fuel type MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: MONTERO, Model: MITSUBISHI MONTERO 2000Pages: 1839, PDF Size: 29.19 MB
Page 218 of 1839

GDI -General Information13A-4
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to
emission control, the engine warning lamp
(check engine lamp) illuminates or flashes
as a warning to the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis
code corresponding to the abnormality is
output.
DThe engine-ECU records the engine
operating condition when the diagnosis
code is set. This data is called “freezeframe” data.
This data can be read by using the MUT-II,
and can then be used in simulation tests
for troubleshooting.
DThe RAM data inside the engine-ECU
related to the sensors and actuators can
be read by means of the MUT-II. In addition,
the actuators can be force-driven under
certain circumstances.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Fuel Pump Control
Turns the fuel pump relay ON so that current
is supplied to the fuel pump while the engine
is cranking or running.
2. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C
ON and OFF.3. Purge Control Solenoid Valve Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
4. EGR Control Servo Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Throttle bodyThrottle bore mm65
Throttle position sensorVariable resistor type
Throttle valve control servoBrushless DC-motor type
Engine-ECUIdentification model No.E2T79271
E2T79272
Engine-Identification model No.E2T76277
A/T-ECU
E2T76278
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 219 of 1839
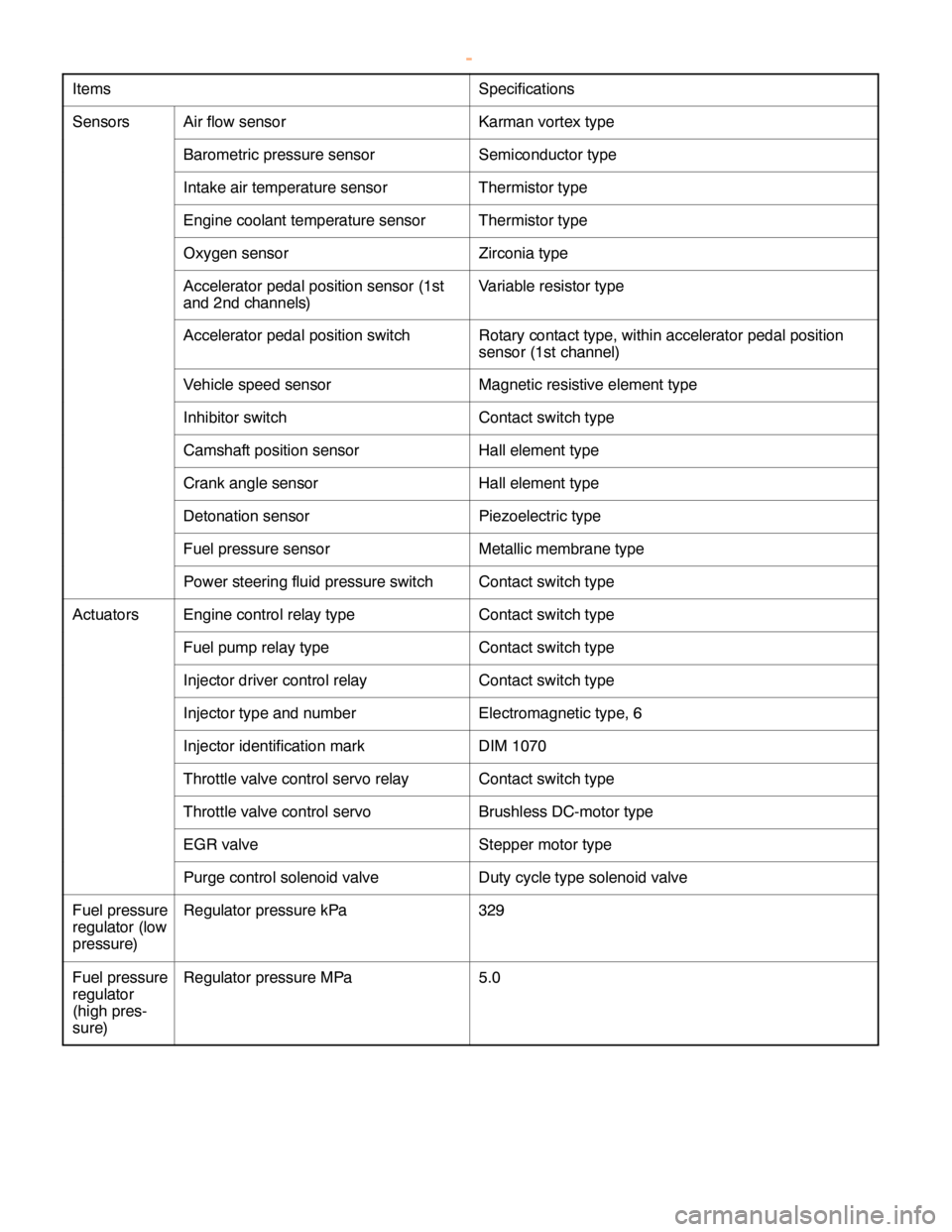
GDI -General Information13A-5
Items Specifications
SensorsAir flow sensorKarman vortex type
Barometric pressure sensorSemiconductor type
Intake air temperature sensorThermistor type
Engine coolant temperature sensorThermistor type
Oxygen sensorZirconia type
Accelerator pedal position sensor (1st
and 2nd channels)Variable resistor type
Accelerator pedal position switchRotary contact type, within accelerator pedal position
sensor (1st channel)
Vehicle speed sensorMagnetic resistive element type
Inhibitor switchContact switch type
Camshaft position sensorHall element type
Crank angle sensorHall element type
Detonation sensorPiezoelectric type
Fuel pressure sensorMetallic membrane type
Power steering fluid pressure switchContact switch type
ActuatorsEngine control relay typeContact switch type
Fuel pump relay typeContact switch type
Injector driver control relayContact switch type
Injector type and numberElectromagnetic type, 6
Injector identification markDIM 1070
Throttle valve control servo relayContact switch type
Throttle valve control servoBrushless DC-motor type
EGR valveStepper motor type
Purge control solenoid valveDuty cycle type solenoid valve
Fuel pressure
regulator (low
pressure)Regulator pressure kPa329
Fuel pressure
regulator
(high pres-
sure)Regulator pressure MPa5.0
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 493 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4M4> -General Information13C-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled fuel injection system consists of sensors which detect the condition of the
diesel engine, an engine-ECU which controls the system based on signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate according to control commands from the engine-ECU.
The engine-ECU carries out operations such as fuel injection rate control, fuel injection timing control
and idle up control. In addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with several self-diagnosis functions which
make troubleshooting easier in the event that a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION RATE CONTROL
The fuel injection completion timing is controlled by means of a solenoid-type spill valve to ensure that
the optimum amount of fuel is supplied to the engine in accordance with gradual changes in the engine
running condition.
Before fuel injection starts, the solenoid-type spill valve is on (energized), so that the valve is closed.
As the plunger turns and rises, fuel is sent out under pressure, and when the fuel flow rate reaches
the target value for fuel injection, the solenoid-type spill valve turns off. When the solenoid-type spill
valve turns off, the fuel under high pressure inside the plunger is leaked out into the pump chamber
and fuel injection is completed.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING CONTROL
The position of the injection pump timer piston is controlled so that fuel injection is carried out at the
optimum timing in accordance with the engine running condition.
The timer piston position is determined by duty control of the timing control solenoid valve which is located
in the line between the high-pressure chamber and the low-pressure chamber of the timer piston.
The fuel injection timing is advanced by increasing the control duty of the timing control solenoid valve.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Controlling the fuel injection rate in accordance with the engine running condition maintains the idle speed
at the optimum condition.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, the engine warning lamp illuminates
to warn the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis code number
corresponding to the problem which occurred is output.
DThe RAM data relating to the sensors and actuators which is stored in the engine-ECU can be read
using the MUT-II. In addition, the actuators can be force-driven under certain conditions.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Power Supply Control
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the relay turns on and power is supplied to components
such as the timing control solenoid valve.
2. Intake Air Throttle Control
When the engine is idling after having warmed up, the throttle valve is half opened to restrict the
amount of intake air in order to reduce vibration and noise.
3. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF
4. Fan motor relay control
The radiator fan and condenser fan operating speeds are controlled in accordance with the engine
coolant temperature and the vehicle speed.
5. Glow Control
Refer to GROUP 16.
6. EGR Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 612 of 1839

DIESEL FUEL <4D5-stepIII>-General/General Information13E-2
GENERAL
OUTLINE OF CHANGE
An electronically-controlled injection pump has been added in order to comply with Regulation STEP
III. Due to this, the following service procedures have been added.
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled fuel injection system consists of sensors which detect the condition of the
diesel engine, an engine-ECU which controls the system based on signals from these sensors, and actuators
which operate according to control commands from the engine-ECU.
The engine-ECU carries out operations such as fuel injection rate control, fuel injection timing control
and idle up control. In addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with several self-diagnosis functions which
make troubleshooting easier in the event that a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION RATE CONTROL
The fuel injection completion timing is controlled by means of a solenoid-type spill valve to ensure that
the optimum amount of fuel is supplied to the engine in accordance with gradual changes in the engine
running condition.
Before fuel injection starts, the solenoid-type spill valve is on (energized), so that the valve is closed.
As the plunger turns and rises, fuel is sent out under pressure, and when the fuel flow rate reaches
the target value for fuel injection, the solenoid-type spill valve turns off. When the solenoid-type spill
valve turns off, the fuel under high pressure inside the plunger is leaked out into the pump chamber
and fuel injection is completed.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING CONTROL
The position of the injection pump timer piston is controlled so that fuel injection is carried out at the
optimum timing in accordance with the engine running condition.
The timer piston position is determined by duty control of the timing control solenoid valve which is located
in the line between the high-pressure chamber and the low-pressure chamber of the timer piston.
The fuel injection timing is advanced by increasing the control duty of the timing control solenoid valve.
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
Controlling the fuel injection rate in accordance with the engine running condition maintains the idle speed
at the optimum condition.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, the engine warning lamp illuminates
to warn the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in any of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis code number
corresponding to the problem which occurred is output.
DThe RAM data relating to the sensors and actuators which is stored in the engine-ECU can be read
using the MUT-II. In addition, the actuators can be force-driven under certain conditions.
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Power Supply Control
When the ignition switch is turned to ON, the relay turns on and power is supplied to components
such as the timing control solenoid valve.
2. Intake Air Throttle Control
When the engine-ECU detects an abnormality in any of the sensors or actuators, the throttle valve
is half opened to restrict the amount of intake air in order to prevent the vehicle from running away.
3. A/C Relay Control
Turns the compressor clutch of the A/C ON and OFF
4. Condenser Fan Motor Relay Control
Controls the condenser fan motor relay based on the A/C switch, engine coolant temperature and
vehicle speed input signals.
5. Glow Control
Refer to GROUP 16.
6. EGR Control
Refer to GROUP 17.
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 735 of 1839

INTAKE AND EXHAUST -General Information/Service Specifications/Sealant15-3
At starting and driving at low speed, the duty control
value of the variable geometry solenoid valve is
increased to apply the vacuum pressure of the
vacuum pump to the variable geometry actuator.
Applying the vacuum pressure to the variable
geometry actuator pulls the actuator rod so that
it can move towards the direction of closing the
variable nozzle of the variable geometry
turbocharger. As closing the nozzle reduces the
exhaust gas mass, the speed of exhaust gas flow
will be increased and efficiency will be improved.
Since the characteristic of boost pressure becomes
a low speed type, boost pressure will suddenly
rise from low speed.
At driving at high speed, the duty control value
of the variable geometry solenoid valve is
decreased to reduce the vacuum pressure from
the vacuum pump so that the actuator rod can
return to the deactivated status and move towards
the direction of opening the nozzle of the variable
geometry turbocharger.Opening the nozzle allows the characteristic of
boost pressure to become a high speed type so
that the appropriate boost pressure can be
maintained.
Therefore, boost pressure can be controlled by
appropriate duty control of the variable geometry
solenoid valve. The engine-ECU calculates the
correct boost pressure based on the engine speed
and fuel injection amount. Furthermore, the duty
control of the variable geometry solenoid valve is
given feedback of the signals from the variable
geometry control pressure sensor and the boost
pressure sensor so that the variable nozzle opening
angle of the variable geometry turbocharger can
be quickly adjusted to obtain the desired boost
pressure.
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
Variable geometry actuator activation vacuum
(Approximately 1 mm stroke) kPaApproximately 10.5 - 12.5
Variable geometry solenoid valve coil resistance
(at 20°C)Ω29 - 35
SEALANT
ItemSpecified sealantRemarks
Thread of the intake manifold mounting
bolts3M Stud Locking No.4170 or equivalentAnaerobic sealant
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 833 of 1839
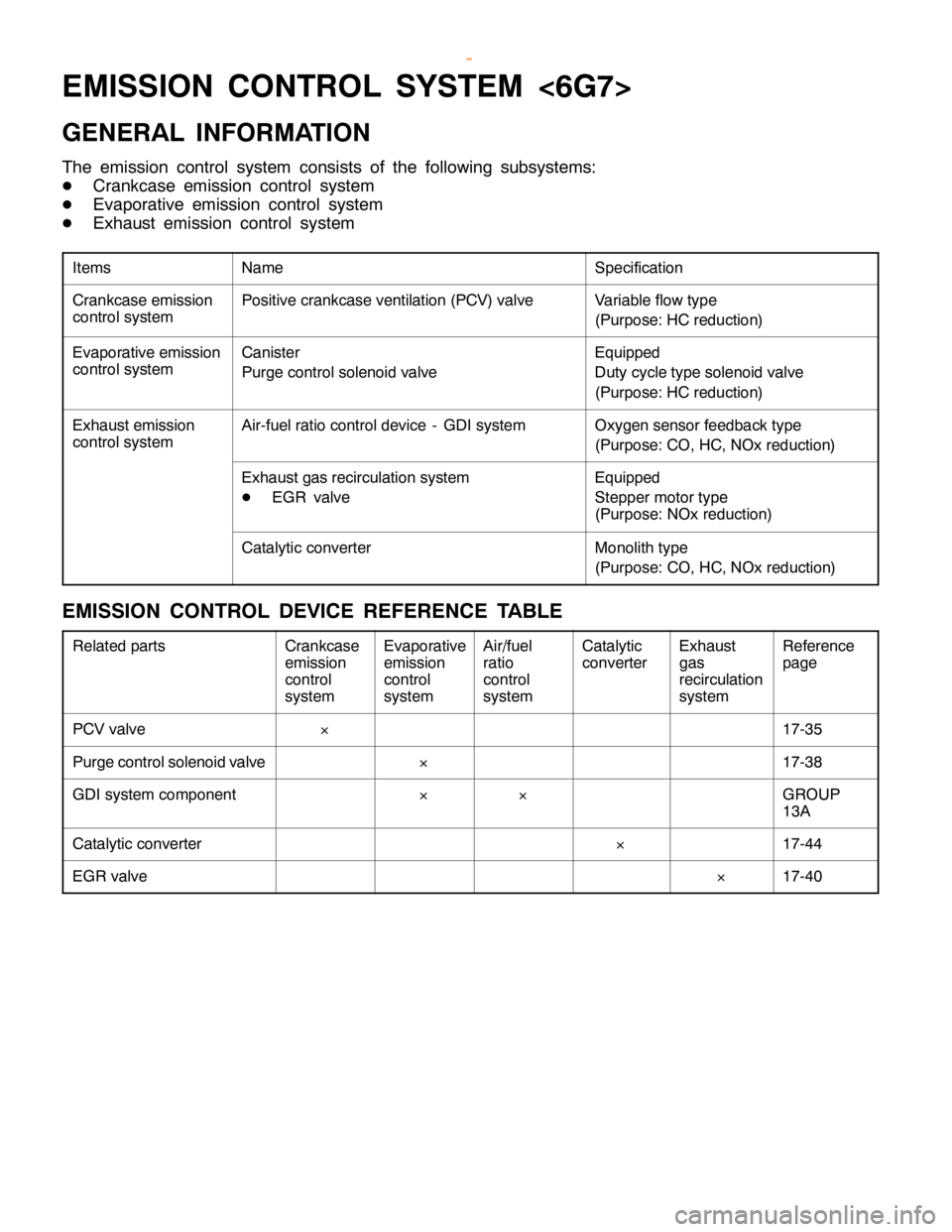
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System <6G7>17-31
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM <6G7>
GENERAL INFORMATION
The emission control system consists of the following subsystems:
DCrankcase emission control system
DEvaporative emission control system
DExhaust emission control system
ItemsNameSpecification
Crankcase emission
control systemPositive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valveVariable flow type
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Evaporative emission
control systemCanister
Purge control solenoid valveEquipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Exhaust emission
control systemAir-fuel ratio control device - GDI systemOxygen sensor feedback type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Exhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valveEquipped
Stepper motor type
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
Catalytic converterMonolith type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE REFERENCE TABLE
Related partsCrankcase
emission
control
systemEvaporative
emission
control
systemAir/fuel
ratio
control
systemCatalytic
converterExhaust
gas
recirculation
systemReference
page
PCV valve´17-35
Purge control solenoid valve´17-38
GDI system component´´GROUP
13A
Catalytic converter´17-44
EGR valve´17-40
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 854 of 1839

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System
<4M4-Vehicles with EGR>17-52
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM <4M4-VEHICLES WITH
EGR>
GENERAL INFORMATION
The electronically-controlled EGR system and the
fuel injection timing control system (load timer)
reduce the level of exhaust gases (NO
x).
ItemsNameSpecification
Exhaust emission
control systemExhaust gas recirculation system
DEGR valve
DEGR solenoid valve No.1
DEGR solenoid valve No.2Electronically-controlled EGR system
Single type
Duty cycle solenoid valve
ON-OFFsolenoid valve
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
EGR solenoid valve No.1/No. 2 resistance (at 20_C)W36 - 44
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Page 1634 of 1839

CHASSIS ELECTRICAL -Clock or Center Display54A-64
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 4
Abnormal driving data are displayed:
DAbnormal average fuel consumption (momentary fuel consumption) and average vehicle speed
DAbnormal cruising distance
Are the average fuel consumption and average vehicle speed dis-
play correctly?NOGo to inspection procedure 3.1.
YES
Does the vehicle information on displayed on the screen meet
with the actual vehicle?
Is the vehicle type (long or short body) recognized correctly?
(Select “Check of units connected into the center display” and
“Check of vehicle information” on the service mode.)NOReplace the center display unit.
YES
Is remained fuel amount displayed correctly on servicemode?YESEnd (no abnormality).
NO
Measure at center display unit connector D-03.
DDisconnect the connector.
DVoltage between terminal 33 and body earth.
OK:0.1 - 3 VNGCheck the wiring harness between center display unit and the
fuel gauge unit, and repair ifnecessary. (relevant units: Combination
meter, fuel gauge unit)
OK
Replace the center display unit.
NOTE
(1) If the remained fuel amount is so small that the fuel gauge unit can not detect a correct amount,
incorrect cruising range may be displayed.
(2) Fuel consumption is updated each time fuel is supplied. Furthermore, the cruising range depends
on road and driving conditions.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 5
Clock runs fast or slow.
NGRepair the fuse and wiring harness.
OK
YES
Does it receive a radio station on differ-
ent region where has timelag?YESTurn off the CT function.
NO
Replace the center display unit.
Measure at center display unit connec-
tor D-03.
DIgnition switch: OFF
DVoltage between terminal 26 and
body earth.
OK:System voltage
Is the symbol “CT” displayed?
NO
www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk
Purchased from www.WorkshopManuals.co.uk