page 48 Oldsmobile Alero 2003 s Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OLDSMOBILE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: Alero, Model: Oldsmobile Alero 2003Pages: 354, PDF Size: 16.74 MB
Page 253 of 354

Brakes
Brake Fluid
Your brake master cylinder reservoir is on the driver’s
side
of the engine compartment. It is filled with
DOT-3 brake fluid. See
Engine Compartment Overview
on page 5- 72.
There are only two reasons why the brake fluid level in
the reservoir might go down. The first is that the
brake fluid goes down to an acceptable level during
normal brake lining wear. When new linings are put in,
the fluid level goes back up. The other reason is
that fluid
is leaking out of the brake system. If it is, you
should have your brake system fixed, since a leak
means that sooner or later your brakes won’t work well,
or won’t work at all.
So, it isn’t a good idea to “top off your brake fluid.
Adding brake fluid won’t correct a leak.
If you add fluid
when your linings are worn, then you’ll have too
much fluid when you get new brake linings. You should
add (or remove) brake fluid, as necessary, only when
work is done on the brake hydraulic system.
If you have too much brake fluid, it can spill on
the engine. The fluid will burn if the engine is
hot enough. You or others could be burned,
and your vehicle could be damaged. Add brake
fluid only when work
is done on the brake
hydraulic system.
5-38
Page 254 of 354

BRAKE
I I
United States
I I
Canada
When your brake fluid falls
to a low level, your brake
warning light will come on. See
Brake System Warning
Light on page
3-28.
What to Add
When you do need brake fluid, use only DOT-3 brake
fluid. Use new brake fluid from a sealed container
only. See
Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants
on page
6- 15.
Always clean the brake fluid reservoir cap and the area
around the cap before removing it.
This will help
keep dirt from entering the reservoir.
\. ._h the wrong kinc~ luid in you1 re
system, your brakes may not work well, or
they may not even work at all.
This could
cause a crash. Always use the proper
brake fluid.
Notice:
Using the wrong fluid can badly damage brake
system parts. For example, just a few drops
of
mineral-based oil, such as engine oil, in your
brake system can damage brake system
parts
so badly that they’ll have to be replaced.
Don’t let someone put in the wrong kind of fluid.
If you spill brake fluid on your vehicle’s painted
surfaces, the paint finish can be damaged. Be careful not to spill brake fluid on your vehicle. If
you do, wash
it off immediately. See
“Appearance Care’’ in the Index.
5-39
Page 255 of 354

Brake Wear
Your vehicle has four-wheel disc brakes.
Disc brake pads have built-in wear indicators that make
a high-pitched warning sound when the brake pads
are worn and new pads are needed. The sound
may come and go or be heard all the time your vehicle
is moving (except when you are pushing on the
brake pedal firmly).
--
le bra wear warning sound means that
soon your brakes won’t work well. That could
lead to an accident. When you hear the brake
wear warning sound, have your vehicle
serviced.
Notice: Continuing to drive with worn-out brake
pads could result in costly brake repair.
Some driving conditions or climates may cause a brake
squeal when the brakes are first applied or lightly
applied. This does not mean something is wrong with
your brakes. Properly torqued
wheel nuts are necessary to help
prevent brake pulsation. When tires are rotated, inspect
brake pads for wear and evenly tighten wheel nuts in
the proper sequence
to GM torque specifications.
Brake linings should always be replaced as complete
axle sets.
See
Brake System Inspection on page 6-14.
Brake Pedal Travel
See your dealer if the brake pedal does not return to
normal height, or
if there is a rapid increase in
pedal travel. This could be a sign of brake trouble.
Brake Adjustment
Every time you make a moderate brake stop, your disc
brakes adjust for wear.
If you rarely make a moderate
or heavier stop, then your brakes might not adjust
correctly. If you drive in that way, then
- very
carefully
- make a few moderate brake stops about
every
1,000 miles (1 600 km), so your brakes will adjust
properly.
5-40
Page 256 of 354

Replacing Brake System Parts
The braking system on a vehicle is complex. Its many
parts have
to be of top quality and work well together if
the vehicle is to have really good braking. Your
vehicle was designed and tested with top-quality
GM
brake parts. When you replace parts of your braking
system
- for example, when your brake linings
wear down and you need new ones put in
- be sure
you get new approved replacement parts. If you
don’t, your brakes may no longer work properly. For
example,
if someone puts in brake linings that are wrong
for your vehicle, the balance between your front and
rear brakes can change
- for the worse. The braking
performance you’ve come
to expect can change in
replacement brake parts.
many other ways if someone puts in the wrong
Battery
Your new vehicle comes with a maintenance free
ACDelco@ battery. When it’s time for a new battery, get
one that has the replacement number shown on the
original battery’s label. We recommend an ACDelcoC”-‘
battery. See
Engine Compartment Overview on
page
5- 12 for battery location.
Warning; Battery posts, terminals and related
accessories contain lead and lead compounds,
chemicals known to the State of California to cause
cancer and reproductive harm. Wash hands after
handling.
Vehicle Storage
If you’re not going to drive your vehicle for 25 days or
more, remove the black, negative
(-) cable from
the battery. This will help keep your battery from
running down.
Batteries have acic bat can burn you and gas
that can explode. You can be badly hurt
if you
aren’t careful. See “Jump Starting” in the Index
for tips
on working around a battery without
I 3--L ’ =
rrnttjqrr hl Irt.
Contact your dealer to learn how to prepare your
vehicle for longer storage periods.
Also, for your audio system, see
Theft-Deterrent
Feature (Non-RDS Radios) on page
3-64 or
I nefi-Deterrent Feature (RDS RaQiosj on page 3-64. -.
5-41
Page 257 of 354

Jump Starting
If your battery has run down, you may want to use
another vehicle and some jumper cables to start your
vehicle. Be sure to follow the steps below to do it safely.
I- Ba..,ries can hi.- - you. ’_ --?y cal. Je c-.lgerous
because:
They contain acid that can burn you.
They contain gas that can explode or
They contain enough electricity to
ignite.
burn you.
If you don’t follow these steps exactly, some
or all of these things can hurt you.
Notice: Ignoring these steps could result in costly
damage to your vehicle that wouldn’t be covered
by your warranty.
Trying to start your vehicle by pushing or pulling
it
won’t work, and it could damage your vehicle.
1. Check the other vehicle. It must have a 12-volt
battery with a negative ground system.
Notice: If the other system isn’t a 12-volt system
with a negative ground, both vehicles can be
damaged.
2. Get the vehicles close enough so the jumper cables
can reach, but be sure the vehicles aren’t touching
each other.
If they are, it could cause a ground
connection you don’t want.
You wouldn’t be able to
start your vehicle, and the bad grounding could
damage the electrical systems.
To avoid the possibility of the vehicles rolling, set
the parking brake firmly on both vehicles involved in
the jump start procedure. Put an automatic
transaxle in PARK (P) or a manual transaxle in
NEUTRAL before setting the parking brake.
Notice: If you leave your radio on, it could be badly
damaged. The repairs wouldn’t be covered by
your warranty.
3. Turn off the ignition on both vehicles. Unplug
unnecessary accessories plugged into the cigarette
lighter. Turn
off the radio and all lamps that aren’t
needed. This will avoid sparks and help save
both batteries. And it could save your radio!
4. Open the hoods and locate the batteries. Find the
positive
(+) and negative (-) terminal locations on
each vehicle. See
Engine Compartment Overview
on page
5-12 for more information on location.
5-42
Page 264 of 354

Bulb Replacement
For the type of bulb to use, see Replacement Bulbs on
page
5-51. For any bulb changing procedure not
listed in this section, contact your dealer.
Halogen Bulbs
1
Halogen bulbs have pressurized gas inside
and can burst if you drop or scratch the bulb.
You or others couiu be injured. Be sure
to read
and
follow the instructions on the bulb
package.
I
Headlamps
1. Lift up on the two retaining clips which secure the
headlamp assembly.
2. Lift the headlamp assembly forward, out of the
3. Remove the rubber cap covering the bulb assembly.
4. Turn the bulb assembly retainer counterclockwise
one-sixth
of a turn and pull out the bulb assembly.
5. Unclip the bulb assembly from the wiring harness.
6. Replace the bulb.
7. Reverse Steps 1 through 5 to reinstall the bulb
mounting
bracket.
assembly and headlamp housing.
5-49
Page 267 of 354

Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
Windshield wiper blades should be inspected at least
twice a year for wear or cracking. See “Wiper Blade
Check in
At Least Twice a Year on page 6-10 for more
information.
Replacement blades come
in different types and are
removed
in different ways. Here’s how to remove
the wiper blade:
1. Pull the windshield wiper arm away from the
windshield.
2. Push the release lever and slide the wiper assembly
toward the driver’s side of the vehicle.
3. Install a new blade by reversing Steps 1 and 2.
For the proper type and size, see Capacities and
Specifications
on page 5-86.
5-52
Page 270 of 354
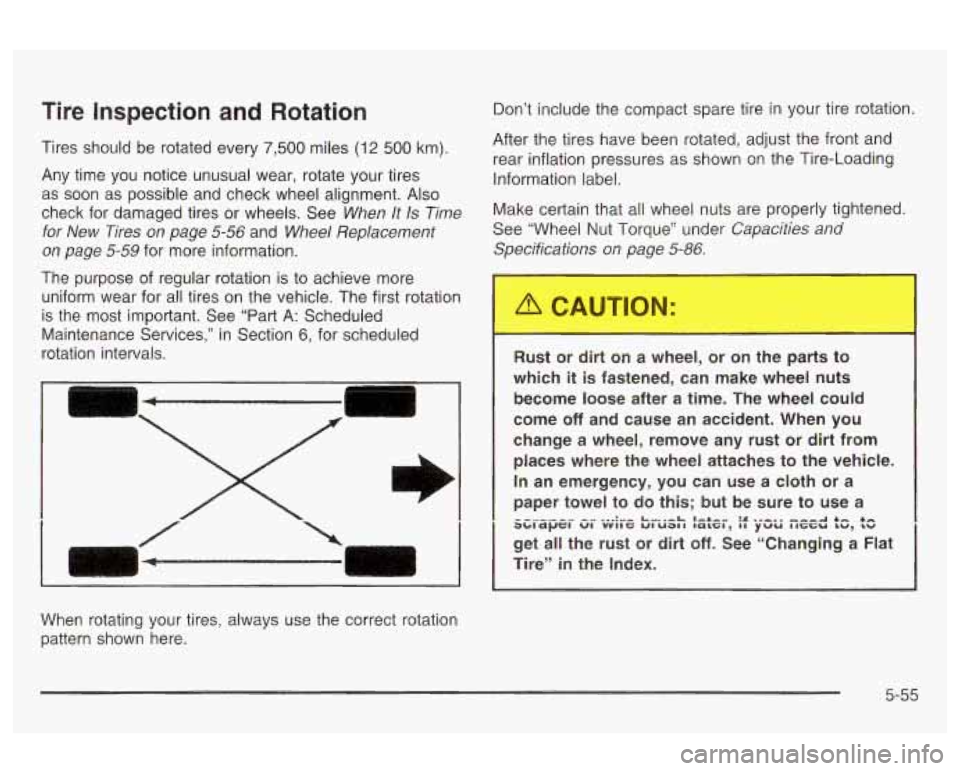
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be rotated every 7,500 miles (12 500 km).
Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your tires
as soon as possible and check wheel alignment. Also
check for damaged tires or wheels. See
When It Is Time
for New Tires on page
5-56 and Wheel Replacement
on page
5-59 for more information.
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation
is the most important. See “Part A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services,” in Section 6, for scheduled
rotation intervals. Don’t include the
compact spare tire in your tire rotation.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown
on the Tire-Loading
Information label.
Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly tightened.
See “Wheel Nut Torque” under
Capacities and
Specifications on page
5-86.
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or or parts to
which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust
or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do
this; but be sure to use a
3cllCapcI VI VVll c; ut U3If IBLGI, II ywu IIG‘CSU LW, LW
get all the rust or dirt off. See “Changing a Flat
Tire”
in the Index.
--_ .------ -_. ... :-- L”..-L I-*-” :+ .--. ~ “...-A 4- 4-
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
5-55
Page 274 of 354

Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked or badly rusted
or corroded. If wheel nuts keep coming loose, the
wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts should be replaced.
If the wheel leaks air, replace it (except some
aluminum wheels, which can sometimes be repaired).
See your dealer
if any of these conditions exist.
Your dealer will know the kind of wheel you need.
Each new wheel should have the same load-carrying
capacity, diameter, width, offset and be mounted
the same way as the one it replaces.
If you need to replace any of your wheels? wheel bolts
or wheel nuts, replace them only with new
GM
original equipment parts. This way, you will be sure to
have the right wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts
for your vehicle. Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel
bolts or
wheel
nuts on your vehicle can be
dangerous.
It could affect the braking and
handling
of your vehicle, make your tires lose
air and make you lose control. You could have
a collision in which you or others could be injured. Always use the correct wheel, wheel
Notice: The wrong wheel can also cause problems
with bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or
odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper height,
vehicle ground clearance and tire or tire chain clearance to the body and chassis.
See
Changing a Flat Tire on page 5-62 for more
mtormatlon.
5-59
Page 278 of 354
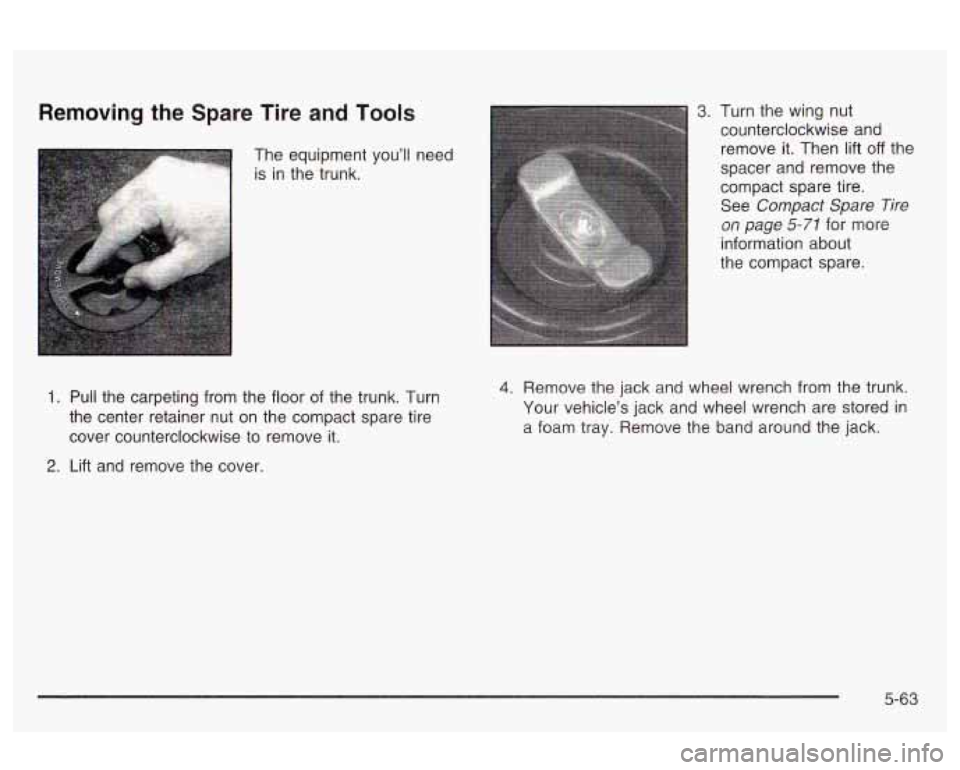
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools
The equipment you’ll need
is in the trunk.
3. Turn the wing nut
counterclockwise and
remove it. Then lift
off the
spacer and remove the
compact spare tire.
See
Compact Spare Tire
on page 5-71 for more
information about
the compact spare.
1. Puii the carpeting from the iioor of the trunk. Turn
the center retainer nut on the compact spare tire
cover counterclockwise to remove it. 4. Remove the jack and wheel wrench from the trunk.
Your vehicle’s jack and wheel wrench are stored in
a foam tray. Remove the band around the jack.
2. Lift and remove the cover
5-63