SPEED MITSUBISHI 380 2005 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: 380, Model: MITSUBISHI 380 2005Pages: 1500, PDF Size: 47.87 MB
Page 849 of 1500
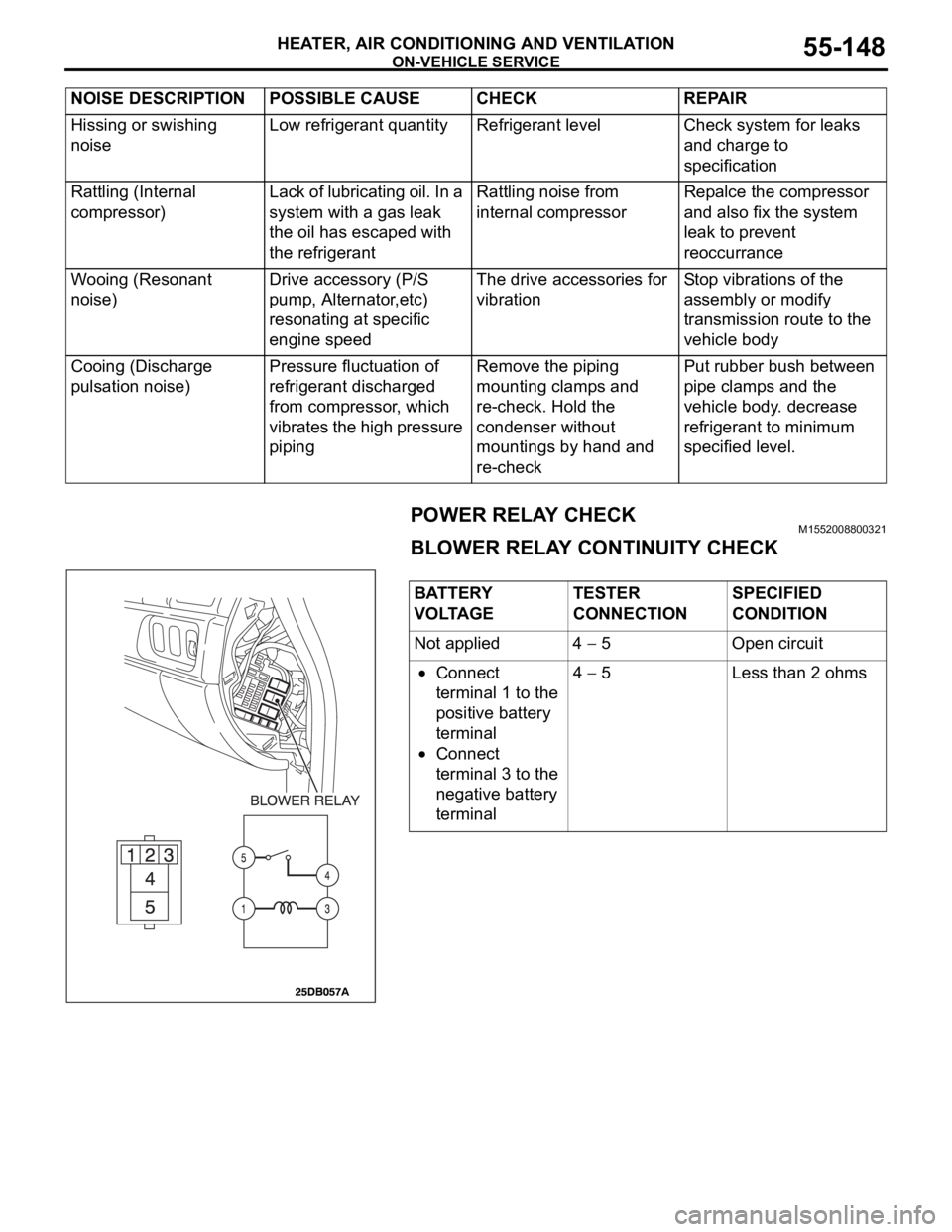
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-148
POWER RELAY CHECKM1552008800321
BLOWER RELAY CONTINUITY CHECK
Hissing or swishing
noiseLow refrigerant quantity Refrigerant level Check system for leaks
and charge to
specification
Rattling (Internal
compressor)Lack of lubricating oil. In a
system with a gas leak
the oil has escaped with
the refrigerantRattling noise from
internal compressorRepalce the compressor
and also fix the system
leak to prevent
reoccurrance
Wooing (Resonant
noise)Drive accessory (P/S
pump, Alternator,etc)
resonating at specific
engine speedThe drive accessories for
vibrationStop vibrations of the
assembly or modify
transmission route to the
vehicle body
Cooing (Discharge
pulsation noise)Pressure fluctuation of
refrigerant discharged
from compressor, which
vibrates the high pressure
pipingRemove the piping
mounting clamps and
re-check. Hold the
condenser without
mountings by hand and
re-checkPut rubber bush between
pipe clamps and the
vehicle body. decrease
refrigerant to minimum
specified level. NOISE DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK REPAIR
BATTERY
VOLTAGETESTER
CONNECTIONSPECIFIED
CONDITION
Not applied 4
5 Open circuit
Connect
terminal 1 to the
positive battery
terminal
Connect
terminal 3 to the
negative battery
terminal4
5 Less than 2 ohms
Page 850 of 1500
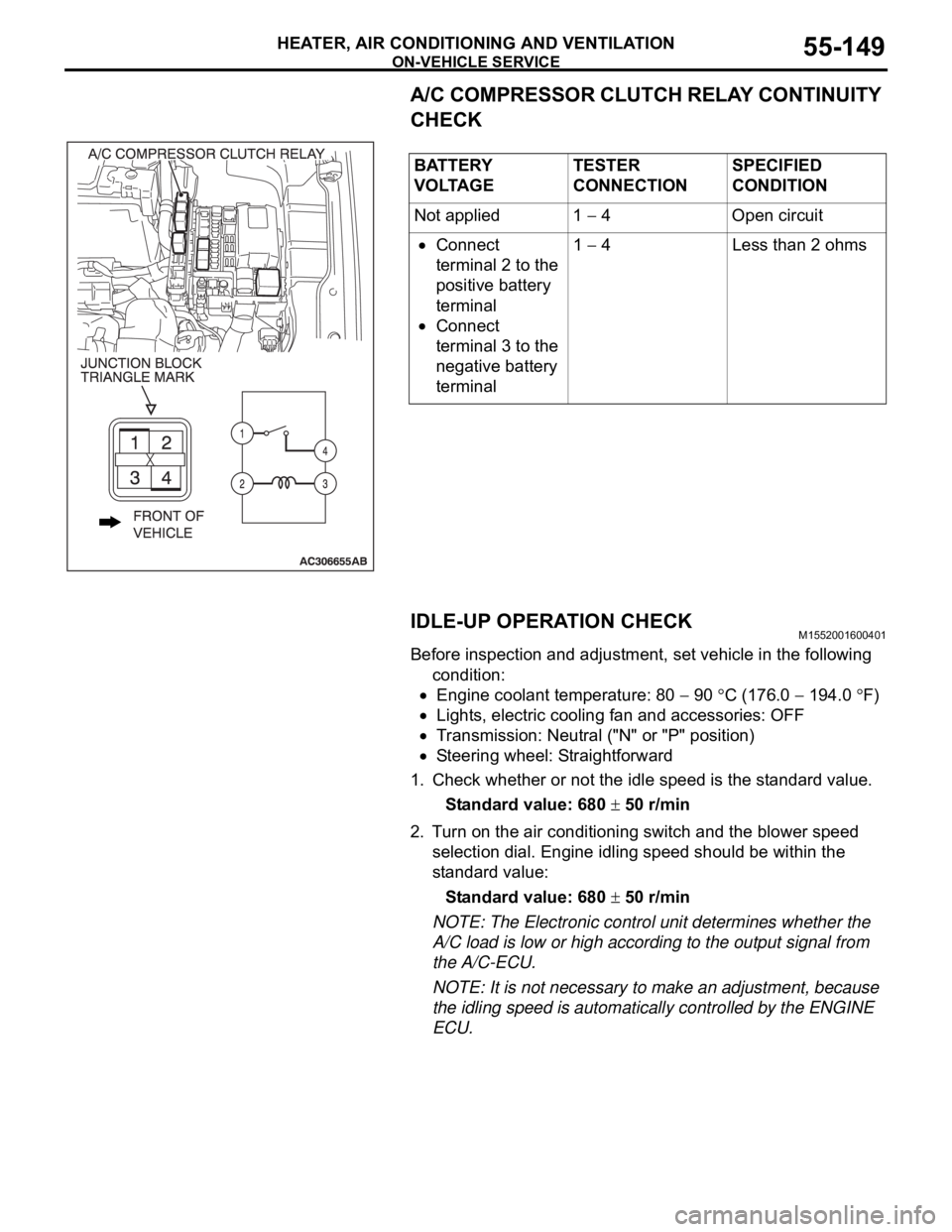
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-149
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY CONTINUITY
CHECK
IDLE-UP OPERATION CHECK
M1552001600401
Before inspection and adjustment, set vehicle in the following
condition:
Engine coolant temperature: 80 90 C (176.0 194.0 F)
Lights, electric cooling fan and accessories: OFF
Transmission: Neutral ("N" or "P" position)
Steering wheel: Straightforward
1. Check whether or not the idle speed is the standard value.
Standard value: 680
50 r/min
2. Turn on the air conditioning switch and the blower speed
selection dial. Engine idling speed should be within the
standard value:
Standard value: 680
50 r/min
NOTE: The Electronic control unit determines whether the
A/C load is low or high according to the output signal from
the A/C-ECU.
NOTE: It is not necessary to make an adjustment, because
the idling speed is automatically controlled by the ENGINE
ECU. BATTERY
V O LTA G ETESTER
CONNECTIONSPECIFIED
CONDITION
Not applied 1
4 Open circuit
Connect
terminal 2 to the
positive battery
terminal
Connect
terminal 3 to the
negative battery
terminal1
4 Less than 2 ohms
Page 879 of 1500
SPECIFICATIONS
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-178
SPECIFICATIONS
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONSM1552012100273
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONSM1552000200262
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONSM1552000300333
LUBRICANTSM1552000400329
ITEM SPECIFICATION
Liquid pipe mounting nut (heater unit side) 4.9
0.9 Nm (43 8 in-lb)
Liquid pipe mounting bolt (condenser side) 4.9
0.9 Nm (44 8 in-lb)
Suction flexible hose mounting nut (compressor side) 25
4 Nm (18 3 ft-lb)
Suction pipe mounting nut (heater unit side) 12
2 Nm (107 17 in-lb)
Suction pipe to suction hose union nut 32
2 Nm
Discharge flexible hose mounting bolt (compressor side) 25
4 Nm (18 3 ft-lb)
Discharge flexible hose mounting nut (condenser side) 12
2 Nm (107 17 in-lb)
ITEM MANUAL AIR CONDITIONING
Heater control Dial type
Air conditioning switch Push-button type
Compressor Type 10S17 (Swashplate type)
Displacement (cm
3)188
Refrigerant Type R134a (HFC-134a)
Amount (grams) 435
475
ITEM STANDARD VALUE
Idle speed r/min 680
50
Idle-up speed r/min 680
50
Air mix damper potentiometer resistance k
1.7 5.0
Air outlet changeover damper potentiometer resistance k
0.8 4.8
Air gap (air conditioning compressor clutch) mm (in) 0.3
0.5 (0.012 0.020)
ITEM SPECIFIED LUBRICANT QUANTITY(ml)
Each connection of refrigerant line ND Oil 8 As required
Compressor refrigerant unit lubricant (ml) ND Oil 8 140
Page 887 of 1500
INSPECTION TERMINAL
COMPONENT LOCATIONS70-8
INSPECTION TERMINALM1701000200354
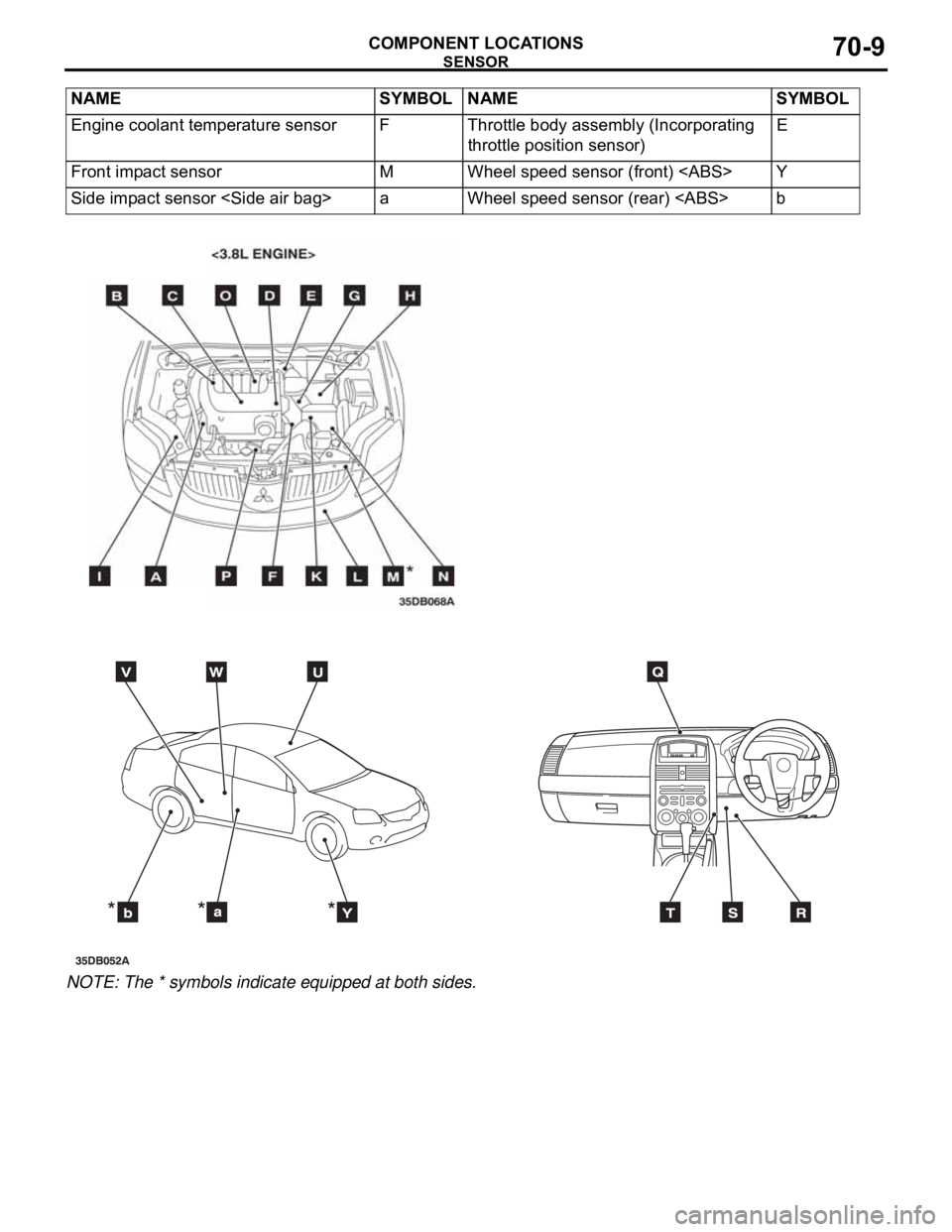
SENSORM1701000600415
NAME SYMBOL NAME SYMBOL
A/C pressure sensor I Interior temperature sensor
A/T control solenoid valve assembly
(Incorporating transmission fluid
temperature sensor)N Knock sensor C
Accelerator pedal position sensor R Left bank heated oxygen sensor (front)
<3.8L Engine>P
Air thermo sensor T Left bank heated oxygen sensor (rear)
<3.8L Engine>P
Ambient temperature sensor L Manifold absolute pressure sensor B
Camshaft position sensor D Mass airflow sensor G
Crankshaft position sensor A Sunroof assembly (Incorporating pulse
sensor)U
Fuel pump module (Incorporating fuel
level sensor (main) and fuel tank
temperature sensor)W Output shaft speed sensor H
Fuel level sensor (sub) V Photo sensor
Right bank heated oxygen sensor
(front) <3.8L Engine>O
Input shaft speed sensor K Right bank heated oxygen sensor (rear)
<3.8L Engine>O
Page 888 of 1500
SENSOR
COMPONENT LOCATIONS70-9
NOTE: The * symbols indicate equipped at both sides.Engine coolant temperature sensor F Throttle body assembly (Incorporating
throttle position sensor)E
Front impact sensor M Wheel speed sensor (front)
Side impact sensor
Page 918 of 1500
ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE COOLING14-3
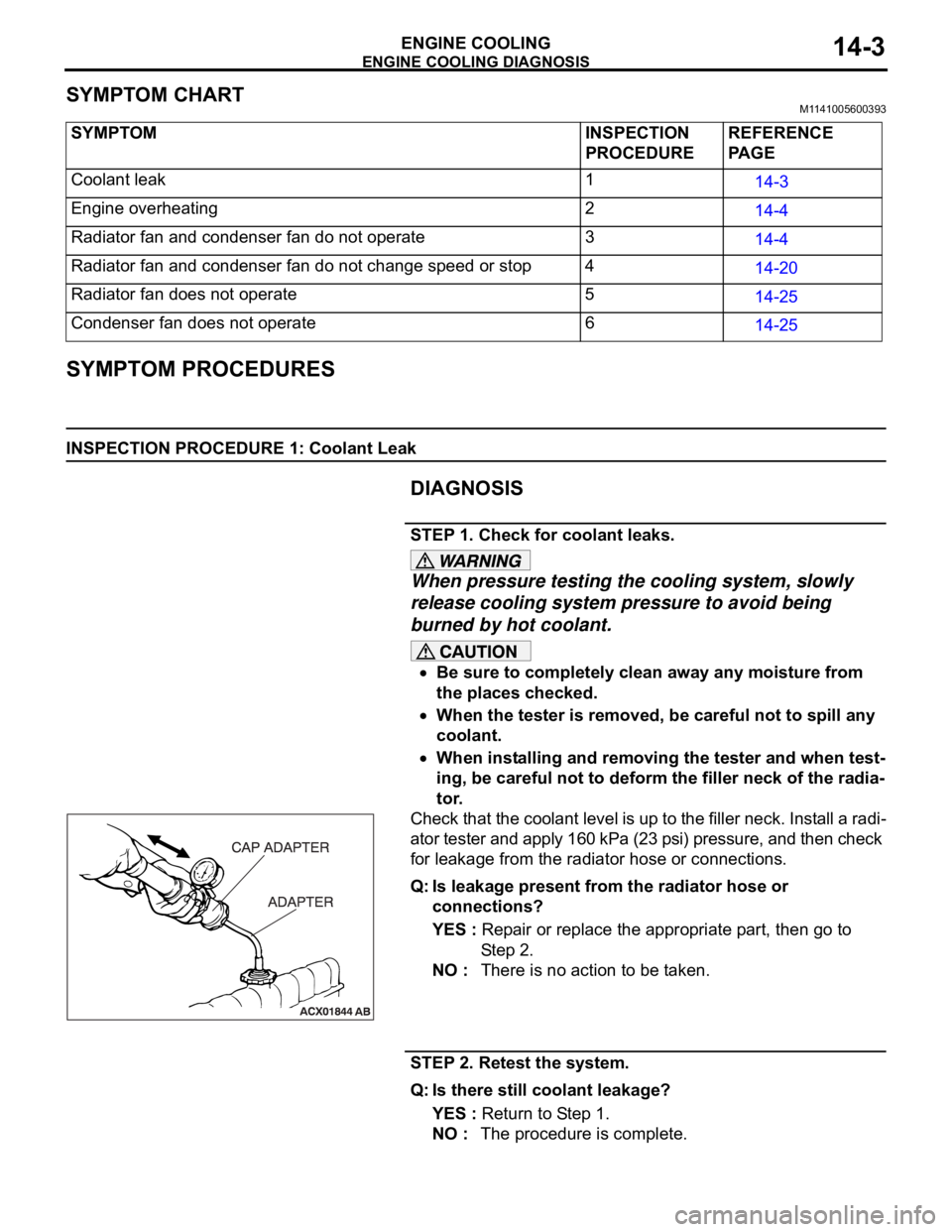
SYMPTOM CHARTM1141005600393
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: Coolant Leak
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check for coolant leaks.
When pressure testing the cooling system, slowly
release cooling system pressure to avoid being
burned by hot coolant.
Be sure to completely clean away any moisture from
the places checked.
When the tester is removed, be careful not to spill any
coolant.
When installing and removing the tester and when test-
ing, be careful not to deform the filler neck of the radia-
tor.
Check that the coolant level is up to the filler neck. Install a radi-
ator tester and apply 160 kPa (23 psi) pressure, and then check
for leakage from the radiator hose or connections.
Q: Is leakage present from the radiator hose or
connections?
YES : Repair or replace the appropriate part, then go to
St e p 2 .
NO : There is no action to be taken.
STEP 2. Retest the system.
Q: Is there still coolant leakage?
YES : Return to Step 1.
NO : The procedure is complete. SYMPTOM INSPECTION
PROCEDUREREFERENCE
PA G E
Coolant leak 1
14-3
Engine overheating 2
14-4
Radiator fan and condenser fan do not operate 3
14-4
Radiator fan and condenser fan do not change speed or stop 4
14-20
Radiator fan does not operate 5
14-25
Condenser fan does not operate 6
14-25
Page 920 of 1500

ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE COOLING14-5
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3: Radiator Fan and Condenser Fan do not Operate
.
CIRCUIT OPERATION
The fan controller is powered from fusible link
No.2.
The engine-ECU uses input signals from the A/C
switch, the water temperature sensor unit and the
vehicle speed sensor
speed sensor to control the speed of the
radiator fan motor and the condenser fan motor.
The engine-ECU controls the fan controller to
activate the radiator fan motor and the condenser
fan motor.
.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The cause could be a malfunction of the fan con-
troller power supply or earth circuit.
If the communication line wiring harness between
the fan controller and the engine-ECU is
short-circuited to earth, the radiator fan motor
and the condenser fan motor will not rotate.
The cause could also be a malfunction of input
signal from the A/C switch, the water temperature
sensor unit and the vehicle speed sensor
or the output shaft speed sensor to the
engine-ECU.
The cause could also be a malfunction of the fan
controller or the engine-ECU.
.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Malfunction of fusible link No.2
Malfunction of fan control relay
Malfunction of cooling fan motor and fan control-
ler
Malfunction of engine-ECU.
Damaged wiring harness or connector
Refer to component locations GROUP-1
Refer to configuration diagrams GROUP-1
Refer to circuit diagrams GROUP-1
Page 935 of 1500

ENGINE COOLING DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE COOLING14-20
STEP 23. MUT-III self-diag code
Check if an MPI system self-diag code is set. (Refer to GROUP
13A - Trouble shooting 13A-5).
Q: Diagnosis code set?
YES : Inspection chart for diagnosis code (Refer to GROUP
13A - Trouble shooting 13A-17)
NO : Replace the engine-ECU (Refer to GROUP 13A,
Engine-ECU 13A-675 ). Then go to Step 24.
STEP 24. Check the symptoms.
Q: Does the radiator fan motor and the condenser fan
motor operate correctly?
YES : This symptom is complete.
NO : Return to Step 1.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 4: Radiator Fan and Condenser Fan do not Change Speed or Stop
.
Radiator Fan and Condenser Fan Drive
Circuit
Refer to 5.
.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The cause could be a malfunction of the fan con-
troller power supply or earth circuit.
If the communication line wiring harness between
the fan controller and the engine-ECU is
short-circuited to earth, the radiator fan motor
and the condenser fan motor will not rotate.
The cause could also be a malfunction of input
signal from the A/C switch, the water temperature
sensor unit and the vehicle speed sensor
or the output shaft speed sensor to the
engine-ECU.
The cause could also be a malfunction of the fan
controller or the engine-ECU.
.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Malfunction of fusible link No.2
Malfunction of fan control relay
Malfunction of cooling fan motor
Malfunction of fan controller
Malfunction of engine-ECU
Damaged wiring harness or connector
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the fan control relay.
Refer to 14-31.
Q: Is the fan control relay in good condition?
YES : Go to Step 2.
NO : Replace the fan control relay. Then go to Step 8.
Page 951 of 1500
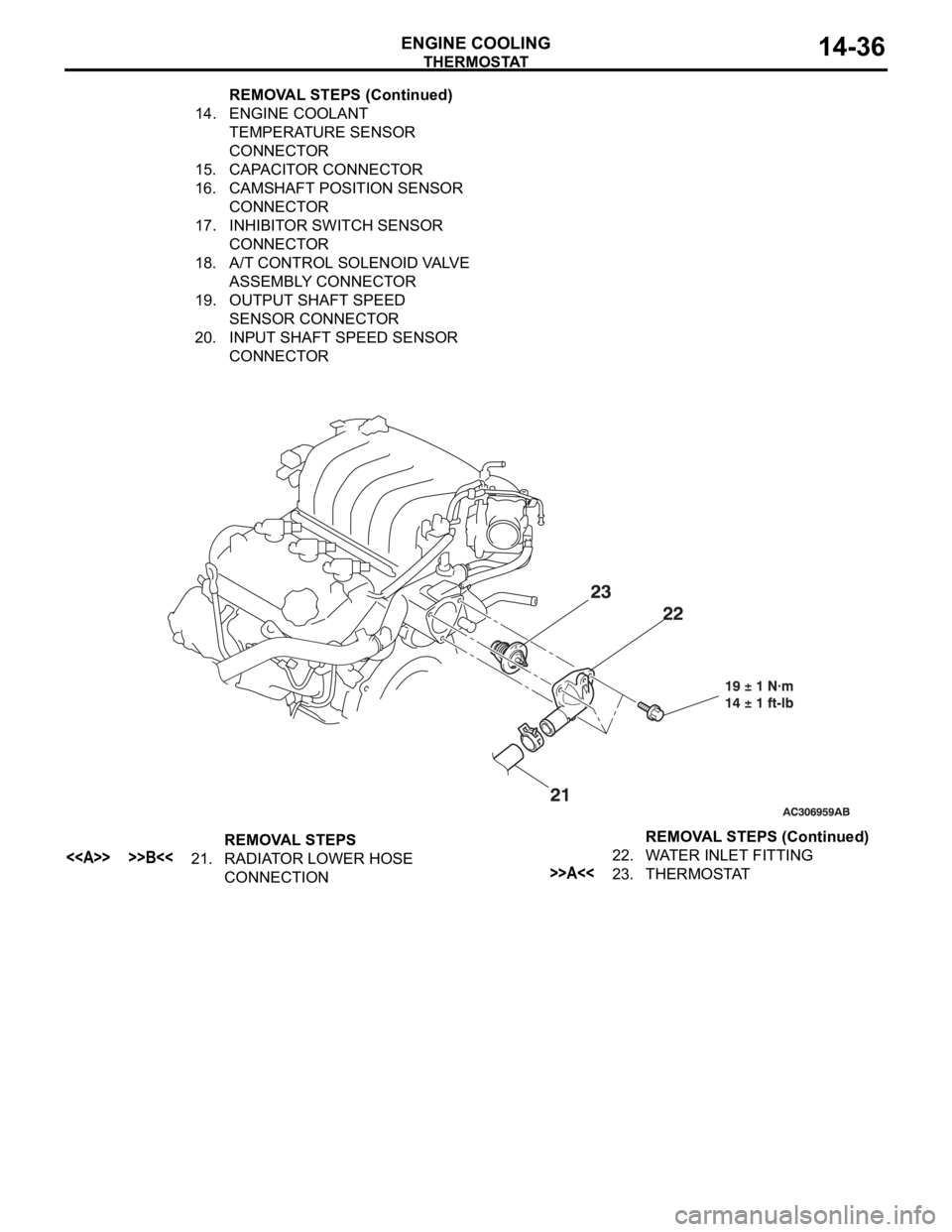
THERMOSTAT
ENGINE COOLING14-36
14. ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
CONNECTOR
15. CAPACITOR CONNECTOR
16. CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CONNECTOR
17. INHIBITOR SWITCH SENSOR
CONNECTOR
18. A/T CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE
ASSEMBLY CONNECTOR
19. OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED
SENSOR CONNECTOR
20. INPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
CONNECTOR REMOVAL STEPS (Continued)
REMOVAL STEPS
<> >>B<<21. RADIATOR LOWER HOSE
CONNECTION22. WATER INLET FITTING>>A<<23. THERMOSTATREMOVAL STEPS (Continued)
Page 979 of 1500
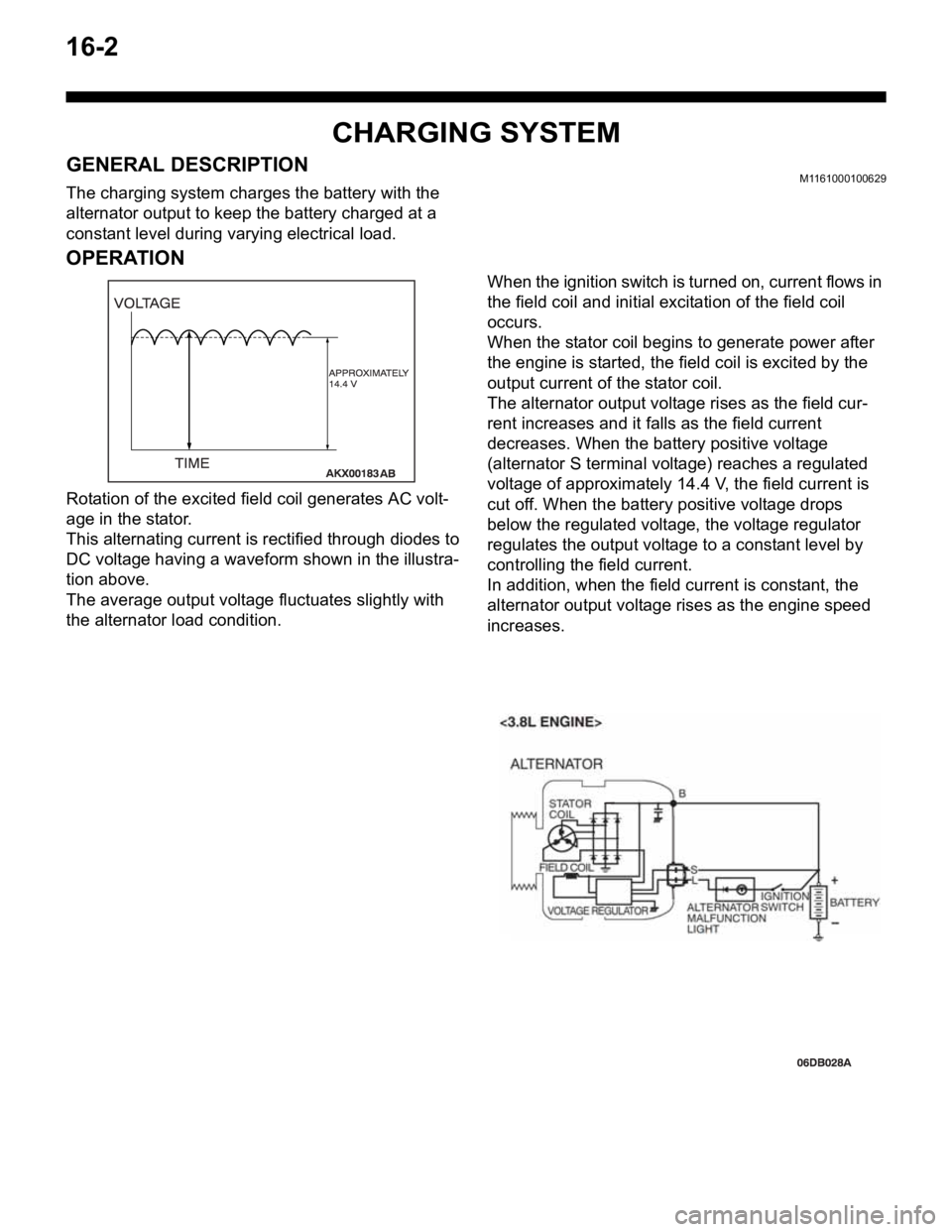
16-2
CHARGING SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1161000100629
The charging system charges the battery with the
alternator output to keep the battery charged at a
constant level during varying electrical load.
OPERATION
Rotation of the excited field coil generates AC volt-
age in the stator.
This alternating current is rectified through diodes to
DC voltage having a waveform shown in the illustra-
tion above.
The average output voltage fluctuates slightly with
the alternator load condition.When the ignition switch is turned on, current flows in
the field coil and initial excitation of the field coil
occurs.
When the stator coil begins to generate power after
the engine is started, the field coil is excited by the
output current of the stator coil.
The alternator output voltage rises as the field cur-
rent increases and it falls as the field current
decreases. When the battery positive voltage
(alternator S terminal voltage) reaches a regulated
voltage of approximately 14.4 V, the field current is
cut off. When the battery positive voltage drops
below the regulated voltage, the voltage regulator
regulates the output voltage to a constant level by
controlling the field current.
In addition, when the field current is constant, the
alternator output voltage rises as the engine speed
increases.