Coil MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1987 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1987, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 1987 1.GPages: 284, PDF Size: 14.74 MB
Page 35 of 284
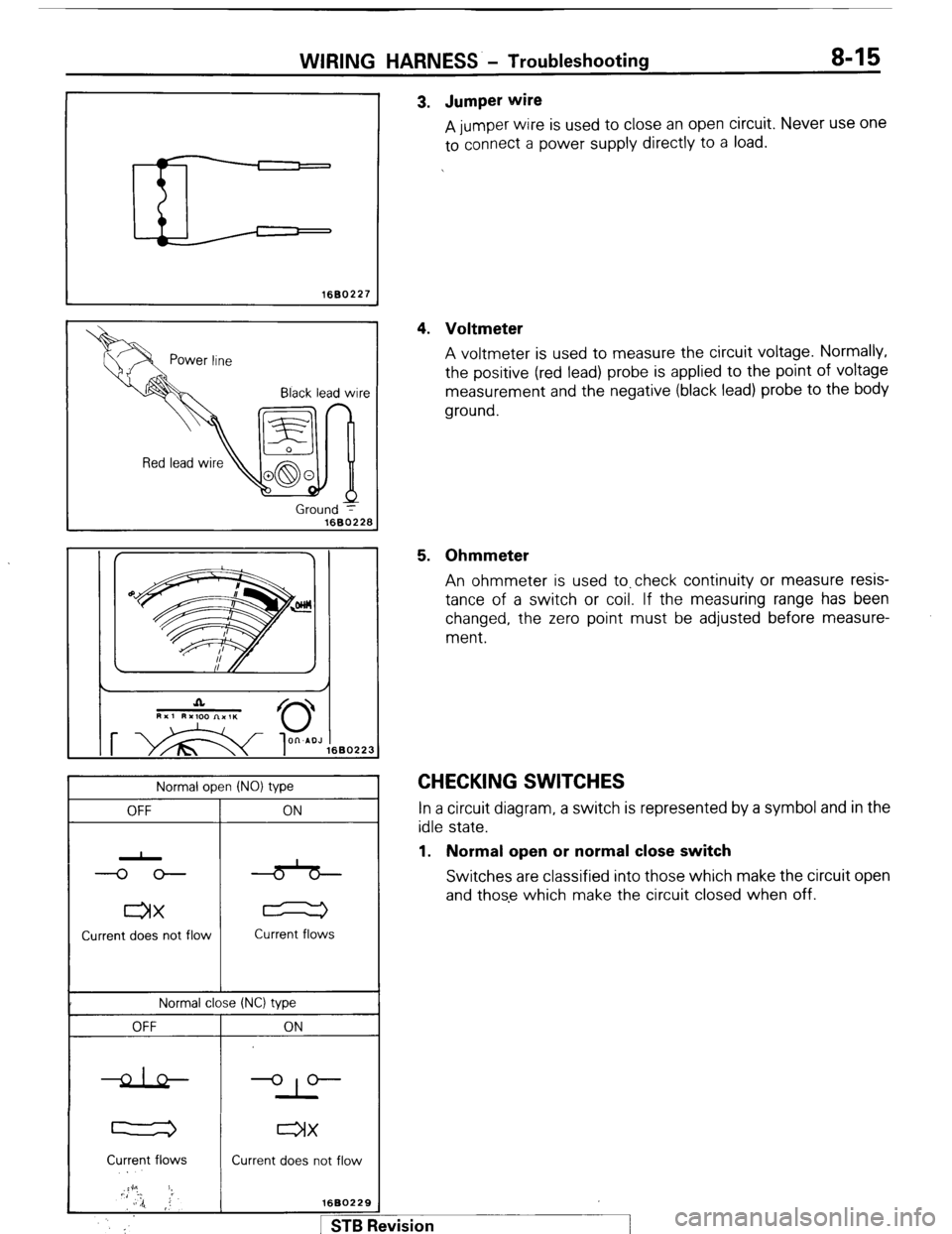
WIRING HARNESS - Troubleshooting 8-15
1660227
Black lead wire
Ground y
1680228
Normal open (NO) type
OFF
ax
Current does not flow ON
Current flows
Normal close (NC) type
OFF
l-2
Current flows ON
-op--
IX
Current does not flow
1680229
pm I 3. Jumper wire
A jumper wire is used to close an open circuit. Never use one
to connect a power supply directly to a load.
4. Voltmeter
A voltmeter is used to measure the circuit voltage. Normally,
the positive (red lead) probe is applied to the point of voltage
measurement and the negative (black lead) probe to the body
ground.
5. Ohmmeter
An ohmmeter is used to.check continuity or measure resis-
tance of a switch or coil. If the measuring range has been
changed, the zero point must be adjusted before measure-
ment.
CHECKING SWITCHES In a circuit diagram, a switch is represented by a symbol and in the
idle state.
1. Normal open or normal close switch
Switches are classified into those which make the circuit open
and those which make the circuit closed when off.
#vision
I
Page 36 of 284
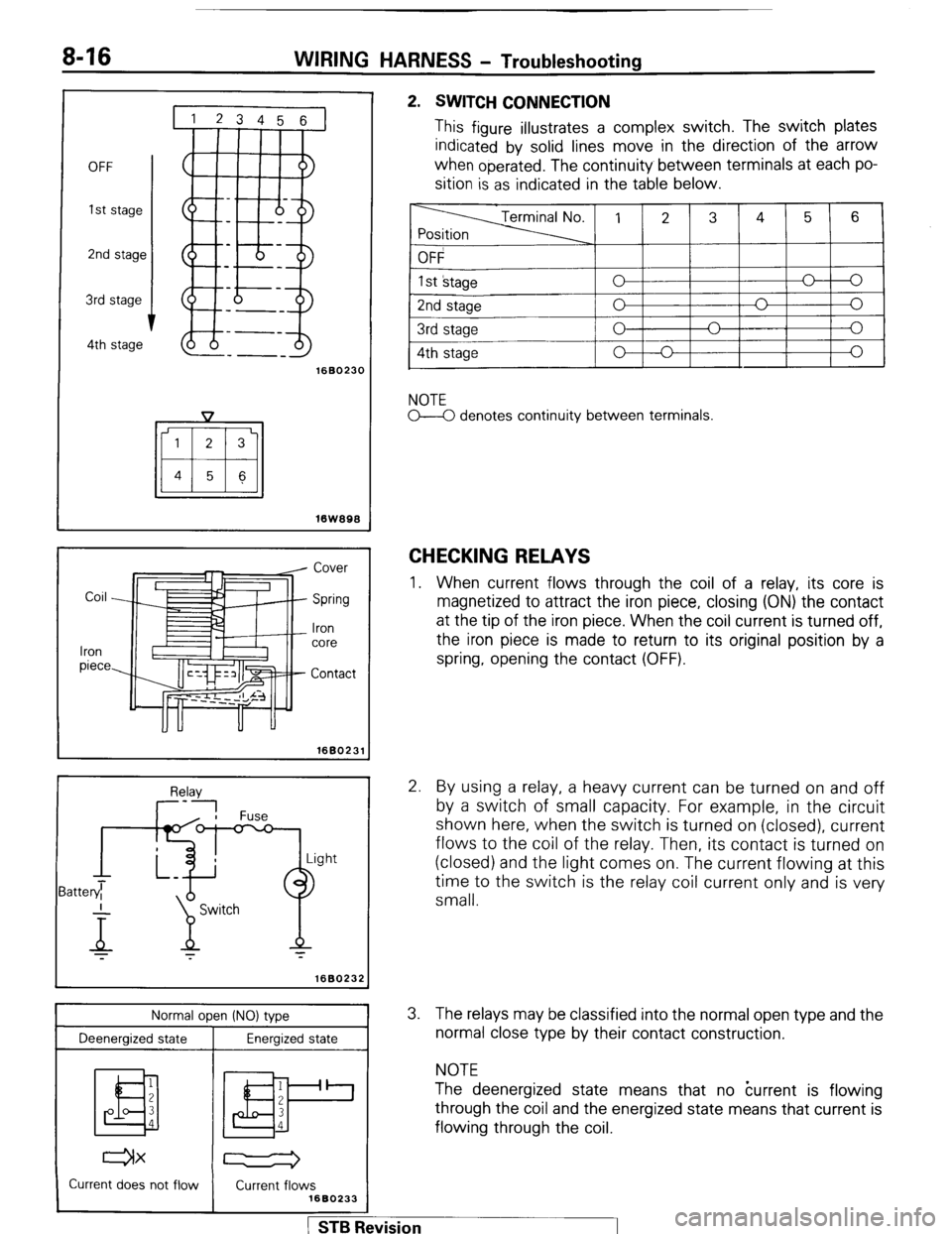
8-16 WIRING HARNESS - Troubleshooting
OFF
1st stage
2nd stage
3rd stage
1
--_
4th stage
1660230
16W896
Cover
Coil
Iron
piece Spring
Iron
core
Contact
1660231
I
l-
Battery:
I
-
d
T Relav
T I
I 1660232 1
Normal ooen (NO) tvoe
Deenergized state Energized state
I
1
2
ED
3
4
1 2
BP
3
4
1 YZZZw;6B0233 CurreZ! not flow
2. SWITCH CONNECTION
This figure illustrates a complex switch. The switch plates
indicated by solid lines move in the direction of the arrow
when
operated. The continuity between terminals at each po-
sition is as indicated in the table below.
NOTE
M denotes continuity between terminals.
CHECKING RELAYS
1. When current flows through the coil of a relay, its core is
magnetized to attract the iron piece, closing (ON) the contact
at the tip of the iron piece. When the coil current is turned off,
the iron piece is made to return to its original position by a
spring, opening the contact (OFF).
2. By using a relay, a heavy current can be turned on and off
by a switch of small capacity. For example, in the circuit
shown here, when the switch is turned on (closed), current
flows to the coil of the relay. Then, its contact is turned on
(closed) and the light comes on. The current flowing at this
time to the switch is the relay coil current only and is very
small.
3. The relays may be classified into the normal open type and the
normal close type by their contact construction.
NOTE
The deenergized state means that no kurrent is flowing
through the coil and the energized state means that current is
flowing through the coil.
J . . . I 1 STB Revmon
Page 46 of 284
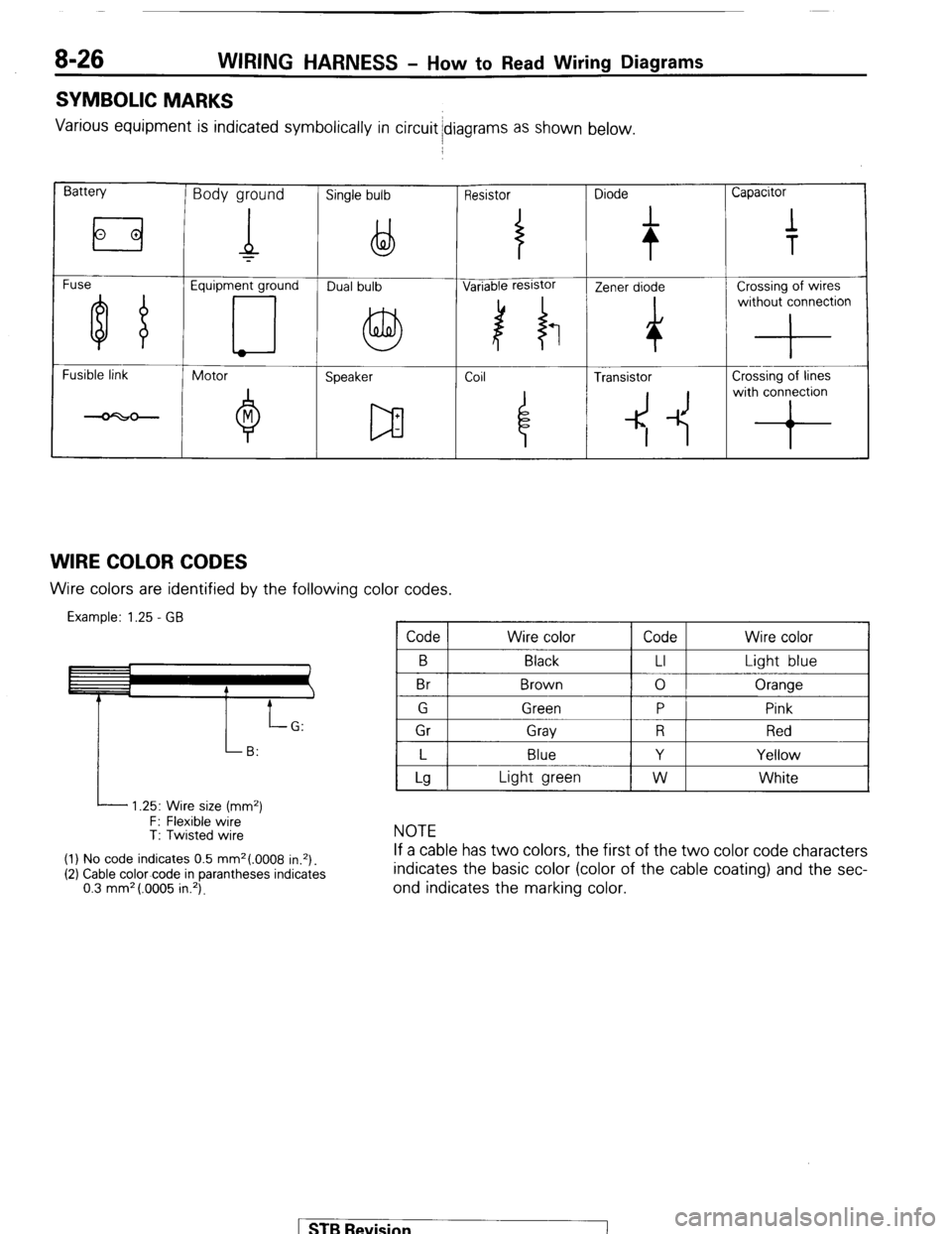
8-26 WIRING HARNESS - HOW to Read Wiring Diagrams
SYMBOLIC MARKS
Various equipment is indicated symbolically in circuit idiagrams as shown below.
Battery Body ground Single bulb Resistor Diode Capacitor
Fuse Equipment ground
Fusible link
Motor
Speaker Coil ~
4 Transistor Crossing of lines
4 -1~ with conron
WIRE COLOR CODES Wire colors are identified by the following color codes.
Example: 1.25 - GB Code Wire color Code Wire color
B
Br Black
Brown LI
0 Light blue
Oranqe
I P
i 1 Gr 1 Grav 1 R 1 Red I
I L I Blue
I Y I Yellow I
L 1.25: Wire size (mm2)
F: Flexible wire
T: Twisted wire
(1) No code indicates 0.5 mm2(.0008 in.*).
(2) Cable color-code in parantheses indicates
0.3 mm* (.0005 in.‘).
Lg Light green W White
NOTE
If a cable has two colors, the first of the two color code characters
indicates the basic color (color of the cable coating) and the sec-
ond indicates the marking color.
STB Revision
Page 49 of 284
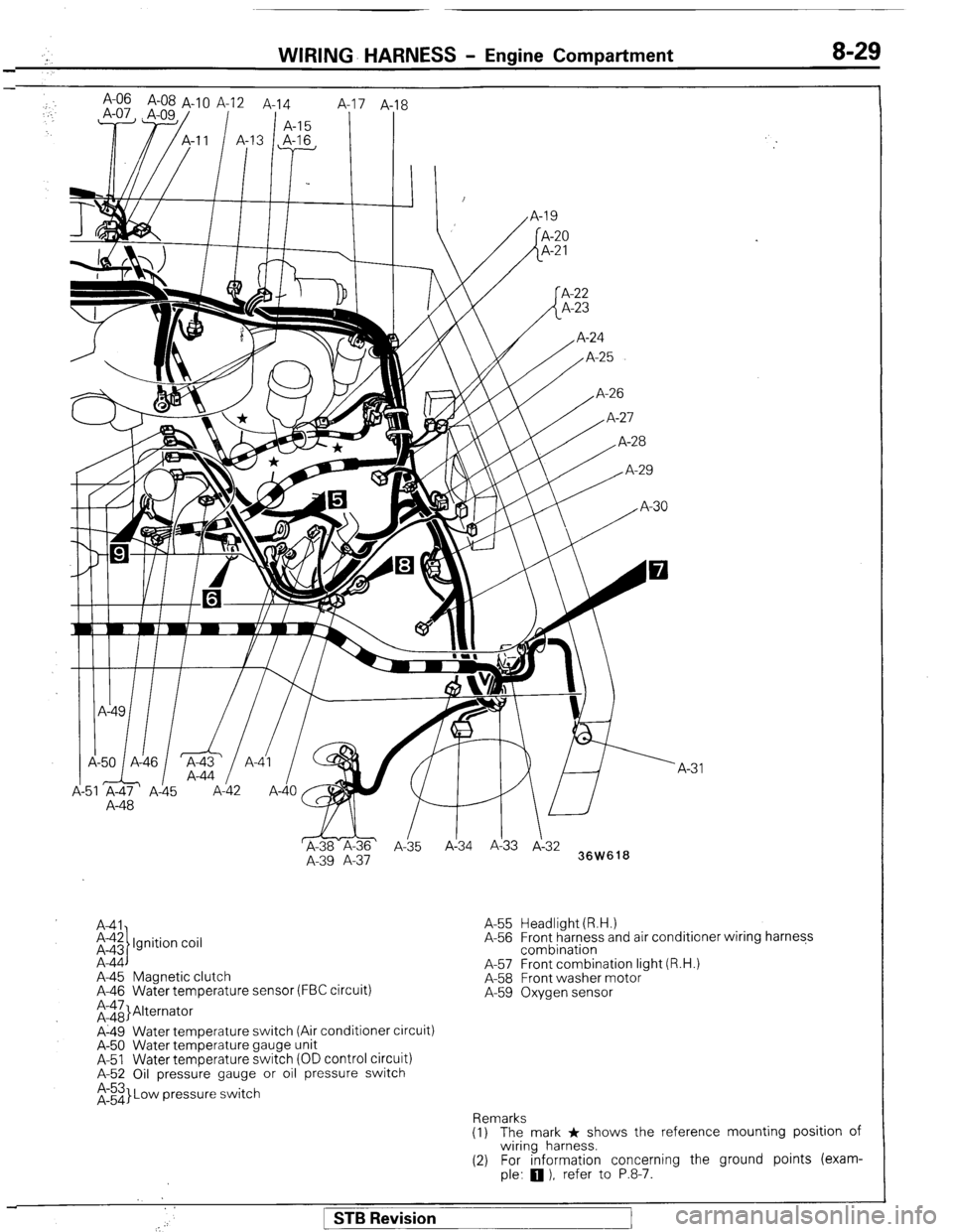
WIRING- HARNESS - Engine Compartment 8-29
; A-06 A-08 A-1 0 A-12 A-14
,.
1 A-15 8
I I
,I I I, I /
A-48
WI
&-ii& ’
A-35 Ai34 A!33 J-3:
A-39 A-37
36W618
A41
i-$ Ignition coil
A-44
A-45 Magnetic clutch
A-46 Water temperature sensor (FBC circuit)
;rii}Alternator
A-49 Water temperature switch (Air conditioner circuit)
A-50 Water temperature gauge unit
A-51 Water temperature switch (OD control circuit)
A-52 Oil pressure gauge or oil pressure switch
$3 Low pressure switch A-55 Headlight (R.H.)
A-56 Front harness and air conditioner wiring harness
combination
A-57 Front combination light (R.H.)
A-58 Front washer motor
A-59 Oxygen sensor
Remarks
(1) The mark * shows the reference mounting position of
wiring harness.
(2) For information concerning the ground points (exam-
ple:
q ), refer to P.8-7.
1 STB Revision
Page 59 of 284
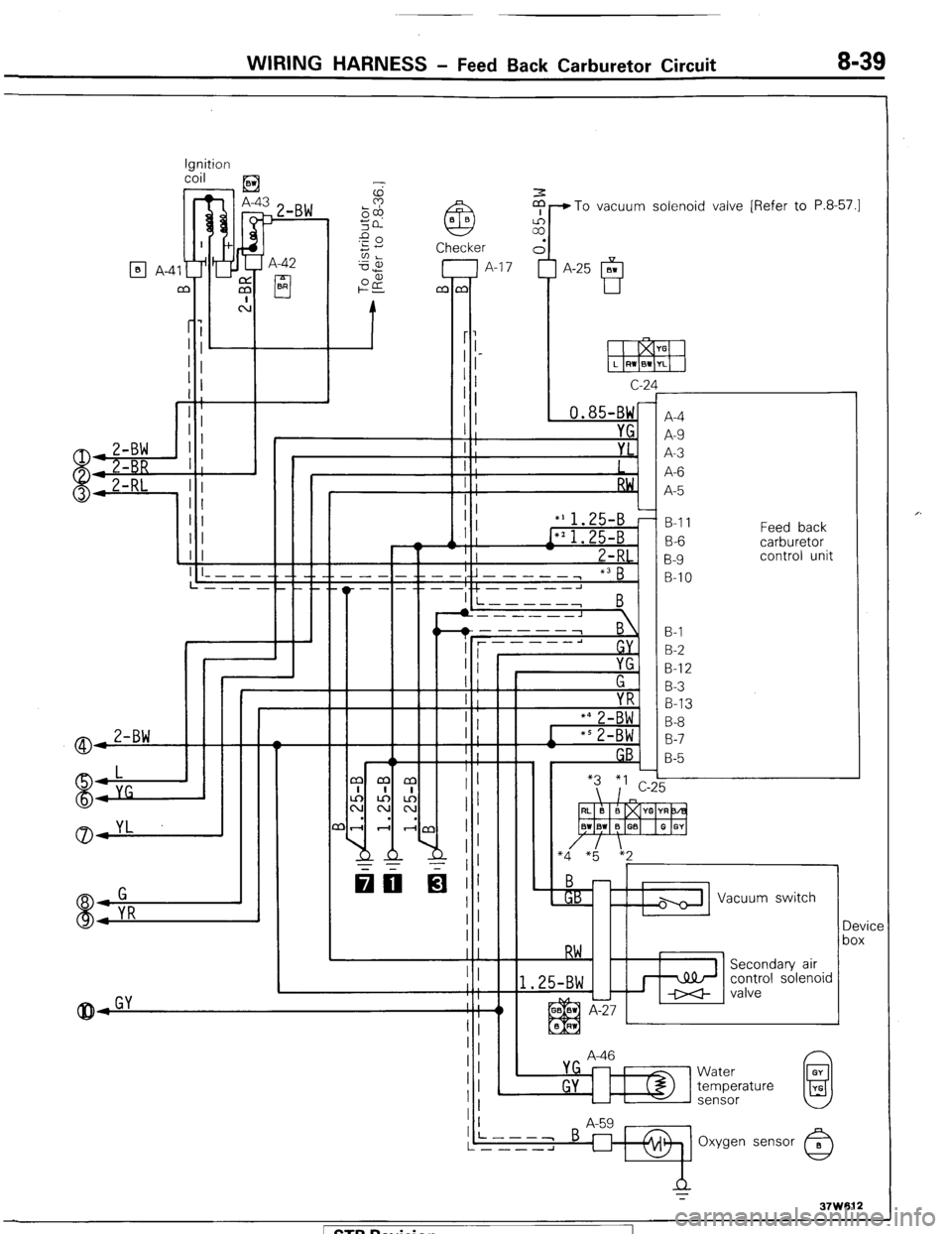
WIRING HARNESS - Feed Back Carburetor Circuit 8-39
Ignition
coil
) _ ,E3
$-To vacuum solenoid valve [Refer to P.8-57.1
7 A-42
cl BR
q A-4
c-2
, 0.85-BW
I YG
I ;
I : YL.
I
I ;
RW,
I :
‘A
f
r
A-4
A-9
A-3
A-6
A-5
B-l 1
B-6
B-9
B-IO Feed back
carburetor
control unit
I
II
II
(I I
1 I ! ! I I- - - - -. -_ __ __
L---- __._._
I +L----J I i-----,
B
B-l
B-2
B-l 2
B-3
B-13
B-8
B-7
B-5
A-46 Vacuum switch
Device
box
control solenoid
L
L
Water
temperature
sensor 1 STB Revision
Page 60 of 284
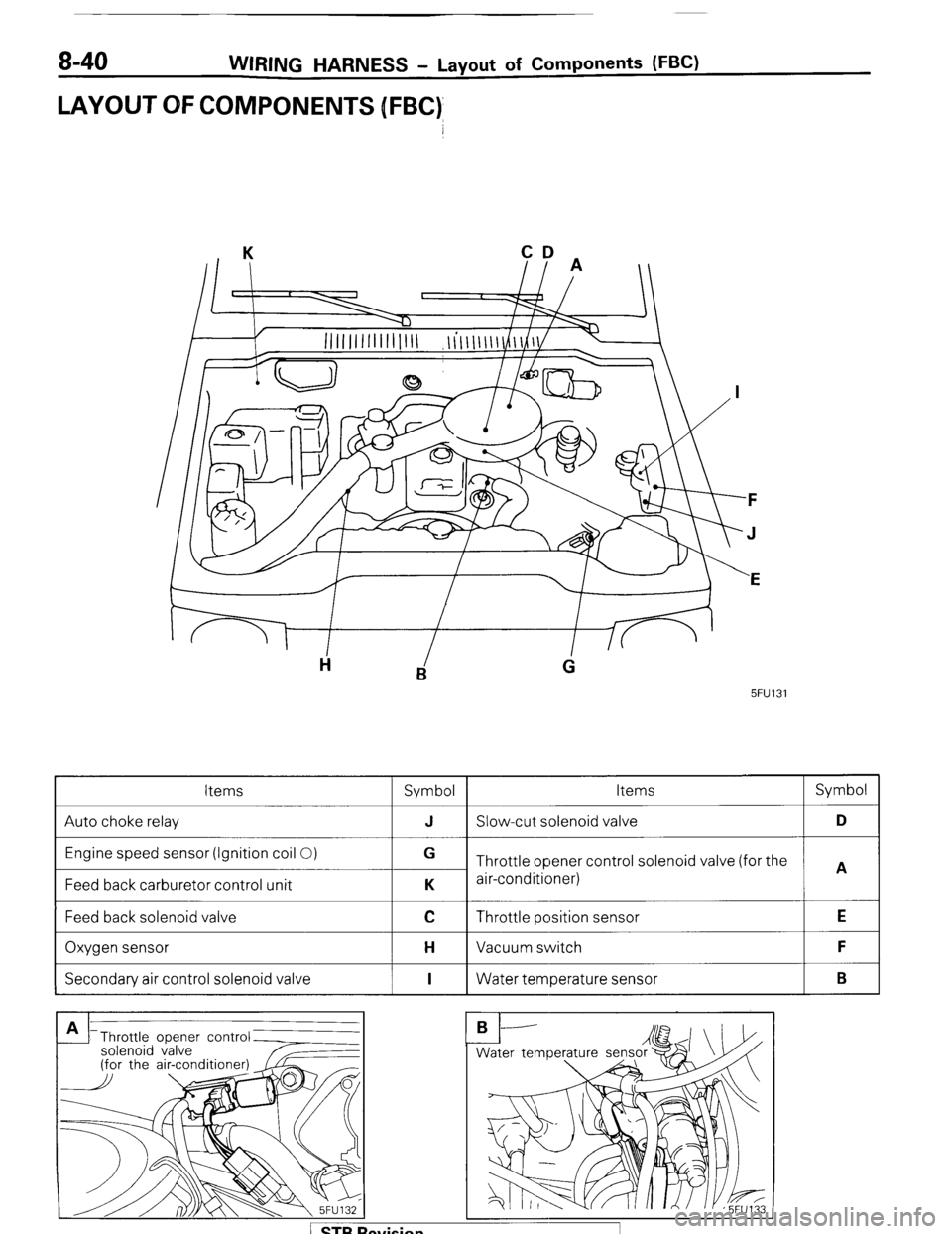
8-40 WIRING HARNESS - Layout of Components WC)
LAYOUT OFCOMPONENJS [FBC)
CD
II A
5FU131
Items
Symbol Items Symbol
Auto choke relay J Slow-cut solenoid valve D
Engine speed sensor (Ignition coil 0)
Feed back carburetor control unit G
Throttle opener control solenoid valve (for the
A
K air-conditioner)
Feed back solenoid valve
I
C Throttle position sensor
I E
Oxygen sensor
I H Vacuum switch
I F
Secondary air control solenoid valve
I I 1 Water temperature sensor
I B
Throttle opener contr
solenoid valve
Page 93 of 284

CHARGING SYSTEM -Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
ALTERNATOR NOOEB-B
Type
Model No.
Part No.
Rated output
VIA
Voltage regulator Items Specifications
~--
Battery voltage sensing
A2T03477
MD1 10318
12150
Electronic built-in type
BAlTERY
Items
Type
1
Ampere hours (5 HR) Ah
Cranking rating [at - 178°C (O”F)] A
Reserve capacity min. Specifications
55824R (S)-MF
36
420
75
NOTES
1. CRANKING RATING is the current a battery can deliver for 30 seconds and maintain a terminal voltage of 7.2 or
greater at a specified temperature.
2. RESERVE CAPACITY RATING is the amount of time a battery can deliver 25 A and maintain a minimum terminal
voltage of 10.5 at 26.7”C (80°F).
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS NOBEC-
Items
Standard values
Regulated voltage V
Ambient temp. at voltage regulator
- 20°C ( - 4°F)
20°C (68°F)
60°C (140°F)
80°C (176°F)
Slip ring O.D. mm (in.)
Field coil resistance R
Limit
Output current A
Slip ring O.D. mm (in.) 14.2-15.4
13.9-14.9
13.4-14.6
13.1-14.5
23 (.906)
3.1
Min. 35
22.2 (.874) Specifications
[ STB Revision
Page 107 of 284
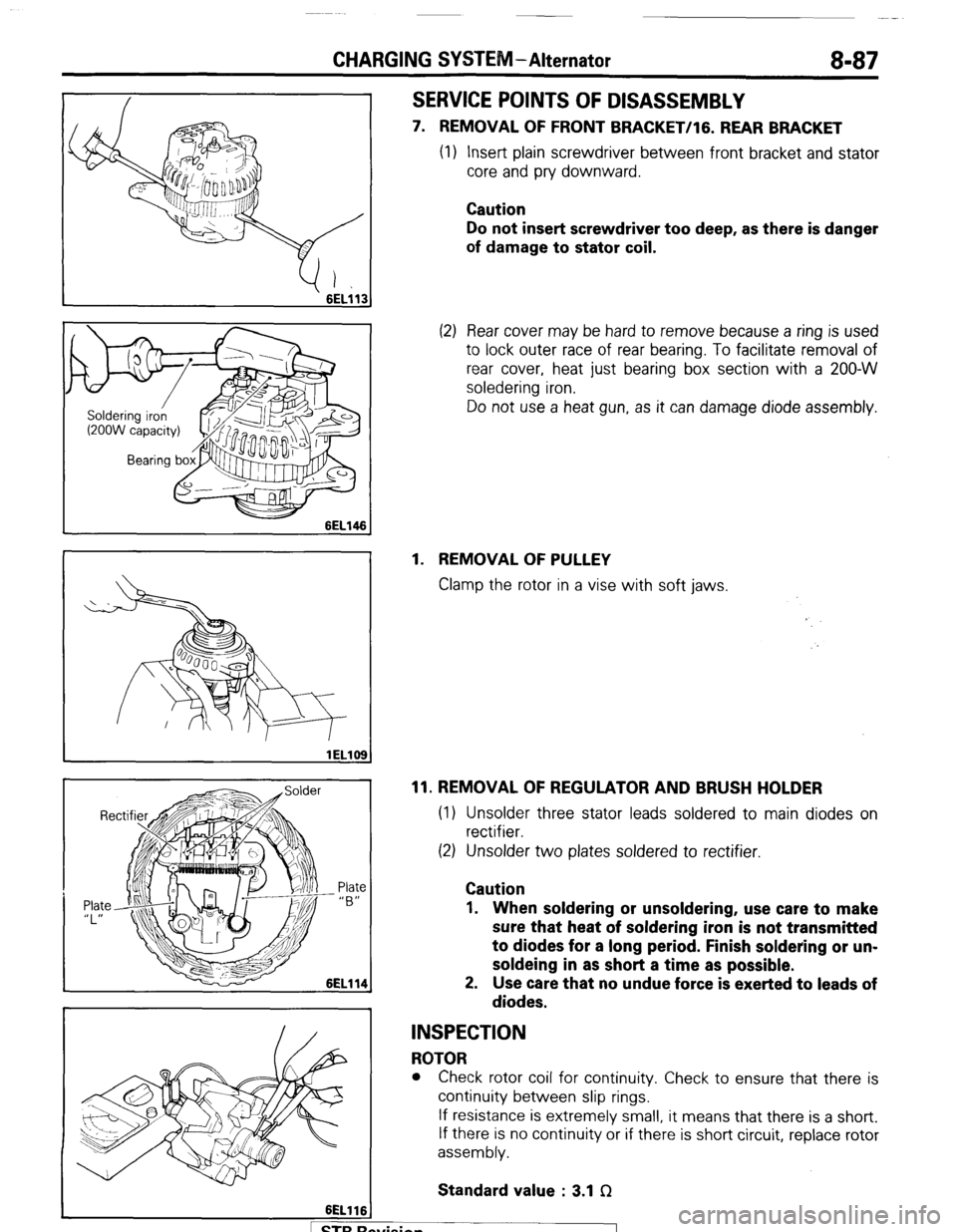
CHARGING SYSTEM-Alternator 8-87
6ELllt
SERVICE POINTS OF DISASSEMBLY
7. REMOVAL OF FRONT BRACKET/lG. REAR BRACKET
(1) Insert plain screwdriver between front bracket and stator
core and pry downward.
Caution
Do not insert screwdriver too deep, as there is danger
of damage to stator coil.
(2) Rear cover may be hard to remove because a ring is used
to lock outer race of rear bearing. To facilitate removal of
rear cover, heat just bearing box section with a 200-W
soledering iron.
Do not use a heat gun, as it can damage diode assembly.
1. REMOVAL OF PULLEY
Clamp the rotor in a vise with soft jaws.
11. REMOVAL OF REGULATOR AND BRUSH HOLDER
(1) Unsolder three stator leads soldered to main diodes on
rectifier.
(2) Unsolder two plates soldered to rectifier.
Caution
1. When soldering or unsoldering, use care to make
sure that heat of soldering iron is not transmitted
to diodes for a long period. Finish soldering or un-
soldeing in as short a time as possible.
2. Use care that no undue force is exerted to leads of
diodes.
INSPECTION
ROTOR
l Check rotor coil for continuity. Check to ensure that there is
continuity between slip rings.
If resistance is extremely small, it means that there is a short.
If there is no continuity or if there is short circuit, replace rotor
assembly.
Standard value : 3.1 f2
. . .
I 1 STB hewsion
Page 108 of 284

8-88 CHARGING SYSTEM-Alternator
6EL115
3ELOlO
lELll0
lELll1
A
) STBRc
l Check rotor coil for grounding. Check to ensure that there is no
continuity between slip ring and core. If there is continuity,
replace rotor assembly.
STATOR
l Make continuity test on stator coil. Check to ensure that there
is continuity between coil leads.
If there is no continuity, replace stator assembly.
l Check coil for grounding. Check to ensure that there is no
continuity between coil and core. If there is continuity, replace
stator assembly.
RECTIFIERS
l Positive rectifier test
Check for continuity between positive rectifier and stator coil
lead connection terminal with a circuit tester. If there is con-
tinuity in both directions, diode is shorted.
Replace rectifier assembly.
l Negative rectifier test
Check for continuity between negative rectifier and stator coil
lead connection terminal. If ther is continuity in both direction,
diode is shorted, and rectifier assembly must be replaced.
evision
-7
Page 111 of 284
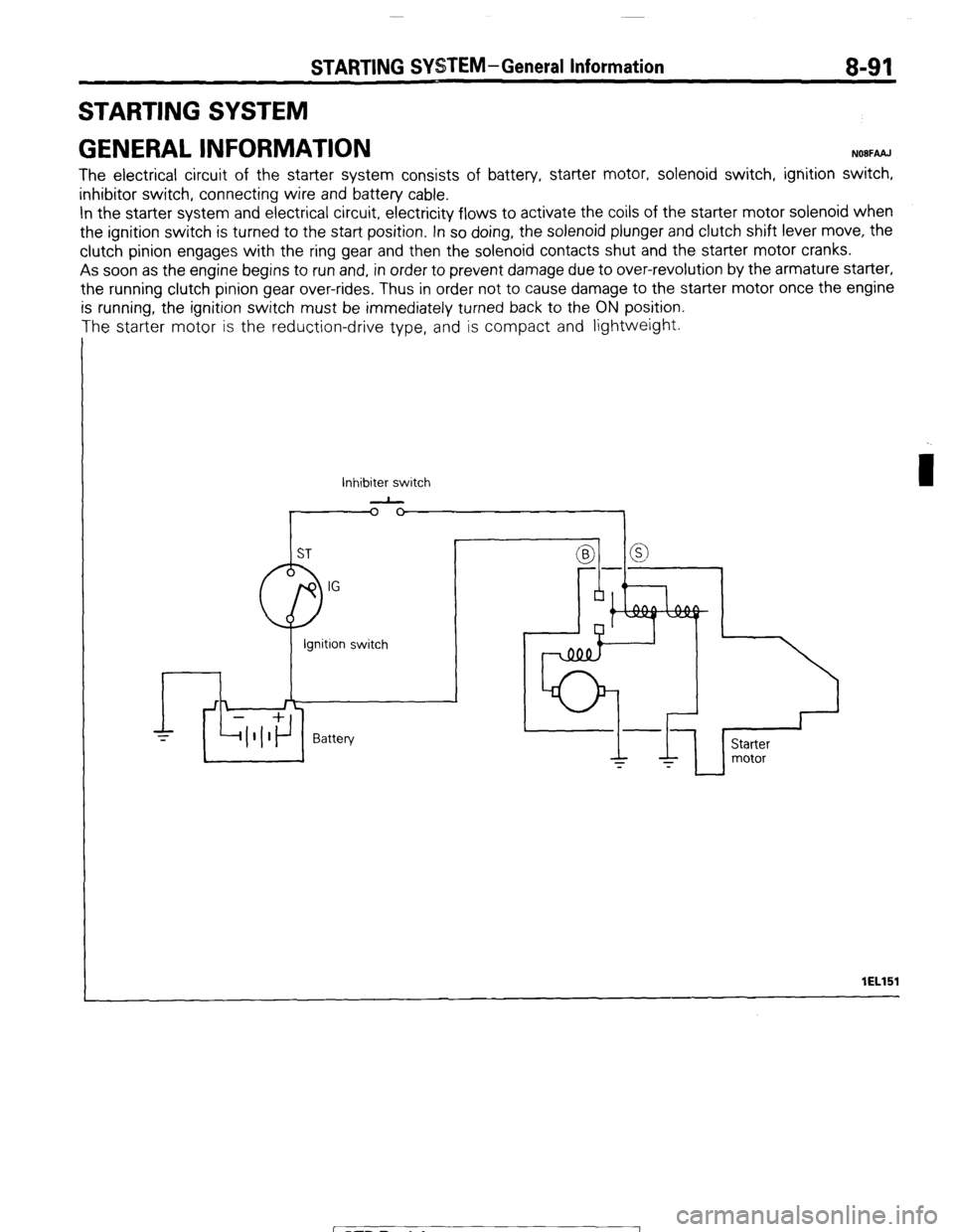
STARTING SYSTEM-General Information 8-91
STARTING SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
NOBFAAJ
The electrical circuit of the starter system consists of battery, starter motor, solenoid switch, ignition switch,
inhibitor switch, connecting wire and battery cable.
In the starter system and electrical circuit, electricity flows to activate the coils of the starter motor solenoid when
the ignition switch is turned to the start position. In so doing, the solenoid plunger and clutch shift lever move, the
clutch pinion engages with the ring gear and then the solenoid contacts shut and the starter motor cranks.
As soon as the engine begins to run and, in order to prevent damage due to over-revolution by the armature starter,
the running clutch pinion gear over-rides, Thus in order not to cause damage to the starter motor once the engine
is running, the ignition switch must be immediately turned back to the ON position.
The starter motor is the reduction-drive type, and is compact and lightweight.
Inhibiter switch
-
I lEL151
1 STB Revision