sensor NISSAN LATIO 2009 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2009, Model line: LATIO, Model: NISSAN LATIO 2009Pages: 4331, PDF Size: 58.04 MB
Page 3 of 4331
ACC
NP
O
ACCELERATOR CONTROL SYSTEM
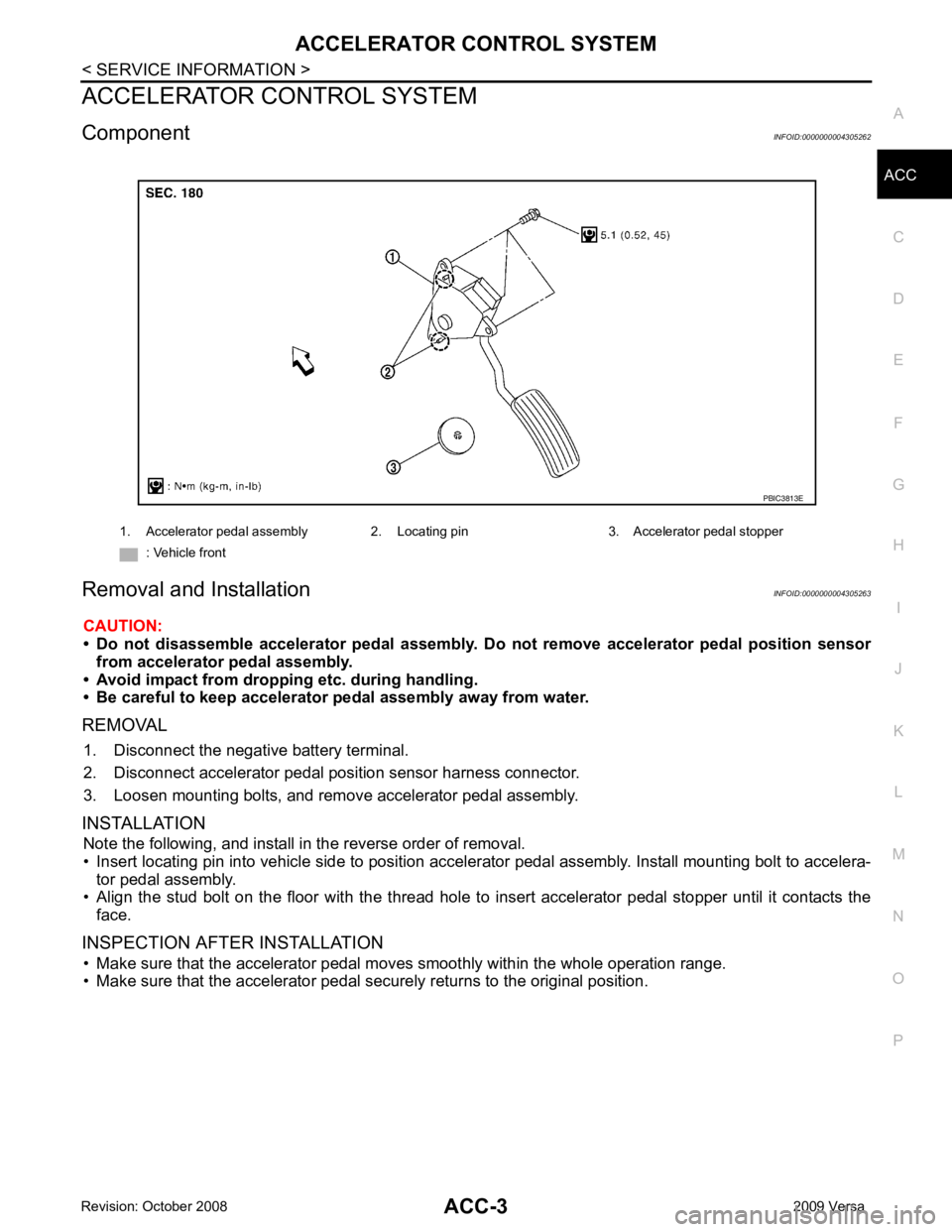
Component INFOID:0000000004305262
Removal and Installation INFOID:0000000004305263
CAUTION:
• Do not disassemble accelerator pedal assembly. Do not remove accelerator pedal position sensor
from accelerator pedal assembly.
• Avoid impact from dropping etc. during handling.
• Be careful to keep accelerator pedal assembly away from water.
REMOVAL 1. Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
2. Disconnect accelerator pedal position sensor harness connector.
3. Loosen mounting bolts, and remove accelerator pedal assembly.
INSTALLATION Note the following, and install in the reverse order of removal.
• Insert locating pin into vehicle side to position accelerator pedal assembly. Install mounting bolt to accelera- tor pedal assembly.
• Align the stud bolt on the floor with the thread hole to in sert accelerator pedal stopper until it contacts the
face.
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION • Make sure that the accelerator pedal mo ves smoothly within the whole operation range.
• Make sure that the accelerator pedal securely returns to the original position. 1. Accelerator pedal assembly 2. Locating pin 3. Accelerator pedal stopper
: Vehicle front
Page 8 of 4331

AT
N
O
P
N
Wiring Diagram - AT -
SSV/B ................................
145
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..146
Component Inspection ........................................ ..147
DTC P1760 OVERRUN CLUTCH SOLENOID
VALVE ............................................................ ..149
Description .......................................................... ..149
CONSULT-III Refe rence Value in Data Monitor
Mode ................................................................... ..
149
On Board Diagnosis Logic .................................. ..149
Possible Cause ................................................... ..149
DTC Confirmation Procedure .............................. ..149
Wiring Diagram - AT - OVRCSV ......................... ..150
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..151
Component Inspection ........................................ ..152
DTC VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR MTR .......... ..154
Description .......................................................... ..154
CONSULT-III Refe rence Value in Data Monitor
Mode ................................................................... ..
154
On Board Diagnosis Logic .................................. ..154
Possible Cause ................................................... ..154
DTC Confirmation Procedure .............................. ..154
Wiring Diagram - AT - VSSMTR ...........................155
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..156
DTC BATT/FLUID TEMP SEN (A/T FLUID
TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT AND TCM POWER
SOURCE) ....................................................... ..
157
Description .......................................................... ..157
CONSULT-III Refe rence Value in Data Monitor
Mode ................................................................... ..
157
On Board Diagnosis Logic .................................. ..157
Possible Cause ................................................... ..157
DTC Confirmation Procedure .............................. ..157
Wiring Diagram - AT - BA/FTS ............................ ..158
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..159
Component Inspection ........................................ ..161
DTC TURBINE REVOLUTION SENSOR ....... ..163
Description .......................................................... ..163
CONSULT-III Refe rence Value in Data Monitor
Mode ................................................................... ..
163
On Board Diagnosis Logic .................................. ..163
Possible Cause ................................................... ..163
DTC Confirmation Procedure .............................. ..163
Wiring Diagram - AT - PT/SEN ........................... ..164
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..165
CONTROL UNIT (RAM), CONTROL UNIT
(ROM) ............................................................. ..
168
Description .......................................................... ..168
On Board Diagnosis Logic .................................. ..168
Possible Cause ................................................... ..168
DTC Confirmation Procedure .............................. ..168
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..168
MAIN POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIR-
CUIT ................................................................ ..169
Wiring Diagram - AT - MAIN ............................... ..169 Diagnosis Procedure ...........................................
..170
PNP, OD SWITCH AND CLOSED THROT-
TLE, WIDE OPEN THROTTLE POSITION
SIGNAL CIRCUI T ............................................ 172
CONSULT-III Reference Va lue in Data Monitor
Mode .................................................................... ..
172
TCM Terminal and Refere nce Value .....................172
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..172
Component Inspection ......................................... ..176
SHIFT POSITION INDICATOR CIRCUIT ........ 177
Description ........................................................... ..177
CONSULT-III Reference Va lue in Data Monitor
Mode .................................................................... ..
177
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..177
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR SYMPTOMS .... 178
Wiring Diagram - AT - NONDTC ......................... ..178
OD OFF Indicator Lamp Does Not Come On ...... ..181
Engine Cannot Be Started in "P" and "N" Position ..183
In "P" Position, Vehicle Moves Forward or Back-
ward When Pushed ............................................. ..
184
In "N" Position, Vehicle Moves ............................ ..184
Large Shock "N" → "R" Position .......................... ..185
Vehicle Does Not Creep Backward in "R" Position ..186
Vehicle Does Not Creep Forw ard in "D", "2" or "1"
Position ................................................................ ..
187
Vehicle Cannot Be Started from D 1 ..................... ..188
A/T Does Not Shift: D 1→ D 2or Does Not Kick-
down: D 4→ D 2 ..................................................... ..190
A/T Does Not Shift: D 2→ D 3 ................................ ..192
A/T Does Not Shift: D 3→ D 4 ................................ ..193
A/T Does Not Perform Lock-up ........................... ..194
A/T Does Not Hold Lock-up Condition ................. ..195
Lock-up Is Not Released ..................................... ..196
Engine Speed Does Not Return to Idle (Light
Braking D 4→ D 3) ................................................. ..197
A/T Does Not Shift: D 4→ D 3, When OD OFF ...... ..198
A/T Does Not Shift: D 3→ 22, When Selector Lever
"D" → "2" Position ............................................... ..
199
A/T Does Not Shift: 2 2→ 11, When Selector Lever
"2" → "1" Position ................................................ ..
200
Vehicle Does Not Decelerate by Engine Brake ... ..202
TCM Self-Diagnosis Does Not Activate ............... ..205
A/T SHIFT LOCK SYSTEM ............................. 207
Description ........................................................... ..207
Shift Lock System Parts Location ........................ ..207
Wiring Diagram - AT - SHIFT .............................. ..208
Diagnosis Procedure ........................................... ..208
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE .......... 211
Removal and Installation ..................................... ..211
SHIFT CONTROL SYSTEM ............................ 212
Control Device Removal an d Installation ...............212
Control Device Disassembly and Assembly ..........215
Selector Lever Knob Remo val and Installation ......215
Adjustment of A/T Position .................................. ..216
Page 10 of 4331
AT
N
O P
SERVICE INFORMATION
INDEX FOR DTC
Alphabetical Index INFOID:0000000004305286
NOTE:
If DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT” is di splayed with other DTCs, first perform the trouble diagnosis for
DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT”. Refer to AT-88 .
*1: These numbers is prescribed by SAE J2012.
*2: When the fail-safe operation occurs, the MIL illuminates.
*3: The MIL illuminates when both the “Revolution sensor signal” and the “Vehicle speed sensor signal” meet the fail-safe condi tion at
the same time.
DTC No. Index INFOID:0000000004305287
NOTE:
If DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT” is di splayed with other DTCs, first perform the trouble diagnosis for
DTC “CAN COMM CIRCUIT”. Refer to AT-88 .
Items
(CONSULT-III screen terms) DTC
*1
Reference page
CONSULT-III or GST
A/T 1ST GR FNCTN P0731 AT-110A/T 2ND GR FNCTN P0732
AT-113A/T 3RD GR FNCTN P0733
AT-116A/T 4TH GR FNCTN P0734
AT-119A/T TCC S/V FNCTN P0744
AT-129ATF TEMP SEN/CIRC P0710
AT-96BATT/FLUID TEMP SEN —
AT-157CAN COMM CIRCUIT U1000
AT-88CONTROL UNIT (RAM) —
AT-168CONTROL UNIT (ROM) —
AT-168ENGINE SPEED SIG P0725
AT-106LINE PRESSURE S/V P0745
AT-134OVERRUN CLUTCH S/V P1760
AT-149PNP SW/CIRC P0705
AT-91SHIFT SOLENOID/V A*
2
P0750AT-139SHIFT SOLENOID/V B*
2
P0755AT-144T/C CLUTCH SOL/V P0740
AT-124TURBINE SENSOR —
AT-163VHCL SPEED SEN-A/T*
3
P0720AT-101VHCL SPEED SEN-MTR —
AT-154DTC
*1
Items
(CONSULT-III screen terms) Reference page
CONSULT-III or GST
P0705 PNP SW/CIRC AT-91P0710 ATF TEMP SEN/CIRC
AT-96P0720
VHCL SPEED SEN-A/T* 3
AT-101P0725 ENGINE SPEED SIG
AT-106P0731 A/T 1ST GR FNCTN
AT-110
Page 11 of 4331

P0733 A/T 3RD GR FNCTN
AT-116P0734 A/T 4TH GR FNCTN
AT-119P0740 T/C CLUTCH SOL/V
AT-124P0744 A/T TCC S/V FNCTN
AT-129P0745 LINE PRESSURE S/V
AT-134P0750
SHIFT SOLENOID/V A* 2
AT-139P0755
SHIFT SOLENOID/V B* 2
AT-144P1760 OVERRUN CLUTCH S/V
AT-149U1000 CAN COMM CIRCUIT
AT-88— BATT/FLUID TEMP SEN
AT-157— CONTROL UNIT (RAM)
AT-168— CONTROL UNIT (ROM)
AT-168— TURBINE SENSOR
AT-163— VHCL SPEED SEN-MTR
AT-154DTC
*1
Items
(CONSULT-III screen terms) Reference page
CONSULT-III or GST
Page 12 of 4331

AT
N
O P
PRECAUTIONS
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT
PRE-TENSIONER" INFOID:0000000004803451
The Supplemental Restraint System such as “A IR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER”, used along
with a front seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severi ty of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain
types of collision. This system includes seat belt switch inputs and dual stage front air bag modules. The SRS
system uses the seat belt switches to determine the front air bag deployment, and may only deploy one front
air bag, depending on the severity of a collision and w hether the front occupants are belted or unbelted.
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in the SRS and SB section of this Service Man-
ual.
WARNING:
• To avoid rendering the SRS inoper ative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death in
the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed by
an authorized NISSAN/INFINITI dealer.
• Improper maintenance, including in correct removal and installation of the SRS can lead to personal
injury caused by unintentional act ivation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air Bag
Module, see the SRS section.
• Do not use electrical test equipm ent on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses can be identi fied by yellow and/or orange harnesses or har-
ness connectors.
• When working near the Airbag Diagnosis Sensor Un it or other Airbag System sensors with the Igni-
tion ON or engine running, DO NOT use air or el ectric power tools or strike near the sensor(s) with a
hammer. Heavy vibration could activate the sensor( s) and deploy the air bag(s), possibly causing
serious injury.
• When using air or electric power tools or hammers , always switch the Ignition OFF, disconnect the
battery, and wait at least 3 minutes before performing any service.
Precaution Necessary for Steering Wh eel Rotation After Battery Disconnect
INFOID:0000000004305289
NOTE:
• This Procedure is applied only to models with Intell igent Key system and NVIS/IVIS (NISSAN/INFINITI
VEHICLE IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM - NATS).
• Remove and install all control units after disconnecti ng both battery cables with the ignition knob in the
″ LOCK ″ position.
• Always use CONSULT-III to perform self-diagnosis as a part of each function inspection after finishing work.
If DTC is detected, perform trouble diagnosis according to self-diagnostic results.
For models equipped with the Intelligent Key system and NVIS/IVIS, an electrically controlled steering lock
mechanism is adopted on the key cylinder.
For this reason, if the battery is disconnected or if the battery is discharged, the steering wheel will lock and
steering wheel rotation will become impossible.
If steering wheel rotation is required when battery pow er is interrupted, follow the procedure below before
starting the repair operation.
OPERATION PROCEDURE 1. Connect both battery cables. NOTE:
Supply power using jumper cables if battery is discharged.
2. Use the Intelligent Key or mechanical key to turn the ignition switch to the ″ACC ″ position. At this time, the
steering lock will be released.
3. Disconnect both battery cables. The steering lock will remain released and the steering wheel can be
rotated.
4. Perform the necessary repair operation.
5. When the repair work is completed, return the ignition switch to the ″LOCK ″ position before connecting
the battery cables. (At this time, the steering lock mechanism will engage.)
6. Perform a self-diagnosis check of al l control units using CONSULT-III.
Page 38 of 4331
AT
N
O P
The line pressure is temporarily reduced corresponding to a change
in engine torque when shifting gears (that is, when the shift solenoid
valve is switched for clutch operation) to reduce shifting shock.
AT LOW FLUID TEMPERATURE • A/T fluid viscosity and frictional characteristics of t he clutch facing change with A/T fluid temperature. Clutch
engaging or band-contacting pressure is compensated for, according to A/T fluid temperature, to stabilize
shifting quality.
• The line pressure is reduced below 60 °C (140 °F) to prevent shift-
ing shock due to high viscosity of A/T fluid when temperature is
low.
• Line pressure is increased to a maximum irrespective of the throt- tle opening when A/T fluid temperature drops to −10 °C (14 °F). This
pressure rise is adopted to prevent a delay in clutch and brake
operation due to extreme drop of A/T fluid viscosity at low temper-
ature.
Shift Control INFOID:0000000004305304
The shift is regulated entirely by electronic cont rol to accommodate vehicle speed and varying engine opera-
tions. This is accomplished by electrical signals trans mitted by the revolution sensor and the ECM (accelerator
pedal position sensor). This results in improved acceleration performance and fuel economy.
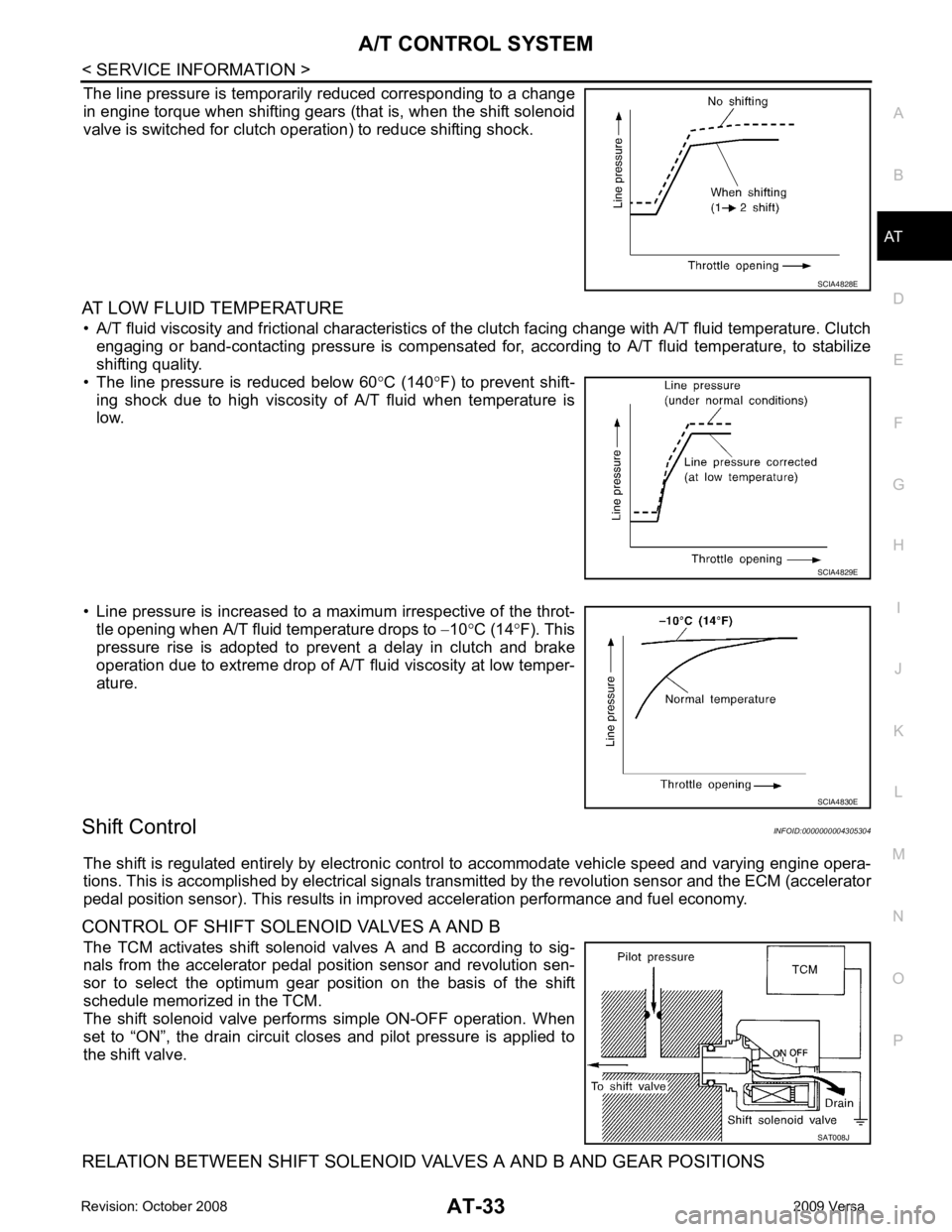
CONTROL OF SHIFT SOLENOID VALVES A AND B The TCM activates shift solenoid valves A and B according to sig-
nals from the accelerator pedal position sensor and revolution sen-
sor to select the optimum gear pos ition on the basis of the shift
schedule memorized in the TCM.
The shift solenoid valve performs simple ON-OFF operation. When
set to “ON”, the drain circuit closes and pilot pressure is applied to
the shift valve.
RELATION BETWEEN SHIFT SOLENOID VALVES A AND B AND GEAR POSITIONS SAT008J
Page 44 of 4331

AT
N
O P
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
Introduction INFOID:0000000004305309
A/T system has two self-diagnostic systems.
The first is emission-related on boar d diagnostic system (OBD-II) performed by the TCM in combination with
the ECM. The malfunction is indicated by the MIL (malf unction indicator lamp) and is stored as a DTC in the
ECM memory but not the TCM memory.
The second is the TCM original self-diagnosis indicated by the OD OFF indicator lamp. The malfunction is
stored in the TCM memory. The detected items are ov erlapped with OBD-II self-diagnostic items. For detail,
refer to AT-79, " CONSULT-III Function (TRANSMISSION) " .
OBD-II Function for A/T System INFOID:0000000004305310
The ECM provides emission-related on board diagnostic (O BD-II) functions for the A/T system. One function
is to receive a signal from the TCM used with OBD-rela ted parts of the A/T system. The signal is sent to the
ECM when a malfunction occurs in the corresponding OBD-re lated part. The other function is to indicate a
diagnostic result by means of the MIL (malfunction indica tor lamp) on the instrument panel. Sensors, switches
and solenoid valves are used as sensing elements.
The MIL automatically illuminates in One or Two Trip Detection Logic when a malfunction is sensed in relation
to A/T system parts.
One or Two Trip Detection Logic of OBD-II INFOID:0000000004305311
ONE TRIP DETECTION LOGIC If a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, the MIL will illuminate and the malfunction will be stored in
the ECM memory as a DTC. The TCM is not provided with such a memory function.
TWO TRIP DETECTION LOGIC When a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, it is stored in the ECM memory as a 1st trip DTC
(diagnostic trouble code) or 1st trip freeze frame data. At this point, the MIL will not illuminate. — 1st trip
If the same malfunction as that experienced during the fi rst test drive is sensed during the second test drive,
the MIL will illuminate. — 2nd trip
The “trip” in the “One or Two Trip Detection Logic” m eans a driving mode in which self-diagnosis is performed
during vehicle operation.
OBD-II Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) INFOID:0000000004305312
HOW TO READ DTC AND 1ST TRIP DTC DTC and 1st trip DTC can be read by the following methods.
( with CONSULT-III or GST) CONSULT-III or GST (Generic Scan Tool) Examples: P0705, P0720 etc.
These DTC are prescribed by SAE J2012.
(CONSULT-III also displays the malfunctioning component or system.)
• 1st trip DTC No. is the same as DTC No.
• Output of the diagnostic troubl e code indicates that the indicated circuit has a malfunction. How-
ever, in case of the Mode II and GST, they do not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring or
occurred in the past and returned to normal.
CONSULT-III can identify them as shown below, therefore, CONS ULT-III (if available) is recom-
mended.
DTC or 1st trip DTC of a malfunction is displayed in SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS mode for “ENGINE” with
CONSULT-III. Time data indicates how many times the vehicle was driven after the last detection of a DTC.
If the DTC is being detected curr ently, the time data will be “0”.
If a 1st trip DTC is stored in the ECM, the time data will be “1t”.
Freeze Frame Data and 1st Trip Freeze Frame Data The ECM has a memory function, which stores the driv ing condition such as fuel system status, calculated
load value, engine coolant temperature, short term f uel trim, long term fuel trim, engine speed and vehicle
speed at the moment the ECM detects a malfunction.
Page 47 of 4331

.
Fail-Safe INFOID:0000000004305315
The TCM has an electronic Fail-safe mode. This allows t he vehicle to be driven even if a major electrical input/
output device circuit is damaged.
Under Fail-Safe, the vehicle always runs in third gear, even with a shift lever position of “1”, “2” or “D”. The cus-
tomer may complain of sluggish or poor acceleration.
Always follow the “ AT-43, " How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate Repair " ”.
The SELF-DIAGNOSIS results will be as follows:
• The first SELF-DIAGNOSIS will indicate damage to t he vehicle speed sensor or the revolution sensor.
• During the next SELF-DIAGNOSIS, performed after checking the sensor, no damages will be indicated.
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION
The following fail-safe functions allow vehicles to be driven even when sensor, switch or solenoid malfunction
occurs.
Vehicle Speed Sensor·A/T (Revolution Sensor)
Vehicle speed sensor·MTR signal is input from combination meter.
Accelerator Pedal Position Signal and Throttle Position Signal
TCM controls the throttle opening angle to a predetermi ned fixed position to enable driving if a malfunctioning
signal is input to TCM.
PNP Switch
When the multiple PNP switch signals are input to TCM, the priority of selector lever position becomes “D”,
“N”, “R”, “2” and “1” in order by internal TCM determination.
The use of 4th gear is inhibited unt il normal operation resumes. Because t he hydraulic circuit of the control
valve is switched by manual valve according to the sele ctor lever position, however, actual operating condition
of vehicle becomes as follows.
Shift Solenoid Valve A and B
If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, use of certain gears is limited. Refer to chart shown below.
Priority Detected items
1 CAN communication line
2 Except above Actual lever position PNP switch input signal Running status
“P” “P” position and other position signals P
“R” “R” position and other position signals R
“N” “N” position and other position signals N
“D” “D” position and other position signals D 1
⇔ D2 ⇔ D3 ⇔ D4
“2” “2” position and other position signals (Except “1” position) 2
1 ⇔ 22 ⇔ 23
“2” position and “1” position signals 2 1 ⇔ 22
“1” “1” position and other position signals (Except “2” position) 1
1
⇔ 12 ⇔ 13
“1” position and “2” position signals 1 1 ⇔ 12
Page 48 of 4331

AT
N
O P
�z
: Solenoid ON
× : Solenoid OFF
–: Non-standard condition
Line Pressure Solenoid Valve If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, line pre ssure solenoid valve is turned OFF to achieve maxi-
mum oil pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, torque conv erter clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to release
lock-up.
Overrun Clutch Solenoid Valve If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, overr un clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to engage overrun
clutch. This will result in more effective engine brake during deceleration.
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate Repair INFOID:0000000004305316
INTRODUCTION The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, accelera-
tor pedal position sensor or PNP switch and provides shift control or
lock-up control via A/T solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal
sent from sensing elements used wit h the OBD-related parts of the
A/T system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is capa-
ble of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can store mal-
functions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the
operation of the A/T system. T he A/T system must be in good oper-
ating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve malfunc-
tion, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a malfunction t hat occurs intermittently rather than continuously. Most
intermittent malfunctions are caused by poor electric c onnections or improper wiring. In this case, careful
checking of suspected circuits may hel p prevent the replacement of good parts.
Shift position
Normal
Malfunction in solenoid
valve A Malfunction in solenoid
valve B Malfunction in solenoid
valves A and B
A B Gear A B Gear A B Gear A B Gear
“D” position �z �z
1st –�z→×
3rd �z
→× –
3rd – –
3rd
×
�z2nd – �z→× × – – –
× × 3rd – x ×– – –
�z ×4th – x �z→× – – –
“2” position �z �z
1st –�z→× �z→× – – –
× �z2nd – �z→× × – – –
× × 3rd – x ×– – –
“1” position �z �z
1st –�z→× �z→× – – –
× �z2nd – �z→× × – – –
× × 3rd – x ×– – –
Page 52 of 4331
AT
N
O P
4.
�† Perform “Road Test”. AT-554-1. “Check Before Engine is Started”
AT-56OD OFF Indicator Lamp Does Not Come On "
,
AT-83 .
�† CAN COMMUNICATION LINE AT-88 .
�† PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION (PNP) SWITCH AT-91 .
�† A/T FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT AT-96 .
�† VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR A/T (REVOLUTION SENSOR) AT-101 .
�† ENGINE SPEED SIGNAL AT-106 .
�† A/T 1ST GEAR FUNCTION AT-110 .
�† A/T 3RD GEAR FUNCTION AT-116 .
�† A/T 4TH GEAR FUNCTION AT-119 .
�† TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID VALVE AT-124 .
�† A/T TCC S/V FUNCTION (LOCK-UP) AT-129 .
�† LINE PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE AT-134 .
�† SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE A AT-139 .
�† SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE B AT-144 .
�† OVERRUN CLUTCH SOLENOID VALVE AT-149 .
�† VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR MTR AT-154 .
�† BATT/FLUID TEMP SEN (A/T FLUID TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT AND TCM POWER SOURCE)
AT-157 .
�† TURBINE REVOLUTION SENSOR AT-163 .
�† CONTROL UNIT (RAM), CONTROL UNIT (ROM) AT-168 .
�† MAIN POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIRCUIT AT-169 .
4-2. “Check at Idle” AT-56Engine Cannot Be Started in "P" and "N" Position " .
�† AT-184, " In "P" Position, Vehicle Moves Forward or Backward When Pushed " .
�† AT-184, " In "N" Position, Vehicle Moves " .
�† AT-185, " Large Shock "N" " .
�† AT-186, " Vehicle Does Not Creep Backward in "R" Position " .
�† AT-187, " Vehicle Does Not Creep Forward in "D", "2" or "1" Position " .