belt MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 1 of 408

HOW TO USE THIS BOOK 1-2
WHERE TOBEGIN l-2
AVOIDINGTROUBLE 1-2
MAINTENANCEORREPAIR? 1-2
AVOIDINGTHEMOSTCOMMONMISTAKES l-2
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT 1-2
SPECIALTOOLS l-4
YOUR VEHICLE SAFELY 1-4
DON'TS l-6
FASTENERS, MEASUREMENTS AND
CONVERSIONS l-6
BOLTS,NUTSANDOTHERTHREADED
RETAINERS 1-6
TORQUE l-7
TORQUEWRENCHES l-7
TORQUEANGLEMETERS 1-9
STANDARDANDMETRIC MEASUREMENTS l-9
SERIAL NUMBER IDENTIFICATION l-10
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER l-10
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER I-10
TRANSAXLEIDENTIFICATION I-10
DRlVEAXLE(AWDGALANTONLY) l-10
TRANSFERCASE(AWDGALANTONLY) l-10
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE AND TUNE-UP l-14
AIRCLEANER(ELEMENT) 1-14
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 1-14
FUELFILTER 1-15
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION l-15
PCVVALVE l-15
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION l-15
EVAPORATIVECANISTER l-16
SERVICING 1-16
BATTERY 1-16
PRECAUTIONS I-16
GENERALMAINTENANCE 1-16
BEL BATTERYFLUID 1-16
CABLES I-17
CHARGING I-18
REPLACEMENT 1-18
TS 1-18
INSPECTiON l-18
ADJUSTMENT 1-18
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION 1-18
TIMINGBELTS l-20
INSPECTION l-20
HOSES I-20
INSPECTION l-20
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
CV-BOOTS 1-21
INSPECTION l-21
SPARKPLUGS l-22
SPARKPLUGHEATRANGE
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
INSPECTION &GAPPING 1.
SPARKPLUG WIRES 1-24
TESTING 1-24
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
DISTRIBUTORCAPANDROTOR
REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
INSPECTION 1-25
IGNITIONTIMING 1-25
. GENERALINFORAMTION l-
lNSPECTlON&ADJUSTMENl
VALVE LASH l-27
ADJUSTMENT l-27
IDLESPEED 1-28 1-21
l-22
l-22
-23
1-24
l-25
l-25
.25
1-26
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM 1-28
SYSTEMSERVlCEiiREPAlR l-28
PREVENTIVEMAINTENANCE 1-28
SYSTEM INSPECTION l-29
WINDSHIELD WIPERS l-29
ELEMENT(REFILL)CARE&
REPLACEMENT l-29
TIRESANDWHEELS l-30
TIRE ROTATION I-30
TIRE DESIGN 1-31
TIRESTORAGE l-31
INFLATION &INSPECTION l-31
CARE OFSPECIALWHEELS l-32 OPERATION INFOREIGNCOUNTRIES l-33
ENGINE l-33
OILLEVELCHECK 1-33
OIL& FILTER CHANGE l-34
MANUALTRANSAXLE l-35
FLUIDRECOMMENDATIONS l-35
LEVELCHECK l-35
DRAIN&REFILL l-36
AUTOMATICTRANSAXLE l-36
FLUIDRECOMMENDATIONS l-36
LEVELCHECK 1-36
DRAIN&REFILL l-36
PAN & FILTERSERVICE 1-36
TRANSFERCASE(AWDGAlANT ONLY) l-38
FLUIDRECOMMENDATIONS l-38
LEVELCHECK l-38
DRAIN&REFILL l-38
REARDRlVEAXLE(AWDGALANTONLY) l-38
FLUIDRECOMMENDATIONS l-38
LEVELCHECK l-38
DRAIN&REFILL l-38
COOLINGSYSTEM l-39
FLUIDRECOMMENDATIONS l-39
iM-41
FLUIDS AND LUBRICANTS 1-33
FLUID DISPOSAL 1-33
FlJELANDENGlNEOILRECOMMENDATlONS
ENGINE OIL l-33
FUEL l-33
Page 5 of 408

1-6 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Fig. 16 Screwdrivers should be kept in good
:ondition to prevent injury or damage which
:ould result it the blade slips from the screw
0
0
PP tccs1022 Fig. 16 Using the correct size wrench will
help prevent the possibility of rounding off
a nut
7
lwo.WIRE CouDuClOR TMREE-WIRE CONO”CTOI
MIRD WIRE GROUNDING GROUNDING TNRU
THE CASE A CmxlIT
.
i$Y$$pQ
p-+
TNHREE-WIRE CONDUCTOR THREE-WIRE CONDUCTOR
ONE WIRE TO 4 GROUND GROUNOlNG TMRU
AN ADAPTER PLUG
tccm21
Fig. 17 Power tools should always be prop-
erly grounded
Fig. 19 NEVER work under a vehicle unless it
is supported using safety stands (jackstands)
l Do, when possible, pull on a wrench handle l Do set the parking brake and block the drive
rather than push on it, and adjust your stance to pre-
vent a fall. wheels if the work requires a running engine.
l Do be sure that adjustable wrenches are
tightly closed on the nut or bolt and pulled so that
the force is on the side of the fixed jaw.
l Do strike squarely with a hammer; avoid glanc-
ing blows. l Don’t run the engine in a garage or anywhere
else without proper ventilation-EVER! Carbon monoxide is poisonous; it takes a long time to leave
the human body and you can build up a deadly sup-
ply of it in your system by simply breathing in a !ittle
every day. You may not realize you are slowly poi-
soning yourself. Always use power vents, windows,
fans and/or open the garage door.
l Don’t work around moving parts while wearing
loose clothing. Short sleeves are much safer than
long, loose sleeves. Hard-toed shoes with neoprene
soles protect your toes and give a better grip on slip-
pery surfaces. Jewelry such as watches, fancy belt
buckles, beads or body adornment of any kind is not
safe working around a vehicle. Long hair should be
tied back under a hat or cap.
l Don’t use pockets for toolboxes. A fall or bump
can drive a screwdriver deep into your body. Even a
rag hanging from your back pocket can wrap around
a spinning shaft or fan.
l Don’t smoke when working around gasoline,
cleaning solvent or other flammable material.
l Don’t smoke when workrng around the battery.
When the battery is being charged, it gives off explo-
sive hydrogen gas.
l Don’t use gasoline to wash your hands; there
are excellent soaps available. Gasoline contains dan-
gerous additives which can enter the body through a
cut or through your pores. Gasoline also removes all
the natural oils from the skin so that bone dry hands
will suck up oil and grease.
l Don’t service the air conditioning system un-
less you are equipped with the necessary tools and
trainmg. When liquid or compressed gas refrigerant
is released to atmospheric pressure it will absorb
heat from whatever it contacts. This will chill or freeze
anything it touches.
l Don’t use screwdrivers for anything other than
driving screws! A screwdriver used as an prying tool
can snap when you least expect it, causing injuries.
At the very least, you’ll ruin a good screwdriver.
. Don’t use an emergency jack (that little ratchet,
scissors, or pantograph jack supplied with the vehi-
cle) for anything other than changing a flat! These
jacks are only Intended for emergency use out on the
road; they are NOT designed as a maintenance tool. If
you are serious about mamtaining your vehicle your-
self, invest in a hydraulic floor jack of at least a 1%
ton capacity, and at least two sturdy jackstands.
sion which can increase the torque necessary to proper installation and safe operation of the vehicle
achieve the desired clamp load for which that fastener afterwards.
was originally selected. Additionally, be sure that the Thread gauges are available to help measure a bolt
p See Figures 20, 21, 22, and 23 driver surface of the fastener has not been compro- or stud’s thread. Most automotive and hardware
mised by rounding or other damage. In some cases a stores keep gauges available to help you select the
Although there are a great variety of fasteners found driver surface may become only partially rounded, al- proper size. In a pinch, you can use another nut or
in the modern car or truck, the most commonly used lowing the driver to catch in only one direction. In bolt for a thread gauge. If the bolt you are replacing is
retainer is the threaded fastener (nuts, bolts, screws, many of these occurrences, a fastener may be in- not too badly damaged, you can select a match by
studs, etc.). Most threaded retainers may be reused, stalled and tightened, but the driver would not be able finding another bolt which will thread in its place. If
provided that they are not damaged in use or during to grip and loosen the fastener again. (This could lead you find a nut which threads properly onto the dam-
the repair. Some retainers (such as stretch bolts or J to frustration down the line should that component aged bolt, then use that nut to help select the replace-
torque prevailing nuts) are designed to deform when ever need to be disassembled again). ment bolt If however, the bolt you are replacing is so
tightened or in use and should not be reinstalled. If you must replace a fastener, whether due to de- badly damaged (broken or drilled out) that its threads
Whenever possible, we will note any special re- sign or damage, you must ALWAYS be sure to use cannot be used as a gauge, you might start by look-
tainers which should be replaced during a procedure. the proper replacement In all cases, a retainer of the ing for another bolt (from the same assembly or a
But you should always inspect the condition of a re- same design, material and strength should be used. similar location on your vehicle) which will thread
tainer when It is removed and replace any that show Markings on the heads of most bolts will help deter- into the damaged bolt’s mounting. If so, the other bolt
signs of damage. Check all threads for rust or corro- mine the proper strength of the fastener. The same
can be used to select a nut; the nut can then be used
material, thread and pitch must be selected to assure
to select the replacement bolt.
Page 10 of 408
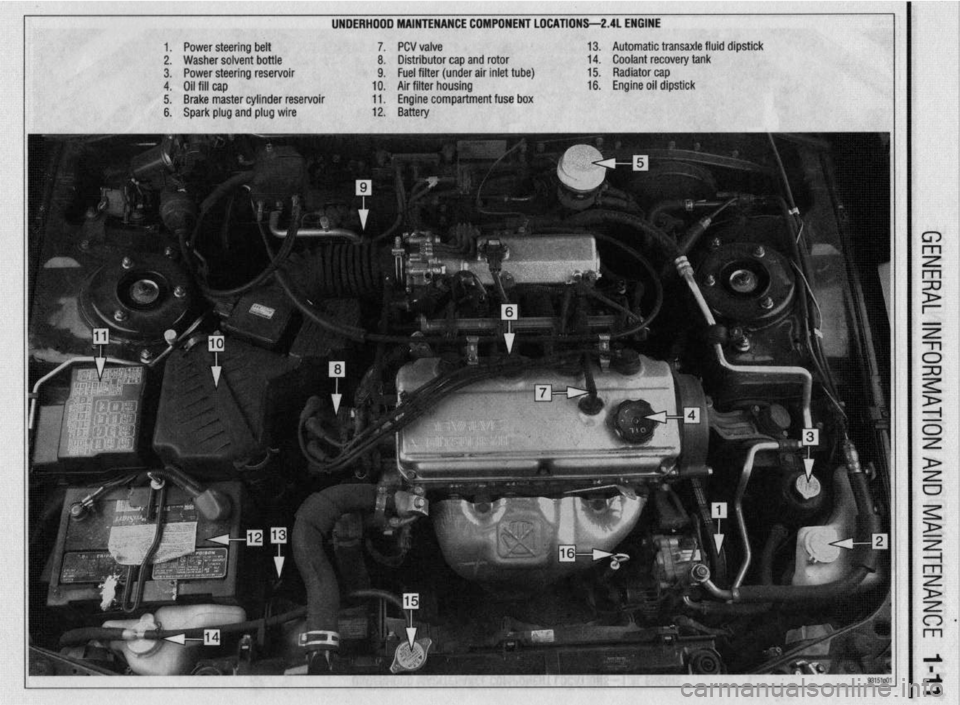
UNDERHDDD MAINTENANCE COMPONENT LOCATIONS-2AL ENGINE
II
1. Power steering belt 7. PCV valve
2. Washer solvent bottle 8. Distributor cap and rotor
3. Power steering reservoir 9. Fuel filter (under air inlet tube)
4. Oil fill cap 10. Air filter housing
5. Brake master cylinder reservoir 11. Engine compartment fuse box
6. Spark plug and plug wire 12. Battery 13. Automatic transaxle fluid dipstick
14. Coolant recovery tank
15. Radiator cap
16. Engine oil dipstick
Page 11 of 408
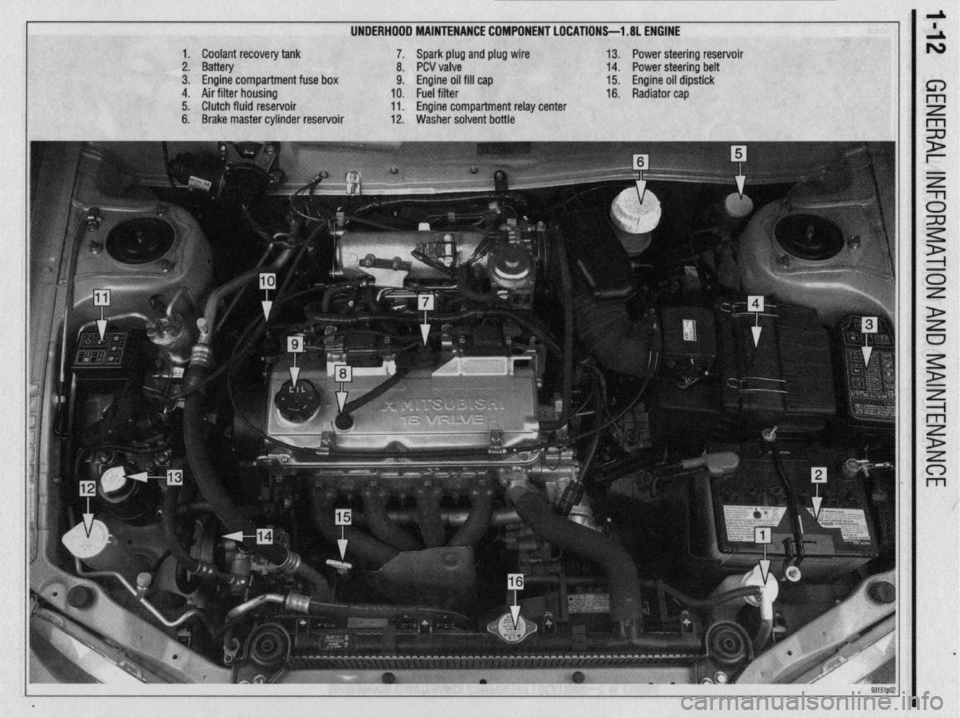
UNDERHOOD MAINTENANCE COMPONENT LOCATIONS-l .8L ENGINE
1. Coolant recovery tank
2. Battery
3. Engine compartment fuse box
4. Air filter housing
5. Clutch fluid reservoir
6. Brake master cylinder reservoir 7. Spark plug and plug wire
8. PCV valve
9. Engine oil fill cap
10. Fuel filter
11. Engine compartment relay center
12. Washer solvent bottle 13. Power steering reservoir
14. Power steering belt
15. Engine oil dipstick
16. Radiator cap
Page 17 of 408

l
1-18 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
the clamps and remove the cables, negative cable
first. On batteries with posts on top, the use of a
puller specially made for this purpose is recom-
mended. These are inexoensive and available in most alternator or turn the adjusting bolt to adjust belt ten-
sion. Once the desired value is reached, secure the
bolt or locknut and recheck tension.
d”t” lJdlL> X”lt;>. 31°C LtXlllllldl lJdllt2)’ MLJIC, dlt’ X- cured with a small bolt. ST& I REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Clean the cable clamps and the battery terminal I
with a wire brush, until all corrosion, grease, etc., is
removed and the metal is shinv. It is esneciallv imnnr-
tant to c
knife is useful nere), since a smart
material or oxidation there will pre Clean the cable clamps and the battery terminal
with a wire brush, until all corrosion, grease, etc., is
removed and the metal is shiny. It is especially impor-
tant to clean the inside of the clamp thoroughly (an old
knife is useful here), since a small deposit of foreign
material or oxidation there will prevent a sound electri-
cal connection and inhibit either starting or charging.
Special tools are available for cleaning these parts,
one type for conventional top post batteries and an-
other type for side terminal batteries. It is also a good
idea to apply some dielectric grease to the terminal, as
this will aid in the prevention of corrosion,
After the clamps and terminals are clean, reinstall
the cables, negative cable last; DO NOT hammer the
clamps onto battery posts. Tighten the clamps se-
curely, but do not distort them. Give the clamps and
terminals a thin external coating of grease after in-
stallation, to retard corrosion.
Check the cables at the same time that the terminals
are cleaned. If the cable insulation is cracked or bro-
ken, or if the ends are frayed, the cable should be re-
placed with a new cable of the same length and gauge.
CHARGING
the cables, negative cable last; DO NOT hammer the
curely, but do not distort them. Give the clamps and
terminals a thin external coating of grease after in-
stallation, to retard corrosion.
Check the cables at the same time that the terminals
are cleaned. If the cable insulation is cracked or bro-
ken, or if the ends are frayed, the cable should be re-
placed with a new cable of the same length and aauae.
CHARGING
Fig. 62 mere are typically 3 types of ac-
cessory drive belts found on vehicles today 1. Loosen the alternator support nut.
2. Loosen the adjuster lock bolt.
3. Rotate the adjuster bolt counter clockwise to
I .I , . . . * . .
I Tn i”et*ll* Fig. 62 There are typically 3 types of ac-
Fig. 64 Deep cracks in this belt will cause
flex, building up heat that will eventually 11, 1.8L, 2.OL and 2.4L Engines
cal connection and inhibit either starting or charging.
Special tools are available for cleaning these parts,
one type for conventional top post batteries and an-
other type for side terminal batterin, I+ if QI@* 3 nnnd
idea to apply some dielectric grr
this will aid in the prevention of ,,vIIuaIUII.
After the clamps and terminals are clean, reinstall 1.5L, 1.6
AL TERNA TOR BE1 T
e See Figures 67,68, and 69
1. Loosen the alternator support nut.
2. Loosen the adjuster lock bolt.
3. Rotate the adjuster bolt counter clockwise to
release the tension on the belt.
4. Remove the belt.
To install:
5. Install the belt on the pulleys.
6. Rotate the adjuster bolt clockwise until the
proper tension is reached.
7. Tighten the adjuster lock bolt and the alternator
support nut.
POWER STEERING BELT
8 See Figures 70 and 71
1. Remove the alternator belt as described above.
2. Loosen the power steering pump adjusting
bolts.
3. Remove the power steering oumo fixed bolt on
R Rntatn the cxiillrtm hnit A&+,& until the r -r- .- .- ._.. ._ .______
7. Tighten the adjuster lock bolt and the alternator
support nut.
POWER STEERING BELT
1 ..“‘.I ““..Y...Y up II”“. ..IU. ..m.*
1 lead to belt failure V.
I
I
The chemical reaction which takes place in - 1 the rear of the bracket.
4. Rotate the pump toward the engine and remove
the belt.
all batteries generates explosive hydrogen
gas. A spark can cause the battery to explode
and splash acid. To avoid serious personal
injury, be sure there is proper ventilation and
take appropriate fire safety precautions when
connecting, disconnecting, or charging a bat-
tery and when using jumper cables. To fnstall:
5. Install the belt on the pulleys.
A battery should be charged at a slow rate to keep
the plates inside from getting too hot. However, if
some maintenance-free batteries are allowed to dis-
charge until they are almost “dead,” they may have to
be charged at a high rate to bring them back to “life.”
Always follow the charger manufacturers instructions
on charging the battery. 85 The cover of this belt ex-
Fig. is worn,
REPLACEMENT
When it becomes necessary to reolace thn haeoN
‘” yyL’“‘J’ I or oreMer
select one with an amperage rating equal tc .
a ----
than the battery originally installed. Deterioration and
just plain aging of the battery cables, starter motor,
and associated wires makes the battery’s job harder
in successive years. The slow increase in electrical
resistance over time makes it prudent to install a new
battery with a greater capacity than the old. 1 Fig. 67 Loosen the adjuster lock bolt . . .
I ‘-
I -. -_ tm1217 Fig. 66 Installing too wide a belt can resylt
in serious belt wear and/or breakage
the belt and run outward. All worn or damaged drive
belts should be replaced immediately. It is best to re-
place all drive belts at one time, as a preventive
uring this service operation. maintenance measure, d
- ADJUSTMENT : *
INSPECTION Excessive belt tension will cause damage to the al-
e See Figures 62, 83, 64, 65, and 88
Inspect the belts for signs of glazing or cracking. A
glazed belt will be perfectly smooth from slippage,
while a good belt will have a slight texture of fabric
visible. Cracks will usually start at the inner edge of pulley bearings, while, on
It tension will
Droduce slin ternator and water pump
the other hand, loose be
r ------ r
and premature wear on the belt. Therefore, be sure to
adjust the belt tension to the proper level.
To
adjust the tension ’ ’ ’ ” ’ ‘* adjusting bolt or fixing b
alternator bracket or tens on a onve Den. loosen me I Fig. 68 . . . then
from the engine remove the alternator
bolt locknut on the alternator,
iion pulley. Then move the
Page 18 of 408

GENERAL INFORMATION AND MAlNTENANdE l-19
792UQ4 Fig. 69 Accessory V-belt routing-Mii
subishf 1.6L, 1.6L,-1.6L, 2.OL and 2.4L en
gines
33151PM Fig. 70 After the adjusting and fixed bolt!
are loosened, rotate the pump . . .
/ F$71t immtl$mm&a the power ::: 6. Rotate the pump until the proper tension is
reached.
7. Tighten the adjusting bolts on the pump.
8. Tighten the fixed bolt on the rear of the bracket.
9. Install the alternator belt.
A/r: COMPRESSOIl BEL f
1. Loosen the tension oullev and remove the belt.
2. The installation is the reverse of the removal.
.3.gL DGHC, 3.OL SOHC (Gaiant models
only) and 3.5L Engines 4. Remove the belt.
To install:
5. Install the belt on the crankshaft and alternator
pulleys.
6. Using the adjusting bolt on the tensioner,
tighten the belt to the desired tension.
7. Tighten the fixing nut to hold the adjustment.
8. Install the undercover and lower the vehicle to
_,
the tloor.
9. Connect the negative battery cable.
POWER SliEERlNG BEL f
6 See Figures 72 and 73 1. Disconnect the neaative batteN cah+P
-I
Wait at least 60 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent poS-
sibie deployment of the air bag.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle and re-
mob re the undercover.
3. Remove the alternator and NC compressor
belt.
4. Lower the vehicle and remove the cruise con-
trol oumn link iW%mblV. 79244Q.37
-- I-- r ---- - _I
Fig. 72 Serpentine belt routing-Mitsubishi 5. Place the power steering hose under the oil
reservoir.
3.OL engines (except 1696-00 Galant mod-
6.
Loosen the tension pulley fixing bolts and re-
els)
Generator pulP
1 move the power steering pump drive belt.
To install:
1 7. install the Dower steerina oumu r+r+v~ hp++
8. Insert an extension bar &eoufvaik;;t”f;;id‘he
opening at the end of the tension pulley bracket and
pivot the pulley to apply tension to the belt.
9. Tighten the fixing bolts.
10. Raise the vehicle and install the alternator and
compressor belt.
Il. Install the undercover and lower +hfi vph+r+p
.I,., .VII.“.Y.
12. Connect the negative battery cable.
I 3.OL SGHC (Diamante Models Onivl Enotne
I ,r ” 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.’ Loosen the lockbolt on the face nf the A/C _ __.- tensioner pulley.
3
Turn the adiustina bolt of the A/C +fincrnner
pulley to loosen the tension of the A/C belt.
4. Remove the A/C compressor belt.
5.
Loosen the locknut on the face of the power
to loosen the tc
7. Remov
Fig. 73 Accessory V-belt routing-Mitsubishi
3.5L and 1996-00 3.OL SOHC Galant en-
gines steering/alternator tensloner pulley.
6. Turn the adjusting bolt of the tensioner pulley
msion of the belt.
‘e the power steering/alternator belt.
To install:
8. Install the power steering/alternator belt first
.* .* . ,^
ssor drive belt. ana tnen tne A/ti compre:
9. Adjust the belts t+
ing the adjusting bolts anu
II~IIWII pueey tlxmg I the proper tension by turn-
A.:-L I-..-.. I,^, .’
nut/bolt.
10. Tighten the mounting nut of the power steer-
ing/alternator tensioner pulley to 36 ft. Ibs. (50 Nm).
Wait at least 60 seconds after the negative
battery cable is disconnected to prevent pos-
sible deployment of the air bag. -The manufacturer does not provide a
torque specification for the bolt that secures
A/C tensioner pulley.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle and re- 11. Connect the negative battery cable.
move the front undercover.
3. Loosen the tension pulley fixing nut and relieve
the tension on the belt by turning the adjusting bolt.
Page 19 of 408

.
l-20 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
INSPECTION
# See Figures 74 thru 81
All engines covered by this manual utilize timing
belts to drive the camshaft from the crankshafts turn-
ing motion and to maintain proper valve timing.
Some manufacturers schedule periodic timing belt
replacement to assure optimum engine performance,
to make sure the motorist is never stranded should
the belt break (as the engine will stop instantly) and
for some (manufacturers with interference motors) to
prevent the possibility of severe internal engine dam-
age
St10Ula the Delt break. Although the 1.5L and 1.8L engines are not listed
as an interference motors (it is not listed by the man-
ufacturer as a motor whose valves might contact the
pistons if the camshaft was rotated separately from
the crankshaft) the first 2 reasons for periodic re-
placement still apply and the timing belt should be
replaced at 60,000 miles (96,000 km). The 1.6L,
2.01,2.4L, 3.OL, and 35L engines are listed as inter-
ference motors, so the timing belt MUST be replaced
at 60,000 miles (96,000 km) to avoid severe engine
damage if the belt should break.
But whether or not you decide to replace the tim-
ing belt in the manufacturers schedule, you would be
wise to check it periodically to make sure it has not
become damaged or worn. Generally speaking, a se-
verelv worn belt mav cause enaine oerformance to
drop~dramatically, but a damaged belt (which could
give out suddenly) may not give as much warning. In
general, any time the engine timing cover(s) is (are)
removed you should inspect the belt for premature
parting, severe cracks or missing teeth. Also, an ac-
cess plug is provided in the upper portion of the tim-
ing cover so that camshaft timing can be checked
without cover removal. If timing is found to be off,
cover removal and further belt inspection or replace-
ment is necessary.
tml245 Fig. 76 look for noticeable cracks or wear
on the belt face
_
For the timing belt removal and installation proce-
dure, please refer to Section 3 of this manual. Fig. 74 Check for premature parting of the
belt
INSPECTION
. 75 Check if the teeth are cracked or
fig. 77 You may only have damage on one
side of the belt; if so, the guide could be
the culprit
b See Figures 82,8S, 84, and 85 .
Upper and lower radiator hoses, along with the
heater hoses, should be checked for deterioration,
leaks and loose hose clamps at least every 30,000
miles (48,000 km). It is also wise to check the hoses
periodically in early spring and at the beginning of
the fall or winter when you are performing other
maintenance. A quick visual inspection could dis-
cover a weakened hose which might have left you
stranded if it had remained unrepaired.
Whenever you are checking the hoses, make sure
the engine and cooling system are cold. Visually in-
spect for cracking, rotting or collapsed hoses, and w-
place as necessary. Run your hand along the length
of the hose. If a weak or swollen spot is noted when
squeezing the hose wall, the hose should be re- Fig. 78 Foreign materials can get in be- Fig. 79 Inspect the timing belt for c
tween the teeth and cause damage fraying, glazing or damage of any kind
Fig. 80 Damage on only one side of the tim-
I I Fig. 81 ALWAYS replace the timing belt at
ing belt may indicate a faulty guide
the interval specified by the manufacturer
, L placed.
Page 25 of 408

.
1-26 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
TDC of the compression stroke. If this happens, the
piston WIII be at the beginning of the power stroke
just as the compressed and ignited air/fuel mixture
forces the piston down and turns the crankshaft. Be-
cause it takes a fraction of a second for the spark
plug to ignite the mixture in the cylinder, the spark
plug must fire a little before the piston reaches TDC.
Otherwise, the mixture will not be completely ignited
as the piston passes TDC and the full power of the
explosion will not be used by the engine.
The timing measurement is given in degrees of
crankshaft rotation before the piston reaches TDC
(BTDC). If the setting for the ignition timing is 10”
BTDC, each spark plug must fire 10 degrees before
each piston reaches TDC. This only holds true, how-
ever, when the engine is at idle speed. The combus-
tion process must be complete by 23”ATDC to main-
tain proper engine performance, fuel mileage, and
low emissions.
As the engine speed increases, the pistons go
faster. The spark plugs have to ignite the fuel even
sooner if it IS to be completely ignited when the pis-
ton reaches TDC. If the ignition is set too far ad-
vanced (BTDC), the ignition and expansion of the fuel
in the cylinder wtll occur too soon and tend to force
the piston down while it is still traveling up. Thus
causes pre ignition or “knockmg and pinging”. If the
ignition spark is set too far retarded, or after TDC
(ATDC), the piston will have already started on its
way down when the fuel is ignited. The piston will be
forced down for only a portion of its travel, resulting
in poor engine performance and lack of power.
Timing marks or scales can be found on the rim of
the crankshaft pulley and the timing cover. The marks
on the pulley correspond to the posrtion of the piston
in the No. 1 cylinder. A stroboscopic (dynamic) tim-
ing light is hooked onto the No. 1 cylinder spark plug
wrre. Every time the spark plug fires, the timing light
flashes. By aiming the light at the timing marks while
the engine is running, the exact position of the piston
within the cylinder can be easily read (the flash of
light makes the mark on the pulley appear to be
standing still). Proper timing is indicated when the
mark and scale are in specified alignment.
When checking timing with the engine run-
ning, take care not to get the timing light
wires tangled in the tan blades and/or drive
belts.
INSPECTION &ADJUSTMENT
1990-96 Models
e See Figures 113 thru 119
1. Set the parking brake, start and run the engine
until normal operating temperature is obtained. Keep
all lights and accessories OFF and the front wheels
straight-ahead. Place the transaxle in
P for automatic
transaxle or Neutral for manual transaxle.
2. If not at specification, set the idle speed to the
correct level.
3. Turn the engine
OFF. Remove the water-
proof cover from the igmtion timing adjusting con-
nector, and connect a jumper wire from this terminal
Fig. 113 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1990-92 Mirage with 1.5L engine
93151QM Fig. 115 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nectar-Galant with 2.OL engines
93151QO1 Fig. 117 Ignition timing adjustment con.
nectar-1994-96 Galant
to a good ground. Refer to the corresponding illustra-
tions for the correct location of the timing adjustment
connector.
4. Connect a conventional power timing light to
the No. 1 cylinder spark plug wire. Start the engine
and run at idle.
5. Aim the timing light at the timing scale lo-
cated near the crankshaft pulley.
6. Loosen the distributor or crank angle sensor
hold-down nut just enough so the housing can be ro-
tated.
7. Turn the housing in the proper direction until
the specified timing is reached. Tighten the hold-
down nut and recheck the timing. Turn the engine
OFF. 8. Remove the jumper wire from the ignition
timing adjusting terminal and install the water-proof
cover.
9. Start the engine and check the actual timing
(the timing without the terminal grounded). This
reading should be approximately 5 degrees more
than the basic timing. Actual timing may increase ac-
cording to altitude. Also, actual timing may fluctuate
because of slight variation accomplished by the ECU.
Fig. 114 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nectar-Miracle with 1.6L enaine
CHECK CONNECTOR 93151QO! Fig. 116 Ignition timing adjustment con.
nectar-1992-96 Oiamante
93151gOB Fig. 116 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1993-96 Mirage with 1.5L engine
Fig. 119 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1993-96 Mirage with 1.6L engine
As long as the basic timing is correct, the engine is
timed correctly.
10. Turn the engine
OFF. 11. Disconnect the timing apparatus and
tachometer.
1997-00 Models
The ignition timing is controlled by the Engine
Control Module (ECM) and is not adjustable. How-
ever it can be inspected using a scan tool.
Page 26 of 408
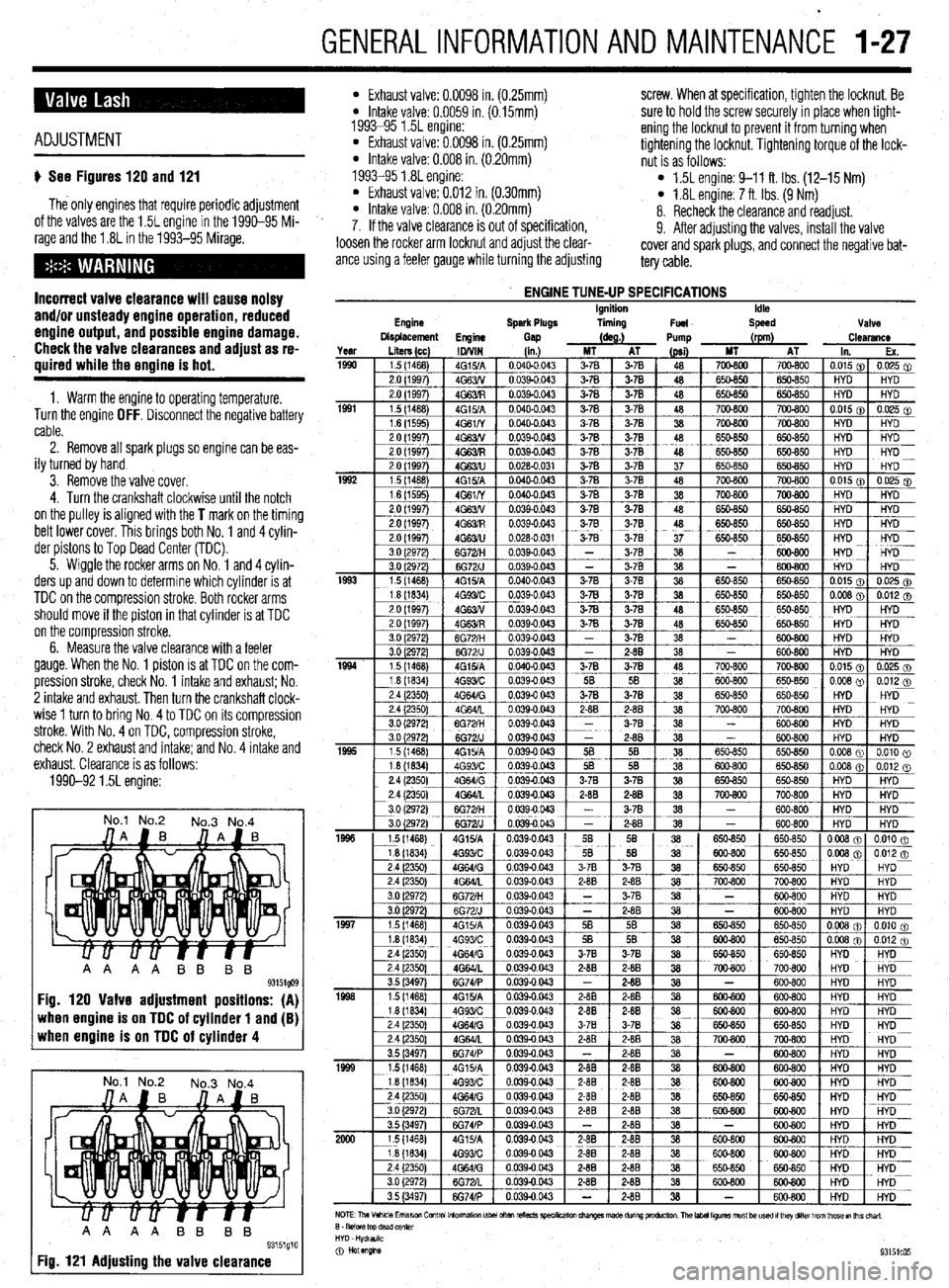
GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAlNTENANdE I-27
ADJUSTMENT
u See Figures 120 and 121
The only engines that require periodic adjustment
of the valves are the 1.5L engine in the 1990-95 Mi-
rage and the 1.8L in the 1993-95 Mirage.
Incorrect valve clearance will cause noisy
and/or unsteady engine operation, reduced
engine output, and possible engine damage.
Check the valve clearances and adjust as re-
quired while the engine is hot.
1. Warm the engine to operating temperature.
Turn the engine OFF. Disconnect the negative battery
cable.
2. Remove all spark plugs so engine can be eas-
ily turned by hand
3. Remove the valve cover.
4. Turn the crankshaft clockwise until the notch
on the pulley is aligned with the
T mark on the timing
belt lower cover. This brings both No. 1 and 4 cylin-
der pistons to Top Dead Center (TDC).
5. Wiggle the rocker arms on No. 1 and 4 cylin-
ders up and down to determine which cylinder is at
TDC on the compression stroke. Both rocker arms
should move if the piston in that cylinder is at TDC
on the compression stroke.
6. Measure the valve clearance with a feeler
gauge. When the No. 1 piston is at TDC on the com-
pression stroke, check No. 1 intake and
exhaust; No.
2 intake and exhaust. Then turn the crankshaft clock-
wise 1 turn to bring No. 4 to TDC on its compression
stroke. With No. 4 on TDC, compression stroke,
check No. 2 exhaust and intake; and No. 4 intake and
exhaust. Clearance is as follows:
1990-92 1.5L engine:
No.1 No.2
No.3 No.4
when engine is on TDC of cylinder 1 and (B) when engine is on TDC of cylinder 4
No.1 No.2
No.3 No.4
AA AA BB BB
93151g10 Fig. 121 Adjusting the valve clearance
l Exhaust valve: 0.0098 in. (0.25mm) screw. When at specification, tighten the locknut. Be l Intake valve: 0.0059 in. (0.15mm)
1993-95 1.5L engine: sure to hold the screw securely in place when tight-
l Exhaust valve: 0.0098 in. (0.25mm) ening the locknut to prevent it from turning when
* Intake valve: 0.008 in. (0.20mm) tightening the locknut. Tightening torque of the lock-
nut is as follows:
1993-95 1.8L engine:
l Exhaust valve: 0.012 in. (0.30mm) l 1.5L engine: 9-11 ft. Ibs. (12-15 Nm)
l Intake valve: 0.008 in. (0.20mm) l 1.8L engine: 7 ft. Ibs. (9 Nm)
8. Recheck the clearance and readjust.
7. If the valve clearance is out of specification,
9. After adjusting the valves, install the valve
loosen the rocker arm locknut and adjust the clear-
ante using a feeler gauge while turning the adjusting cover and spark plugs, and connect the negative bat-
tery cable.
Engine
ENGINE TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS Ignition
Spark Plugs liming
Fuel Idle
Speed Valve
Displacement
Engine
Gap (as.) Pump (rpm)
Clearance
Page 28 of 408

GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAlNTENANdE 1-29
i
*Bug screens which are mounted in front of
the condenser (unless they are original
equipment) are regarded as obstructtons.
l The condensation drain tube expels any water
which accumulates on the bottom of the evaporator
housing into the engine compartment. If this tube is
obstructed, the air conditioning performance can be
restricted and condensation buildup can spill over
onto the vehicle’s floor.
l Make sure the air passage selection lever is
operating correctly. Start the engine and warm it to
normal operating temperature, then make sure the
temperature selection lever is operating correctly.
-w
~1 ELEMENT(REFILL)CARE& REPLACEMENT
SYSTEM INSPECTION
b See Figure 125 b See Figures 126 thru 135
For maximum effectiveness and longest element
Although the A/C system should not be serviced
by the do-it-yourselfer, preventive maintenance can
be practiced and A/C system inspections can be per-
formed to help maintain the efficiency of the vehicle’s
A/C system. For A/C system inspection, perform the
following:
The easiest and often most important check for the
air conditioning system consists of a visual inspec-
tion of the system components. Visually inspect the
air conditioning system for refrigerant leaks, dam-
aged compressor clutch, abnormal compressor drive
belt tension and/or condition, plugged evaporator
drain tube, blocked condenser fins, disconnected or
broken wires, blown fuses, corroded connections and
poor insulation.
A refrigerant leak will usually appear as an oily
residue at the leakage point in the system. The oily
residue soon picks up dust or dirt particles from the
surrounding air and appears greasy. Through time,
this will build up and appear to be a heavy dirt im-
pregnated grease.
For a thorough visual and operational inspection,
check the following: * Check the surface of the radiator and con-
denser for dirt, leaves or other material which might
block air flow.
l Check for kinks in hoses and lines. Check the
system for leaks.
l Make sure the drive belt is properly tensioned.
When the air conditioning is operating, make sure the
drive belt is free of noise or slippage.
l Make sure the blower motor operates at all ap-
propriate positions, then check for distribution of the
air from all outlets with the blower on HIGH or MAX.
*Keep in mind that under conditions of high
humidity, air discharged from the A/C vents
may not feel as cold as expected, even if the
system is working properly. This is because
vaporized moisture in humid air retains heat
more effectively than dry air, thereby making
humid air more difficult to cool.
lifp thp winrkhi&i nnri winor hlarlP~ shmM hP kmt . ..“. .I.” . . * ““I.. “.” I..” ...r”* “.“““” “, ,““,” “” ,~“r~ clean. Dirt, tree sap, road tar and so on will cause
streaking, smearing and blade deterioration if left on
the glass. It is advisable to wash the windshield care-
fully with a commercial glass cleaner at least once a
month. Wipe off the rubber blades with the wet rag
afterwards. Do not attempt to move wipers across the
windshield by hand; damage to the motor and drive
mechanism will result.
To inspect and/or replace the wiper blade ele-
ments, place the wiper switch in the LOW speed po-
sition and the ignition switch in the ACC position.
When the wiper blades are approximately vertical on
the windshield, turn the ignition switch to OFF.
Examine the wiper blade elements. If they are
found to be cracked, broken or torn, they should be
replaced immediately. Replacement intervals will vary
with usage, although ozone deterioration usually lim-
its element life to about one year. If the wiper pattern
is smeared or streaked, or if the blade chatters across
the glass, the elements should be replaced. It is easi-
est and most sensible to replace the elements in
pairs.
If your vehicle is equipped with aftermarket blades,
there are several different types of refills and your vehi-
tcca-23 Fig. 126 Bosch@ wiper blade and fft kit
Fig. 129 T&o* wioer blade and fit kit tCS1224
lW1Z?5 Fig. 127 LexoP wiper blade and fit kit
Fig. 128 Pylon@ wiper blade and adapter
Fig. 131 To remove and install a LexoP
Fig, 130 Tripledge@ wiper blade and fit kit wiper blade refill, slip out the old insert and
slide in a new one