ESP MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 682 of 1449

FUEL SUPPLY - General Information/On-vehicle Service13B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
DThe steel fuel tank is located under the floor of the rear seats to provide increased safety and increase
the amount of luggage compartment space.
DThe fuel tank has been equipped with a valve assembly which incorporates a fuel cut-off valve to
prevent fuel from leaking out in the event of a collision for adjusting the pressure inside the fuel
tank.
DThe fuel pump module contains a fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel pressure regulator.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
FUEL PUMP AND GAUGE ASSEMBLY (FUEL
PUMP)
1. FUEL PUMP OPERATION CHECK
Refer to GROUP 13A - On-vehicle service
2. FUEL PUMP REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the rear seat cushion assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
(2) Remove the service hole cover.
(3) Disconnect the harness connector, high-pressure fuel
tube, suction hose and return hose.
(4) Unscrew the mounting nuts to remove the fuel pump
and gauge assembly.
(5) Replace the fuel pump. (Refer to P.13B-7.)
(6) Install the fuel pump and gauge assembly. Tighten
the mounting nuts to the specified torque.
Specified torque: 2.5± 0.5 N·m
(7) Connect the harness connector, high-pressure fuel
tube, suction hose, and return hose.
Caution
1) Snap the high-pressure fuel hose or suction
hose one-touch joint into place, then pull back
slightly on the hose to assure it is securely
fitted. However, the connection should have
a play of approx. 3 mm.
2) Insert the return hose for 20 - 30 mm for
connection.
(8) Install the service hole cover.
(9) Install the rear seat cushion assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
Harness
connectorHigh-pressurefuel tube
Suction hose
Return hose
3mm
Corresponding
sideHigh-pressure fuel tube
Page 686 of 1449

FUEL SUPPLY - Fuel Tank13B-6
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
"AAHIGH-PRESSURE FUEL HOSE/SUCTION HOSE
INSTALLATION
Caution
Snap the high-pressure fuel hose or suction hose
one-touch joint into place, then pull back slightly on the
hose to assure it is securely fitted. However, the
connection should have a play of approx. 3 mm.
"BAFUEL TANK RETURN HOSE INSTALLATION
Caution
Insert the return hose for 20 - 30 mm for connection.
3mm
Corresponding
sideHigh-pressure fuel tube
Page 708 of 1449

INTAKE AND EXHAUST -General Information15-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
SUPERCHARGING PRESSURE CONTROL
By controlling the duty of the waste gate solenoid valve, the waste gate actuator functions to control the supercharging
pressure. This allows a supercharged pressure matching the engine operation state to be attained. Control is carried
out to prevent excessive supercharging and thereby prevent engine damage.
SECONDARY AIR CONTROL
When decelerating during high-speed travel, the secondary air is introduced into the upstream of the turbocharger
to prevent the turbine speed from dropping and to increase the acceleration responsiveness after deceleration.
The secondary air is introduced into each cylinder of the exhaust manifold to maximize the effect.
Secondary air
control solenoid
valve
Air
inletSecondary
air valve
Waste gate
solenoid
valve
Waste gate
actuator
TurbochargerVacuum
tank
Page 758 of 1449
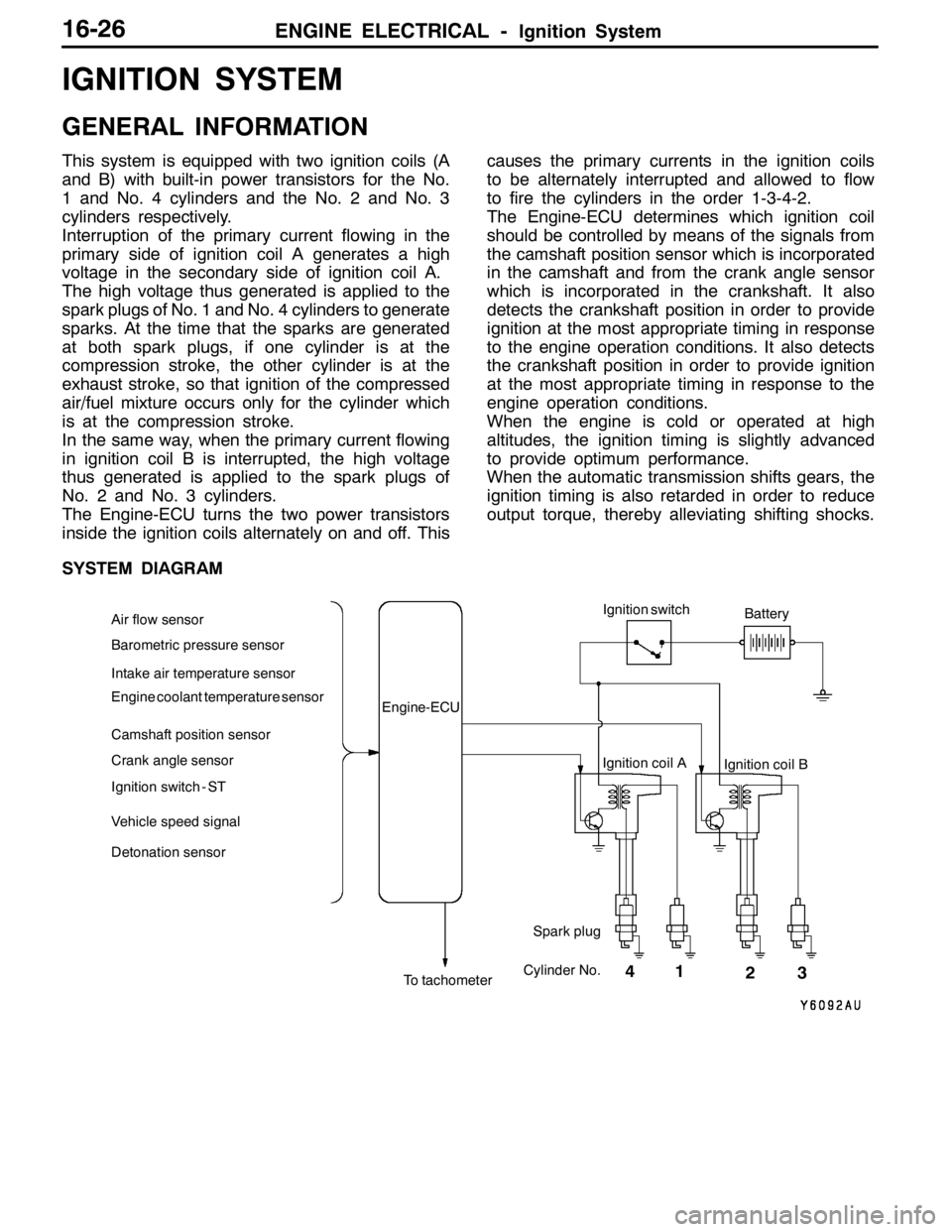
ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-26
IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
This system is equipped with two ignition coils (A
and B) with built-in power transistors for the No.
1 and No. 4 cylinders and the No. 2 and No. 3
cylinders respectively.
Interruption of the primary current flowing in the
primary side of ignition coil A generates a high
voltage in the secondary side of ignition coil A.
The high voltage thus generated is applied to the
spark plugs of No. 1 and No. 4 cylinders to generate
sparks. At the time that the sparks are generated
at both spark plugs, if one cylinder is at the
compression stroke, the other cylinder is at the
exhaust stroke, so that ignition of the compressed
air/fuel mixture occurs only for the cylinder which
is at the compression stroke.
In the same way, when the primary current flowing
in ignition coil B is interrupted, the high voltage
thus generated is applied to the spark plugs of
No. 2 and No. 3 cylinders.
The Engine-ECU turns the two power transistors
inside the ignition coils alternately on and off. Thiscauses the primary currents in the ignition coils
to be alternately interrupted and allowed to flow
to fire the cylinders in the order 1-3-4-2.
The Engine-ECU determines which ignition coil
should be controlled by means of the signals from
the camshaft position sensor which is incorporated
in the camshaft and from the crank angle sensor
which is incorporated in the crankshaft. It also
detects the crankshaft position in order to provide
ignition at the most appropriate timing in response
to the engine operation conditions. It also detects
the crankshaft position in order to provide ignition
at the most appropriate timing in response to the
engine operation conditions.
When the engine is cold or operated at high
altitudes, the ignition timing is slightly advanced
to provide optimum performance.
When the automatic transmission shifts gears, the
ignition timing is also retarded in order to reduce
output torque, thereby alleviating shifting shocks.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Ignition switch - ST
Vehicle speed signalEngine-ECU
Ignition coil A
Ignition coil B Ignition switch
Spark plugBattery
To tachometerCylinder No. Air flow sensor
1 4
23
Detonation sensor
Page 772 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Engine Control System17-2
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
A cable-type accelerator mechanism and a
suspended-type pedal have been adopted.
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
Accelerator cable play mm1-2
Engineidlespeedr/min850±50Engineidle speed±/min850±50
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND
ADJUSTMENT
1. Turn A/C and lamps OFF.
Inspect and adjust at no load.
2. Warm engine until stabilized at idle.
3. Confirm idle speed is at prescribed value.
Standard value: 850±50 r/min
4. Stop engine (ignition switch OFF).
5. Confirm there are no sharp bends in accelerator cable.
6. Check inner cable for correct slack.
Standard value: 1 - 2 mm
7. If there is too much slack or no slack, adjust play by
the following procedures.
(1) Loosen the adjusting bolt to release the cable.
(2) Move the plate until the inner cable play is at the
standard value, and then tighten the adjusting bolt
to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 5.0±1.0 N·m
plate
Adjusting bolt
Page 774 of 1449
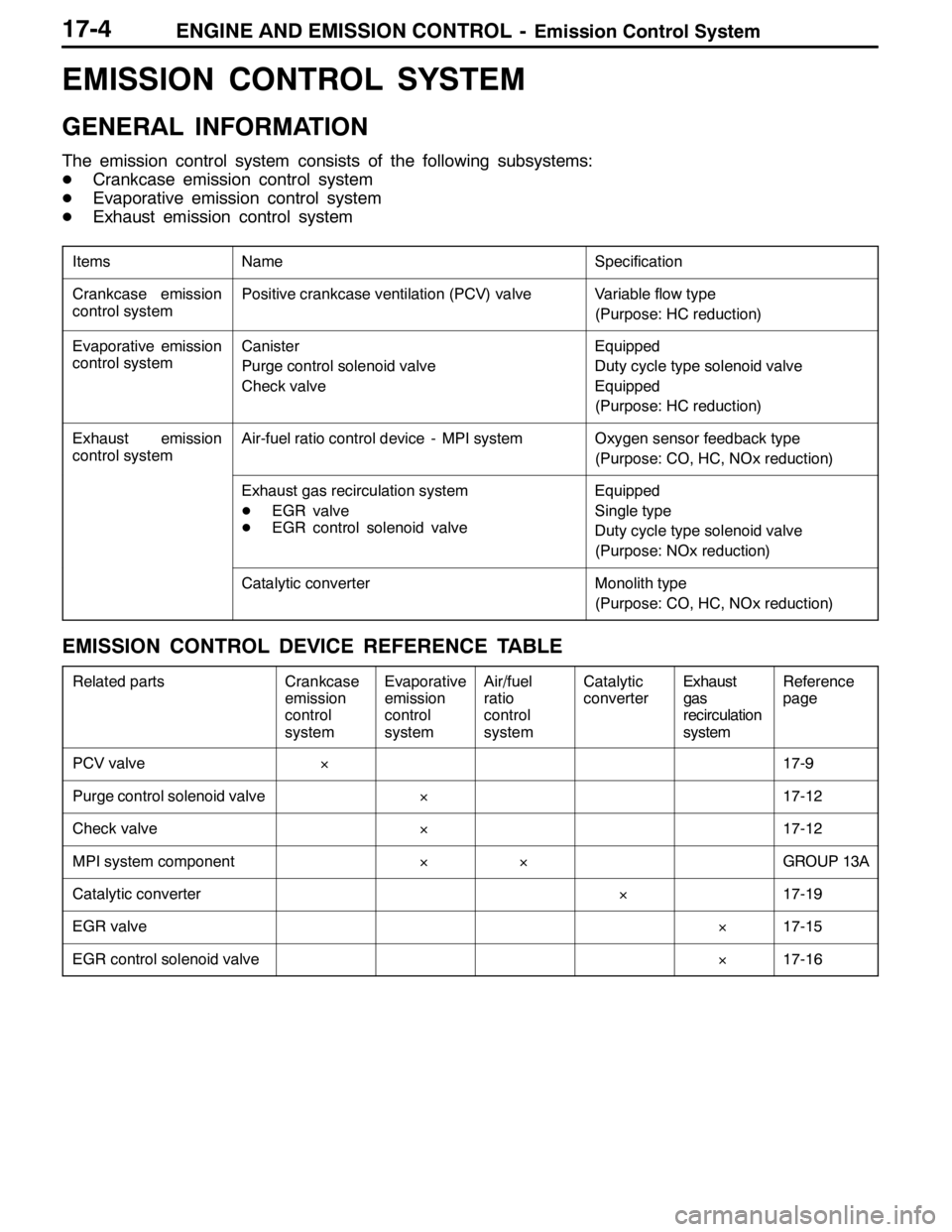
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-4
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The emission control system consists of the following subsystems:
DCrankcase emission control system
DEvaporative emission control system
DExhaust emission control system
ItemsNameSpecification
Crankcase emission
control systemPositive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valveVariable flow type
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Evaporative emission
control systemCanister
Purge control solenoid valve
Check valveEquipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Equipped
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Exhaust emission
control systemAir-fuel ratio control device - MPI systemOxygen sensor feedback type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Exhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valve
DEGR control solenoid valveEquipped
Single type
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
Catalytic converterMonolith type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE REFERENCE TABLE
Related partsCrankcase
emission
control
systemEvaporative
emission
control
systemAir/fuel
ratio
control
systemCatalytic
converterExhaust
gas
recirculation
systemReference
page
PCV valve×17-9
Purge control solenoid valve×17-12
Check valve×17-12
MPI system component××GROUP 13A
Catalytic converter×17-19
EGR valve×17-15
EGR control solenoid valve×17-16
Page 810 of 1449

22A-2
MANUAL
TRANSMISSION
CONTENTS
GENERAL 3.................................
Outline of Changes 3...........................
GENERAL INFORMATION 3..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATION 3..................
LUBRICANTS 3..............................
SPECIAL TOOLS 4...........................
TROUBLESHOOTING
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 40....................
Transmission Oil Check 40......................
Transmission Oil Replacement 40................
Transfer Oil Check 40..........................
Transfer Oil Replacement 40....................
Fluid Check
Bleeding
Hydraulic Pressure Check
Wheel Speed Sensor Output Voltage
Measurement
TRANSMISSION CONTROL* 46...............
TRANSFER ASSEMBLY 49...................
TRANSMISSION ASSEMBLY 52...............
4WD-ECU
SENSOR, SWITCH AND RELAY
AYC> 56.....................................
HYDRAULIC UNIT Refer to GROUP27B.......
WARNING REGARDING SERVICING OF SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) EQUIPPED VEHICLES
WARNING!
(1) Improper service or maintenance of any component of the SRS, or any SRS-related component, can lead to personal
injury or death to service personnel (from inadvertent firing of the air bag) or to driver and passenger (from rendering
the SRS inoperative).
(2) Service or maintenance of any SRS component or SRS-related component must be performed only at an authorized
MITSUBISHI dealer.
(3) MITSUBISHI dealer personnel must thoroughly review this manual, and especially its GROUP 52B - Supplemental
Restraint System (SRS) before beginning any service or maintenance of any component of the SRS or any SRS-related
component.
NOTE
The SRS includes the following components: SRS-ECU, SRS warning lamp, air bag module, clock spring, and interconnecting
wiring. Other SRS-related components (that may have to be removed/installed in connection with SRS service or maintenance) are
indicated in the table of contents by an asterisk (*).
Page 816 of 1449

MANUAL TRANSMISSION - Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURES FOR DIAGNOSIS CODES
Code No.12 Power supply voltage (valve power supply)
systemProbable cause
The power supply circuit opens or short-circuits if the power supply voltage of the
4WD-ECU is below 9 V or above 18 V.
Or code No.12 is output when the battery voltage drops.DDefective harness or connector
DDefective battery
DDefective 4WD-ECU
NOTE
Refer to the corresponding item if any other diagnosis code is being output.
OKOK
NG
NG
OK
Check the battery.
NG→Replace
Measure at 4WD-ECU connector C-44.
DMeasure the ECU terminal voltage.
DIgnition switch: ON
DVoltage between terminal 13 and earth
OK:System voltageCheck the following connectors:
NG→Repair
MUT-IIData List
DNo.10 battery voltage
OK:System voltage
OK→Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - Points to
Note for Intermittent Malfunctions)
OK
Check the following connector:C-44
NG→Repair
MUT-IIData List
DNo.10 battery voltage
OK:System voltage
NG→Replace the 4WD-ECU
OK→Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - Points to
Note for Intermittent Malfunctions)
Check the harness between the ignition switch and 4WD-ECU
DCheck for the open circuit, short circuit, or damage of the
power supply
NG→Repair
Code No.13 Fail-safe relay system
Code No.13 will be output as the open circuit or short circuit of the fail-safe relay
when the voltage is above 6 V during failsafe relay OFF or when the voltage is
below 6 V during ON.DDefective 4WD-ECU
Replace the 4WD-ECU.
Page 817 of 1449

MANUAL TRANSMISSION - Troubleshooting
Code No.21 Wheel speed sensor
Code No.22 Wheel speed sensor
Code No.23 Wheel speed sensor
Code No.24 Wheel speed sensor
A diagnosis code corresponding to the open circuit or short circuit of the wheel
speed sensor is output when one wheel speed sensor has detected a vehicle
speed of above 15 km/h, but any one of the remaining three wheel speed
sensors could not detect the vehicle speed.DWheel speed sensor fault
DRotor fault
DWheel bearing fault
DHarness or connector fault
DABS-ECU fault
D4WD-ECU fault
OKNGYES
NO
OK
Measure at 4WD-ECU connector C-44.
DMeasure the ECU terminal voltage.
DIgnition switch: ON
DRotate the tire corresponding to the measured terminal by
one and a half to one rotate per second.
(1) Voltage between terminal 9 and body earth
(2) Voltage between terminal 6 and body earth
(3) Voltage between terminal 7 and body earth
(4) Voltage between terminal 8 and body earth
OK:Changes at 0 V↔5VCheck the following connector:C-44
NG→Repair
Check the following connectors:
NG→Repair
MUT-IIDiagnosis Code
DAre the ABS Diagnosis Code Numbers.11, 12, 13, 14, 21,
22, 23, and 24 output?Refer to GROUP 35B - Troubleshooting.
NG
MUT-IIData List
DNo.01 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.02 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.03 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.04 Vehicle speed sensor
OK:The speed meter display and MUT-IIdisplay match.
OK→Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - Points to
Note for Intermittent Malfunctions.)
OK
Check the harness between 4WD-ECU and ABS-ECU.
DCheck for open circuit, ground, and short-circuit of the
output line.
NG→Repair
MUT-IIData List
DNo.01 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.02 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.03 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.04 Vehicle speed sensor
OK:The speed meter display and MUT-IIdisplay match.
NG→Replace the 4WD-ECU
OK→Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - Points to
Note for Intermittent Malfunctions.)
Page 819 of 1449

MANUAL TRANSMISSION - Troubleshooting
Code No.25 Wrong-diameter tireProbable cause
Code No.25 is output as wrong-diameter tire when one of the four vehicle
speeds is outside the range of specified values in respect to the average of the
four vehicle speed sensors, when the vehicle speed is above 20 km/h with the
steering wheel in the straight ahead position.
However the warning lamp does not light up.DTire fault
DWheel speed sensor fault
DRotor fault
DWheel bearing fault
DHarness or connector fault
DABS-ECU fault
D4WD-ECU fault
OK NG
OK
Check the following connector:C-44
NG→Repair
Check the following connectors:
NG→Repair OKYES
OK
OK
Check the wheel speed sensor and rotor.
(Refer to GROUP 35B - Wheel Speed Sensor.)
NG→Repair
Check the wheel speed sensor output voltage. (Refer to
GROUP 35B - On-vehicle Service.)OK
Check the wheel speed sensor installation.
NG→Repair
NG
OK
Check the wheel beearing. (Refer to GROUP 26 - On-vehicle
Service, and GROUP 27B - Rear Hub Assembly.)
NG→Repair
OK
Check the following connectors:
C-146, C-111, C-128, A-43
C-146, C-111, C-128, C-136
NG→Repair NG
MUT-IIData List
DNo.01 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.02 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.03 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.04 Vehicle speed sensor
OK:The speed meter display and MUT-IIdisplay match.
OK→Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - Points to
Note for Intermittent Malfunctions.)
Measure at 4WD-ECU connector C-44.
DMeasure the ECU terminal voltage.
DIgnition switch: ON
DRotate the tire corresponding to the measured terminal by
one and a half to one rotate per second.
(1) Voltage between terminal 9 and body earth
(2) Voltage between terminal 6 and body earth
(3) Voltage between terminal 7 and body earth
(4) Voltage between terminal 8 and body earth
OK:Changes by 0 V↔5V.
MUT-IIData List
DNo.01 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.02 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.03 Vehicle speed sensor
DNo.04 Vehicle speed sensor
OK:The speed meter display and MUT-IIdisplay match.
NG→Replace the 4WD-ECU.
OK→Intermittent malfunction (Refer to GROUP 00 - Points to
Note for Intermittent Malfunctions)
Refer to GROUP 35B - Troubleshooting. (Refer to Diagnosis
Code No.11, 12, 13, 14, 21, 22, 23, and 24.)
Are all four wheels mounted to normal tires?
NO→Repair
Check the harness between the ABS-ECU and each wheel
speed sensor.
DCheck for open circuit and ground of the output line.
DCheck for open circuit and damage of the earth line.
NG→Repair
OK
Check the harness between the 4WD-ECU and
ABS-ECU.
DCheck for open circuit, ground and damage of
the power line.
NG→RepairOK