height MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 651 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-119
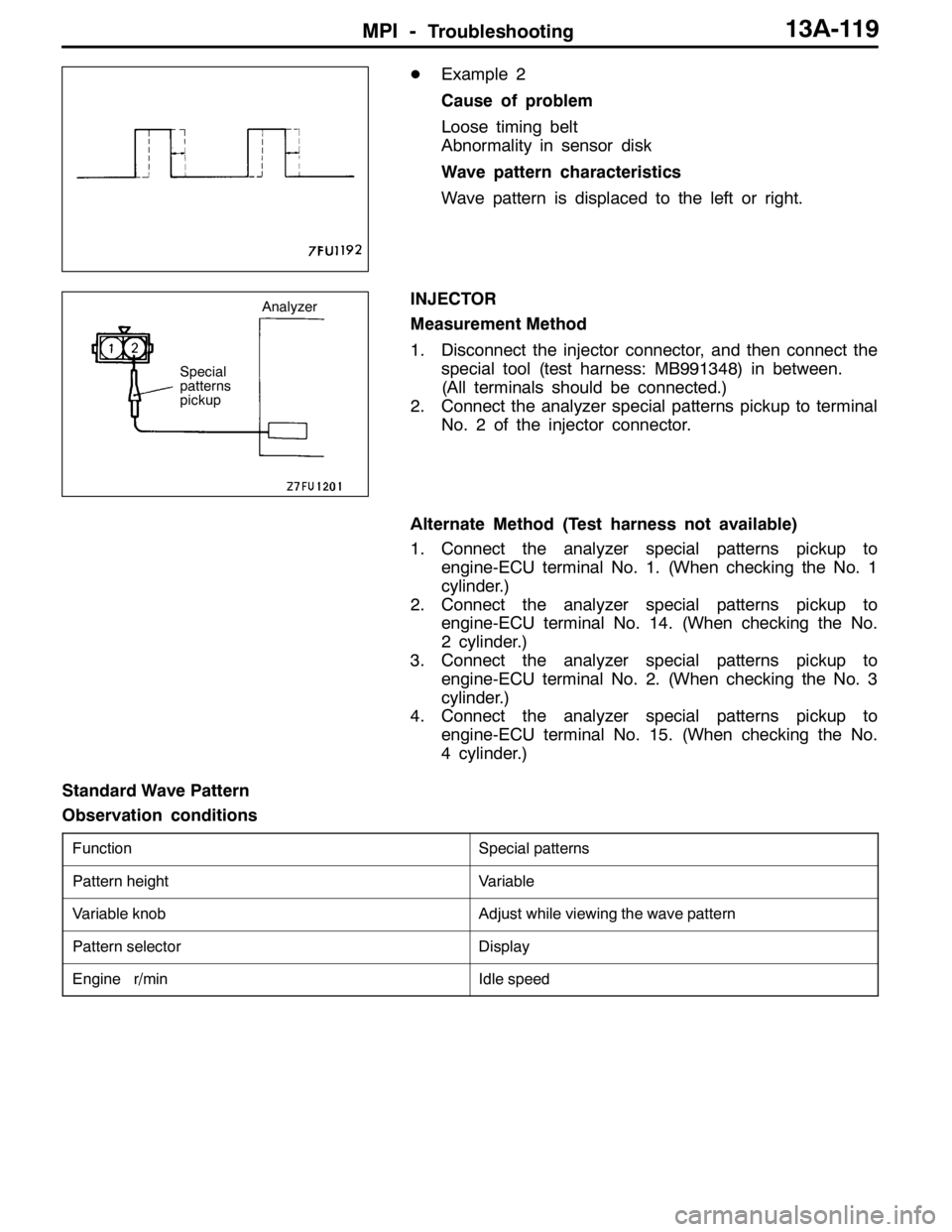
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Loose timing belt
Abnormality in sensor disk
Wave pattern characteristics
Wave pattern is displaced to the left or right.
INJECTOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the injector connector, and then connect the
special tool (test harness: MB991348) in between.
(All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to terminal
No. 2 of the injector connector.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 1. (When checking the No. 1
cylinder.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 14. (When checking the No.
2 cylinder.)
3. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 2. (When checking the No. 3
cylinder.)
4. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 15. (When checking the No.
4 cylinder.)
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightVariable
Variable knobAdjust while viewing the wave pattern
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minIdle speed
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 652 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-120
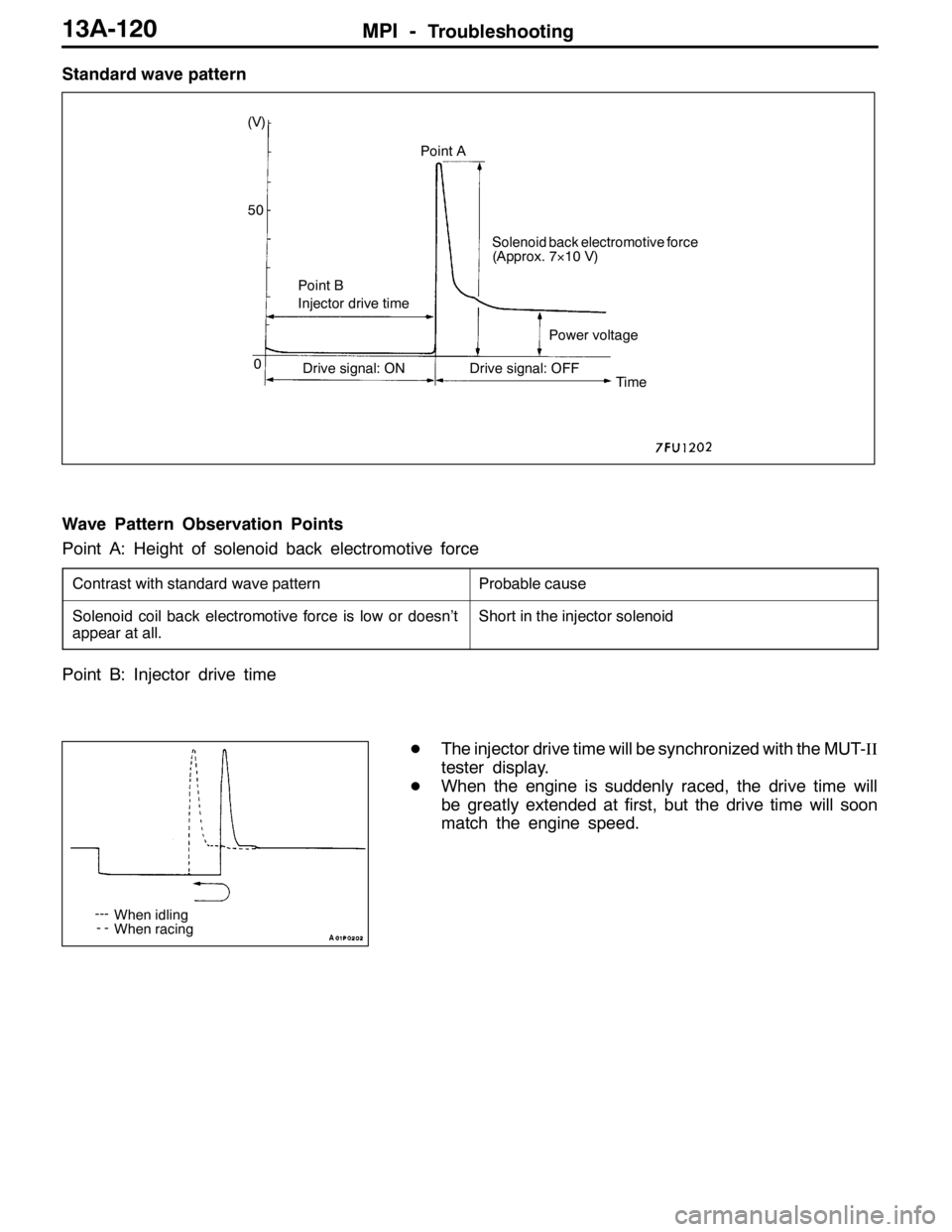
Standard wave pattern
(V)
Point A
Point BSolenoid back electromotive force
(Approx. 7×10 V)
Injector drive time
Power voltage
Drive signal: ON Drive signal: OFF
Time 50
0
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Point A: Height of solenoid back electromotive force
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Solenoid coil back electromotive force is low or doesn’t
appear at all.Short in the injector solenoid
Point B: Injector drive time
DThe injector drive time will be synchronized with the MUT-II
tester display.
DWhen the engine is suddenly raced, the drive time will
be greatly extended at first, but the drive time will soon
match the engine speed.
When idling
When racing ---
--
Page 653 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-121
IDLE SPEED CONTROL SERVO (STEPPER MOTOR)
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the idle speed control servo connector, and
connect the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in
between.
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to the idle
speed control servo-side connector terminal No. 1,
terminal No. 3, terminal No. 4 and terminal No. 6
respectively.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 4, connection terminal No. 5,
connection terminal No. 17, and connection terminal No.
18 respectively.
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightHigh
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine conditionWhen the engine coolant temperature is 20_C or below, turn the ignition switch from “LOCK”
(OFF) position to “ON” position (without starting the engine).
While the engine is idling, turn the A/C switch to ON.
Immediately after starting the warm engine
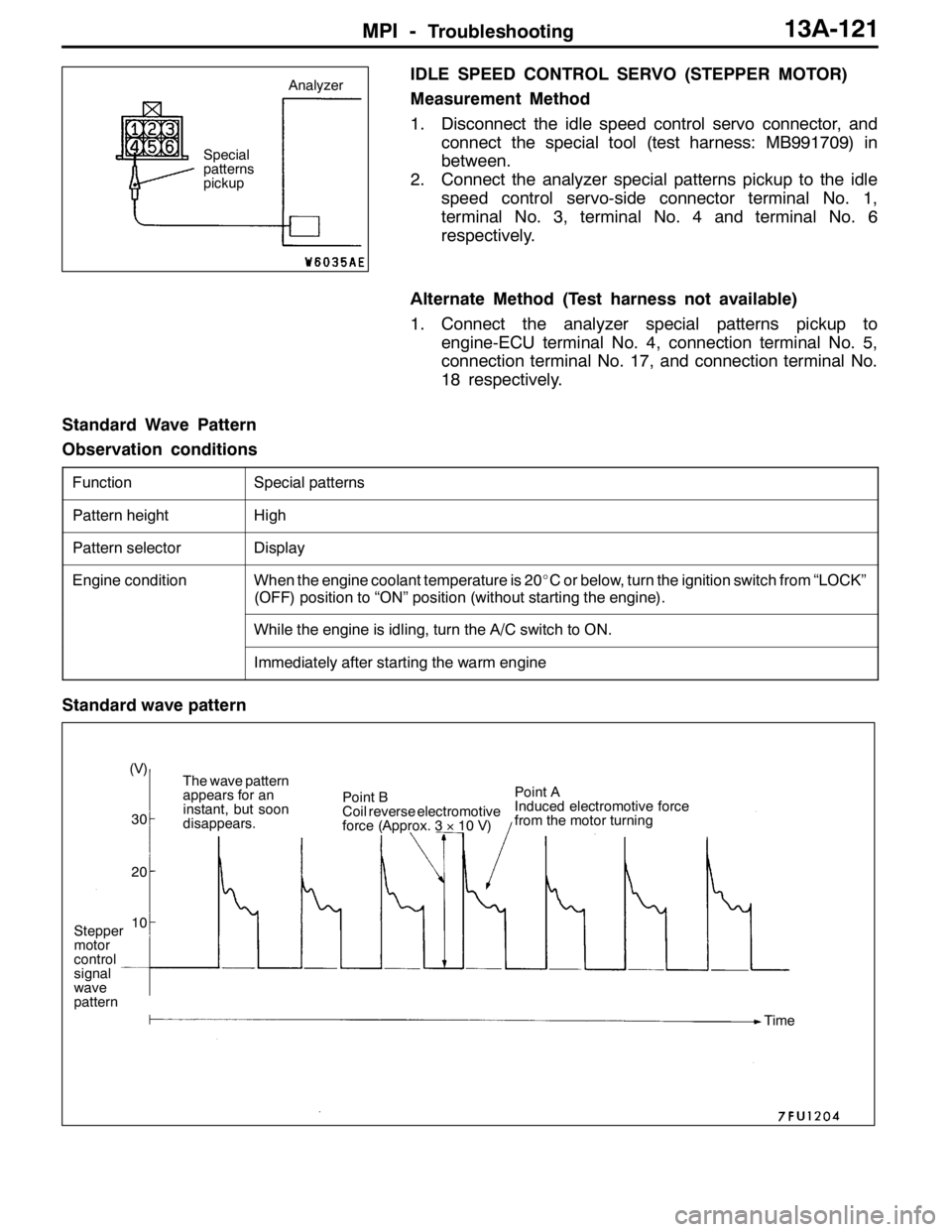
Standard wave pattern
Stepper
motor
control
signal
wave
pattern(V)
30
20
10The wave pattern
appears for an
instant, but soon
disappears.Point B
Coil reverse electromotive
force (Approx. 3×10 V)Point A
Induced electromotive force
from the motor turning
Time
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 654 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-122
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Check that the standard wave pattern appears when the stepper motor is operating.
Point A: Presence or absence of induced electromotive force from the motor turning. (Refer to the abnormal
wave pattern.)
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Induced electromotive force does not appear or is extremely small.Motor is malfunctioning
Point B: Height of coil reverse electromotive force
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Coil reverse electromotive force does not appear or is extremely small.Short in the coil
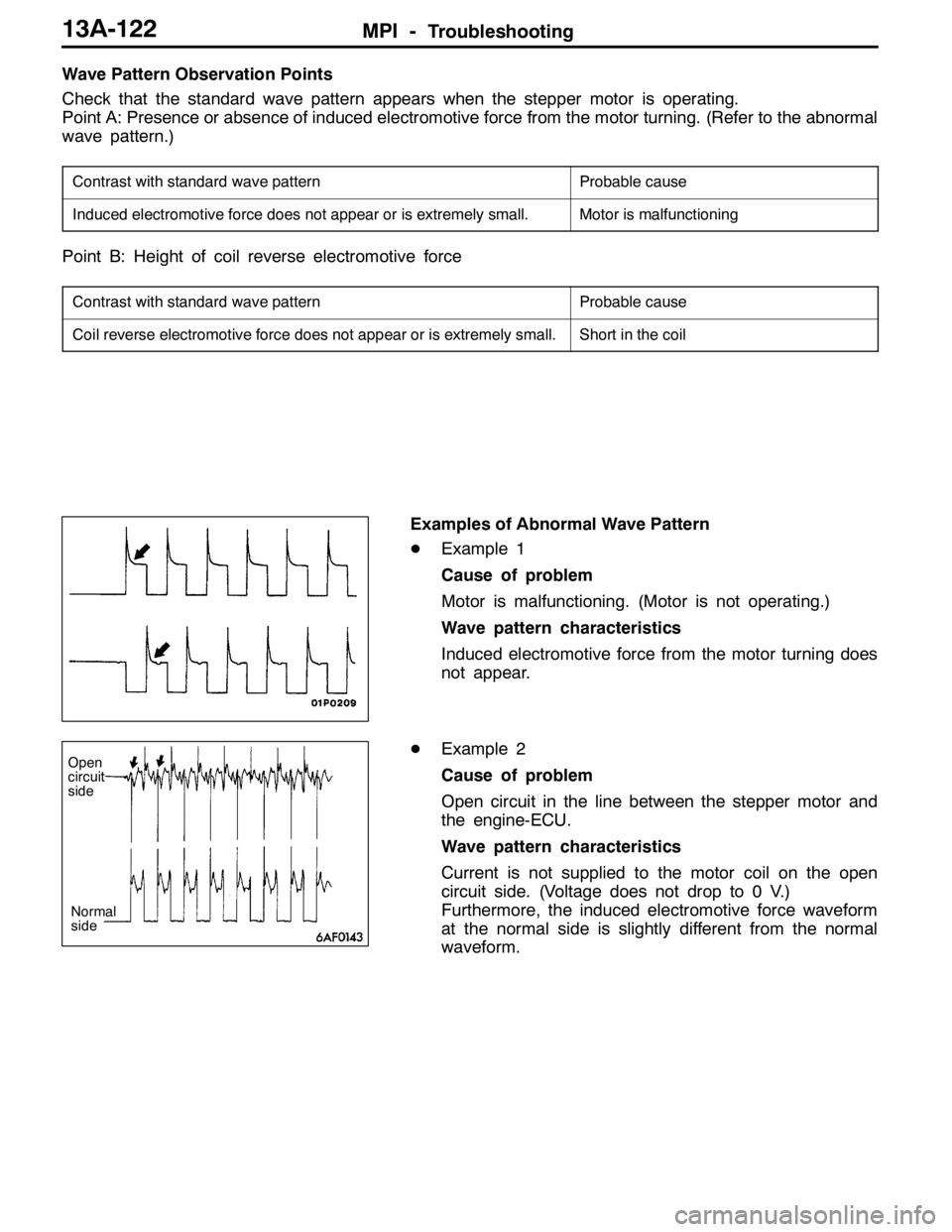
Examples of Abnormal Wave Pattern
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Motor is malfunctioning. (Motor is not operating.)
Wave pattern characteristics
Induced electromotive force from the motor turning does
not appear.
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Open circuit in the line between the stepper motor and
the engine-ECU.
Wave pattern characteristics
Current is not supplied to the motor coil on the open
circuit side. (Voltage does not drop to 0 V.)
Furthermore, the induced electromotive force waveform
at the normal side is slightly different from the normal
waveform.
Open
circuit
side
Normal
side
Page 655 of 1449
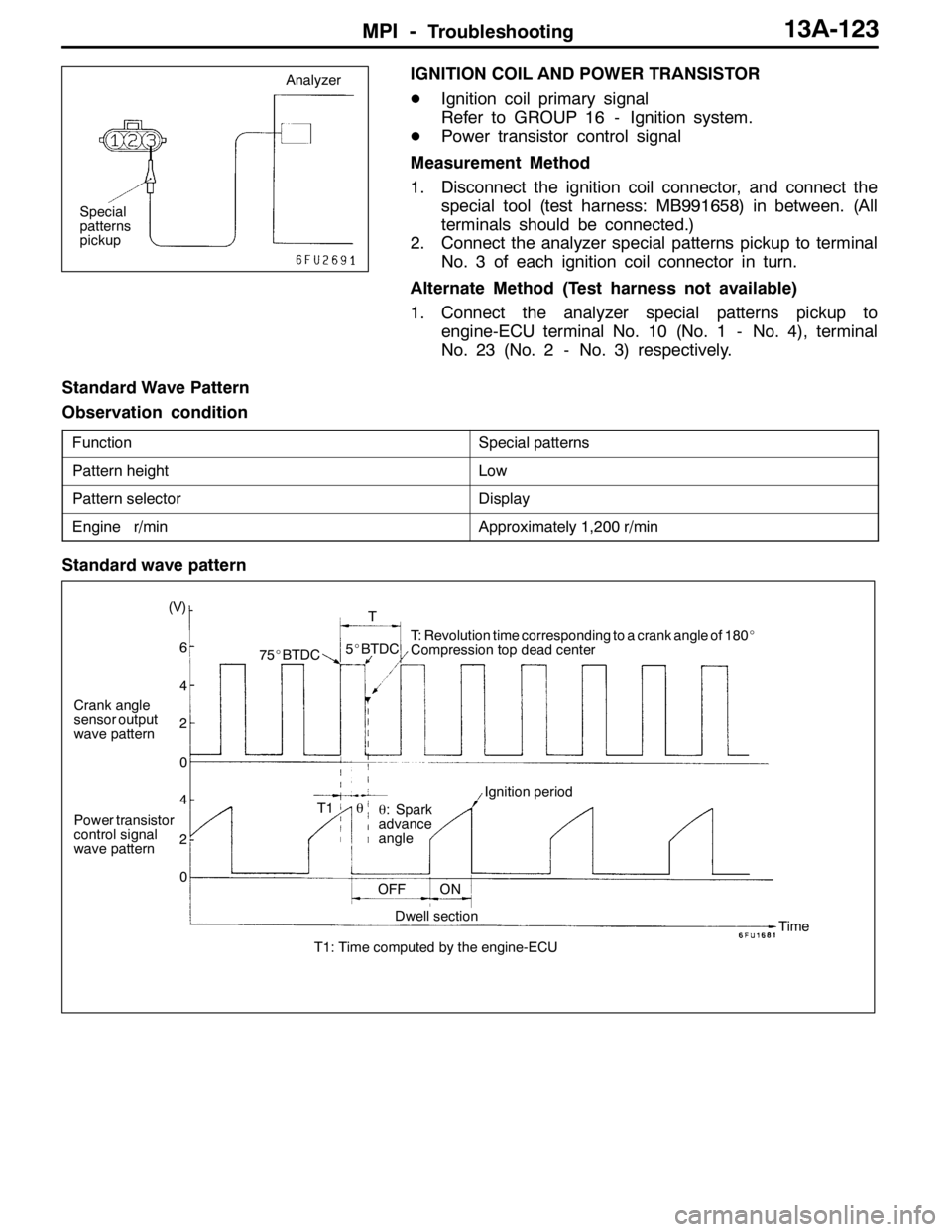
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-123
IGNITION COIL AND POWER TRANSISTOR
DIgnition coil primary signal
Refer to GROUP 16 - Ignition system.
DPower transistor control signal
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the ignition coil connector, and connect the
special tool (test harness: MB991658) in between. (All
terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to terminal
No. 3 of each ignition coil connector in turn.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 10 (No. 1 - No. 4), terminal
No. 23 (No. 2 - No. 3) respectively.
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation condition
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightLow
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minApproximately 1,200 r/min
Standard wave pattern
Crank angle
sensor output
wave pattern
Power transistor
control signal
wave pattern(V)
75_BTDC5_BTDCT: Revolution time corresponding to a crank angle of 180_
Compression top dead center
θ: Spark
advance
angleIgnition period
OFF ON
Dwell section
T1: Time computed by the engine-ECUTime θ T1T
6
4
2
0
4
2
0
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 683 of 1449

FUEL SUPPLY - On-vehicle Service/Fuel tank13B-3
FUEL PUMP AND GAUGE ASSEMBLY, PIPE
AND GAUGE ASSEMBLY (FUEL GAUGE UNIT)
1. Remove the rear seat cushion assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
2. Remove the service hole cover.
3. Disconnect the harness connector, high-pressure fuel
tube, suction hose, and return hose.
4. Unscrew the mounting nuts to remove the fuel pump
and gauge assembly or pipe and gauge assembly.
5. Fuel gauge unit check. (Refer to GROUP 54 -
Combination Meter.)
NOTE
If the inspection shows that the basic resistance and
the height of float are out of the standard value, replace
the gauge unit.
(Refer to P.13B-8.)
6. Install the fuel pump and gauge assembly or pipe and
gauge assembly. Tighten the mounting nuts to the
specified torque.
Specified torque: 2.5± 0.5 N·m
7. Connect the harness connector, high-pressure fuel tube,
suction hose, and return hose.
Caution
(1) Snap the high-pressure fuel hose or suction hose
one-touch joint into place, then pull back slightly
on the hose to assure it is securely fitted. However,
the connection should have a play of approx. 3
mm.
(2) Insert the return hose for 20 - 30 mm for
connection.
8. Install the rear seat cushion assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
FUEL TANK
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Pre-removal Operation
DDraining Fuel
DFuel Pump Connector Disconnection
(How To Reduce Fuel Pressure)
(Refer to GROUP 13A - On-vehicle Service.)
DCenter Exhaust Pipe Removal
(Refer to GROUP 15.)Post-installation Operation
DCenter Exhaust Pipe Removal
(Refer to GROUP 15.)
DRefilling Fuel
DChecking for Fuel Leaks
High-pressurefuel tubeHarness
connector
Suction hose
Return hose
Suction hose
Harness connector
Page 700 of 1449
ENGINE COOLING -Thermostat14-12
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINTS
"AATHERMOSTAT INSTALLATION
Install the thermostat being careful not to fold over or scratch
the rubber ring.
Caution
Make absolutely sure that no oil is adhering to the rubber
ring of the thermostat. In addition, be careful not to fold
over or scratch the rubber ring when inserting. If the
rubber ring is damage, replace the thermostat.
"BARADIATOR UPPER HOSE CONNECTION
1. Insert each hose as far as the projection of the water
outlet fitting.
2. Align the mating marks on the radiator hose and hose
clamp, and then connect the radiator hose.
INSPECTION
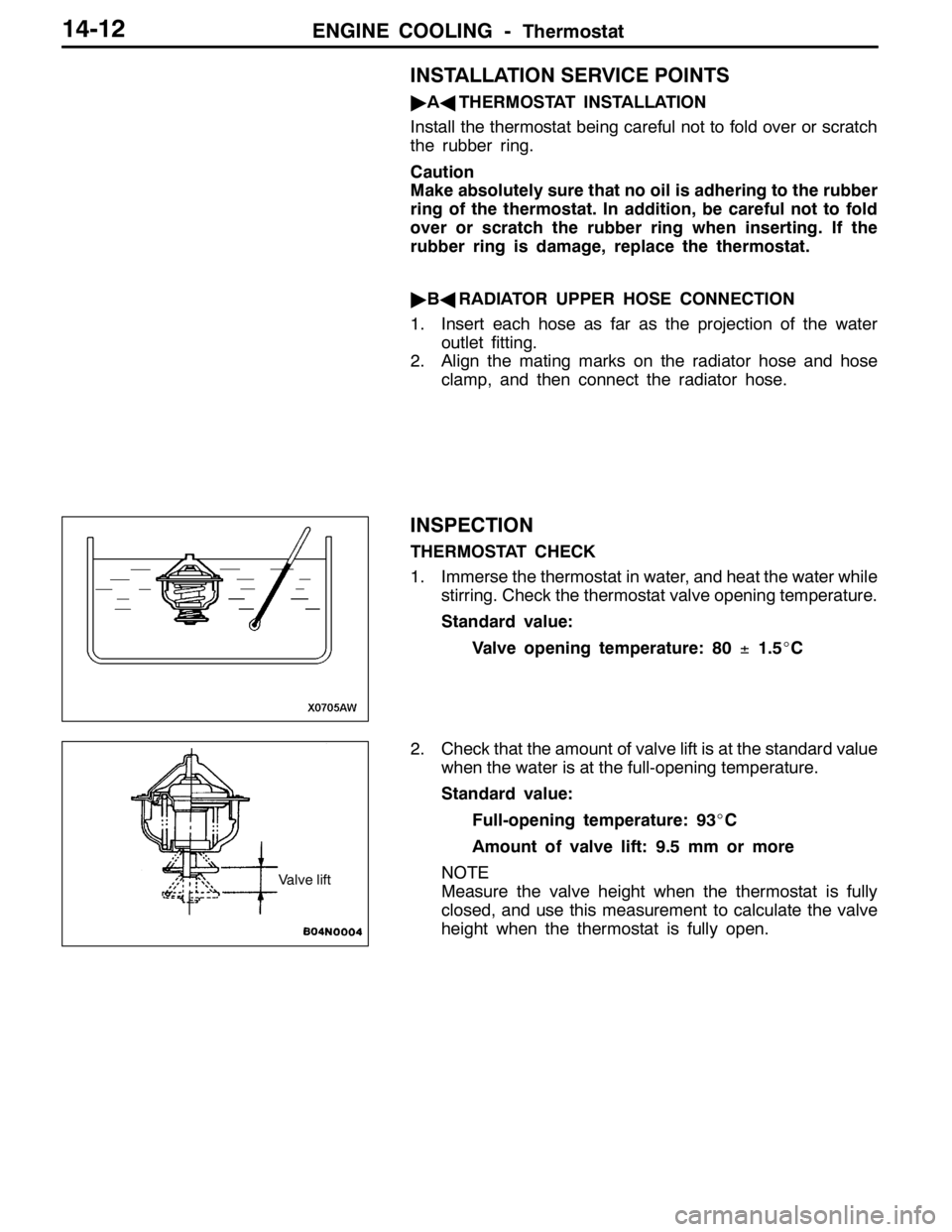
THERMOSTAT CHECK
1. Immerse the thermostat in water, and heat the water while
stirring. Check the thermostat valve opening temperature.
Standard value:
Valve opening temperature: 80±1.5_C
2. Check that the amount of valve lift is at the standard value
when the water is at the full-opening temperature.
Standard value:
Full-opening temperature: 93_C
Amount of valve lift: 9.5 mm or more
NOTE
Measure the valve height when the thermostat is fully
closed, and use this measurement to calculate the valve
height when the thermostat is fully open.
Valve lift
Page 740 of 1449
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Charging System16-8
(14)If the voltage reading conforms to the value
in the voltage regulation, then the voltage
regulator is operating normally.
If the voltage is not within the standard value,
there is a malfunction of the voltage regulator
or of the alternator.
(15)After the test, lower the engine speed to the
idle speed.
(16)Turn the ignition switch to the “LOCK” (OFF)
position.(17)Remove the tachometer or the MUT-II.
(18)Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(19)Disconnect the ammeter and voltmeter.
(20)Connect the alternator output wire to the
alternator “B” terminal.
(21)Remove the special tool, and return the
connector to the original condition.
(22)Connect the negative battery cable.
Voltage Regulation Table
Standard value:
Inspection terminalVoltage regulator ambient temperature_CVoltage V
Terminal “S”-2014.2 - 15.4
2013.9 - 14.9
6013.4 - 14.6
8013.1 - 14.5
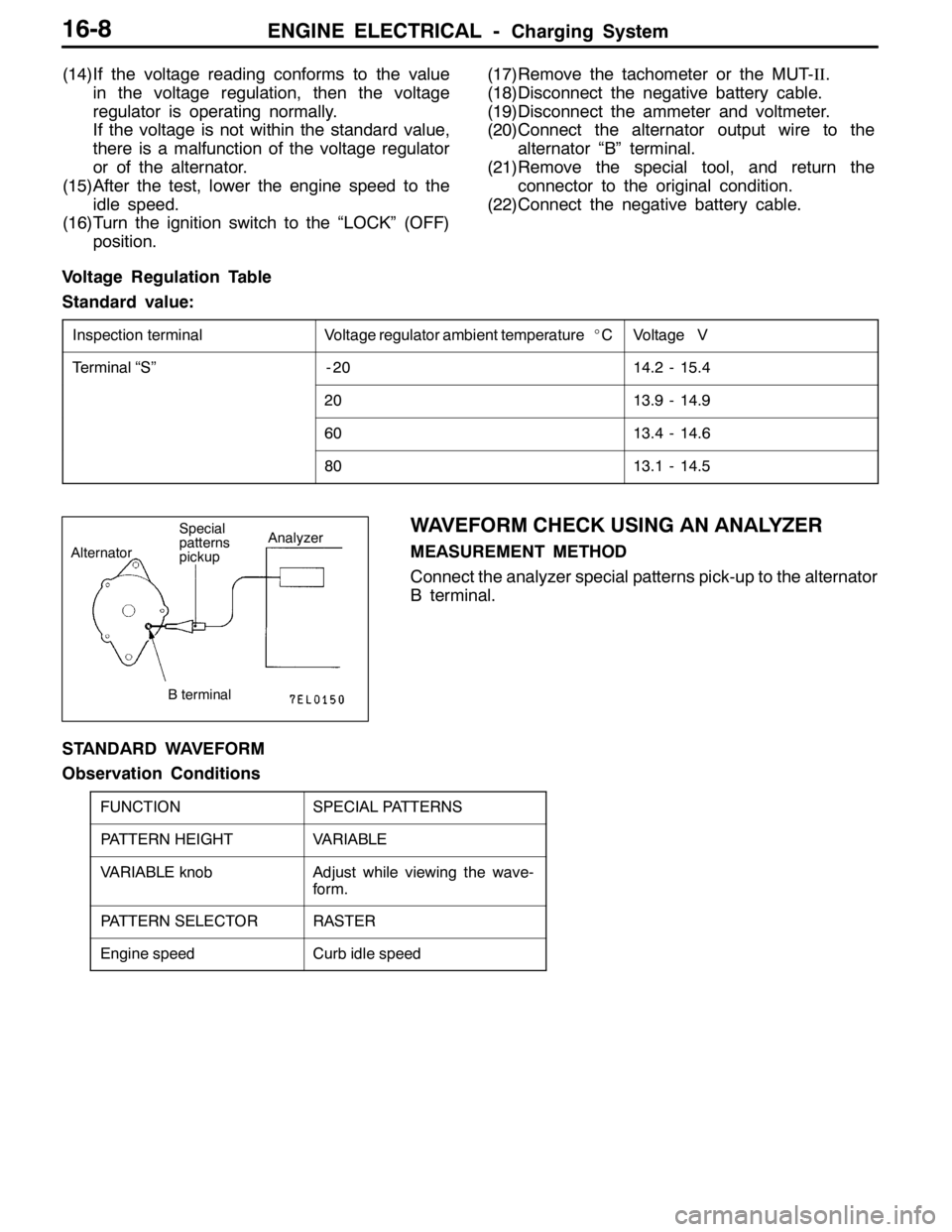
WAVEFORM CHECK USING AN ANALYZER
MEASUREMENT METHOD
Connect the analyzer special patterns pick-up to the alternator
B terminal.
STANDARD WAVEFORM
Observation Conditions
FUNCTIONSPECIAL PATTERNS
PATTERN HEIGHTVARIABLE
VARIABLE knobAdjust while viewing the wave-
form.
PATTERN SELECTORRASTER
Engine speedCurb idle speed
AlternatorSpecial
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
B terminal
Page 763 of 1449
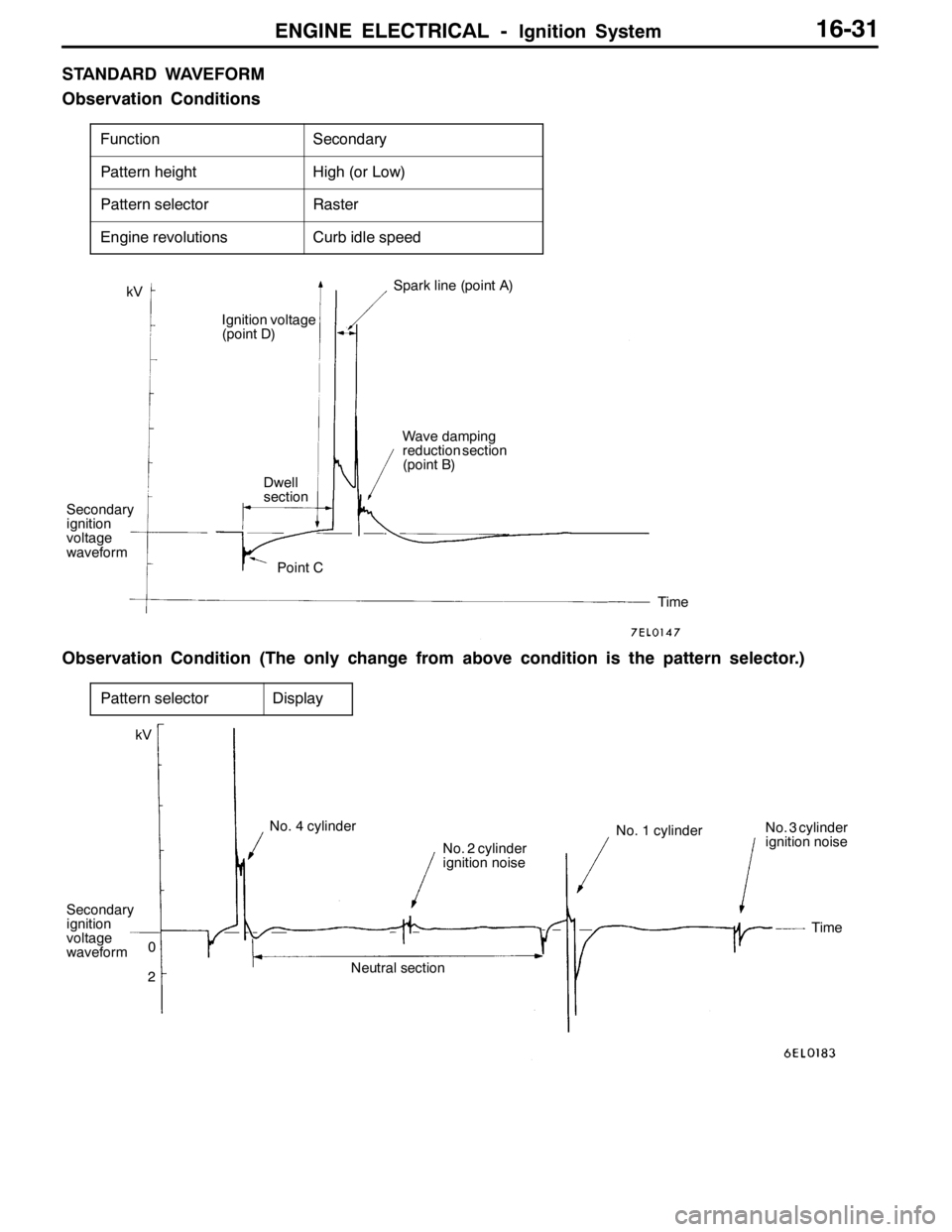
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-31
STANDARD WAVEFORM
Observation Conditions
FunctionSecondary
Pattern heightHigh (or Low)
Pattern selectorRaster
Engine revolutionsCurb idle speed
kV
Secondary
ignition
voltage
waveformIgnition voltage
(point D)
Dwell
section
Point CSpark line (point A)
Wave damping
reduction section
(point B)
Time
Observation Condition (The only change from above condition is the pattern selector.)
Pattern selectorDisplay
Secondary
ignition
voltage
waveformkV
No. 4 cylinder
No. 2 cylinder
ignition noiseNo. 1 cylinderNo. 3 cylinder
ignition noise
Neutral section 0
2Time
Page 764 of 1449
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-32
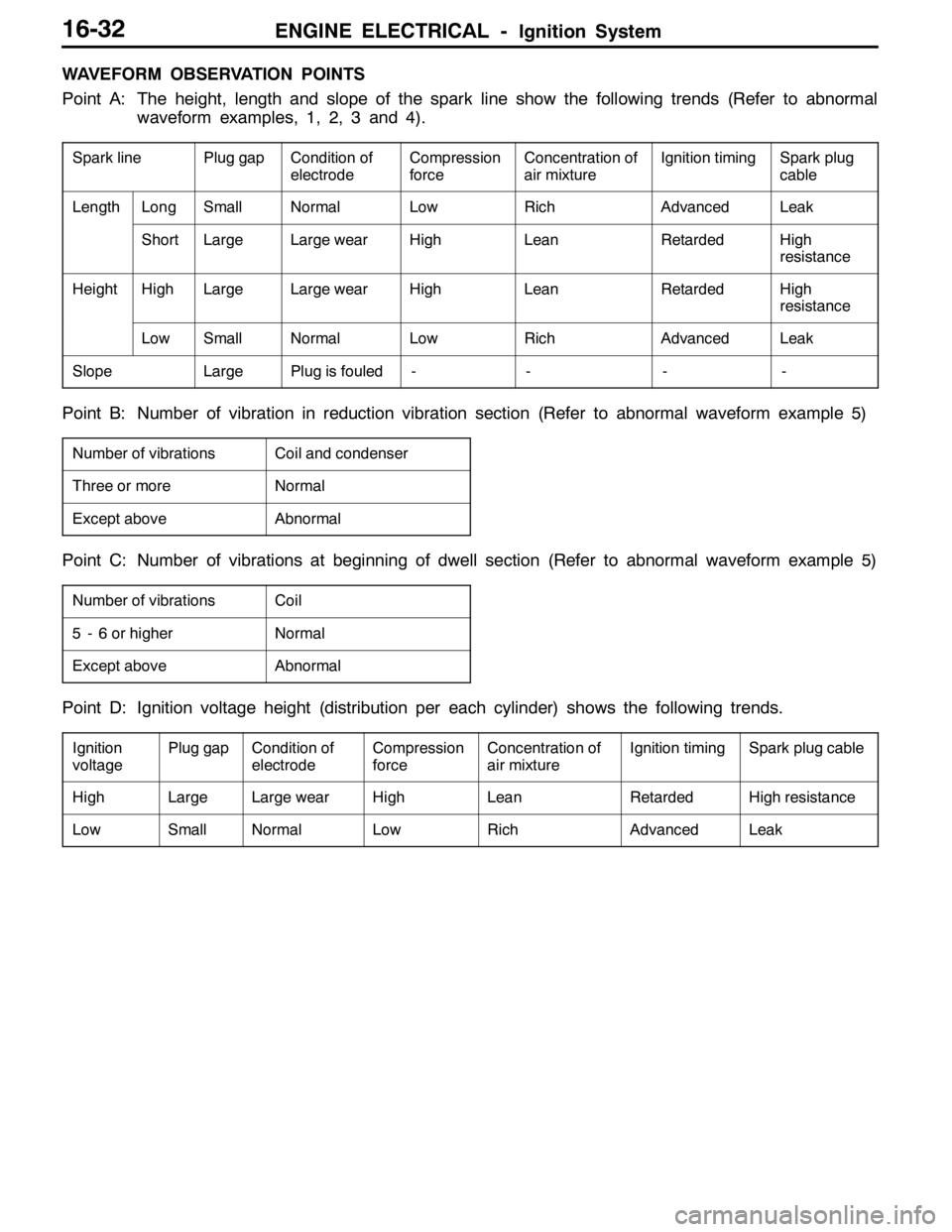
WAVEFORM OBSERVATION POINTS
Point A: The height, length and slope of the spark line show the following trends (Refer to abnormal
waveform examples, 1, 2, 3 and 4).
Spark linePlug gapCondition of
electrodeCompression
forceConcentration of
air mixtureIgnition timingSpark plug
cable
LengthLongSmallNormalLowRichAdvancedLeak
ShortLargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh
resistance
HeightHighLargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh
resistance
LowSmallNormalLowRichAdvancedLeak
SlopeLargePlug is fouled----
Point B: Number of vibration in reduction vibration section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Number of vibrationsCoil and condenser
Three or moreNormal
Except aboveAbnormal
Point C: Number of vibrations at beginning of dwell section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Number of vibrationsCoil
5 - 6 or higherNormal
Except aboveAbnormal
Point D: Ignition voltage height (distribution per each cylinder) shows the following trends.
Ignition
voltagePlug gapCondition of
electrodeCompression
forceConcentration of
air mixtureIgnition timingSpark plug cable
HighLargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh resistance
LowSmallNormalLowRichAdvancedLeak