check engine NISSAN PICK-UP 1998 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: NISSAN PICK-UP 1998Pages: 1659, PDF Size: 53.39 MB
Page 79 of 1659
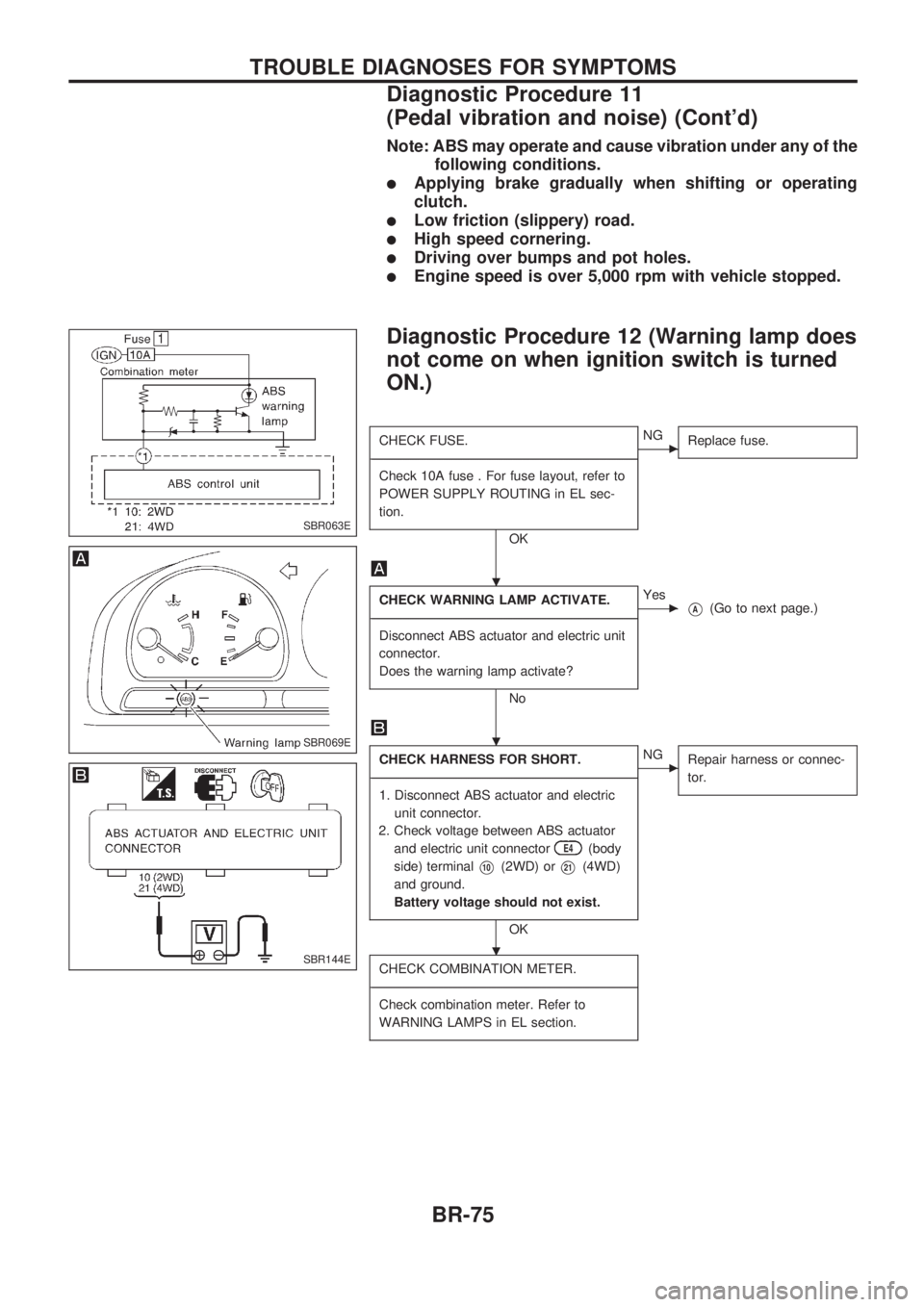
Note: ABS may operate and cause vibration under any of the
following conditions.
lApplying brake gradually when shifting or operating
clutch.
lLow friction (slippery) road.
lHigh speed cornering.
lDriving over bumps and pot holes.
lEngine speed is over 5,000 rpm with vehicle stopped.
Diagnostic Procedure 12 (Warning lamp does
not come on when ignition switch is turned
ON.)
CHECK FUSE.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Check 10A fuse . For fuse layout, refer to
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING in EL sec-
tion.
OK
cNG
Replace fuse.
CHECK WARNING LAMP ACTIVATE.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Disconnect ABS actuator and electric unit
connector.
Does the warning lamp activate?
No
cYes
VA(Go to next page.)
CHECK HARNESS FOR SHORT.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Disconnect ABS actuator and electric
unit connector.
2. Check voltage between ABS actuator
and electric unit connector
E4(body
side) terminal
V10(2WD) orV21(4WD)
and ground.
Battery voltage should not exist.
OK
cNG
Repair harness or connec-
tor.
CHECK COMBINATION METER.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Check combination meter. Refer to
WARNING LAMPS in EL section.
SBR063E
SBR069E
SBR144E
.
.
.
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES FOR SYMPTOMS
Diagnostic Procedure 11
(Pedal vibration and noise) (Cont'd)
BR-75
Page 93 of 1659
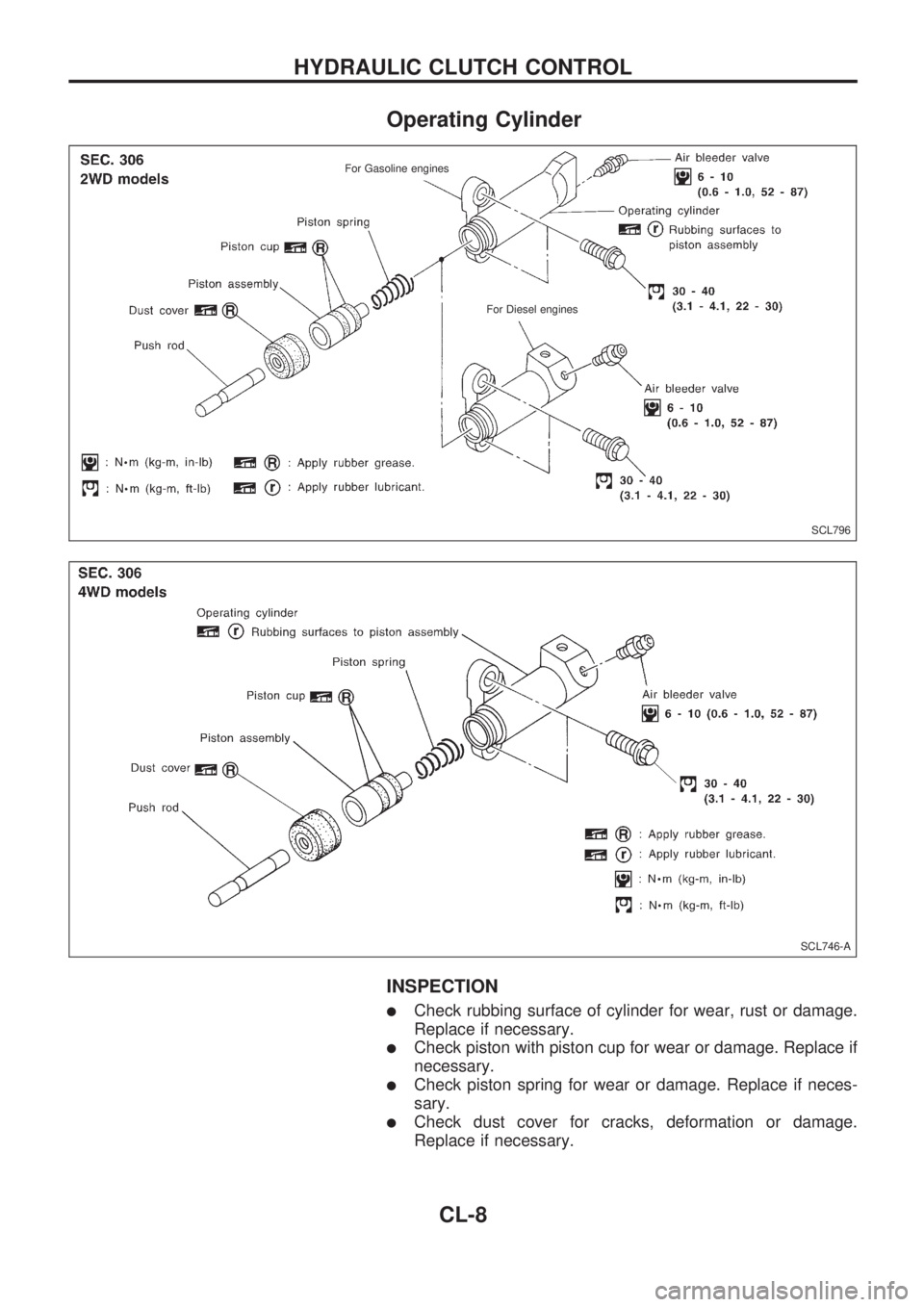
Operating Cylinder
INSPECTION
lCheck rubbing surface of cylinder for wear, rust or damage.
Replace if necessary.
lCheck piston with piston cup for wear or damage. Replace if
necessary.
lCheck piston spring for wear or damage. Replace if neces-
sary.
lCheck dust cover for cracks, deformation or damage.
Replace if necessary.
SCL796
.
For Gasoline engines
.
For Diesel engines
SCL746-A
.
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH CONTROL
CL-8
Page 97 of 1659
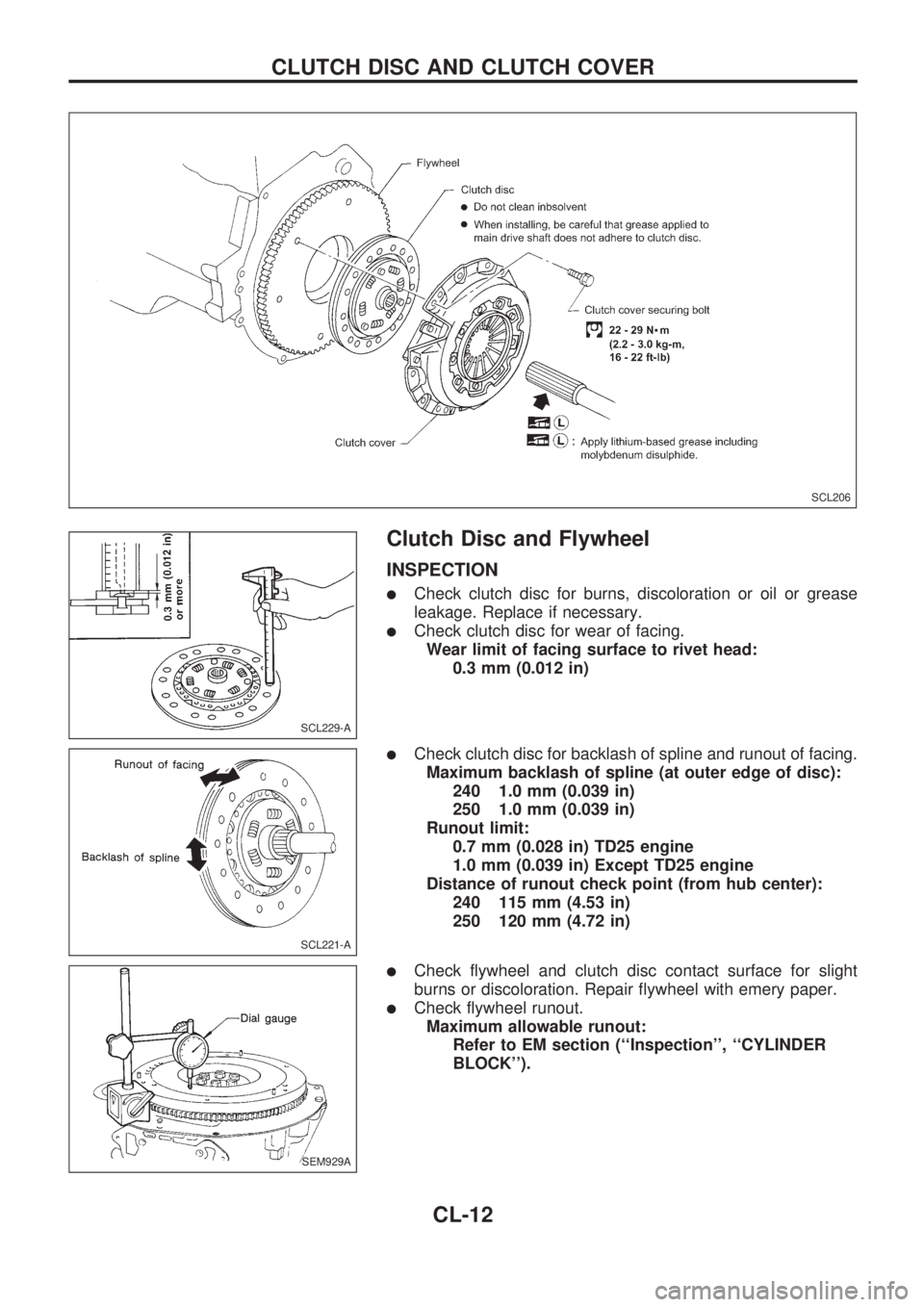
Clutch Disc and Flywheel
INSPECTION
lCheck clutch disc for burns, discoloration or oil or grease
leakage. Replace if necessary.
lCheck clutch disc for wear of facing.
Wear limit of facing surface to rivet head:
0.3 mm (0.012 in)
lCheck clutch disc for backlash of spline and runout of facing.
Maximum backlash of spline (at outer edge of disc):
240 1.0 mm (0.039 in)
250 1.0 mm (0.039 in)
Runout limit:
0.7 mm (0.028 in) TD25 engine
1.0 mm (0.039 in) Except TD25 engine
Distance of runout check point (from hub center):
240 115 mm (4.53 in)
250 120 mm (4.72 in)
lCheck flywheel and clutch disc contact surface for slight
burns or discoloration. Repair flywheel with emery paper.
lCheck flywheel runout.
Maximum allowable runout:
Refer to EM section (``Inspection'', ``CYLINDER
BLOCK'').
SCL206
SCL229-A
SCL221-A
SEM929A
CLUTCH DISC AND CLUTCH COVER
CL-12
Page 98 of 1659

INSTALLATION
lApply recommended grease to contact surface of spline por-
tion.
Too much lubricant might cause clutch disc facing damage.
Clutch Cover
INSPECTION
lAdjust unevenness of diaphragm spring with Tool.
Uneven limit:
250 0.5 mm (0.020 in)
240 0.5 mm (0.020 in) Except TD25 engine
0.7 mm (0.028 in) TD25 engine
lSet Tool and check height and unevenness of diaphragm
spring.
Set 0.2 mm (0.008 in) feeler gauges on distance pieces
(ST20050100) when checking 240 or 250.
Diaphragm spring height ``A'':
240 37.5 - 39.5 mm (1.476 - 1.555 in)
250 37.0 - 39.0 mm (1.457 - 1.535 in)
lCheck thrust rings for wear or damage by shaking cover
assembly up and down to listen for chattering noise, or lightly
hammering on rivets for a slightly cracked noise. Replace
clutch cover assembly if necessary.
lCheck pressure plate and clutch disc contact surface for
slight burns or discoloration. Repair pressure plate with
emery paper.
lCheck pressure plate and clutch disc contact surface for
deformation or damage. Replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
lInsert Tool into clutch disc hub while installing clutch cover
and disc.
lBe careful not to allow grease to contaminate clutch facing.
lTighten bolts in numerical order, in two steps.
First step:
:10-20Nzm (1.0 - 2.0 kg-m,7-14ft-lb)
Final step:
:22-29Nzm (2.2 - 3.0 kg-m, 16 - 22 ft-lb)
SCL466-A
SCL219-A
SCL749
CLUTCH DISC AND CLUTCH COVER
Clutch Disc and Flywheel (Cont'd)
CL-13
Page 99 of 1659
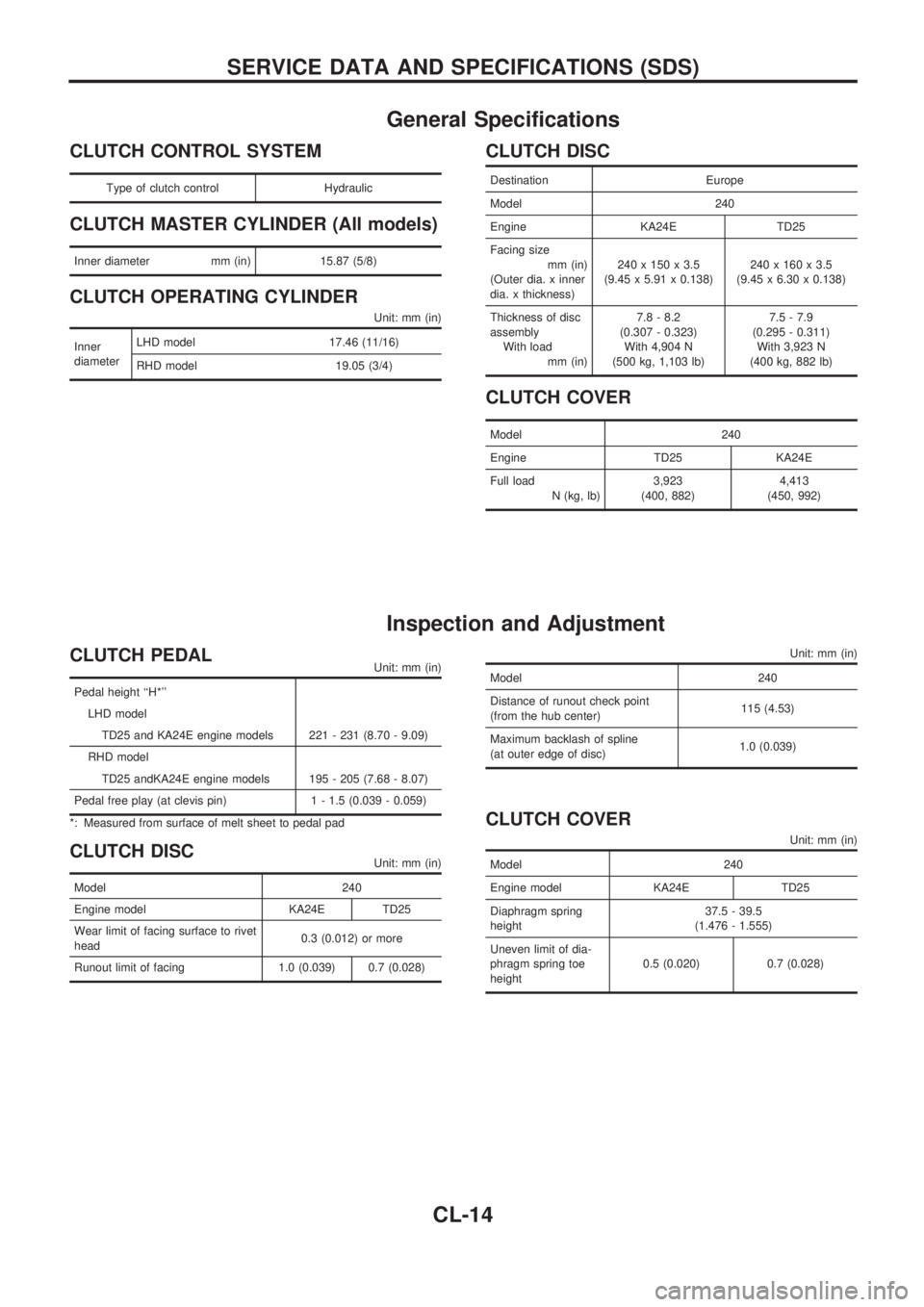
General Specifications
CLUTCH CONTROL SYSTEM
Type of clutch control Hydraulic
CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER (All models)
Inner diameter mm (in) 15.87 (5/8)
CLUTCH OPERATING CYLINDER
Unit: mm (in)
Inner
diameterLHD model 17.46 (11/16)
RHD model 19.05 (3/4)
CLUTCH DISC
Destination Europe
Model 240
Engine KA24E TD25
Facing size
mm (in)
(Outer dia. x inner
dia. x thickness)240 x 150 x 3.5
(9.45 x 5.91 x 0.138)240 x 160 x 3.5
(9.45 x 6.30 x 0.138)
Thickness of disc
assembly
With load
mm (in)7.8 - 8.2
(0.307 - 0.323)
With 4,904 N
(500 kg, 1,103 lb)7.5 - 7.9
(0.295 - 0.311)
With 3,923 N
(400 kg, 882 lb)
CLUTCH COVER
Model 240
Engine TD25 KA24E
Full load
N (kg, lb)3,923
(400, 882)4,413
(450, 992)
Inspection and Adjustment
CLUTCH PEDALUnit: mm (in)
Pedal height ``H*''
LHD model
TD25 and KA24E engine models 221 - 231 (8.70 - 9.09)
RHD model
TD25 andKA24E engine models 195 - 205 (7.68 - 8.07)
Pedal free play (at clevis pin) 1 - 1.5 (0.039 - 0.059)
*: Measured from surface of melt sheet to pedal pad
CLUTCH DISCUnit: mm (in)
Model 240
Engine model KA24E TD25
Wear limit of facing surface to rivet
head0.3 (0.012) or more
Runout limit of facing 1.0 (0.039) 0.7 (0.028)
Unit: mm (in)
Model 240
Distance of runout check point
(from the hub center)115 (4.53)
Maximum backlash of spline
(at outer edge of disc)1.0 (0.039)
CLUTCH COVER
Unit: mm (in)
Model 240
Engine model KA24E TD25
Diaphragm spring
height37.5 - 39.5
(1.476 - 1.555)
Uneven limit of dia-
phragm spring toe
height0.5 (0.020) 0.7 (0.028)
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)
CL-14
Page 150 of 1659
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
SECTION
EC
CONTENTS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE INDEX................... 1
Alphabetical & Numerical Index for DTC
(KA engine) ............................................................ 1
PRECAUTIONS AND PREPARATION..................... 2
Special Service Tools ............................................ 2
Commercial Service Tool....................................... 4
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ``AIR
BAG'' (4WD models).............................................. 4
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ``AIR
BAG'' (2WD models).............................................. 4
KA
PRECAUTIONS AND PREPARATION..................... 5
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System .............. 5
Precautions ............................................................ 6
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL
SYSTEM..................................................................... 8
Circuit Diagram ...................................................... 8
System Diagram .................................................... 9
ECCS Component Parts Location ....................... 10
Vacuum Hose Drawing ........................................ 12
System Chart ....................................................... 13
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION..................................... 14
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System.................. 14
Distributor Ignition (DI) System............................ 17
Air Conditioning Cut Control ................................ 18
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed) .................................................................. 18
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM..................... 19
Description ........................................................... 19
Inspection ............................................................. 19POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION................ 21
Description ........................................................... 21
Inspection ............................................................. 21
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURE............................. 22
Fuel Pressure Release ........................................ 22
Fuel Pressure Check ........................................... 22
Injector Removal and Installation ........................ 23
Fast Idle Cam (FIC) Inspection and
Adjustment ........................................................... 24
Idle Speed/Ignition Timing/Idle Mixture Ratio
Adjustment ........................................................... 25
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION......................................................... 36
Introduction .......................................................... 36
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) .......................... 36
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) ........................ 38
CONSULT ............................................................ 45
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - Introduction.................. 54
Introduction .......................................................... 54
Diagnostic Worksheet .......................................... 54
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - Work Flow..................... 56
Work Flow ............................................................ 56
Description for Work Flow ................................... 57
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - Basic Inspection.......... 58
Basic Inspection ................................................... 58
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS - General Description..... 61
Fail-Safe Chart ..................................................... 61
Symptom Matrix Chart ......................................... 62
CONSULT Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode .................................................................... 64
Major Sensor Reference Graph in Data
Monitor Mode ....................................................... 66
ECM Terminals and Reference Value ................. 68
EC
Page 151 of 1659

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR POWER SUPPLY.... 75
Main Power Supply and Ground Circuit .............. 75
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``CAMSHAFT
POSI SEN'' (DTC 11).............................................. 82
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS) ..................... 82
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``MASS AIR
FLOW SEN'' (DTC 12)............................................ 89
Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAFS) ............................ 89
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``COOLANT TEMP
SEN'' (DTC 13)........................................................ 95
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS) ..... 95
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``IGN SIGNAL-
PRIMARY'' (DTC 21)............................................... 99
Ignition Signal ...................................................... 99
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``OVER HEAT''
(DTC 28)................................................................. 106
Overheat ............................................................ 106
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``INT AIR TEMP
SEN'' (DTC 41)...................................................... 109
Intake Air Temperature Sensor ......................... 109
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR ``THROTTLE POSI
SEN'' (DTC 43)...................................................... 113
Throttle Position Sensor .................................... 113
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR
NON-DETECTABLE ITEMS.................................. 118
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) ............................ 118
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
- LHD Models - .................................................. 123
Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater
- LHD Models - .................................................. 127
Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) - Auxiliary Air
Control (AAC) Valve .......................................... 131
Neutral Position Switch ...................................... 136
EVAP Canister Purge Control Solenoid Valve .. 140
Injector ............................................................... 144
Start Signal ........................................................ 149
Fuel Pump.......................................................... 151
Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch ................. 157
Swirl Control Valve Control Solenoid Valve ...... 161
IACV-FICD Solenoid Valve ................................ 168
MIL & Data Link Connectors ............................. 173
TD
INJECTION SYSTEM............................................ 176
Fuel System ....................................................... 176
INJECTION PUMP................................................. 178
Inspection ........................................................... 178
Removal ............................................................. 178
Installation and Adjustment................................ 180
Disassembly ....................................................... 183
Load Timer Adjustment...................................... 183
Start Q Adjustment Lever .................................. 184
INJECTION NOZZLE............................................. 186Removal and Installation ................................... 186
Disassembly ....................................................... 186
Inspection ........................................................... 187
Cleaning ............................................................. 187
Assembly............................................................ 189
Test and Adjustment .......................................... 189
FUEL SYSTEM CHECK........................................ 191
Bleeding Fuel System ........................................ 191
Bleeding Fuel Filter ............................................ 192
Checking Priming Pump .................................... 192
Checking Fuel Filter Switch ............................... 192
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION.............. 193
Description ......................................................... 193
Inspection ........................................................... 193
QUICK-GLOW SYSTEM........................................ 194
Component Parts Location ................................ 194
Circuit Diagram .................................................. 195
Description ......................................................... 196
Wiring Diagram .................................................. 197
Glow Control Unit Circuit Inspection (For Cold
Areas)................................................................. 203
Glow Control Unit Circuit Inspection (Except
for Cold Areas)................................................... 206
Component Inspection ....................................... 208
EGR SYSTEM........................................................ 210
Component Parts Location ................................ 210
Description ......................................................... 211
Operation ........................................................... 212
Wiring Diagram .................................................. 213
System Inspection.............................................. 217
Component Inspection ....................................... 218
SOLENOID TIMER................................................ 220
Description ......................................................... 220
Operation ........................................................... 220
Wiring Diagram .................................................. 222
Inspection ........................................................... 224
FUEL CUT SYSTEM.............................................. 225
Wiring Diagram .................................................. 225
FUEL HEATER SYSTEM...................................... 226
Description ......................................................... 226
Wiring Diagram .................................................. 227
System Inspection.............................................. 228
Component Inspection ....................................... 228
FAST IDLE CONTROL CIRCUIT.......................... 230
Wiring Diagram .................................................. 230
Electrical Components Inspection ..................... 231
KA
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS). 232
General Specifications ....................................... 232
Inspection and Adjustment ................................ 232
Page 156 of 1659

Commercial Service Tool
FOR KA ENGINE MODELS
Tool name Description
Fuel filler cap adapter
NT653
Checking fuel tank vacuum relief valve opening
pressure
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ``AIR
BAG'' (4WD models)
The Supplemental Restraint System ``AIR BAG'', used along with a seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or
severity of injury to the driver in a frontal collision. The Supplemental Restraint System consists of an air
bag module (located in the center of the steering wheel), a diagnosis sensor unit, warning lamp, wiring har-
ness and spiral cable. Information necessary to service the system safely is included in theRS sectionof
this Service Manual.
WARNING:
lTo avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be per-
formed by an authorized NISSAN dealer.
lImproper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system.
lDo not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses are covered with yellow insulation either just before the
harness connectors or for the complete harness, for easy identification.
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ``AIR
BAG'' (2WD models)
The Supplemental Restraint System ``AIR BAG'', used along with a seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or
severity of injury to the driver in a frontal collision. The Supplemental Restraint System consists of an air
bag module (located in the center of the steering wheel), a diagnosis sensor unit, warning lamp, wiring har-
ness and spiral cable. Information necessary to service the system safely is included in theRS sectionof
this Service Manual.
WARNING:
lTo avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be per-
formed by an authorized NISSAN dealer.
lImproper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system.
lDo not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS.
PRECAUTIONS AND PREPARATION
EC-4
Page 171 of 1659
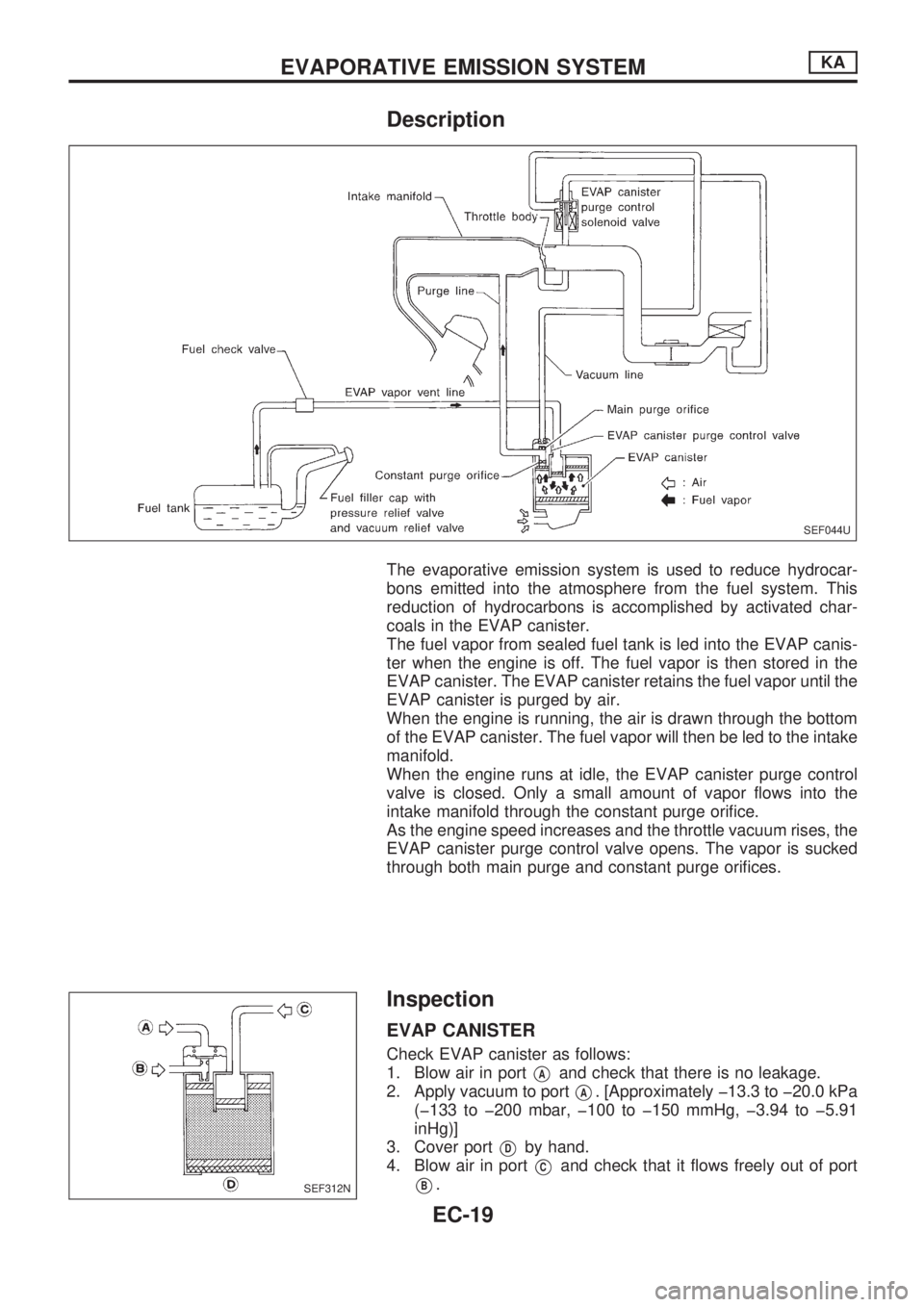
Description
The evaporative emission system is used to reduce hydrocar-
bons emitted into the atmosphere from the fuel system. This
reduction of hydrocarbons is accomplished by activated char-
coals in the EVAP canister.
The fuel vapor from sealed fuel tank is led into the EVAP canis-
ter when the engine is off. The fuel vapor is then stored in the
EVAP canister. The EVAP canister retains the fuel vapor until the
EVAP canister is purged by air.
When the engine is running, the air is drawn through the bottom
of the EVAP canister. The fuel vapor will then be led to the intake
manifold.
When the engine runs at idle, the EVAP canister purge control
valve is closed. Only a small amount of vapor flows into the
intake manifold through the constant purge orifice.
As the engine speed increases and the throttle vacuum rises, the
EVAP canister purge control valve opens. The vapor is sucked
through both main purge and constant purge orifices.
Inspection
EVAP CANISTER
Check EVAP canister as follows:
1. Blow air in port
VAand check that there is no leakage.
2. Apply vacuum to port
VA. [Approximately þ13.3 to þ20.0 kPa
(þ133 to þ200 mbar, þ100 to þ150 mmHg, þ3.94 to þ5.91
inHg)]
3. Cover port
VDby hand.
4. Blow air in port
VCand check that it flows freely out of port
VB.
SEF044U
SEF312N
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEMKA
EC-19
Page 173 of 1659

Description
This system returns blow-by gas to the intake manifold collector.
The positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve is provided to
conduct crankcase blow-by gas to the intake manifold.
During partial throttle operation of the engine, the intake mani-
fold sucks the blow-by gas through the PCV valve.
Normally, the capacity of the valve is sufficient to handle any
blow-by and a small amount of ventilating air.
The ventilating air is then drawn from the air duct into the crank-
case. In this process the air passes through the hose connect-
ing air inlet tubes to the rocker cover.
Under full-throttle condition, the manifold vacuum is insufficient
to draw the blow-by flow through the valve. The flow goes
through the hose connection in the reverse direction.
On vehicles with an excessively high blow-by, the valve does not
meet the requirement. This is because some of the flow will go
through the hose connection to the intake collector under all
conditions.
Inspection
PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) VALVE
With engine running at idle, remove PCV valve from breather
separator. A properly working valve makes a hissing noise as air
passes through it. A strong vacuum should be felt immediately
when a finger is placed over the valve inlet.
PCV HOSE
1. Check hoses and hose connections for leaks.
2. Disconnect all hoses and clean with compressed air. If any
hose cannot be freed of obstructions, replace.
SEF156E
SEF559A
SEC137A
ET277
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATIONKA
EC-21