lock NISSAN PULSAR 1987 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 1987, Model line: PULSAR, Model: NISSAN PULSAR 1987Pages: 238, PDF Size: 28.91 MB
Page 4 of 238
FRONT SUSPENSION............................ 156
Specifications......................................................... 156
Front suspension tr ouble shooting ........................ 156
Description ............................................................ 157
Steering knuckle.................................................... 157
Suspension unit..................................................... 159
Control arm ........................................................... 161
Stabiliser bar ........................................................ 162
Suspension and steering angles .......................... 163
REAR SUSPENSION................................ 164
Specifications ........................................................ 164
Rear suspension tr ouble shooting ........................ 164
Description ............................................................ 165
Rear hub ............................................................... 166
Suspension unit .................................................... 167
Control arm ........................................................... 169
Knuckle assembly.................................................. 170
Stabiliser bar ........................................................ 170
Rear wheel alignment ........................................... 171
BRAKES...................................................... 172
Specifications......................................................... 172
Brakes trouble shooting ........................................ 172
Description ............................................................ 174
Master cyli nder...................................................... 175
Brake servo unit .................................................... 177
Front brakes ......................................................... 178
Rear disc brakes................................................... 181
Rear drum brakes ................................................. 184
Handbrake cable and le ver assembly ................... 186
Brake adjustments ................................................ 187
Brake pedal ........................................................... 187
Hydraulic system................................................... 188
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM............................ 190
Specifications......................................................... 190
Battery and charging system trouble shooting ....... 190
Battery and starting system trouble shooting ........ 191
Lighting system trouble shooting ........................... 192
Turn signal lamp trouble shooting ........................ 192
Test equipment and so me applications................. 193
Battery ................................................................... 194
Alternator ............................................................... 196
Starter motor ......................................................... 201
Ignition system ...................................................... 206
Steering wheel ....................................................... 206
Switches and controls........................................... 206
Instrument cluster.................................................. 209
Blower fan .............................................................. 209
Radio/cassette...................................................... 209
lamp units ............................................................ 210
Windscreen wiper ................................................. 213
Fuses, fusible links and relays ............................. 215
Trailer wiring ......................................................... 216
Wiring diagrams ................................................... 218
BODY........................................................... 225
Windscreen and re ar glass .................................. 225
Front doors ........................................................... 225
Rear doors............................................................ 228
Engine bonnet...................................................... 231
Tailgate and lock — hatchback ............................ 231
Luggage compartment lid and lock — sedan ........ 233
Radiator grille.............................................................. 234
Centre console...................................................... 234 Dashboard ............................................................ 235
Scat belts ............................................................. 236
Seats .................................................................... 236
Vehicle cleaning ........................................................... 237
CONVERSION TABLES.......................... 238
Page 7 of 238

VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION AND GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
1. VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION
When purchasing spare parts or when
registering
or insuring a vehicle, it may be necessary to quote
various vehicle identification codes. The location of
these codes are as follows: The Engine Number is stamped on the front
face
of the engine block below No. 4 spark plug. The Chassis Number is stamped on the bulkhead
above and to the right of the brake booster. The Vehicle Identification Plate is located on the
bulkhead to the left of the MAP sensor and contains
codings relating to body style, engine capacity,
model,
transaxle type, engine number, paint, trim and build
date. The Compliance Plate contains information on
the vehicle make, model, month and year of manu-
facture, chassis number, seating, capacity and the
Australian Design Rules (ADR) with which the vehi-
cle complies. This plate is affixed to the bulkhead
above and to the left of the brake booster. The Tire Placard, which is located on the inside
of the glove compartment, contains information
on
the tire size, rim size, tire pressure and load ratings.
2. GENERAL VEHICLE SPECIFICATIONS
Length:
Pulsar ................................................... 4 030 mm
Astra hatchback .................................. 4 035 mm
Vector ..................................................4215 mm
Astra sedan.......................................... 4 255 mm
Width:
Nissan.................................................. 1 640 mm
Holden ................................................. 1 655 mm
Height ........................................................ 1 380 mm
Wheelbase .................................................. 2 430 mm
Wheel track:
Front .................................................... 1 435 mm
Rear ..................................................... I 430 mm
View of the engine compartment showing the location
of various vehicle identification information.
Minimum ground clearance:
Nissan.................................................... 128 mm
Holden ................................................... 110 mm
Turning circle kerb to kerb .......................... 10.8 m
Fuel tank capacity:
Nissan.................................................... 47 liters
Holden ................................................... 50 liters
Towing capacity:
Without trailer brakes............................ 400 kg
With trailer brakes ................................. 900 kg
*Fuel consumption:
L/100km L/100km
(City) (Highway)
Manual transaxle 8.5 6.6
Automatic transaxle 9.0 7.2
*The fuel consumption information is based on
tests made according to Australian Standard 2877.
The actual fuel consumption will depend on many
factors including driving habits, vehicle condition
and equipment and the prevailing conditions.
Page 10 of 238

10 General Information
If tools are to be stored for any length of time, it is
good policy to wipe them with an oily cloth.
Bladed screwdrivers should be checked for dam-
age to the tip. If necessary, the tip can be returned to
its original profile by careful grinding. Do not grind
screwdriver tips to a sharp point.
Hammer heads should be secure on their handles
and should be regularly checked for cracking or other
damage.
Chisels and punches should be checked for dam-
age or 'mushrooming' of the head. Any faults should
be rectified by grinding.
Hydraulic jacks should be regularly checked for
fluid leaks. Chassis stands and car ramps should be
checked for damage and cracks. Any equipment that
is suspect should not be used.
STORES
For routine maintenance, stores of automotive
oils, greases and additives should be kept on hand.
The following is a suggested list.
Engine oil.
Brake fluid.
Manual transmission or automatic transmission
oil — automatic transmission oil is also used in
the power steering system.
Rear axle oil.
Cooling system corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze.
Chassis grease.
High melting point grease, for hub bearings etc.
Penetrating oil or spray.
Kerosene or similar cleaning solvent.
Methylated spirits.
Oils and greases are available in handy pack size for
do-it-yourself lube jobs.
2. SAFETY
PERSONAL SAFETY
Safety when working on a motor vehicle is basical-
ly a matter of commonsense. Some safety precautions
to prevent personal in juries are as follows.
Raising a Vehicle
Always jack a vehicle on firm, level ground and at
the specified jacking points . Ensure that the wheels
remaining on the ground are fully chocked.
After raising the vehicle, place chassis stands
underneath and allow the weight of the vehicle to rest
on them. Do not use bricks, blocks of wood or similar
material.
NOTE: Never work under a vehicle which is
only supported by a jack.
Electrical System
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal
when working on any electrical components. Avoid
wearing metal watches, rings and chains which may
short across live terminals.
As battery gases are explosive, keep naked flames
and sparks clear of the work area. When connecting
and disconnecting jumper leads, use extreme caution
to avoid sparking.
Electronic Ignition Systems
Electronic ignition systems produce dangerous
high tension voltages in bo th the primary and second-
ary circuits which can be fatal. Exercise extreme
caution when working on or near any ignition system
components. Do not disconnect high tension leads
while the engine is running.
Work Area
Do not run the engine in a confined space. Ensure
that the work area is adequately ventilated.
Spilt oil or water should be cleaned immediately
to avoid the possibility of slipping.
Fuel System
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal
when working on any fuel components. Do not smoke.
Keep naked flames and sparks clear of the work area.
Do not siphon fuel using the mouth. Use a hand
pump or suitable siphon.
Do not attempt to repair a fuel tank by welding it.
This is an extremely hazardous procedure and should
be entrusted to a specialist.
Cooling System
To avoid scalding, use caution when releasing the
radiator cap on an engine wh ich is at normal operating
temperature. Turn the cap anti-clockwise to the first
stop and allow any pressure in the system to release.
When the pressure is released, remove the cap from
the radiator.
Brakes
As asbestos is used in some brake lining material,
avoid inhaling brake dust. Do not use compressed air
to remove the dust. Gentle brushing with a small
brush or using a vacuum cleaner with a hose attach-
ment are the safest methods of cleaning the brakes.
The above precautions also apply to the clutch plate
lining material.
Page 12 of 238
12 General Information
Damaged threads can be repaired using a die nut
on studs and bolts, and a tap on nuts and threaded
holes in castings. If the threads of a threaded hole are
damaged beyond repair, it will be necessary to drill
and tap the hole to a larger size. Alternatively, a
Helicoil insert can be used to Testore the hole to the
original thread size.
STUDS
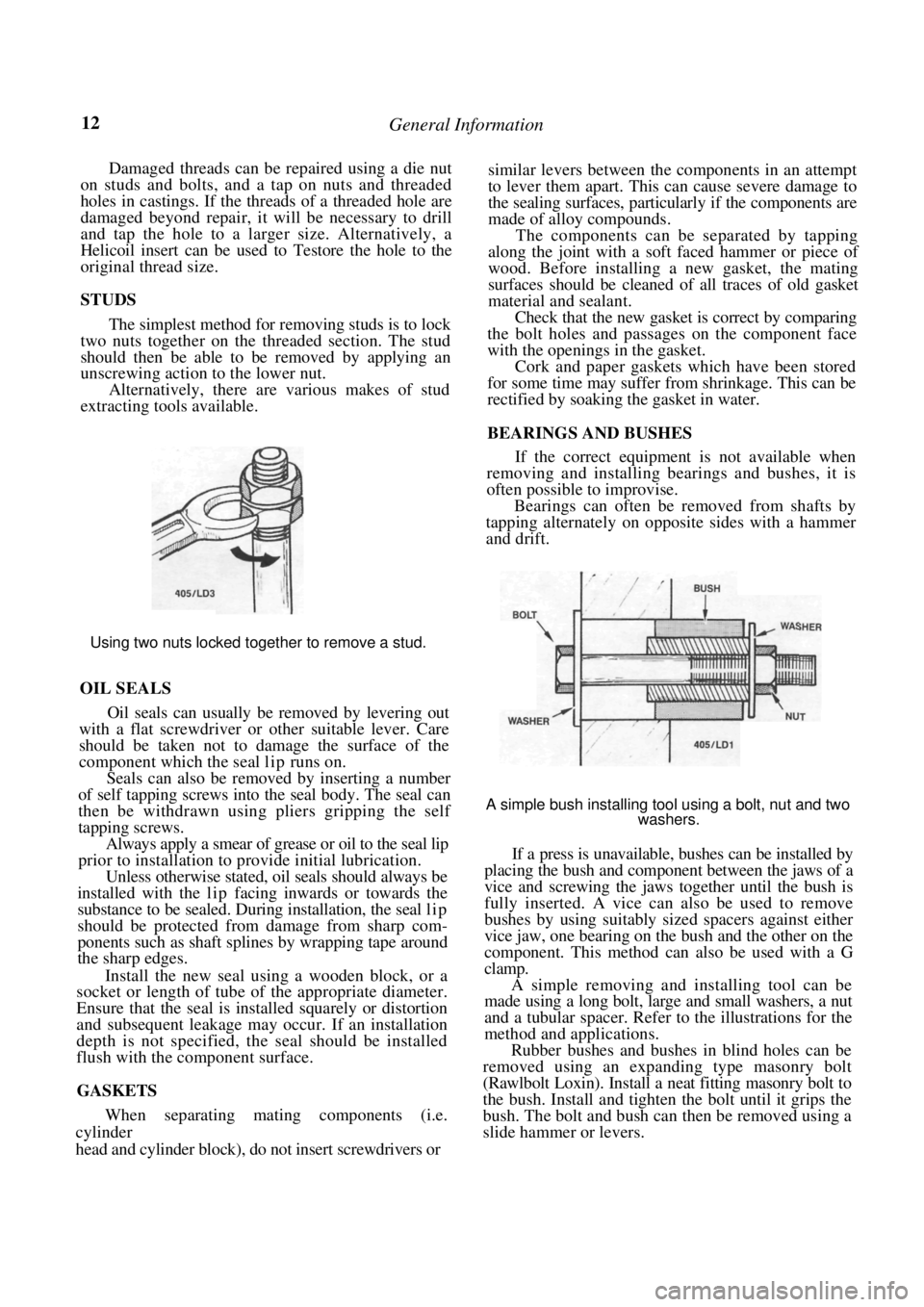
The simplest method for removing studs is to lock
two nuts together on the threaded section. The stud
should then be able to be removed by applying an
unscrewing action to the lower nut.
Alternatively, there are various makes of stud
extracting tools available.
Using two nuts locked together to remove a stud.
OIL SEALS
Oil seals can usually be removed by levering out
with a flat screwdriver or other suitable lever. Care
should be taken not to damage the surface of the
component which the seal lip runs on.
Seals can also be removed by inserting a number
of self tapping screws into the seal body. The seal can
then be withdrawn using pliers gripping the self
tapping screws.
Always apply a smear of grease or oil to the seal lip
prior to installation to provide initial lubrication.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals should always be
installed with the lip facing inwards or towards the
substance to be sealed. Duri ng installation, the seal l i p
should be protected from damage from sharp com-
ponents such as shaft splines by wrapping tape around
the sharp edges.
Install the new seal using a wooden block, or a
socket or length of tube of the appropriate diameter.
Ensure that the seal is installed squarely or distortion
and subsequent leakage may occur. If an installation
depth is not specified, th e seal should be installed
flush with the component surface.
GASKETS
When separating mating components (i.e.
cylinder
head and cylinder block), do not insert screwdrivers or
similar levers between the components in an attempt
to lever them apart. This can cause severe damage to
the sealing surfaces, particularly if the components are
made of alloy compounds.
The components can be separated by tapping
along the joint with a soft faced hammer or piece of
wood. Before installing a new gasket, the mating
surfaces should be cleaned of all traces of old gasket
material and sealant.
Check that the new gasket is correct by comparing
the bolt holes and passages on the component face
with the openings in the gasket.
Cork and paper gaskets which have been stored
for some time may suffer from shrinkage. This can be
rectified by soaking the gasket in water.
BEARINGS AND BUSHES
If the correct equipment is not available when
removing and installing bearings and bushes, it is
often possible to improvise.
Bearings can often be removed from shafts by
tapping alternately on opposite sides with a hammer
and drift.
A simple bush installing tool using a bolt, nut and two
washers.
If a press is unavailable, bushes can be installed by
placing the bush and component between the jaws of a
vice and screwing the jaws together until the bush is
fully inserted. A vice can also be used to remove
bushes by using suitably sized spacers against either
vice jaw, one bearing on the bush and the other on the
component. This method can also be used with a G
clamp.
A simple removing and installing tool can be
made using a long bolt, large and small washers, a nut
and a tubular spacer. Refer to the illustrations for the
method and applications.
Rubber bushes and bushes in blind holes can be
removed using an expanding type masonry bolt
(Rawlbolt Loxin). Install a neat fitting masonry bolt to
the bush. Install and tighten the bolt until it grips the
bush. The bolt and bush can then be removed using a
slide hammer or levers.
Page 25 of 238

25
ENGINE TUNE-UP
CAUTION: To prevent severe electrical shock, extreme care must be taken when
working on or near the electronic ignition system as dangerous high tension voltages
are produced in both the primary and secondary circuits. See the text fo\
r
precautionary notes.
1. TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS
Firing orde r................................................... 1 -3-4-2
Spark plugs:
Type .............................................NGK BPR 6ES
Gap ........................................................... 1.1 mm
Tightening torque...................................... 20 Nm
Ignition timing with diagnostic link
connector jumped........................... 10 deg BTDC
Idle speed (ECU controlled):
Manual transaxle 1.8 liter ............ 850 ± 50 rpm
Manual transaxle 1.6 liter............800 ± 50 rpm
Automatic transaxle
(Park or Neutral).......................... 825 ± 50 rpm
Drive belt deflection:
Alternator ........................................... 14-16 mm
Power steering pump ......................... 14-16 mm
Air conditioner compressor .................. 9-11 mm
NOTE: When performing an engine tune-
up, a/ways compare the above Specifications
with the emission control information label
inside the engine compartment.
2. TUNE-UP OPERATIONS
Special Equipment Required:
To Test Compression — Compression gauge
TO SERVICE AIR CLEANER
The air cleaner is equipped with a paper element.
The element should be regu larly inspected but should
not be cleaned in service.
The element should be renewed every 40 000 km.
This distance is only a guide for normal operating
conditions and should be reduced accordingly if the
vehicle is operating under ex tremely dusty conditions.
NOTE: Paper air cleaner elements should
not be washed in petrol or any other type of
cleaning solvent. If the element has been
washed in solvent or has become oil soaked,
it should be discarded and a new element
installed.
1.8 Liter Engine
(1) Release the clamp securing the air intake
hose to the throttle body and disconnect the throttle
cable from the support bracket. (2) Release the clips reta ining the upper air
cleaner housing to the lowe r air cleaner housing and
raise the upper housing while disconnecting the air
intake hose from the throttle body. Remove the air
cleaner element.
The air cleaner element should be renewed at 40 000
km intervals. 1.8 liter engine.
(3) Clean the inside of the air cleaner housing
using a damp rag to remove all traces of dust and
check the upper housing and air inlet hose for cracks
and air leaks. Renew if necessary. (4) Install a new air cleaner element to the lower
housing ensuring that the element is correctly seated
around the edges. (5) Install the upper housing and lock the clips,
securing it to the lower housing. Connect the air
intake hose to the throttle body and the throttle cable
to the support bracket. Tighten the hose clamp
securely. (6) Start the engine and check the air cleaner
assembly for air leaks.
Page 28 of 238
Engine Tune-up
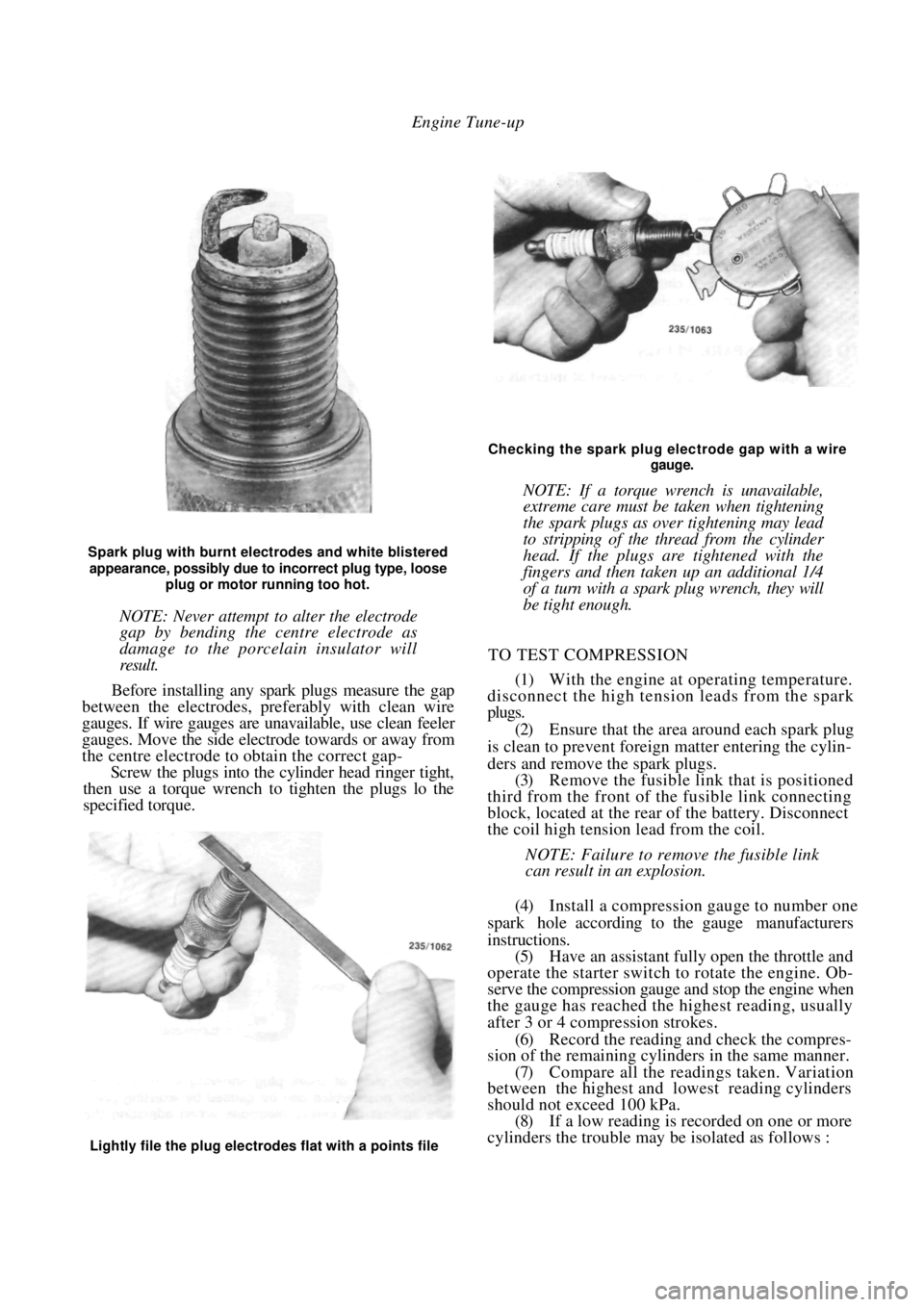
Spark plug with burnt electrodes and white blistered
appearance, possibly due to incorrect plug type, loose
plug or motor running too hot.
NOTE: Never attempt to alter the electrode
gap by bending the centre electrode as
damage to the porcelain insulator will
result.
Before installing any spark plugs measure the gap
between the electrodes, pref erably with clean wire
gauges. If wire gauges are una vailable, use clean feeler
gauges. Move the side electrode towards or away from
the centre electrode to obtain the correct gap-
Screw the plugs into the cylinder head ringer tight,
then use a torque wrench to tighten the plugs lo the
specified torque.
Checking the spark plug electrode gap with a wire
gauge.
NOTE: If a torque wrench is unavailable,
extreme care must be taken when tightening
the spark plugs as over tightening may lead
to stripping of the thread from the cylinder
head. If the plugs are tightened with the
fingers and then taken up an additional 1/4
of a turn with a spark plug wrench, they will
be tight enough.
TO TEST COMPRESSION
(1) With the engine at operating temperature.
disconnect the high tension leads from the spark
plugs.
(2) Ensure that the area around each spark plug
is clean to prevent foreign matter entering the cylin-
ders and remove the spark plugs. (3) Remove the fusible link that is positioned
third from the front of th e fusible link connecting
block, located at the rear of the battery. Disconnect
the coil high tension lead from the coil.
NOTE: Failure to remove the fusible link
can result in an explosion.
(4) Install a compression gauge to number one
spark hole according to the gauge manufacturers
instructions. (5) Have an assistant fully open the throttle and
operate the starter switch to rotate the engine. Ob-
serve the compression gauge and stop the engine when
the gauge has reached the highest reading, usually
after 3 or 4 compression strokes.
(6) Record the reading a nd check the compres-
sion of the remaining cylinders in the same manner.
(7) Compare all the readings taken. Variation
between the highest and lowest reading cylinders
should not exceed 100 kPa. (8) If a low reading is recorded on one or more
cylinders the trouble may be isolated as follows :
Lightly file the plug electrodes flat with a points file
Page 35 of 238

Roadside Trouble Shooting 35
View showing the location of the fuel pump fuse and the EGI and fuel pump relays.
switch. When starting the engine, the fuel
pump will not operate until the oil pressure
is sufficient to extinguish the oil pressure
warning lamp. Therefore it will be necessary
to operate the starter motor for a longer
period than usual to start the engine.
(3) If the fuel pump cannot be felt operating,
check the fuel pump fuse located in the fuse panel
adjacent to the steering column.
If the fuel pump fuse is serviceable, refer to the
Fuel and Engine Management section for detailed
tests on the fuel pump.
(4) Check that all fuel hose connections are
secure.
(5) Remove the spark plugs and check for petrol
saturation of the electrodes which indicates flooding.
Thoroughly clean and dry the spark plugs before
replacement. Fully depress the throttle pedal and turn the
ignition switch to the start position. If the engine does
not start, proceed as follows.
Check that the MAP sensor hose is not blocked or split
and ensure that all electrical connections are clean and
secure.
If flooding persists, refer to the Fuel and Engine
Management section.
(6) Check that all EFI electrical wiring connec-
tors are clean and secure.
(7) Check that the MAP sensor vacuum hose is
securely connected at each end and is not split or
blocked.
4. TO CHECK MECHANICAL SYSTEM
The following check procedure assumes that the
starter motor will rotate the engine. If not, on manual
transaxle models, depress the clutch pedal to disen-
gage the engine from the tr ansaxle in case the fault lies
within the transaxle.
If the starter motor will not rotate the engine, it
will be necessary to remove the starter motor and
attempt to turn the engine over manually. This will
establish whether the fault lies with the starter motor,
which could be jammed or defective, or with the
engine, which could be seized or have broken internal
components such as connecting rods, pistons and
crankshafts etc.
If the starter motor is not at fault and the engine
will not rotate manually, refer to the Engine Mechan-
ical Trouble Shooting heading in the Engine section.
It should be noted that the only way that cylinder
compression can be accurately tested is with a com-
pression gauge. The method described in the following
procedure is only intended to give a rough indication
when checking for causes of engine breakdown,
(I) When the engine is cool, check for loss of
coolant from the cooling system.
If coolant loss is evident, check carefully for any
indication of external leakage. Remove the engine oil
dipstick and check for wate r contamination (emulsi-
fication) of the oil. When oil mixes with water it will
Ensure that all fuel connections are securely tightened.
Page 36 of 238
36 Roadside Trouble Shooting
Check the engine oil for level and dilution on the dipstick.
turn creamy. The oil level will also have increased. If
the oil is emulsified, proceed to operation (5).
(2) Remove the fusible link that is positioned
third from the front of th e fusible link connection
block, located at the rear of the battery. Disconnect
the coil high tension lead from the coil. (3) Remove all of the spark plugs except one.
(4) Have an assistant operate the ignition switch
to rotate the engine and listen to the sound made by
the engine as it is being turned over. Move the spark
plug to a different cylinder and repeat the lest. By performing the same test on all cylinders, a
rough comparison can be made to determine if there
is any loss of compression in any cylinder. This will be
apparent by the different sound made by the engine as
it is being turned over.
Normally, if the compression is satisfactory the
cylinder with the spark plug installed will create a
resistance to the rotating engine.
However, if the compression is low in a particular
cylinder, the engine will tu rn over easily and smoothly
when that spark plug is in place.
(5) If the above checks show a loss of coolant
which is present in the engine oil or on the spark plug,
one or more of the following faults may be the cause:
Blown cylinder head gasket.
Cracked cylinder or cylinder head.
If the compression check showed any weak or
inconsistent compressions, in addition to the above
faults any of the following could also be the cause:
Broken piston{s)
Burnt or broken valve(s).
Provided the previous checks do not indicate an
View showing the location of the fusible links.
internal leakage of coolant, proceed with the follow-
ing:
(6) Remove the distributor cap and, with the aid
of an assistant operating th e starter motor, check that
the rotor arm rotates as the engine turns over. (7) Remove the camshaft hous ing top cover and.
again with an assistant operating the ignition switch,
check that all the valves open and close as the engine
turns over.
If the rotor arm or valves do not operate with
engine rotation, one of the following faults may be the
cause:
Rotor arm does not turn but valves operate:
Distributor drive shaft broken.
Rotor arm and valves do not operate: Broken
camshaft drive belt. Sheare d crankshaft timing gear
drive key. Sheared camshaft liming gear drive dowel.
Provided that all the previous checks have been
performed correctly and the operator is satisfied that
none of the components are at fault, all that remains
is for the ignition and valve timing to be checked. It
should be noted, however, that if loss of valve timing
proves to be the fault, th e cause of this occurrence
must be sought and rectified.
(8) In order to check the valve timing it will be
necessary to remove the distributor cap and the
camshaft housing top cover and turn the engine
clockwise via the crankshaft pulley until No. 1 piston
is at TDC on the compression stroke. In this position
the valves of No. 1 cylinder should be closed, the
valves of No. 4 should be rocking and the distributor
rotor should be pointing to the No. 1 high tension lead
segment in the distributor cap.
Page 37 of 238

37
ENGINE
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
Type........................................................... 4cyl OHC
Models ............................................. 1.6 liter, 1.8 liter
Capacity:
1.6 liter ................................................... 1 598 cc
1.8 liter ................................................... 1 796 cc
Firing order ...................................................... 1 -3-4-2
Bore:
1.6 liter.................................................. 80.0 mm
1.8 liter.................................................. 84.8 mm
Stroke ........................................................... 79.5 mm
Maximum compression pressure
variation between cylinders ......................... 100 kPa
NOTE: Specifications re garding engine tun-
ing arc listed in the Engine Tune-up section.
CYLINDER BLOCK
Type......................................................... 4 cyl in line
Material ........................................................ Cast iron
Bore diameter:
1.6 liter ............... 79. 995-80.065 in three groups
1.8 liter .................84. 755-84.905 in four groups
Bore taper limit ......................................... 0. 013 mm
Bore ovality limit ..................................... 0.013 mm
Block face distortion limit .......................... 0.10 mm
Maximum height of piston above block
face at top dead centre:
1.6 liter.................................................. 0.00 mm
1.8 liter.................................................. 0.50 mm
Bore oversize................................................ 0.50 mm
CYLINDER HEAD
Type........................................... One piece, cross flow
Material ............................................ Aluminum alloy
Distortion limit .......................................... 0.025 mm
Machining li mit ........................................... 0.25 mm
Minimum overall height after machining:
1.6 liter .................................................95.50 mm
1.8 liter .................................................94.80 mm
Valve seat angle ..........................................45 degrees
Valve seat contact width:
Inlet................................................... 1.0-1.5 mm
Exhaust ............................................. 1.7-2.2 mm
Valve stem protrusion ................. 18.4 mm from top
of cylinder head
Valve guide height .......... 12.2-12.5 mm from top of
cylinder head
VALVES AND SPRINGS
Valve length .............................................. 104. 2 mm
Valve head diameter:
1.6 liter —
Inlet........................................................ 36.0 mm
Exhaust .................................................. 32.0 mm
1.8 liter -
Inlet....................................................... 41.8 mm
Exhaust ................................................. 36.5 mm
Valve stem diameter:
Inlet...........................................6. 998-7.012 mm
Exhaust .....................................6.978-6.992 mm
Valve stem to guide clearance:
Inlet...........................................0.018-0.052 mm
Exhaust .....................................0.038-0.072 mm
Oversize valve system availability......... 0.075, 0.150
and 0.250 mm
Valve face angle ......................................... 44 degrees
Valve spring tension:
Valve closed .......................... 300 N at 37.5 mm
Valve open............................. 765 N at 26.5 mm
TAPPETS
Type .............................................................Hydraulic
Operating length ........................................ 63.26 mm
Diameter ....................................... 21.392-21.405mm
Leak down rate ............. 2-10 sec onds for 3.175 mm
PISTONS AND GUDGEON PINS
Piston type ....................................... Aluminum alloy
Diameter:
1.6 liter ........ 79. 955-80.035 mm in 8 categories
in increments of 0.01 mm
1.8 liter .......84.725-84.885 mm in 16 categories
in increments of 0.01 mm
Page 41 of 238

Engine 41
DROP IN OIL PRESSURE
(1) Oil level low in the sump: Check and replen-
ish the oil to the full mark on the dipstick.
(2) Thin or diluted oil: Change to the correct oil
grade and rectify the source of dilution. (3) Oil pump relief valve stuck or spring broken;
Free up the relief valve or renew the broken relief
valve spring. (4) Excessive bearing clearance: Renew the bear-
ing shells or recondition the crankshaft journals as
necessary.
(5) Excessive wear of the oil pump components:
Renew or recondition the oil pump.
NOTE: If the vehicle is not equipped with an
oil pressure gauge re move the oil sender unit
and connect a pressure gauge into the oil
gallery. Check the oil pressure with the
engine cold and hot. If the oil pump or relief
valve are faulty. low pressure will be indi-
cated with the engine both hot and cold.
However, if the bearings are at fault a fairly
high oil pressure will be indicated when the
engine is cold, but a marked drop in pressure
will occur when the engine is hot.
ENGINE WILL NOT ROTATE
(1) Starter motor drive jammed: Remove the
starter motor. Check and renew the damaged drive
and/or flywheel ring gear.
(2) Engine overheated an d seized: Remove and
dismantle the engine. Check and renew any damaged
components. See the following note.
(3) Water in the cylinder due to a blown head
gasket or cracked cylinder block or head: Remove the
cylinder head. If the gasket is blown, check for
cylinder block and head distortion and reface if
necessary. Renew the cylinder head and/or cylinder
block if cracked.
(4) Broken crankshaft, connecting rod. piston
etc. due to overheating, fatigue etc: Remove and
dismantle the engine. Examine and renew any com-
ponents as necessary. (5) Valve head broken off due to overheating,
fatigue etc: Remove the cylinder head and check the
head, piston and cylinder bore for damage. Repair or
renew as necessary.
NOTE: Invariably when an engine seizes
because of overheating due to lack of oil
and/or water, damage is done to the bear-
ings, pistons etc. Although there may be
instances where an engine will start and run
after it has cooled down and the oil and
water have been replenished, it will usually
be found that oil consumption increases, oil
pressure decreases and the engine will be
noisier, depending on the degree of damage.
When a cylinder head gasket blows allow-
ing water into the cylinders, or compression
loss between the cylinders, it is essential to
check the gasket faces on the cylinder block
and head for distortion. Sufficient water can
enter a cylinder because of a blown head
gasket, cracked cylinder or head to prevent
an engine from rotating.
This is normally preceded by difficult
starting, misfiring, excessive steam from the
exhaust and loss of water from the radiator.
Frequent jamming of the starter motor
drive with the flywheel ring gear can be due
to a bent starter armature shaft or damaged
teeth on the drive and/or ring gear. With the
starter motor removed, the flywheel ring
gear teeth can be examined through the
starter motor mounting aperture. Renewal
of the ring gear requires removal of the
transaxle, clutch and flywheel on manual
transaxle models and the removal of the
transaxle and drive plate on automatic
transaxle models. To check for a bent arma-
ture shaft, rotate the shaft by hand while
holding the end in close proximity to a fixed
object.
2. DESCRIPTION
The 1.6 and 1.8 liter engines are basically identi-
cal in design.
Both engines share the same stroke. The 1.8 liter
engine has a larger bore thus giving it increased
capacity.
The engine is a four cylinder, inline, overhead
camshaft design transversely mounted in the front of
the vehicle.
The camshaft runs in five integral support bear-
ings in the camshaft housing which in turn is mounted
directly on to the cylinder head and retained by the
cylinder head bolts.
Camshaft end float is controlled by a retaining
plate engaged in a groove machined in the rear
camshaft journal. The camshaft is driven by the
crankshaft timing gear vi a a reinforced rubber belt.
The aluminum cross flow cylinder head houses
the tappets, rocker arms a nd valve assemblies. An oil
pressure relief valve is installed to the cylinder head to
maintain oil pressure to the hydraulic tappets at a
predetermined setting.
The exhaust valve springs are equipped with
rotators mounted below the valve springs which rotate
the exhaust valve assemblies. The rocker arms pivot
on hydraulic tappet assemblies and locate in notched
lash pads mounted on the valve stems. The camshaft
lobes bear directly onto the rocker arms and due to
the characteristics of the hydraulic tappet assemblies,
no provision is made for tappet clearance adjustment.