battery location OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 4888 of 6000

6E–231 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0406 EGR High Voltage
D06RW106
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the EGR
valve pintle position input to ensure that the valve
responds properly to command from the PCM. If current
pintle position voltage indicates more than 4.8 V and last
more than 10 seconds, then the PCM will set DTC P0406.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Ignition voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
EGR pintle position output voltage is more than 4.8 volt
and last more than 10 sec.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) as soon as failure detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0404 can be cleared by using Tech 2 “Clear Info”
function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to
be OK, observe the EGR actual position display on
Tech 2 while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
related to EGR valve. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
Page 4916 of 6000

6E–259 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1640 Driver-1-Input High Voltage
Circuit Description
Output driver modules (ODMs) are used by the
powertrain control module (PCM) to turn “ON” many of
the current-driven devices that are needed to control
various engine and transmission functions. Each ODM is
capable of controlling up to 7 separate outputs by
applying ground to the device which the PCM is
commanding “ON.”
Unlike the Quad Driver Modules (QDMs) used in prior
model years, ODMs have the capability of diagnosing
each output circuit individually. DTC P1640 set indicates
an improper voltage level has been detected on an ODM
output.
Since A/C is an option, No A/C will cause the air
conditioning clutch relay output to always fault. If a fault is
seen on the air conditioning clutch relay output, it will not
be logged as a fault until the A/C request input interrupts a
high voltage, indicating that A/C has been installed.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Ignition “ON.”
Engine running.
No DTC 1618.
Ignition voltage is above 13.2 volts for 4 seconds.
Output voltage does not equal ignition voltage when
output is “OFF” or output voltage is not less than 1 volt
when output is “ON.”
Above conditions occur for at least 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records only. This
information will not be stored as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1640 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the PCM, turn the ignition “ON” and observe a
voltmeter connected to the suspect driver circuit at the
PCM harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses relates to the MIL. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Poor connection at component – Examine for
damaged connectors, unplugged connector, or
damaged terminals at the following locations:
Instrument cluster harness, canister purge solenoid,
A/C clutch relay. An open ignition feed circuit at any of
these components will cause DTC P1640 to be set.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
The following PCM pins are controlled by output driver
modules (ODMs):
A13 – “Check Engine Lamp”
A14 – SVS (”Check Trans”)
B14 – A/C Clutch
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
6. The Tech 2 Driver Module Status indicates the PCM
pin that is affected.
11. The Tech 2 may indicate “short circuit” even when
the problem is an open circuit. The cause of an
open circuit may be in the component itself-lamp,
purge, solenoid, or A/C compressor relay.
13.A short to ground on the ignition side of the
component will blow the fuse. Since the fuse was
checked in Step 4, a short to ground would be
between the affected component and the PCM.
Page 5011 of 6000

6E–354
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ILLUSTRATIONTOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
5-8840-2607-0
(J 41413)
EVAP Pressure/Purge
Diagnostic Station
5-8840-2608-0
(J 41416)
Ultrasonic Leak Detector
1. 5-8840-2607-0 (J-41413)EVAP Pressure/Purge
Diagnostic Station is a multipurpose tool which is
used to perform several diagnostic procedures for
enhanced emission testing. The station will
accommodate a nitrogen gas filled cylinder which is
used to pressurize the vehicle EVAP system for a
leakdown test and leak location test when a vehicle is
repaired for leakage in the enhanced evaporative
emission control system. It also has two additional
gauges (inches of mercury and inches of water) which
are used to measure both source vacuum and EVAP
canister purge vacuum to verify correct operation and
vapor flow within the canister purge circuit.
2. 5-8840-2608-0 (J-41416) Ultrasonic Leak Detector is
a microprocessor-based device used to detect leaks
in the enhanced evaporative emission control
system. The evaporative system is pressurized to 30
inches of water using the 5-8840-2607-0 (J-41413)
EVAP Pressure/Purge Diagnostic System. Small
leaks in the EVAP system will emit sound at a high
frequency undetectable by a human ear but
detectable with the 5-8840-2608-0 (J-41416). The
technician traces along the evaporative system and
can pinpoint leaks due to corroded lines, cracked
hoses, or a damaged EVAP component. The
detector includes a high quality set of headphones to
block out surrounding shop noise and the LED
sensitivity meter allows a visual reference for locating
leaks in conjunction with the audio output heard
through the headphones. Powered by (1) nine volt
battery.
Page 5473 of 6000
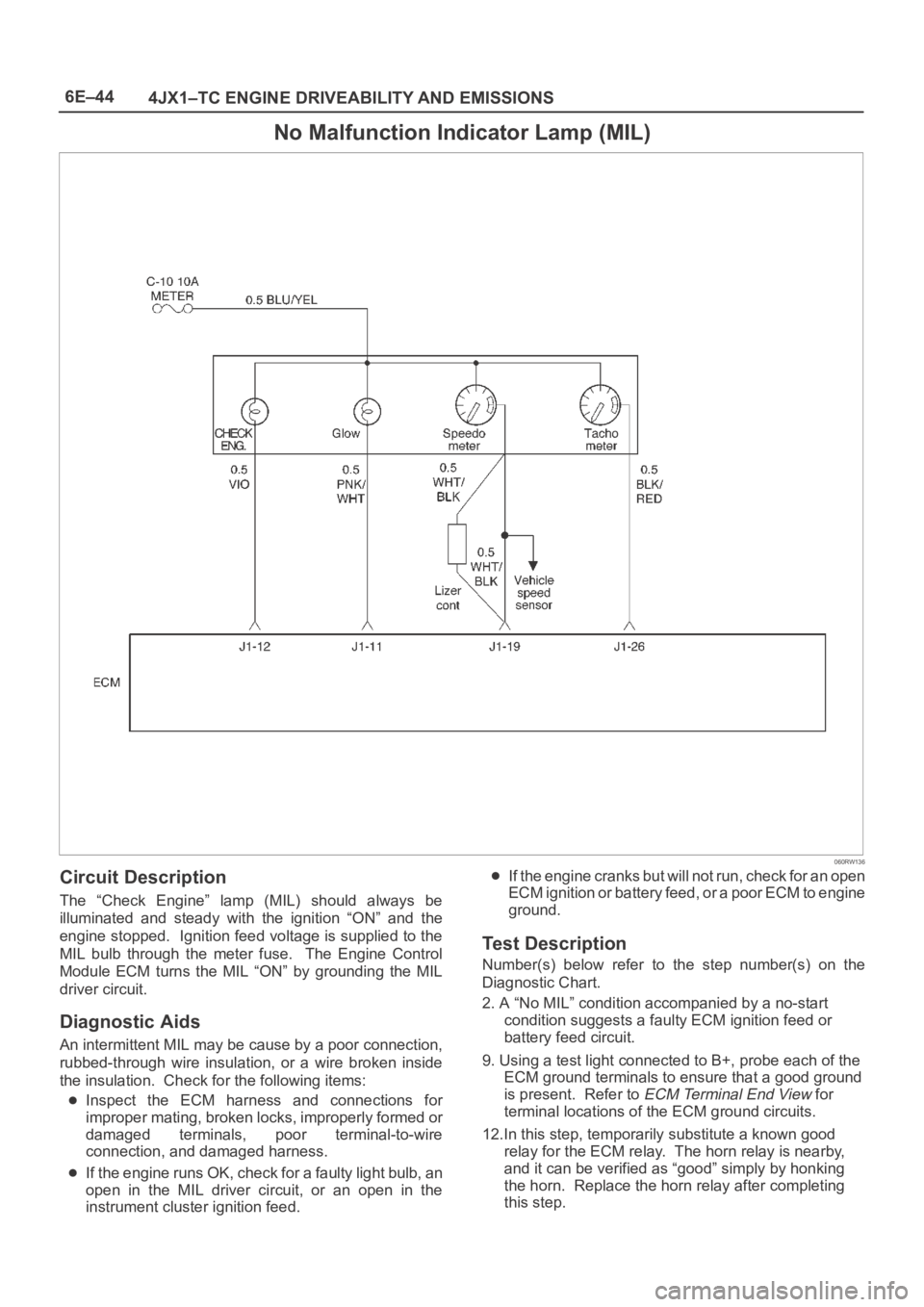
6E–44
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
060RW136
Circuit Description
The “Check Engine” lamp (MIL) should always be
illuminated and steady with the ignition “ON” and the
engine stopped. Ignition feed voltage is supplied to the
MIL bulb through the meter fuse. The Engine Control
Module ECM turns the MIL “ON” by grounding the MIL
driver circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent MIL may be cause by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
Inspect the ECM harness and connections for
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire
connection, and damaged harness.
If the engine runs OK, check for a faulty light bulb, an
open in the MIL driver circuit, or an open in the
instrument cluster ignition feed.
If the engine cranks but will not run, check for an open
ECM ignition or battery feed, or a poor ECM to engine
ground.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. A “No MIL” condition accompanied by a no-start
condition suggests a faulty ECM ignition feed or
battery feed circuit.
9. Using a test light connected to B+, probe each of the
ECM ground terminals to ensure that a good ground
is present. Refer to
ECM Terminal End View for
terminal locations of the ECM ground circuits.
12.In this step, temporarily substitute a known good
relay for the ECM relay. The horn relay is nearby,
and it can be verified as “good” simply by honking
the horn. Replace the horn relay after completing
this step.
Page 5485 of 6000

6E–56
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 (Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum).
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC P0107
will be set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0107 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Turn on the ignition switch and stop the engine. At this
time, the boost pressure will be equal to the
atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will
increase.
Check for intermittent codes.
The MAP sensor shares a ground with the ECT sensor,
and the Transmission Fluid Temperature sensor.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0107 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P0107 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 5487 of 6000
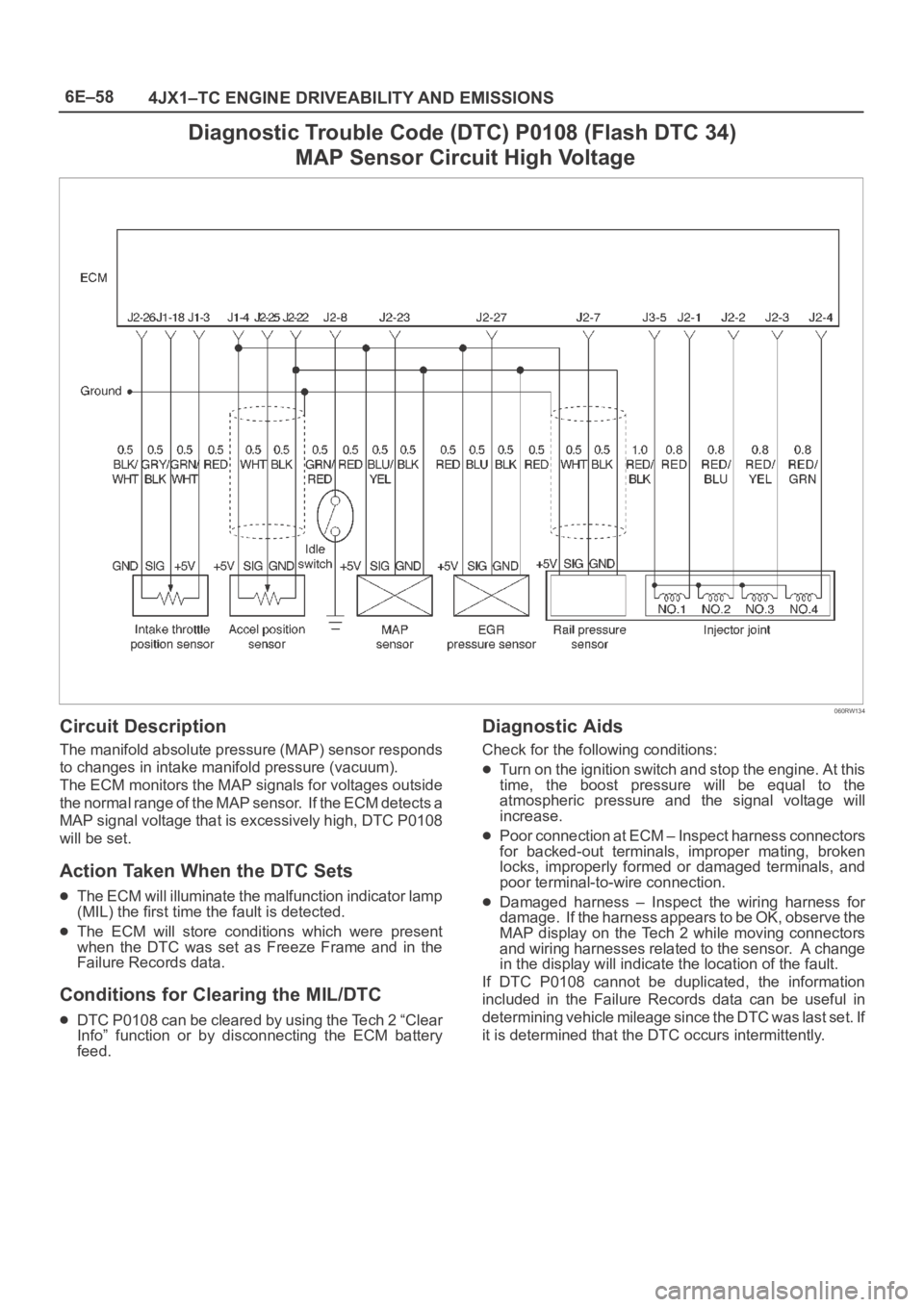
6E–58
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108 (Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum).
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is excessively high, DTC P0108
will be set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0108 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Turn on the ignition switch and stop the engine. At this
time, the boost pressure will be equal to the
atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will
increase.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0108 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If
it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Page 5489 of 6000

6E–60
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0112 (Flash DTC 23)
IAT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The Engine Control Module ECM applies 5 volts
through a pull-up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower, causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage. DTC
P0112 will set when the ECM detects an excessively low
signal voltage on the Intake air temperature sensor signal
circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0112 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the IAT sensor. A change
in the IAT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0112 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 5491 of 6000

6E–62
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0113 (Flash DTC 23)
IAT Sensor Circuit High Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The Engine Control Module ECM applies 5 volts
through a pull-up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage. DTC
P0113 will set when the ECM detects an excessively high
signal voltage on the intake air temperature sensor signal
circuit.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0113 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the IAT sensor. A change
in the IAT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0113 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
Page 5494 of 6000

6E–65 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0117 (Flash DTC 14)
ECT Sensor Low Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted on a coolant crossover pipe at the
rear of the engine. The Engine Control Module ECM
applies a voltage (about 5 volts) through a pull-up resistor
to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine coolant is cold,
the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the
ECM will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine
coolant warms, the sensor resistance becomes lower,
and the ECT signal voltage measured at the ECM drops.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0117 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, brokenlocks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the ECT sensor. A
change in the ECT display will indicate the location of
the fault.
If DTC P0117 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Verifies that the fault is present.
3. If DTC P0117 can be repeated only by duplicating
the Failure Records conditions, refer to the
“Temperature vs. Resistance Values” table. The
table may be used to test the ECT sensor at various
temperatures to evaluate the possibility of a
“shifted” sensor that may be shorted above or below
a certain temperature. If this is the case, replace
the ECT sensor. If the ECT sensor appears to be
OK, the fault is intermittent; refer to
Diagnostic Aids.
Page 5496 of 6000

6E–67 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0118 (Flash DTC 14)
ECT Sensor High Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted in on a coolant crossover pipe at the
rear of the engine. The Engine Control Module ECM
applies a voltage (about 5 volts) through a pull-up resistor
to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine coolant is cold,
the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the
ECM will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine
coolant warms, the sensor resistance becomes less, and
the ECT signal voltage measured at the ECM drops.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0118 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the ECT sensor. A
change in the ECT display will indicate the location of
the fault.
If DTC P0118 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.