MOTOR MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000Pages: 1839, PDF Size: 29.19 MB
Page 493 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -General Information13C-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled fuel injection system consists of sensors which detect the condition of the
diesel engine, an engine-ECU which controls the system based on signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate according to control commands from the engine-ECU.
The engine-ECU carries out operations such as fuel injection rate control, fuel injection timing control
and idle up control. In addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with several self-diagnosis functions which
make troubleshooting easier in the event that a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION RATE CONTROL
The fuel injection completion timing is controlled by means of a solenoid-type spill valve to ensure that
the optimum amount of fuel is supplied to the engine in accordance with gradual changes in the engine
running condition.
Before fuel injection starts, the solenoid-type spill valve is on (energized), so that the valve is closed.
As the plunger turns and rises, fuel is sent out under pressure, and when the fuel flow rate reaches
the target value for fuel injection, the solenoid-type spill valve turns off. When the solenoid-type spill
valve turns off, the fuel under high pressure inside the plunger is leaked out into the pump chamber
and fuel injection is completed.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING CONTROL
The position of the injection pump timer piston is controlled so that fuel injection is carried out at the
optimum timing in accordance with the engine running condition.
The timer piston position is determined by duty control of the timing control solenoid valve which is located
in the line between the high-pressure chamber and the low-pressure chamber of the timer piston.
The fuel injection timing is advanced by increasing the control duty of the timing control solenoid valve.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Controlling the fuel injection rate in accordance with the engine running condition maintains the idle speed
at the optimum condition.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, the engine warning lamp illuminates
to warn the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis code number
corresponding to the problem which occurred is output.
DThe RAM data relating to the sensors and actuators which is stored in the engine-ECU can be read
using the MUT-II. In addition, the actuators can be force-driven under certain conditions.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Power Supply Control
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the relay turns on and power is supplied to components
such as the timing control solenoid valve.
2. Intake Air Throttle Control
When the engine is idling after having warmed up, the throttle valve is half opened to restrict the
amount of intake air in order to reduce vibration and noise.
3. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF
4. Fan motor relay control
The radiator fan and condenser fan operating speeds are controlled in accordance with the engine
coolant temperature and the vehicle speed.
5. Glow Control
Refer to GROUP 16.
6. EGR Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 558 of 1839
DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -Troubleshooting13C-3
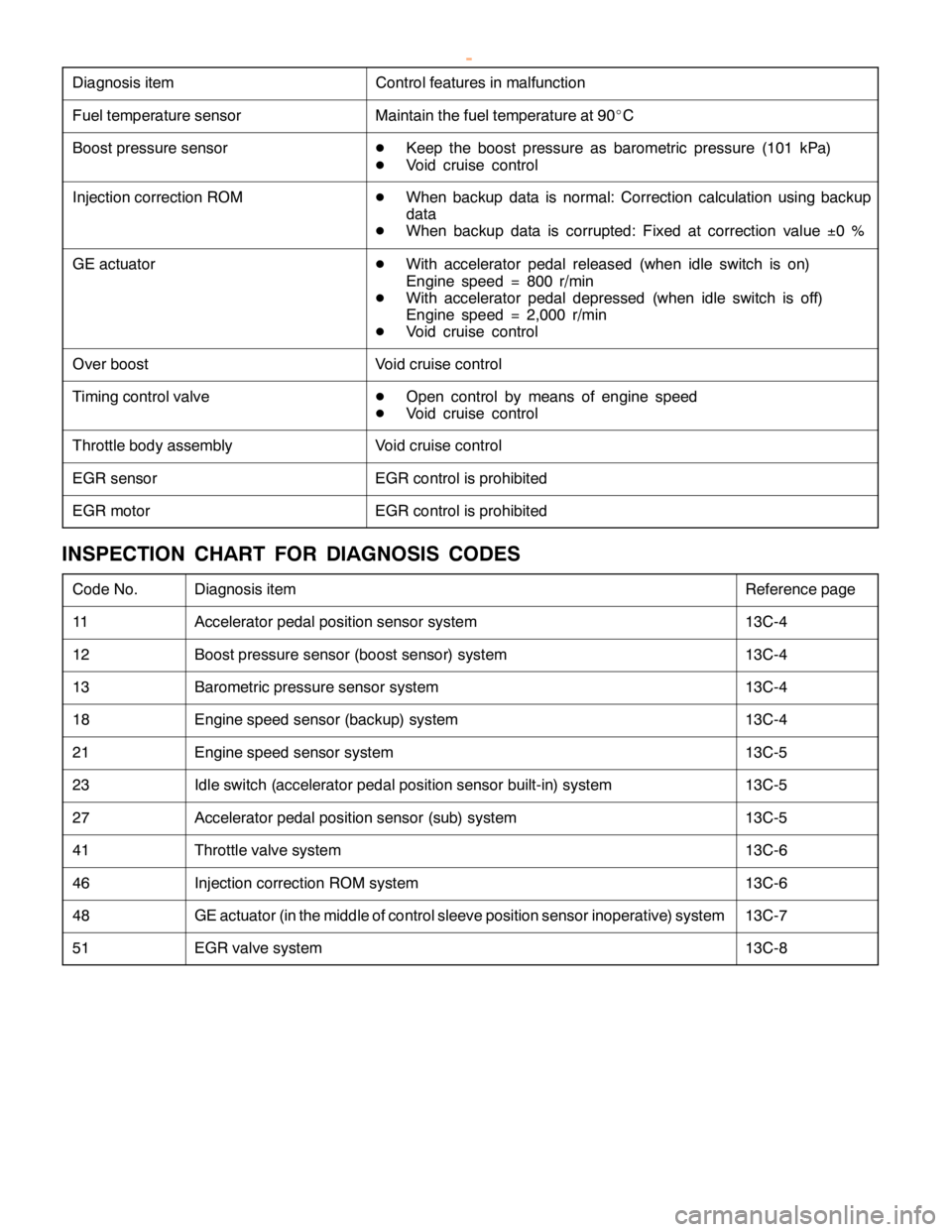
Diagnosis item Control features in malfunction
Fuel temperature sensorMaintain the fuel temperature at 90_C
Boost pressure sensorDKeep the boost pressure as barometric pressure (101 kPa)
DVoid cruise control
Injection correction ROMDWhen backup data is normal: Correction calculation using backup
data
DWhen backup data is corrupted: Fixed at correction value±0%
GE actuatorDWith accelerator pedal released (when idle switch is on)
Engine speed = 800 r/min
DWith accelerator pedal depressed (when idle switch is off)
Engine speed = 2,000 r/min
DVoid cruise control
Over boostVoid cruise control
Timing control valveDOpen control by means of engine speed
DVoid cruise control
Throttle body assemblyVoid cruise control
EGR sensorEGR control is prohibited
EGR motorEGR control is prohibited
INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODES
Code No.Diagnosis itemReference page
11Accelerator pedal position sensor system13C-4
12Boost pressure sensor (boost sensor) system13C-4
13Barometric pressure sensor system13C-4
18Engine speed sensor (backup) system13C-4
21Engine speed sensor system13C-5
23Idle switch (accelerator pedal position sensor built-in) system13C-5
27Accelerator pedal position sensor (sub) system13C-5
41Throttle valve system13C-6
46Injection correction ROM system13C-6
48GE actuator (in the middle of control sleeve position sensor inoperative) system13C-7
51EGR valve system13C-8
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 566 of 1839
DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -Troubleshooting13C-11
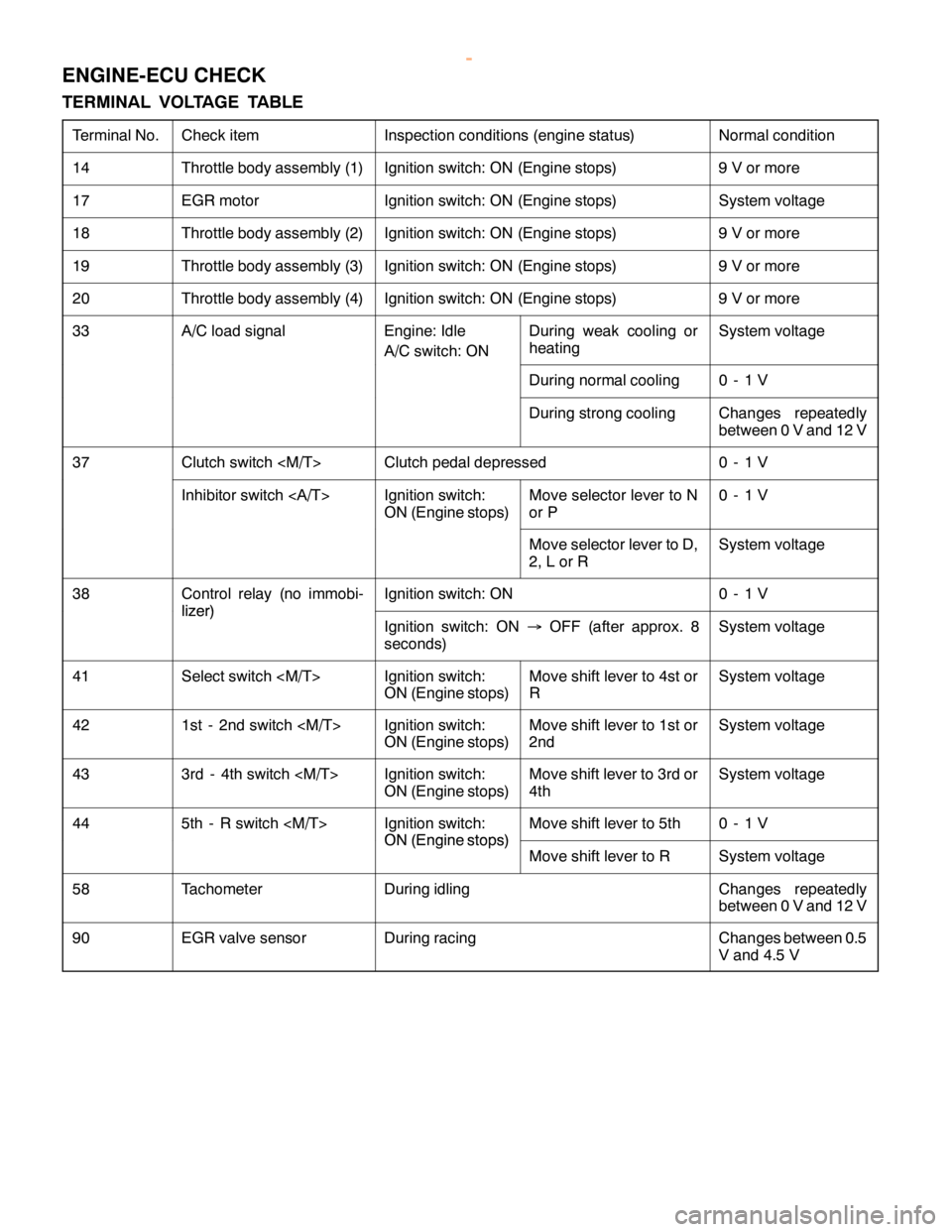
ENGINE-ECU CHECK
TERMINAL VOLTAGE TABLE
Terminal No.Check itemInspection conditions (engine status)Normal condition
14Throttle body assembly (1)Ignition switch: ON (Engine stops)9 V or more
17EGR motorIgnition switch: ON (Engine stops)System voltage
18Throttle body assembly (2)Ignition switch: ON (Engine stops)9 V or more
19Throttle body assembly (3)Ignition switch: ON (Engine stops)9 V or more
20Throttle body assembly (4)Ignition switch: ON (Engine stops)9 V or more
33A/C load signalEngine: Idle
A/C switch: ONDuring weak cooling or
heatingSystem voltage
During normal cooling0-1V
During strong coolingChanges repeatedly
between 0 V and 12 V
37Clutch switch
Inhibitor switch Ignition switch:
ON (Engine stops)Move selector lever to N
or P0-1V
Move selector lever to D,
2, L or RSystem voltage
38Control relay (no immobi-
lizer)
Ignition switch: ON0-1V
lizer)
Ignition switch: ON→OFF (after approx. 8
seconds)System voltage
41Select switch
ON (Engine stops)Move shift lever to 4st or
RSystem voltage
421st - 2nd switch
ON (Engine stops)Move shift lever to 1st or
2ndSystem voltage
433rd - 4th switch
ON (Engine stops)Move shift lever to 3rd or
4thSystem voltage
445th - R switch
ON(Enginestops)
Move shift lever to 5th0-1V
ON(Engine stops)
Move shift lever to RSystem voltage
58TachometerDuring idlingChanges repeatedly
between 0 V and 12 V
90EGR valve sensorDuring racingChanges between 0.5
V and 4.5 V
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 612 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4D5-stepIII>-General/General Information13E-2
GENERAL
OUTLINE OF CHANGE
An electronically-controlled injection pump has been added in order to comply with Regulation STEP
III. Due to this, the following service procedures have been added.
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled fuel injection system consists of sensors which detect the condition of the
diesel engine, an engine-ECU which controls the system based on signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate according to control commands from the engine-ECU.
The engine-ECU carries out operations such as fuel injection rate control, fuel injection timing control
and idle up control. In addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with several self-diagnosis functions which
make troubleshooting easier in the event that a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION RATE CONTROL
The fuel injection completion timing is controlled by means of a solenoid-type spill valve to ensure that
the optimum amount of fuel is supplied to the engine in accordance with gradual changes in the engine
running condition.
Before fuel injection starts, the solenoid-type spill valve is on (energized), so that the valve is closed.
As the plunger turns and rises, fuel is sent out under pressure, and when the fuel flow rate reaches
the target value for fuel injection, the solenoid-type spill valve turns off. When the solenoid-type spill
valve turns off, the fuel under high pressure inside the plunger is leaked out into the pump chamber
and fuel injection is completed.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING CONTROL
The position of the injection pump timer piston is controlled so that fuel injection is carried out at the
optimum timing in accordance with the engine running condition.
The timer piston position is determined by duty control of the timing control solenoid valve which is located
in the line between the high-pressure chamber and the low-pressure chamber of the timer piston.
The fuel injection timing is advanced by increasing the control duty of the timing control solenoid valve.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Controlling the fuel injection rate in accordance with the engine running condition maintains the idle speed
at the optimum condition.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, the engine warning lamp illuminates
to warn the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis code number
corresponding to the problem which occurred is output.
DThe RAM data relating to the sensors and actuators which is stored in the engine-ECU can be read
using the MUT-II. In addition, the actuators can be force-driven under certain conditions.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Power Supply Control
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the relay turns on and power is supplied to components
such as the timing control solenoid valve.
2. Intake Air Throttle Control
When the engine-ECU detects an abnormality in any of the sensors or actuators, the throttle valve
is half opened to restrict the amount of intake air in order to prevent the vehicle from running away.
3. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF
4. Condenser Fan Motor Relay Control
Controls the condenser fan motor relay based on the A/C switch, engine coolant temperature and
vehicle speed input signals.
5. Glow Control
Refer to GROUP 16.
6. EGR Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 646 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4D5-stepIII>-Troubleshooting13E-36
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 19
A/C condenser fan operating problem
Probable cause
The power transistor inside the engine-ECU turns on and off to control the A/C
condenser fan motor relay.DMalfunction of A/C condenser fan motor relay
DMalfunction of A/C condenser fan motor
DMalfunction of thermostat
DOpen circuit or short-circuit in circuit, or poor
connector contact
DMalfunction of engine-ECU
Check the following connector:D-110
OK
Measure at engine-ECU connector D-110.
DDisconnect the connector and measure at the harness
side.
DCheck the A/C condenser fan condition.
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK:Fan stopped
DVoltage between 7 and the earth
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK:System voltage
DShort out 7 and the earth
(Ignition switch: ON)
OK:A/C condenser fan turnsNGA/C condenser fan motor circuit check
(Refer to the wiring harness configuration diagram.)
OK
MUT-IIData list
02 Engine coolant temperature sensor
OK:When engine is idling after having warmed up, the en-
gine coolant temperature and the MUT-IIdisplay temper-
ature are identicalNGEngine coolant temperature sensor check
(Refer to Code 15 on P.13E-59.)
Check the trouble symptoms.OK
Replace the engine-ECU.NG
Repair
Thermostat checkNG
NGReplace
OK
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 749 of 1839
16-1
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
CONTENTS
CHARGING SYSTEM 2................
GENERAL INFORMATION 2................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 3..............
SPECIAL TOOL 4.........................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 5..................
Alternator Output Line Voltage Drop Test 5....
Output Current Test 6.......................
Regulated Voltage Test 8....................
Waveform Check Using An Analyzer 11.......
ALTERNATOR 13.........................
STARTING SYSTEM 23................
GENERAL INFORMATION 23..............
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 24............
STARTER MOTOR 24.....................
IGNITION SYSTEM 37.................
GENERAL INFORMATION 37..............
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 38............
SPECIAL TOOL 38.......................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 38................
Ignition Coil (With Built-in Power Transistor)
Check 38...................................
Spark Plug Check and Cleaning 39...........
Ignition Failure Sensor Check 40.............
Camshaft Position Sensor Check, Crank angle
Sensor Check, Detonation Sensor Check 40...
IGNITION COIL <6G7> 41.................
CRANKSHAFT ANGLE SENSOR
<6G7> 42................................
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
<6G7> 42................................
DETONATION SENSOR <6G7> 43.........
GLOW SYSTEM 44....................
GENERAL INFORMATION 44..............
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 45............
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 45................
Self-regulating Glow System Check 45........
Glow & EGR Control Unit Check 48..........
Engine ECU Check 49.......................
Glow Plug Relay Check 50..................
Glow Plug Check 51........................
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Check 51...................................
GLOW PLUG 52..........................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 804 of 1839

17-2
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM 36..............................
General Information 36......................
System Diagram 36.........................
Component Location 36......................
Purge Control System Check 37..............
Purge Port Vacuum Check 37................
Purge Control Solenoid Valve Check 38.......
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM 39..............................
General Information 39......................
Operation 39................................
System Diagram 39.........................
Component Location 39......................
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control
System Check 40...........................
EGR Valve (Stepper Motor) Check 40........
EGR VALVE 42...........................
CANISTER 43............................
CATALYTIC CONVERTER 44..............
General Information 44......................
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
<4D5> 45.............................
GENERAL INFORMATION 45..............
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 45............
SEALANT 45.............................
SPECIAL TOOL 45.......................
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM 46..............................
General Information 46......................
System Diagram 46.........................
Component Location 46......................
Function Check 47..........................
EGR Solenoid Valve Operation Check 47.....
EGR Solenoid Valve Resistance Check 48....
Lever Position Sensor (LPS) Adjustment 48...
Engine Speed Sensor Check 49..............
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Check 49...................................
CHECK AT THE GLOW & EGR CONTROL
UNIT 51..................................
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
<4M4-VEHICLES WITH EGR> 52........
GENERAL INFORMATION 52..............
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 52............
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM 53..............................
General Information 53......................
System Diagram 53.........................
Component Location 53......................
Function Check 54..........................
EGR Solenoid Valve Operation Check 54.....
EGR Solenoid Valve Resistance Check 55....
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APS),
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor, Intake
Air Temperature Sensor, Fuel Temperature
Sensor Check 55............................
Check at Engine-ECU 55....................
CATALYTIC CONVERTER 55..............
General Information 55......................
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 833 of 1839
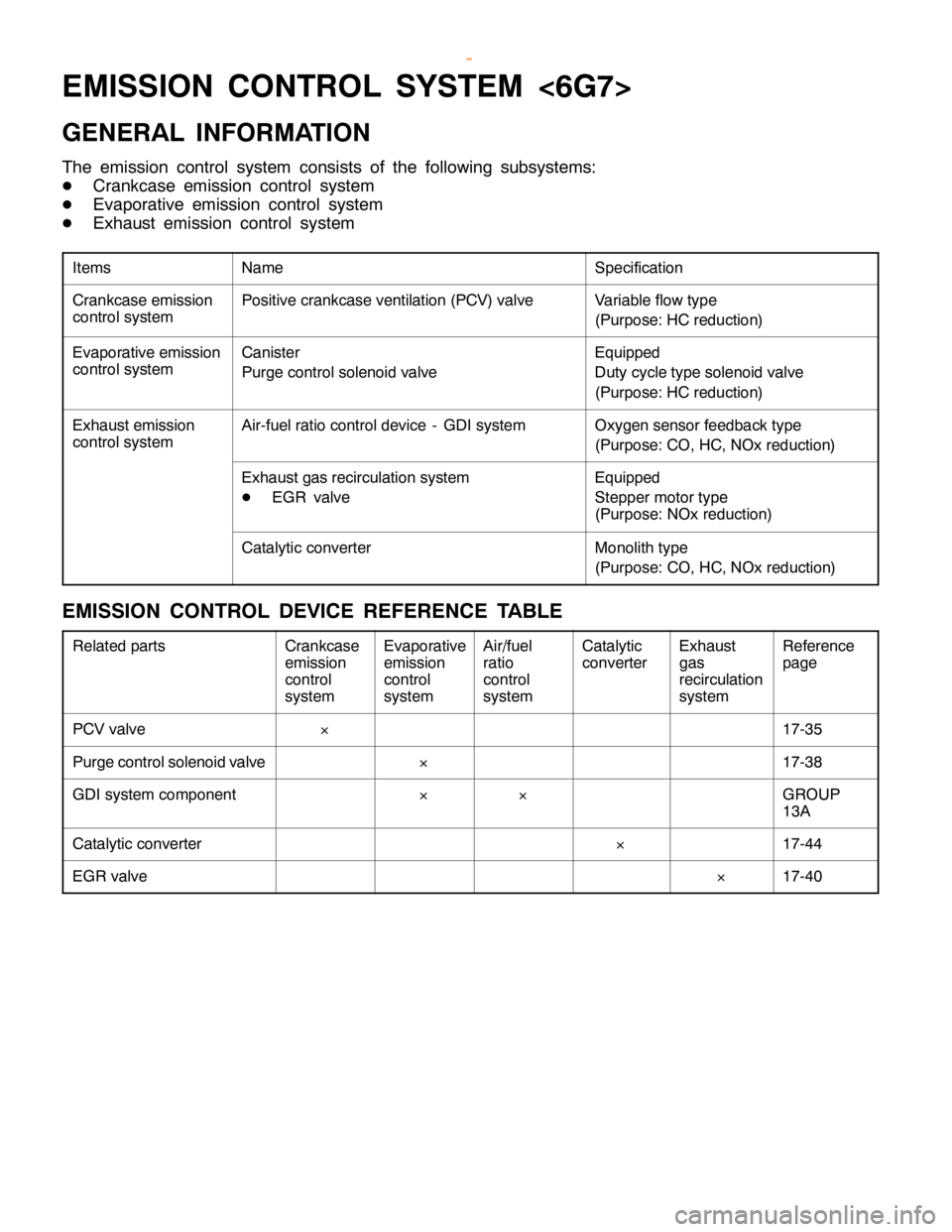
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System <6G7>17-31
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM <6G7>
GENERAL INFORMATION
The emission control system consists of the following subsystems:
DCrankcase emission control system
DEvaporative emission control system
DExhaust emission control system
ItemsNameSpecification
Crankcase emission
control systemPositive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valveVariable flow type
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Evaporative emission
control systemCanister
Purge control solenoid valveEquipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Exhaust emission
control systemAir-fuel ratio control device - GDI systemOxygen sensor feedback type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Exhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valveEquipped
Stepper motor type
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
Catalytic converterMonolith type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE REFERENCE TABLE
Related partsCrankcase
emission
control
systemEvaporative
emission
control
systemAir/fuel
ratio
control
systemCatalytic
converterExhaust
gas
recirculation
systemReference
page
PCV valve´17-35
Purge control solenoid valve´17-38
GDI system component´´GROUP
13A
Catalytic converter´17-44
EGR valve´17-40
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 988 of 1839
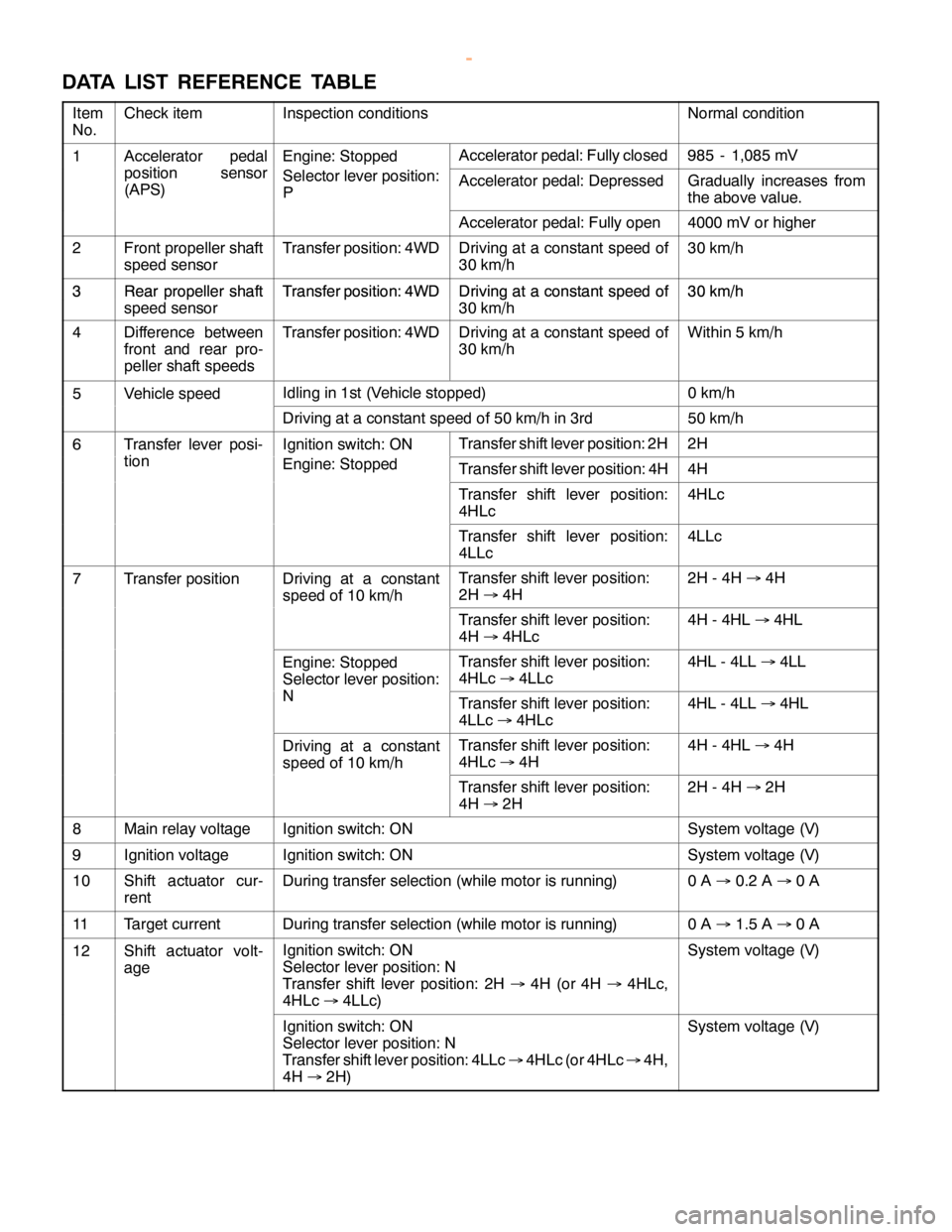
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -Troubleshooting
DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE
Item
No.Check itemInspection conditionsNormal condition
1Accelerator pedalEngine: StoppedAccelerator pedal: Fully closed985 - 1,085 mV
position sensor
(APS)Selector lever position:
PAccelerator pedal: DepressedGradually increases from
the above value.
Accelerator pedal: Fully open4000 mV or higher
2Front propeller shaft
speed sensorTransfer position: 4WDDriving at a constant speed of
30 km/h30 km/h
3Rear propeller shaftTransfer position: 4WDDriving at a constant speed of30 km/h3Rear propeller shaft
speed sensorTransfer position: 4WDDriving at a constant speed of
30 km/h30 km/h
4Difference between
front and rear pro-
peller shaft speedsTransfer position: 4WDDriving at a constant speed of
30 km/hWithin 5 km/h
5Vehicle speedIdling in 1st (Vehicle stopped)0 km/h
Driving at a constant speed of 50 km/h in 3rd50 km/h
6Transfer lever posi-Ignition switch: ONTransfer shift lever position: 2H2H
tionEngine: StoppedTransfer shift lever position: 4H4H
Transfer shift lever position:
4HLc4HLc
Transfer shift lever position:
4LLc4LLc
7Transfer positionDriving at a constant
speed of 10 km/hTransfer shift lever position:
2H®4H2H - 4H®4H
Transfer shift lever position:
4H®4HLc4H - 4HL®4HL
Engine: Stopped
Selector lever position:Transfer shift lever position:
4HLc®4LLc4HL - 4LL®4LL
NTransfer shift lever position:
4LLc®4HLc4HL - 4LL®4HL
Driving at a constant
speed of 10 km/hTransfer shift lever position:
4HLc®4H4H - 4HL®4H
Transfer shift lever position:
4H®2H2H - 4H®2H
8Main relay voltageIgnition switch: ONSystem voltage (V)
9Ignition voltageIgnition switch: ONSystem voltage (V)
10Shift actuator cur-
rentDuring transfer selection (while motor is running)0A®0.2 A®0A
11Target currentDuring transfer selection (while motor is running)0A®1.5 A®0A
12Shift actuator volt-
ageIgnition switch: ON
Selector lever position: N
Transfer shift lever position: 2H®4H (or 4H®4HLc,
4HLc®4LLc)System voltage (V)
Ignition switch: ON
Selector lever position: N
Transfer shift lever position: 4LLc®4HLc (or 4HLc®4H,
4H®2H)System voltage (V)
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1210 of 1839

35A-2
BASIC BRAKE
SYSTEM
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 3..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 5.................
LUBRICANTS 6..............................
SPECIAL TOOLS 6..........................
TROUBLESHOOTING
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 19...................
Brake Pedal Check and Adjustment 19..........
Hydraulic Brake Booster (HBB) Operation Check
HBB Check
HBB Motor Relay Continuity Check
Brake Booster Operating Test
Check Valve Operation Check
Load Sensing Spring Length Check and
Adjustment
Load Sensing Proportioning Valve Function
Test
Bleeding
Brake Fluid Level Sensor Check 30.............
Brake Booster Vacuum Switch Check
Disc Brake Pad Check and Replacement 31.....
Disc Brake Rotor Check 32.....................
Brake Disc Thickness Check 32.................
Brake Disc Run-out Check and Correction 33....
BRAKE PEDAL 34..........................
HYDRAULIC BRAKE BOOSTER (HBB)
HBB BUZZER
MASTER CYLINDER AND BRAKE
BOOSTER
Master Cylinder 43.............................
FRONT DISC BRAKE 44....................
REAR DISC BRAKE 49......................
LOAD SENSING PROPORTIONING
VALVE
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk