the service manual descrip-
tion to verify normal system operation.
Operate the system to see the symptoms. Look
for other symptoms that were not reported by the
customer, or on the work order, that may be
related to the problem.
DETERMINE POSSIBLE CAUSES
Compare the confirmed symptoms to the diagnostic
symptom indexes to find the right diagnosis proce-
dure.
If the confirmed symptoms cannot be found on any
symptom index, determine other possible causes.
Analyze the system diagrams and list all possible
causes for the problem symptoms.
Rank all these possible causes in order of proba-
bility, based on how much of the system they
cover, how likely they are to be the cause, and
how easy they will be to check. Be sure to take
experience into account. Consider the causes of
similar problems seen in the past. The list of
causes should be ranked in order from general to
specific, from most-likely to least-likely, and from
easy-to-check to hard-to-check.
FIND THE PROBLEM
After the symptoms have been confirmed, and prob-
able causes have been identified, the next step is to
make step-by-step checks of the suspected system
components, junctions, and links in logical order.
Use the diagnostic procedures in the service manual
whenever possible. Follow these procedures care-
fully to avoid missing an important step in the diagno-
sis sequence. It might be the skipped step that leads
to the solution of the problem.
If the service manual doesn't have step-by-step pro-
cedures to help diagnose the problem, make a series
of checks based on the ranked list of probable
causes. Troubleshooting checks should be made in
the order that the list of causes was ranked:
general to specific
most-likely to least-likely
easy-to-check to hard-to-check
REPAIR THE PROBLEM
When the step-by-step troubleshooting checks find a
fault, perform the proper repairs. Make sure to fix the
root cause of the problem, not just the symptom. Just
fixing the symptom, without fixing the root cause, will
cause the symptom to eventually return.
VERIFY THE REPAIR
After repairs are made, recheck the operation of the
system to confirm that the problem is eliminated. Be
sure to check the system thoroughly. Sometimes
new problems are revealed after repairs have been
made.
Page 1228 of 1500

HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING/INSPECTION SERVICE POINTS
GENERAL00-7
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING/INSPECTION SERVICE
POINTS
TROUBLESHOOTING CONTENTSM1001013300062
During diagnosis, a DTC code associated with
other system may be set when the ignition
switch is turned on with connector(s) discon-
nected. On completion, confirm all systems
for DTC code(s). If DTC code(s) are set, erase
them all.
When the DIAGNOSTIC TOOL (MUT-III)
detects a diagnostic trouble code, its display
informs users whether a mechanical problem
currently exists (“current trouble”) or whether
it existed before but normal operation has
been restored (“past trouble”). However, if an
MPI, TPMS or SRS airbag-related DTC is set,
“Active DTC/Stored DTC” is not displayed. In
this case, follow the diagnosis procedure for
current trouble.
If a trouble, detected in a CAN communica-
tion-capable system, can be reproduced,
diagnose the CAN bus lines (Refer to GROUP
54C, Can Bus Line Diagnostics Chart
P.54C-15 or P.54C-15).
Troubleshooting of electronic control systems for
which the MUT -III can be used follows the basic out-
line described below. Even in systems for which the
MUT-III cannot be used, part of these systems still
follow this outline.
1. STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLESHOOTING
Troubleshooting strategy is shown in each group.
2. SYSTEM OPERATION AND SYMPTOM
VERIFICATION TESTS
If verification of the symptom(s) is difficult, proce-
dures for checking operation and verifying symptoms
are shown.
3. DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTION
The following trouble code diagnoses are shown.
How to read diagnostic trouble codes
How to erase diagnostic trouble codes
Input inspection service points
4. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
If the MUT-III displays a diagnostic trouble code, find
the applicable inspection procedure according to this
chart.
5. SYMPTOM CHART
If there are symptoms, even though the MUT-III
shows that no DTCs are set, inspection procedures
for each symptom will be found by using this chart.
6. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
PROCEDURES
Indicates the inspection procedures corresponding to
each diagnostic trouble code. (Refer to P.00-9).
7. SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
Indicates the inspection procedures corresponding to
each symptom listed in the Symptom Chart (Refer to
P.00-9).
8. SERVICE DATA REFERENCE TABLE
Inspection items and normal judgment values have
been provided in this chart as reference information.
9. CHECK AT ECU TERMINALS
Terminal numbers for the ECU connectors, inspec-
tion items, and standard values have been provided
in this chart as reference information.
.
TERMINAL VOLTAGE CHECKS
1. Use correct tool to check each pin location on the
ENGINE-ECU Check harnes MB992044 and
measure with voltmeter.
Short-circuiting the positive (+) test probe
between a connector terminal and ground could
damage the vehicle wiring, the sensor, the ECU,
or all three. Use care to prevent this!
2. Insert the correct terminal tool into each of the
ENGINE-ECU check harness connector
terminals, and measure the voltage while referring
to the check chart.
NOTE: Measure voltage with the ECU connectors
connected.
You may find it convenient to pull out the ECU to
make it easier to connect the ENGINE-ECU check
harness.
Page 1235 of 1500
HOW TO USE TROUBLESHOOTING/INSPECTION SERVICE POINTS
GENERAL00-14
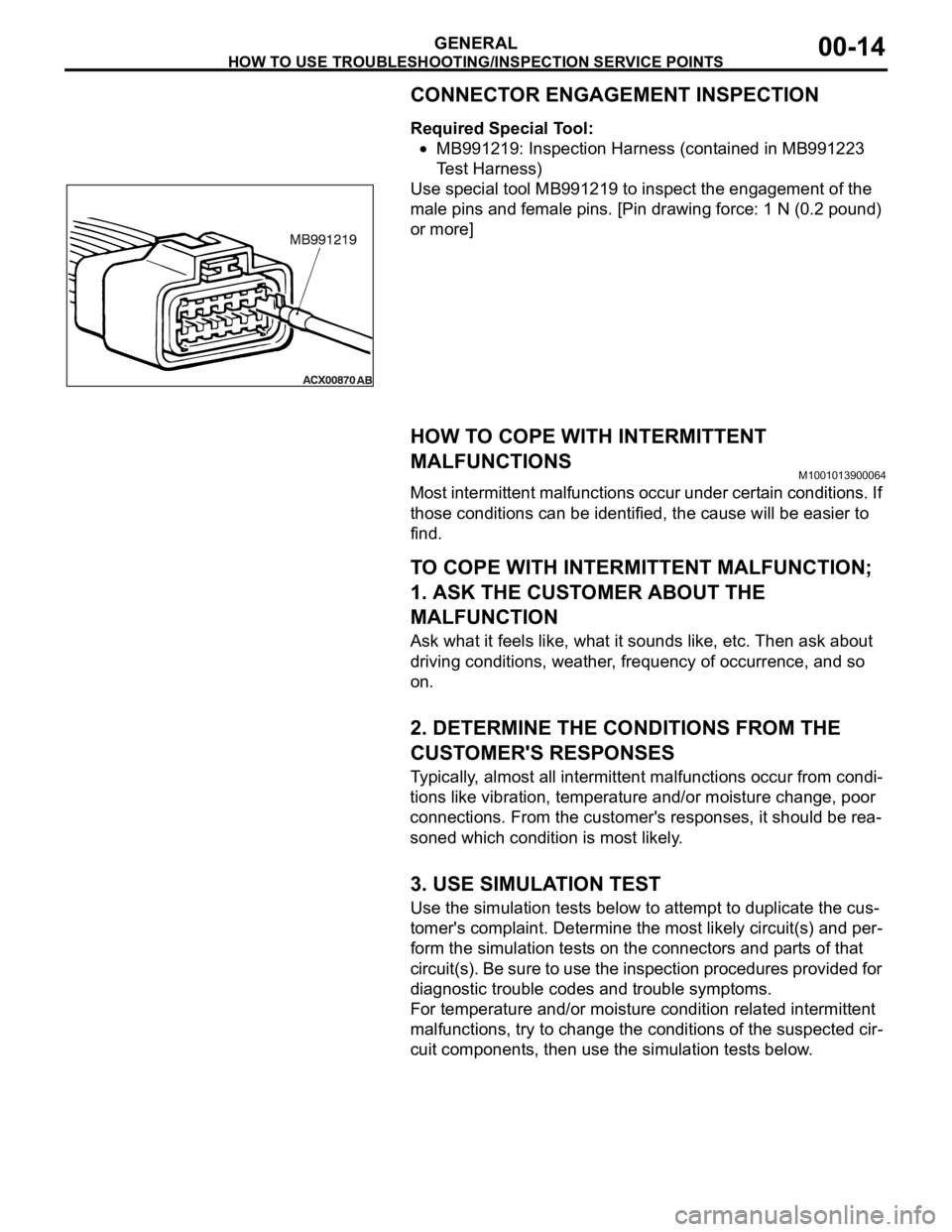
CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT INSPECTION
Required Special Tool:
MB991219: Inspection Harness (contained in MB991223
Test Harness)
Use special tool MB991219 to inspect the engagement of the
male pins and female pins. [Pin drawing force: 1 N (0.2 pound)
or more]
HOW TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT
MALFUNCTIONS
M1001013900064
Most intermittent malfunctions occur under certain conditions. If
those conditions can be identified, the cause will be easier to
find.
.
TO COPE WITH INTERMITTENT MALFUNCTION;
1. ASK THE CUSTOMER ABOUT THE
MALFUNCTION
Ask what it feels like, what it sounds like, etc. Then ask about
driving conditions, weather, frequency of occurrence, and so
on.
.
2. DETERMINE THE CONDITIONS FROM THE
CUSTOMER'S RESPONSES
Typically, almost all intermittent malfunctions occur from condi-
tions like vibration, temperature and/or moisture change, poor
connections. From the customer's responses, it should be rea-
soned which condition is most likely.
.
3. USE SIMULATION TEST
Use the simulation tests below to attempt to duplicate the cus-
tomer's complaint. Determine the most likely circuit(s) and per-
form the simulation tests on the connectors and parts of that
circuit(s). Be sure to use the inspection procedures provided for
diagnostic trouble codes and trouble symptoms.
For temperature and/or moisture condition related intermittent
malfunctions, try to change the conditions of the suspected cir-
cuit components, then use the simulation tests below.
.