air condition MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION X, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008Pages: 241, PDF Size: 8.26 MB
Page 42 of 241
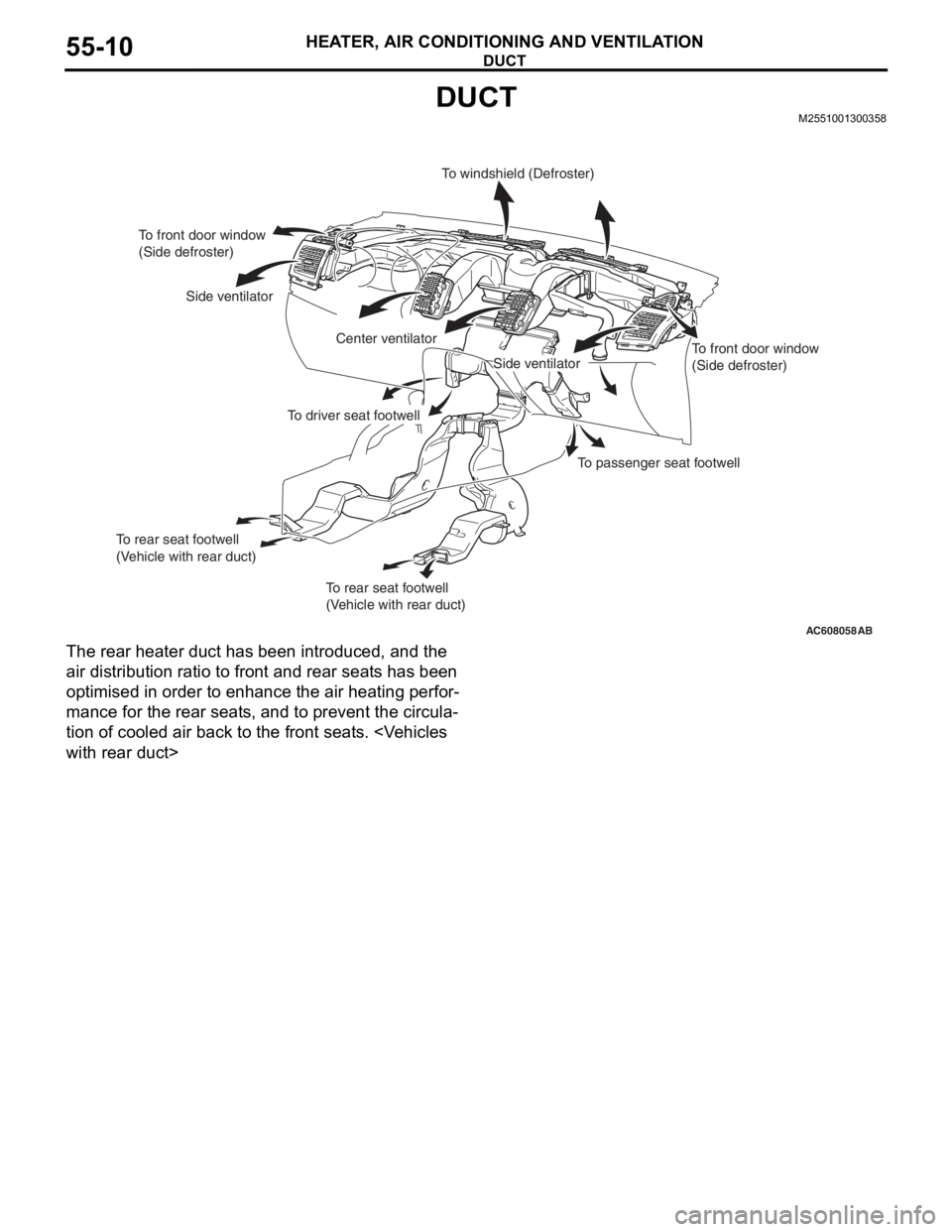
DUCT
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-10
DUCTM2551001300358
The rear heater duct has been introduced, and the
air distribution ratio to front and rear seats has been
optimised in order to enhance the air heating perfor
-
mance for the rear seats, and to prevent the circula-
tion of cooled air back to the front seats.
AC608058
To front door window
(Side defroster)
Side ventilator
Center ventilatorTo windshield (Defroster)
To front door window
(Side defroster)
To passenger seat footwell
To driver seat footwell
To rear seat footwell
(Vehicle with rear duct)
To rear seat footwell
(Vehicle with rear duct)
Side ventilator
AB
Page 43 of 241
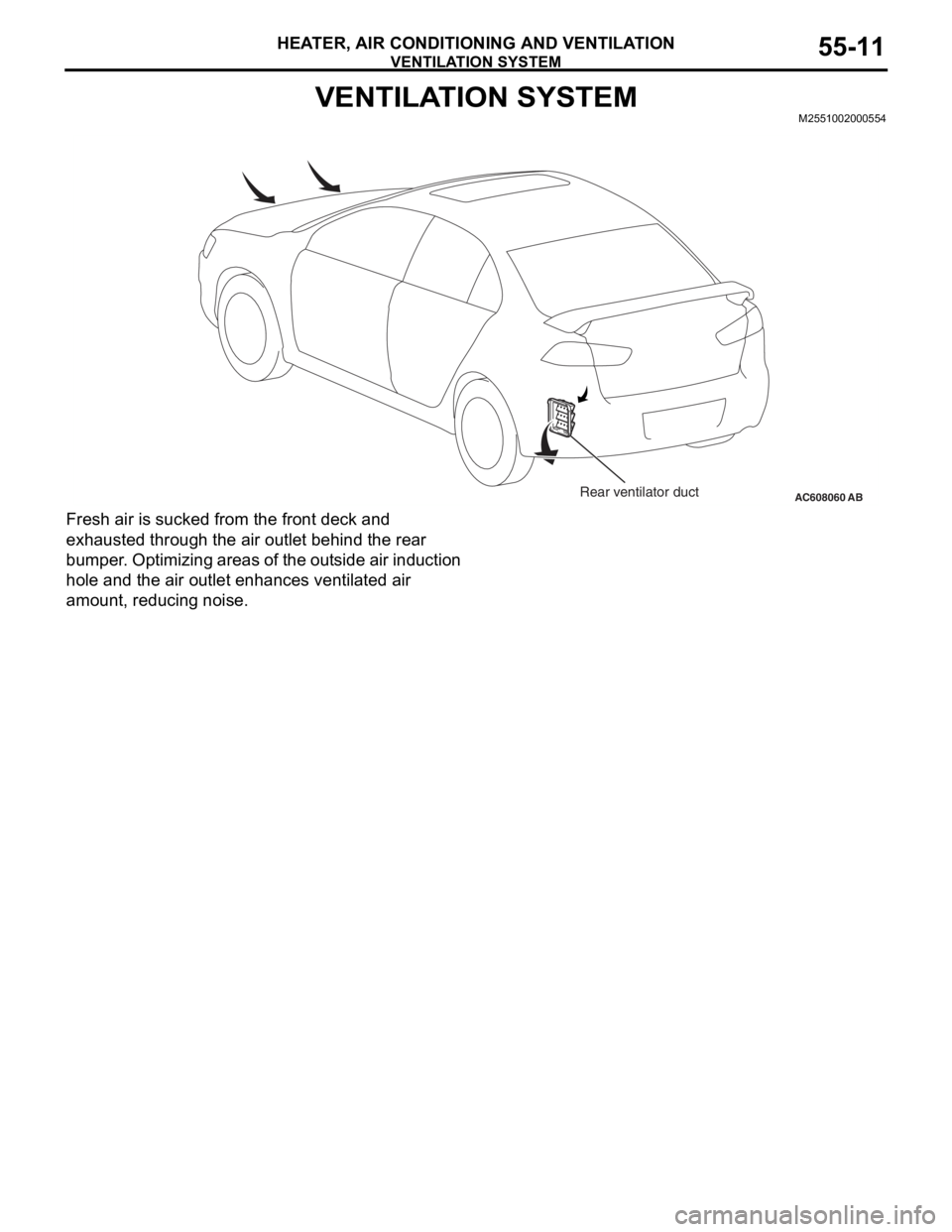
VENTILATION SYSTEM
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-11
VENTILATION SYSTEMM2551002000554
Fresh air is sucked from the front deck and
exhausted through the air outlet behind the rear
bumper. Optimizing areas of the outside air induction
hole and the air outlet enhances ventilated air
amount, reducing noise.
AC608060Rear ventilator ductAB
Page 72 of 241
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-10
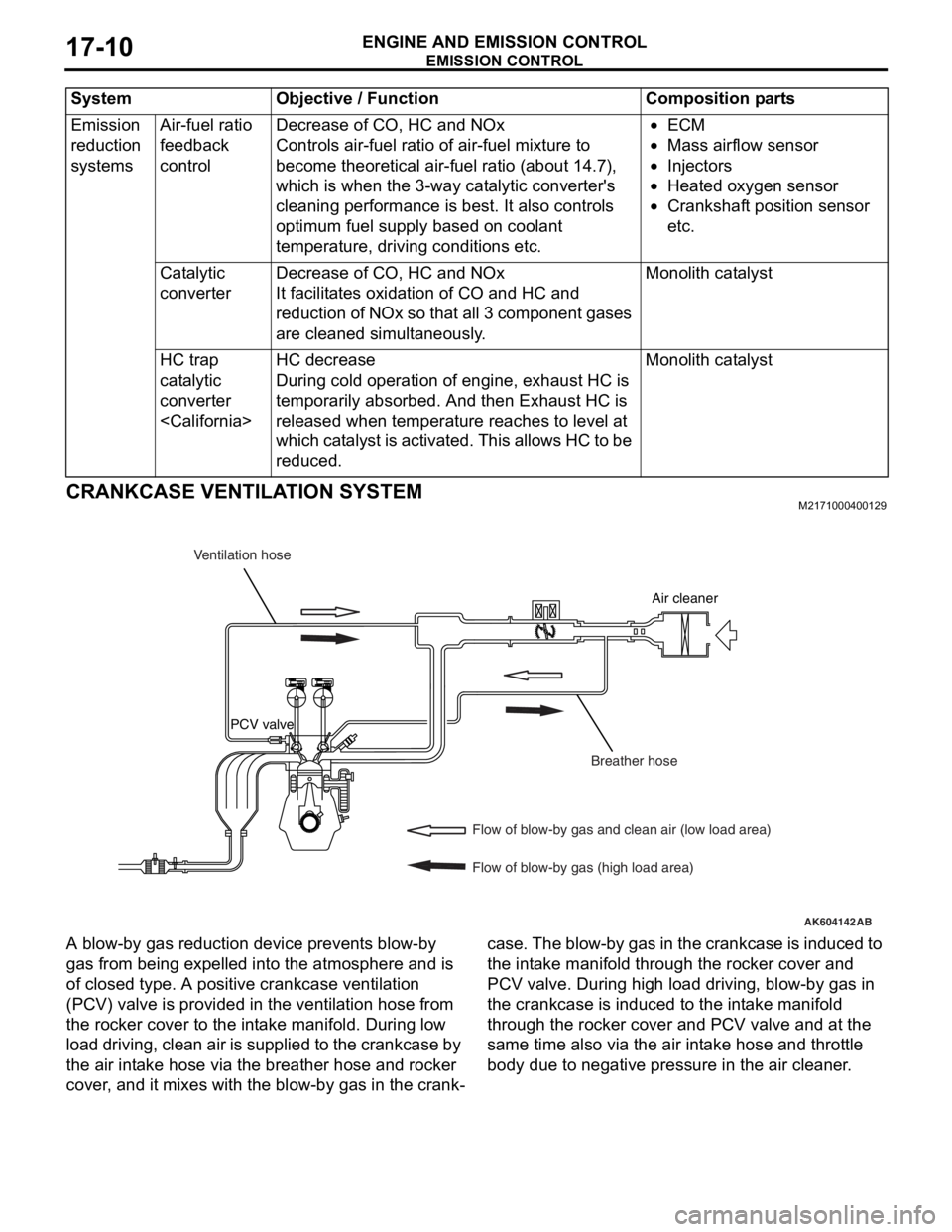
CRANKCASE VENTILATION SYSTEMM2171000400129
A blow-by gas reduction device prevents blow-by
gas from being expelled into the atmosphere and is
of closed type. A positive crankcase ventilation
(PCV) valve is provided in the ventilation hose from
the rocker cover to the intake manifold. During low
load driving, clean air is supplied to the crankcase by
the air intake hose via the breather hose and rocker
cover, and it mixes with the blow-by gas in the crank
-
case. The blow-by gas in the crankcase is induced to
the intake manifold through the rocker cover and
PCV valve. During high load driving, blow-by gas in
the crankcase is induced to the intake manifold
through the rocker cover and PCV valve and at the
same time also via the air intake hose and throttle
body due to negative pressure in the air cleaner.
Emission
reduction
systemsAir-fuel ratio
feedback
controlDecrease of CO, HC and NOx
Controls air-fuel ratio of air-fuel mixture to
become theoretical air-fuel ratio (about 14.7),
which is when the 3-way catalytic converter's
cleaning performance is best. It also controls
optimum fuel supply based on coolant
temperature, driving conditions etc.
•ECM
•Mass airflow sensor
•Injectors
•Heated oxygen sensor
•Crankshaft position sensor
etc.
Catalytic
converterDecrease of CO, HC and NOx
It facilitates oxidation of CO and HC and
reduction of NOx so that all 3 component gases
are cleaned simultaneously.
Monolith catalyst
HC trap
catalytic
converter
During cold operation of engine, exhaust HC is
temporarily absorbed. And then Exhaust HC is
released when temperature reaches to level at
which catalyst is activated. This allows HC to be
reduced.
Monolith catalyst
System Objective / Function Composition parts
AK604142
Air cleaner
PCV valve
AB
Ventilation hose
Breather hose
Flow of blow-by gas and clean air (low load area)
Flow of blow-by gas (high load area)
Page 74 of 241
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-12
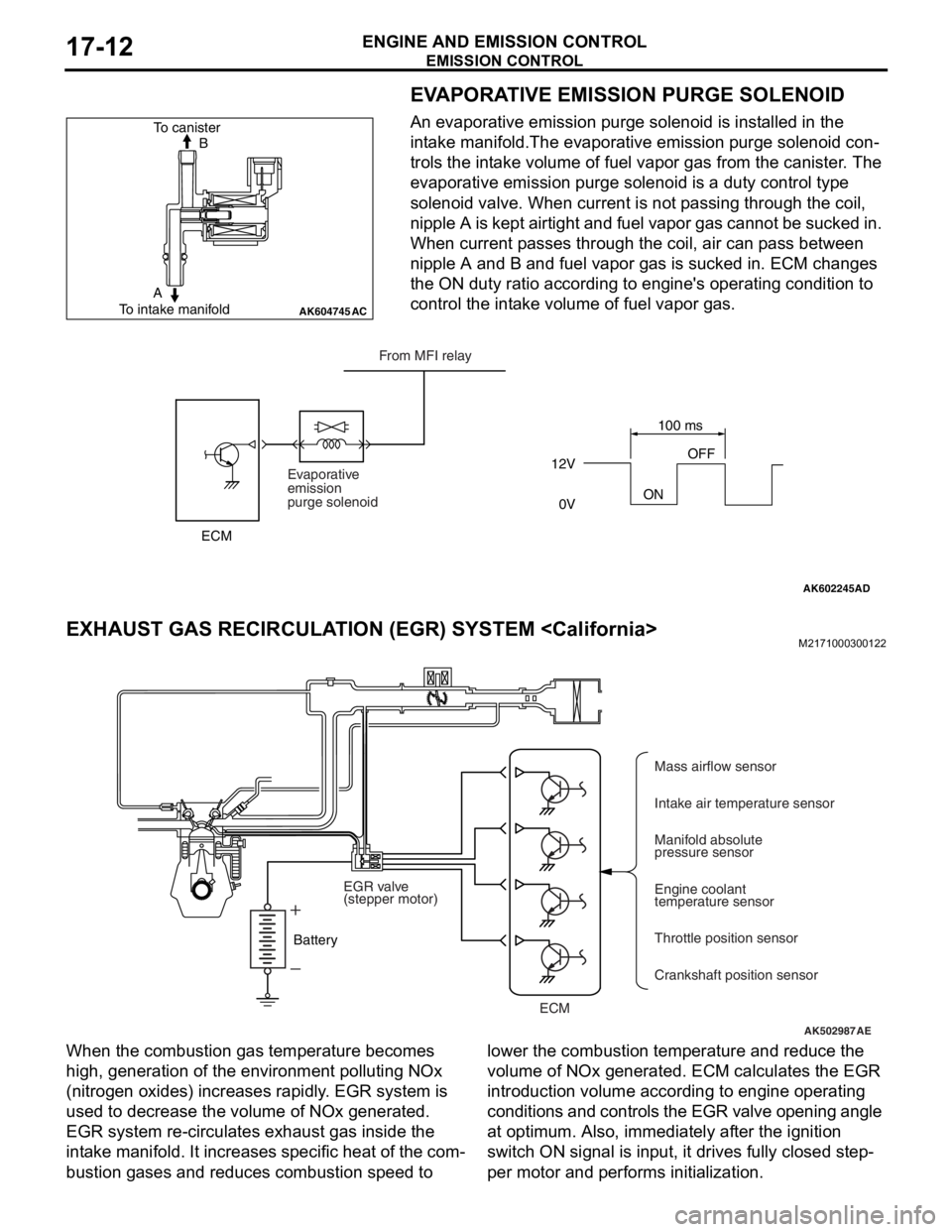
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION PURGE SOLENOID
An evaporative emission purge solenoid is installed in the
intake manifold.The evaporative emission purge solenoid con
-
trols the intake volume of fuel vapor gas from the canister. The
evaporative emission purge solenoid is a duty control type
solenoid valve. When current is not passing through the coil,
nipple A is kept airtight and fuel vapor gas cannot be sucked in.
When current passes through the coil, air can pass between
nipple A and B and fuel vapor gas is sucked in. ECM changes
the ON duty ratio according to engine's operating condition to
control the intake volume of fuel vapor gas.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
When the combustion gas temperature becomes
high, generation of the environment polluting NOx
(nitrogen oxides) increases rapidly. EGR system is
used to decrease the volume of NOx generated.
EGR system re-circulates exhaust gas inside the
intake manifold. It increases specific heat of the com
-
bustion gases and reduces combustion speed to lower the combustion temperature and reduce the
volume of NOx generated. ECM calculates the EGR
introduction volume according to engine operating
conditions and controls the EGR valve opening angle
at optimum. Also, immediately after the ignition
switch ON signal is input, it drives fully closed step
-
per motor and performs initialization.
AK604745AC
B To canister
To intake manifoldA
AK602245AD
12V
ONOFF
0V100 ms
Evaporative
emission
purge solenoidFrom MFI relay
ECM
AK502987AE
ECMMass airflow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Throttle position sensor
Crankshaft position sensor BatteryEGR valve
(stepper motor)
Page 120 of 241
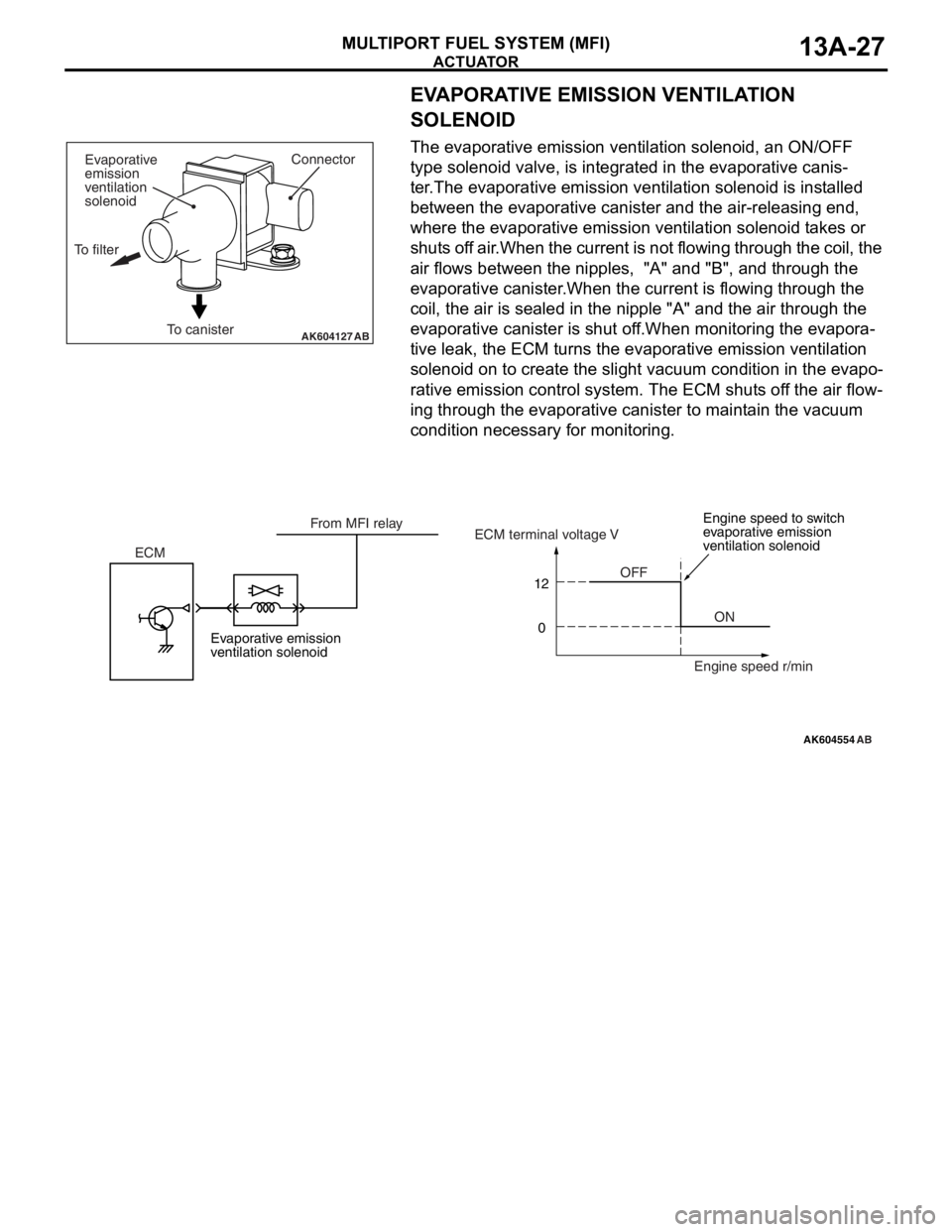
ACTUATOR
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-27
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION VENTILATION
SOLENOID
The evaporative emission ventilation solenoid, an ON/OFF
type solenoid valve, is integrated in the evaporative canis
-
ter.The evaporative emission ventilation solenoid is installed
between the evaporative canister and the air-releasing end,
where the evaporative emission ventilation solenoid takes or
shuts off air.When the current is not flowing through the coil, the
air flows between the nipples, "A" and "B", and through the
evaporative canister.When the current is flowing through the
coil, the air is sealed in the nipple "A" and the air through the
evaporative canister is shut off.When monitoring the evapora
-
tive leak, the ECM turns the evaporative emission ventilation
solenoid on to create the slight vacuum condition in the evapo
-
rative emission control system. The ECM shuts off the air flow-
ing through the evaporative canister to maintain the vacuum
condition necessary for monitoring.
AK604127ABTo canisterConnector
Evaporative
emission
ventilation
solenoid
To filter
AK604554
12
0
AB
OFF
ON ECMECM terminal voltage V
Engine speed r/min From MFI relay
Evaporative emission
ventilation solenoidEngine speed to switch
evaporative emission
ventilation solenoid
Page 122 of 241
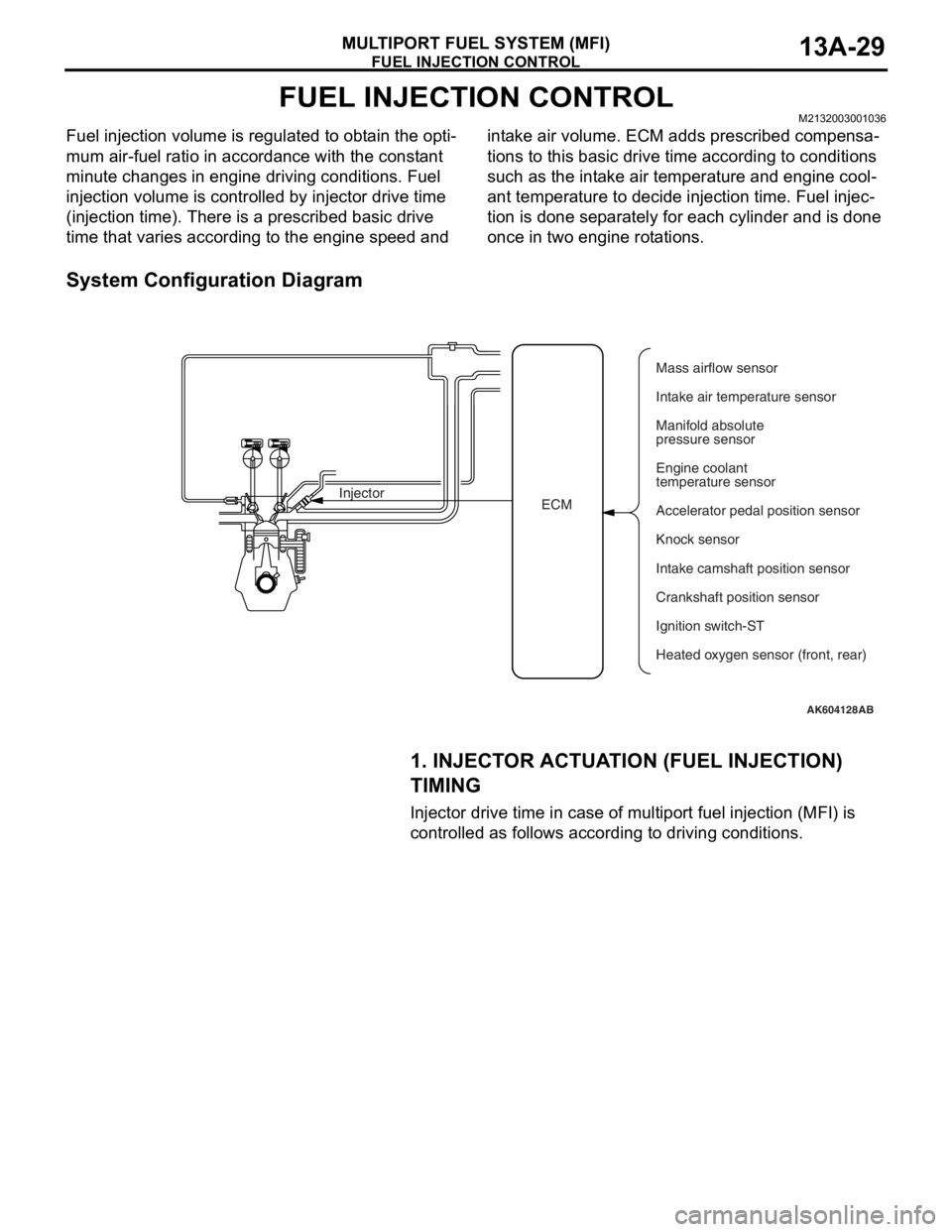
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-29
FUEL INJECTION CONTROLM2132003001036
Fuel injection volume is regulated to obtain the opti-
mum air-fuel ratio in accordance with the constant
minute changes in engine driving conditions. Fuel
injection volume is controlled by injector drive time
(injection time). There is a prescribed basic drive
time that varies according to the engine speed and intake air volume. ECM adds prescribed compensa
-
tions to this basic drive time according to conditions
such as the intake air temperature and engine cool
-
ant temperature to decide injection time. Fuel injec-
tion is done separately for each cylinder and is done
once in two engine rotations.
System Configuration Diagram
1. INJECTOR ACTUATION (FUEL INJECTION)
TIMING
Injector drive time in case of multiport fuel injection (MFI) is
controlled as follows according to driving conditions.
AK604128AB
ECM InjectorMass airflow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Accelerator pedal position sensor
Knock sensor
Intake camshaft position sensor
Ignition switch-ST
Heated oxygen sensor (front, rear) Crankshaft position sensor
Page 124 of 241
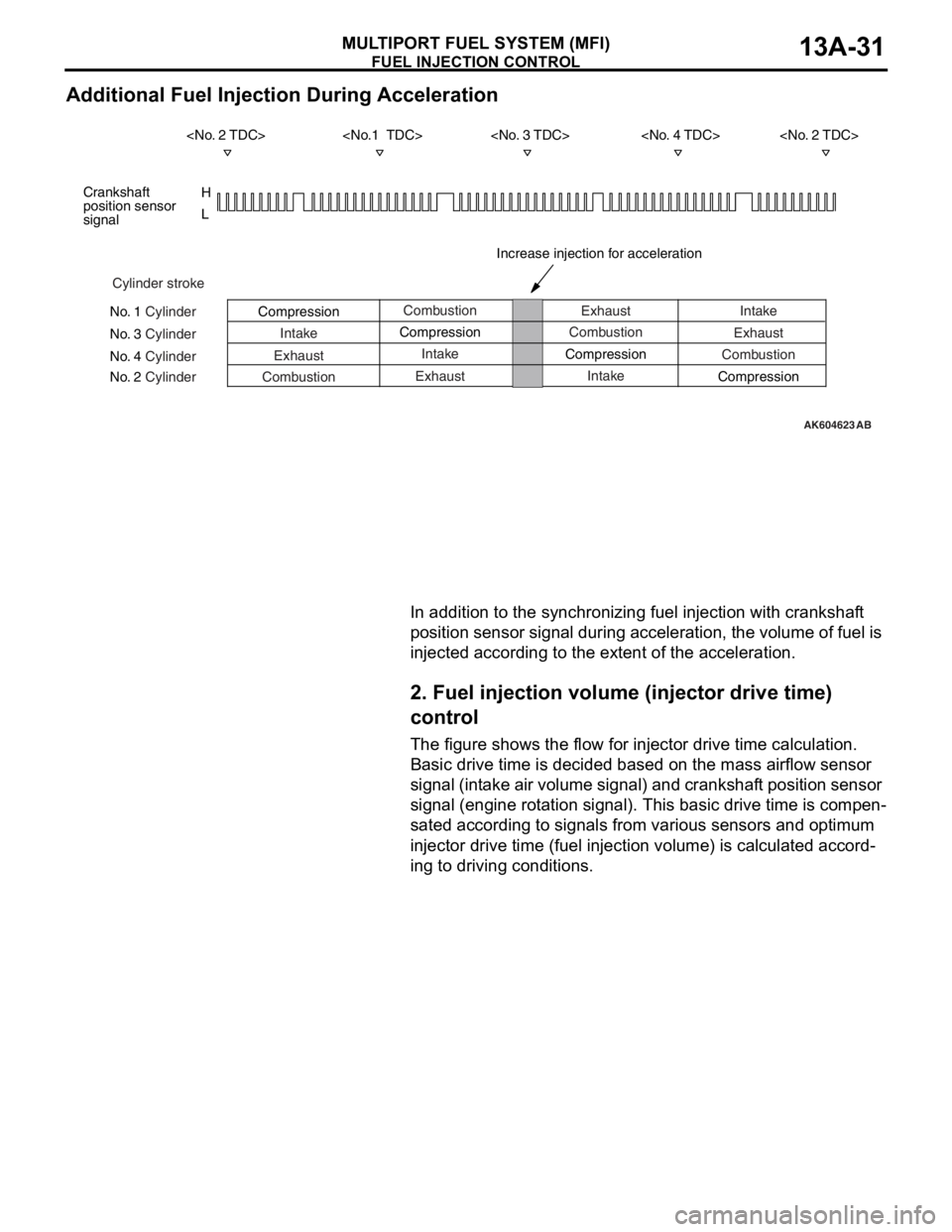
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-31
Additional Fuel Injection During Acceleration
In addition to the synchronizing fuel injection with crankshaft
position sensor signal during acceleration, the volume of fuel is
injected according to the extent of the acceleration.
2. Fuel injection volume (injector drive time)
control
The figure shows the flow for injector drive time calculation.
Basic drive time is decided based on the mass airflow sensor
signal (intake air volume signal) and crankshaft position sensor
signal (engine rotation signal). This basic drive time is compen
-
sated according to signals from various sensors and optimum
injector drive time (fuel injection volume) is calculated accord
-
ing to driving conditions.
AK604623
H
L
AB
Cylinder stroke
No. 1 Cylinder
No. 3 Cylinder
No. 4 Cylinder
No. 2 CylinderCombustion
Intake
Exhaust
CombustionExhaust
Compression
Intake
Exhaust CompressionCombustion
Intake CompressionIntake
Exhaust
Combustion
Compression Crankshaft
position sensor
signal
Increase injection for acceleration
Page 127 of 241
![MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 User Guide FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-34
[Injector drive time compensation]
After calculating the injector basic drive time, the ECM makes
the following compensations to control the o MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION X 2008 User Guide FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-34
[Injector drive time compensation]
After calculating the injector basic drive time, the ECM makes
the following compensations to control the o](/img/19/57326/w960_57326-126.png)
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-34
[Injector drive time compensation]
After calculating the injector basic drive time, the ECM makes
the following compensations to control the optimum fuel injec
-
tion volume according to driving conditions.
List of main compensations for fuel injection control
.
[Fuel limit control during deceleration]
ECM limits fuel when decelerating downhill to prevent exces-
sive rise of catalytic converter temperature and to improve fuel
efficiency.
.
[Fuel-cut control when over-run]
When engine speed exceeds a prescribed limit (6,600 r/min),
ECM cuts fuel supply to prevent overrunning and thus protect
the engine. Also, if engine speed exceeds 4,000 r/min for 15
seconds while vehicle is stationary (no load), it cuts fuel supply
and controls the throttle valve opening angle to protect the
engine.
CompensationsContent
Heated oxygen sensor feedback compensationThe heated oxygen sensor signal is used for
making the compensation to get air-fuel ratio with
best cleaning efficiency of the 3-way catalytic
converter. This compensation might not be made
sometimes in order to improve drivability,
depending on driving conditions. (Air-fuel ratio
compensation is made.)
Air-fuel ratio compensationUnder driving conditions where heated oxygen
sensor feedback compensation is not performed,
compensation is made based on pre-set map
values that vary according to engine speed and
intake air volume.
Engine coolant temperature compensationCompensation is made according to the engine
coolant temperature. The lower the engine coolant
temperature, the greater the fuel injection volume.
Acceleration/ Deceleration compensationCompensation is made according to change in
intake air volume. During acceleration, fuel injection
volume is increased. Also, during deceleration, fuel
injection volume is decreased.
Fuel injection compensationCompensation is made according to the pressure
difference between atmospheric pressure and
manifold absolute pressure. The greater the
difference in pressure, the shorter the injector drive
time.
Battery voltage compensationCompensation is made depending on battery
voltage. The lower the battery voltage, the greater
the injector drive signal time.
Learning value for fuel compensationCompensation amount is learned to compensate
feedback of heated oxygen sensor. This allows
system to compensate in accordance with engine
characteristics.
Page 128 of 241
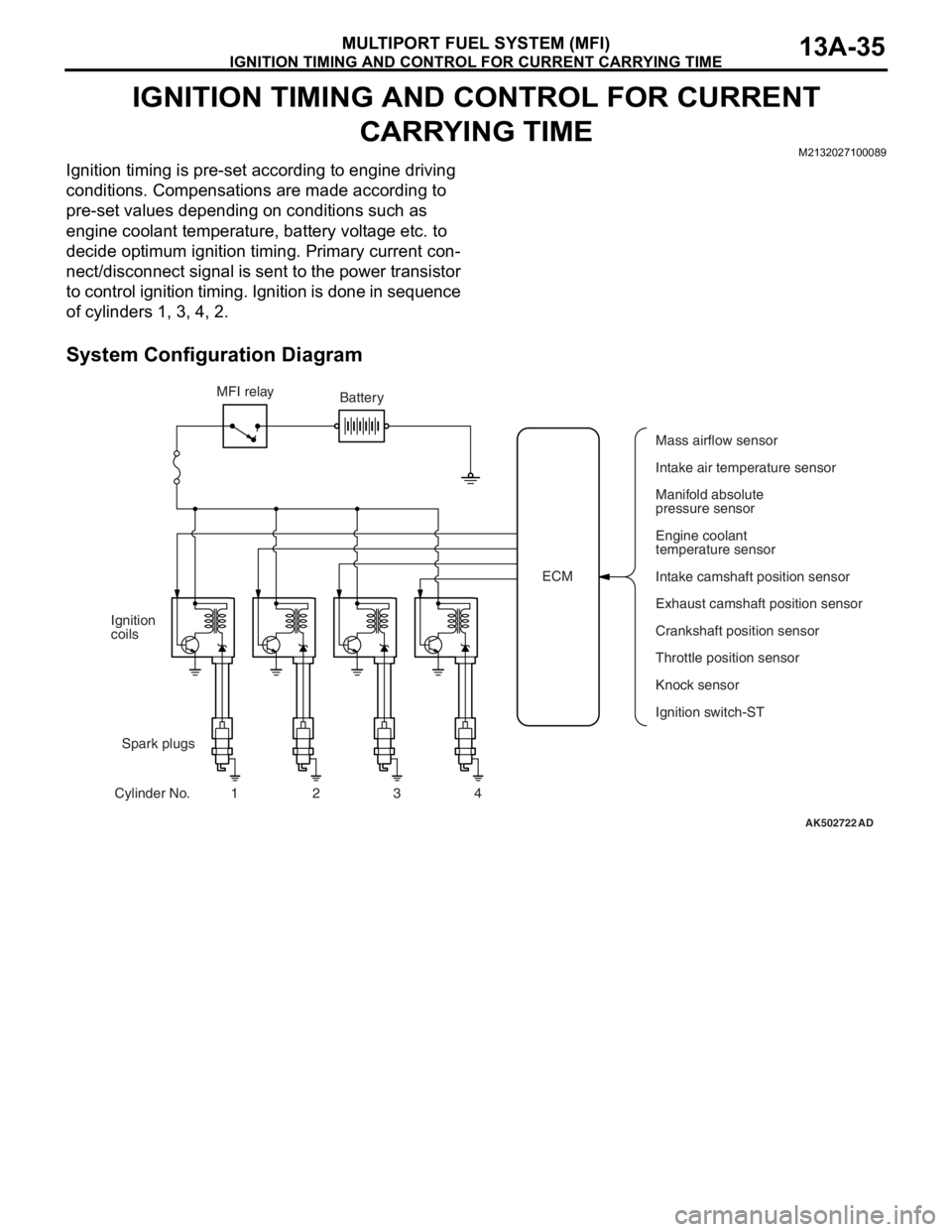
IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-35
IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT
CARRYING TIME
M2132027100089
Ignition timing is pre-set according to engine driving
conditions. Compensations are made according to
pre-set values depending on conditions such as
engine coolant temperature, battery voltage etc. to
decide optimum ignition timing. Primary current con
-
nect/disconnect signal is sent to the power transistor
to control ignition timing. Ignition is done in sequence
of cylinders 1, 3, 4, 2.
System Configuration Diagram
AK502722AD
ECM MFI relay
Spark plugs Ignition
coils
Cylinder No. 1 2 3 4Battery
Mass airflow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Manifold absolute
pressure sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Intake camshaft position sensor
Exhaust camshaft position sensor
Crankshaft position sensor
Knock sensor
Ignition switch-ST Throttle position sensor
Page 137 of 241
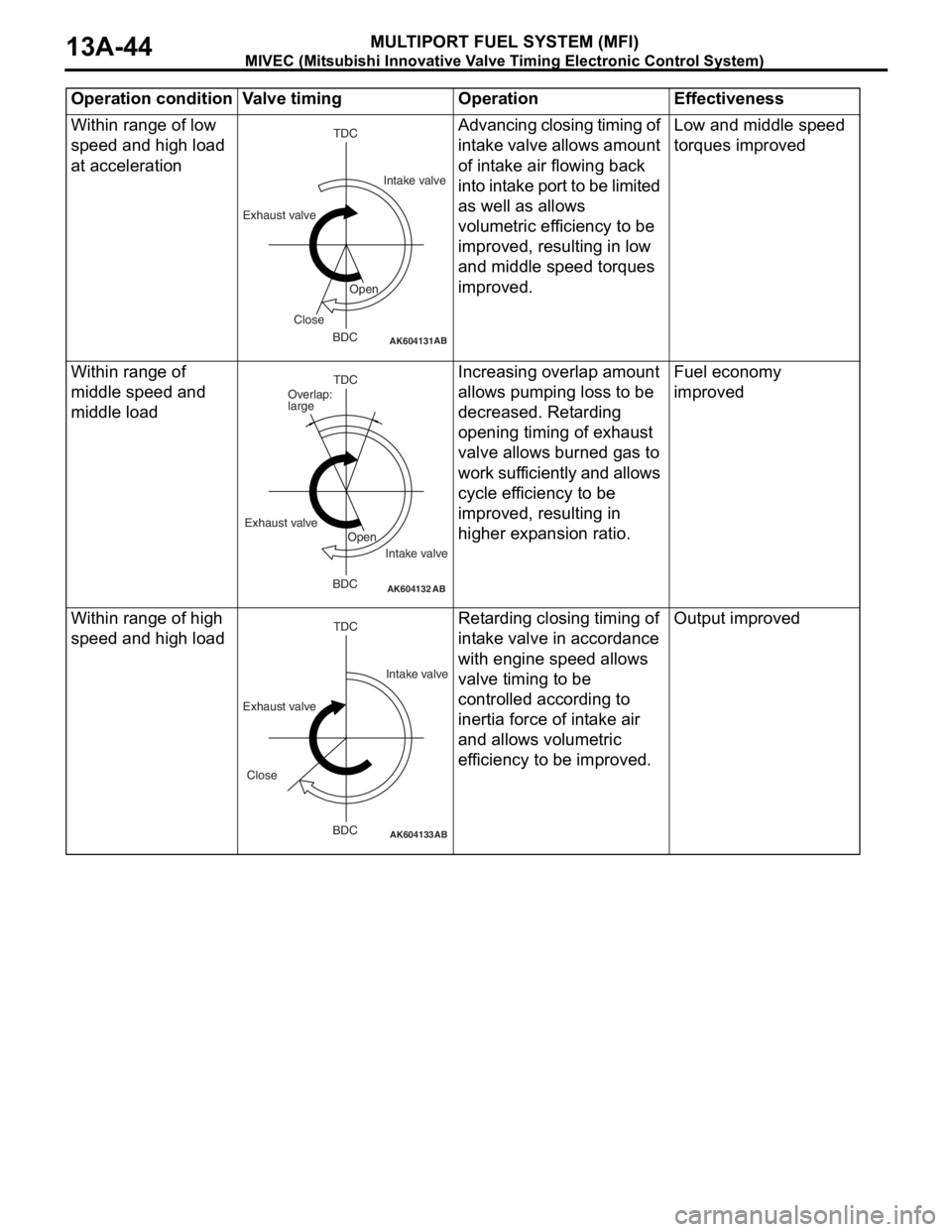
MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control System)
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)13A-44
Within range of low
speed and high load
at accelerationAdvancing closing timing of
intake valve allows amount
of intake air flowing back
into intake port to be limited
as well as allows
volumetric efficiency to be
improved, resulting in low
and middle speed torques
improved.Low and middle speed
torques improved
Within range of
middle speed and
middle loadIncreasing overlap amount
allows pumping loss to be
decreased. Retarding
opening timing of exhaust
valve allows burned gas to
work sufficiently and allows
cycle efficiency to be
improved, resulting in
higher expansion ratio.Fuel economy
improved
Within range of high
speed and high loadRetarding closing timing of
intake valve in accordance
with engine speed allows
valve timing to be
controlled according to
inertia force of intake air
and allows volumetric
efficiency to be improved.Output improved
Operation condition Valve timing Operation Effectiveness
AK604131AB
TDC
BDC Exhaust valveIntake valve
Open
Close
AK604132AB
TDC
BDC Exhaust valve
Intake valve Overlap:
large
Open
AK604133
TDC
BDC
AB
Exhaust valveIntake valve
Close