wiring diagram NISSAN TIIDA 2007 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2007, Model line: TIIDA, Model: NISSAN TIIDA 2007Pages: 5883, PDF Size: 78.95 MB
Page 3208 of 5883
GI-14
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
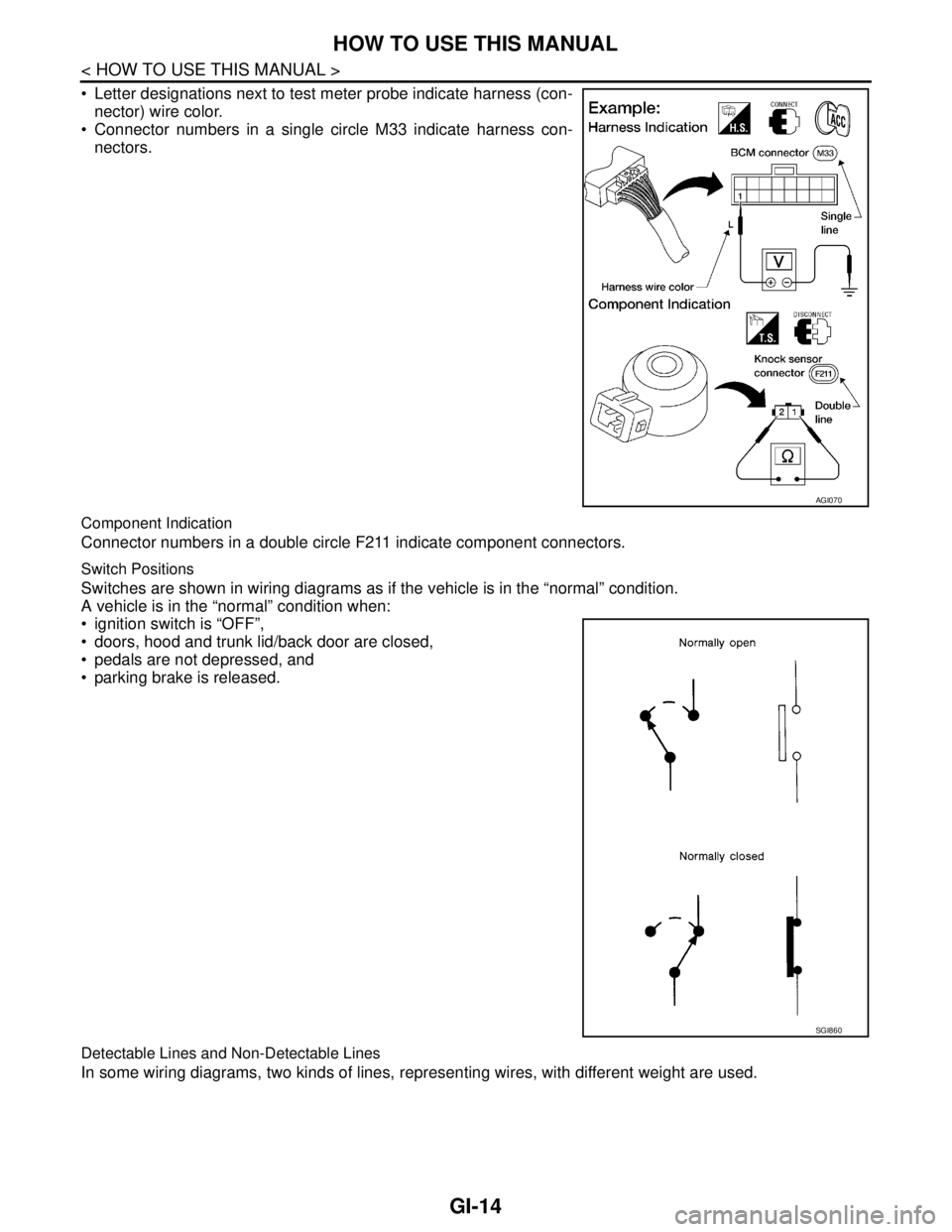
Letter designations next to test meter probe indicate harness (con-
nector) wire color.
Connector numbers in a single circle M33 indicate harness con-
nectors.
Component Indication
Connector numbers in a double circle F211 indicate component connectors.
Switch Positions
Switches are shown in wiring diagrams as if the vehicle is in the “normal” condition.
A vehicle is in the “normal” condition when:
ignition switch is “OFF”,
doors, hood and trunk lid/back door are closed,
pedals are not depressed, and
parking brake is released.
Detectable Lines and Non-Detectable Lines
In some wiring diagrams, two kinds of lines, representing wires, with different weight are used.
AGI070
SGI860
Page 3209 of 5883
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
GI-15
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
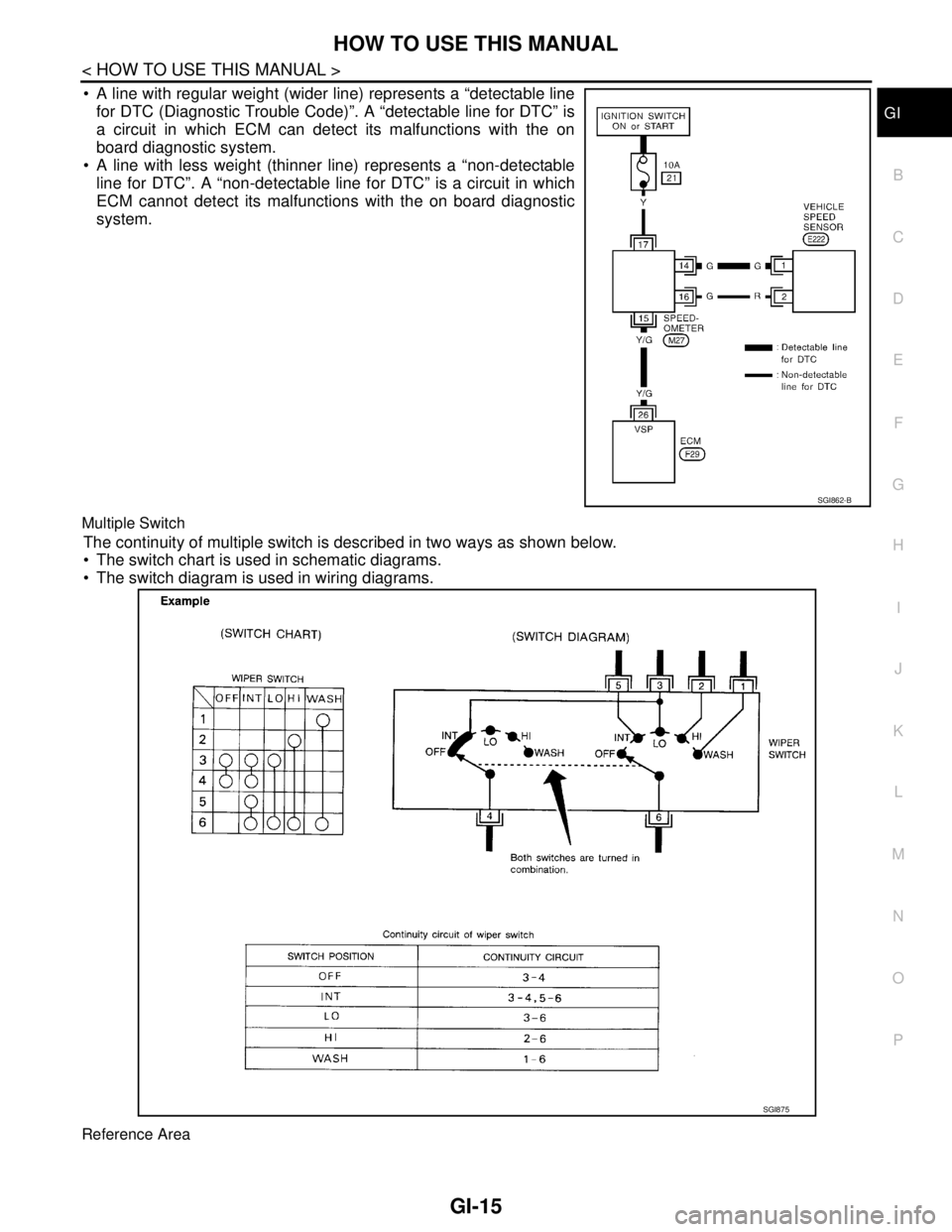
A line with regular weight (wider line) represents a “detectable line
for DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code)”. A “detectable line for DTC” is
a circuit in which ECM can detect its malfunctions with the on
board diagnostic system.
A line with less weight (thinner line) represents a “non-detectable
line for DTC”. A “non-detectable line for DTC” is a circuit in which
ECM cannot detect its malfunctions with the on board diagnostic
system.
Multiple Switch
The continuity of multiple switch is described in two ways as shown below.
The switch chart is used in schematic diagrams.
The switch diagram is used in wiring diagrams.
Reference Area
SGI862-B
SGI875
Page 3210 of 5883
GI-16
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
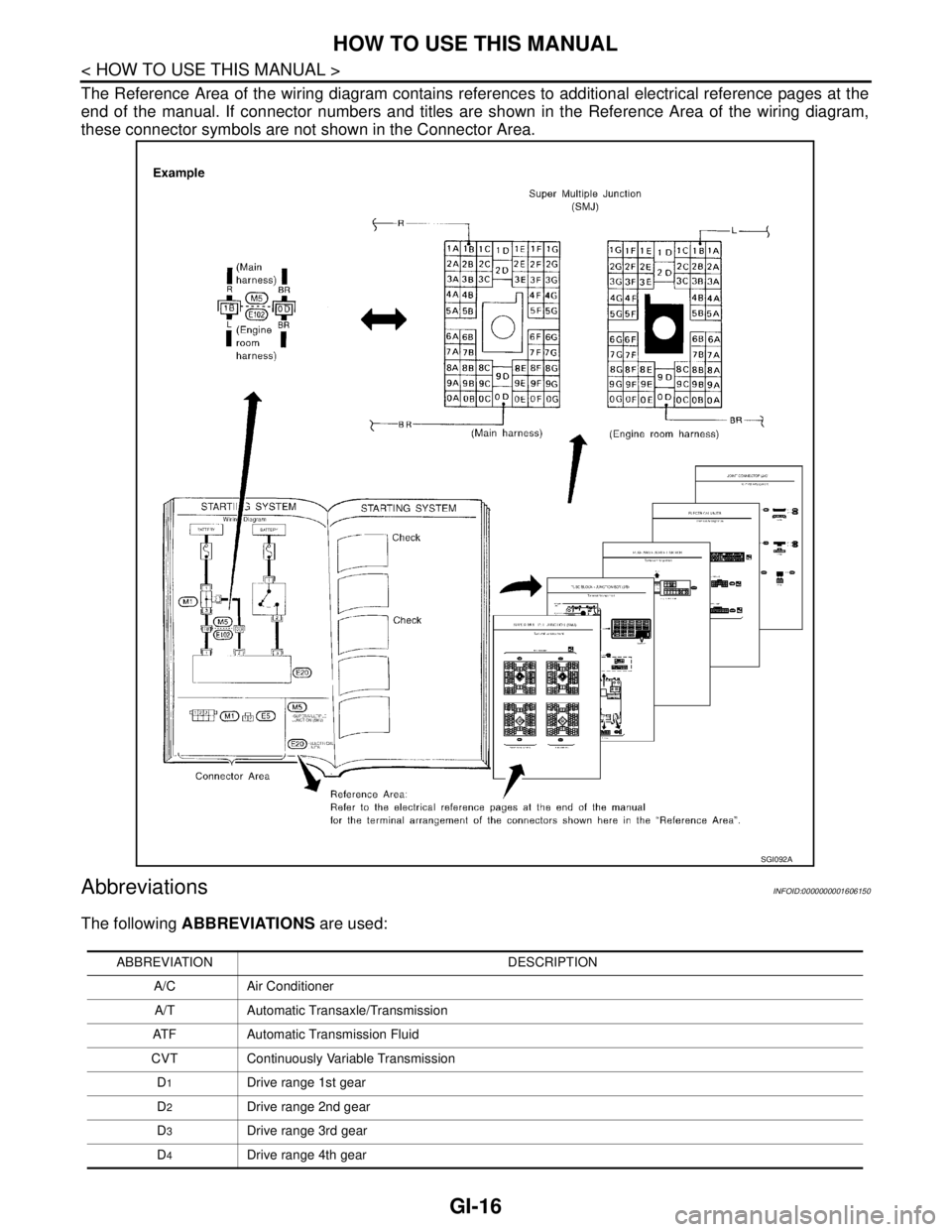
The Reference Area of the wiring diagram contains references to additional electrical reference pages at the
end of the manual. If connector numbers and titles are shown in the Reference Area of the wiring diagram,
these connector symbols are not shown in the Connector Area.
AbbreviationsINFOID:0000000001606150
The following ABBREVIATIONS are used:
SGI092A
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
A/C Air Conditioner
A/T Automatic Transaxle/Transmission
ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid
CVT Continuously Variable Transmission
D
1Drive range 1st gear
D
2Drive range 2nd gear
D
3Drive range 3rd gear
D
4Drive range 4th gear
Page 3212 of 5883

GI-18
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
HOW TO FOLLOW TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
HOW TO FOLLOW TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001691457
NOTICE:
Trouble diagnoses indicate work procedures required to diagnose problems effectively. Observe the following
instructions before diagnosing.
Before performing trouble diagnoses, read the “Work Flow” in each section.
After repairs, re-check that the problem has been completely eliminated.
Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Location for the Systems described in each section for
identification/location of components and harness connectors.
When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should be OFF.
Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness connectors in more detail, such as when a sub-har-
ness is used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section and Harness Layout in PG section for identi-
fication of harness connectors.
Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery voltage.
After accomplishing the Diagnosis Procedures and Electrical Components Inspection, make sure that all
harness connectors are reconnected as they were.
How to Follow Test Groups in Trouble DiagnosisINFOID:0000000001691458
1. Test group number and test group title
Test group number and test group title are shown in the upper portion of each test group.
2. Work and diagnosis procedure
Start to diagnose a problem using procedures indicated in enclosed test groups.
3. Questions and results
Questions and required results are indicated in test group.
4. Action
Next action for each test group is indicated based on result of each question.
JPAIA0021GB
Page 3215 of 5883
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
GI-21
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PHOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Connector symbolsINFOID:0000000001691460
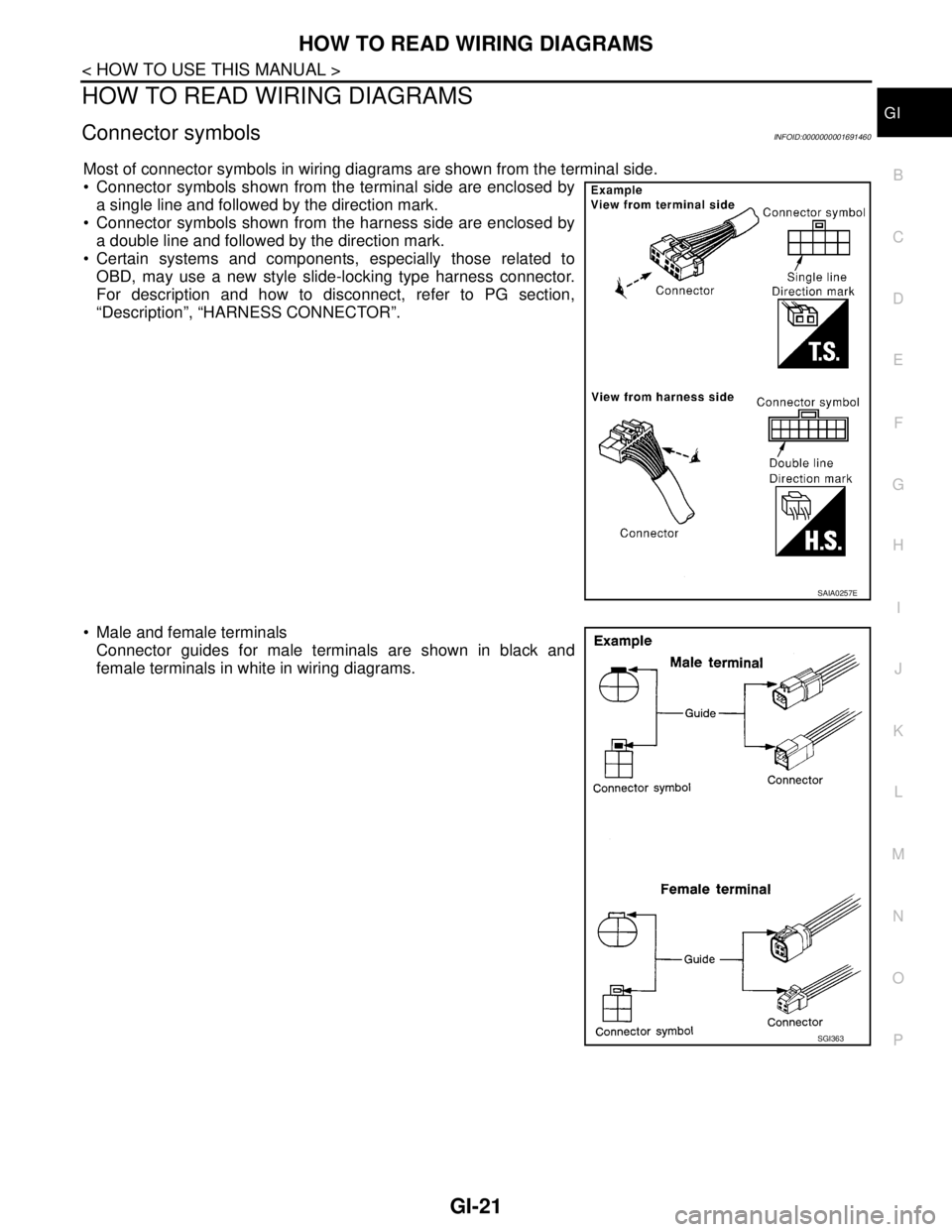
Most of connector symbols in wiring diagrams are shown from the terminal side.
Connector symbols shown from the terminal side are enclosed by
a single line and followed by the direction mark.
Connector symbols shown from the harness side are enclosed by
a double line and followed by the direction mark.
Certain systems and components, especially those related to
OBD, may use a new style slide-locking type harness connector.
For description and how to disconnect, refer to PG section,
“Description”, “HARNESS CONNECTOR”.
Male and female terminals
Connector guides for male terminals are shown in black and
female terminals in white in wiring diagrams.
SAIA0257E
SGI363
Page 3216 of 5883
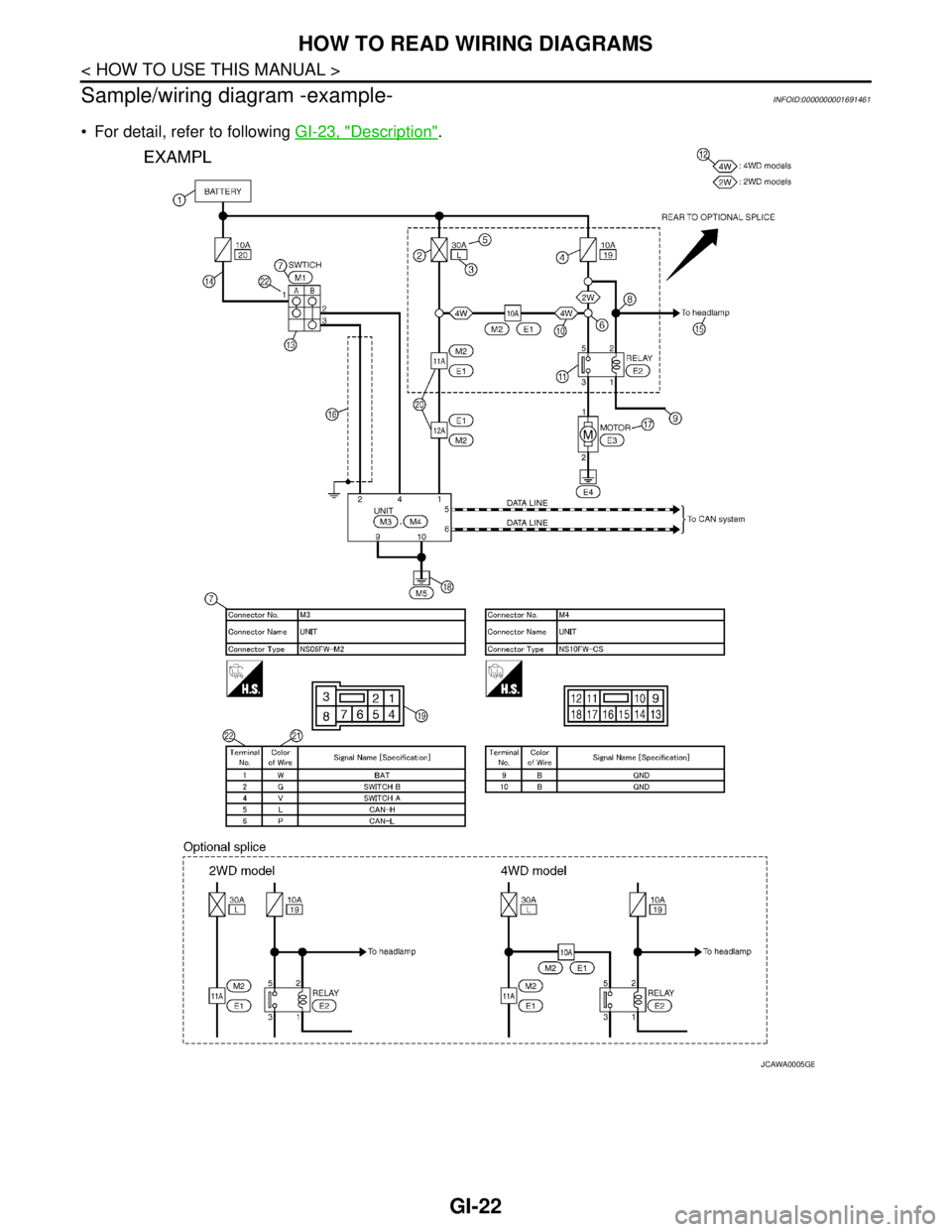
GI-22
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
Sample/wiring diagram -example-
INFOID:0000000001691461
For detail, refer to following GI-23, "Description".
JCAWA0005GB
Page 3217 of 5883

HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
GI-23
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001691462
SWITCH POSITIONS
Switches are shown in wiring diagrams as if the vehicle is in the “normal” condition.
A vehicle is in the “normal” condition when:
Number Item Description
1 Power supply This means the power supply of fusible link or fuse.
2 Fusible link “X” means the fusible link.
3Number of fusible link/
fuse This means the number of fusible link or fuse location.
4 Fuse “/” means the fuse.
5Current rating of fus-
ible link/fuse This means the current rating of the fusible link or fuse.
6 Optional splice The open circle shows that the splice is optional depending on vehicle application.
7 Connector number The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
Example “M”: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to ELECTRICAL
UNIT LOCATION in PG, HARNESS LAYOUT in PG.
8Splice
The shaded circle “ ” means the splice.
9 Page crossing This circuit continues to an adjacent page.
10 Option abbreviation
This means the vehicle specifications which layouts the circuit between “ ”.
11 Relay This shows an internal representation of the relay.
12 Option description This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
13 Switch This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A
position. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
14 Circuit (Wiring) This means the wiring.
15 System branch This shows that the circuit is branched to other systems.
16 Shielded line The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
17 Component name This shows the name of a component.
18 Ground (GND) This shows the ground connection.
19 Connector This means the connector information.
This unit-side is described by the connector symbols.
20 Connectors This means that a transmission line bypasses two connectors or more.
21 Wire color This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light GreenBR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as
shown below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
22 Terminal number This means the terminal number of a connector.
Page 3218 of 5883
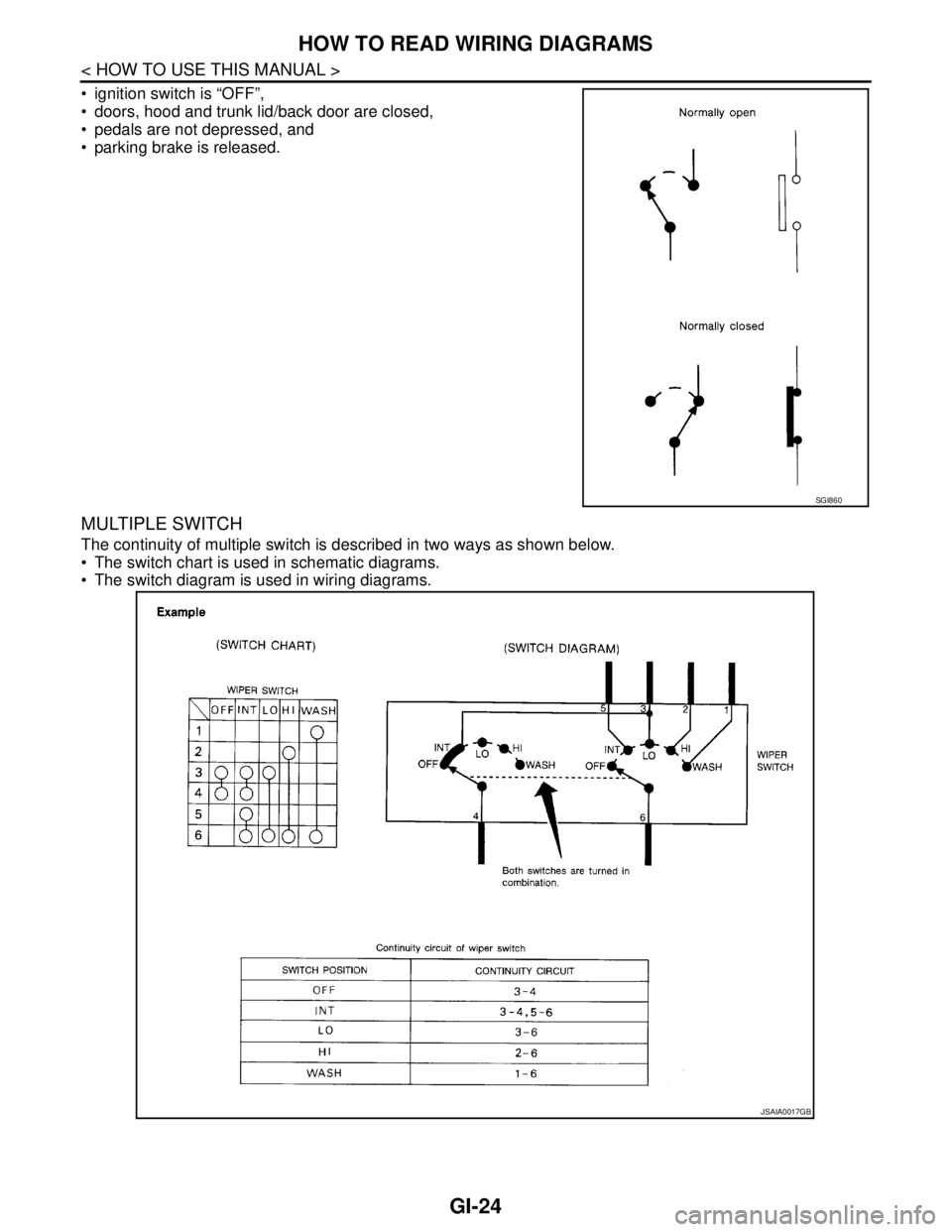
GI-24
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS
ignition switch is “OFF”,
doors, hood and trunk lid/back door are closed,
pedals are not depressed, and
parking brake is released.
MULTIPLE SWITCH
The continuity of multiple switch is described in two ways as shown below.
The switch chart is used in schematic diagrams.
The switch diagram is used in wiring diagrams.
SGI860
JSAIA0017GB
Page 3250 of 5883
GI-56
< BASIC INSPECTION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics: Vehicle vibration
Heat sensitive
Freezing
Water intrusion
Electrical load
Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
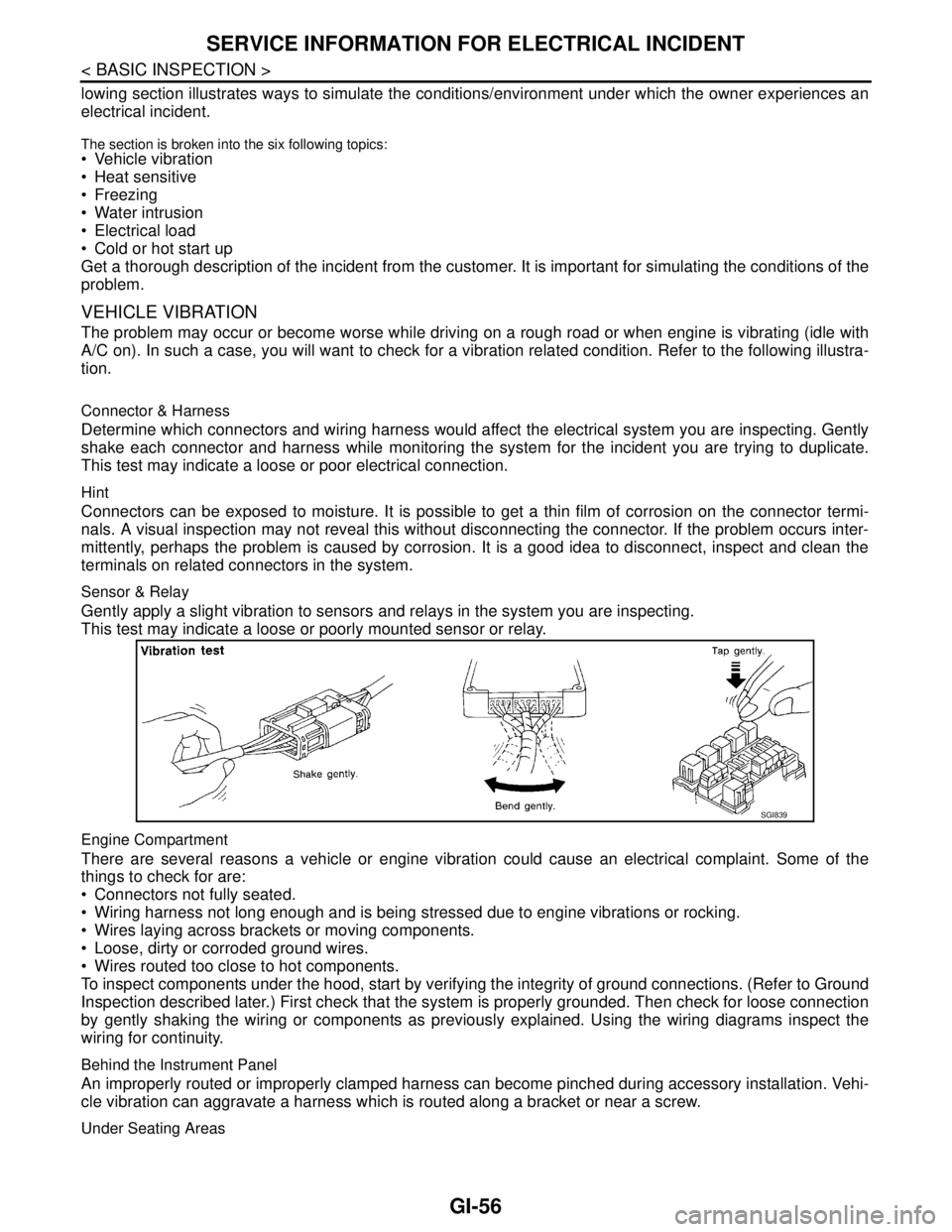
VEHICLE VIBRATION
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
Connector & Harness
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
Hint
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
Sensor & Relay
Gently apply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
Engine Compartment
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could cause an electrical complaint. Some of the
things to check for are:
Connectors not fully seated.
Wiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to engine vibrations or rocking.
Wires laying across brackets or moving components.
Loose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
Wires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integrity of ground connections. (Refer to Ground
Inspection described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded. Then check for loose connection
by gently shaking the wiring or components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams inspect the
wiring for continuity.
Behind the Instrument Panel
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become pinched during accessory installation. Vehi-
cle vibration can aggravate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
Under Seating Areas
SGI839
Page 3258 of 5883

GI-64
< BASIC INSPECTION >
CONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
*1: With Intelligent Key System.
*2: With automatic transmission.
*3: Without Intelligent Key System.
CONSULT-III Data Link Connector (DLC) CircuitINFOID:0000000001691474
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
If the CONSULT-III cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
NOTE:
The CAN and DDL2 circuits from DLC pins 6, 7 and 14 may be connected to more than one system. A short in
any circuit connected to a control unit in one system may affect CONSULT-III access to other systems.
Symptom Check item
CONSULT-III cannot access
any system. CONSULT-III DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 8) and ground circuit (Terminal 4)
CONSULT-III cannot access in-
dividual system. (Other sys-
tems can be accessed.) Power supply and ground circuit for the control unit of the system (For detailed circuit, refer to wiring
diagram for each system.)
Open or short circuit between the system and CONSULT-III DLC (For detailed circuit, refer to wiring
diagram for each system.)
Open or short circuit CAN communication line. Refer to LAN-22, "
Trouble Diagnosis Flow Chart".